Methods for maintaining hepatocytes in culture and for differentiating embryonic stem cells along a hepatocyte lineage
a technology of embryonic stem cells and hepatocytes, which is applied in the field of maintaining hepatocytes in culture and differentiating embryonic stem cells along a hepatocyte lineage, can solve the problems of xenozoonose, cell seeding, and pathologic immune responses, and the number of donor livers is inadequa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
Culture of Mouse ES Cells
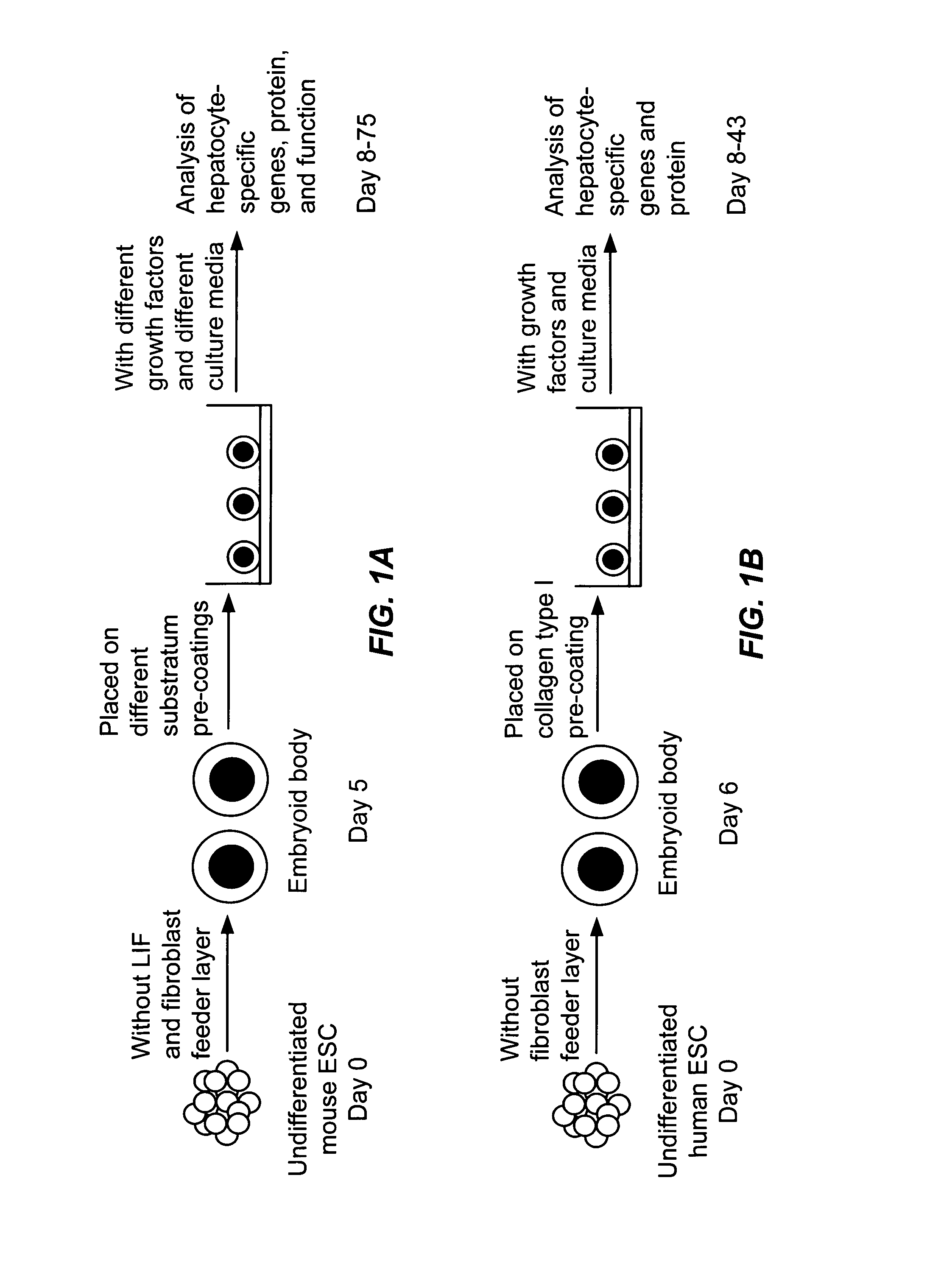
[0135] Mouse ES cell line ES-D3 and mouse STO fibroblasts were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, Va. ES cells were expanded on STO fibroblast feeder layers in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (unless specified, cell culture supplies were from Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.) containing 15% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1 mM L-glutamine, 60 μM non-essential amino acid solution, 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, Mo.), 1400 U / ml leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (Chemicon International, Temecula, Calif.), and penicillin / streptomycin at standard concentrations. To prepare feeder layers, STO fibroblasts were cultured until confluent and treated with 10 μg / ml mitomycin C (Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 hours. Mitomycin C-treated STO fibroblasts were then re-seeded at a density of 7-8×104 / cm2 one day before plating ES cells. As illustrated in FIG. 1A, differentiation of ES cells was in
example 2
Development of Culture Conditions for Hepatocyte-Specific Differentiation
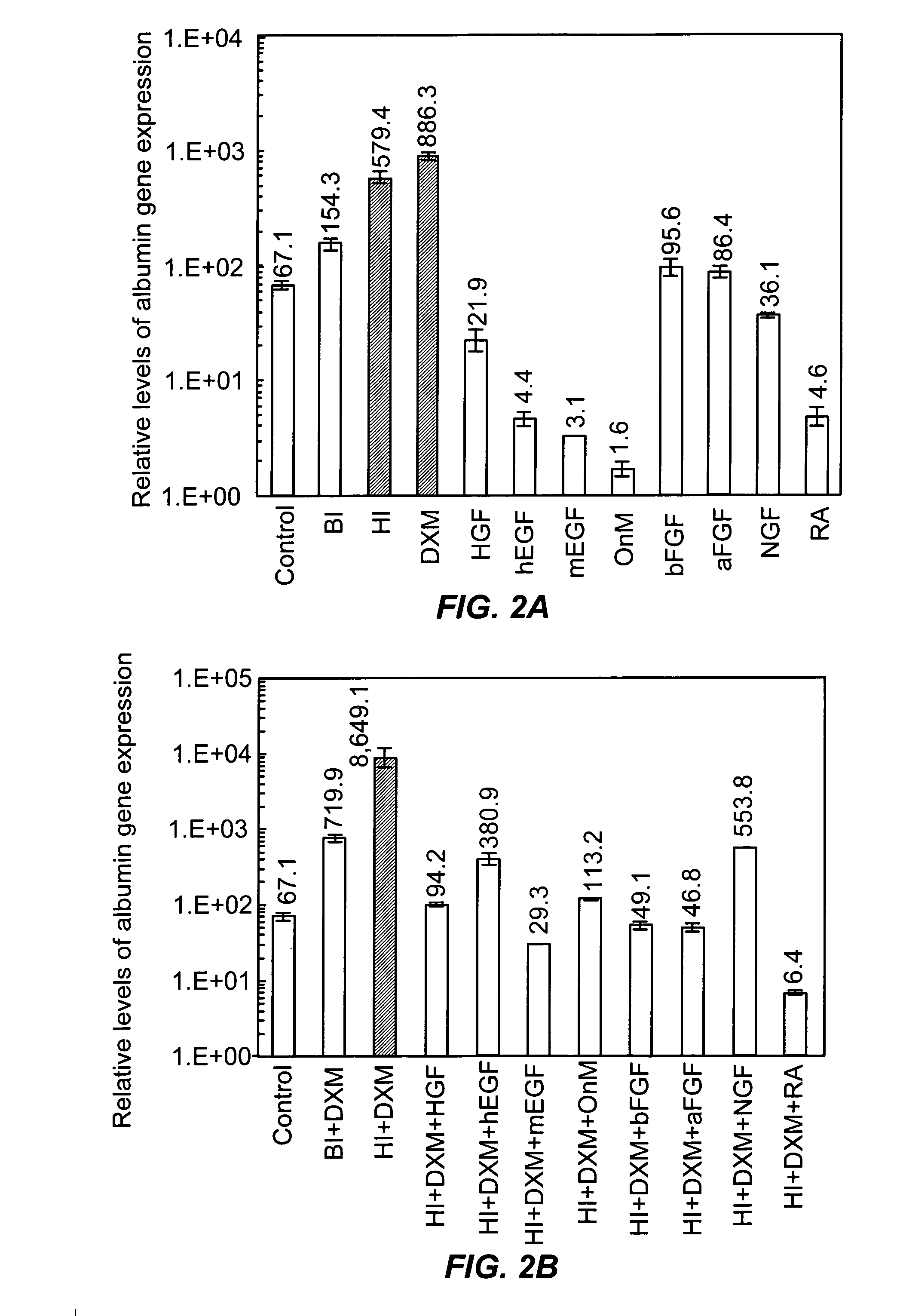
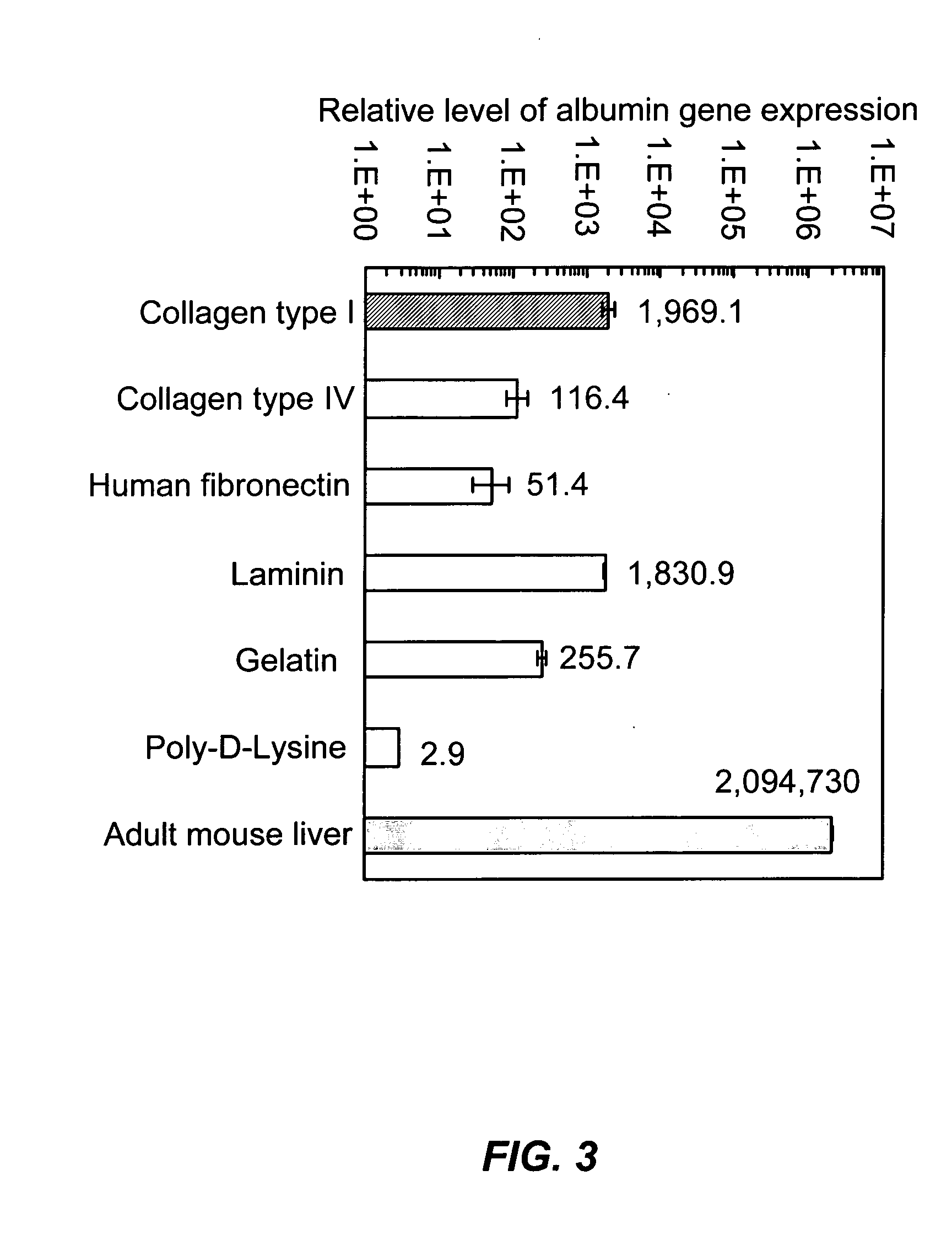
[0143] Because albumin synthesis is generally considered to be an excellent marker of hepatocyte differentiation, albumin expression was determined in extensive screening experiments by real-time quantitative RT-PCR to identify the culture condition yielding the highest level of hepatocellular differentiation (albumin expression) in mouse ES cells. In initial experiments, we evaluated the effects of different substratum pre-coatings, culture media, and growth factors. The evaluated growth factors included HGF, NGF, hEGF, mEGF, bFGF, aFGF, RA, OnM, dexamethasone, and human and bovine insulin. Among these growth and differentiation factors, human insulin and dexamethasone were found to be the most effective in enhancing albumin gene expression (FIG. 2A). Furthermore, albumin gene expression was enhanced approximately 10-fold when a combination of human insulin with dexamethasone was added to the culture in compari
example 3
[0151] This Example discusses the results of the studies reported conducted in the course of the present invention.
[0152] Stem cells are, by definition, capable of self-renewal and differentiation, and thus can theoretically provide a limitless supply of differentiated cells, such as hepatocytes. The findings in the present study demonstrate that mouse ES cells differentiated in vitro into an endodermal cell type with a hepatocyte phenotype and that mouse EBs cultured under the optimal hepatocyte differentiation conditions express significant levels of hepatocyte-specific markers, such as albumin, prealbumin, and G6P, but not the cholangiocyte markers CK 19 and GGT.
[0153] To develop culture conditions for hepatocyte differentiation, we tested numerous factors, including HGF, hEGF, mEGF, OnM, aFGF, bFGF, NGF, RA, dexamethasone, and human and bovine insulin. These factors are thought to be important for hepatocyte differentiation during embryonic development, and individual factors or
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap