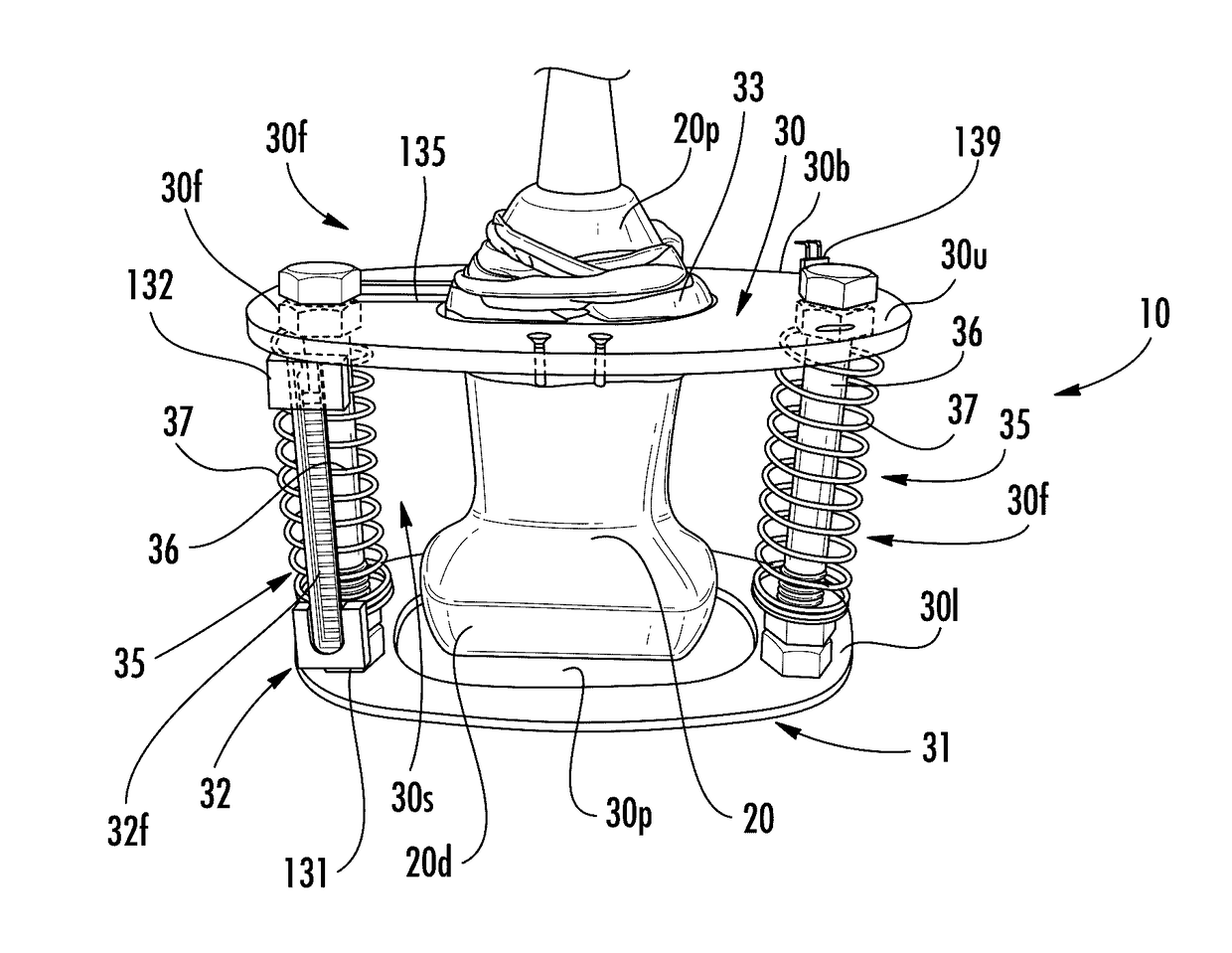
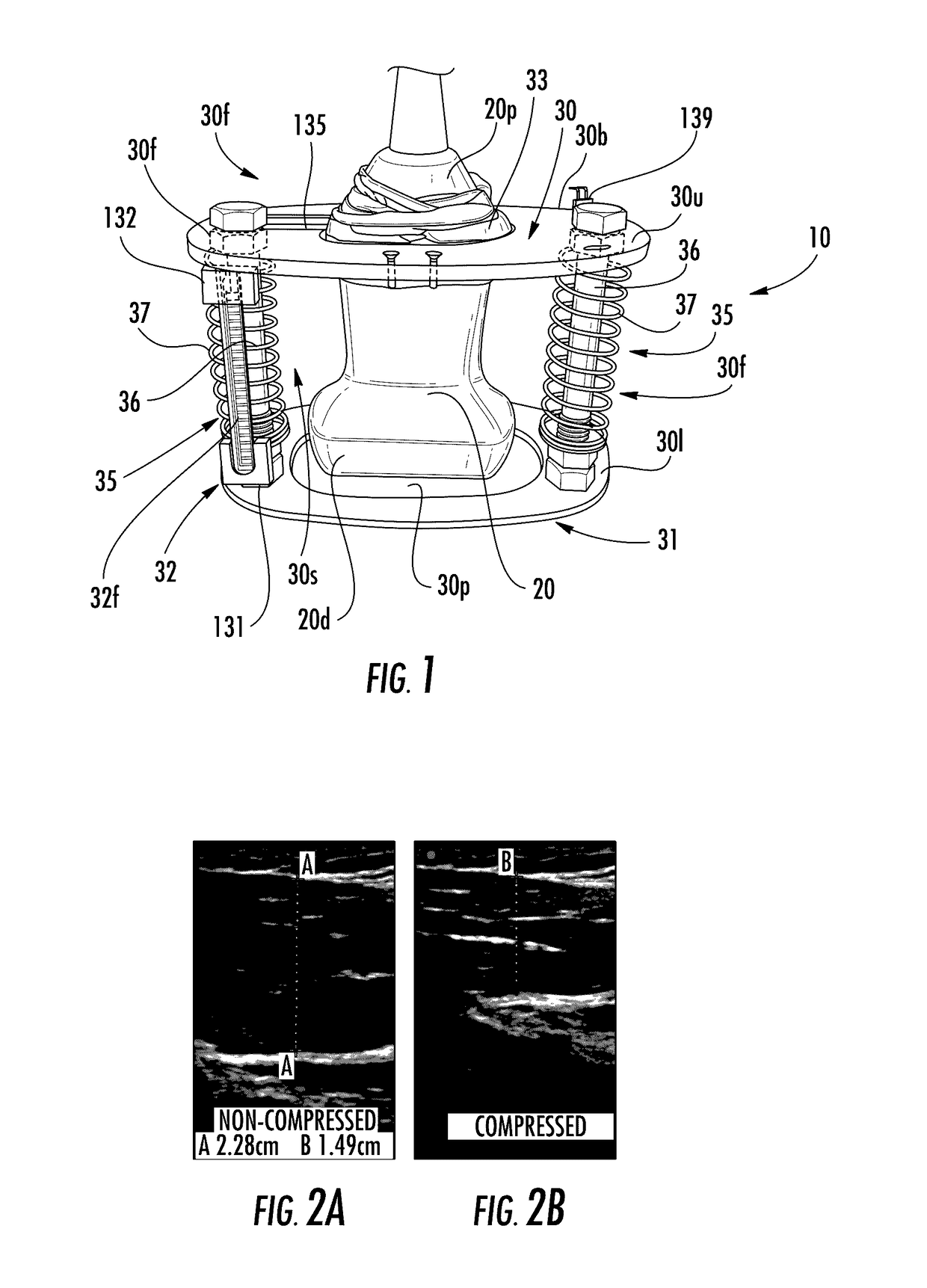
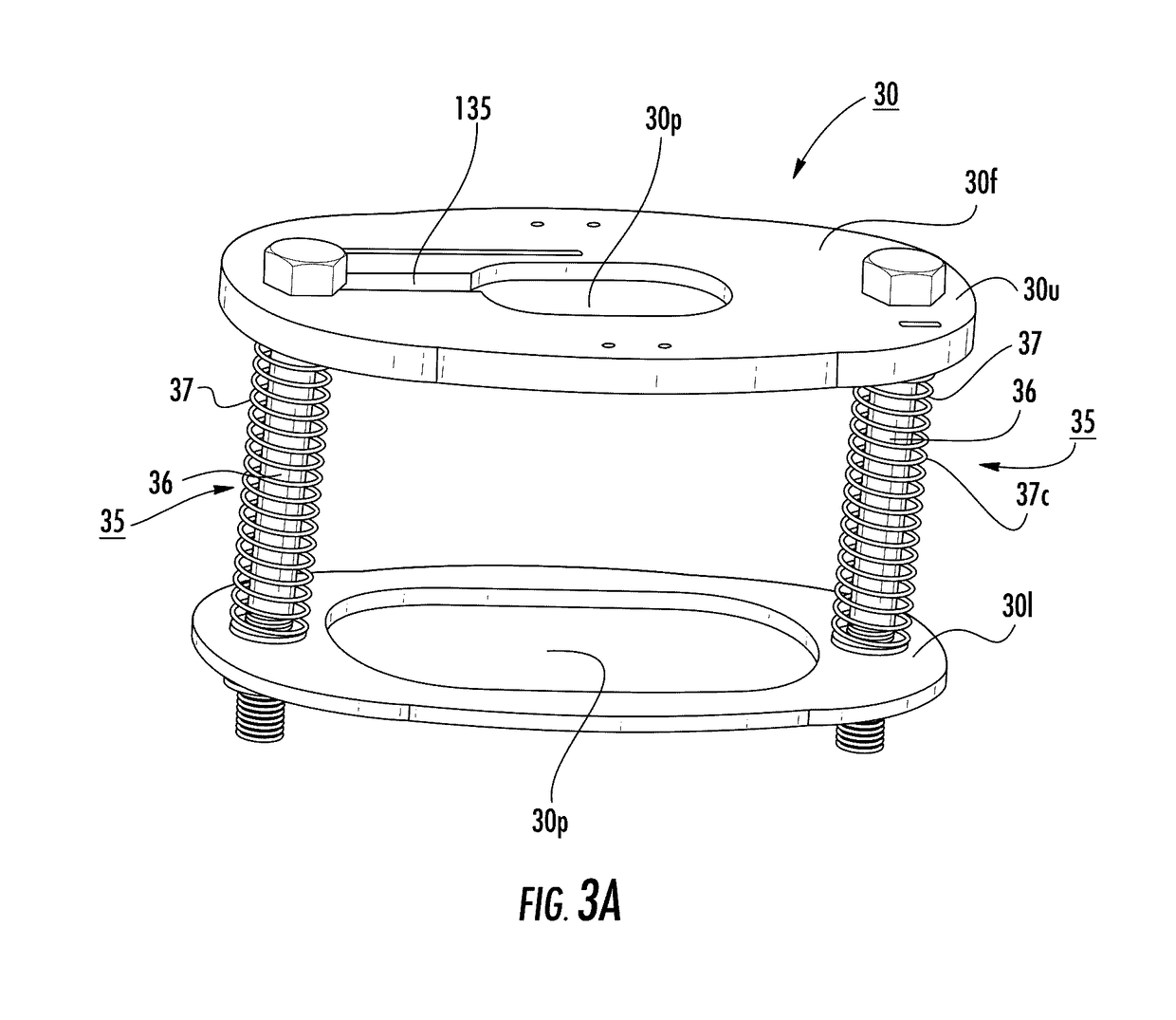
Devices that cooperate with ultrasound probes for muscoskeletal evaluations and related systems and methods
a technology of ultrasound probes and musculoskeletal evaluation, applied in the field of ultrasonic elastography, can solve the problems of unfavorable patient treatment, unfavorable patient treatment, and degenerative disease, and achieve the effects of improving patient comfort, reducing patient pain, and improving patient comfor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0118]To demonstrate proof of concept a polyvinyl alcohol cryogel (PVA-C) phantom was created and analyzed using the device shown in FIG. 1. During the validation study, the material was subjected to stress using an ultrasound transducer and strain was assessed from the ultrasound images using a manual measurement. FIG. 13 shows the computed stress-strain curve on one gel sample. The measured stress-strain curve was monotonic linear (R2>0.99), with an inherent dampening offset of 2.4996 kPa. The Young's modulus in this test was 30.291 kPa, which is similar to values for this material that are reported in the literature. See, e.g., Fromageau et al., “Estimation of polyvinyl alcohol cryogel mechanical properties with four ultrasound elastography methods and comparison with gold standard testings,”Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control, IEEE Transactions on, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 498-509, March 2007 and Fromageau et al., “Characterization of PVA cryogel for intravascular ultrasou
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap