Adaptive millimeter wave beam tracking method based on extended Kalman filtering
An extended Kalman and adaptive technology, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, space transmit diversity, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve effective tracking, rapid accumulation of errors, mutual influence, etc., to extend the effective tracking time, The effect of reducing overhead and improving tracking accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0068] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
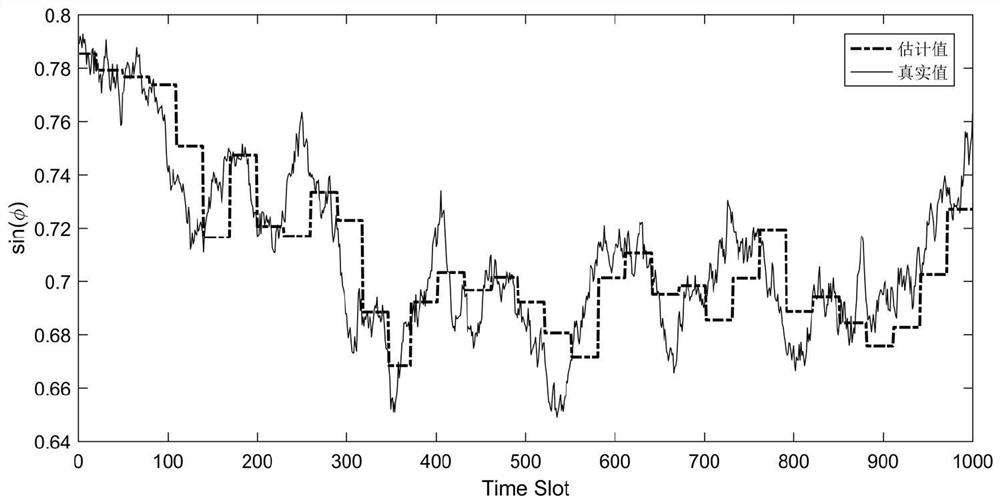
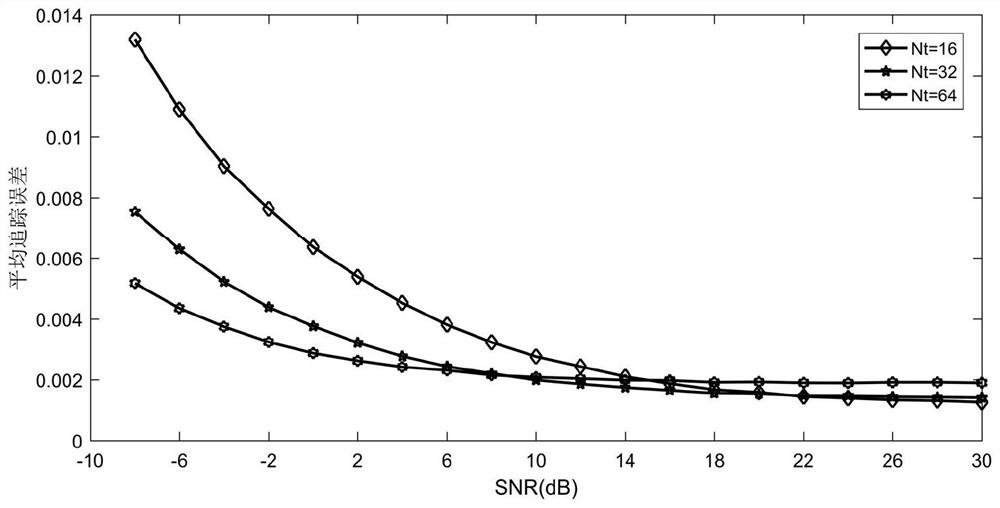
[0069] The method disclosed in the present invention does not need to know the instantaneous gain of the channel, but only needs to take the angle change of the channel as the quantity to be estimated, and can automatically adjust the frequency of beam tracking in real time according to the rate of change of the angle of the communication channel, while ensuring the tracking accuracy, it is effective Extend the time of beam tracking and reduce the overhead of beam tracking.
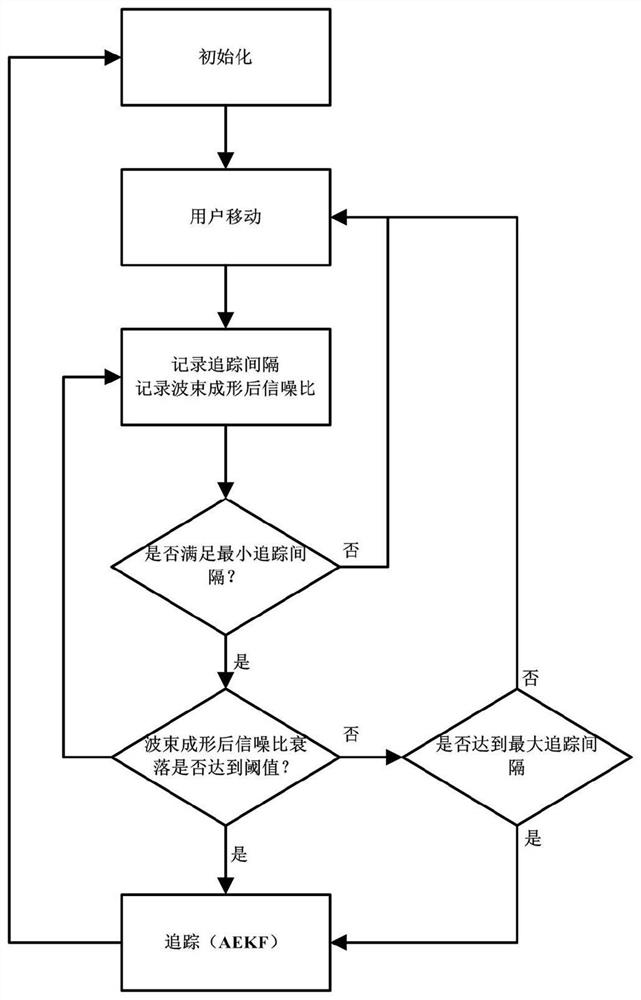
[0070] The present invention is an adaptive millimeter-wave beam tracking method based on extended Kalman filter, and its algorithm flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, this example includes the following steps:
[0071] Consider the following mmWave communication field: the transmitting end Tx sends the pilot signal, and the receiving end Rx receives the pilot signal.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap