Method for determining gold-palladium contents in circuit boards of mobile phones
A circuit board and mobile phone technology, applied in the field of resource recycling, can solve the problem of no clear method for metal content determination, and achieve the effect of short digestion time and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
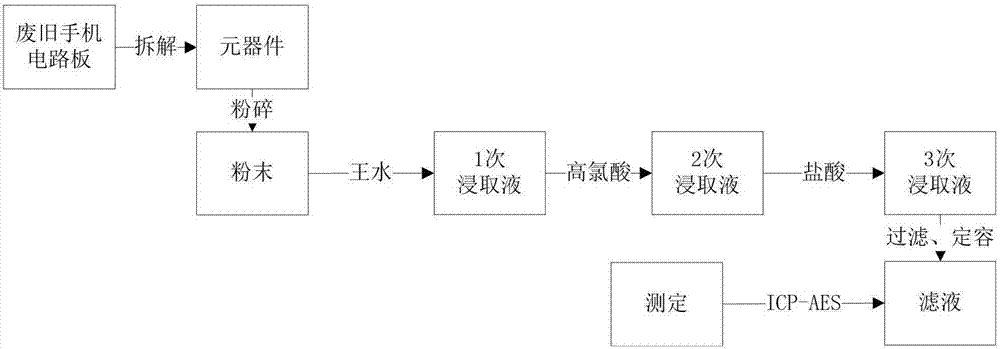
[0025] Use tools such as electric heat guns or electric furnaces to process the components of printed circuit boards in waste mobile phones in batches, and heat the solder at the contact position between the components and the light board. The temperature is controlled at 210 ° C. At the same time, with vibration, the components are heated and quickly fall off. The disassembled waste mobile phone circuit board components are crushed, ground, and sieved to reach 20-200 meshes to obtain the required samples; the obtained samples are mixed with aqua regia solution and placed on an electric heating plate for reaction. The reaction parameters are: aqua regia: sample solid-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:13, reaction time 1 = 100min, reaction temperature 180°C; add perchloric acid to continue digestion, and its perchloric acid digestion parameters are: high chlorine Acid: Sample solid-to-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:5, reaction time 1 = 60min, reaction temperature 200°C; add hydroc
Embodiment 2
[0027] Use tools such as electric heat guns or electric furnaces to process the components of printed circuit boards in waste mobile phones in batches, and heat the solder at the contact position between the components and the light board. The temperature is controlled at 200 ° C. At the same time, with vibration, the components are heated and quickly fall off. The disassembled waste mobile phone circuit board components are crushed, ground, and sieved to reach 20-200 meshes to obtain the required samples; the obtained samples are mixed with aqua regia solution and placed on an electric heating plate for reaction. The reaction parameters are: aqua regia: sample solid-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:15, reaction time 1 = 105min, reaction temperature 170°C; add perchloric acid to continue digestion, and its perchloric acid digestion parameters are: high chlorine Acid: sample solid-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:7, reaction time 1 = 70min, reaction temperature 190°C; add hydrochlo
Embodiment 3
[0029] Use tools such as electric heat guns or electric furnaces to process the components of printed circuit boards in waste mobile phones in batches, and heat the solder at the contact position between the components and the light board. The disassembled waste mobile phone circuit board components are crushed, ground, and sieved to reach 20-200 meshes to obtain the required samples; the obtained samples are mixed with aqua regia solution and placed on an electric heating plate for reaction. The reaction parameters are: aqua regia: sample solid-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:17, reaction time 1 = 90min, reaction temperature 200°C; add perchloric acid to continue digestion, and its perchloric acid digestion parameters are: high chlorine Acid: sample solid-to-liquid ratio (mass / volume) = 1:9, reaction time 1 = 80min, reaction temperature 170°C; add hydrochloric acid to catch nitrate, and the filtrate after nitrate use suction filter or filter device to remove the remaining non-
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap