Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1 results about "Gaussian" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gaussian /ˈɡaʊsiən/ is a general purpose computational chemistry software package initially released in 1970 by John Pople and his research group at Carnegie Mellon University as Gaussian 70. It has been continuously updated since then. The name originates from Pople's use of Gaussian orbitals to speed up molecular electronic structure calculations as opposed to using Slater-type orbitals, a choice made to improve performance on the limited computing capacities of then-current computer hardware for Hartree–Fock calculations. The current version of the program is Gaussian 16. Originally available through the Quantum Chemistry Program Exchange, it was later licensed out of Carnegie Mellon University, and since 1987 has been developed and licensed by Gaussian, Inc.
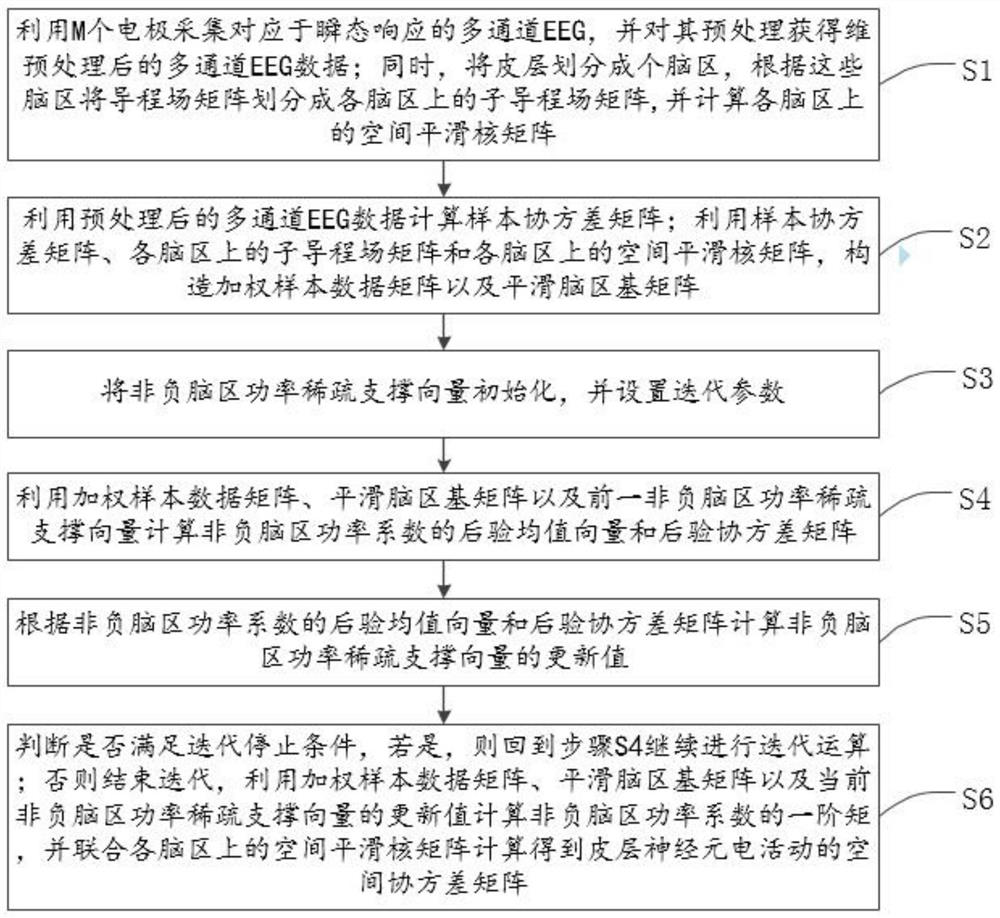
Transient brain power supply positioning method and system based on non-negative block sparse Bayesian learning
ActiveCN113995422AImprove source locationImprove targetingMathematical modelsSensorsMachine learningGaussian
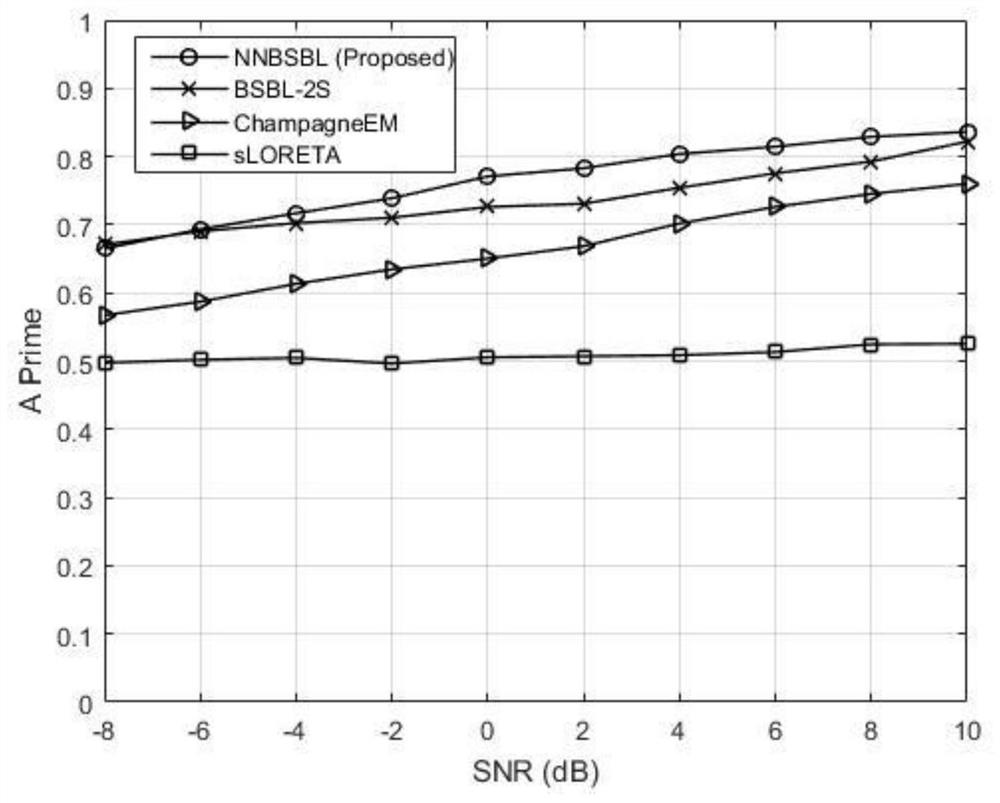
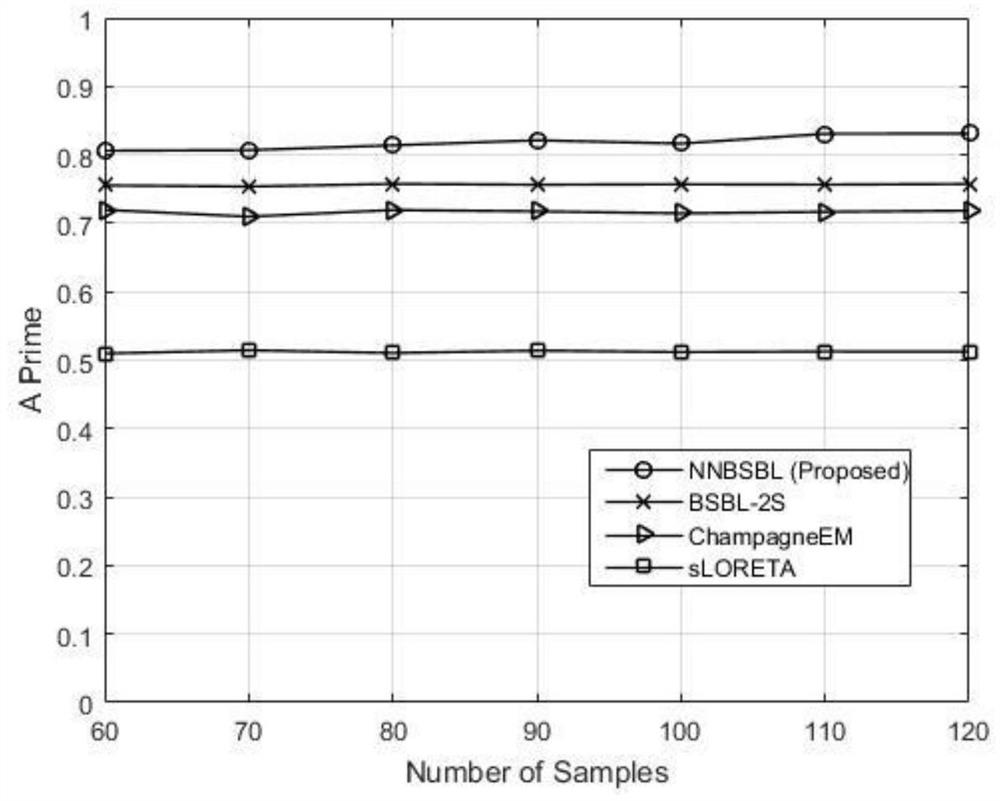
The invention discloses a transient brain power supply positioning method and system based on non-negative block sparse Bayesian learning. The method comprises the steps: firstly collecting a transient multi-channel EEG, calculating a sample covariance matrix, and weighting each column of the matrix, which can be represented as non-negative block sparse representation on each brain region after Laplace smoothing; then setting an iteration stop condition and an initial value of a non-negative brain region power sparse support vector; iteratively updating a posterior mean value and a covariance of the non-negative brain region power vector based on non-negative Gaussian distribution, and updating a non-negative brain region power sparse support vector according to the posterior mean value and the covariance; and finally, giving a source positioning result by using the latest non-negative brain region power sparse support vector. According to the invention, brain region non-negative block sparse representation of covariance vectors is utilized, expectation and variance of non-negative Gaussian posterior distribution are combined, and the transient EEG source localization NNBSBL method is given; and the method does not need to predict or estimate a noise covariance matrix, is high in positioning precision and resolution, and provides a technical means for the fields of cognitive psychology, brain-computer interfaces, nerve diagnosis and treatment and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap