Pulse analyzer
a pulse analysis and pulse technology, applied in the field of pulse analysis, can solve the problem of high cost of ultra-fast sampling circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
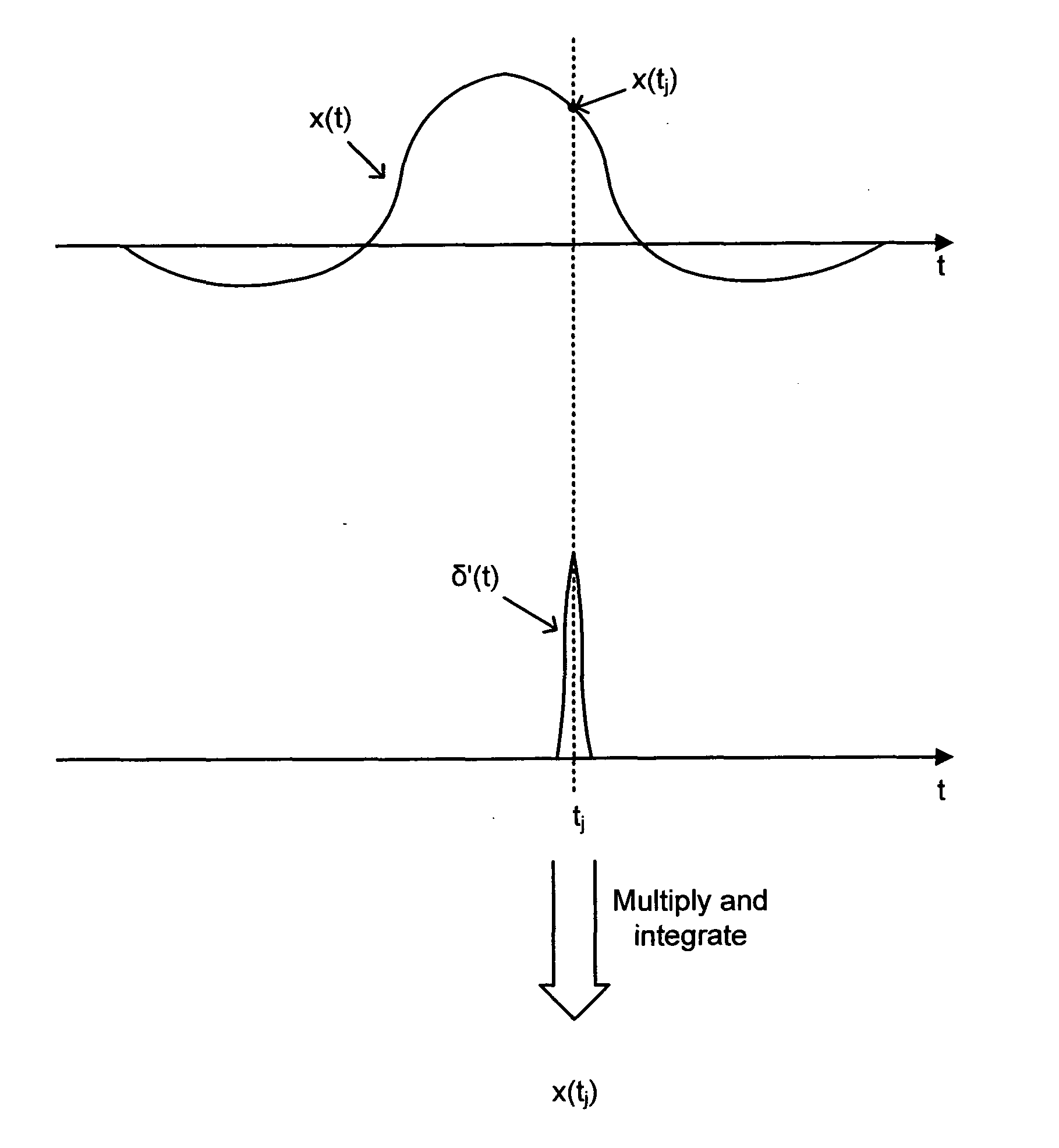
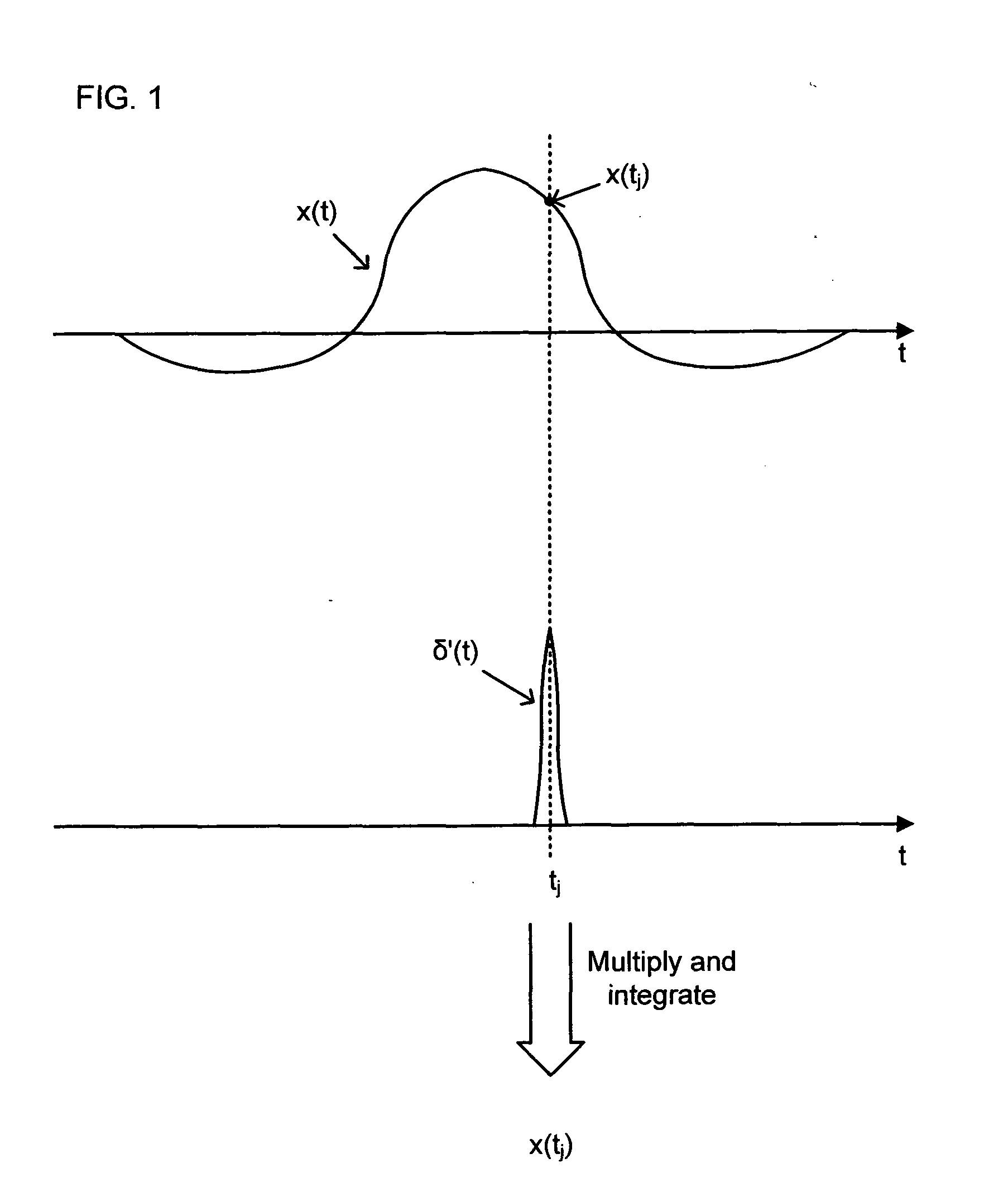
[0016]Suppose that a wideband pulse x(t) of finite duration and unknown shape is to be sampled at a plurality of J time instants t1, t2, . . . , tj, . . . , tJ. It is assumed that the pulse duration is limited by some maximum value T, and that the pulse time-of-arrival is approximately known. The acquired samples of the pulse x(t) are then used to determine some pulse descriptors such as shape and its moments, including location and time spread. The pulse under examination may be regarded as being observed at the output of a suitable sensor that has captured a portion of electromagnetic radiation scattered by a remote object of interest.
[0017]From the ‘sifting’ property of the Dirac delta function, or Dirac impulse, δ(t) it follows that a sample at time tj of a pulse x(t), i.e. the value x(tj), can be determined from the integral
x(tj)=∫0Tx(t)δ(t-tj)t
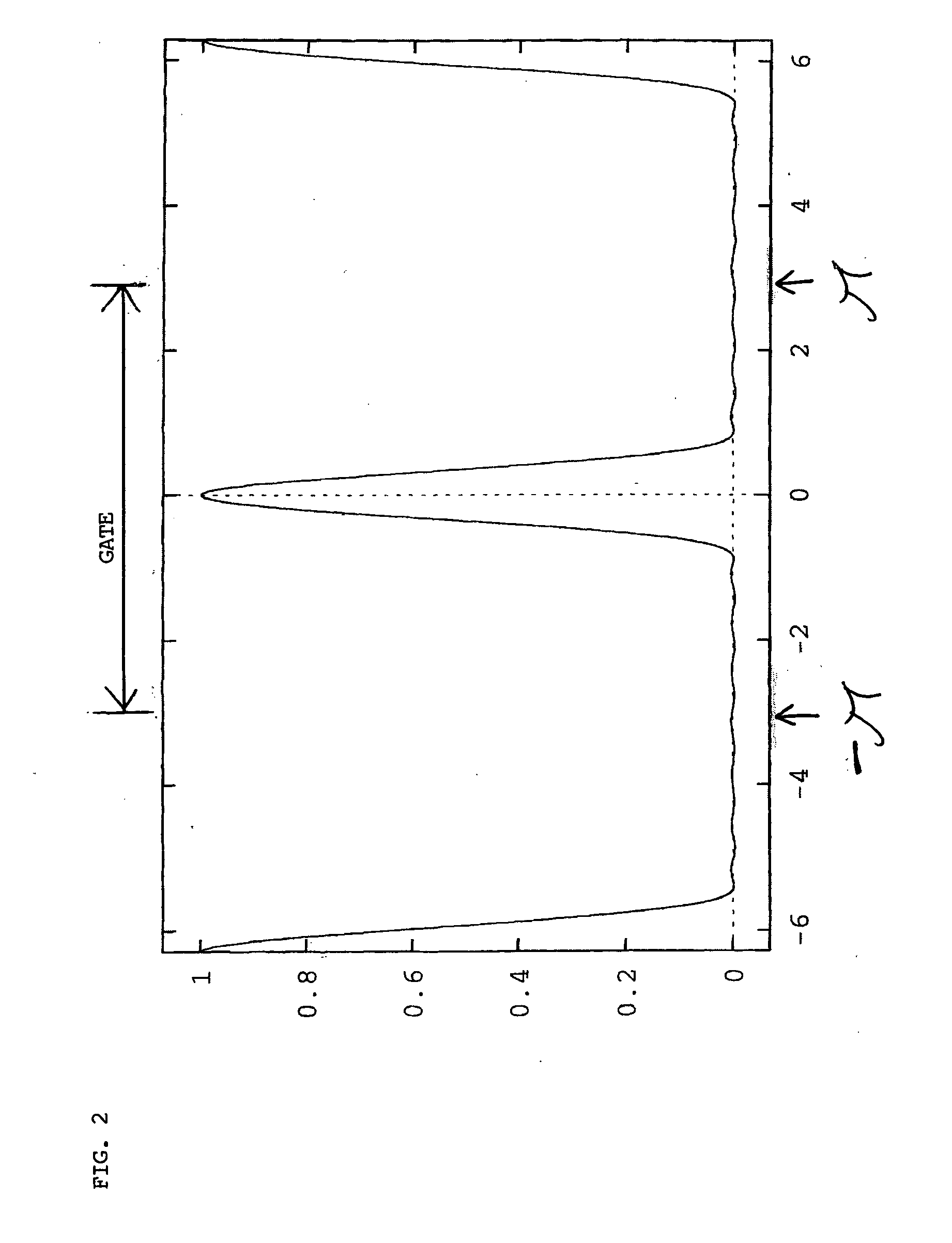
[0018]FIG. 1 depicts an example of a pulse x(t) being sampled at time tj with the use of a function δ′(t) approximating the Dirac impulse
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap