Synchronizing Uplink and Downlink Transmissions in a Wireless Device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
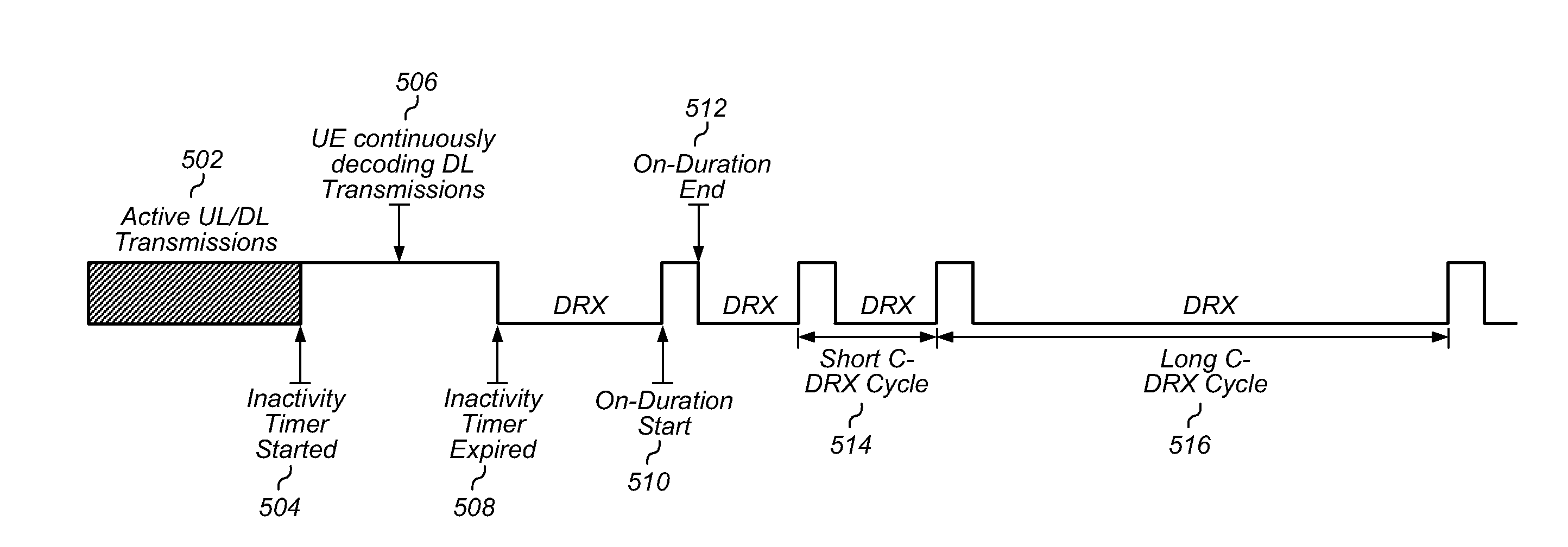
[0019]While features described herein are susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific embodiments thereof are shown by way of example in the drawings and are herein described in detail. It should be understood, however, that the drawings and detailed description thereto are not intended to be limiting to the particular form disclosed, but on the contrary, the intention is to cover all modifications, equivalents and alternatives falling within the spirit and scope of the subject matter as defined by the appended claims.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS
Acronyms
[0020]The following acronyms are used in the present patent application:
[0021]UE: User Equipment
[0022]BS: Base Station
[0023]GSM: Global System for Mobile Communication
[0024]UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
[0025]LTE: Long Term Evolution
[0026]PDCCH: Physical Downlink Control Channel
[0027]PUCCH: Physical Uplink Control Channel
[0028]PDSCH: Physical Downlink Shared Channel
[0029]PUSCH: Physic
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap