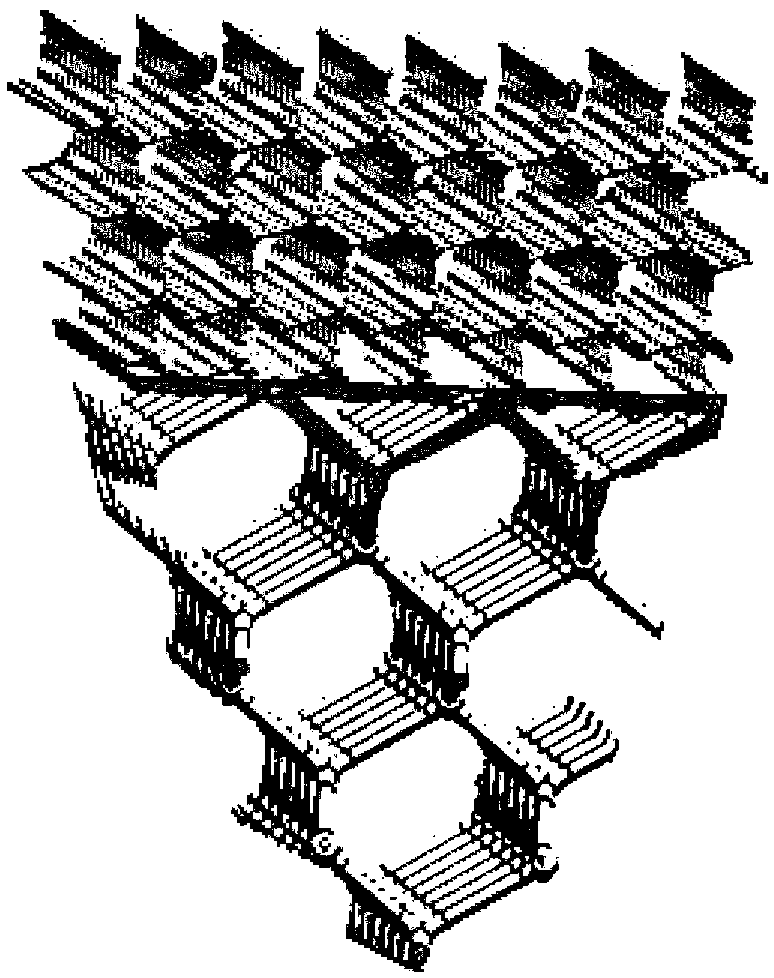Preparation method of 3D printing component and 3D printing space component
A 3D printing and component technology, applied in the field of 3D molding, can solve the problems of restricting the application of continuous fiber printing parts, difficult to add fibers, and restricting the application of continuous fiber printing technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
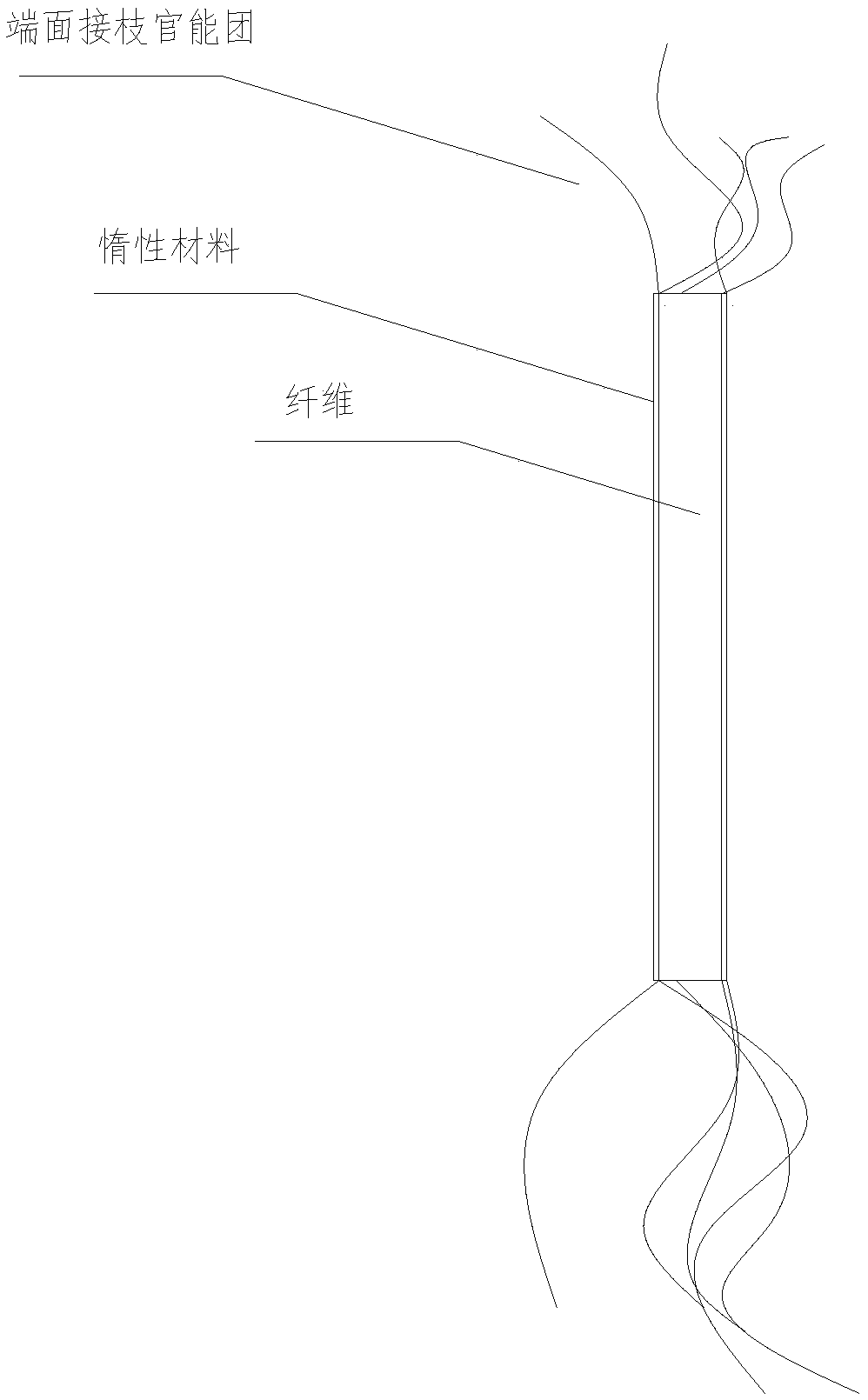
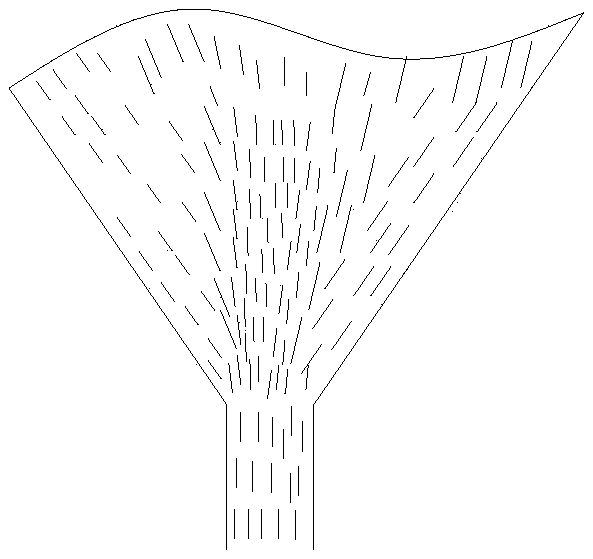
[0036] As stated in the background technology, at this stage, when using continuous fibers as 3D printing raw materials for printing, it is difficult to add fibers on the non-printing plane; The obvious difference in bearing capacity restricts the application of continuous fiber printed parts on structural parts. At the same time, because the wire contains continuous fibers, it is difficult to use 3D printing technology when forming spatial components (such as lattice structures), which limits the application of continuous fiber printing technology in lightweight structures or hollow structures. To solve this problem, as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a 3D printing material, including several modified chopped fibers and a component comprising at least a thermoplastic resin, wherein any of the modified chopped fibers are grafted with active groups on the end faces, And the remaining part of any modified chopped fiber except the end surface is
Embodiment 1
[0071] Printing process of carbon fiber reinforced polypropylene resin
[0072] Main material: 12K carbon fiber (without sizing agent), polypropylene resin
[0073] Fiber coating process: brush the surface of carbon fiber with epoxy resin solution, the content is 1%-1.5%, and heat and cure;
[0074] Fiber cutting: cutting carbon fiber into 0.5mm long short cut material;
[0075] Fiber chemical treatment: Soak the short fiber in a chemical solution for surface grafting reaction; obtain a material with double bond groups on the end surface.
[0076] Manufacture of granules: add processed fiber (30% v), polypropylene (63% v), styrene (6% v) and catalyst (1% v) into twin-screw equipment for extrusion granulation;
[0077] Manufacturing wire: use wire forming equipment to prepare 1.75mm printing wire (can be omitted, and print directly with pellets);
[0078] Heating and melting: This part is the beginning stage of printing. The wire starts to melt when it is heated at the nozzle (
Embodiment 2
[0083] Printing process of carbon fiber reinforced polyethylene resin
[0084] Main material: 12K carbon fiber (without sizing agent), polyethylene resin
[0085] Fiber coating process: brush the surface of carbon fiber with epoxy resin solution, the content is 1%-1.5%, and heat and cure;
[0086] Fiber cutting: cutting carbon fiber into 1mm long short cut;
[0087] Fiber chemical treatment: Soak the short fibers in a chemical solution for surface grafting reaction; obtain a material with carboxyl groups on the end surface.
[0088] Manufacture particles: polyethylene (73% v), epoxy resin (6% v) and catalyst (1% v) of terminal hydroxyl group, join in twin-screw equipment and carry out extruding granulation and with above-mentioned processed fiber (20 %v) uniform mixing;
[0089] Manufacture wire: use wire forming equipment to prepare 3mm printing wire (can be omitted, and print directly with pellets);
[0090] Heating and melting: This part is the beginning stage of printing. T
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mechanical strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap