Vertical field effect transistor formation with critical dimension control
a technology of vertical field effect transistor and critical dimension control, which is applied in the direction of basic electric elements, electrical apparatus, and semiconductor devices. it can solve the problems of corresponding increase in short channel effects and vfet performance variations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
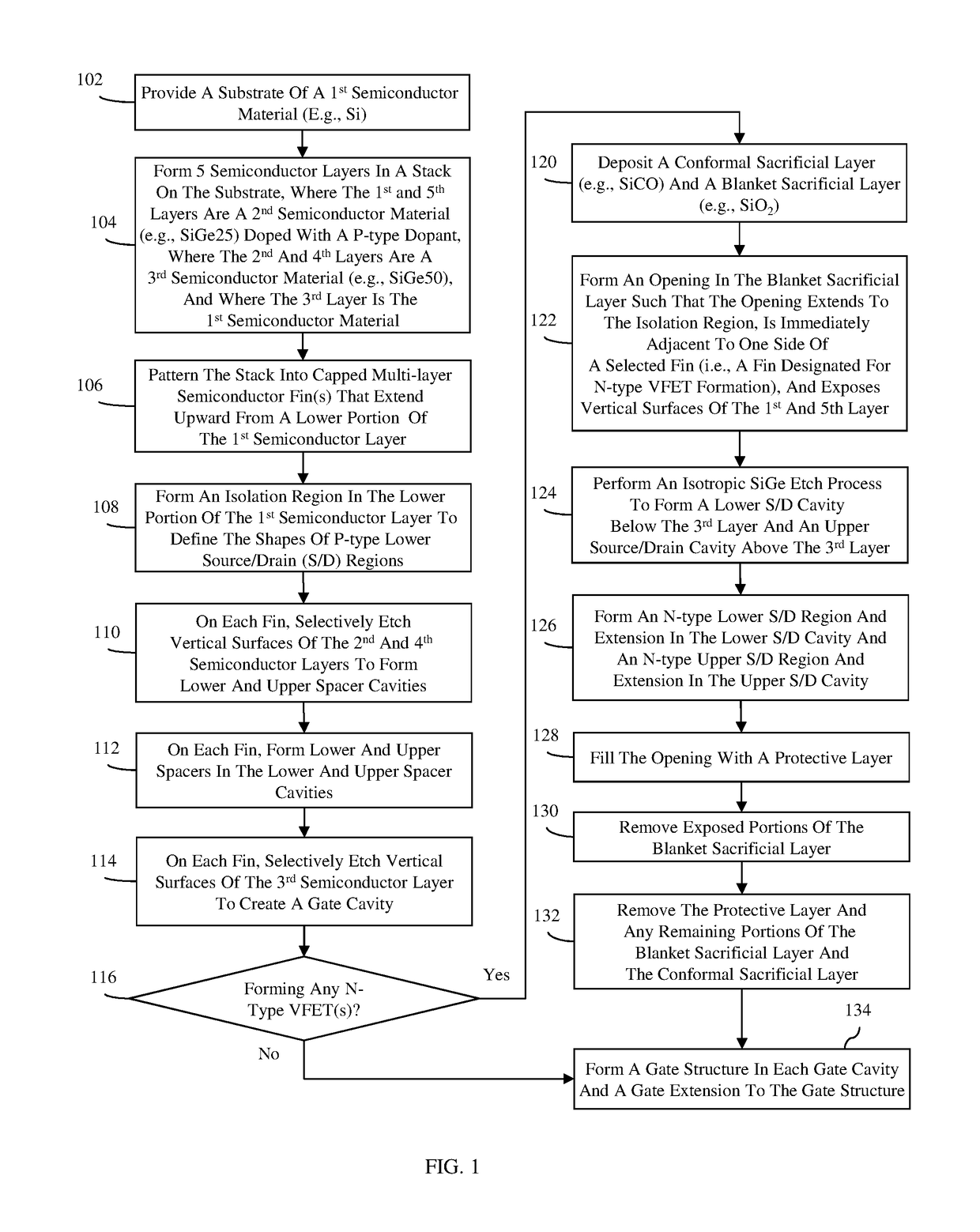
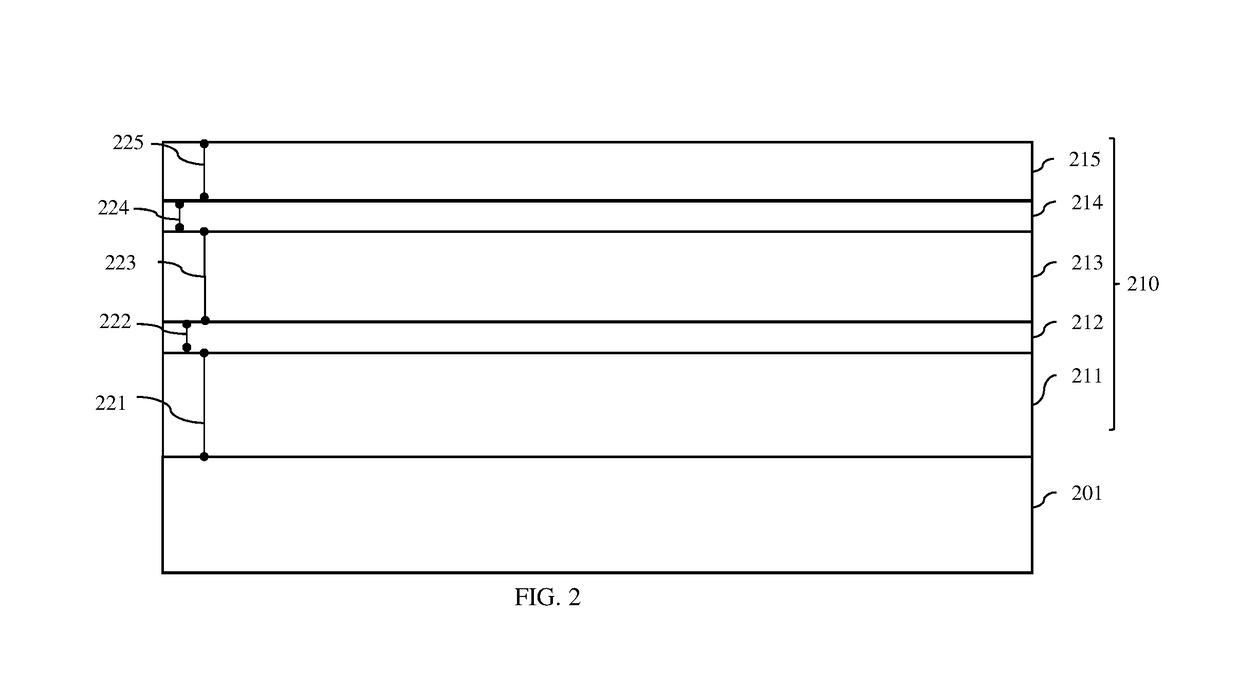
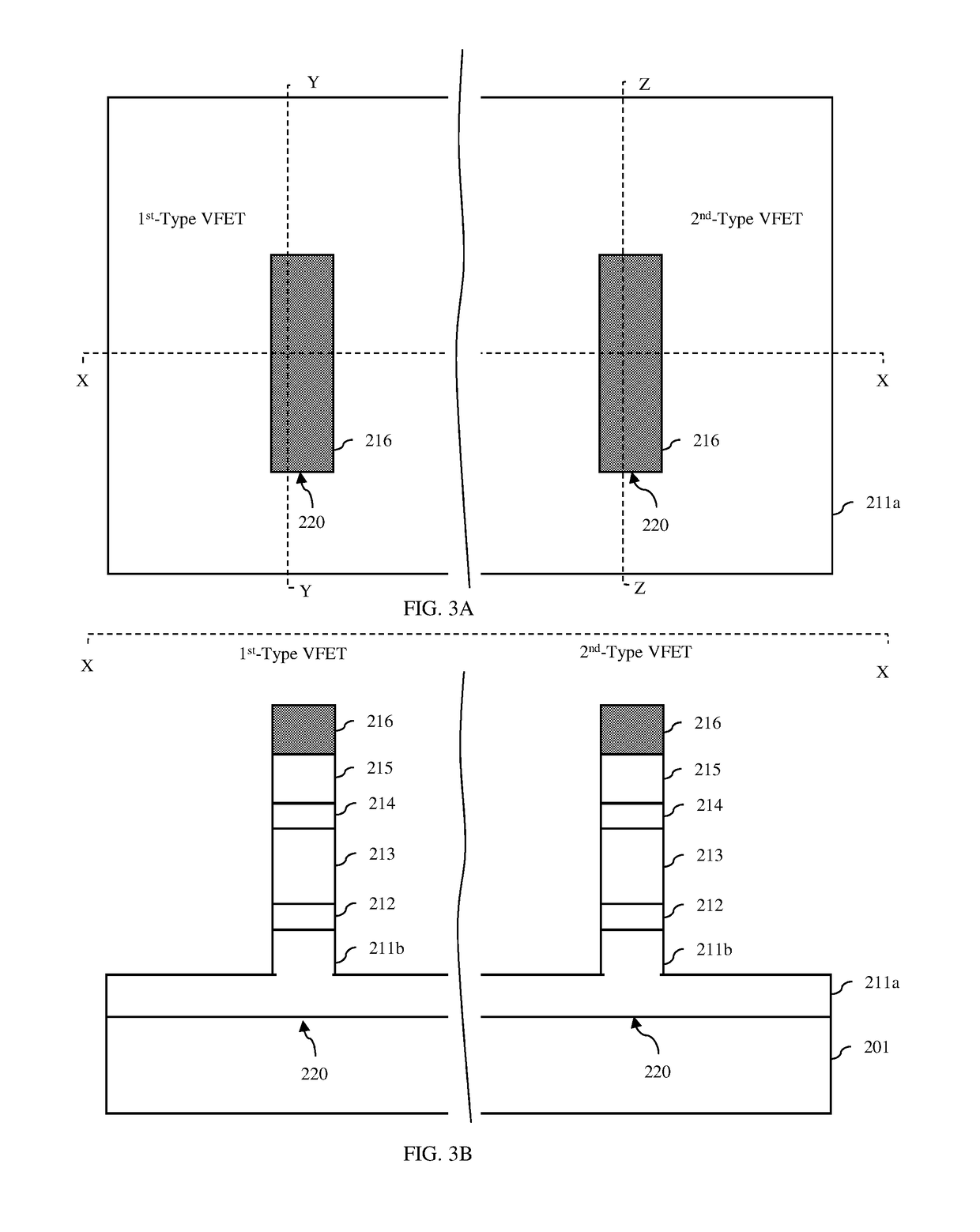
[0037]As mentioned above, as mentioned above critical dimension control (e.g., control of gate length, control of alignment of top and bottom junction doping to gate edges, etc.) can be challenging with current methods of forming vertical field effect transistors (VFETs). For example, the lengths of the lower and upper spacers, which define the spacing between the channel region and the lower and upper source / drain regions, respectively, of a VFET are achieved by depositing spacer material and then recessing the spacer material using a timed etch process. Similarly, the length of the gate of a VFET is defined by depositing sacrificial gate material and then recessing the sacrificial gate material using a timed etch process. However, those skilled in the art will recognize that there can be a lot of process variation when using timed etch processes. As a result, VFET performance variations (e.g., variations in threshold voltage) can occur.
[0038]In view of the foregoing, disclosed here
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap