Method for Regulating Hardmask Over-Etch for Multi-Patterning Processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
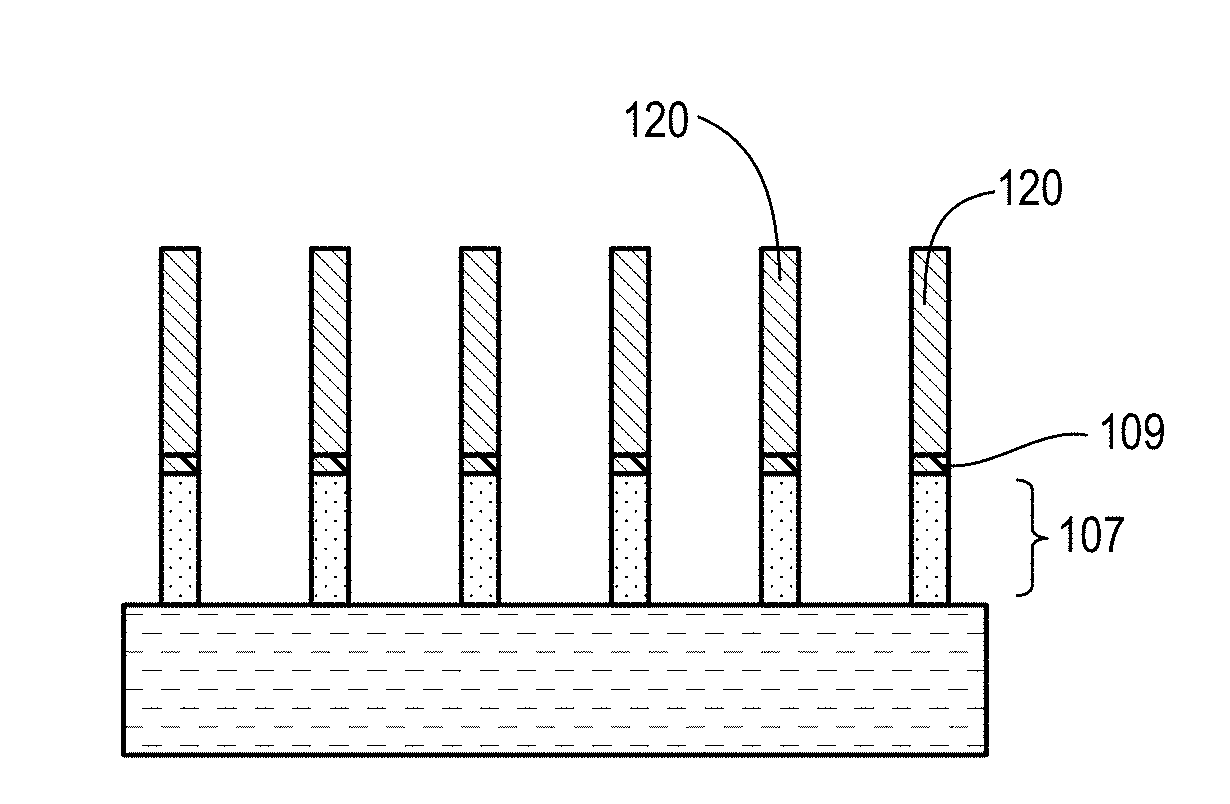
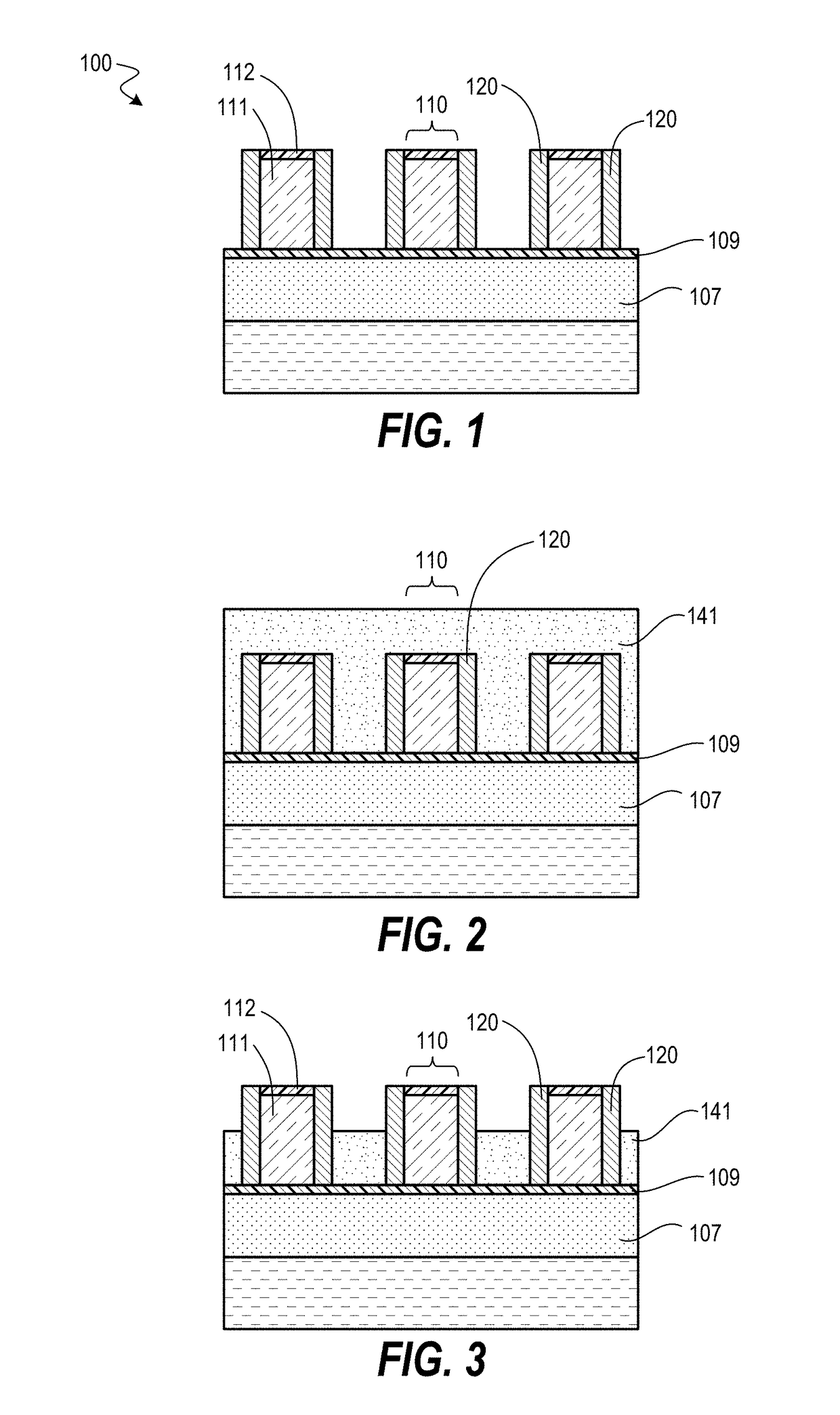
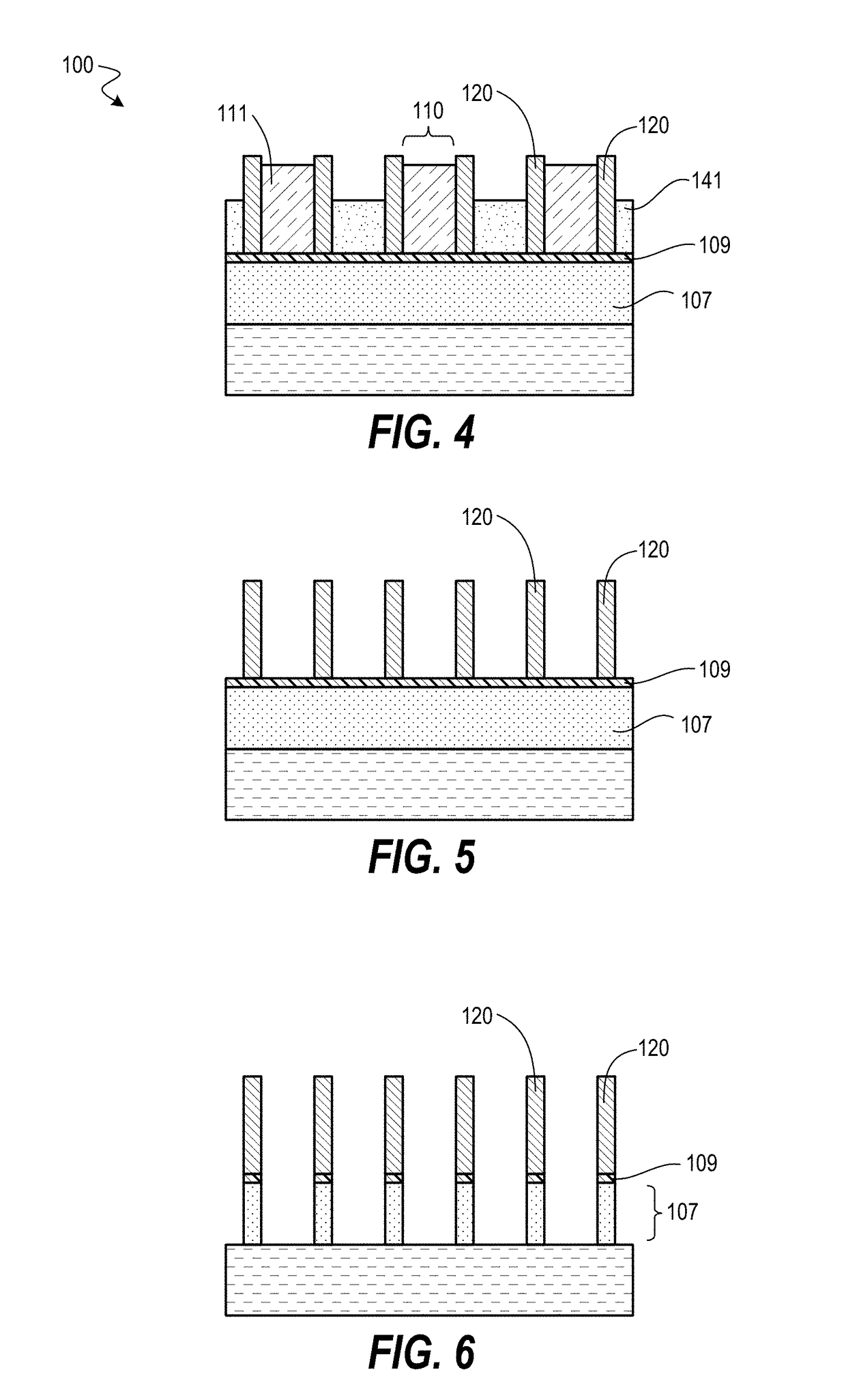
[0021]Techniques herein include patterning processes to prevent over-etching for various multi-patterning processes. Multi-patterning processes typically involve creation of sidewall spacers and removal of mandrels on which sidewall spacers are formed. In some patterning flows gouging of underlying layers can occurs during the various multi-patterning steps. Techniques herein include methods to prevent such gouging by using a planarization layer recessed sufficiently to removed desired materials and protect others. Such techniques can remove bi-layer mandrels without gouging underlying layers.
[0022]SAQP patterning for FEOL (front-end-of-line) applications can be implemented using many different stack and deposition films (amorphous-Silicon, amorphous carbon at 600° C. etc.) because the maximum processing temperature can be approximately 700° C. in some integration schemes. In contrast, when SAQP is used for BEOL (back-end-of-line) applications, the maximum processing temperature is gov
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap