Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3 results about "Numerical aperture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface. The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an objective (and hence its light-gathering ability and resolution), and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it.
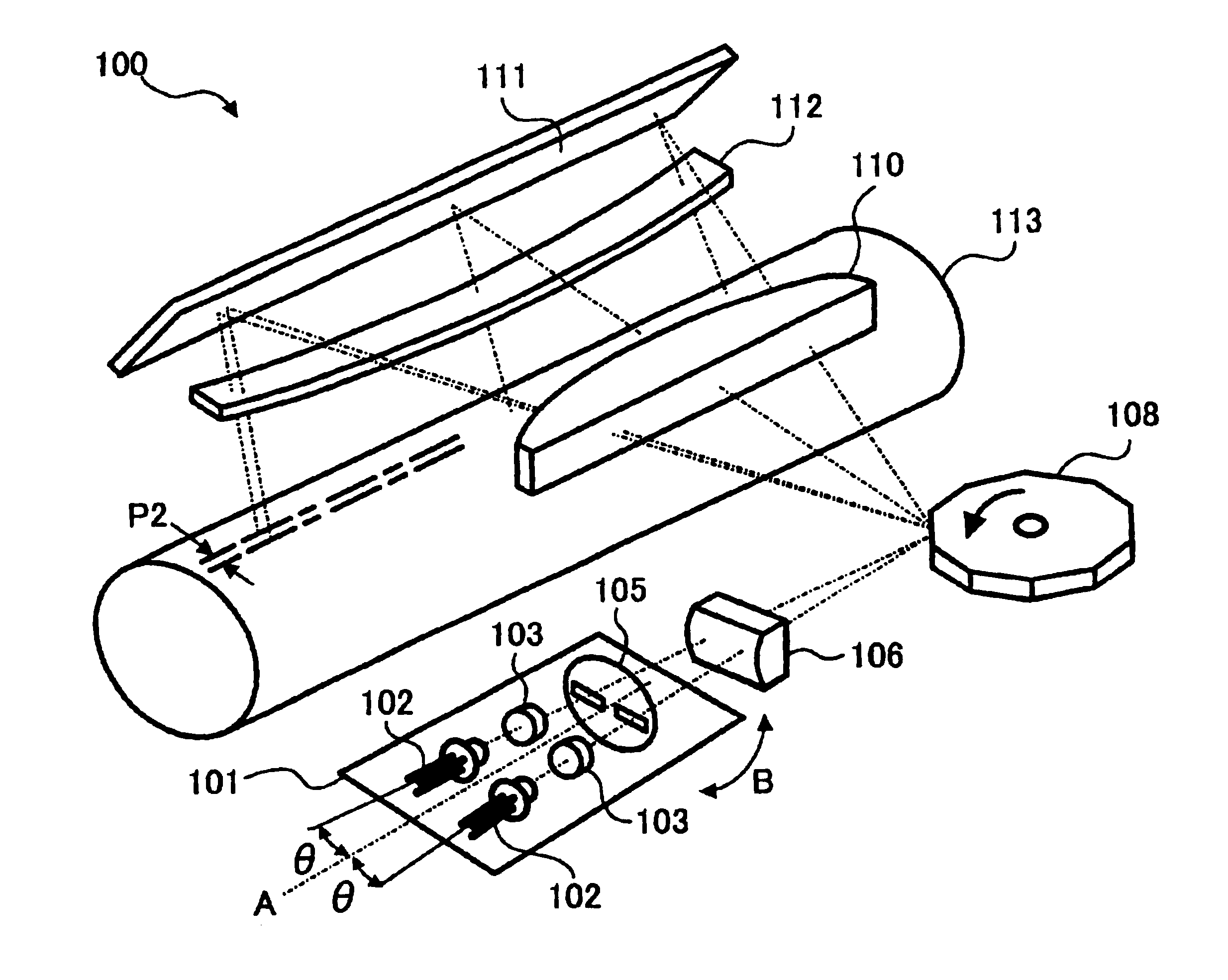
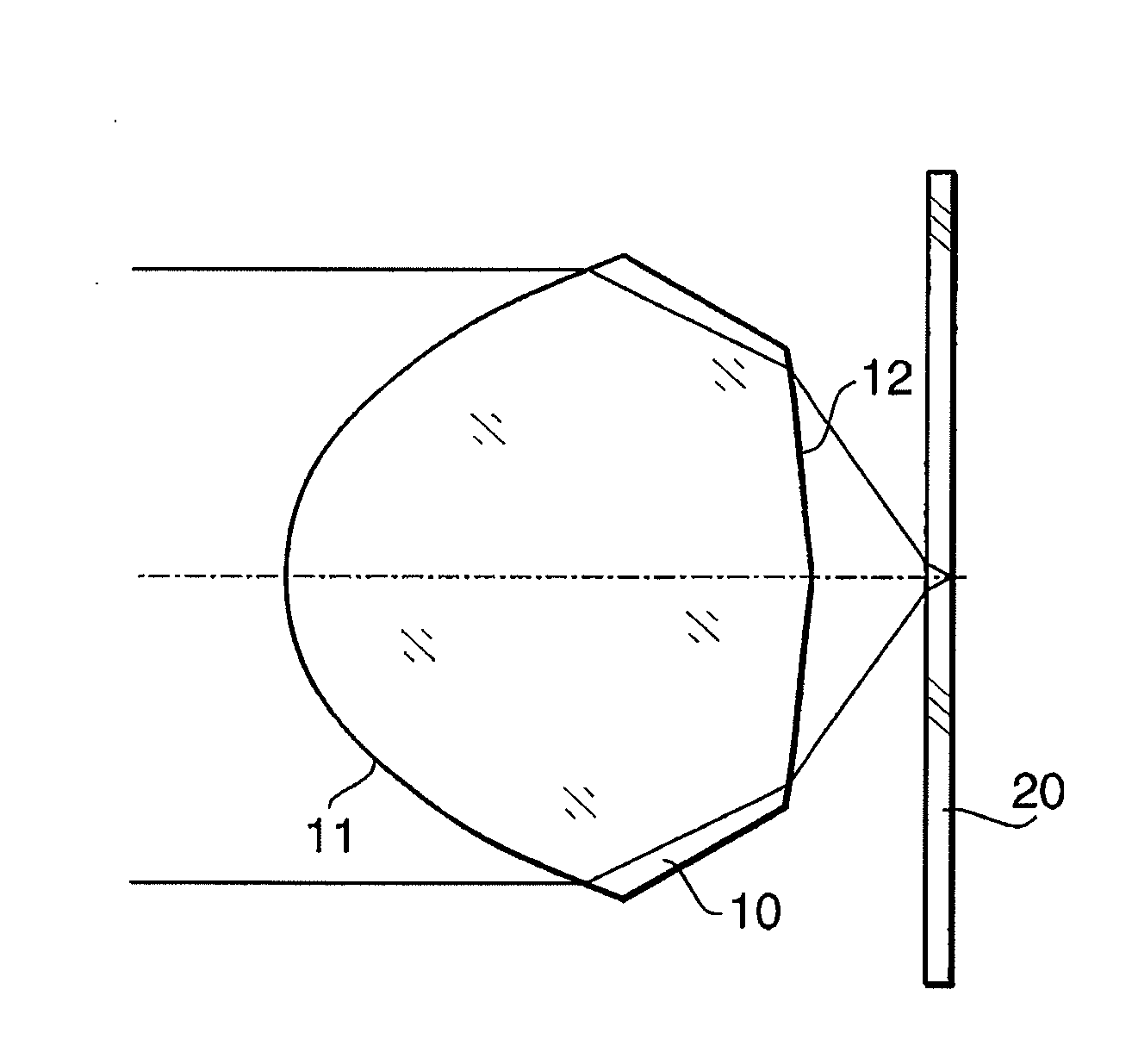
Method and apparatus for multi-beam optical scanning capable of effectively adjusting a scanning line pitch
Owner:RICOH KK
Sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method
ActiveCN105842257AGuaranteed Quantitative MeasurementsGuaranteed stabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicron scaleGrating
The invention discloses a sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method. A light source part of the device comprises a super-continuum luminous spectrum light source and a single-mode optical fiber circulator; a reference arm and sample arm part comprises a first collimating lens, a 45-degree cylindrical reflecting mirror, a reference objective, a reference reflecting mirror, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a sample objective and a part to be detected; a detection arm part comprises a second collimating lens, a transmission grating, a focusing lens, a photoelectric detector and a computer. The method comprises the steps that light of a reference arm and light of a sample arm return back to the single-mode optical fiber circulator in the same way, light beams of the two arms encounter, and interference is caused; interfered light beams are subjected to light splitting through the transmission grating and then focused on different pixel elements of the photoelectric detector through the focusing lens, the photoelectric detector inputs collected signals into the computer, the signals are processed, and faultage images of different positions are obtained. According to the sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method, the ultra-wide band light source, the high-power aperture imaging objectives and the common light path imaging structure are adopted, and the three-dimensional structure of sub-micron scale glass subsurface cracks is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
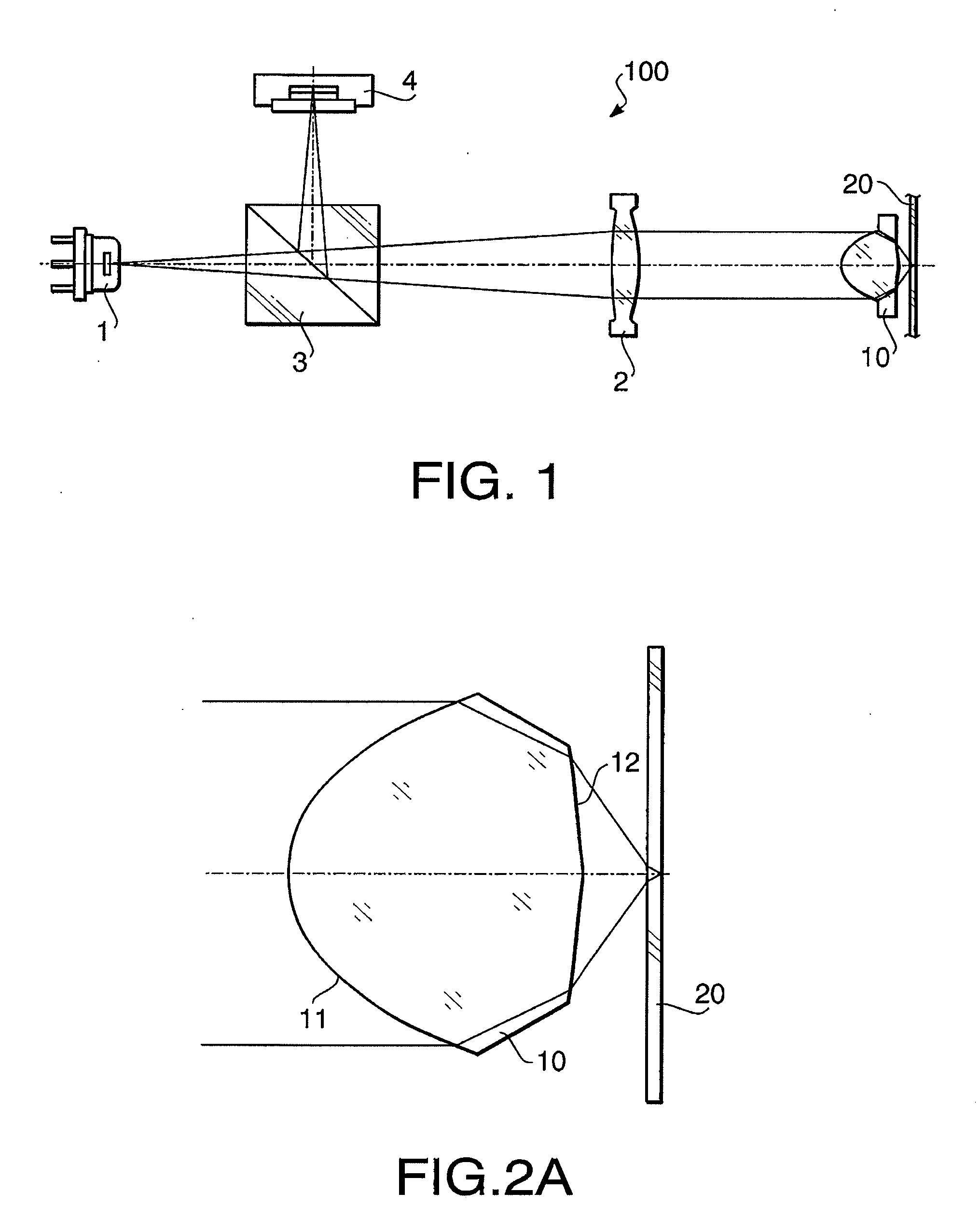
Objective Lens for Optical Pick-Up
ActiveUS20080180815A1Convenient coatingEasy to measureOptical beam guiding meansRecord information storageSingle elementNumerical aperture
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap