Content distribution system and method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
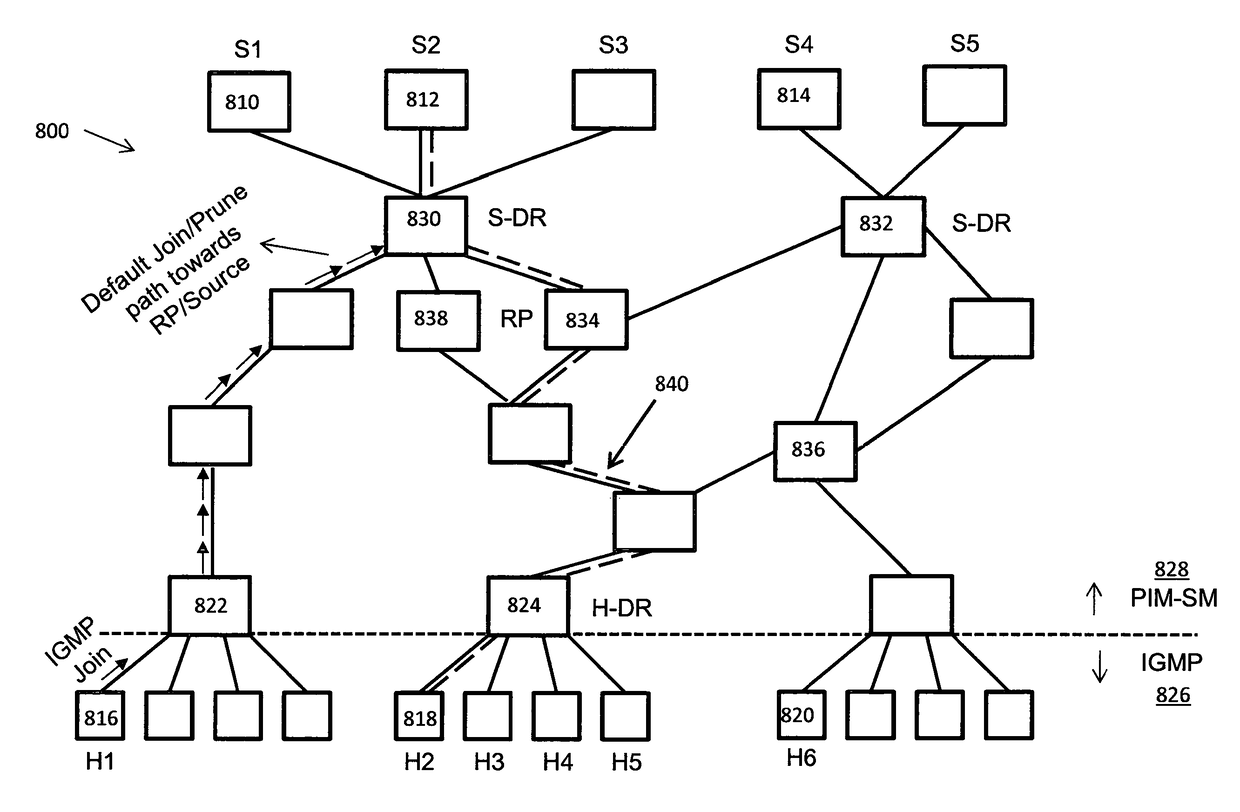
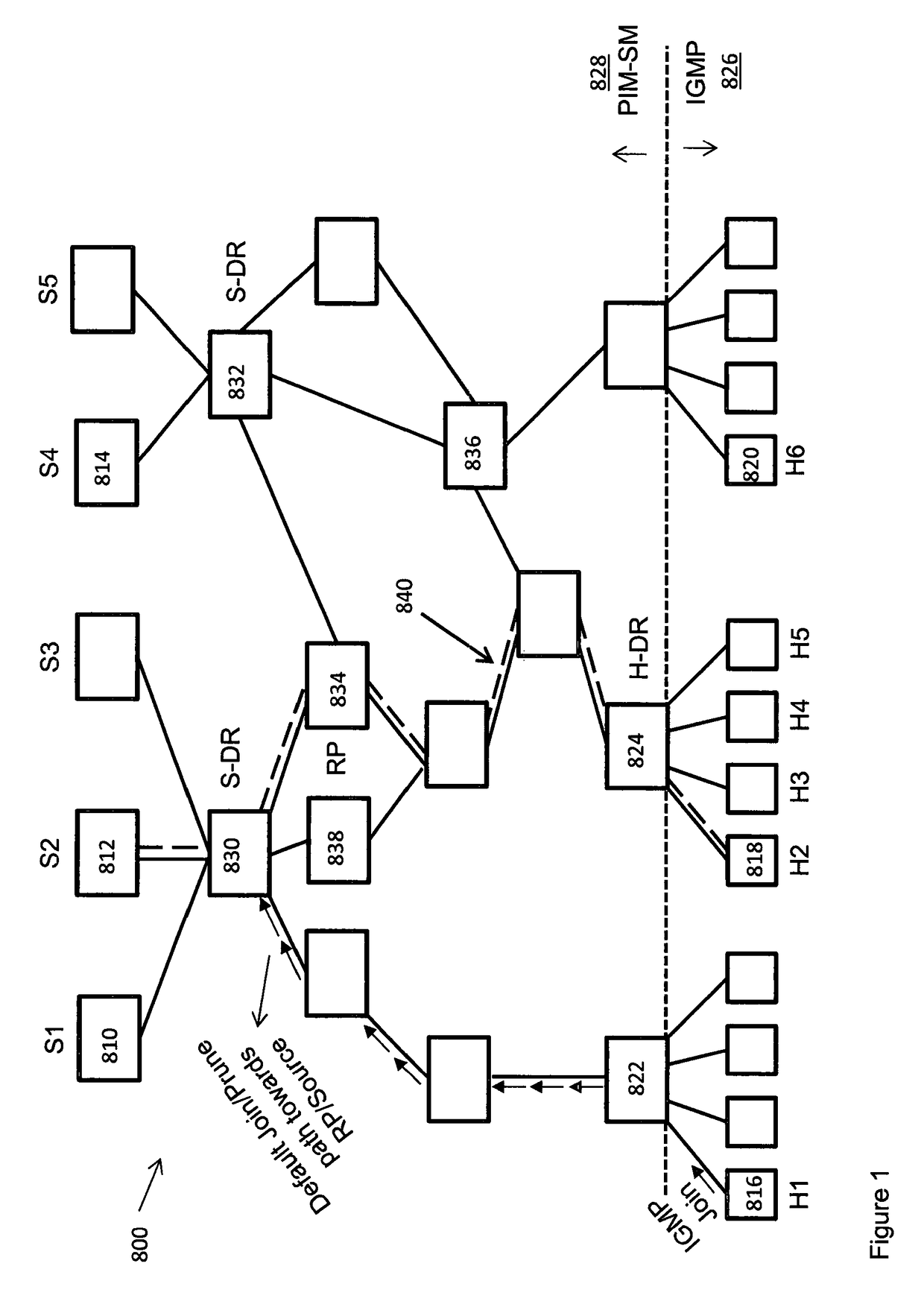
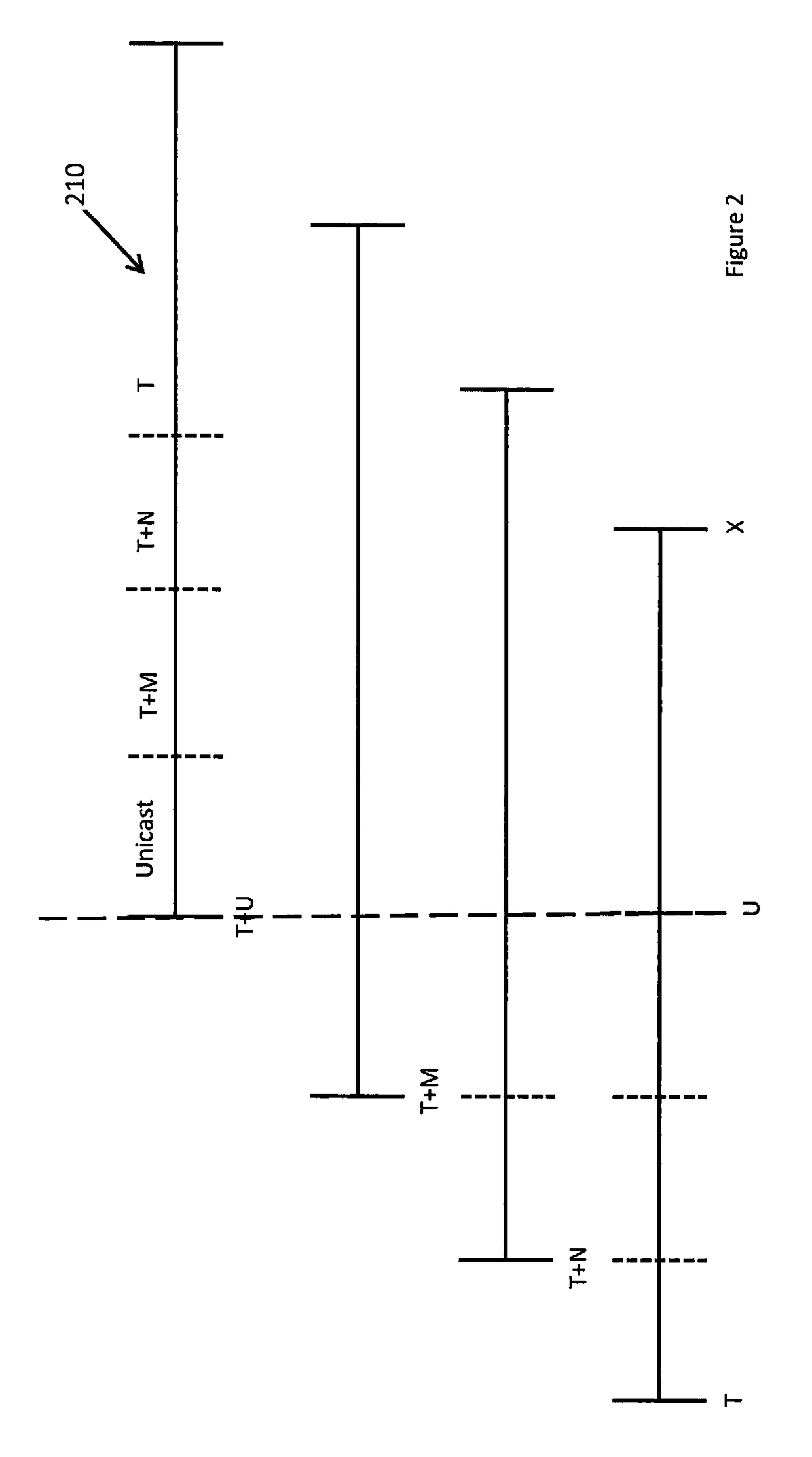
[0033]As set out above, aspects of the system described herein create multiple time-staggered multicast streams for the same piece of content. In some embodiments, the source uses intelligent data analytics to decide which hosts should subscribe to which of those (one or more) multicast streams. The source can then trigger subscription of the hosts to the chosen streams. The hosts re-assemble the multiple streams which provide data from different starting points, and leave multicast trees once they no longer receive unreplicated content from that tree. This affects host-to-group membership and also results in better use of network resources by minimising the number of unicast streams in the network for a piece of content. Embodiments of each of the elements set out above are now described in more detail, but an embodiment of a network in which the present system may be implemented is first described.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PRESENT EXAMPLE EMBODIMENTS
[0034]In the following description,
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap