Medium Access Control in Industrial and Automotive Wireless with Combined Wired and Wireless Sensor Networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034]The making and using of the presently preferred embodiments are discussed in detail below. It should be appreciated, however, that the present invention provides many applicable inventive concepts that can be embodied in a wide variety of specific contexts. The specific embodiments discussed are merely illustrative of specific ways to make and use the invention, and do not limit the scope of the invention.
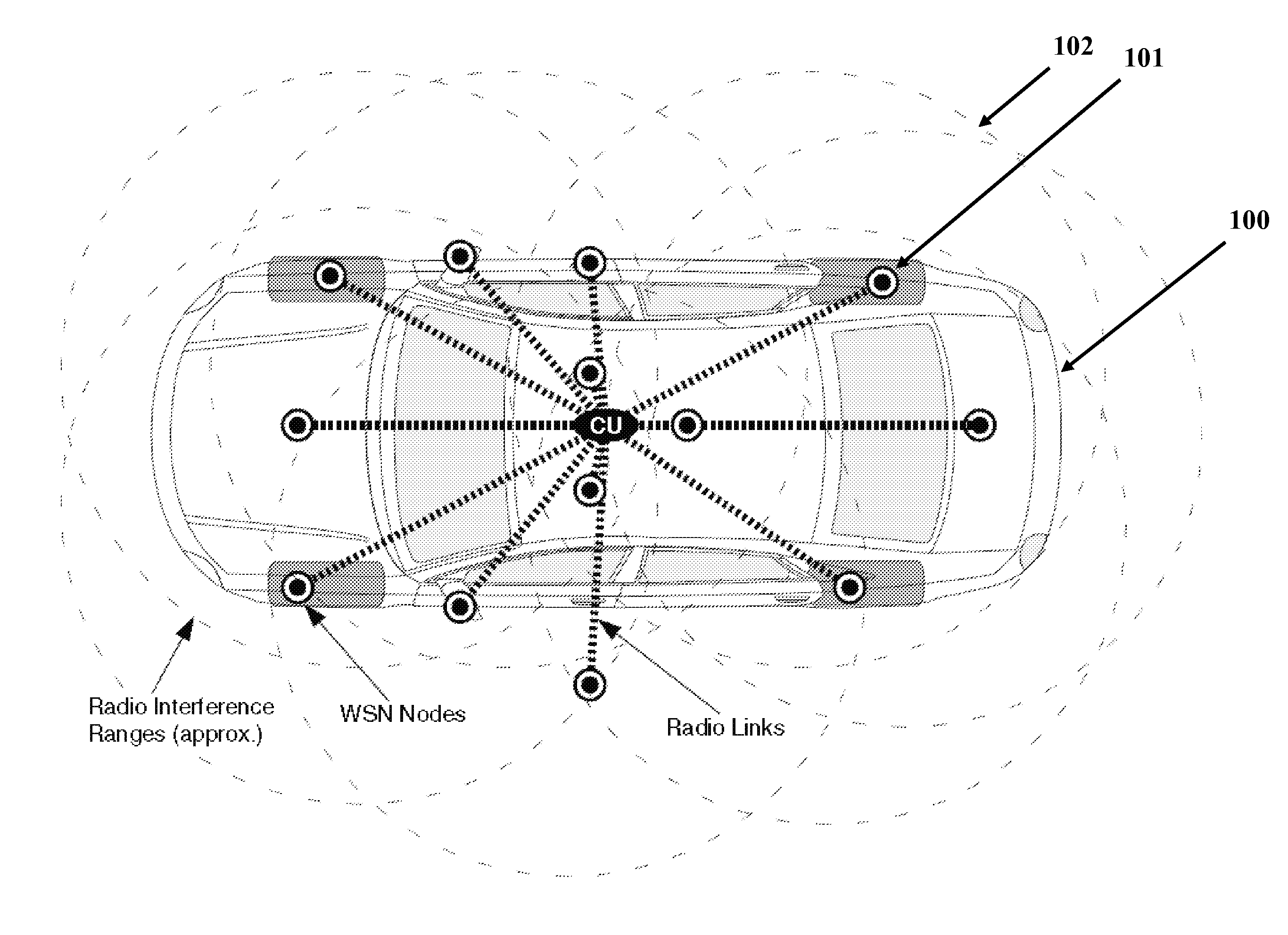
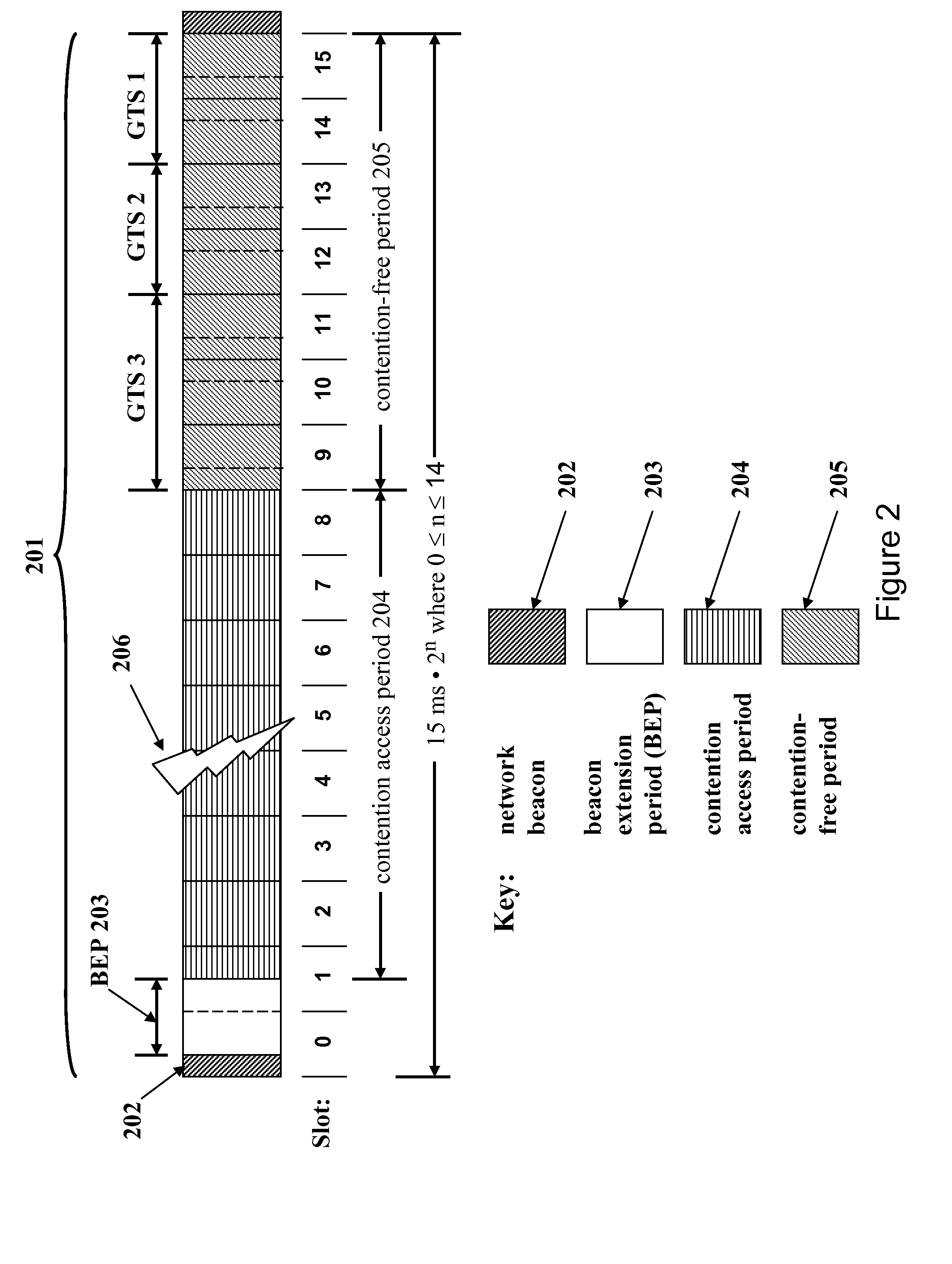
[0035]The present invention will be described with respect to exemplary embodiments in a specific context, namely a wireless sensor network configured to coordinate medium access for periodic, aperiodic, and event-driven periodic messages to provide contention-free access for selected network nodes. A wireless network in an exemplary embodiment includes a combination of wired and wireless gateways to provide an adaptable hybrid virtual star communication arrangement for network nodes.
[0036]An embodiment of the invention may be applied to various wireless sensor network arrangeme
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap