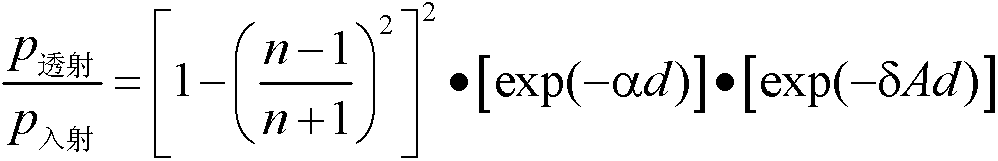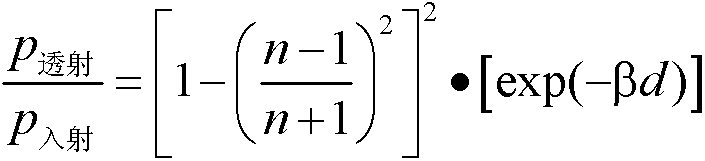Polymer dispersed liquid crystal thin box micro-displacement sensor and measuring method thereof
A micro-displacement sensor and displacement technology, applied in the field of displacement sensors, can solve the problems of adding unstable factors, interference, and liquid crystal dynamic scattering to the sensor, and achieve simple and accurate measurement, convenient production, and avoiding interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
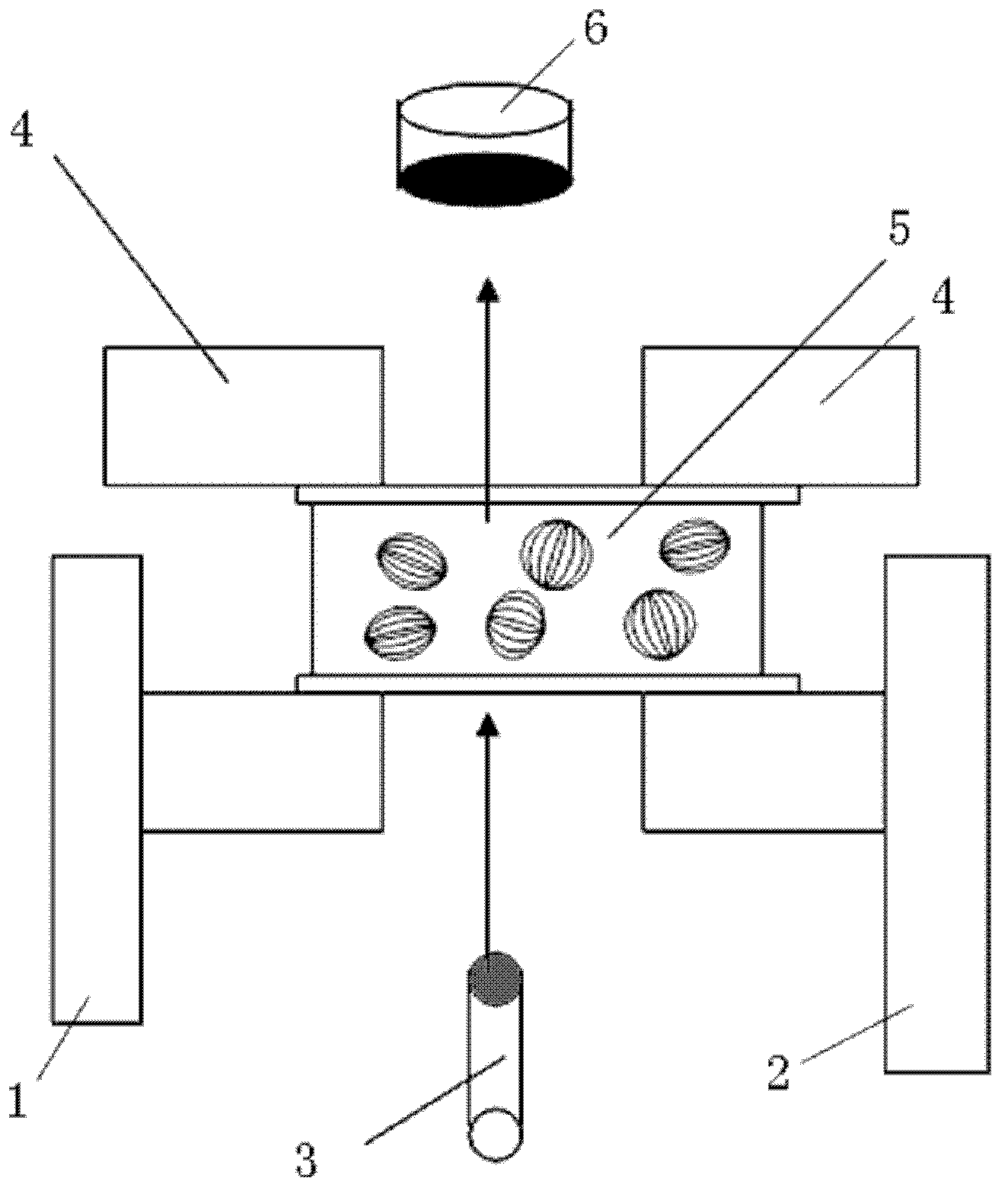
[0021] The present invention achieves micro-displacement sensing measurements by using polymer dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC) thin cells. Specifically, the micro-displacement sensor of the present invention includes a thin PDLC cell, a laser that provides a light source incident on the PDLC thin cell, and a photodetector that receives light transmitted through the PDLC thin cell.
[0022] The principle of the present invention is based on the calendering effect of the PDLC thin cell, that is, its light transmittance changes with pressure. Therefore, the scattering loss per unit length of the PDLC thin cell can be found through the relationship between the incident light and the transmitted light of the PDLC thin cell when the measured object is not placed or when the measured object is placed, and then, by measuring the measured object The relationship between the incident light and the transmitted light can be used to measure the thickness of the PDLC thin cell, and the displac
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap