Method and Apparatus for Reducing Jitter in Multi-Gigahertz Systems
a multi-gigahertz system and jitter reduction technology, applied in the field of signal processing systems, can solve the problems of large jitter reduction difficulty in current systems, high jitter in random jitter (rj) and other problems, and achieve the effect of low jitter and less jitter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental embodiment
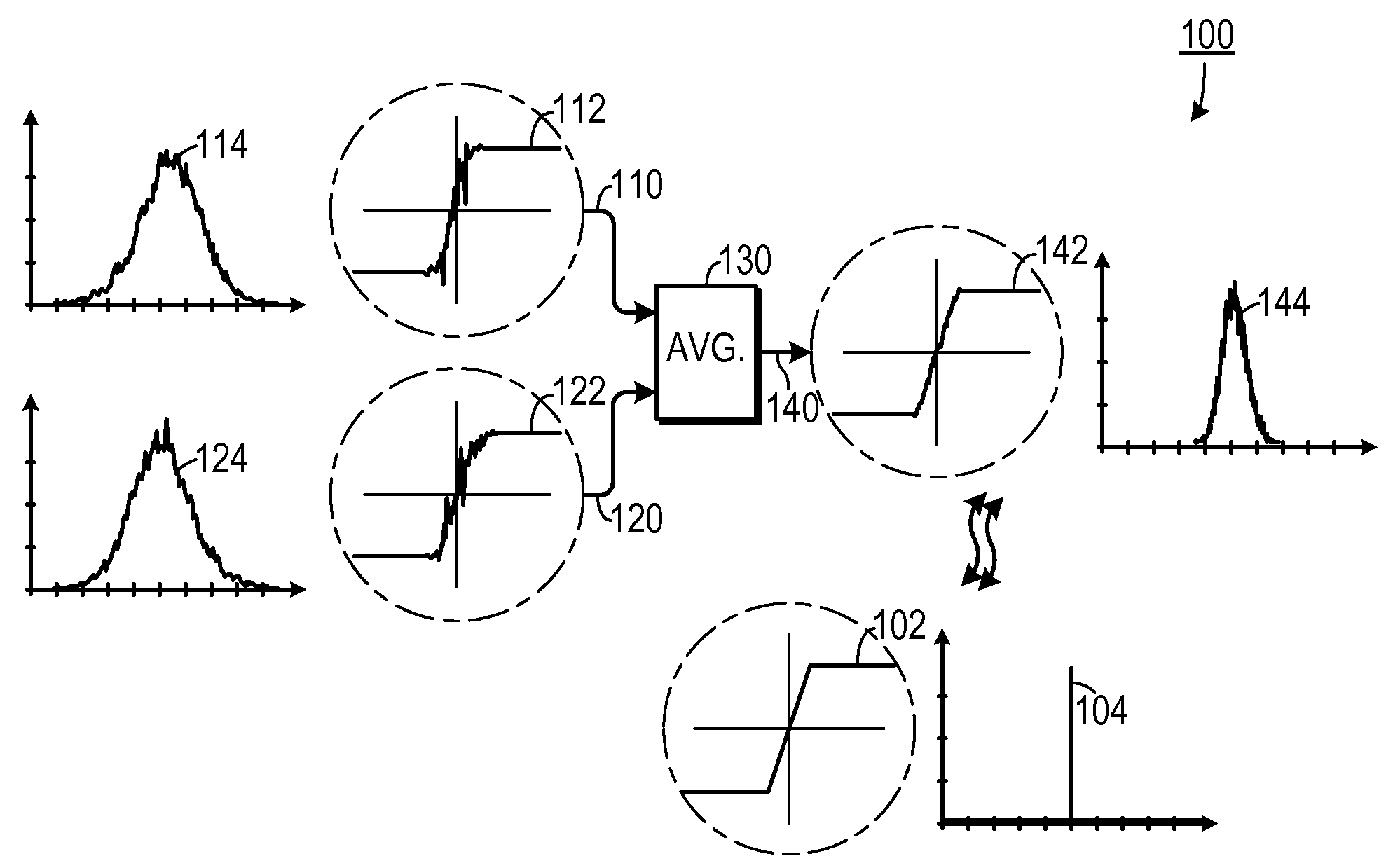
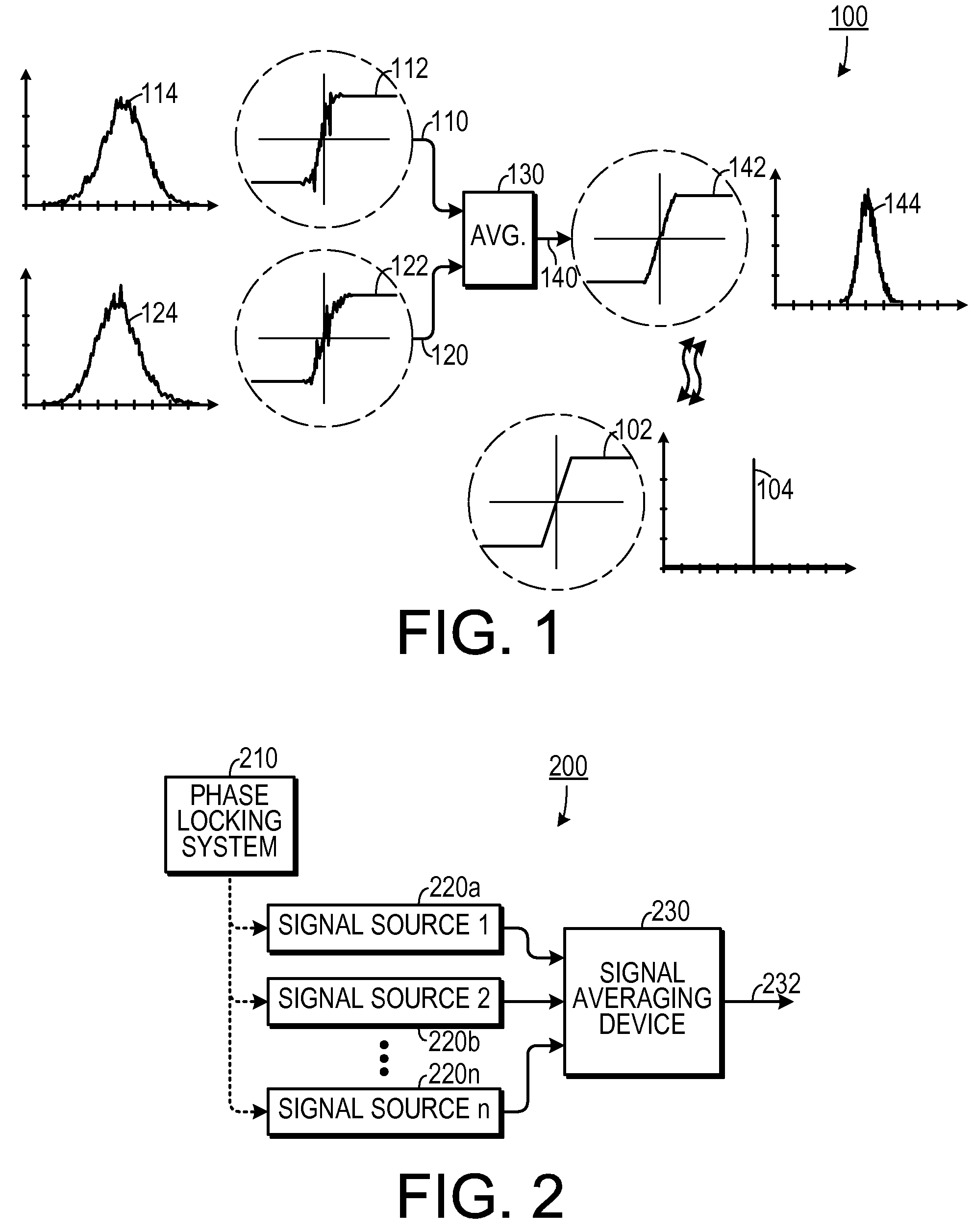
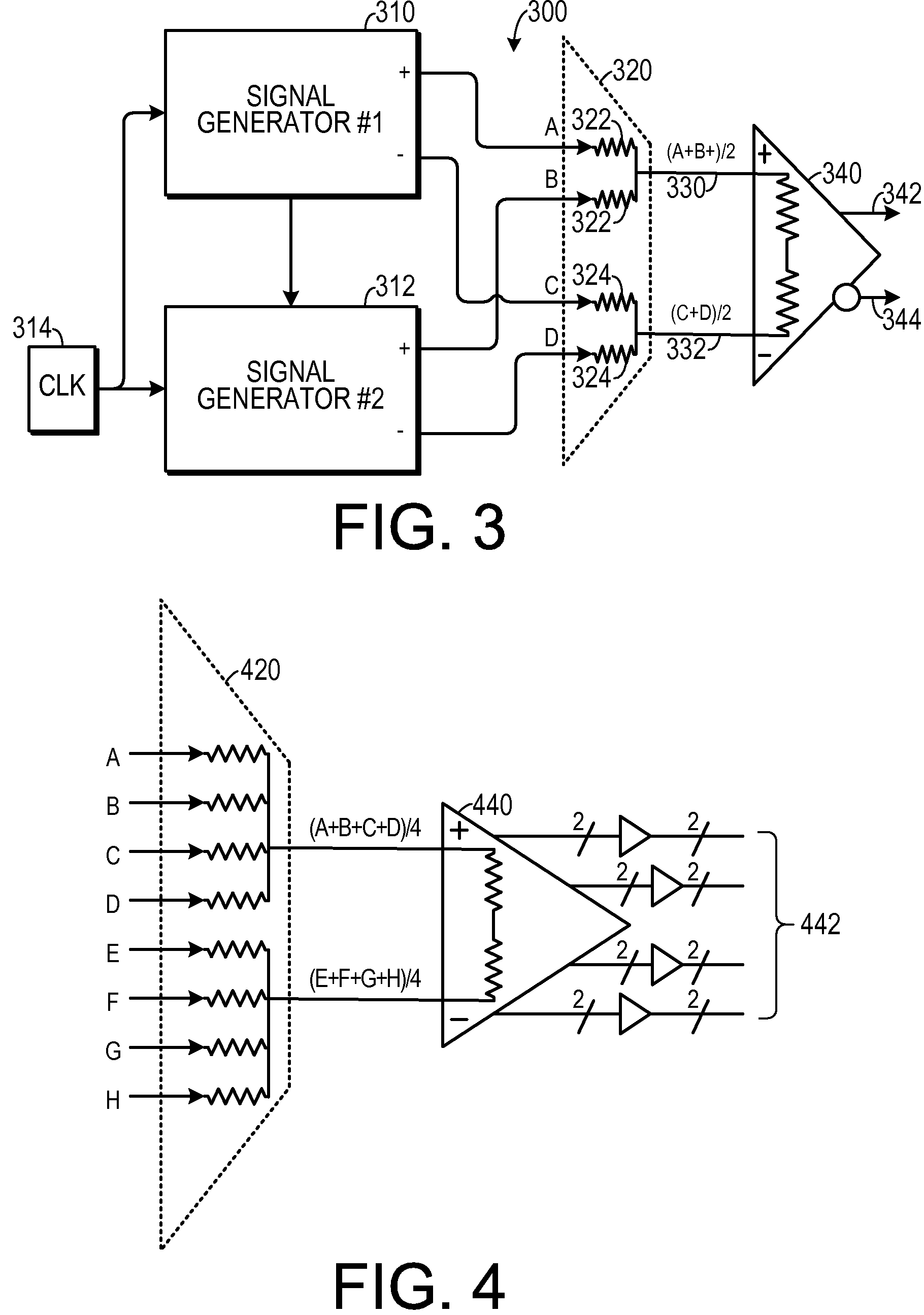
[0028]One experimental embodiment and supporting theory is now disclosed. Because testing at multi-gigahertz frequencies is so dependent on high-accuracy timing signals, it may be necessary to utilize more automated test equipment (“ATE”) resources for the most critical signals (such as clocks and timing references). In one experimental embodiment, multiplexing and demultiplexing modules were added to loadboards to synthesize multi-gigahertz test patterns using multiple 1 Gbps ATE channels.
[0029]Several “Driver” and “Receiver” modules were used to provide over 80 multi-Gbps differential channels in a combination of HyperTransport (1.6 Gbps per channel) and PCI-express (at 2.5 Gbps per channel). The ATE jitter level was typically in the range of 4 ps-8 ps, which is not sufficiently low for our testing needs in the 3 to 10 Gbps range. Therefore, a low-jitter (˜1.4 ps) RF clock source was used to provide a programmable timing reference to each of the modules. This level of jitter is a fac
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap