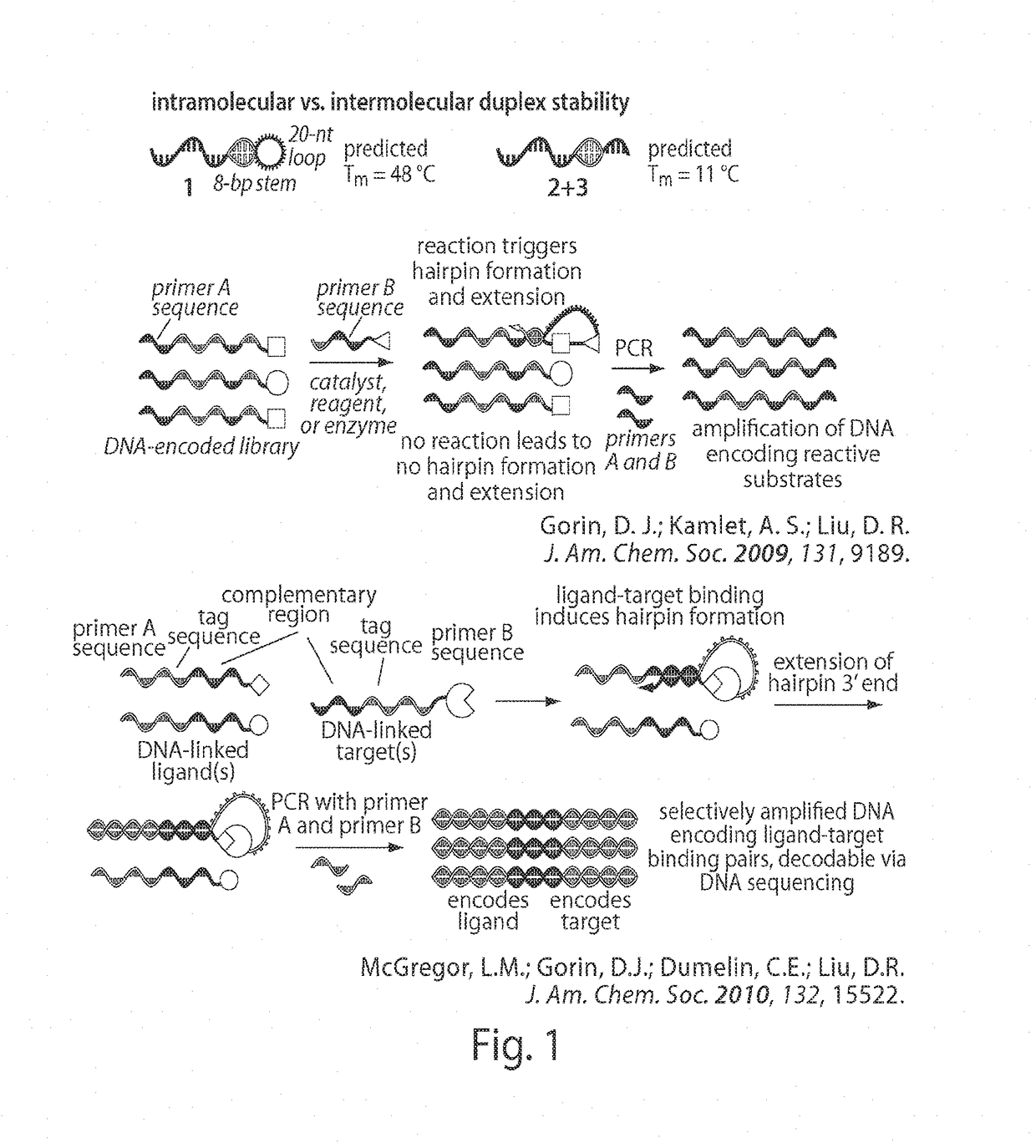
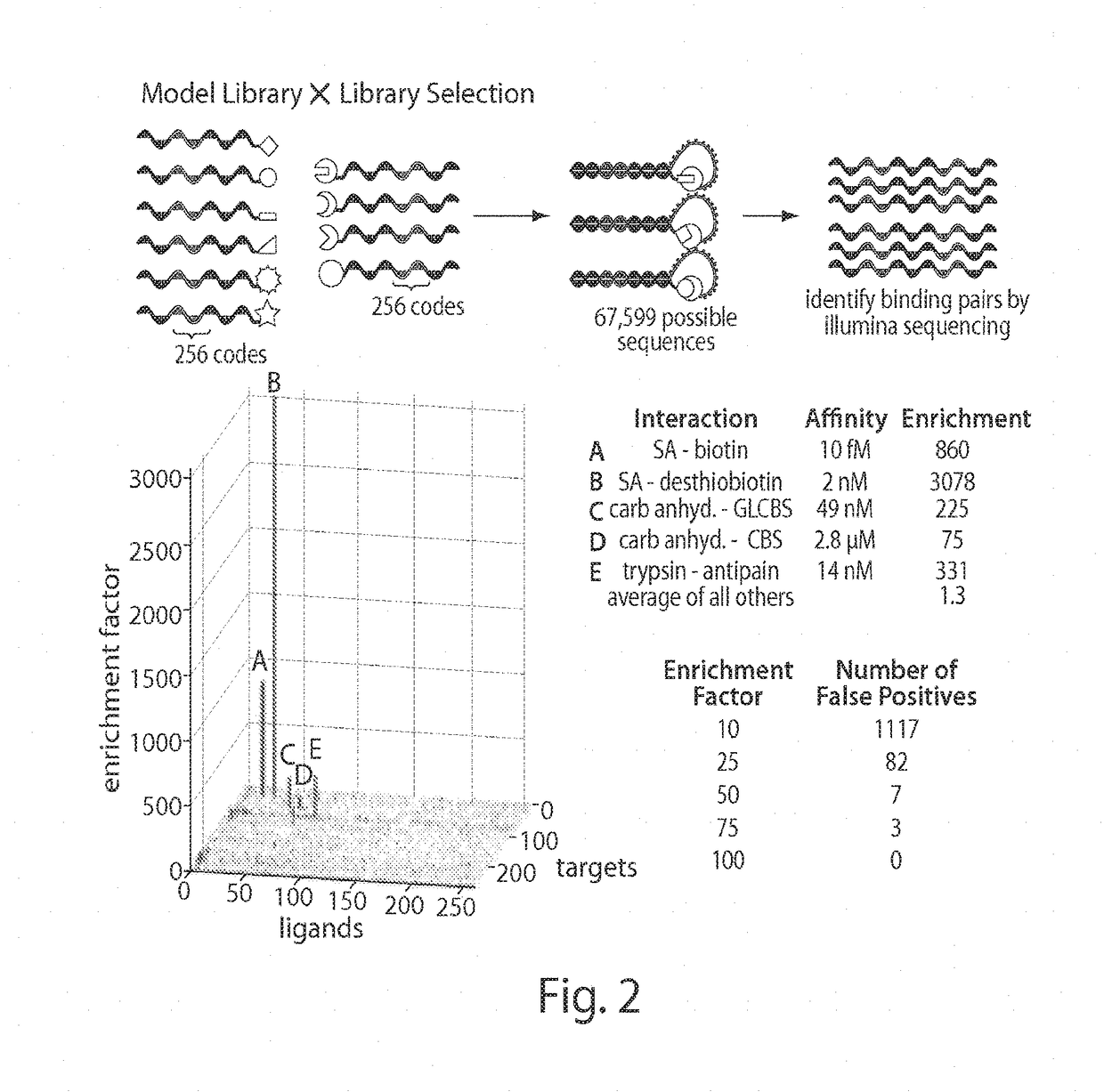
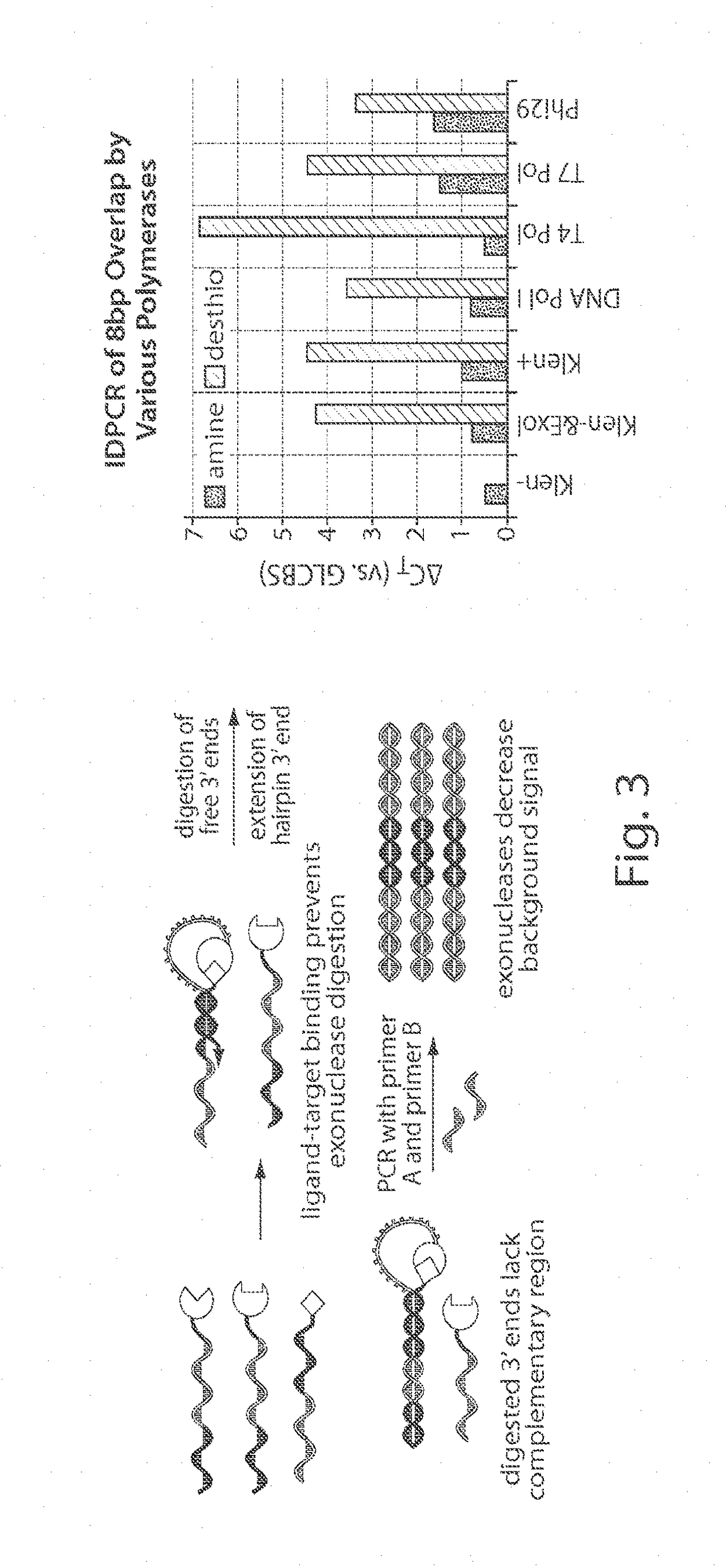
In situ interaction determination
a technology of in situ interaction and determination method, which is applied in the field of in situ interaction determination, can solve the problems of inability to identify ligands for such targets, inability to bind to membranes, and inability to bind to membranes, and achieve the effect of rapid identification of ligand:target interactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Materials and Methods
[0121]Unless otherwise noted, chemical reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Water was purified with a Milli-Q purification system. Modified DNA oligonucleotides were synthesized on a PerSeptive Biosystems Expedite 8909 DNA synthesizer. Standard DNA oligonucleotides were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies. All reagents and phosphoramidites for DNA synthesis were purchased from Glen Research. All oligonucleotides were synthesized and deprotected according to manufacturer's protocols. Oligonucleotides were purified by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC, Agilent 1200) using a C18 stationary phase (Eclipse-XDB C18, 5 μm, 9.4×200 mm) and an acetonitrile / 100 mM triethylammonium acetate gradient. Oligonucleotide concentrations were quantitated by UV spectroscopy using a Nanodrop ND1000 spectrophotometer. Non-commercial oligonucleotides were characterized by LC / ESI-MS; reverse-phase separation was performed on an Alliance 2695 (Waters
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Interaction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap