Method for determining corrections for artillery fire
a technology for artillery fire and correction methods, applied in the field of artillery fire, can solve the problems of high insufficient accuracy of 10 mrad, heavy and bulky, and add a non-negligent cost to the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
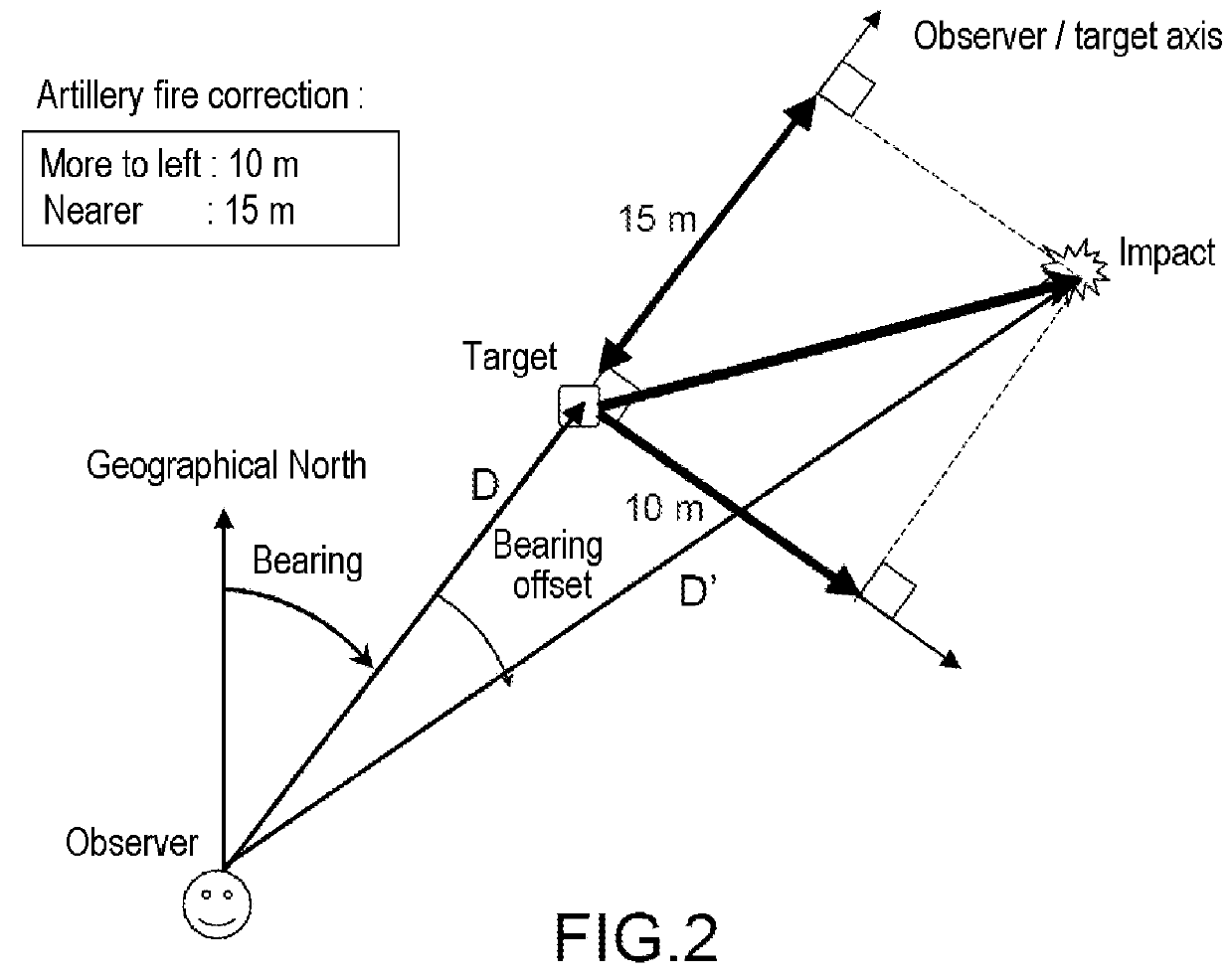
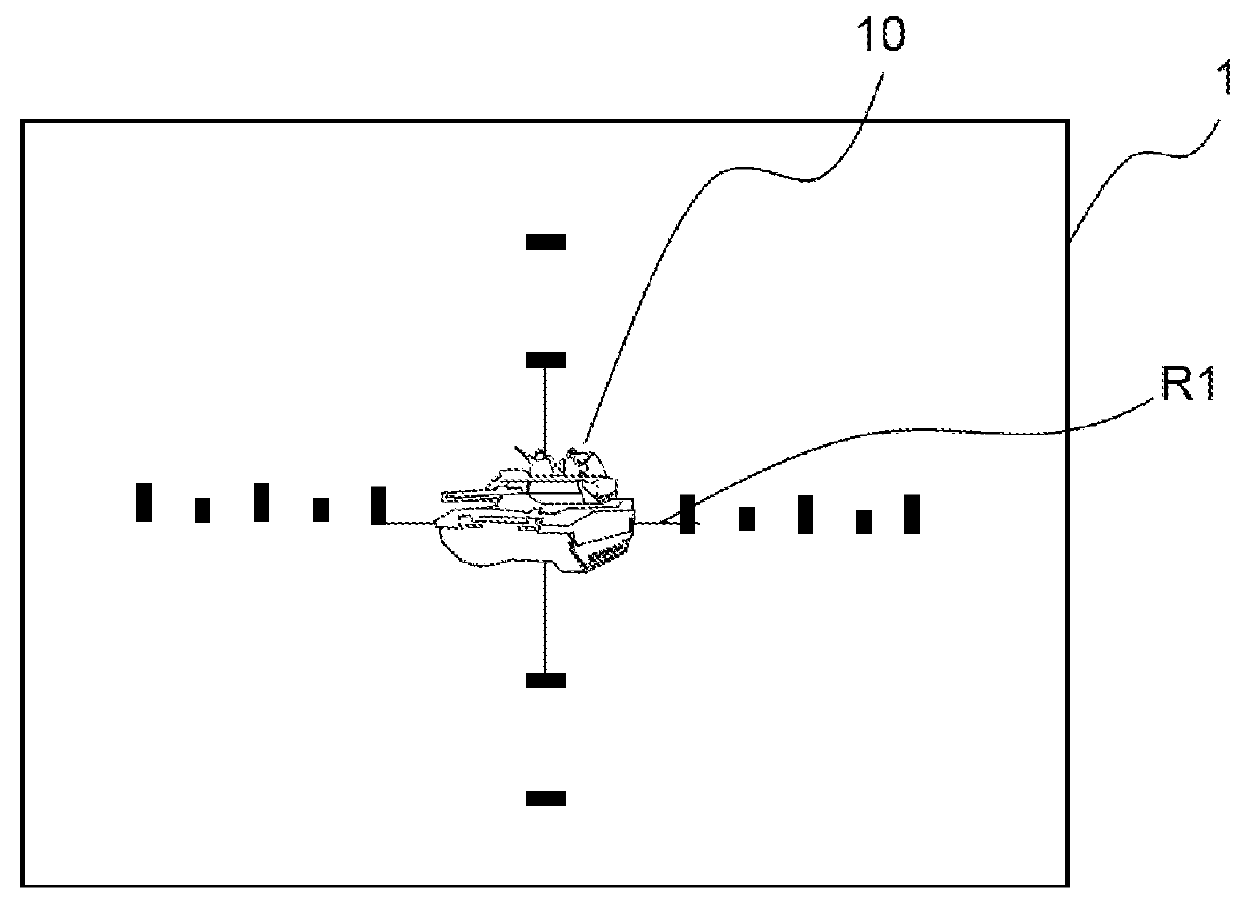
[0047]It is considered that a first firing often referred to as a test firing takes place after the transmission of the coordinates of the target to the artillery pieces. The observer awaits the impact of this test firing, keeping the crosshair R1 over the image of the target, without modifying the orientation of the observation system. R1 is generally at the center of the display screen 1.
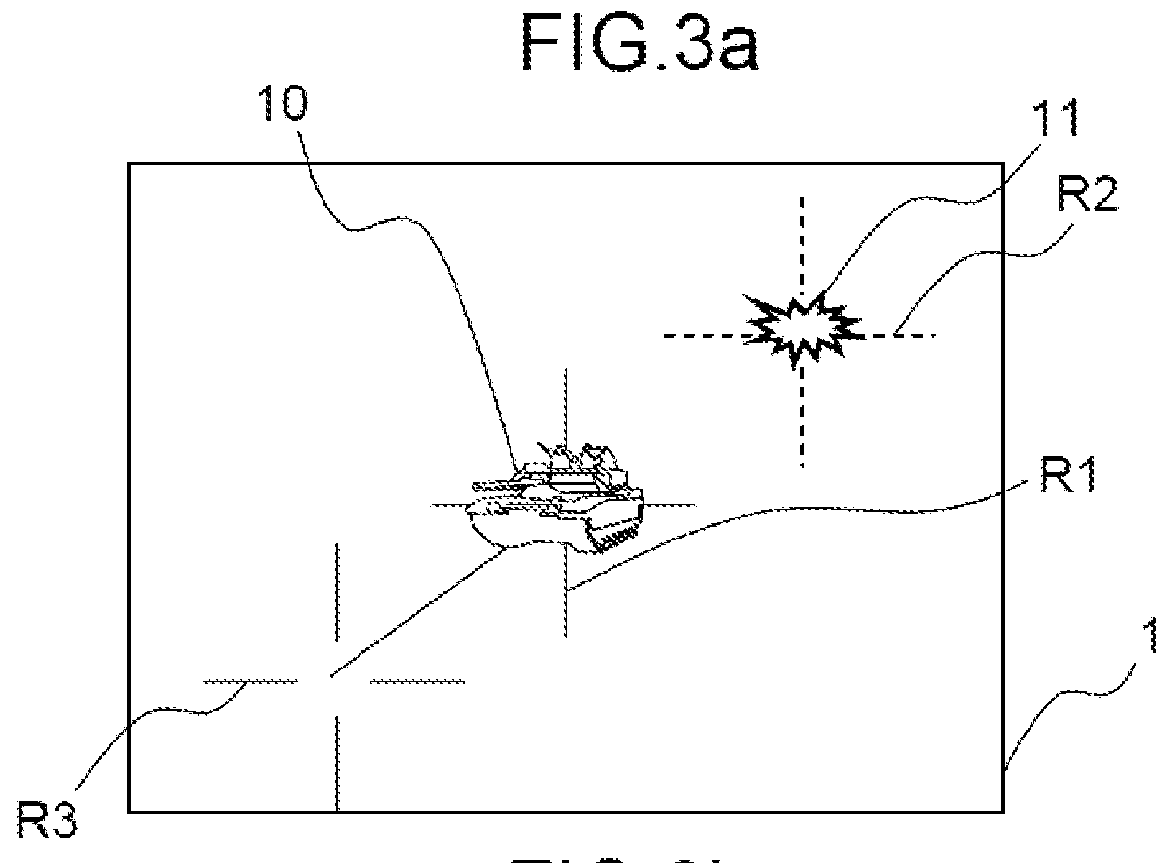
[0048]On impact, using means for displaying and moving a second crosshair R2 on the screen, the operator places this crosshair R2 over the image 11 of the impact point on the screen without modifying the orientation of the binoculars, as shown in FIG. 3a. These means for moving a crosshair comprise for example a joystick or pushbuttons or a device scanning the retina of the observer. Positioning the crosshair R2 over the image 11 of the impact point makes it possible to measure Δx (=horizontal offset of R2 relative to R1), which makes it possible to determine the offset in bearing with the very hi...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap