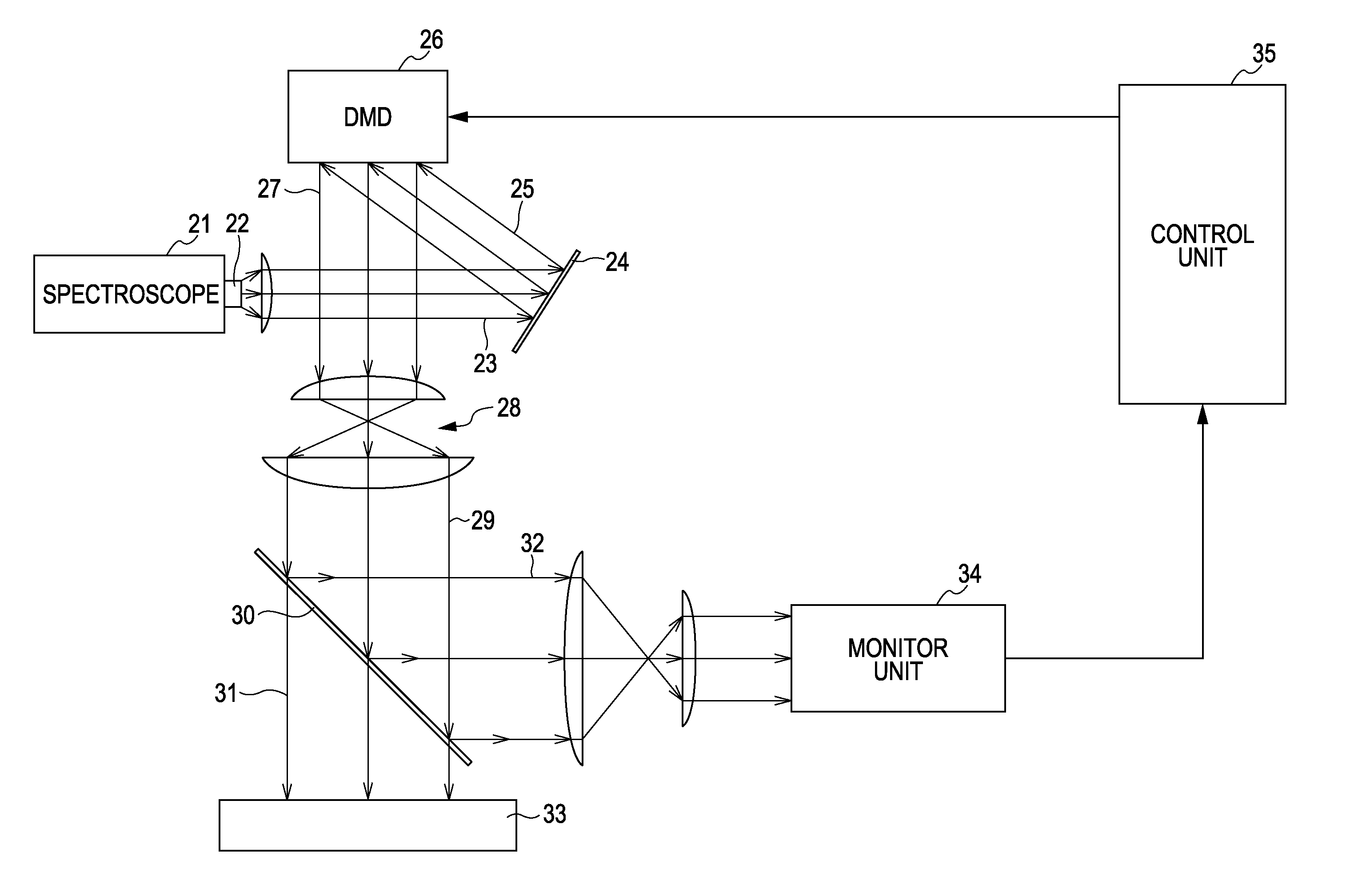
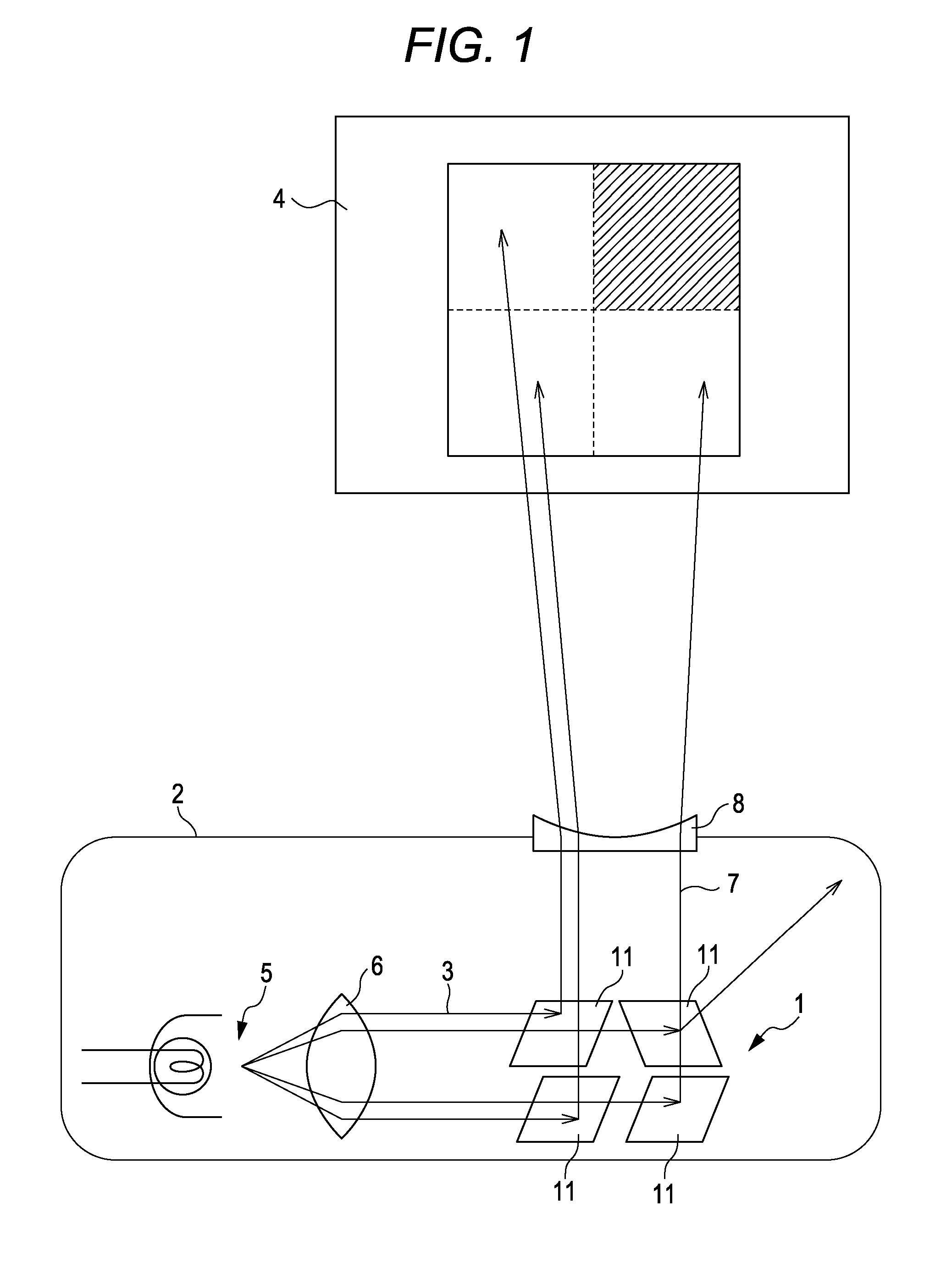
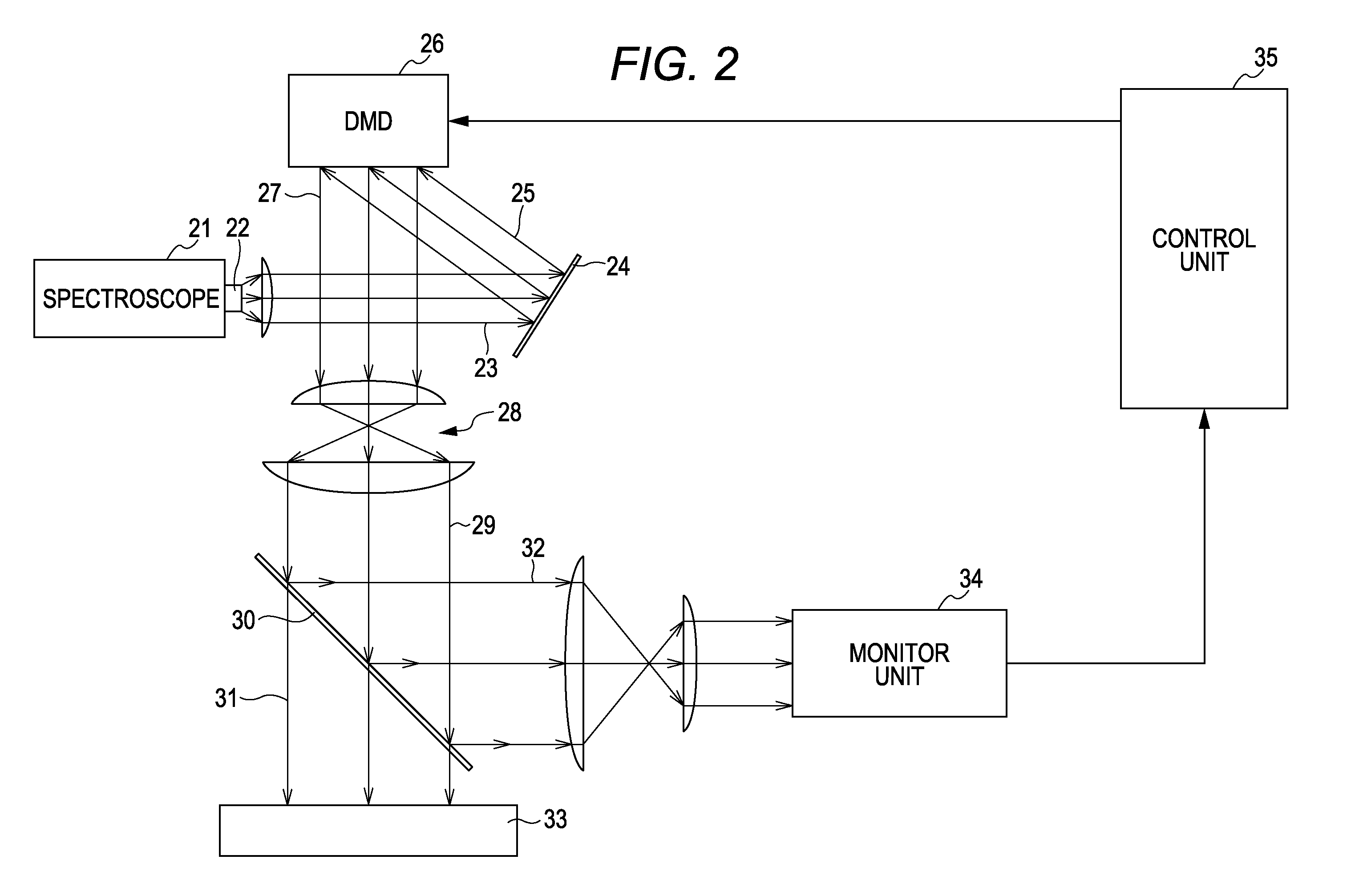
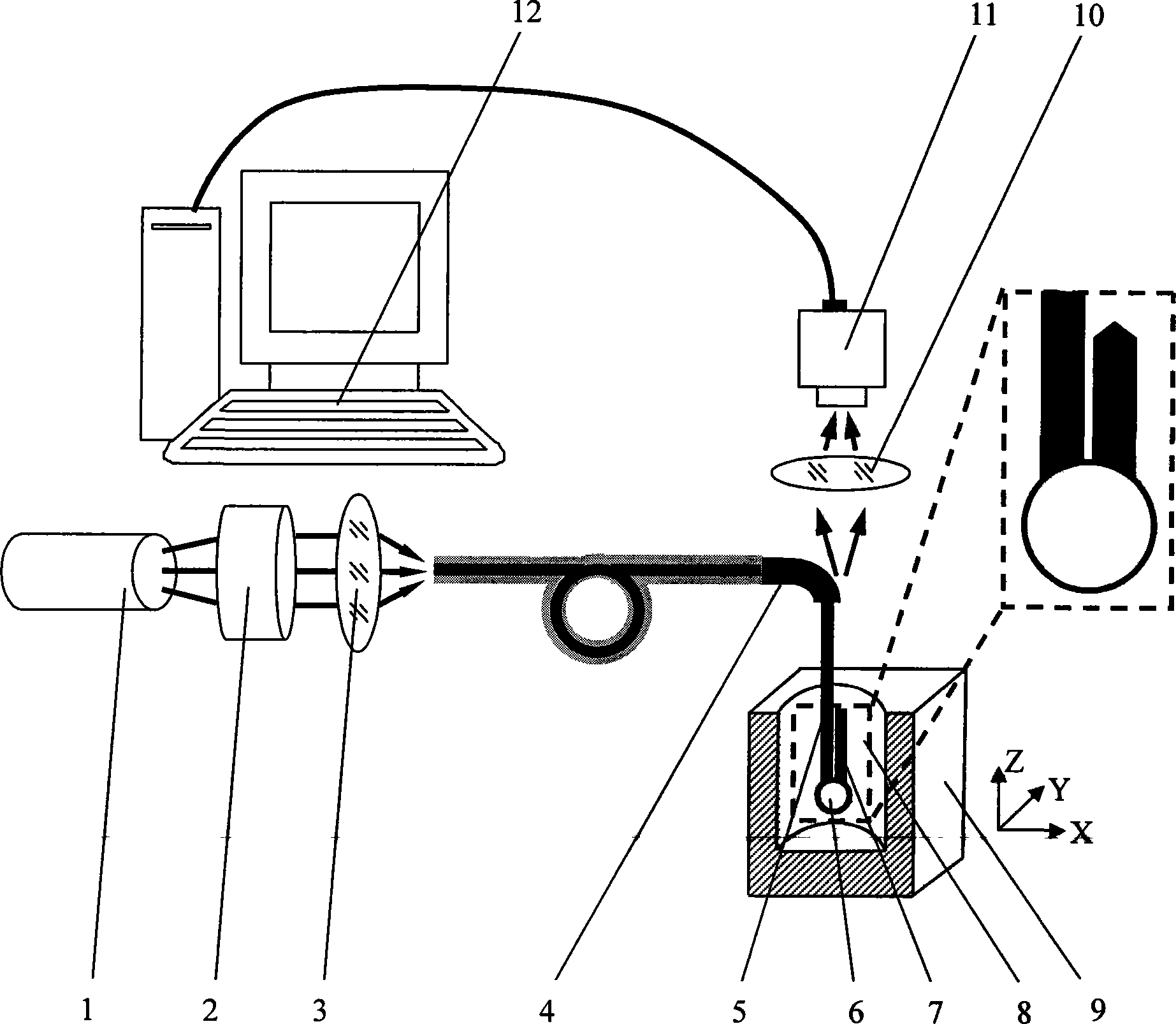
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131 results about "Light beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
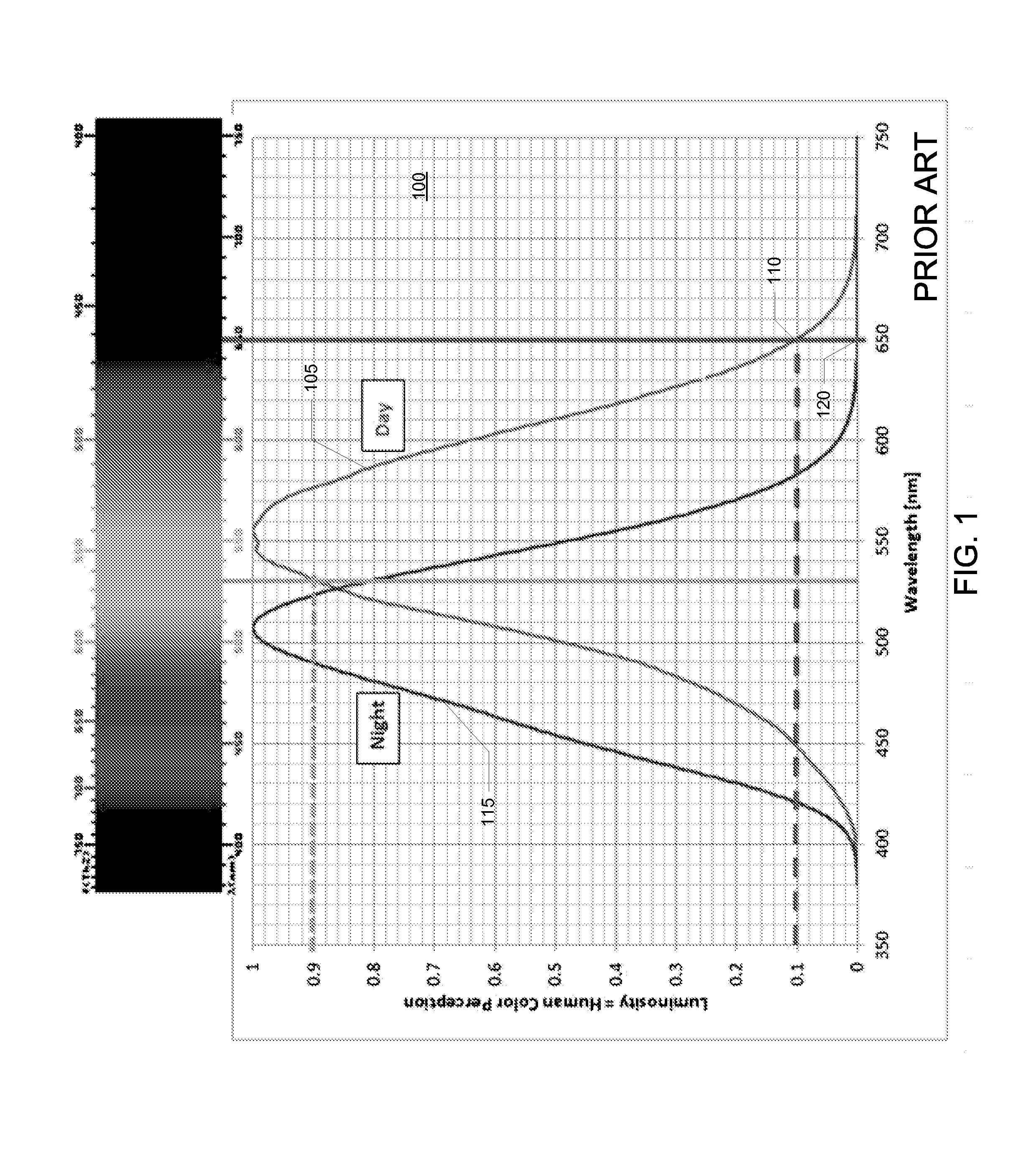
A light beam or beam of light is a directional projection of light energy radiating from a light source. Sunlight forms a light beam (a sunbeam) when filtered through media such as clouds, foliage, or windows. To artificially produce a light beam, a lamp and a parabolic reflector is used in many lighting devices such as spotlights, car headlights, PAR Cans and LED housings. Light from certain types of laser has the smallest possible beam divergence.
Replaceable LED bulb with interchageable lens optic
InactiveUS6846101B2Easy to replaceReliable electrical connectionPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesCamera lensElectrical connection
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Beam adjustment mechanism for an LED light fixture
Owner:COOPER TECH CO
Security threat detection system
Owner:WONG THOMAS K
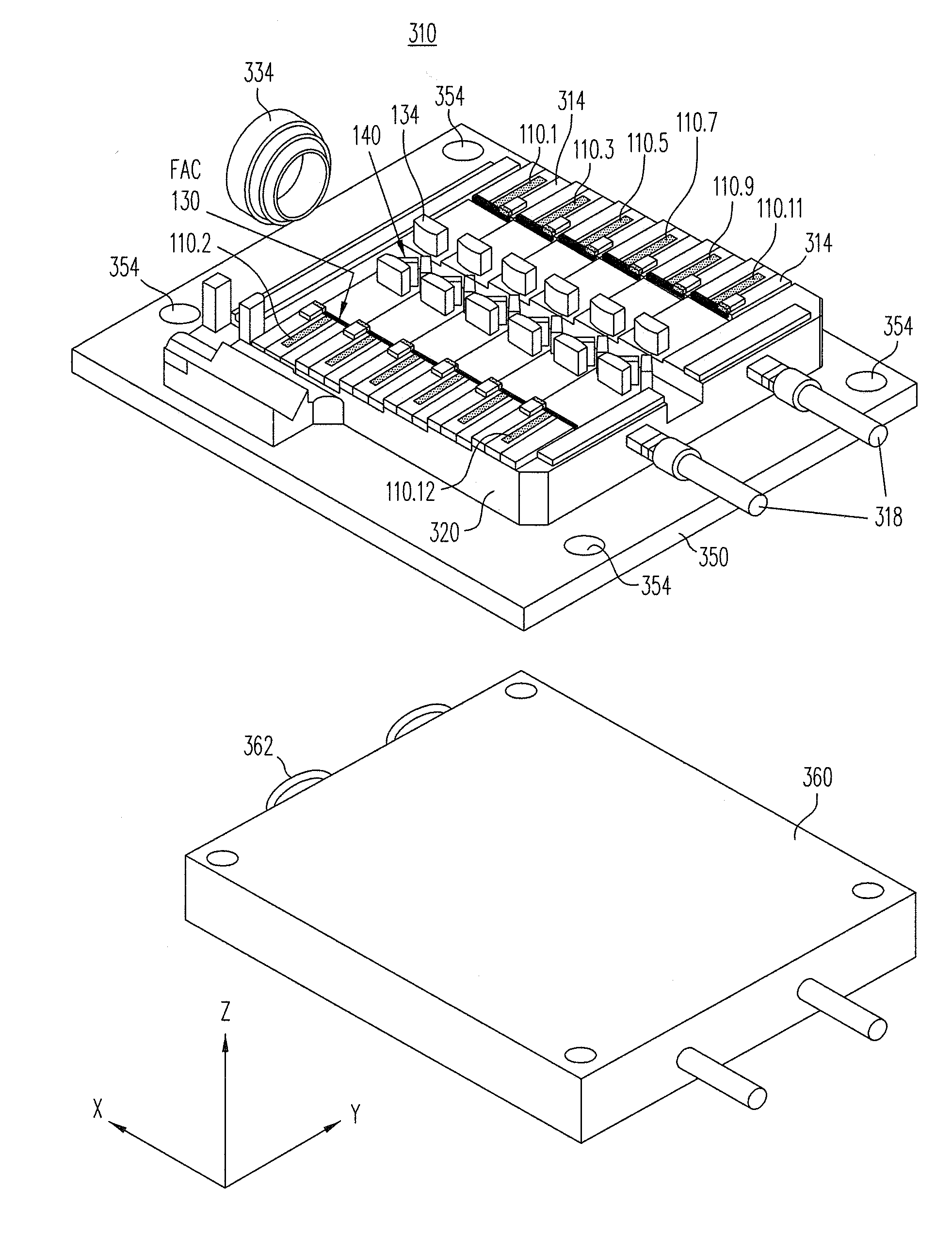
VCSEL and VCSEL array having integrated microlenses for use in a semiconductor laser pumped solid state laser system
InactiveUS20050025211A1High power outputImprove cooling effectSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical resonator shape and constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Method and apparatus for multi-beam optical scanning capable of effectively adjusting a scanning line pitch
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical microscopic imaging system and imaging method
The invention relates to an optical microscopic imaging system and imaging method, belonging to field of optical microscopes. The system comprises a laser, a half-wave plate, a polarization beam splitter prism, a beam expander collimator, a microscope objective, a reflective mirror, a beam combining mirror, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a computer. After the laser emits laser light, the polarization beam splitter prism divides the laser light into two light beams, and one of the light beams transmits a transparent object. The two light beams pass through the beam combining mirror and interfere with each other to form an image on the CCD, and the CCD transmits the obtained image into the computer. A microscopic strength image and a phase image of the object are obtained through digital reconstruction in the computer, so that a three-dimensional microscopic of the object is obtained.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG
Focus detection device and imaging apparatus having the same
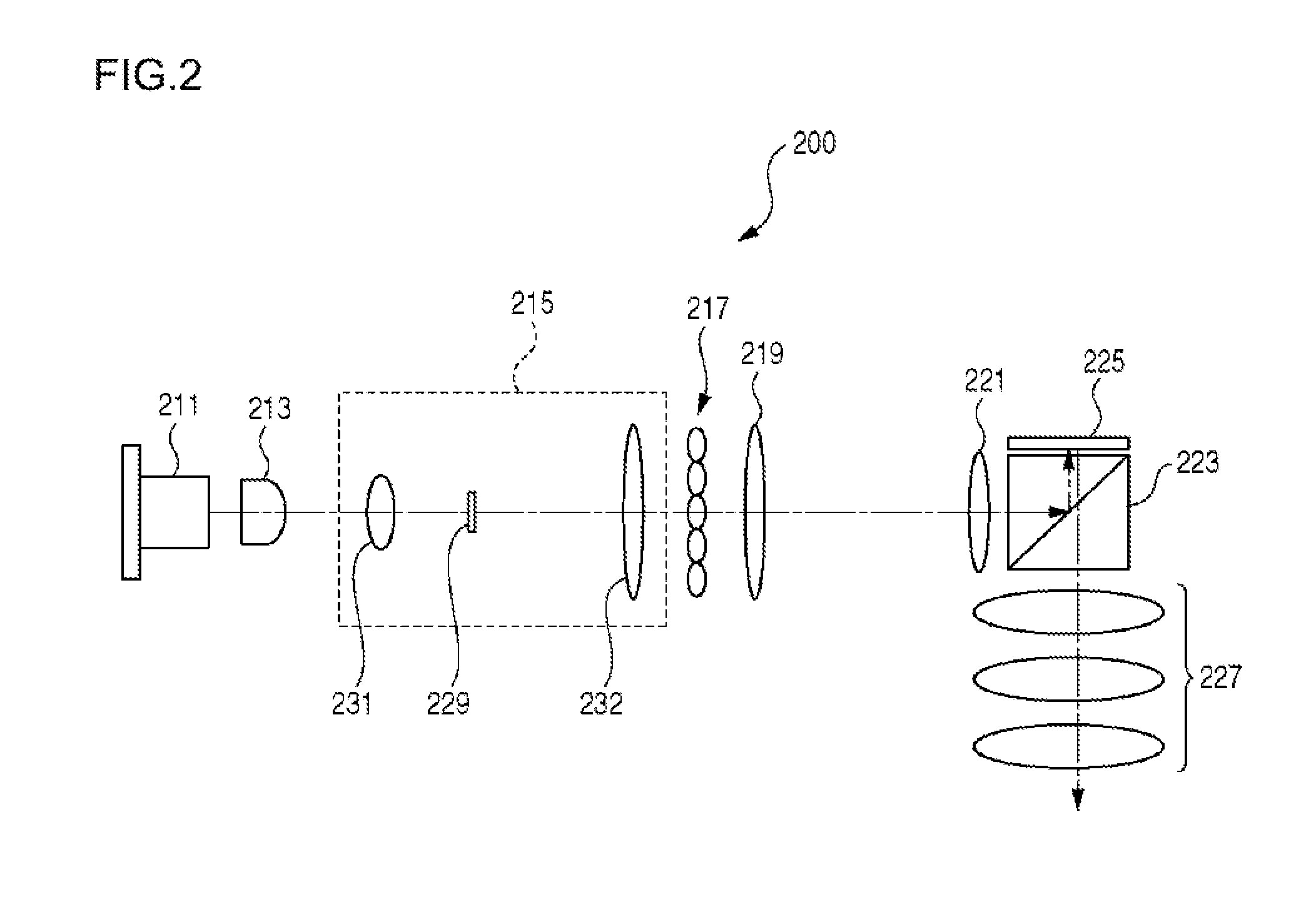
A focus detection device having imaging pixels and focus-detecting pixels using a phase-difference focus detection method implements high-precision focus detection. In the focus detection device, a plurality of pixels each having a photoelectric conversion unit for converting an incident light flux into signal charges, and a microlens having a focus position near the photoelectric conversion unit are arranged. The plurality of pixels include a plurality of imaging pixels for generating a shot image, and a plurality of focus-detecting pixels for generating an image signal for focus detection by the phase-difference focus detection method. An opening for giving a pupil division function to the focus-detecting pixel is formed using electrodes arranged to read out signal charges from the photoelectric conversion unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
Owner:RICOH KK
Close-lit holographic nightlight display lighting system
InactiveUS6072606ALarge apertureSuitable for useHalographic mechanical componentsFixed installationLight beamLighting system
Owner:HUETHER JAMES L
Method of fabricating light-emitting apparatus with improved light extraction efficiency and light-emitting apparatus fabricated using the method
ActiveUS20100120183A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamSingle crystal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
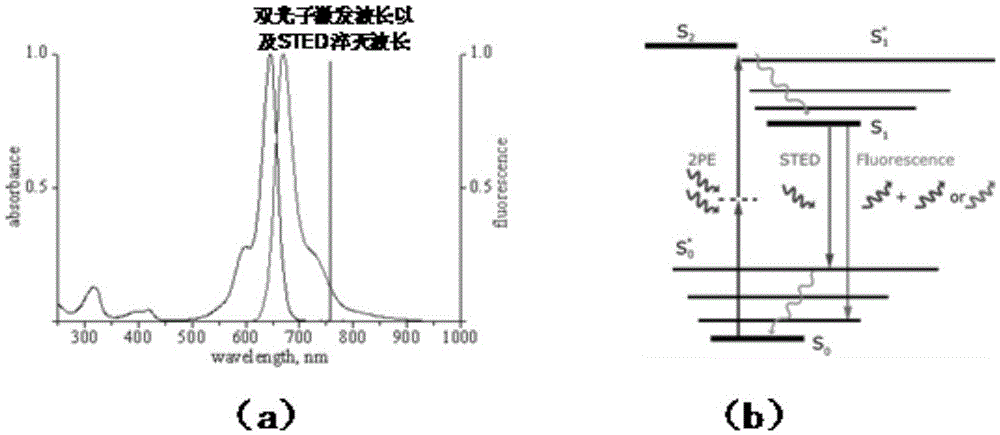
System and method for providing enhanced background rejection in thick tissue with differential-aberration two-photon microscopy
InactiveUS20090084980A1Improve discriminationIncreased rejectPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersExcitation beamLight beam
A system for providing enhanced background rejection in thick tissue contains an aberrating element for introducing controllable extraneous spatial aberrations in an excitation beam path; at least one mirror capable of directing received laser pulses to the aberrating element; an objective; a beam scanner imaged onto a back aperture of the objective so that the beam scanner steers beam focus within the thick tissue; and a detector for recording signals produced by the tissue. An associated method comprises the steps of acquiring two-photon excited fluorescence of thick tissue without extraneous aberrations; introducing an extraneous aberration pattern in an excitation beam path; acquiring two-photon excited fluorescence of the thick tissue having the introduced extraneous aberration pattern; and subtracting the two-photon excited fluorescence with extraneous aberrations from the acquired standard two-photon excited fluorescence of the thick tissue without extraneous aberrations.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
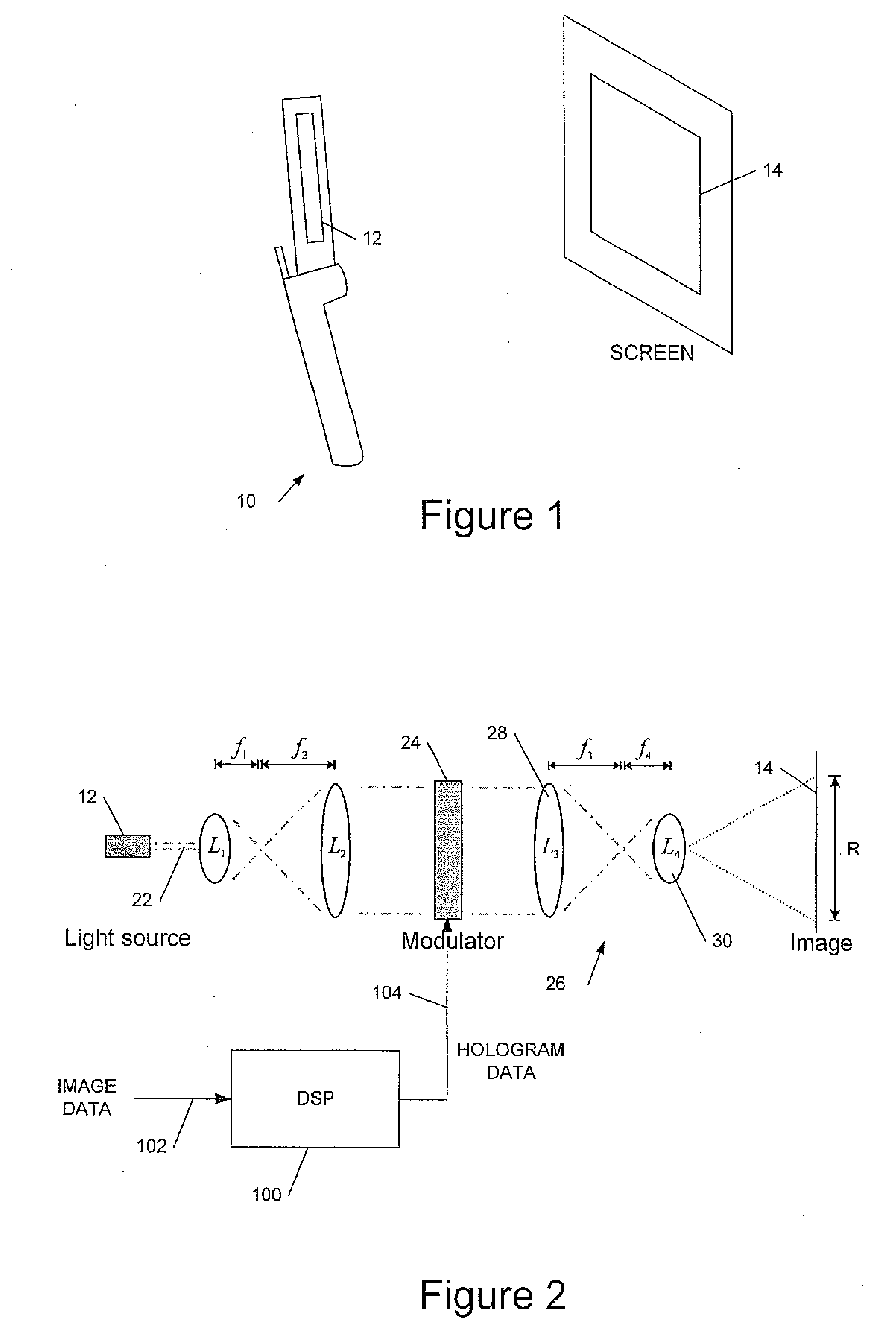
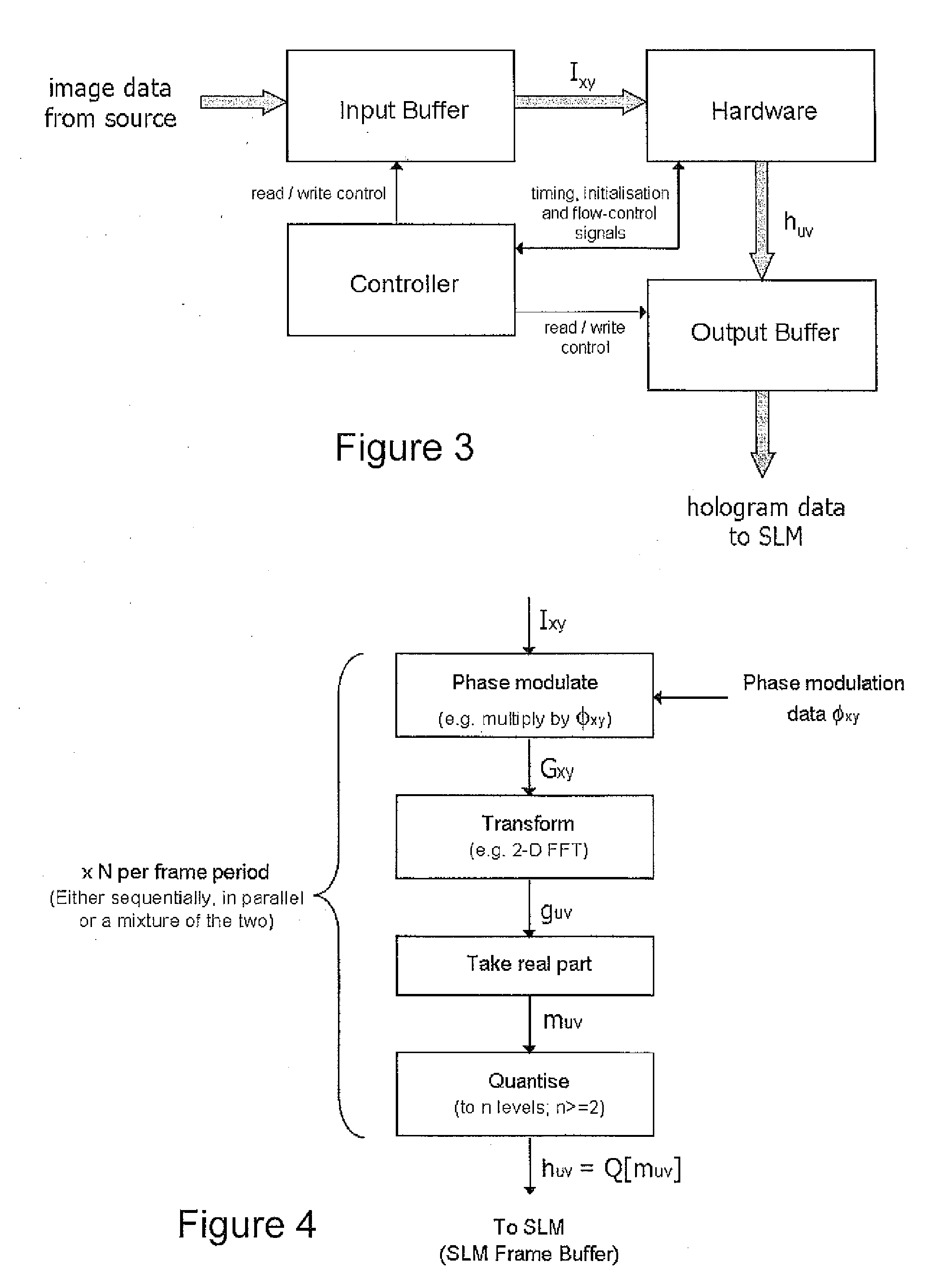
Holographic display devices
InactiveUS20090207466A1Television system detailsHolographic optical componentsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Solid-state light sources for curing and surface modification
InactiveUS20060274421A1Improve stabilityExtended service lifePoint-like light sourcePretreated surfacesMultiwavelength spectroscopyLight beam
Owner:HERAEUS NOBLELIGHT AMERICA
Sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method
ActiveCN105842257AGuaranteed Quantitative MeasurementsGuaranteed stabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicron scaleGrating
The invention discloses a sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method. A light source part of the device comprises a super-continuum luminous spectrum light source and a single-mode optical fiber circulator; a reference arm and sample arm part comprises a first collimating lens, a 45-degree cylindrical reflecting mirror, a reference objective, a reference reflecting mirror, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a sample objective and a part to be detected; a detection arm part comprises a second collimating lens, a transmission grating, a focusing lens, a photoelectric detector and a computer. The method comprises the steps that light of a reference arm and light of a sample arm return back to the single-mode optical fiber circulator in the same way, light beams of the two arms encounter, and interference is caused; interfered light beams are subjected to light splitting through the transmission grating and then focused on different pixel elements of the photoelectric detector through the focusing lens, the photoelectric detector inputs collected signals into the computer, the signals are processed, and faultage images of different positions are obtained. According to the sub-micron scale glass subsurface defect detection device and method, the ultra-wide band light source, the high-power aperture imaging objectives and the common light path imaging structure are adopted, and the three-dimensional structure of sub-micron scale glass subsurface cracks is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Concentric Dual Drum Raster Scanning Beam System and Method
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
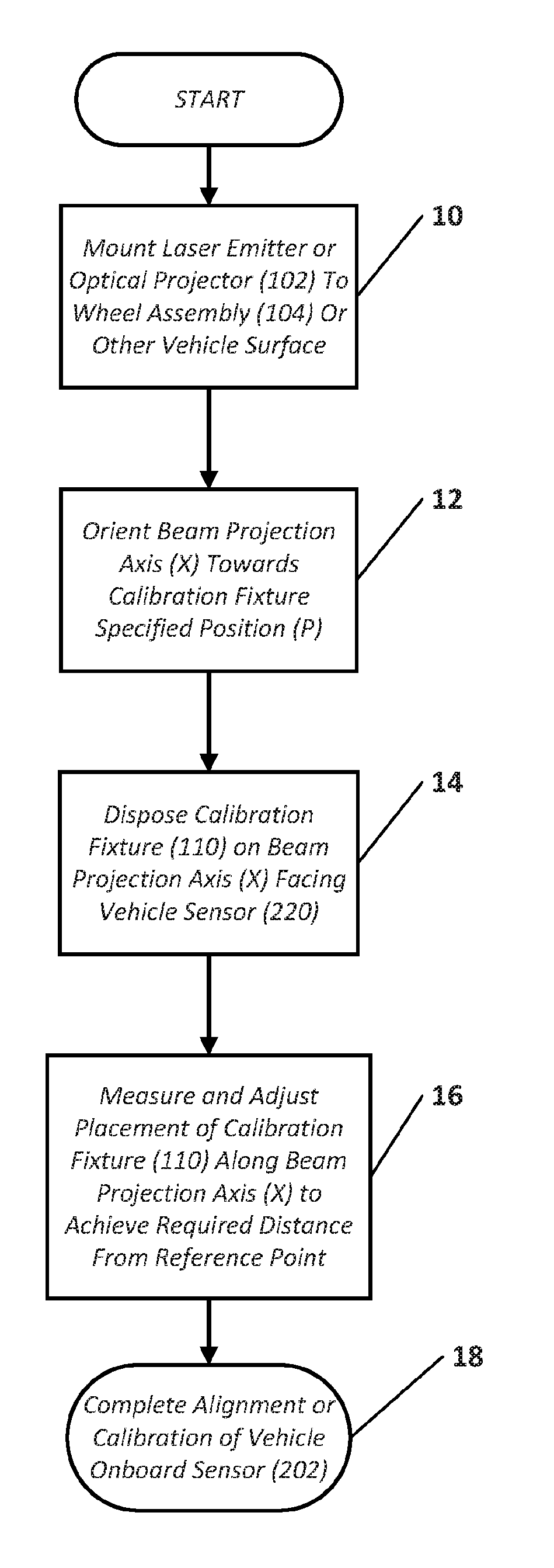
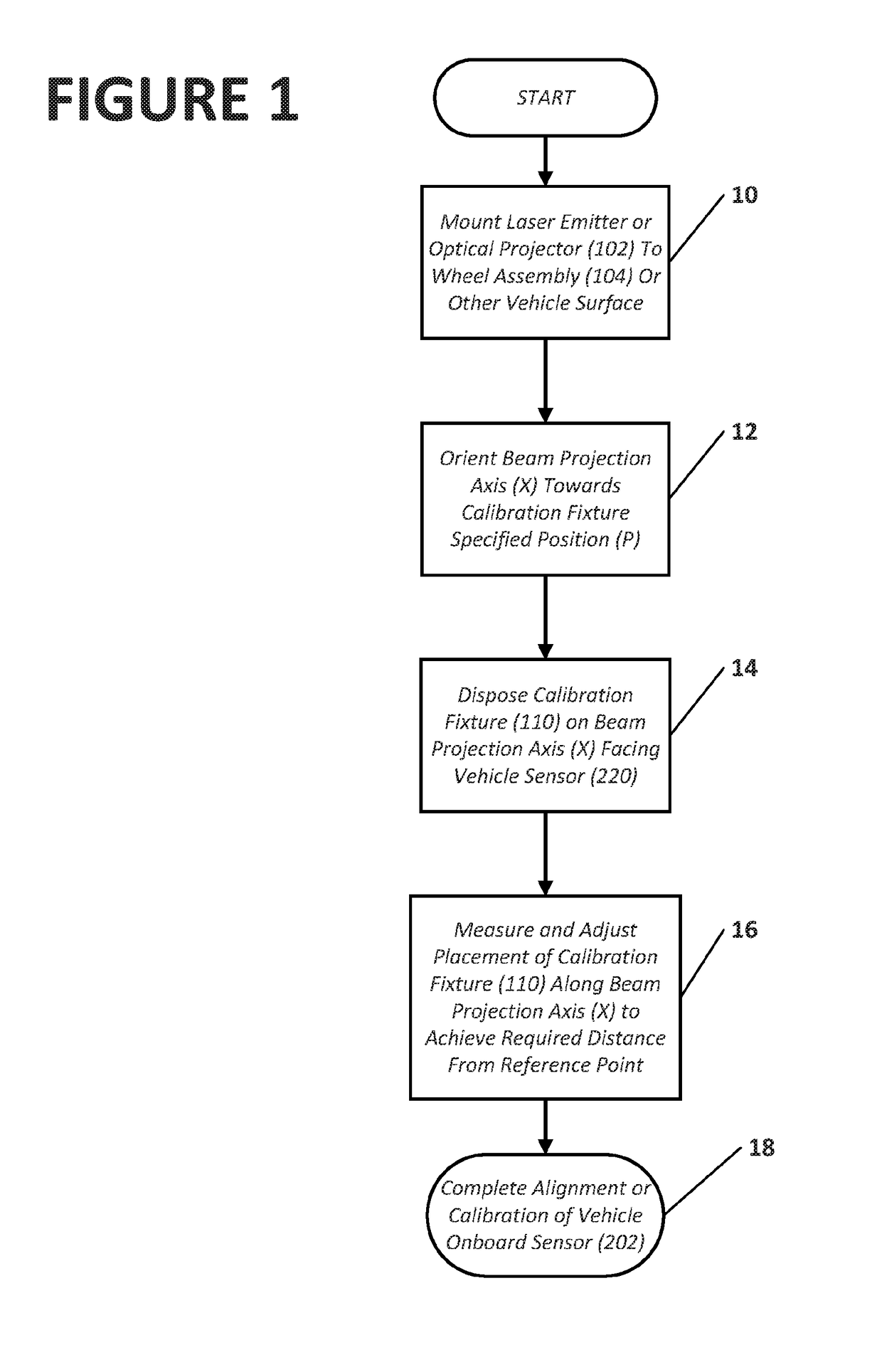
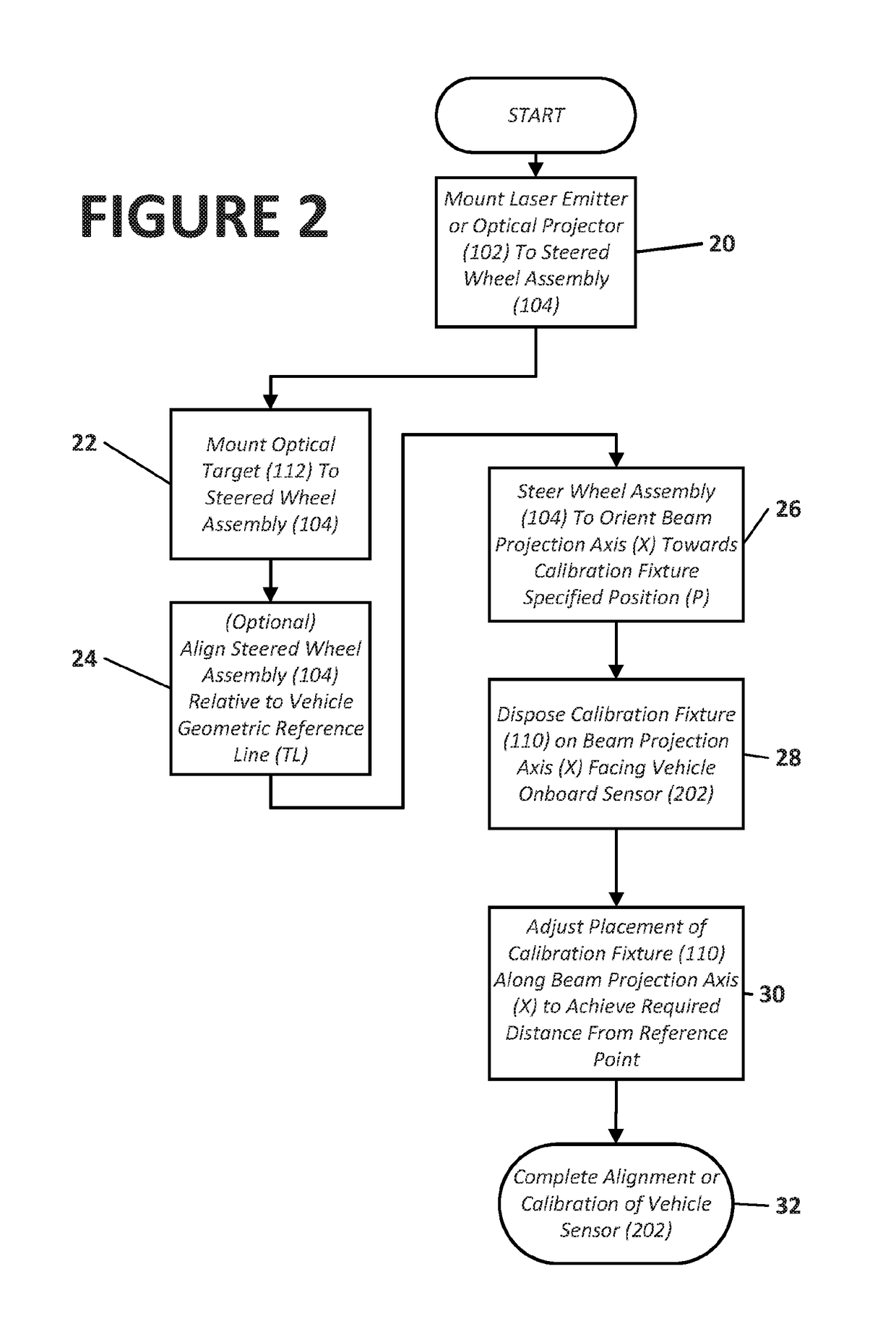
Method And Apparatus For Alignment Of Vehicle Blind Spot Monitoring Sensor
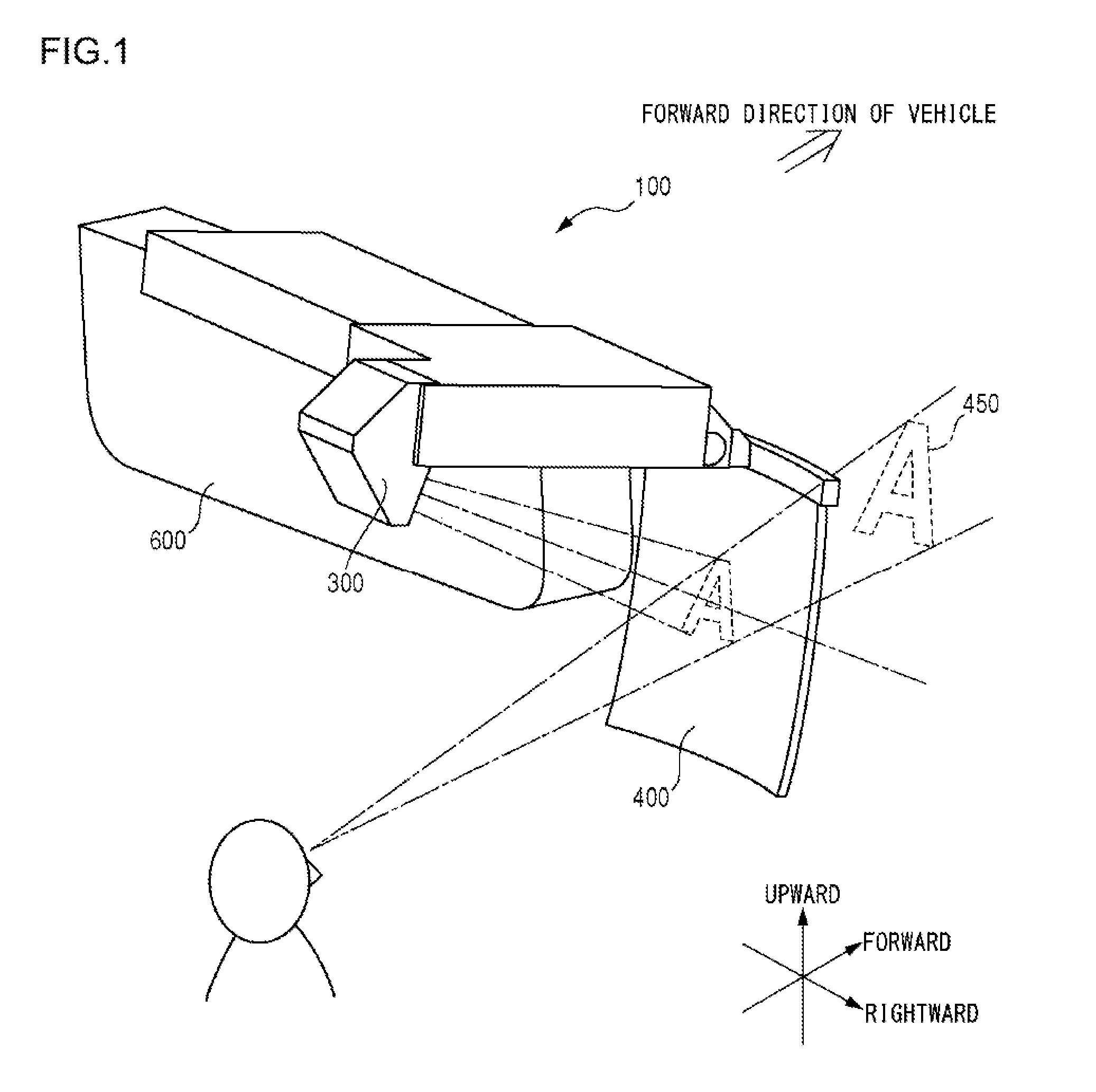
ActiveUS20180052223A1Help positioningUsing optical meansVehicle position/course/altitude controlLaser transmitterLight beam
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Laser diode combiner modules
InactiveUS20120081893A1Reduce the heating effectImprove thermal stabilityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight beamThermal stability
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
Flow cytometer
ActiveUS20080079929A1Improve stabilityNarrow distributionMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisInstabilityLight beam
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Littrow interferometer
An apparatus and method for measuring displacement includes a light beam directed to an interferometer core that splits the light beam into first and second component beams. The first component beam is directed to a diffraction grating at approximately a Littrow angle. A diffraction is received by the interferometer core and is combined with the second component beam. The combination of the first and second component beams is measured to determine displacement of the diffraction grating.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for controlling multiple beams illuminating projected images
The power and response curves of one or more beams or primaries of beams of a laser projection system illuminating an image on a viewing surface are controlled to desired characteristics during exhibition by monitoring the scanning beams in real time by using at least part of the horizontal blanking time during the scanning of a motion or still image to project a test pattern with one or more of the beams onto a sensor or sensors. The system and method permits real-time balancing and maintenance of the response curves and power levels of each of the beams, and of primary beams of combined beams, to desired targets so as to produce a display field without artifacts and at desired brightness on the viewing surface.
Owner:MAGIC LANTERN
Charged particle beam writing apparatus and charged particle beam writing method
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Illumination apparatus and method for obtaining illuminance with high uniformity
InactiveUS20100274392A1Improve uniformityMaintain consistencySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlLight equipmentIlluminance
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Double-fiber ball-shared coupling micro-measuring-force targeting sensor with end face micro-structure
InactiveCN103900468AImprove resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansFiberMicro structure
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
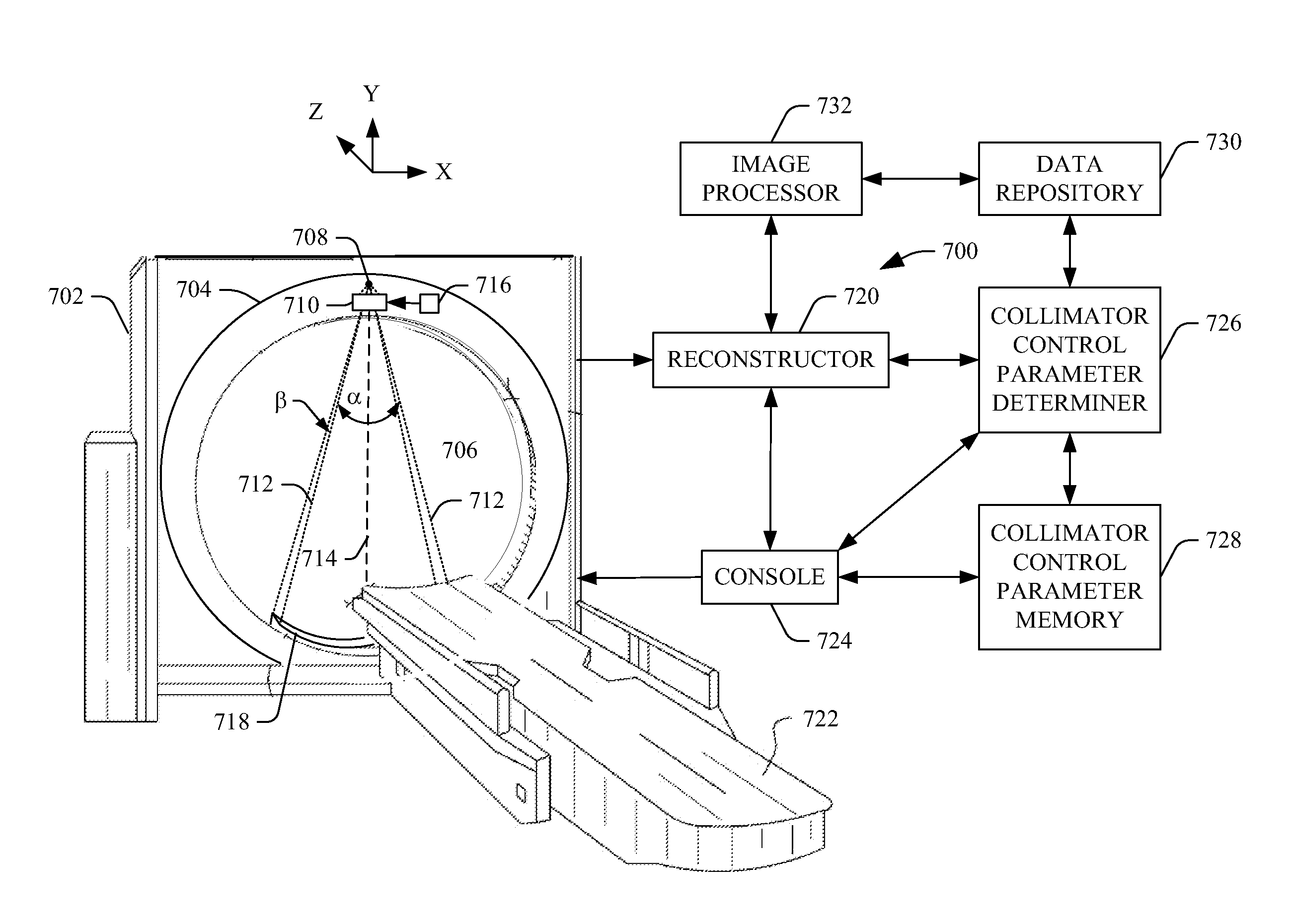
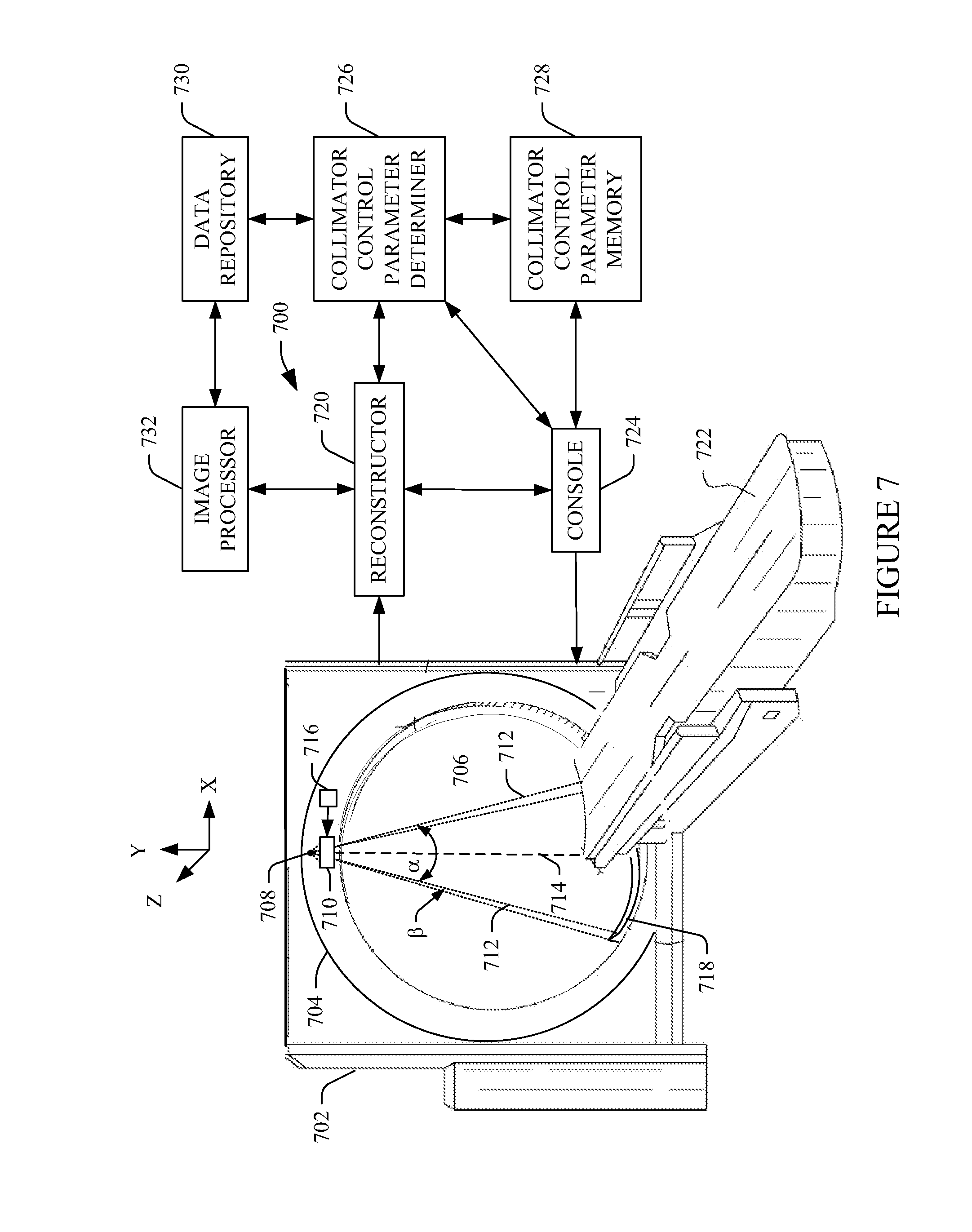
Dynamic collimation
ActiveUS20140177782A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLight beamRadiation beam
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Image display device
ActiveUS20150124227A1Improve utilization efficiencyReduce the impactDiffusing elementsProjectorsDisplay deviceLight beam
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Base Transceiver Station with Radiation Beam Steering and Active Antenna
ActiveUS20120129575A1No extra expenseSimple calculationSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionLight beamControl data
A base transceiver station for a mobile communications network for communicating with a plurality of subscriber devices within a coverage area comprises an active antenna array with a tilt adaption arrangement to adjust a vertical tilt angle of an antenna beam in dependence of beam tilting control data, and thereby dynamically change the coverage area served by the base transceiver station. The base transceiver station further comprises a beam control device for evaluating the distance of the subscriber devices in the coverage area to the active antenna array and calculating from the distances the beam tilting control data. As the distance of a subscriber device to the antenna is a parameter that may be extracted directly from data that is available anyhow for at least some subscriber devices, this data can be acquired at no extra expense.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Robotic Laser Pointer Apparatus and Methods
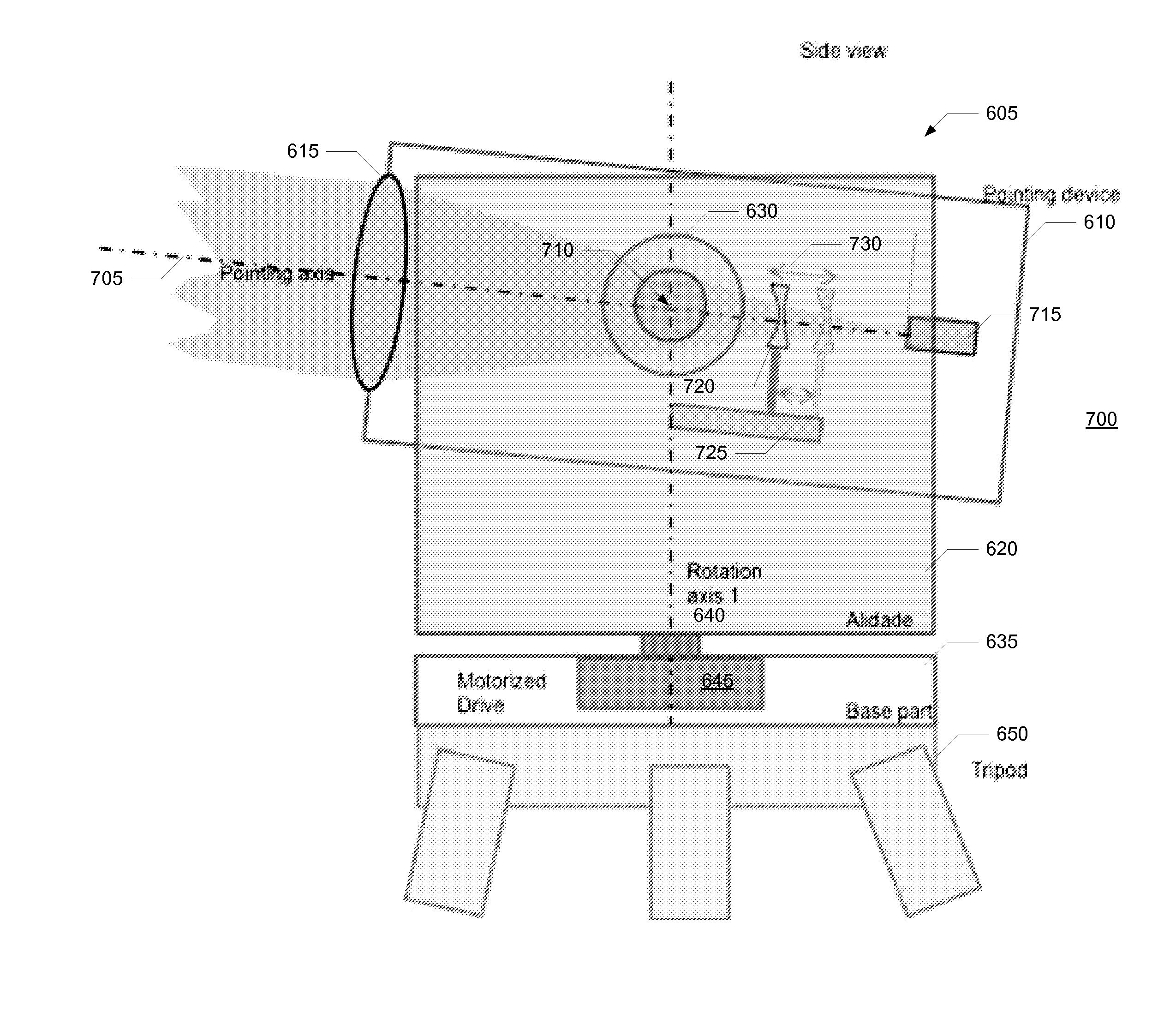
ActiveUS20140123508A1Increase brightnessImprove visibilityActive open surveying meansHeight/levelling measurementLight beamClassical mechanics
Owner:TRIMBLE A B A CORP OF SWEDEN
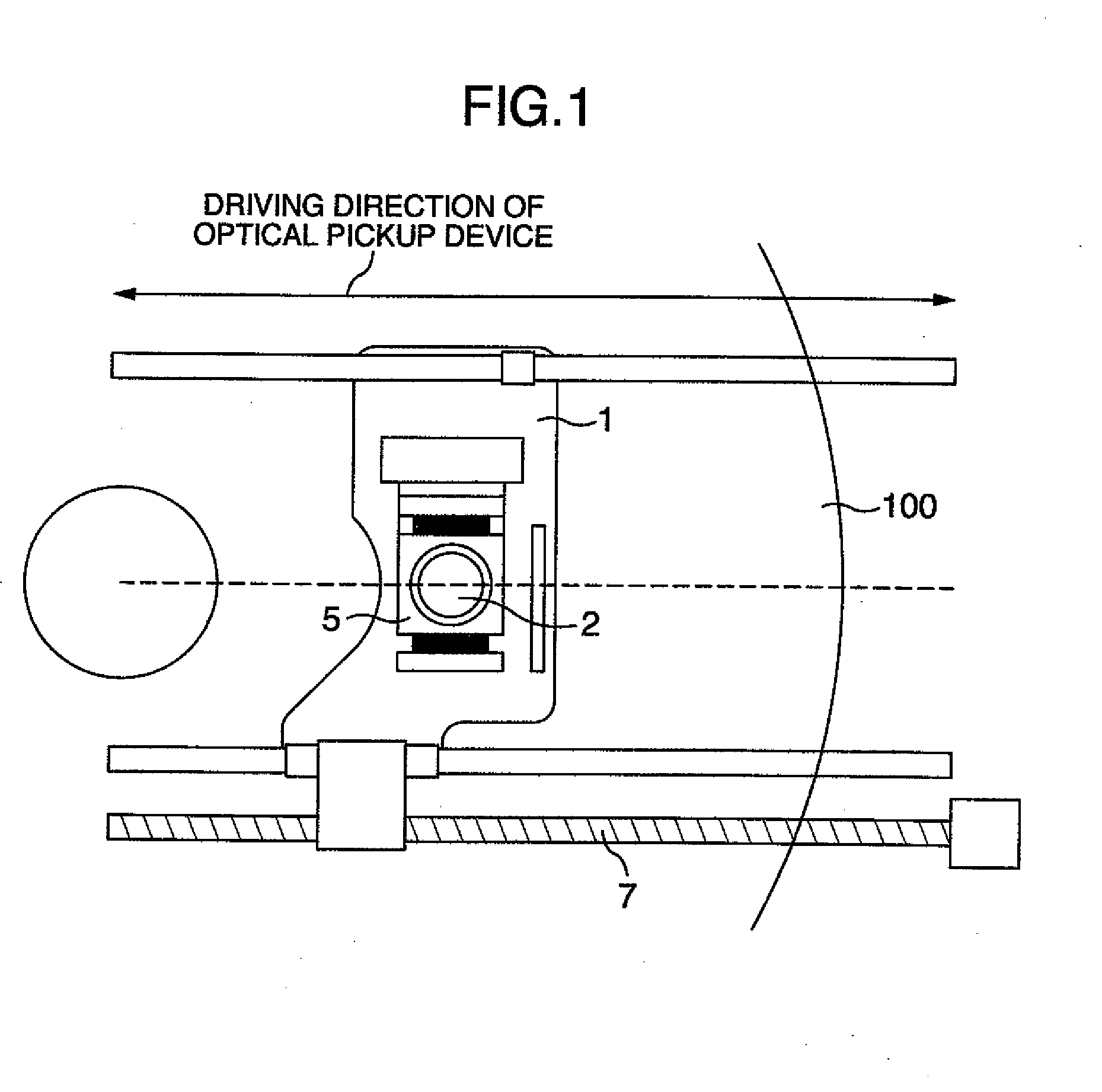
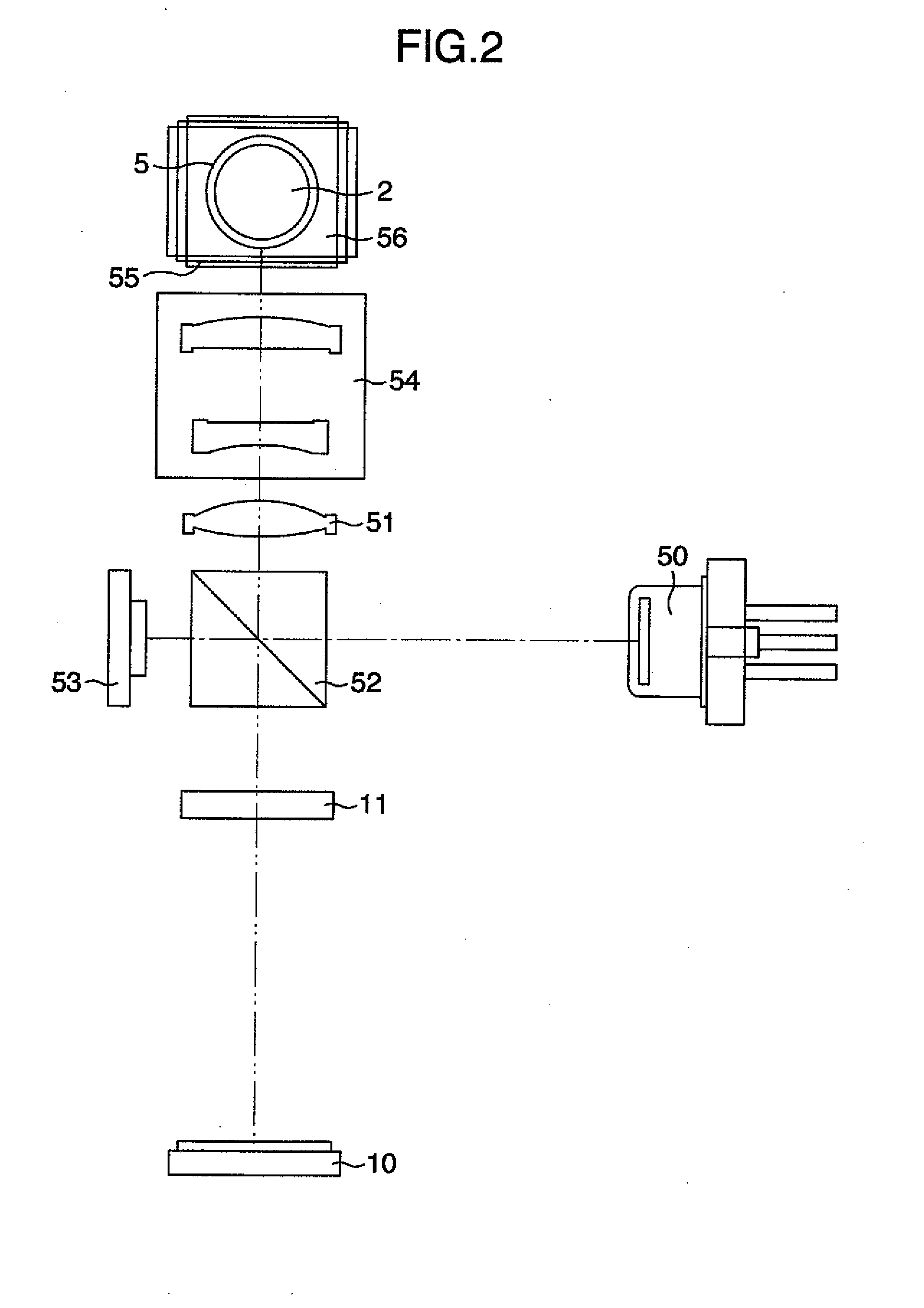
Optical pickup device and optical disc apparatus
ActiveUS20100061202A1Low utilization efficiencyOptical detectorsOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupPhotovoltaic detectors
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
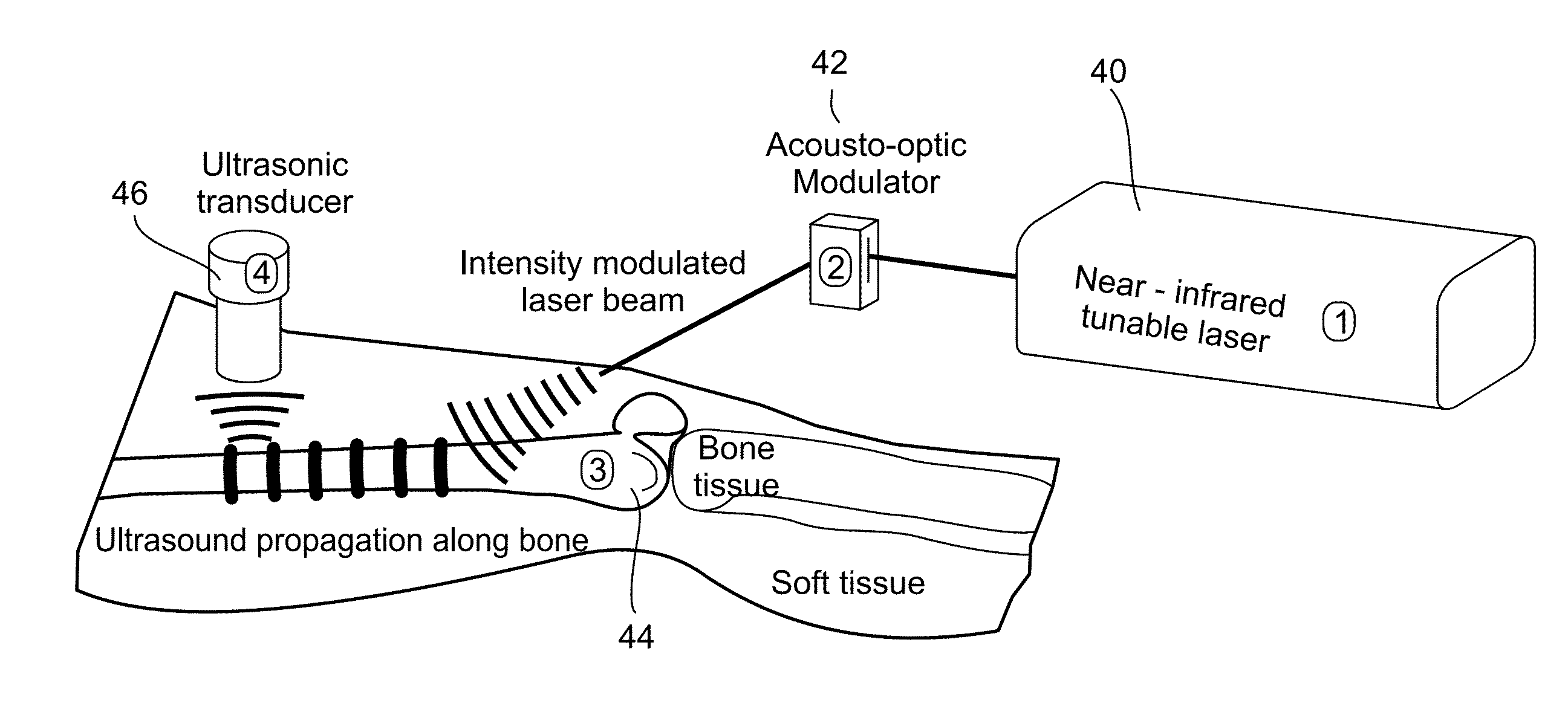
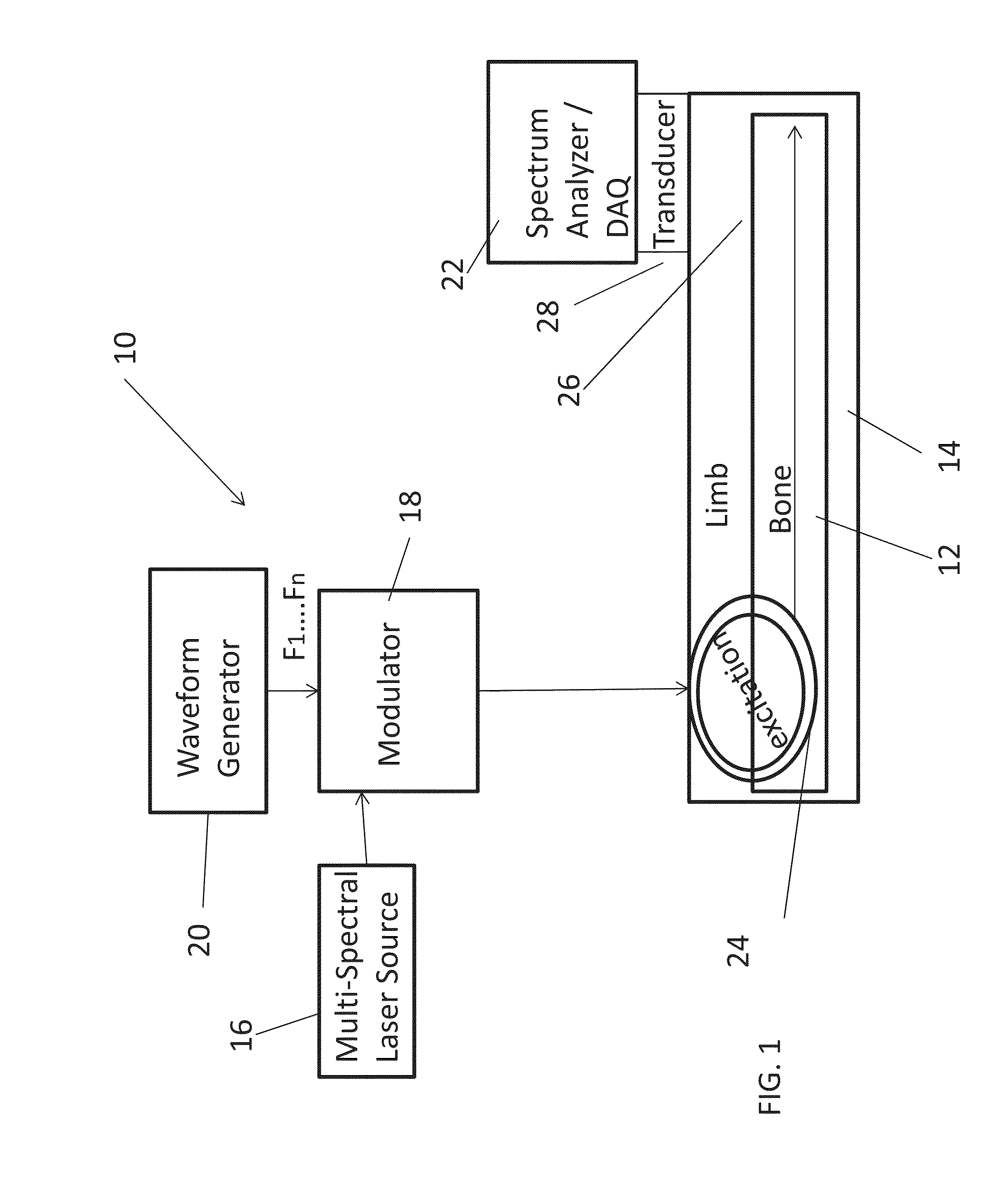
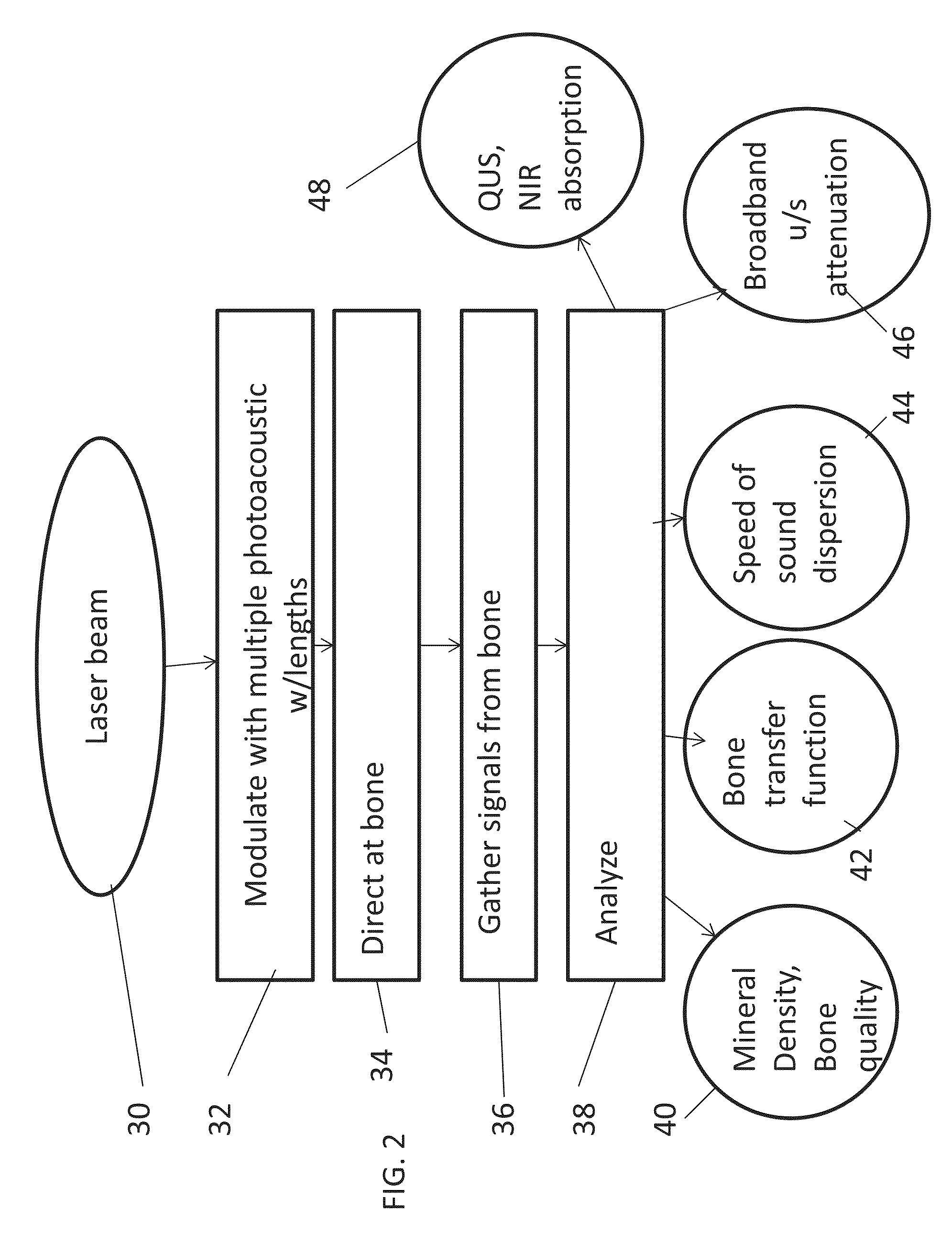
Detection, diagnosis and monitoring of osteoporosis by a photo-acoustic method
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap