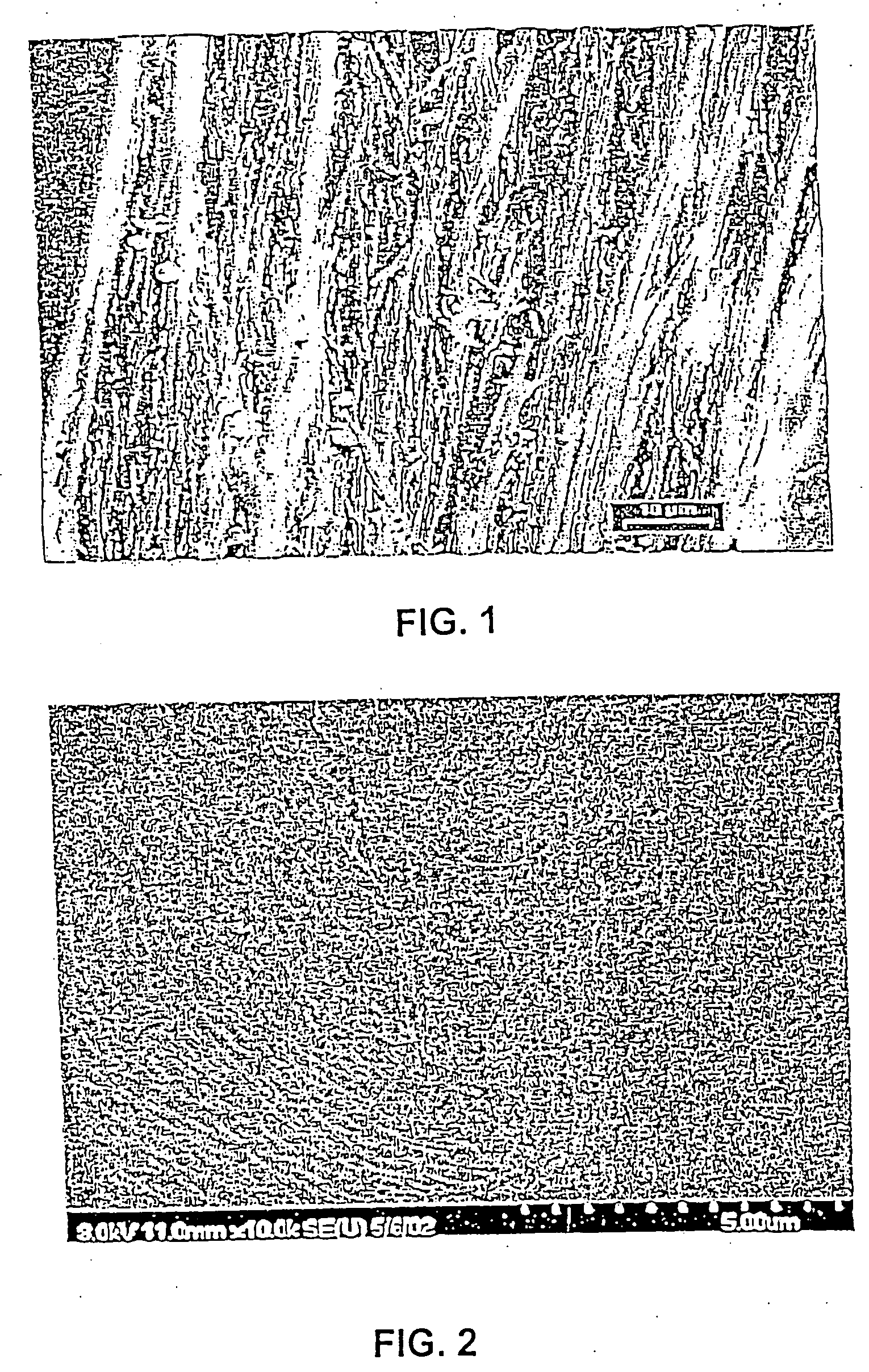
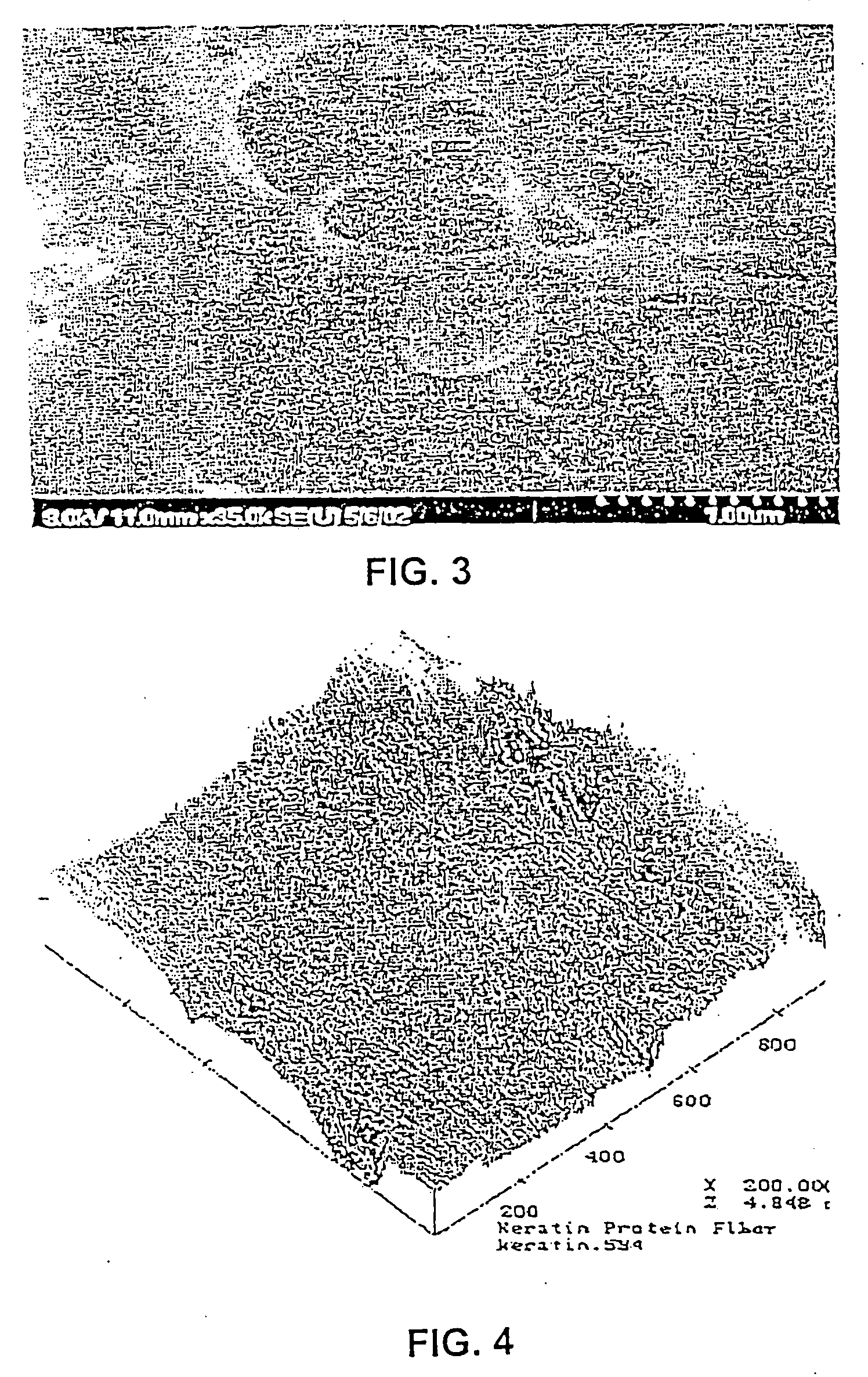
Use of fibrous protein fibers for chemical sensing and radiation detection
a technology of fibrous protein fibers and radiation detection, which is applied in the direction of instruments, liquid/fluent solid measurement, biomass after-treatment, etc., can solve the problems of mass panic, radiation sickness, and death of thousands of people, and achieve the effects of reducing the number of people affected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0084] The following detailed description is of the best currently contemplated modes of carrying out the invention. The description is not to be taken in a limiting sense, but is made merely for the purpose of illustrating the general principles of the invention, since the scope of the invention is best defined by the appended claims.
[0085] One aspect of the present invention is a method for detecting and / or determining a chemical species or analyte by using fibrous protein fibers. The chemical species or analyte to be detected can be in gas or liquid form. The chemical species can be inorganic or organic. For example, the chemical species can be a heavy metal such as strontium, cesium, lead, copper, cadmium, mercury, vanadium, radium, zinc, chromium, gold, silver, manganese, cobalt, nickel, or uranium. In another alternative, the chemical species can be a cyano or chloro complex of gold, silver, or platinum. Alternatively, the chemical species can be an organic species such as an
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap