Method for designing discrete layering angles of laminated board
A design method and laminated board technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high solution efficiency, large storage space and computing time consumption, difficult to handle complex design requirements, etc., to achieve optimal problem scale, The effect of reducing the number of variables and meeting engineering requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
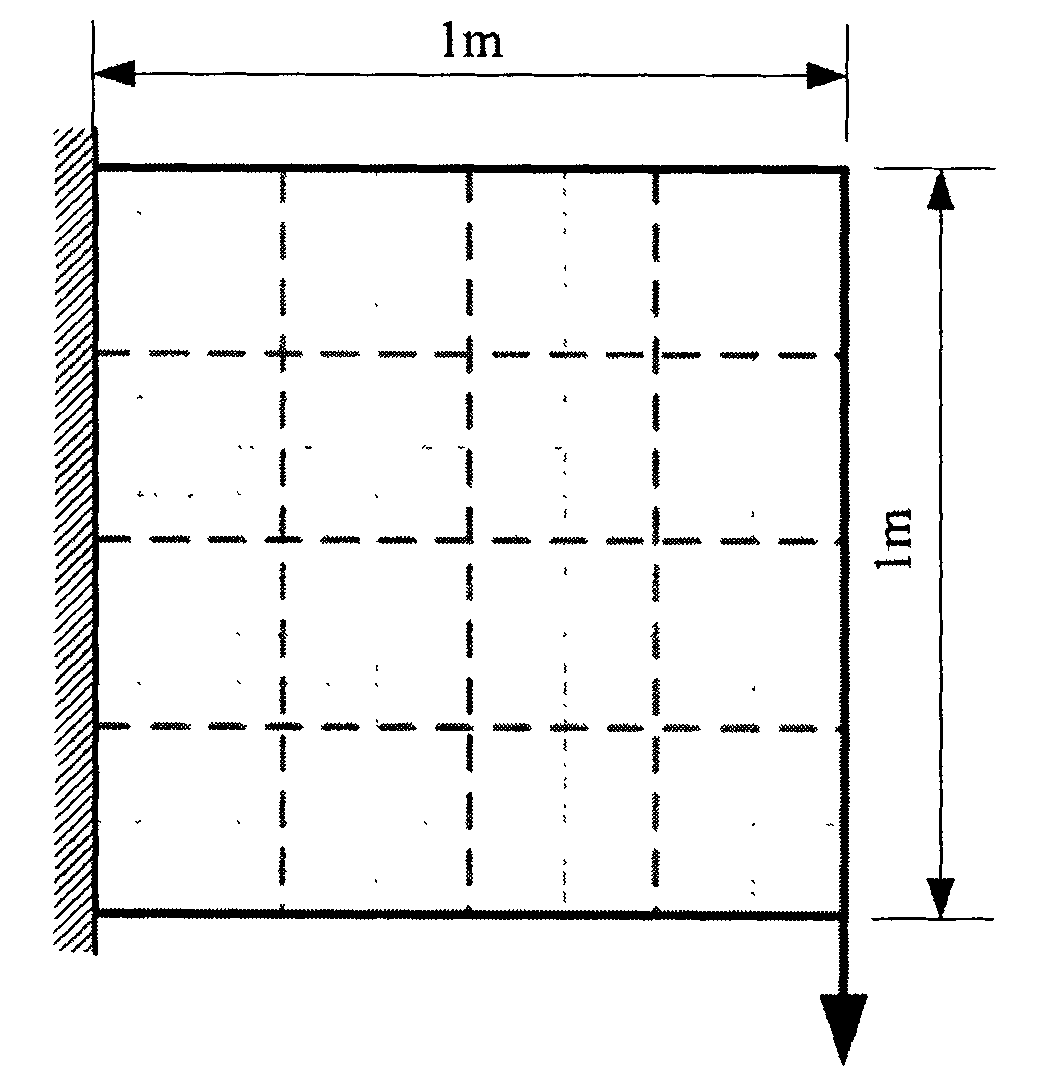
[0032] Example 1: (a) Divide a square planar structure with a length and width of 1m into a square grid of 16×16; every 4×4 units constitute a design area, and all units have the same laying angle; the left side of the structure Laterally fixed support, the load is the concentrated load F=1000N acting on the lower right corner of the structure; orthotropic material property: E x =146.86GPa,E y =10.62GPa,G xy =5.45GPa, v xy =0.33; the number of ply angles m=4, the ply angles are 90° / 45° / 0° / -45° respectively; given the initial value of the design variable x ik =0.
[0033] For m ply angle design problems, the number of design variables required for each unit Establish the finite element model of laminate design space and the initial value of design variable x ik =0, where i represents the unit number, and k represents the kth design variable corresponding to the unit; the stiffness matrix of unit i under the given j-th ply angle is K i (j) ; Use the following formula
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: (a) Divide the rectangular planar structure with a length and width of 6m and 1m into a square grid of 240×40; every 10×10 units constitute a design area, and all units have the same ply angle ;The structure is simply supported, and the load is a concentrated load acting on the symmetry axis of the structure F=1000N; Orthotropic material properties Orthotropic material properties: E x =146.86GPa,E y =10.62GPa,G xy =5.45GPa, v xy =0.33; the number of ply angles m=36, the ply angles are
[0051] 90° / 85° / 80° / 75° / 70° / 65° / 60° / 55° / 50° / 45° / 40° / 35° / 30° / 25° / 20° / 15° / 10° / 5° / 0° / -5° / -10° / -15° / -20° / -25° / -30° / -35° / -40° / -45° / -50° / -55° / -60° / -65° / -70° / -75° / -80° / -85°; given initial value of design variable x ik =0; use the following formula to set the coefficient s jk value of
[0052] s jk = 1
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap