Method for supplementing digital image with picture element, and digital image encoder and decoder using the same
a technology of digital image and encoder, which is applied in the field of supplementing digital image with picture elements, and using the same digital image encoder and decoder, which can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, large processing volume, and long delay time, and achieves small volume of calculation, short delay time, and less errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
exemplary embodiment 1
(Exemplary Embodiment 1)
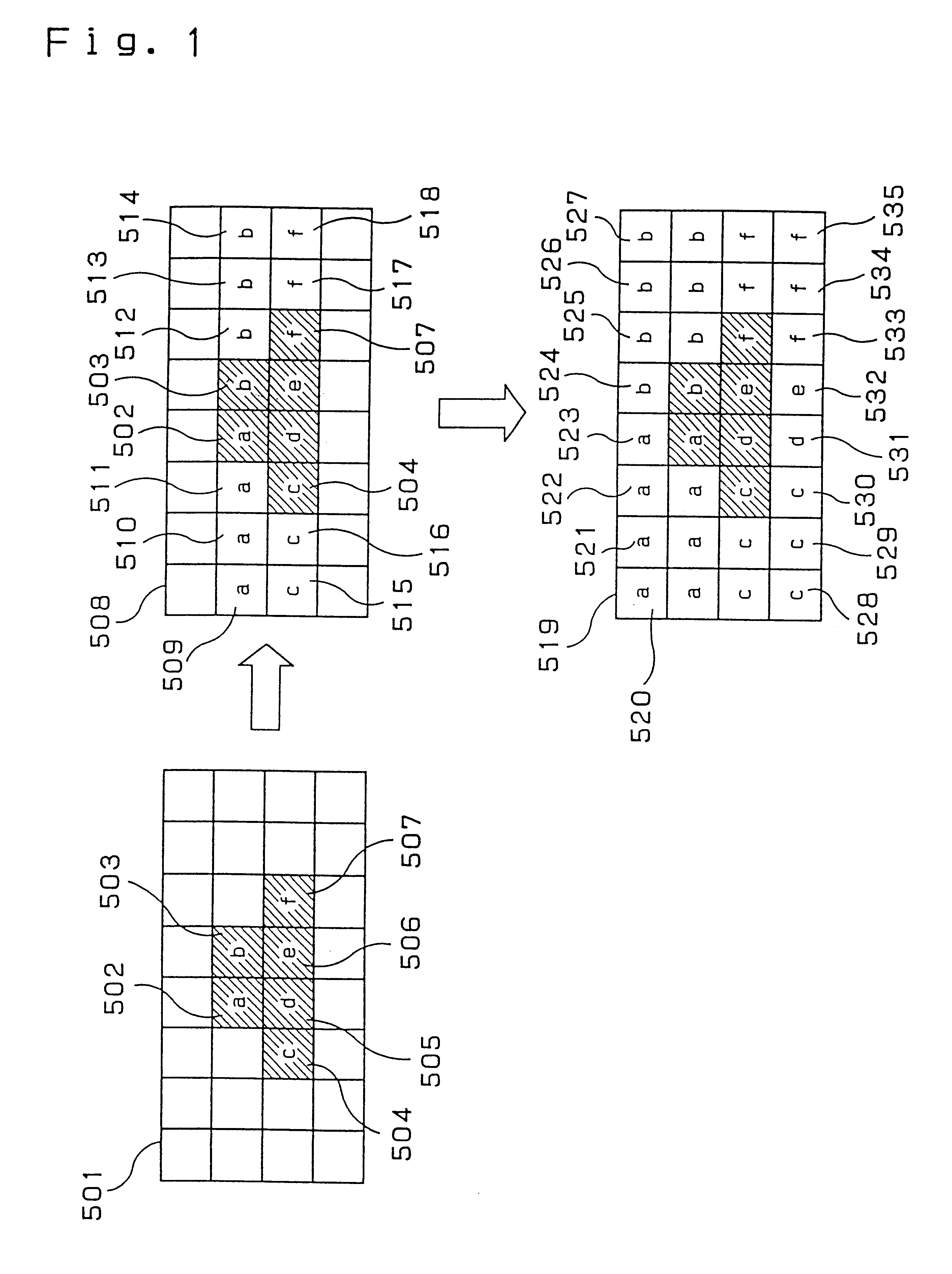
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram depicting a padding method of a digital picture in a first exemplary embodiment of the present invention. A picture 501 is a subject picture to be padded. Each lattice in the picture 501 represents a pixel i.e., a sample from the picture. Pixels 502-507 are significant samples, and other samples are insignificant.
In this embodiment, a shape signal of the picture is referred to for determining whether a sample is significant or insignificant. When the shape signal is “0”, the sample is insignificant, and when the shape signal is “1”, the sample is significant.
When a picture 508 is produced from the picture 501, each insignificant sample is padded as described below:First, scan each line of the picture 501. In this scanning process, when a significant sample is detected, a value thereof is substituted to an insignificant sample, e.g., when the first line is scanned, padding process is not done because of no significant sample, and whe
exemplary embodiment 2
(Exemplary Embodiment 2)
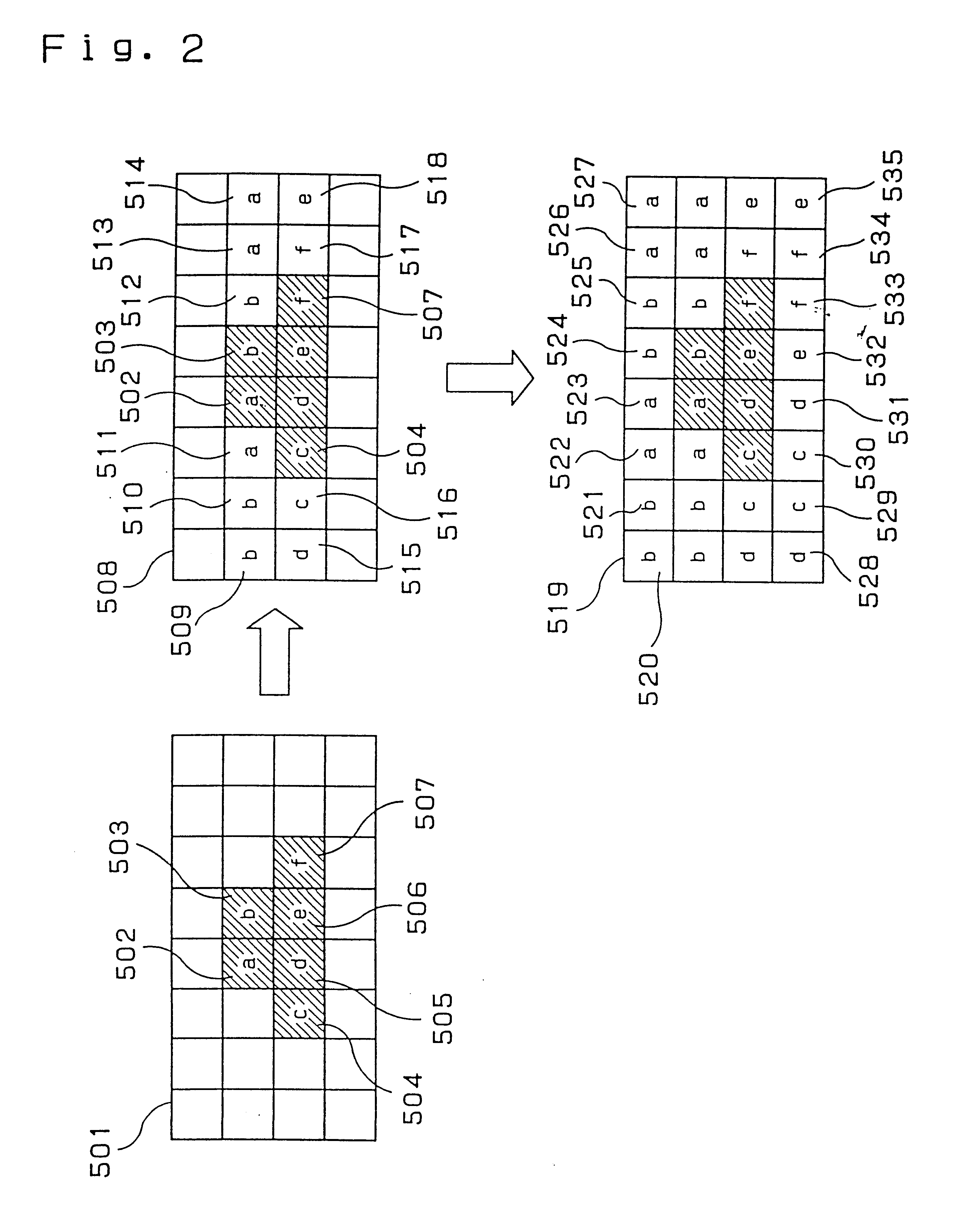
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram depicting a padding method of a digital picture in a second exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
A picture 801 comprises collected significant samples 802. First, scan the picture 801 horizontally, and substitute significant sample values into the nearest insignificant samples to produce a picture 803. At the same time, scan the picture 801 vertically, and substitute significant samples into the nearest insignificant samples to produce a picture 804.
An average of the pictures 803 and 804 is taken to produce a picture 806. An average of the collected significant samples 802 would result in the same value, thus the averaging is not needed.
Since there are some samples values double padded in the picture 803 and 804, an average of both the padded values is taken. If there is only one padded value available, this value becomes the padded value of the picture 806. In the padding process of the pictures 803 and 804, a sample havin
exemplary embodiment 3
(Exemplary Embodiment 3)
FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram depicting a padding method of a digital picture in a third exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
A picture 901 comprises collected significant samples 902. In this embodiment, a region 904 surrounding the collected significant samples 902 is determined and an insignificant sample is padded within the region 904. The same padding method detailed above is utilized also in this embodiment. A remaining region 905 is padded through a simple method by referring to the padded region 904, thus all insignificant samples are padded (Ref. to FIG. 906.)
The region 904 is preferably rectangular; however, it may be another shape. The region 904 may be the smallest rectangular which includes the collected significant samples 902, or a rectangular after extending the smallest rectangular by “k” samples. The value “k” is determined so that a size of the rectangular can satisfy a predetermined condition, e.g., “k” is determined so that the siz
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap