Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1 results about "Nuclear fusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic "binding energy" between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Fusion is the process that powers active or "main sequence" stars, or other high magnitude stars.
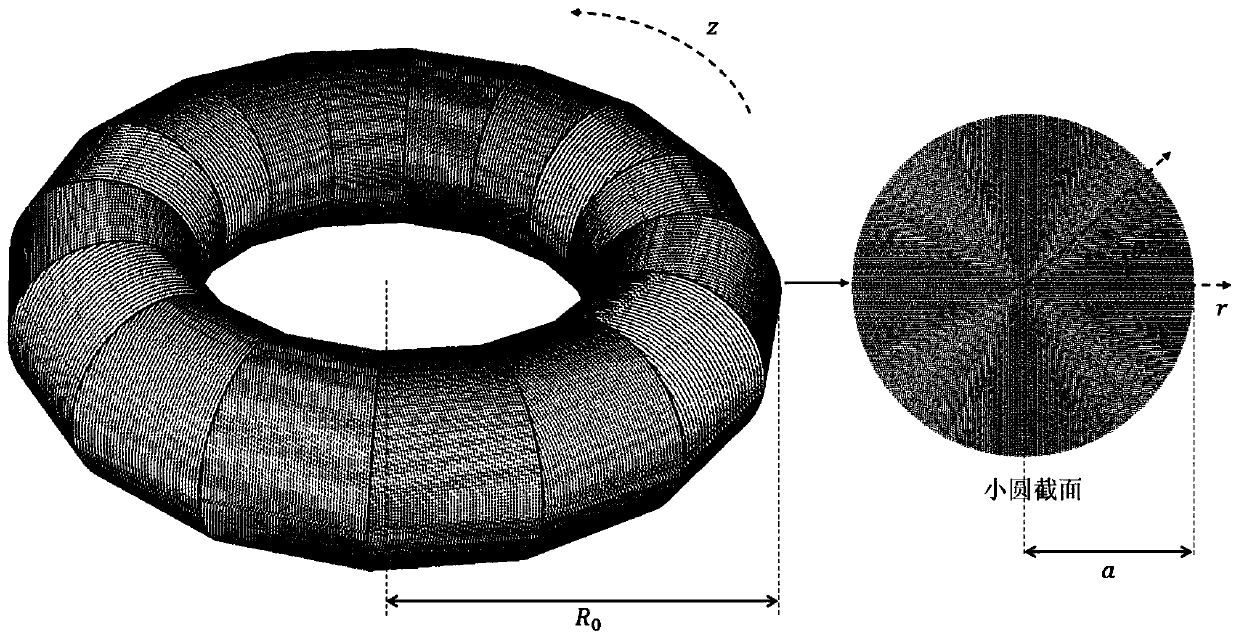
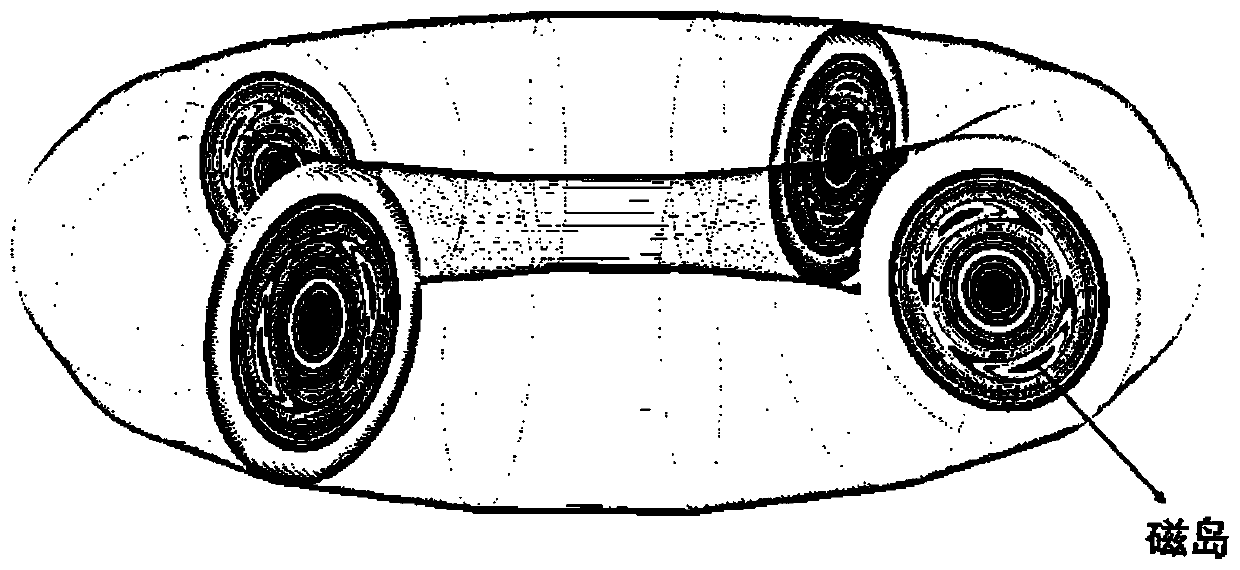
Simulation method for controlling novel classic tearing mode through resonance magnetic disturbance in tokamak
ActiveCN110232205AGood combination experimentImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical stabilityMagnetic disturbance
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap