Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2 results about "Magnetic dipole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the size of the source is reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric dipole, but the analogy is not perfect. In particular, a magnetic monopole, the magnetic analogue of an electric charge, has never been observed. Moreover, one form of magnetic dipole moment is associated with a fundamental quantum property—the spin of elementary particles.
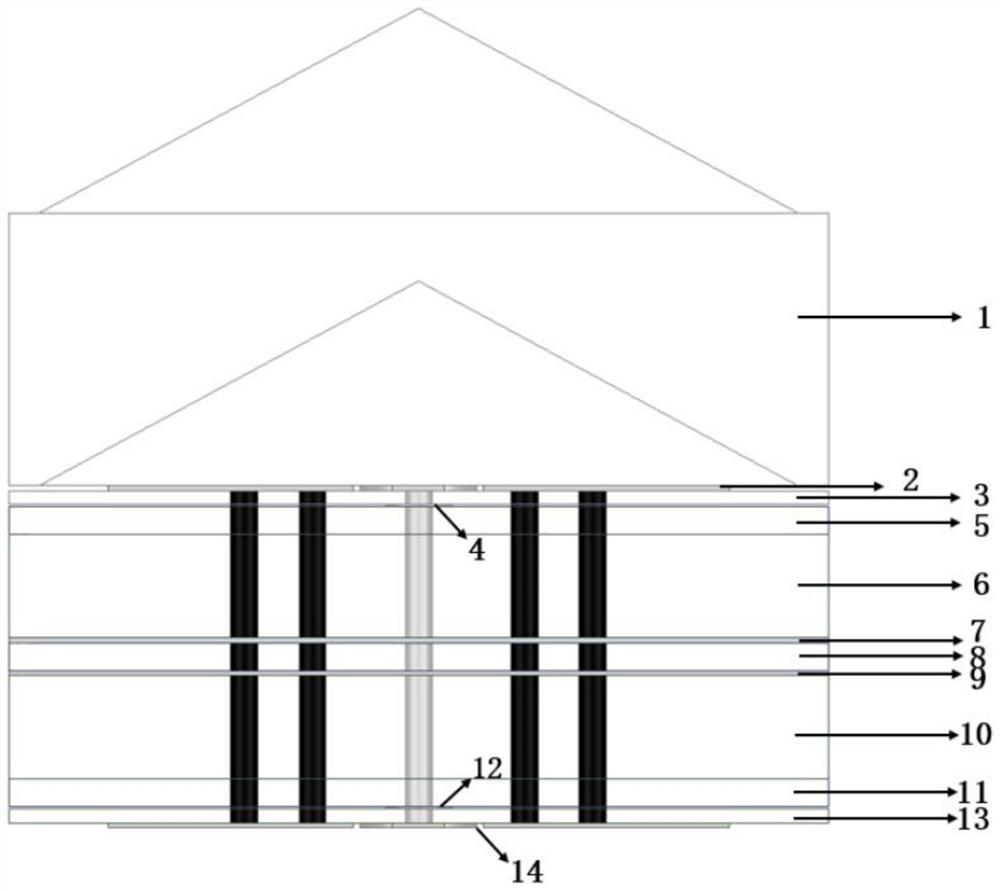
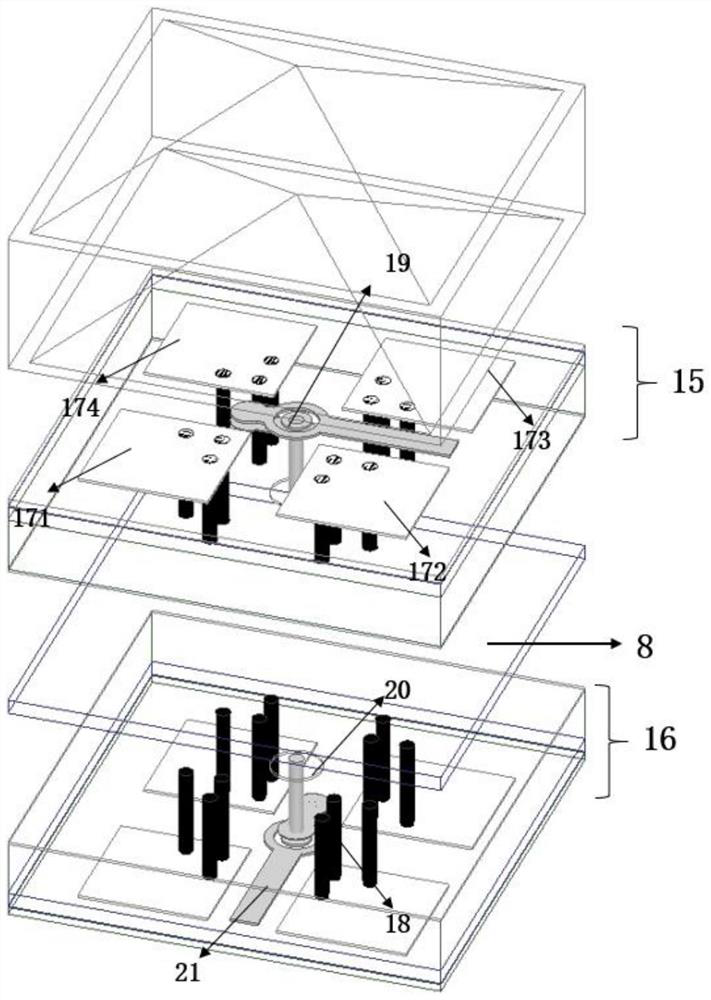
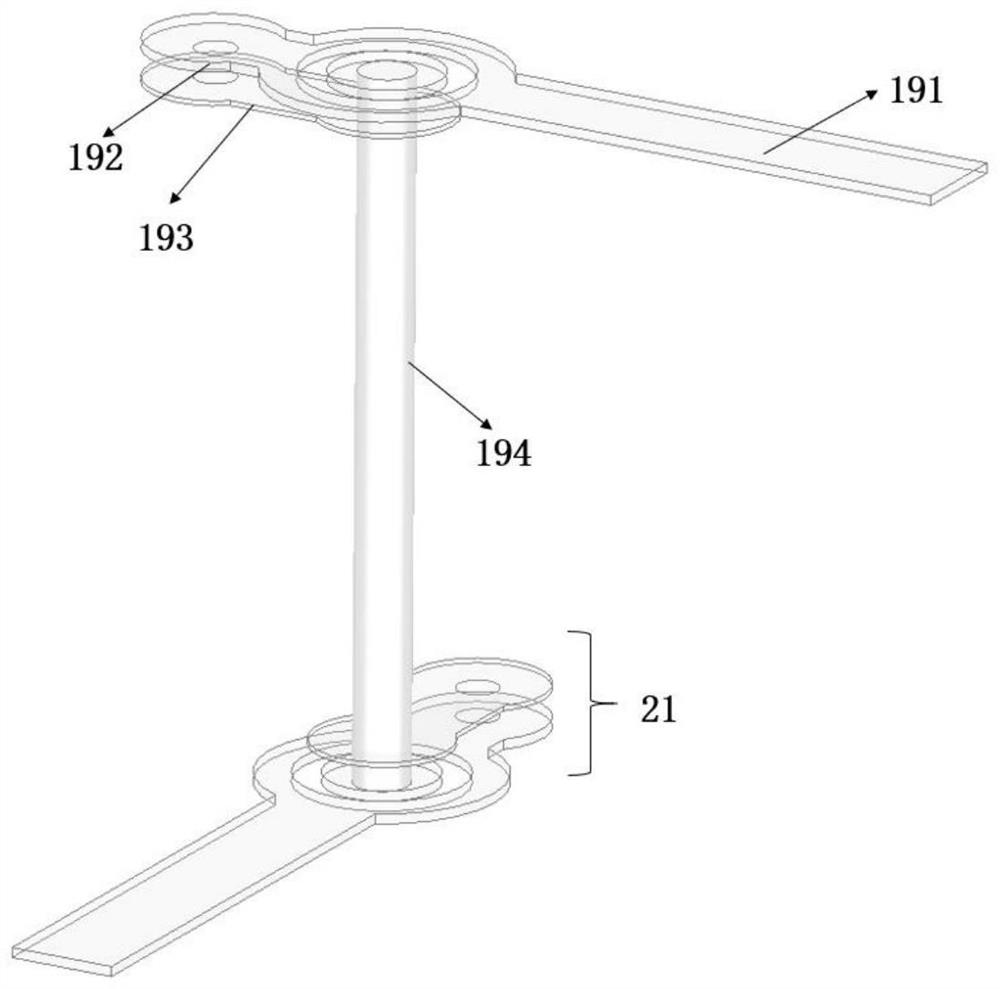
Non-contacting method in measuring the tire internal transformation
InactiveCN101187545AElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementNormal resonanceContact method
The invention relates to a non-contact type measuring method of tire deflection. The steel wire cord in the tire belted layer is applied with magnetic field from the outside, ensuring that the two ends of the belted layer form a magnetic dipole after the current passes through the inside of the steel wire cord. The current flows by the inside of the belted layer to form a resonance circuit integrally, through which the deflection in the tire is measured by adopting the normal resonance frequency formula.
Owner:HANKOOK TIRE WORLDWIDE
Magnetoelectric dipole broadband polarization torsion lens antenna and phase compensation method thereof
PendingCN113851861ALow subwavelength thickness profileLow costParticular array feeding systemsIndividually energised antenna arraysEngineeringBroadbanding
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap