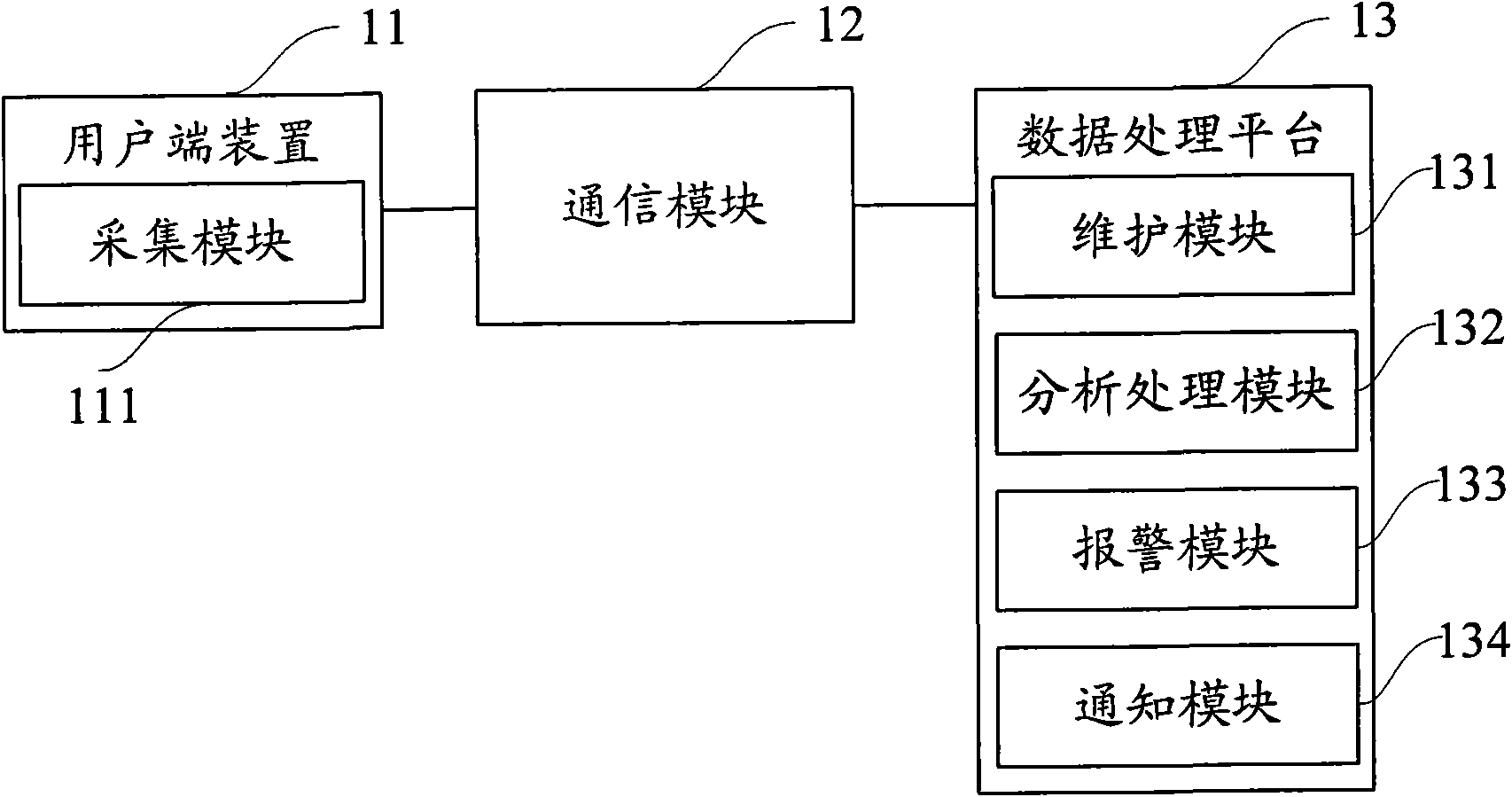
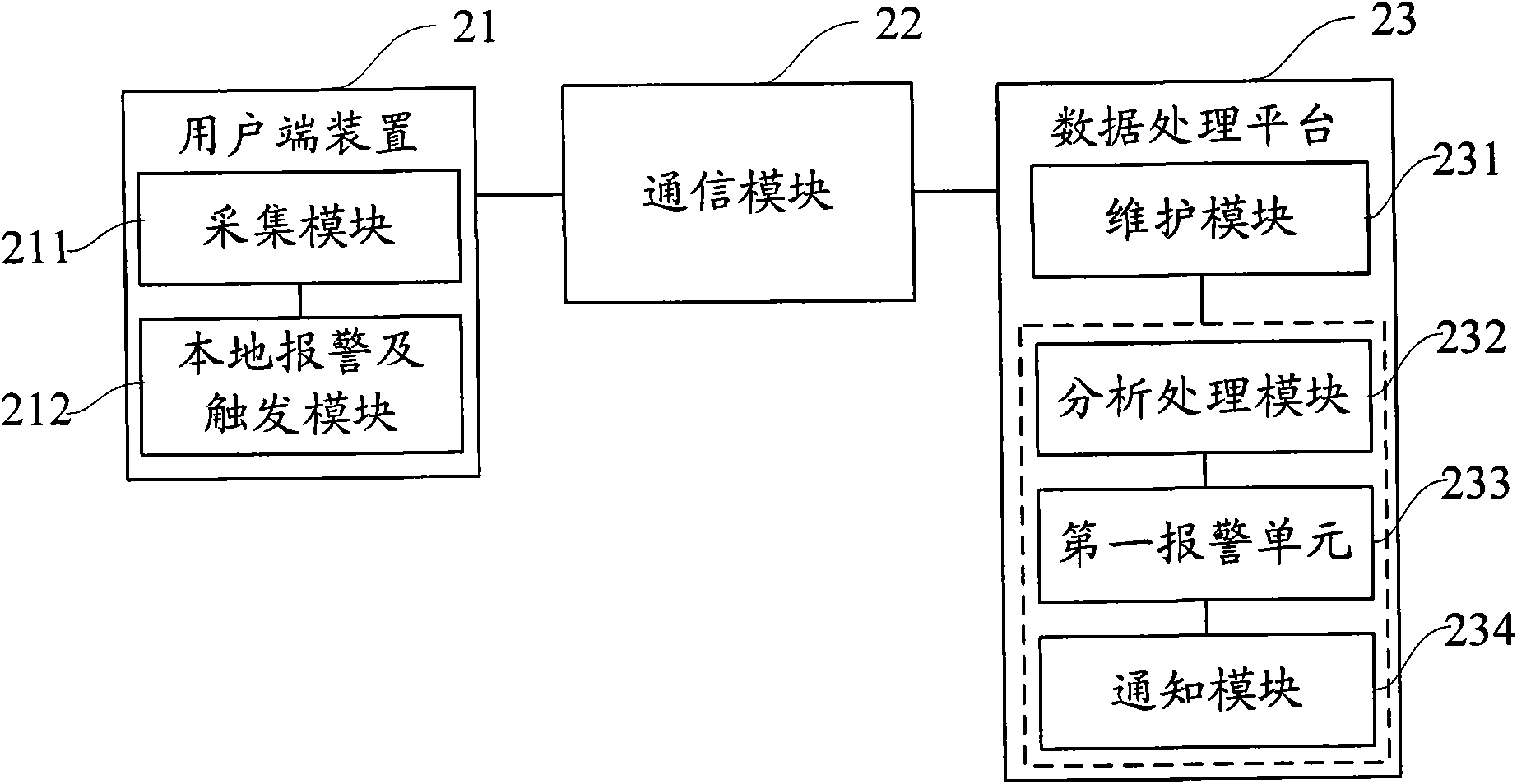
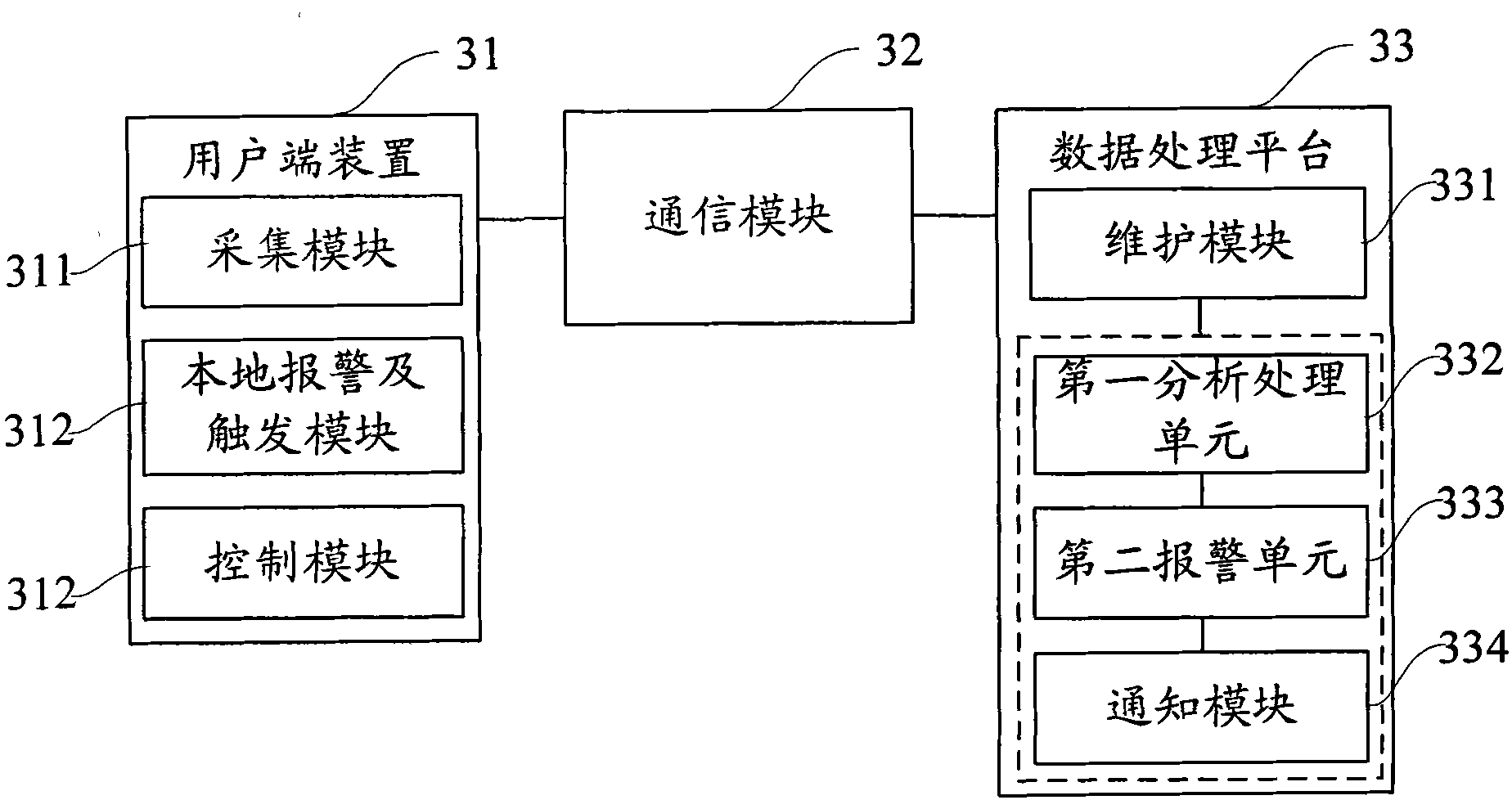
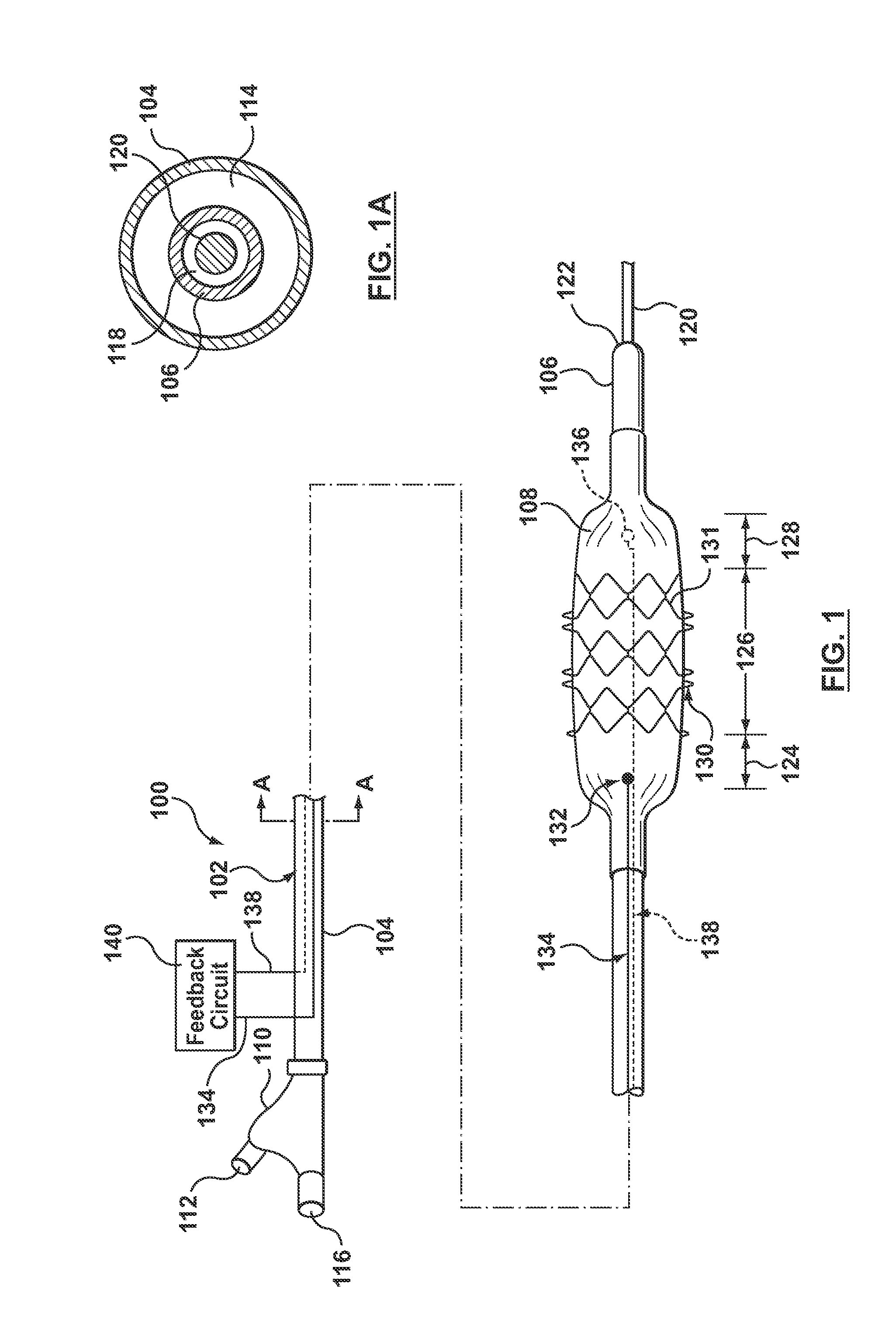
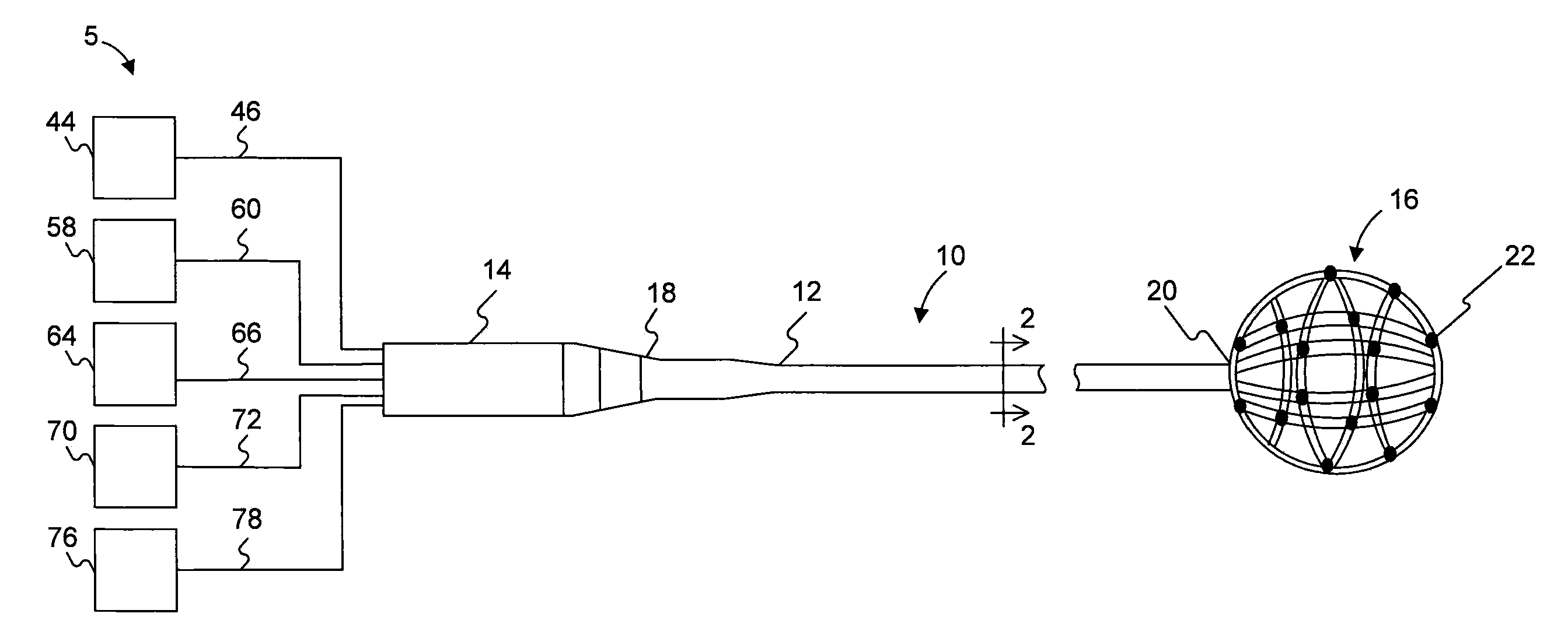
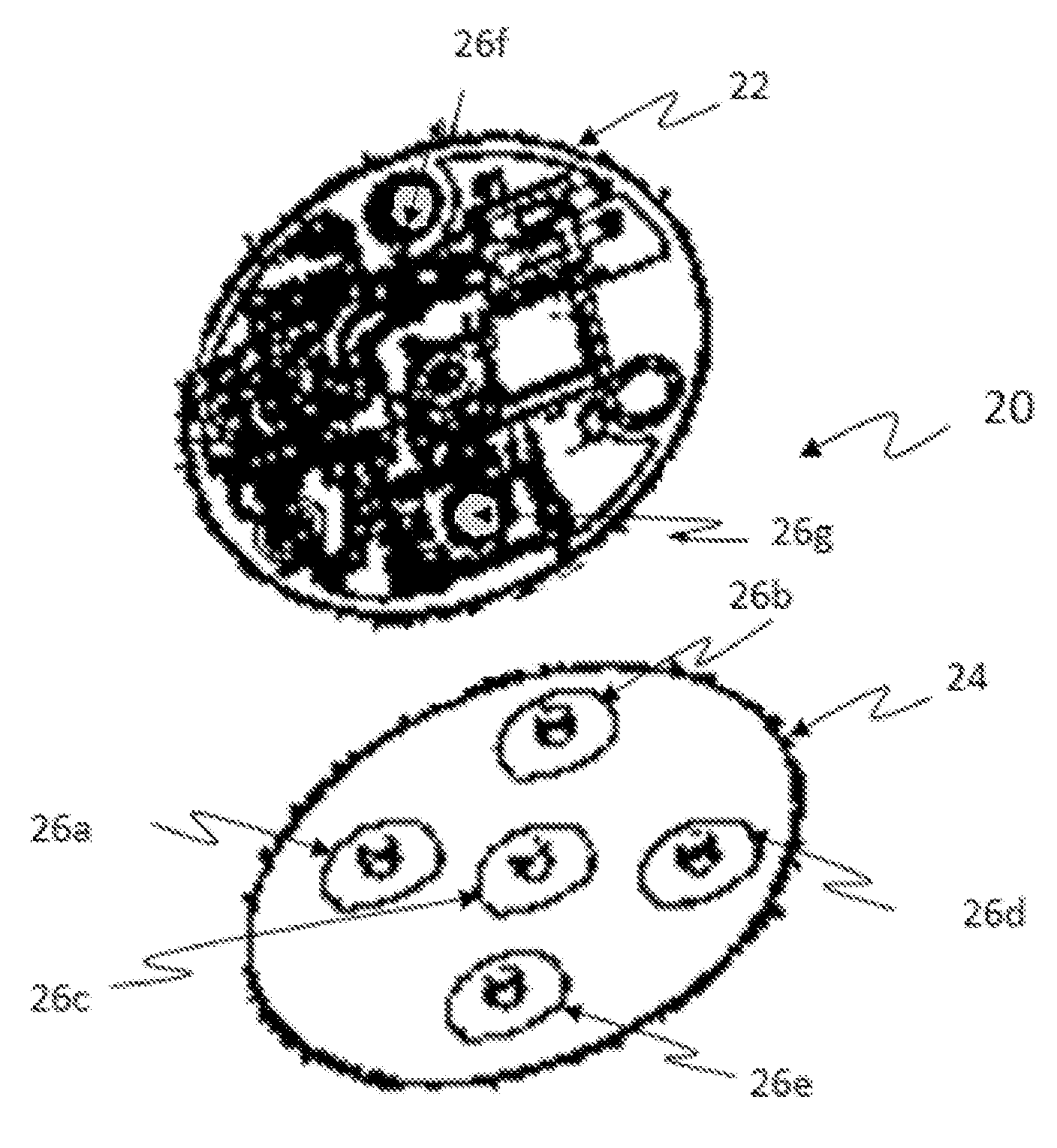
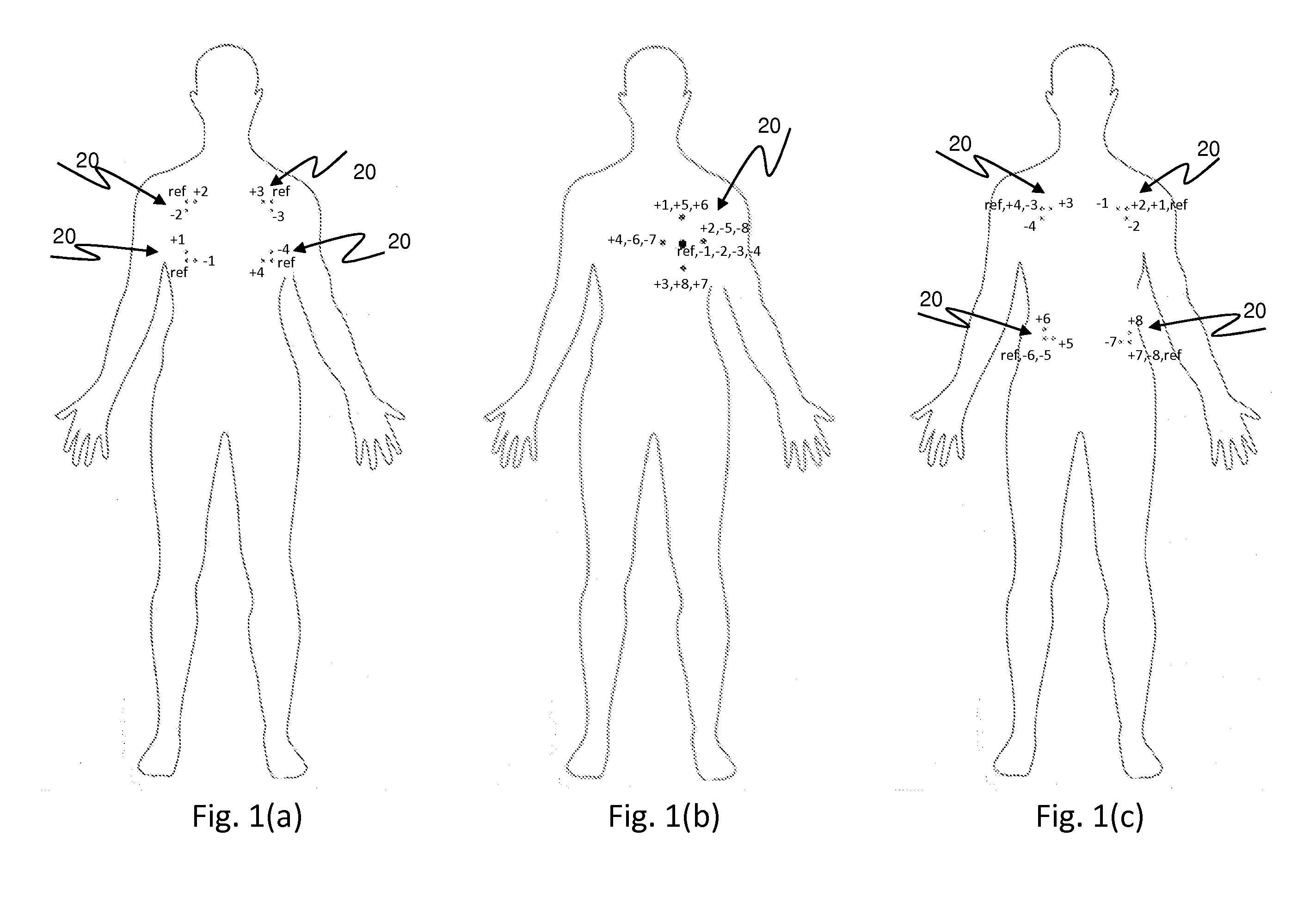
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278results about "Sensors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS7110803B2Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingWithdrawing sample devicesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteImplanted device
Owner:DEXCOM
Method and apparatus for performing stereotactic surgery
A stereotactic navigation system for navigating an instrument to a target within a patient may include a stereotactic head frame, an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller and a display. The stereotactic head frame is coupled to the patient and is used to assist in guiding the instrument to the target. The imaging device captures image data of the patient and of the stereotactic head frame. The tracking device is used to track the position of the instrument relative to the stereotactic head frame. The controller receives the image data from the imaging device and identifies the stereotactic head frame in the image data and automatically registers the image data with navigable patient space upon identifying the stereotactic head frame, while the display displays the image data.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
Methods, Systems, and Computer Program Products For Hierarchical Registration Between a Blood Vessel and Tissue Surface Model For a Subject and a Blood Vessel and Tissue Surface Image For the Subject
Methods, systems, and computer program products for hierarchical registration (102) between a blood vessel and tissue surface model (100) for a subject and a blood vessel and tissue surface image for the subject are disclosed. According to one method, hierarchical registration of a vascular model to a vascular image is provided. According to the method, a cascular model is mapped to a target image using a global rigid transformation to produce a global-rigid-transformed model. Piecewise rigid transformations are applied in a hierarchical manner to each vessel tree in the global-rigid-transformed model to perform a piecewise-rigid-transformed model. Piecewise deformable transformations are applied to branches in the vascular tree in the piecewise-transformed-model to produce a piecewise-deformable-transformed model.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Computer-assisted surgery tools and system
A surface digitizing tool has a film of micro-sensor elements, with each micro-sensor element related in a network affected by a shape of the film. The film is flexible to conform to a shape of a selected surface of an object. A processing unit receives signals from the micro-sensor elements of the network. The processing unit has a model generator producing a model of the selected surface of the object from the signals of the network of resistive elements. A positioning frame aligns a position and orientation of a drilling tool with respect to a bone element.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Robotic catheter system
ActiveUS20100256558A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceRobotic systemsUser input
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Gas sampling line
ActiveUS20110237969A1Improve accuracyReduce distortion problemsDispersed particle separationRespiratory organ evaluationGas analysisPolyethylene oxide
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Methods and systems for utilizing quantitative imaging
Systems and methods for analyzing pathologies utilizing quantitative imaging are presented herein. Advantageously, the systems and methods of the present disclosure utilize a hierarchical analytics framework that identifies and quantify biological properties / analytes from imaging data and then identifies and characterizes one or more pathologies based on the quantified biological properties / analytes. This hierarchical approach of using imaging to examine underlying biology as an intermediary to assessing pathology provides many analytic and processing advantages over systems and methods that are configured to directly determine and characterize pathology from underlying imaging data.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Patient interface with respiratory gas measurement component
InactiveUS20060249160A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing filtersAirway adaptorCatheter
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Connector for interfacing intravascular sensors to a physiology monitor
InactiveUS7274956B2Prevent movementEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical conductorElectrical contacts
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Physiological data monitoring system and method
ActiveCN102043894AEasy to usePortableSensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer terminalData monitoring
Owner:PEKING UNIV
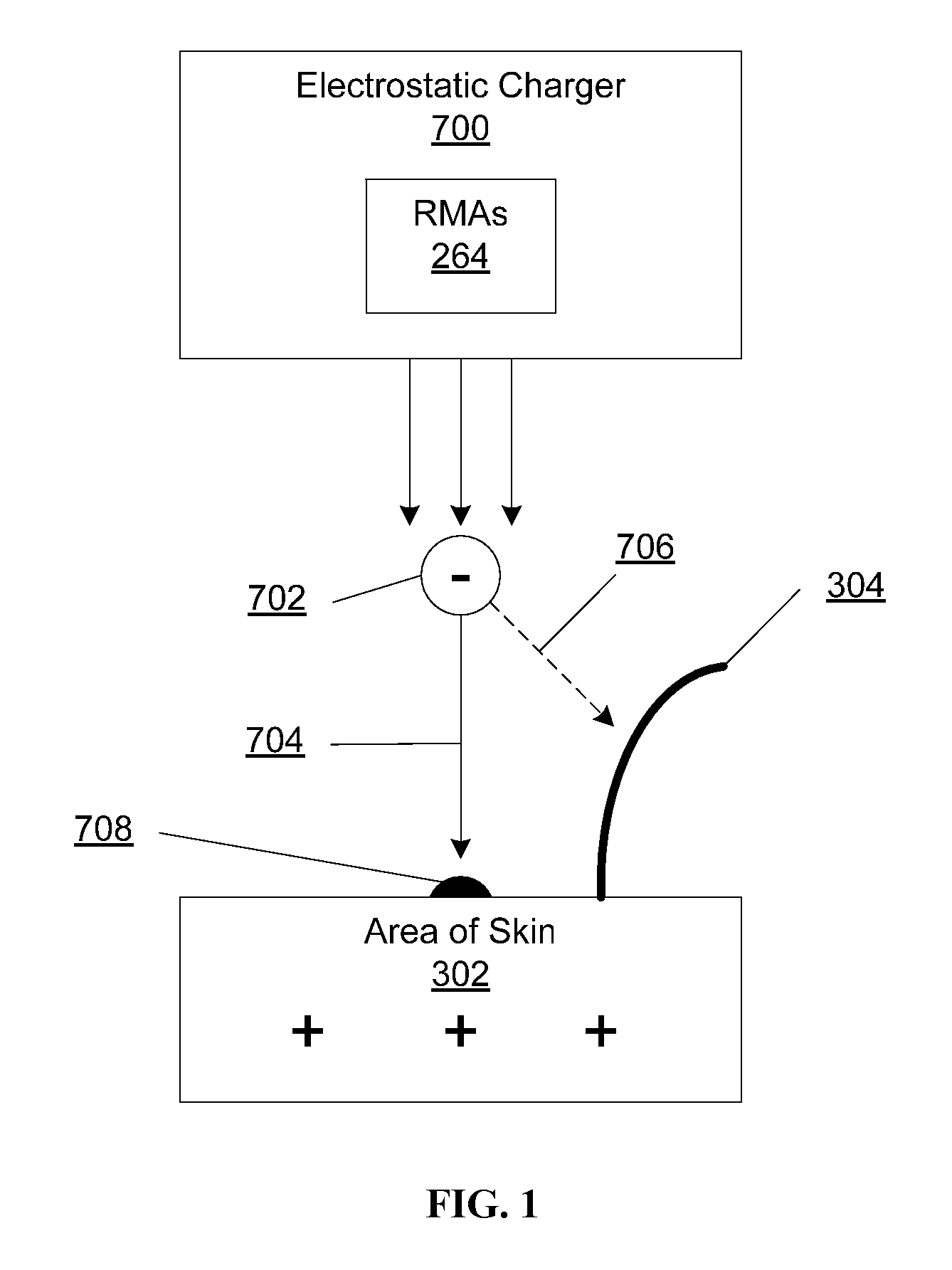
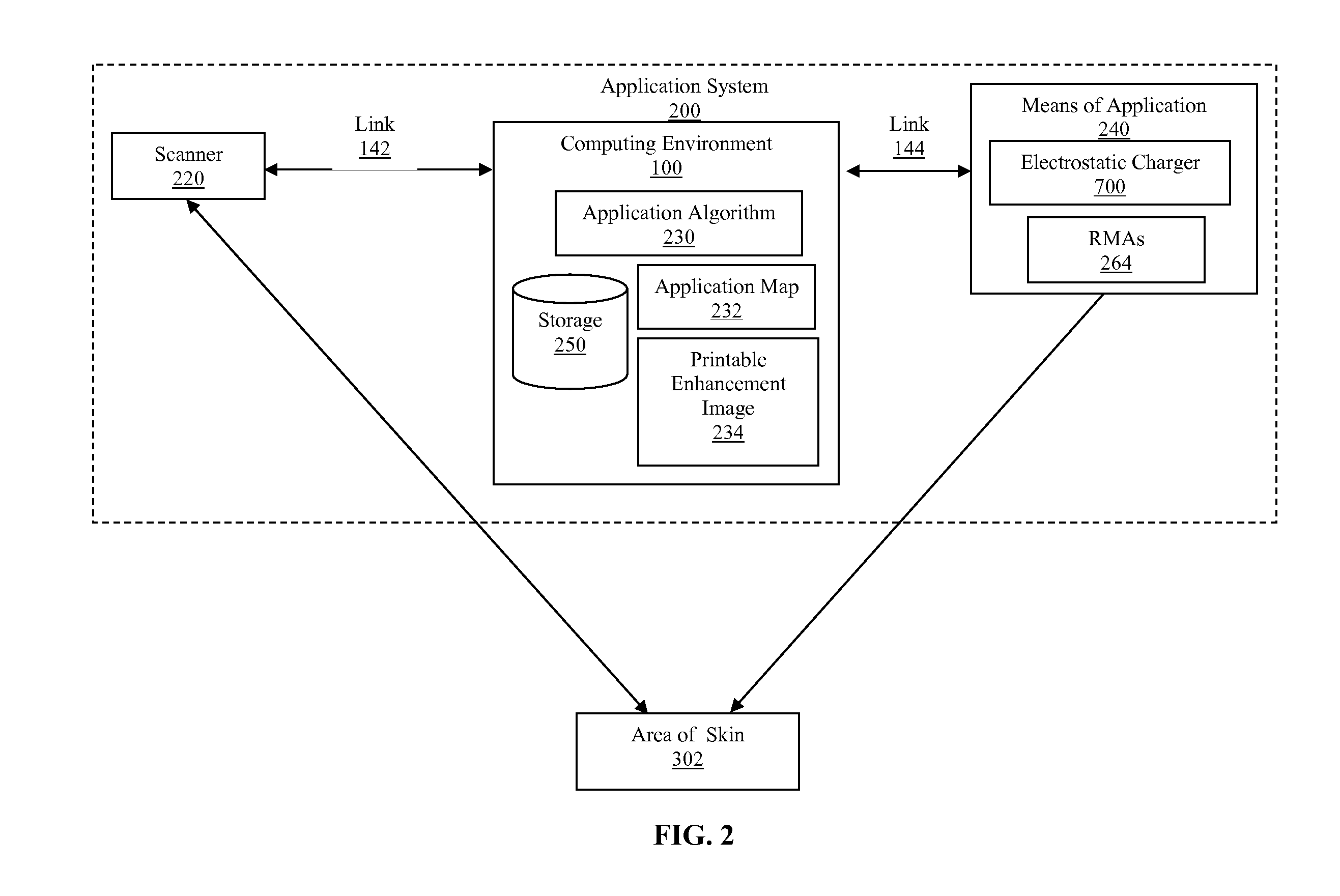
System and method for applying a reflectance modifying agent electrostatically to improve the visual attractiveness of human skin
ActiveUS20080194971A1Enhanced surface irregularityTypewritersMedical applicatorsComputer control systemHuman skin
Owner:TCMS TRANSPARENT BEAUTY LLC
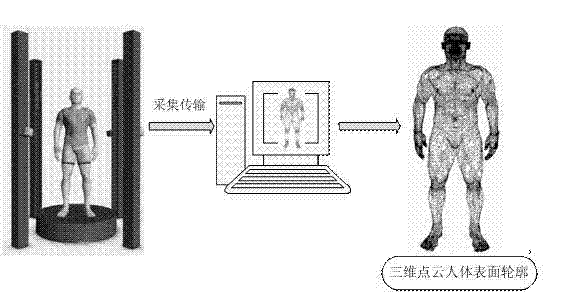
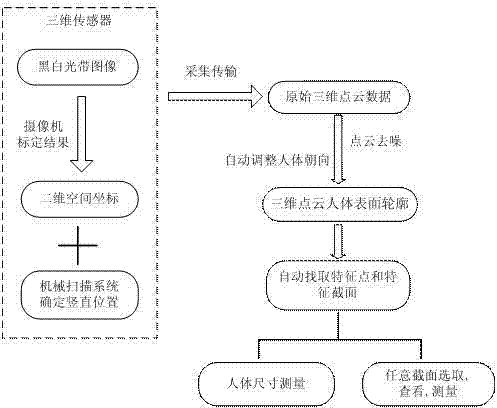
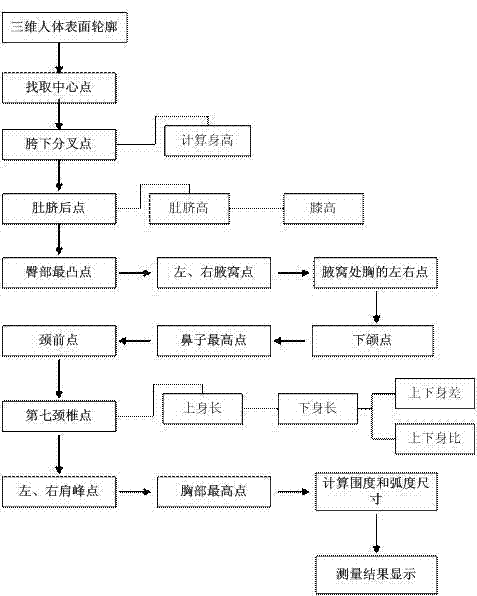
Method for automatically measuring human body dimensions on basis of three-dimensional point cloud data
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
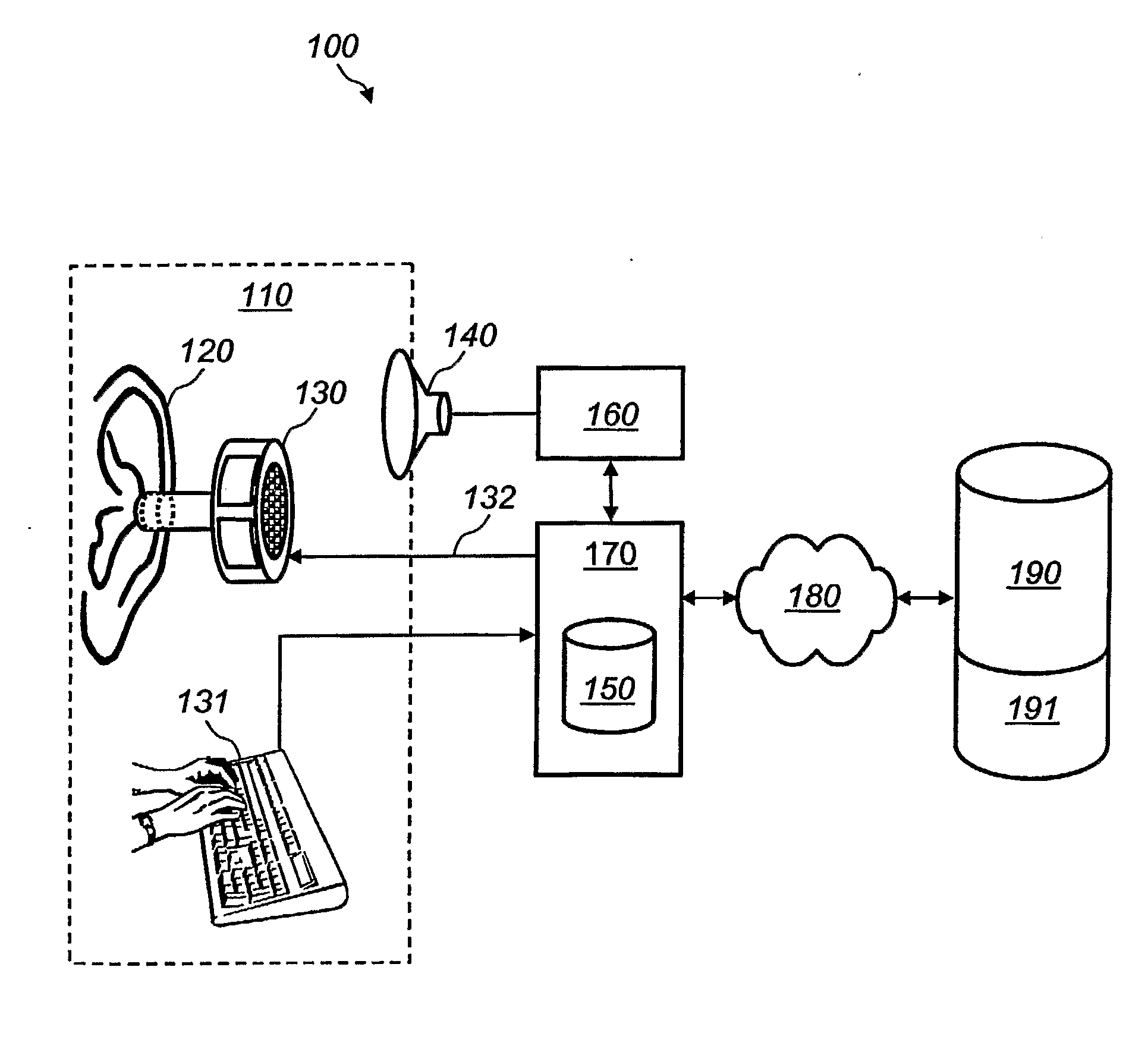
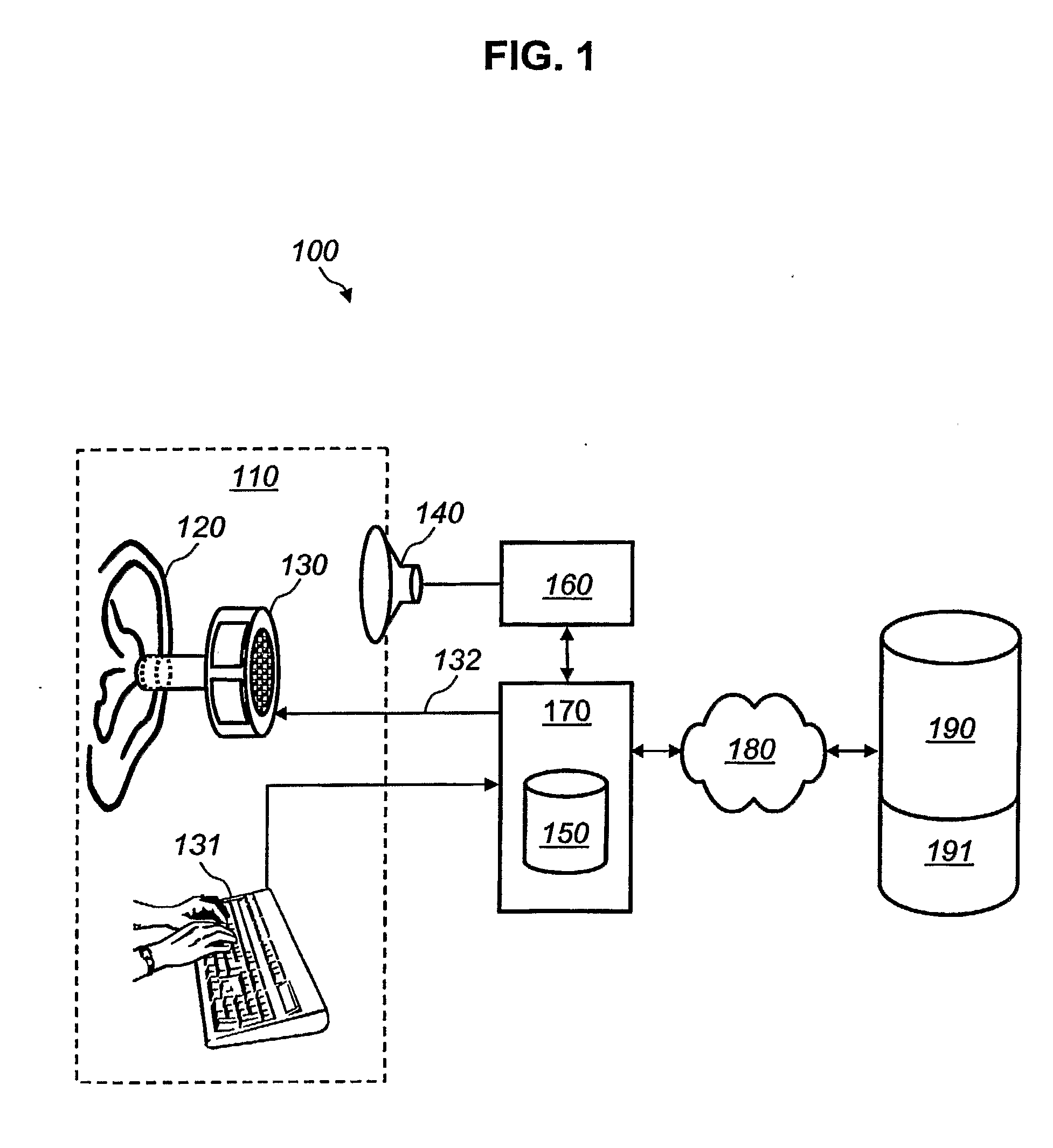
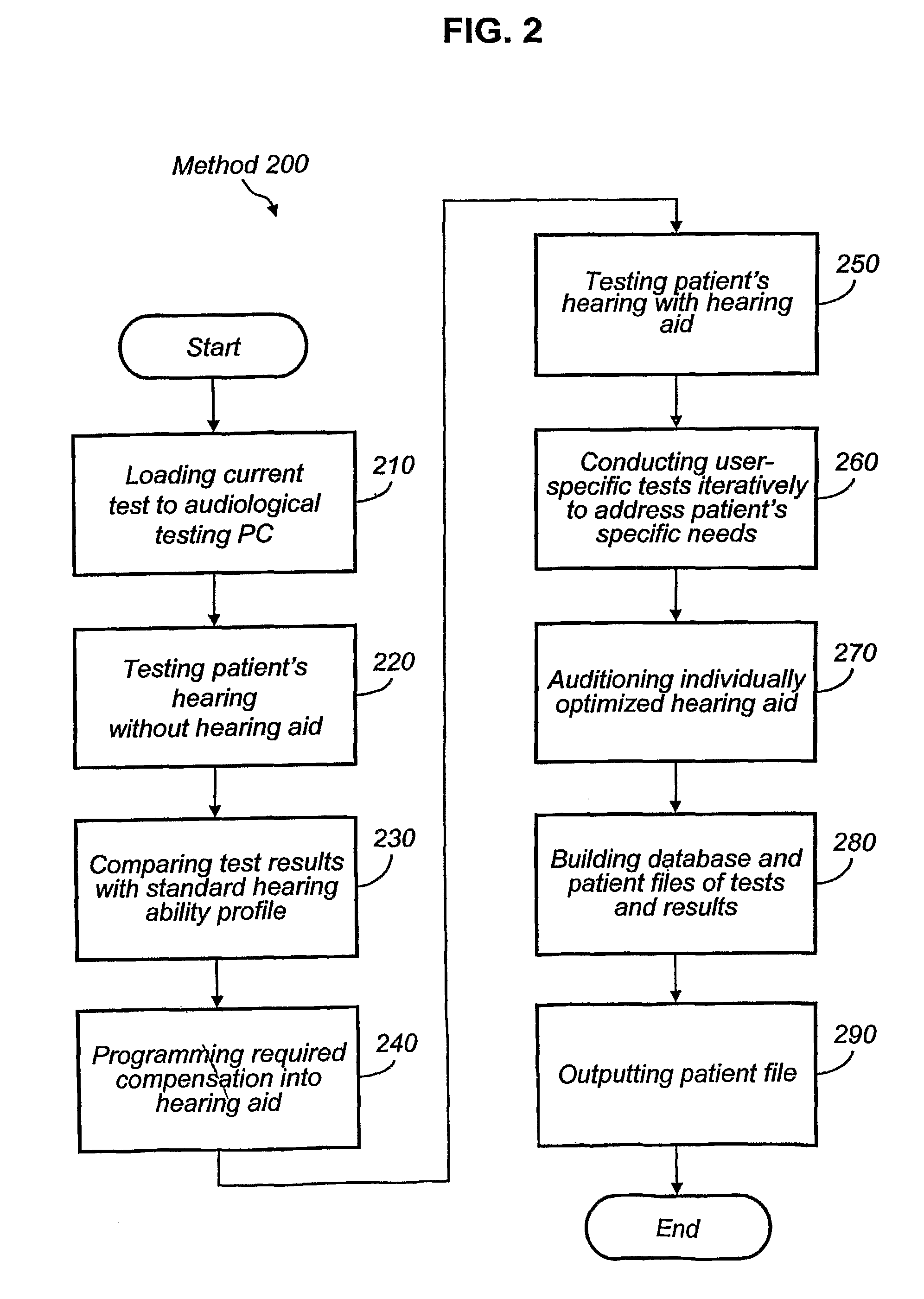
System for and Method of Optimizing an Individual's Hearing Aid
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
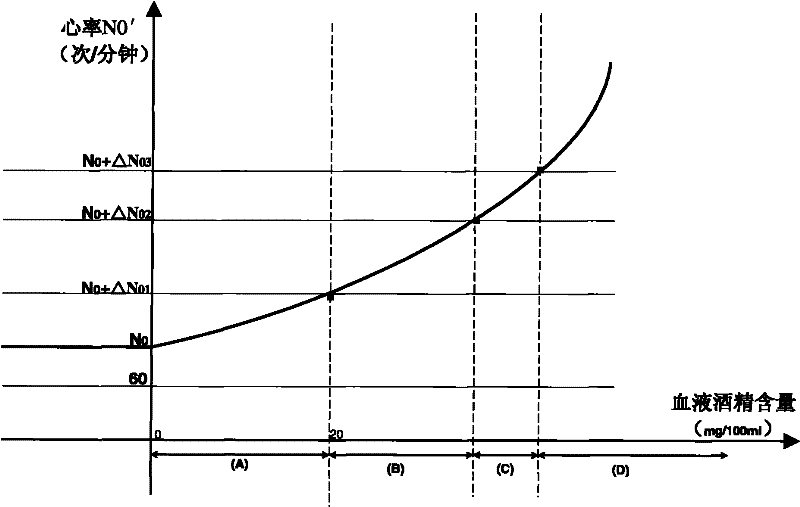
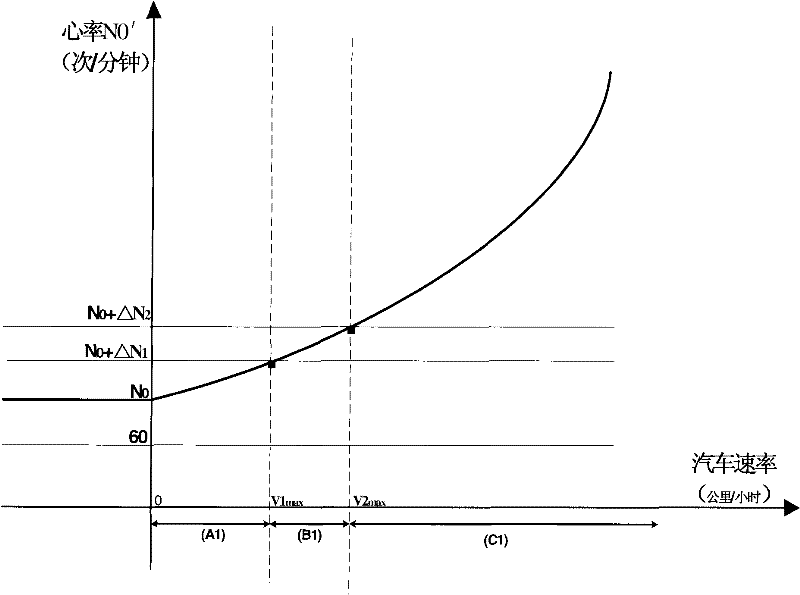
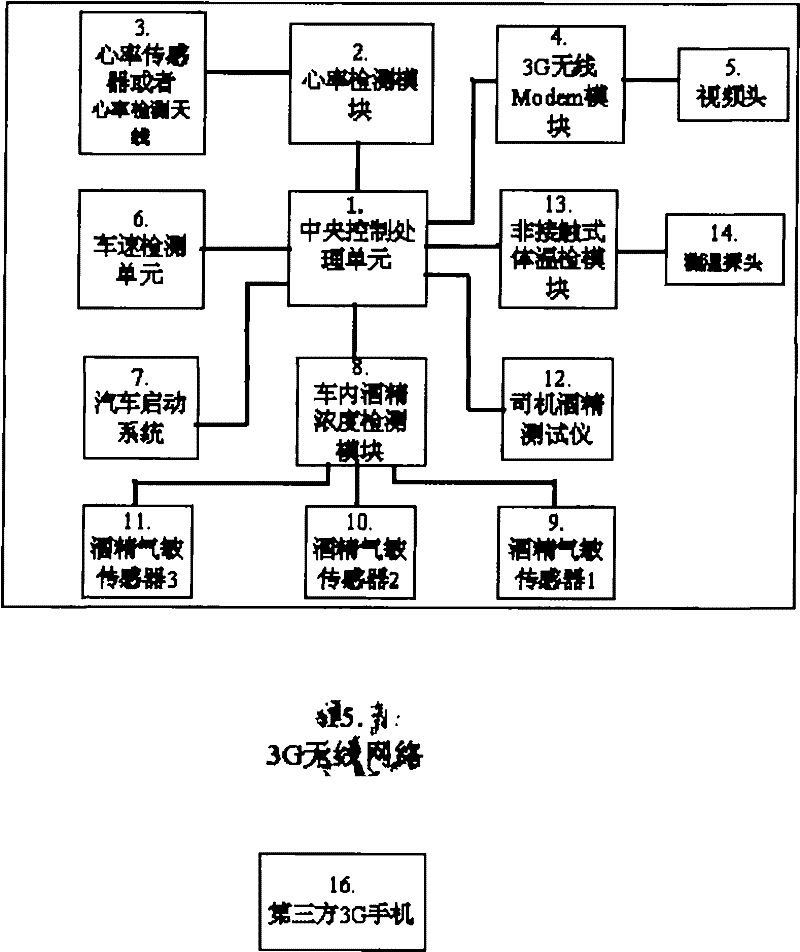
An anti-drunk driving and safe-health driving method
InactiveCN102163362AWays to Prevent Drunk DrivingGood for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular healthSensorsAlarmsThird partyDrunk driving
Owner:谢国华
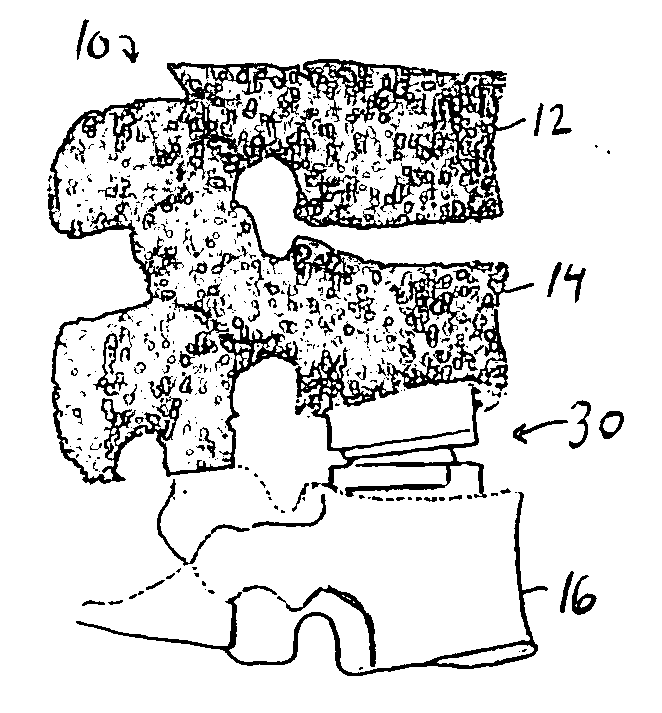
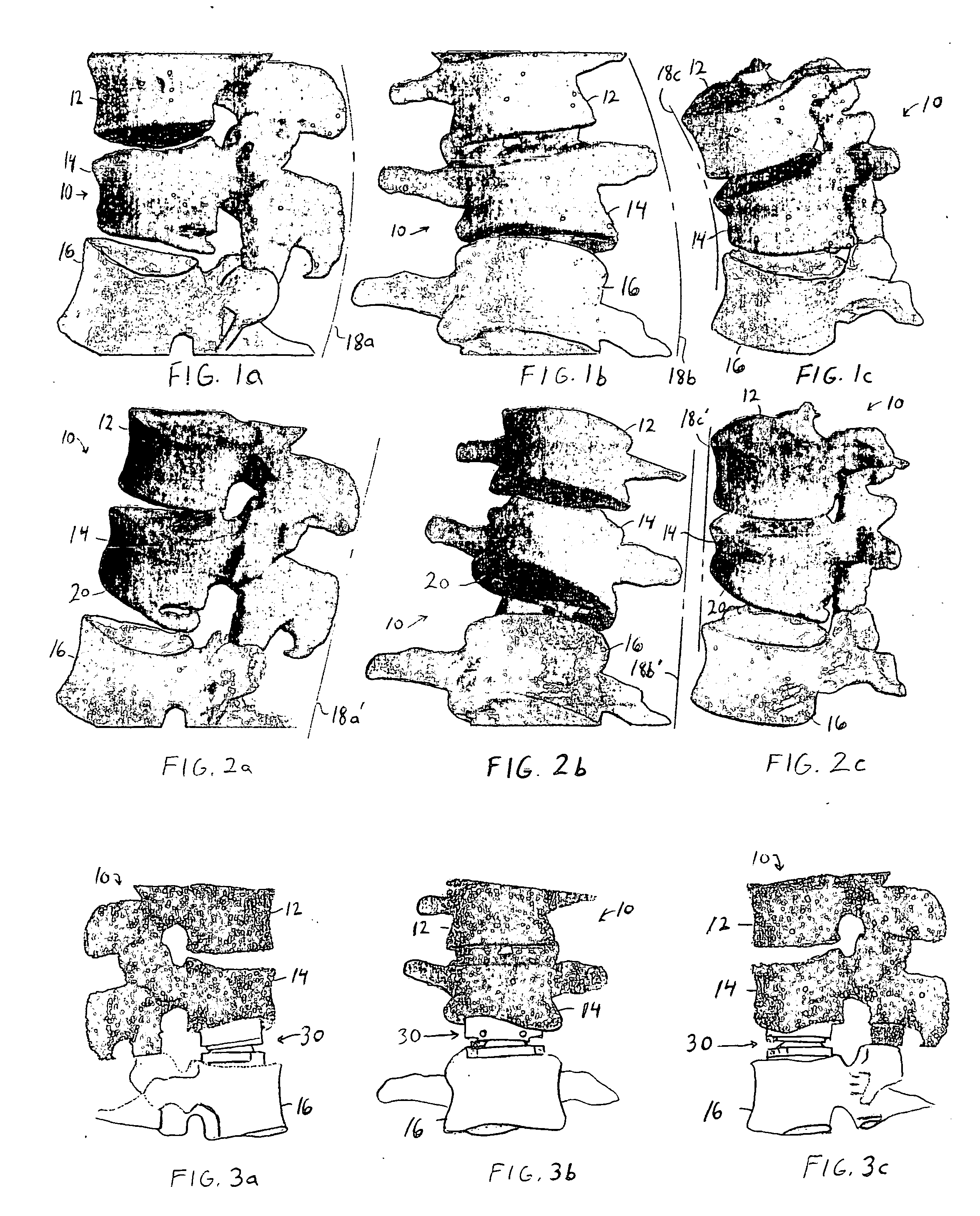
Customizing an intervertebral implant
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Automatic classification method for electrocardiogram signals
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Prosthetic sensing systems and methods
Owner:COLLEGE PARK IND INC
Portable Alveolar Gas Meter
ActiveUS20070232950A1Withdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationMeasurement deviceEngineering
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for detection, characterization and imaging of heterogeneity using shear wave induced resonance
InactiveUS20110130660A1Ultrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical resonanceAcoustics
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Materials and methods for treating neuropathies and related disorders including those involving a keystone nerve
InactiveUS20160030408A1Increase blood flowAlter perception of painBiocideElectrotherapyDiseaseMedicine
Methods, apparatus, compositions and kits for inhibiting a disorder in a human patient, including non-cerebral neurovascular disorder or muscular headache pain, or loss of motor or sensory function, sympathetic tone or range or fluidity of motion that affect a nerve pathway at more than one locus associated with the disorder to inhibit the disorder. Alternatively or in addition, neuropathy associated with a disorder is treatable by palpating to determine a Keystone nerve essential to the neuropathy, applying pressure to determine a point of maximum discomfort or trigger of increased symptoms to identify a Levin Sign as a locus of initial intervention, and intervening to treat the neuropathy at the location of the Levin Sign by administering a pharmaceutically active agent, internal implanted or external neuro stimulation affecting the nerve pathway to inhibit the neuropathy.
Owner:BHL PATENT HLDG
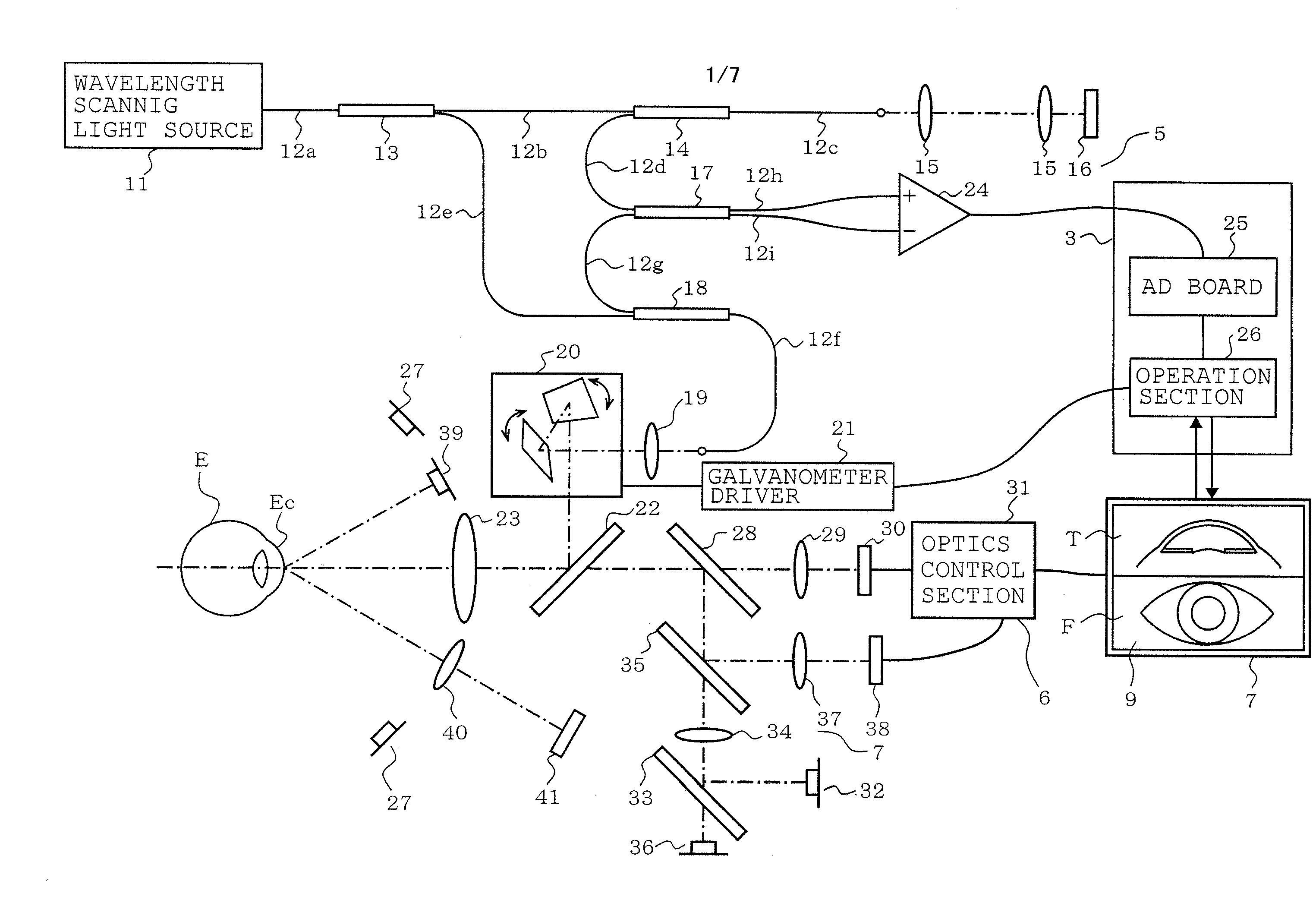
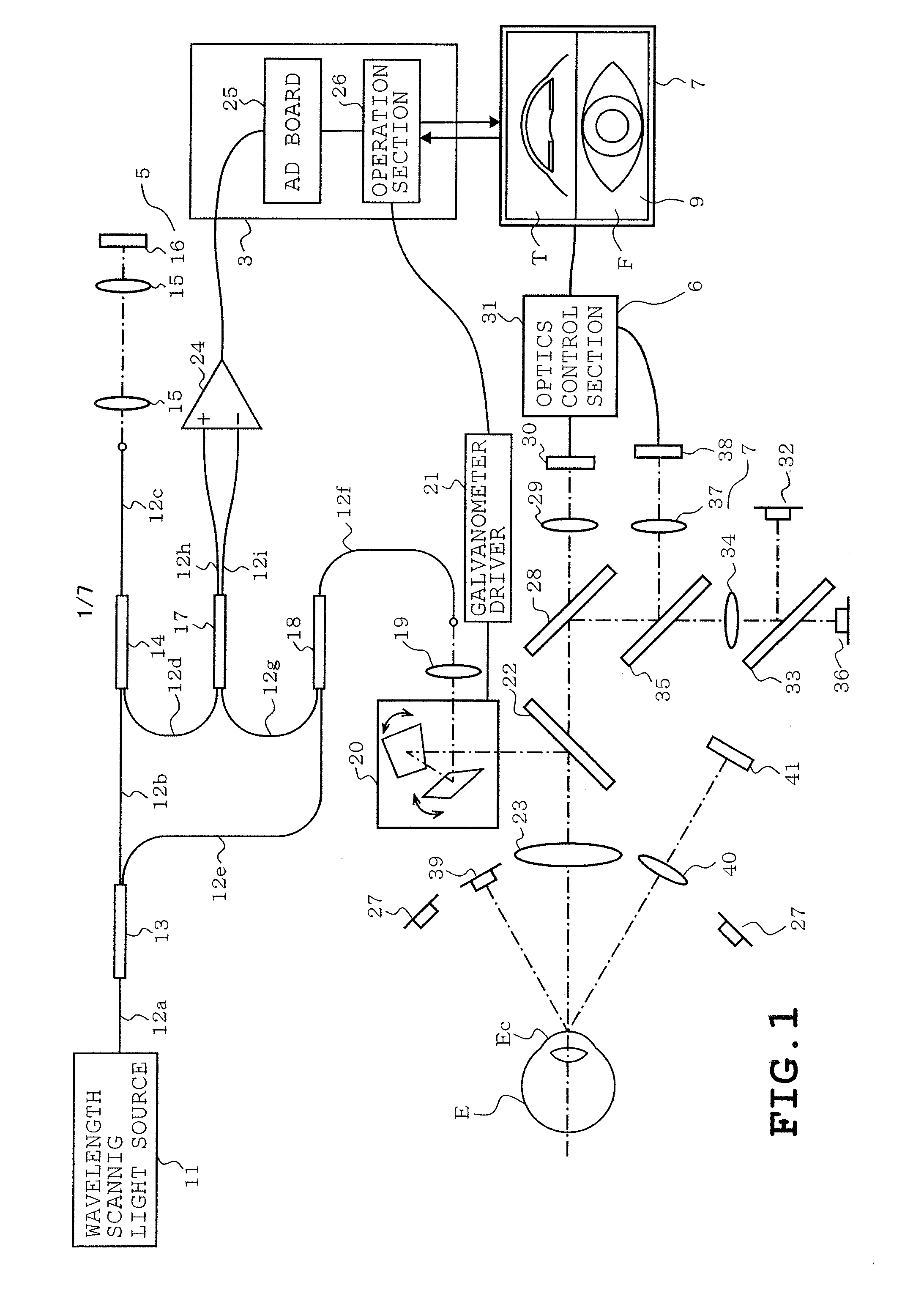
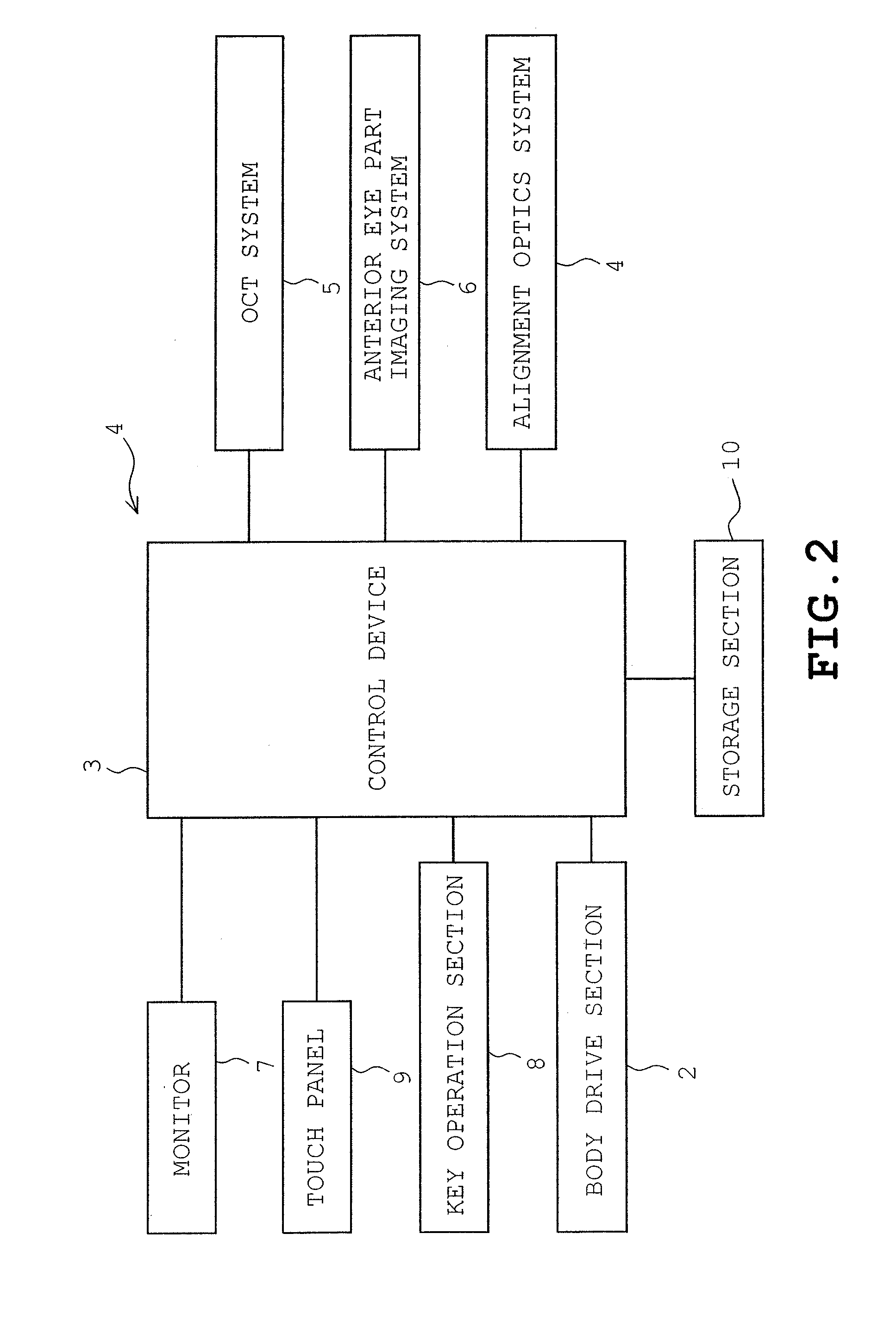
Apparatus and method for imaging anterior eye part by optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20090149742A1Short timeShorten the time periodPerson identificationSensorsScan lineOcular imaging
Owner:TOMEY CORP
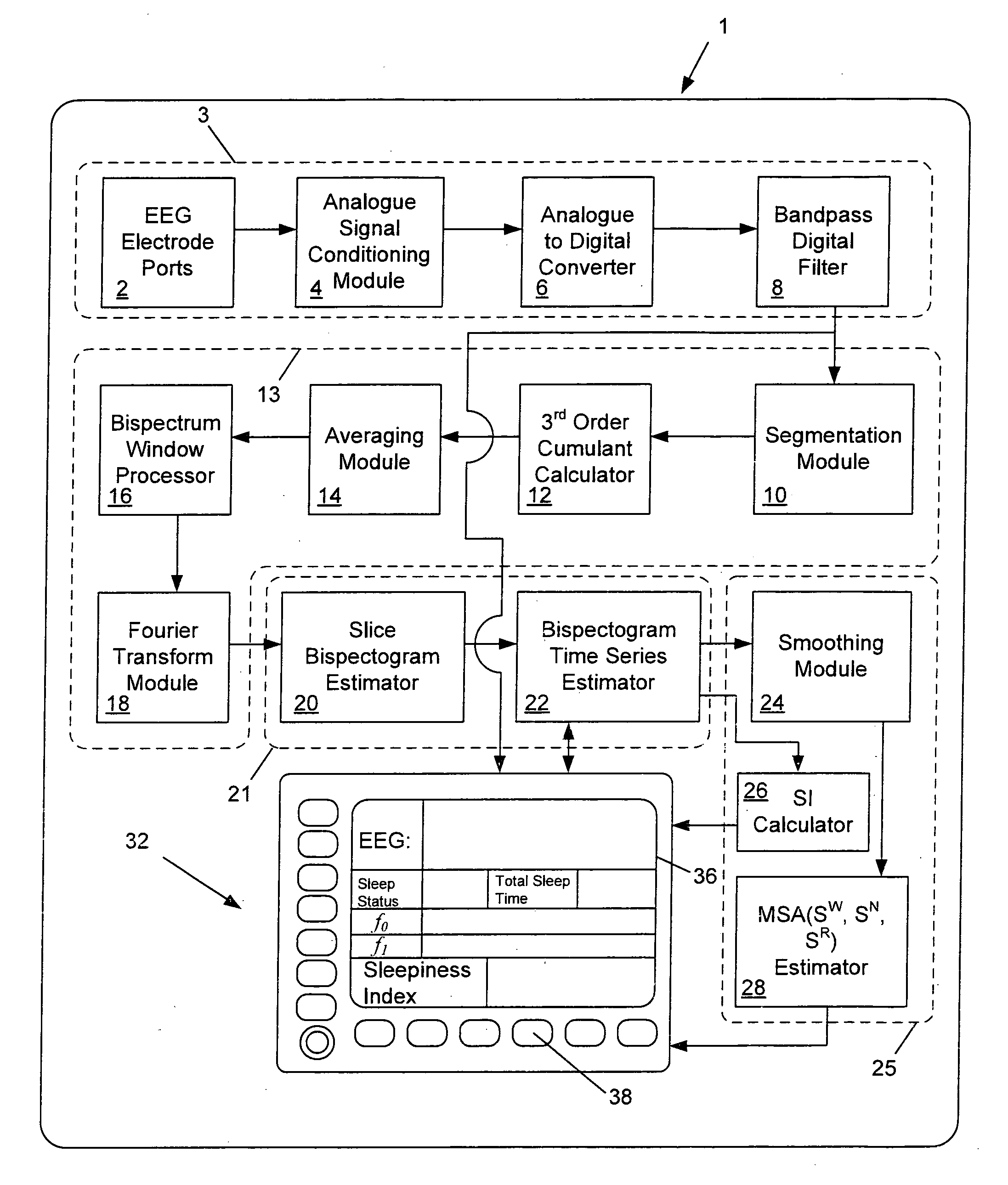
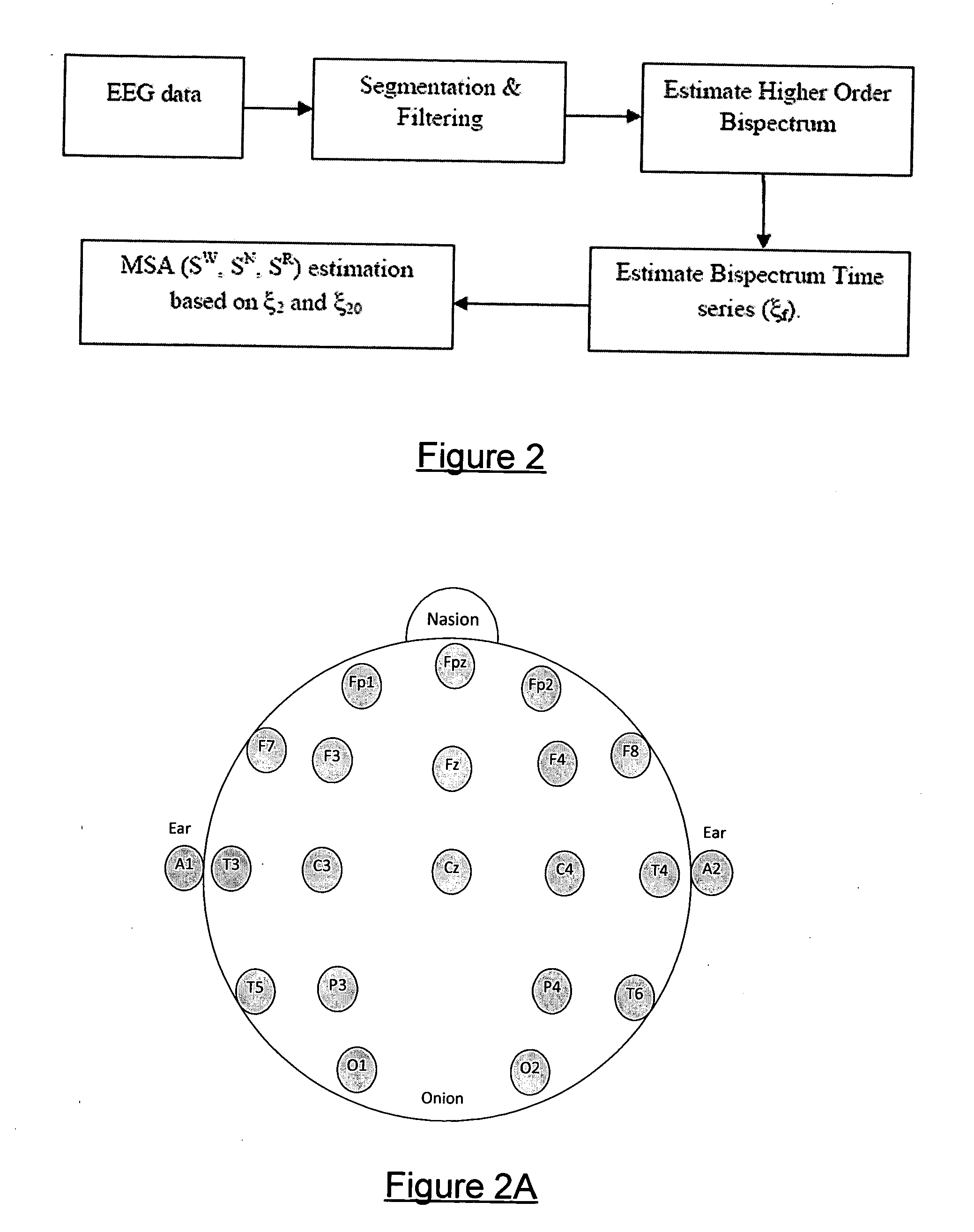
Method and apparatus for determining sleep states
ActiveUS20110301487A1Accurate calculationElectroencephalographyMedical simulationSleep architectureElectricity
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method of sensing forces on a working instrument
ActiveUS8052621B2Accurate estimateEliminate forceSurgical needlesPerson identificationCouplingRobot control
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Brain-computer interfaces and use thereof
InactiveUS20130130799A1ElectroencephalographyInput/output for user-computer interactionVisual evoked potentialsDisplay device
A computerized method for decoding visual evoked potentials involves obtaining a set of brain activity signals, the brain activity signals being recorded from a subject's brain during displaying a set of targets on a display having a display frame duration, at least one target being modulated periodically at a target-specific modulation parameter and decoding a visual evoked potential (VEP) from the brain activity signals. The decoding includes, at least for the at least one target being modulated at a target-specific modulation parameter, determining a representative time track from the obtained brain activity signals, the representative time track having a length being integer multiples of the display frame duration, analyzing at least one amplitude feature in the representative time track, and determining a most likely target of interest or absence thereof based on said analyzing.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Rehabilitation apparatus using game device
InactiveUS20120116258A1Solve problemsPerson identificationSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSacroiliac joint
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Detecting human cancer through spectral optical imaging using key water absorption wavelengths
InactiveUS20060173355A1Reliable noninvasive diagnosisDiagnostics using lightSensorsHuman cancerCervix
Spectral optical imaging at one or more key water absorption fingerprint wavelengths measures the difference in water content between a region of cancerous or precancerous tissue and a region of normal tissue. Water content is an important diagnostic parameter because cancerous and precanerous tissues have different water content than normal tissues. Key water absorption wavelengths include at least one of 980 nanometers (nm), 1195 nm, 1456 nm, 1944 nm, 2880 nm to 3360 nm, and 4720 nm. In the range of 400 nm to 6000 nm, one or more points of negligible water absorption are used as reference points for a comparison with one or more key neighboring water absorption wavelengths. Different images are generated using at least two wavelengths, including a water absorption wavelength and a negligible water absorption wavelength, to yield diagnostic information relevant for classifying a tissue region as cancerous, precancerous, or normal. The results of this comparison can be used to identify regions of cancerous tissue in organs such as the breast, cervix and prostate.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R +3
Stent Delivery System for Detecting Wall Apposition of the Stent During Deployment
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Methods and systems for detection and thermal treatment of lower urinary tract conditions
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Leadless wireless ECG measurement system and method for measuring of bio-potential electrical activity of the heart
Owner:KHAIR MOHAMMAD
Imaging probe and method of obtaining position and/or orientation information
ActiveUS20150080710A1Facilitate three-dimensional mappingImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic fieldNuclear magnetic resonance
A method of obtaining information about the position and / or orientation of a magnetic component relatively to a magnetometric detector, the magnetic component and the magnetometric detector being moveable independently from each other relatively to a static secondary magnetic field, the method comprising the steps of: measuring in the presence of the combination of both the magnetic field of the magnetic component and the static secondary magnetic field essentially simultaneously the strength and / or orientation of a magnetic field at at least a first position and a second position spatially associated with the magnetometric detector, the second position being distanced from the first position; and combining the results of the measurements to computationally eliminate the effect of the secondary magnetic field and derive the information about the position and / or orientation of the magnetic component.
Owner:EZONO
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap