Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
758results about "Solid-state devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
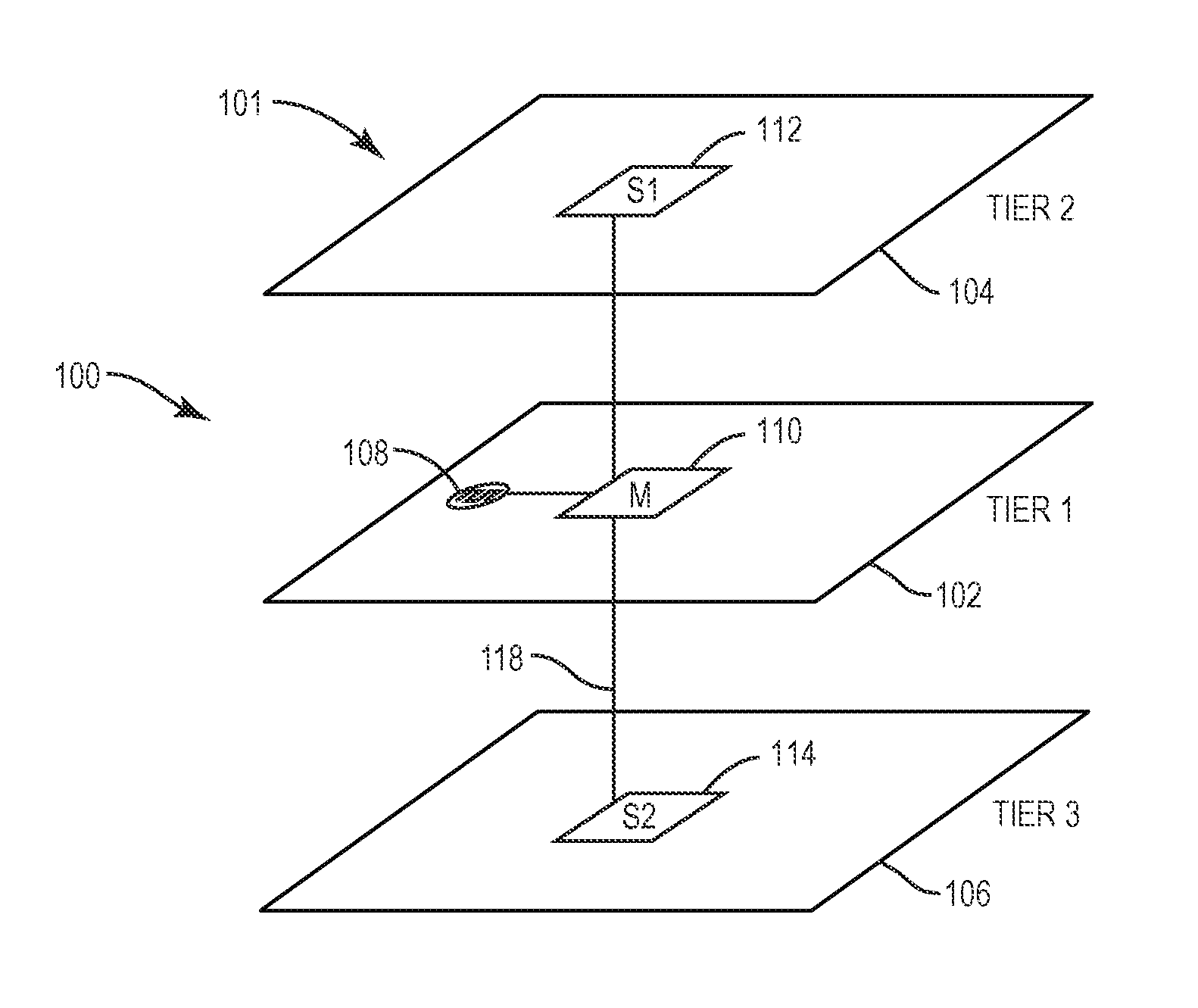
Flip-flops in a monolithic three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuit (IC) (3DIC) and related methods
ActiveUS20140253196A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Photonic crystal light emitting device
InactiveUS20050205883A1Easy to shapeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonic crystal structureResonant cavity
Owner:LUMILEDS
Lighting device having first, second and third groups of solid state light emitters, and lighting arrangement
ActiveUS20110031894A1Sharp contrastPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsLength waveLight emitter
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
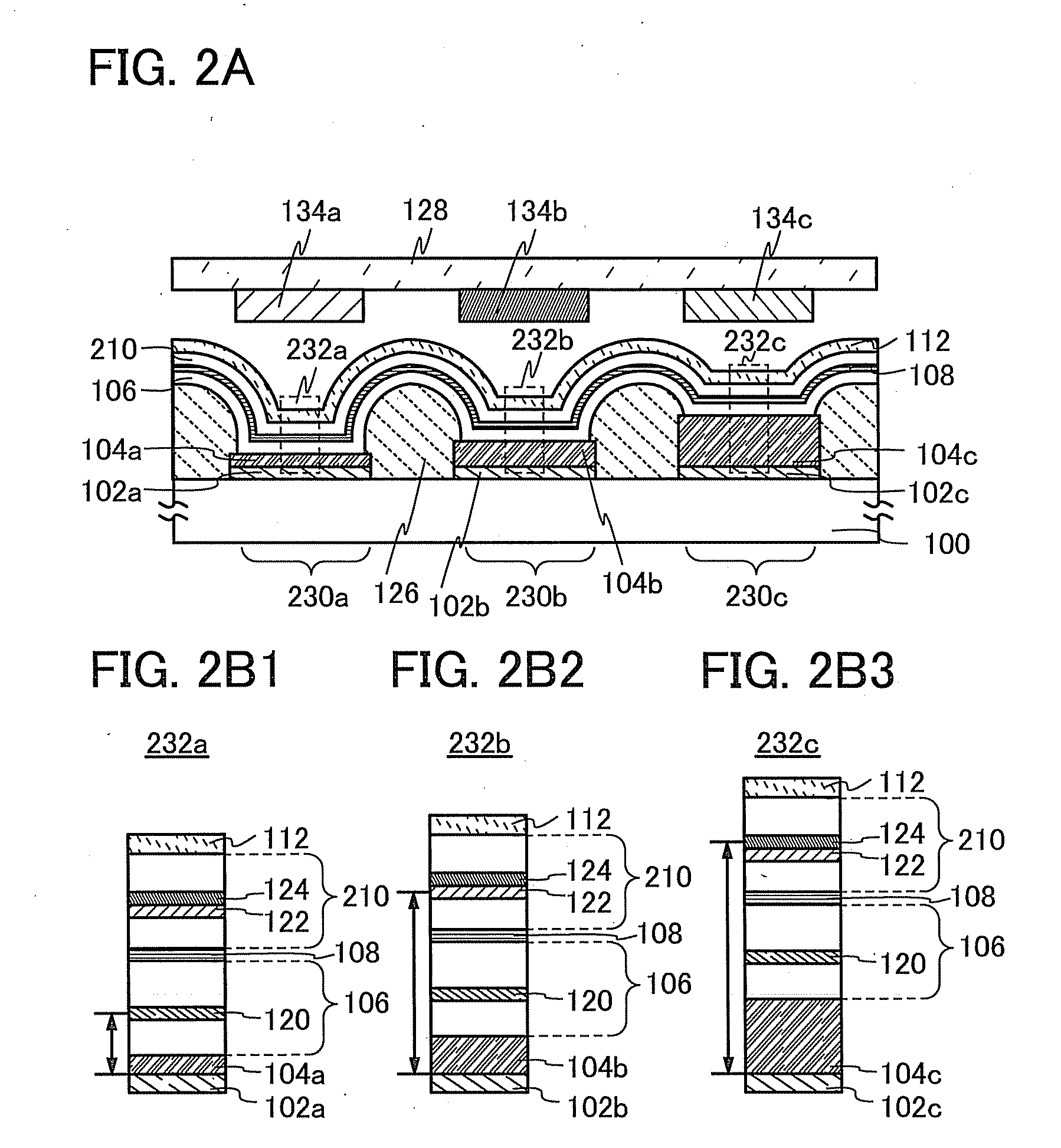
Electronics module having high density interconnect structures incorporating an improved dielectric lamination adhesive
InactiveUS6294741B1Improve electrical performanceAdequate processing propertyInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPrinted electric component incorporationComposite filmHigh density
A multi-chip electronics module is provided which utilizes benzocyclobutene as a laminate adhesive for bonding the upper dielectric films in a high density interconnect structure. The benzocyclobutene thermosetting polymer is spin coated on a polyimide film, and baked at low temperature to remove any solvent to leave a B-staged coating on the polyimide film. The composite film can be laminated to an underlying electrical structure using a vacuum laminator and heat. As the heat is applied, the BCB layer softens, flows and then cures to bond the polyimide film to the underlying electrical structure.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
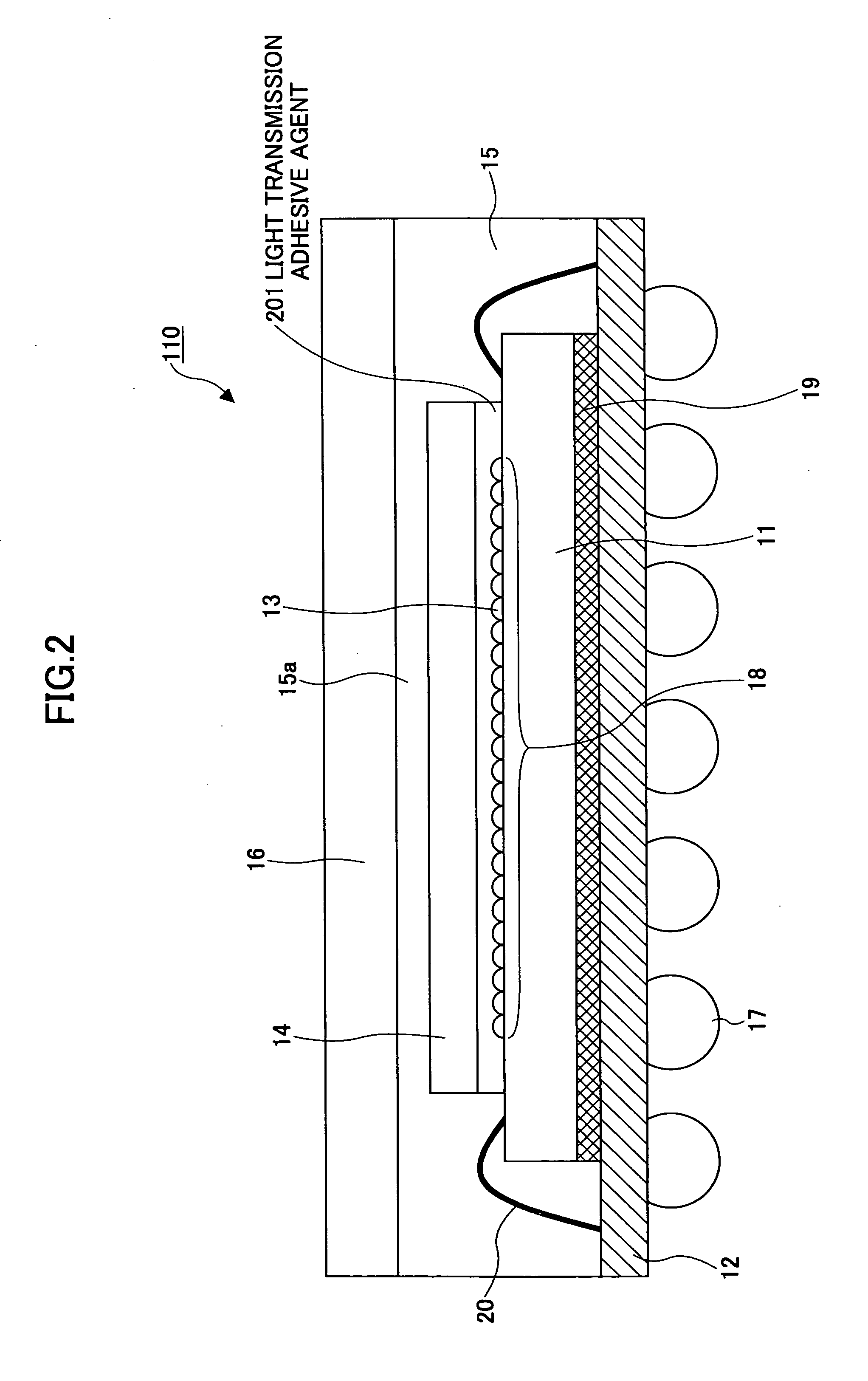
Light emitting device and sealing material
InactiveUS20050173708A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRefractive indexThermal expansion
A light emitting device has: a light emitting element; a conducting portion to supply power to the light emitting element; an element housing portion that houses the light emitting element therein; and a sealing material that seals the light emitting element housed in the element housing portion. The sealing material contains a transparent resin material and a transparent filler with a thermal expansion coefficient smaller than the transparent resin material, and the transparent filler has a refractive index nearly equal to the transparent resin material.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
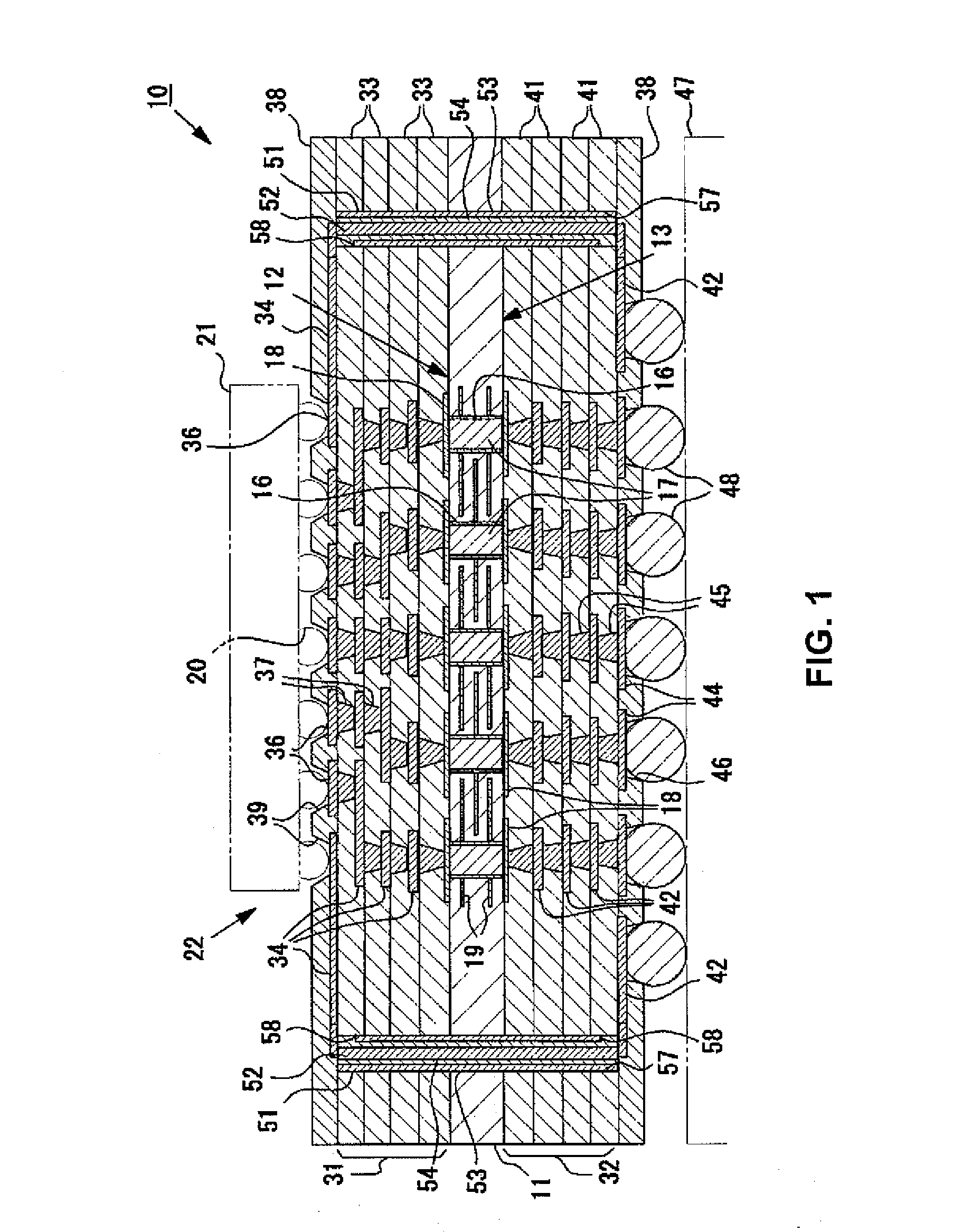
Exposed lead interposer leadframe package
ActiveUS7245007B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrically conductiveInterposer
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
CMOS image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof
ActiveUS20120033118A1Improve dynamic rangeWide dynamic range performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSProcessing element
Disclosed are a CMOS image sensor having a wide dynamic range and a sensing method thereof. Each unit pixel of the CMOS image sensor of the present invention includes multiple processing units, so that one shuttering section for the image generation of one image frame can be divided into multiple sections to separately shutter and sample the divided sections by each processing unit. Thus, the image sensor of the present invention enables many shuttering actions to be performed in the multiple processing units, respectively, and the multiple processing units to separately sample each floating diffusion voltage caused by the shuttering actions, thereby realizing a wide dynamic range.
Owner:ZEEANN
Electronic Devices With Retractable Displays
ActiveUS20170060183A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
An electronic device may have a pair of elongated housings. A flexible display may be placed in a first position in which the display is retracted within one of the housings and a second position in which the flexible display is deployed and extends between the housings in a planar shape for viewing by a user. Support structures such as rigid slats that run parallel to the housings and bistable slats that run perpendicular to the rigid slats may be used to support the flexible display. Speakers, microphones, cameras, and other components can be mounted in the housings. The housings may be held together using magnets and may contain electrical components such as integrated circuits, batteries, and other devices. The components may be mounted on printed circuit boards that rotate within a rotating roller around which the display is wrapped when retracted.
Owner:APPLE INC
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing the same, and camera
InactiveUS20090147101A1Reduce probabilityReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPhotoelectric conversionTransistor
A solid-state imaging device is provided. The solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of arrayed pixels, an optical inner filter layer, and an inner-layer lens. Each of the plurality of arrayed pixels includes a photoelectric conversion portion and a pixel transistor. The optical inner filter layer is configured to block infrared light and faces a light-receiving surface of the photoelectric conversion portion of a desired pixel among the arrayed pixels. The inner-layer lens is formed below the optical inner filter layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
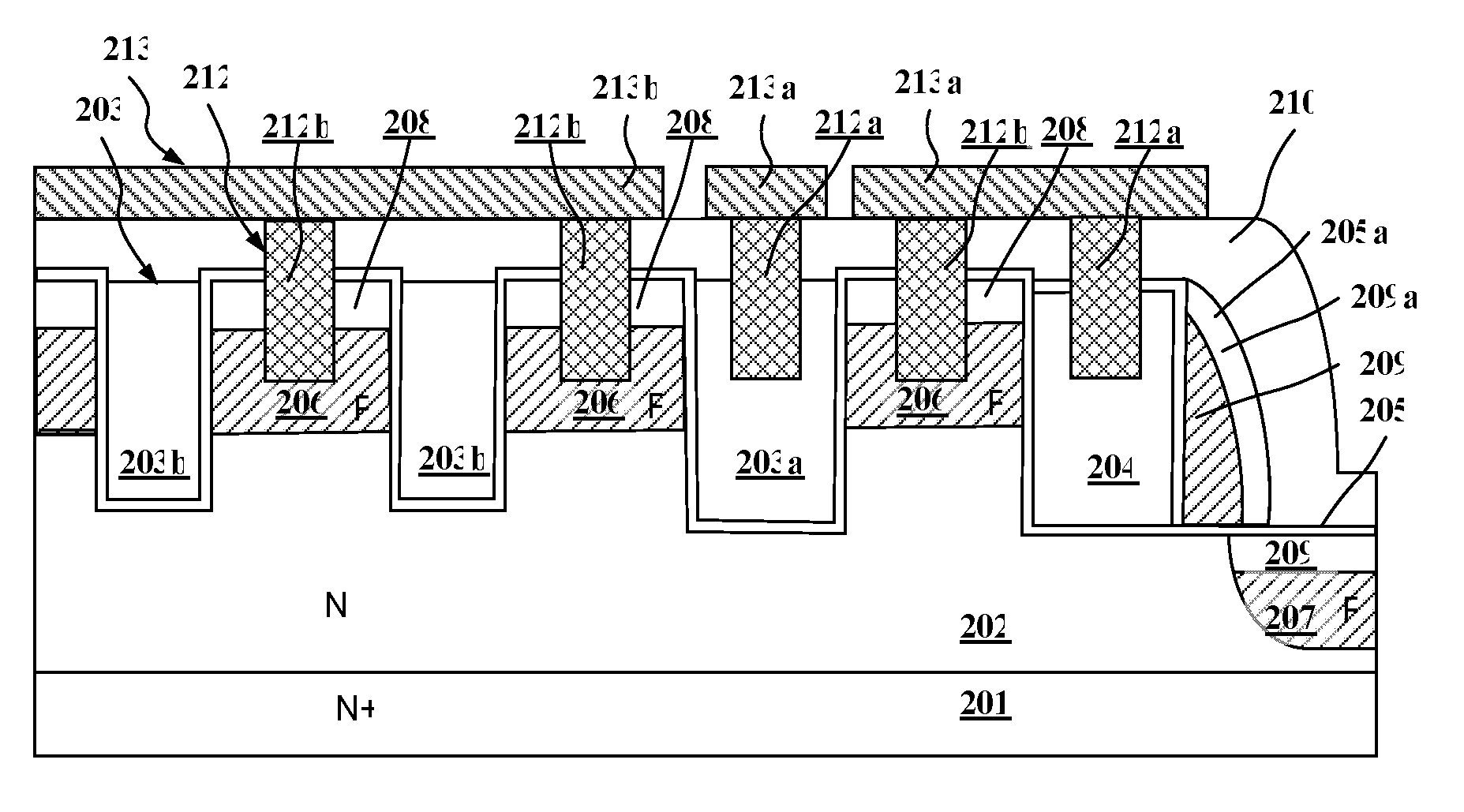
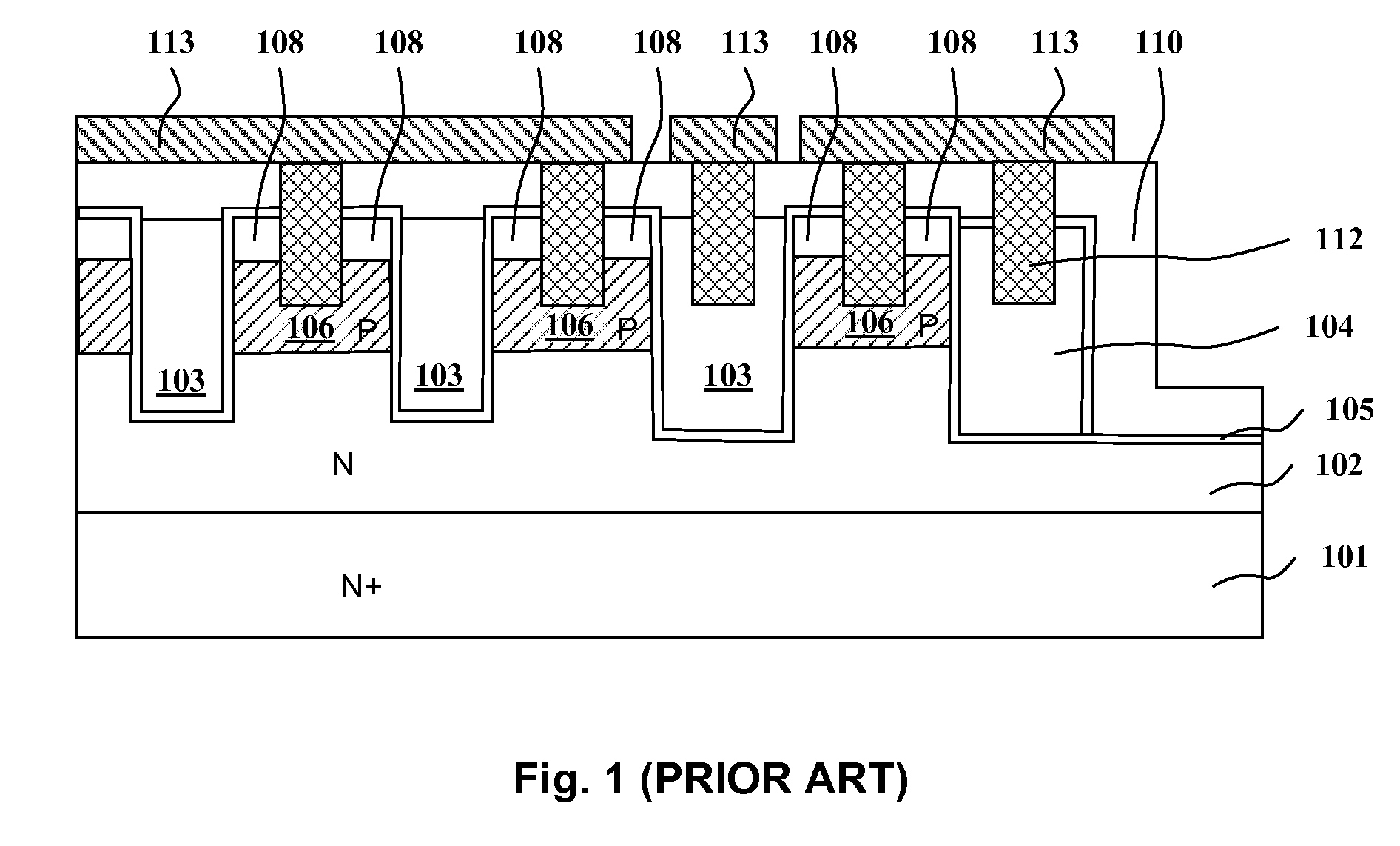
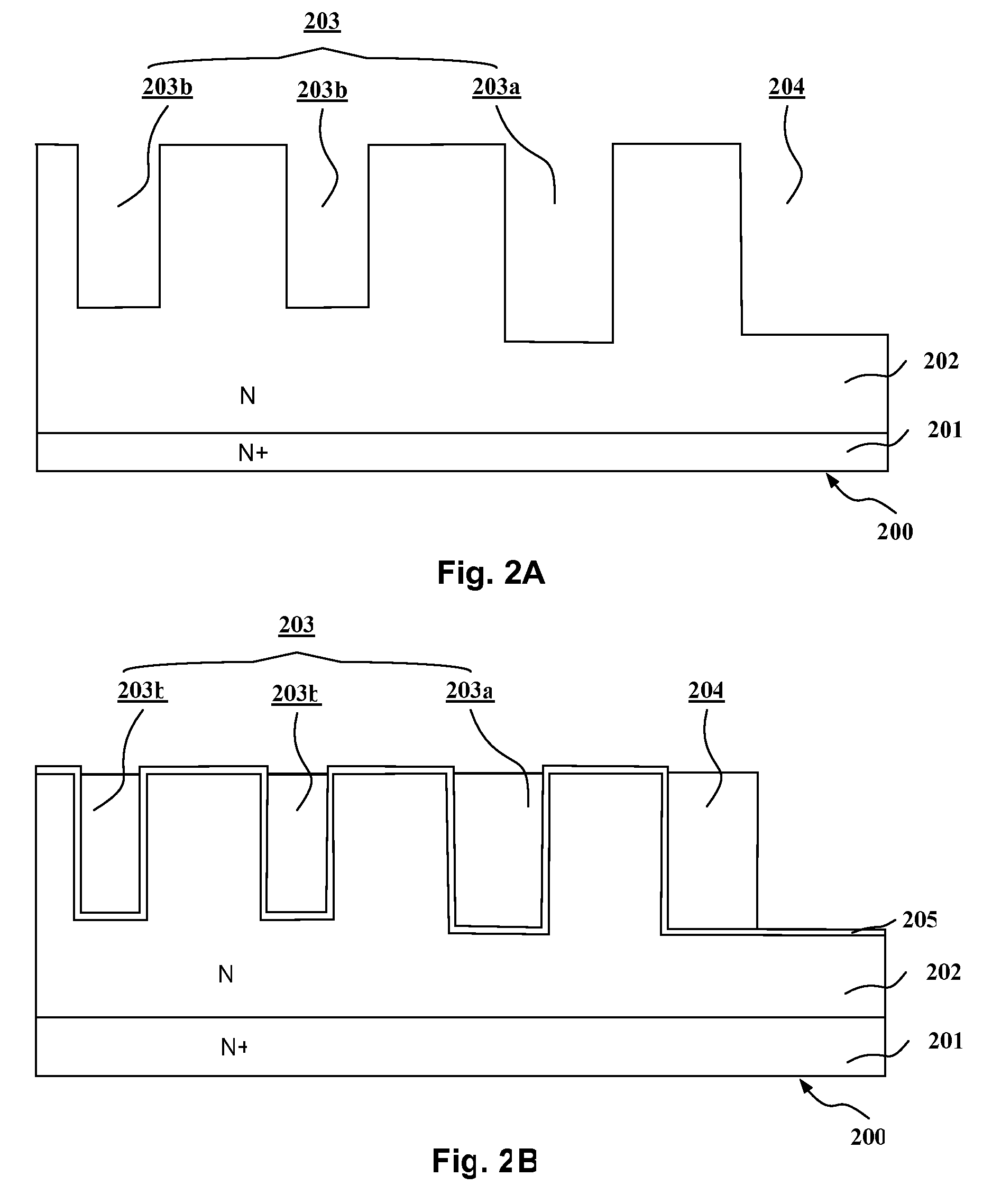
Trench MOSFET with Trench Termination and manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20090057756A1Lower on-resistanceImprove device ruggednessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorBody region
A trench MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) with a trench termination, including a substrate including a drain region which is strongly doped and a doping epi layer region, which is weekly doped the same type as the drain region, on the drain region; a plurality of source and body regions formed in the epi layer; a metal layer including a plurality of metal layer regions which are connected to respective source and body, and gate regions forming metal connections of the MOSFET; a plurality of metal contact plugs connected to respective metal layer regions; a plurality of gate trenches filled with polysilicon to form a plurality of trenched gates on top of epi layer; an insulating layer deposited on the epi layer formed underneath the metal layer with a plurality of metal contact holes therein for contacting respective source and body regions; a margin terminating gate trench which is around the gate trenches; and a margin terminating active region which is formed underneath the margin terminating gate trench.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7091070B2Improve substrate adhesionReduce adhesiveness of substrateTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
To provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device including a transfer step that is capable of controlling the adhesiveness of a substrate and an element-formed layer in the case of separating the element-formed layer including a semiconductor element or an integrated circuit formed over the substrate from the substrate and bonding it to another substrate. An adhesive agent made of a good adhesiveness material is formed between the semiconductor element or the integrated circuit comprising plural semiconductor elements formed over the substrate (a first substrate) and the substrate, and thus it is possible to prevent a semiconductor element from peeling off a substrate in manufacturing the semiconductor element, and further, to make it easier to separate the semiconductor element from the substrate by removing the adhesive agent after forming the semiconductor element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
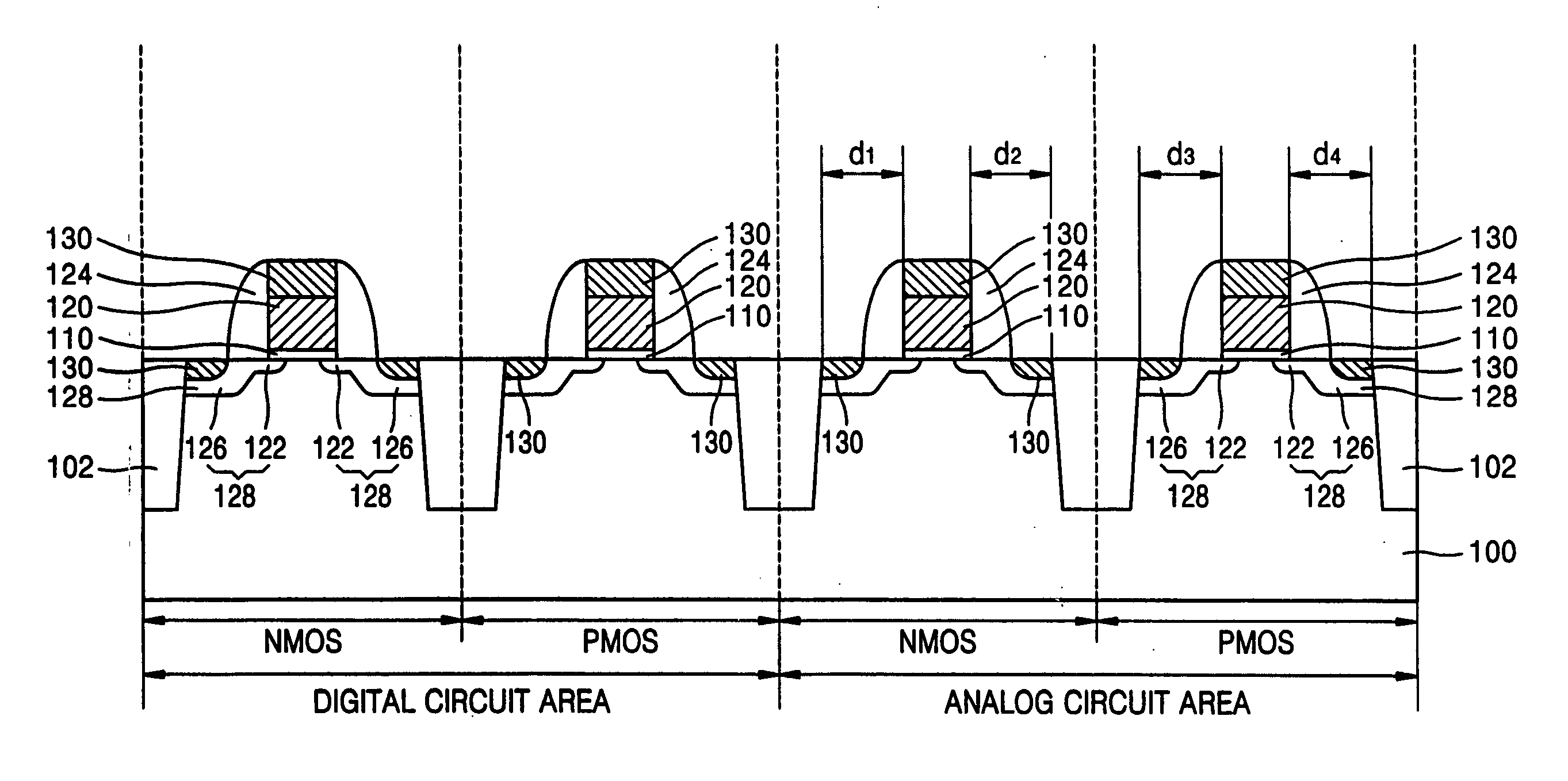
Low noise and high performance LSI device, layout and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20050218455A1Improve device performanceReduce the impactTransistorSolid-state devicesLow noiseLow speed
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050145987A1Reduce distractionsDesired characteristicTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceDevice material
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Method of manufacturing electro-optical device, electro-optical device, transferred chip, transfer origin substrate
InactiveUS7169652B2Low costProduct yield is lowTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
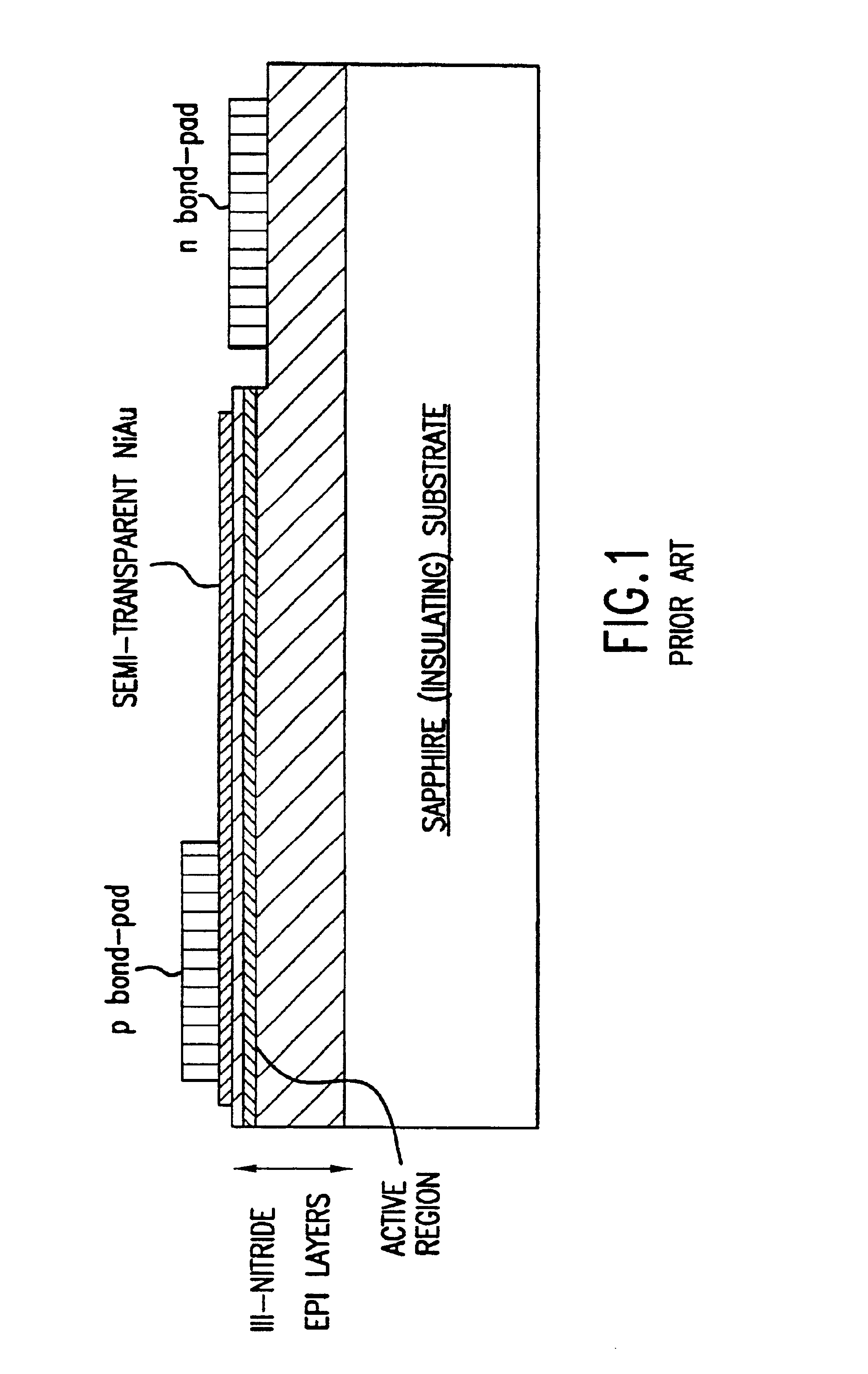
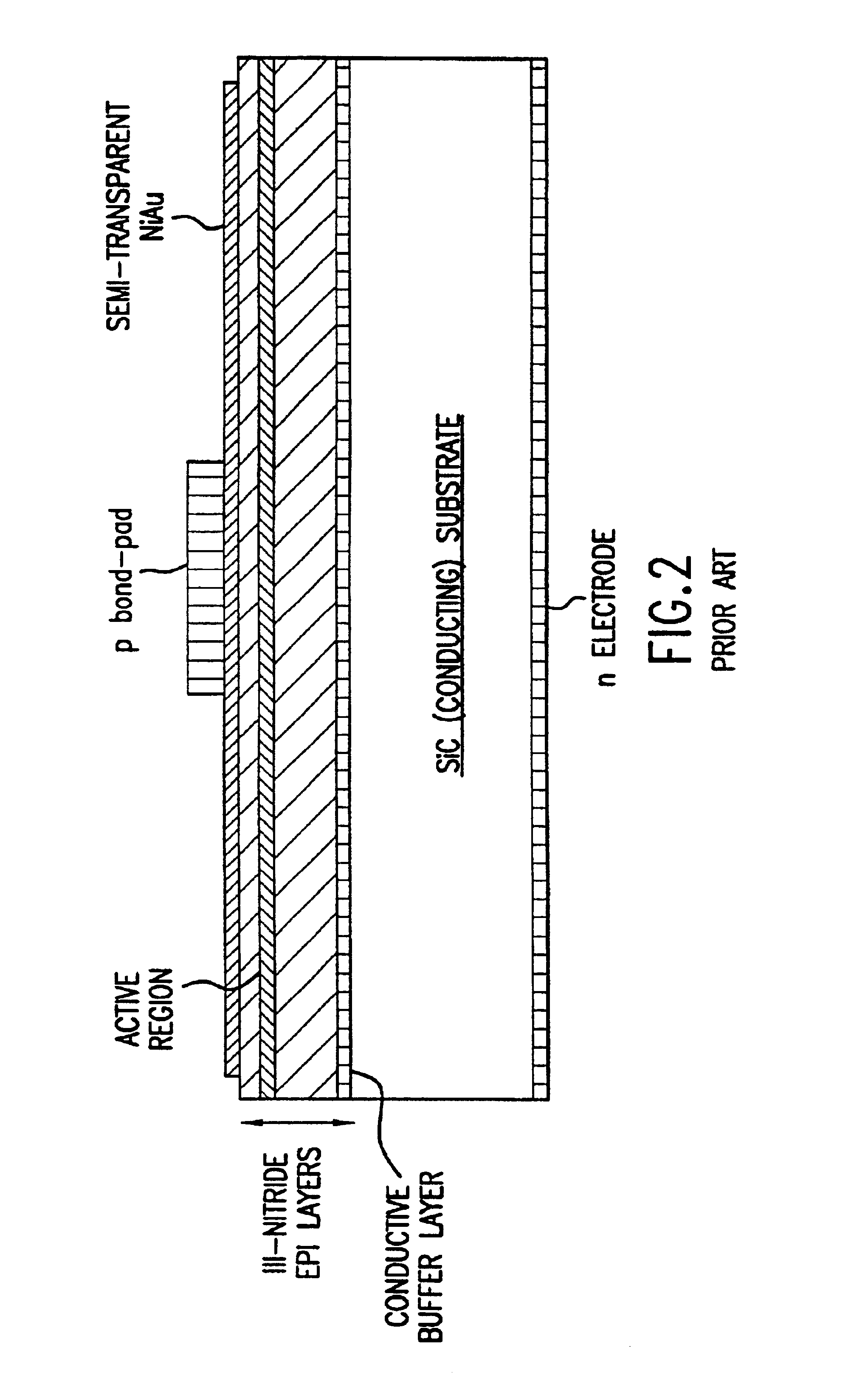
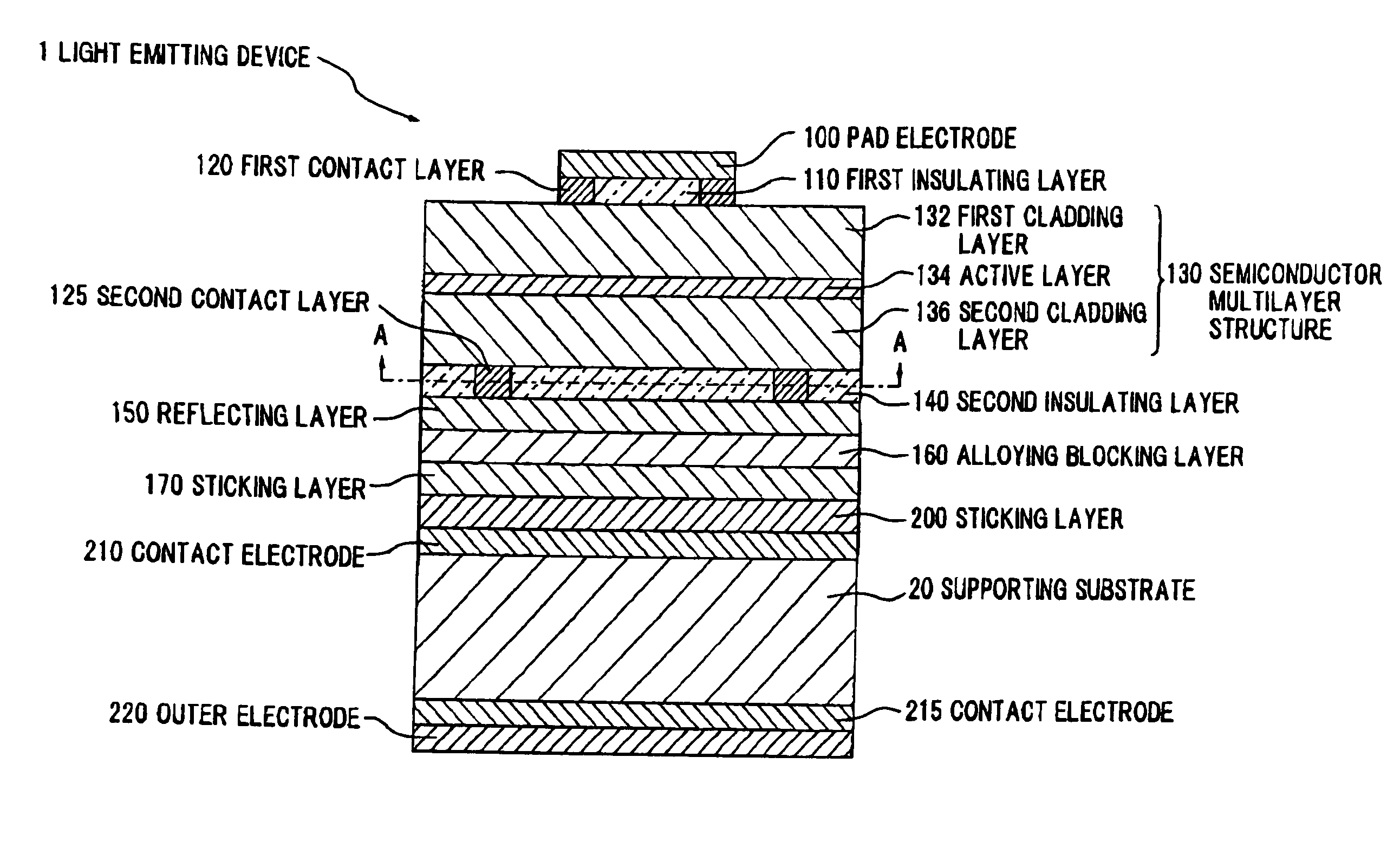
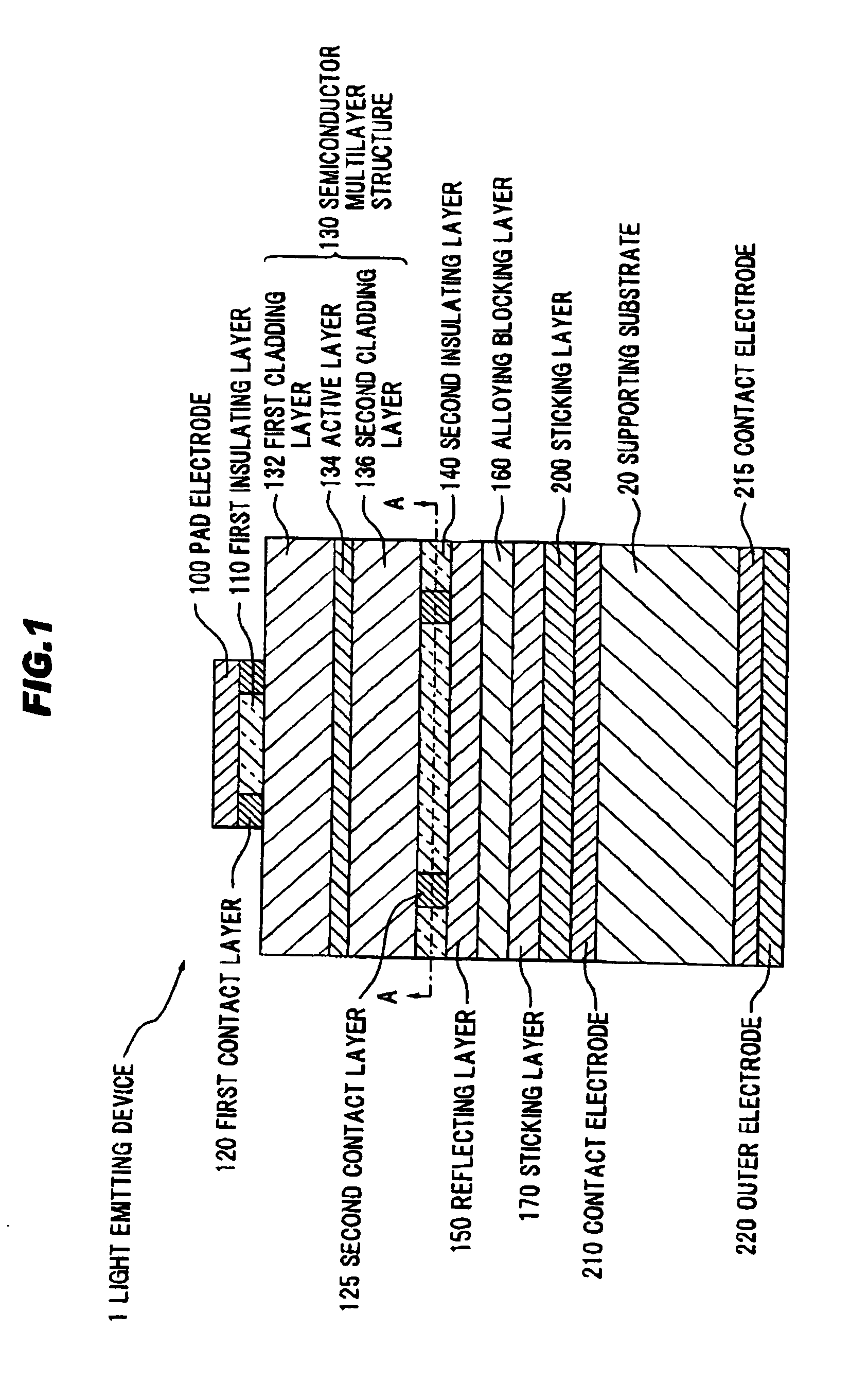
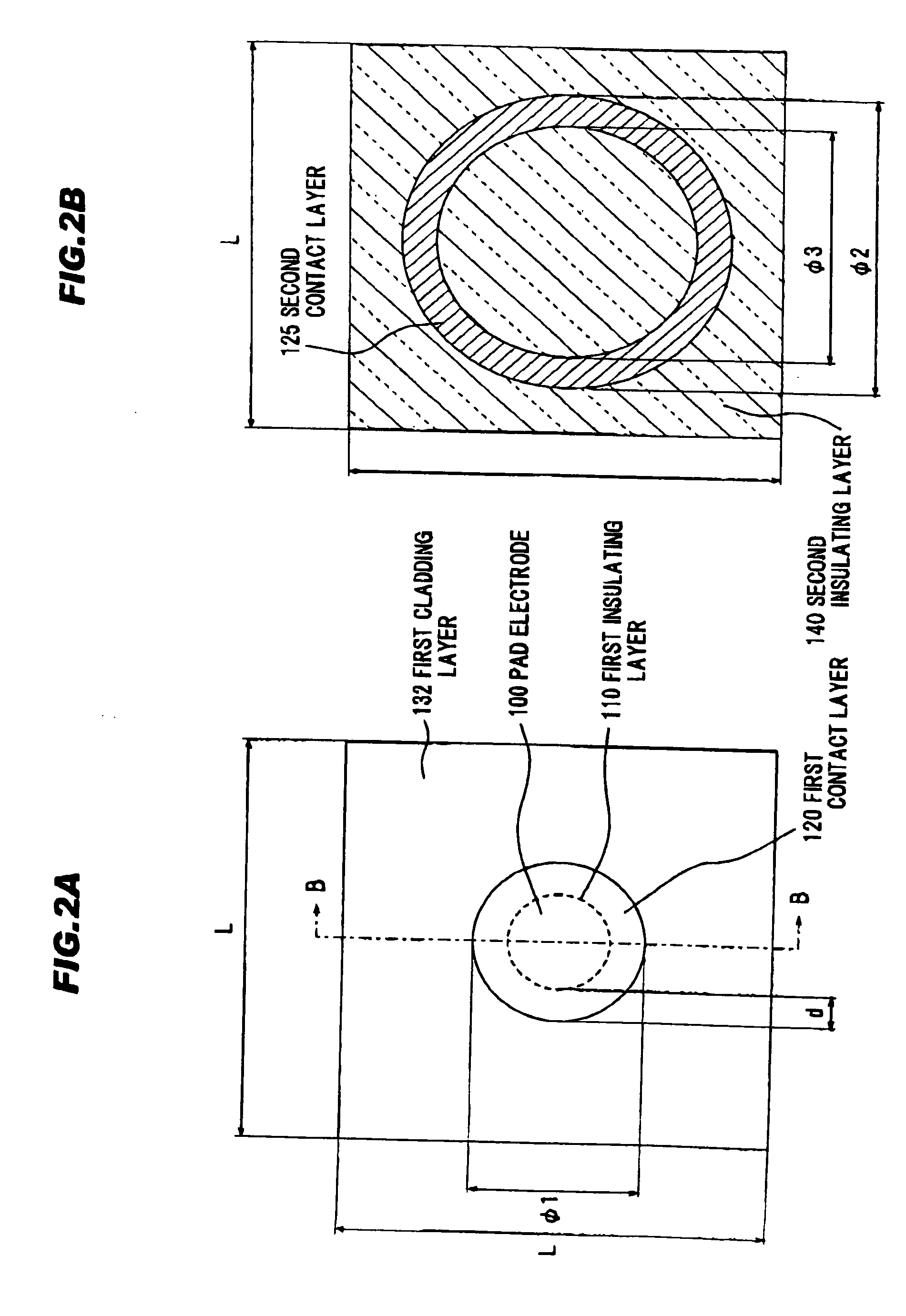
III-nitride light-emitting device with increased light generating capability
InactiveUS6844571B2Low series resistanceExcellent current spreadingStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPeak valueElectricity
The present invention is an inverted III-nitride light-emitting device (LED) with enhanced total light generating capability. A large area device has an n-electrode that interposes the p-electrode metallization to provide low series resistance. The p-electrode metallization is opaque, highly reflective, and provides excellent current spreading. The p-electrode at the peak emission wavelength of the LED active region absorbs less than 25% of incident light per pass. A submount may be used to provide electrical and thermal connection between the LED die and the package. The submount material may be Si to provide electronic functionality such as voltage-compliance limiting operation. The entire device, including the LED-submount interface, is designed for low thermal resistance to allow for high current density operation. Finally, the device may include a high-refractive-index (n>1.8) superstrate.
Owner:LUMILEDS +1
Wireless transmission system and wireless transmission method
ActiveUS20110038282A1Limited rangeFixed station waveguides transmission systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWireless transmissionEngineering
Disclosed herein is a wireless transmission system, including: a plurality of systems of millimeter wave signal transmission lines capable of individually transmitting information in a millimeter waveband independently of each other; a sending section disposed on one end side of each of the plural systems of millimeter wave signal transmission lines; and a reception section disposed on the other end side of each of the plural systems of millimeter wave signal transmission lines. The sending section is adapted to convert a signal of an object of transmission into a millimeter wave signal and supply the millimeter wave signal to the millimeter signal transmission line. The reception section is adapted to receive the millimeter wave signal transmitted thereto through the millimeter wave signal transmission line and convert the received millimeter wave signal into the signal of the object of transmission.
Owner:SONY CORP
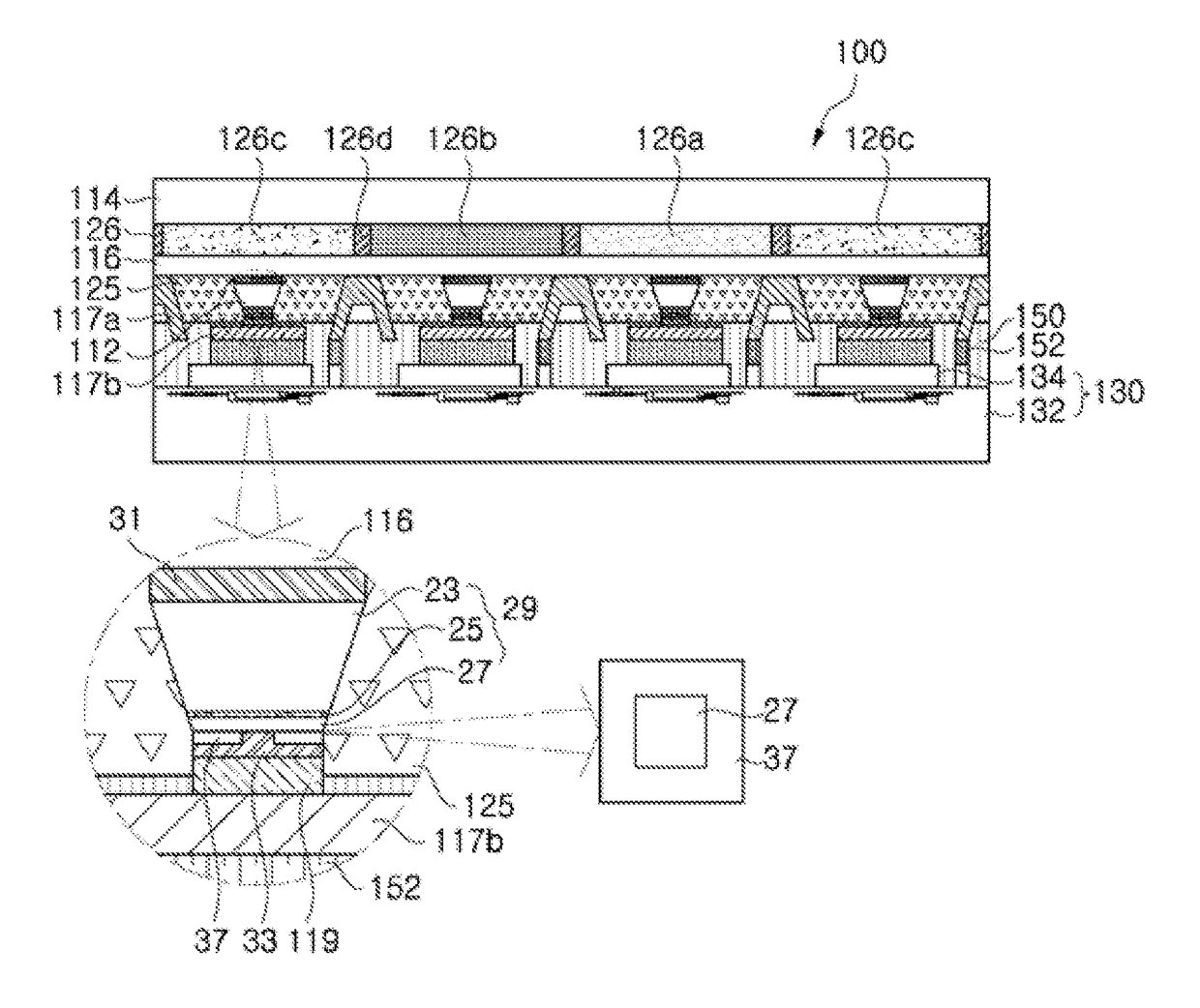
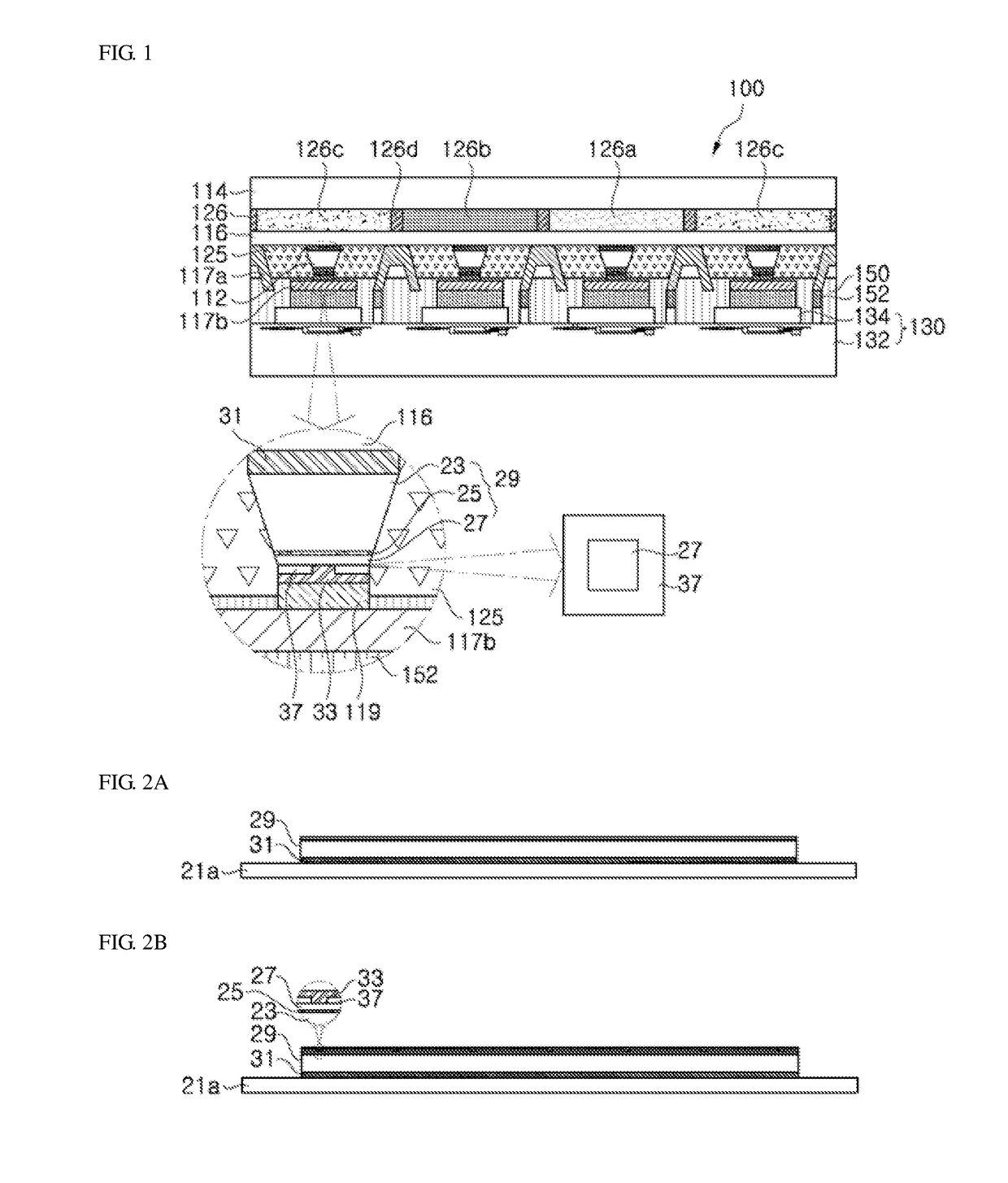
Display apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20170358624A1High resolutionReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeDiode
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Fabrication of graphene nanoelectronic devices on SOI structures
ActiveUS20110114918A1Eliminates thermal budget limitationGood substrateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureGraphene
A semiconductor-on-insulator structure and a method of forming the silicon-on-insulator structure including an integrated graphene layer are disclosed. In an embodiment, the method comprises processing a silicon material to form a buried oxide layer within the silicon material, a silicon substrate below the buried oxide, and a silicon-on-insulator layer on the buried oxide. A graphene layer is transferred onto the silicon-on-insulator layer. Source and drain regions are formed in the silicon-on-insulator layer, and a gate is formed above the graphene. In one embodiment, the processing includes growing a respective oxide layer on each of first and second silicon sections, and joining these silicon sections together via the oxide layers to form the silicon material. The processing, in an embodiment, further includes removing a portion of the first silicon section, leaving a residual silicon layer on the bonded oxide, and the graphene layer is positioned on this residual silicon layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
White Light Illumination System with Narrow Band Green Phosphor and Multiple-Wavelength Excitation
Owner:INTEMATIX
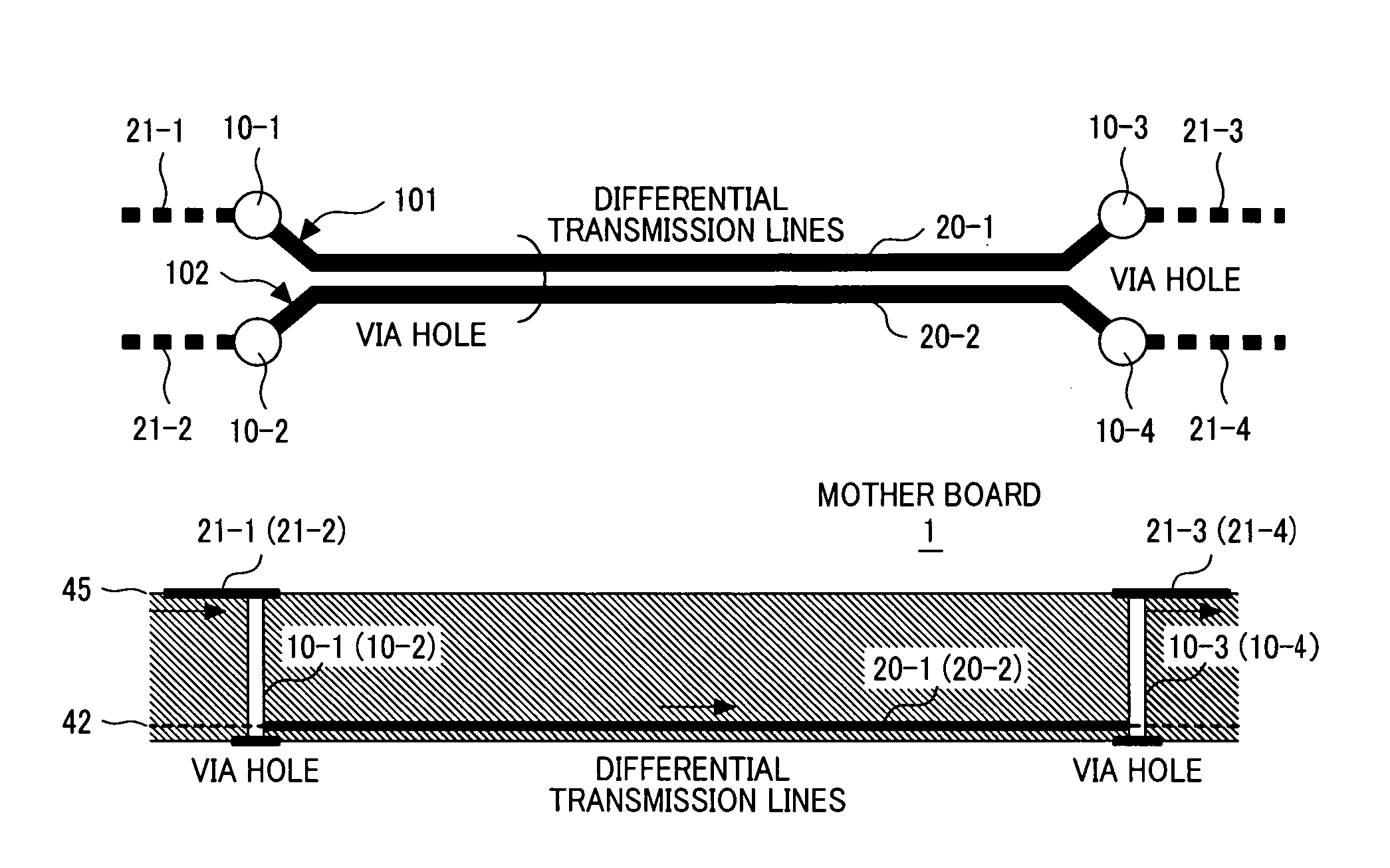
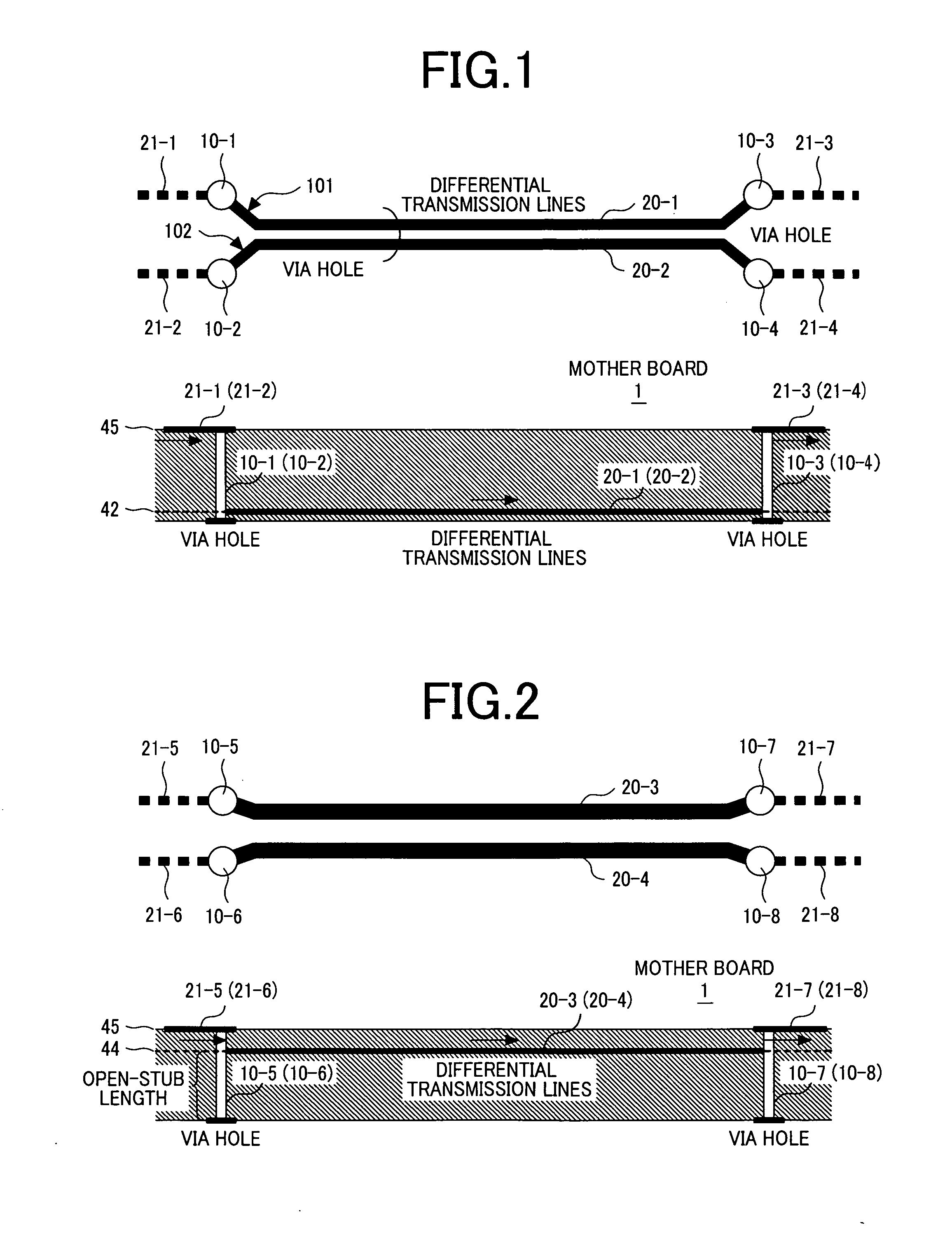
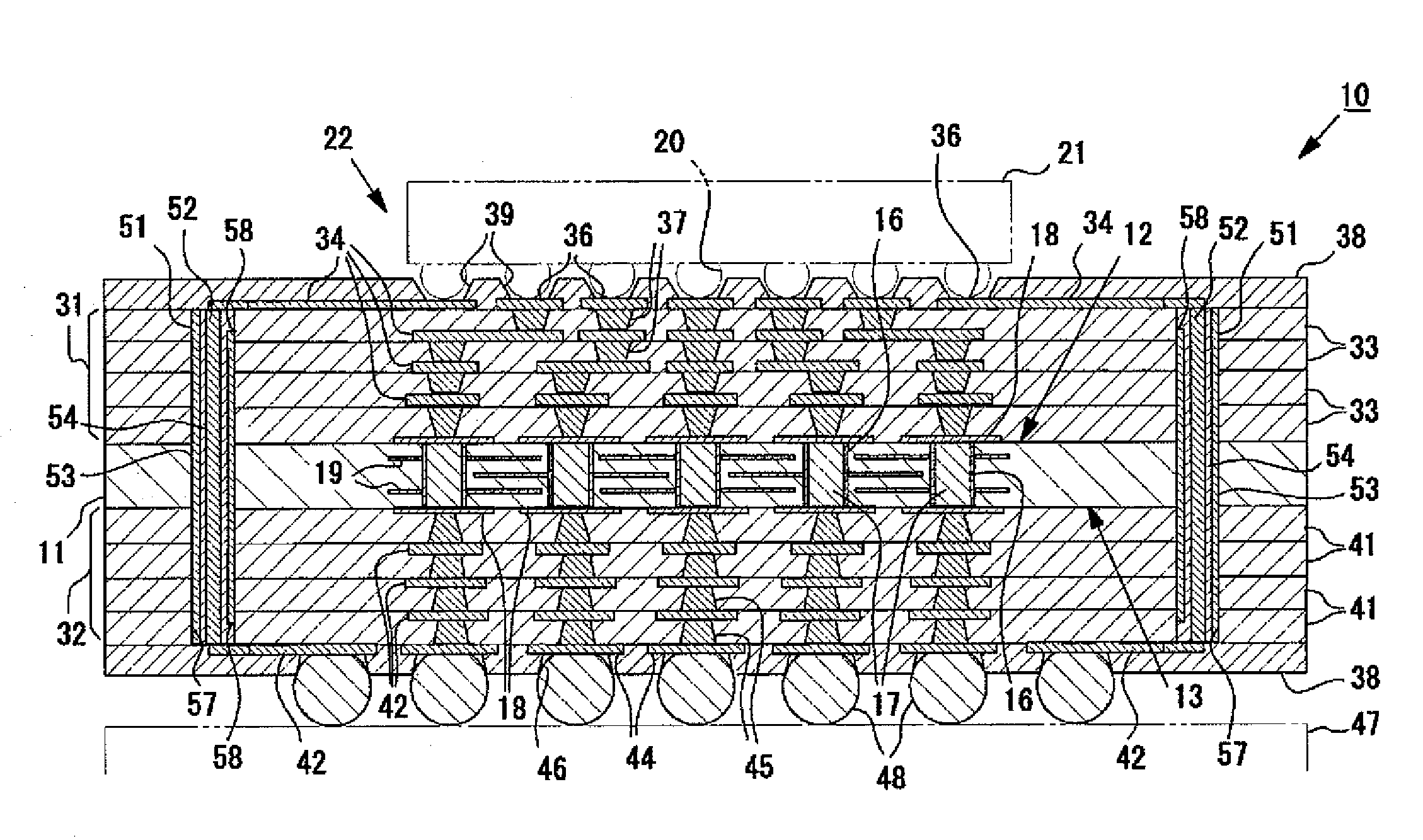
Multilayer printed circuit board for high-speed differential signal, communication apparatus, and data storage apparatus
InactiveUS20070130555A1Decreasing reflection of backwardReduce jitterRotary current collectorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCouplingDifferential transmission
Owner:HITACHI LTD
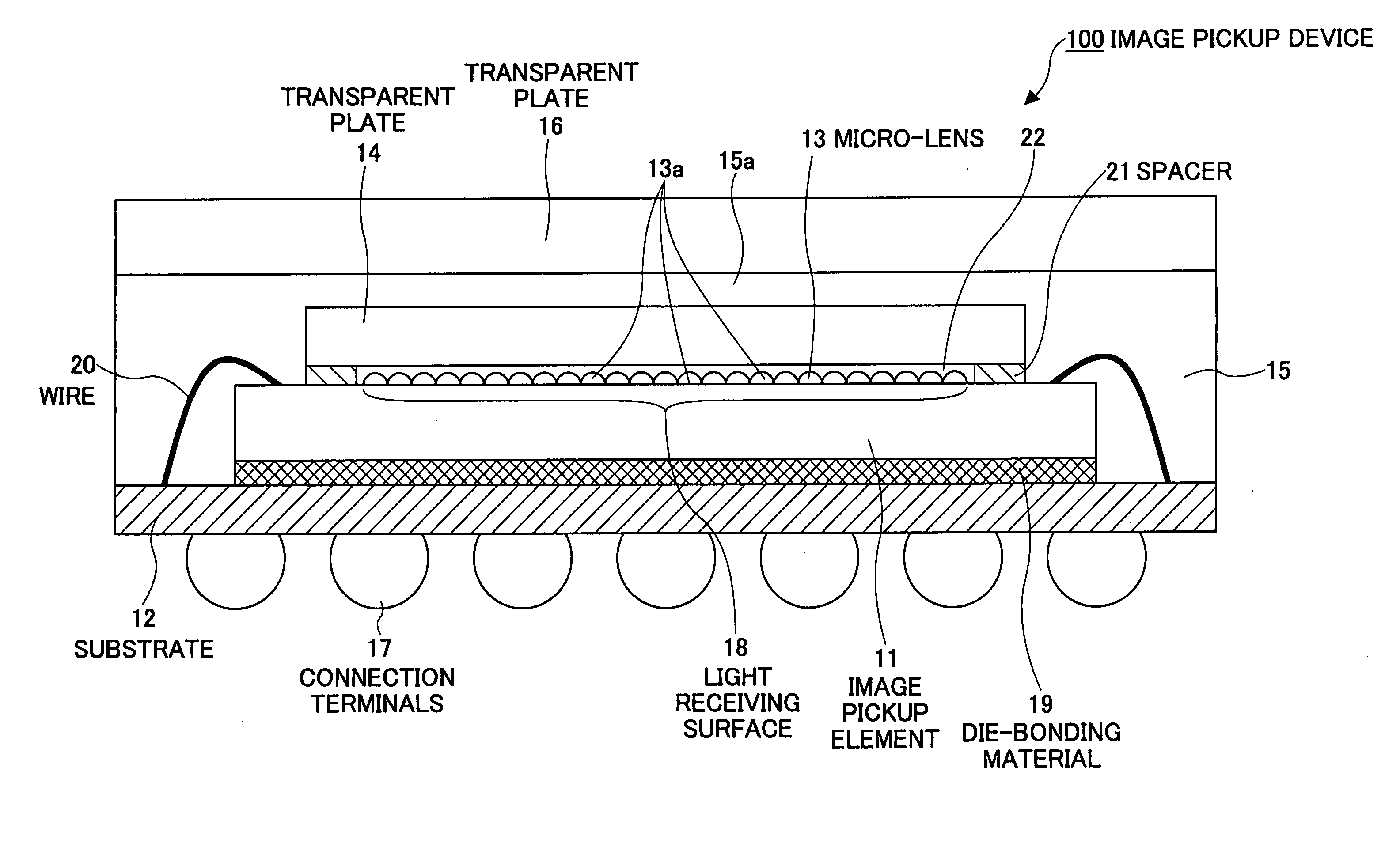
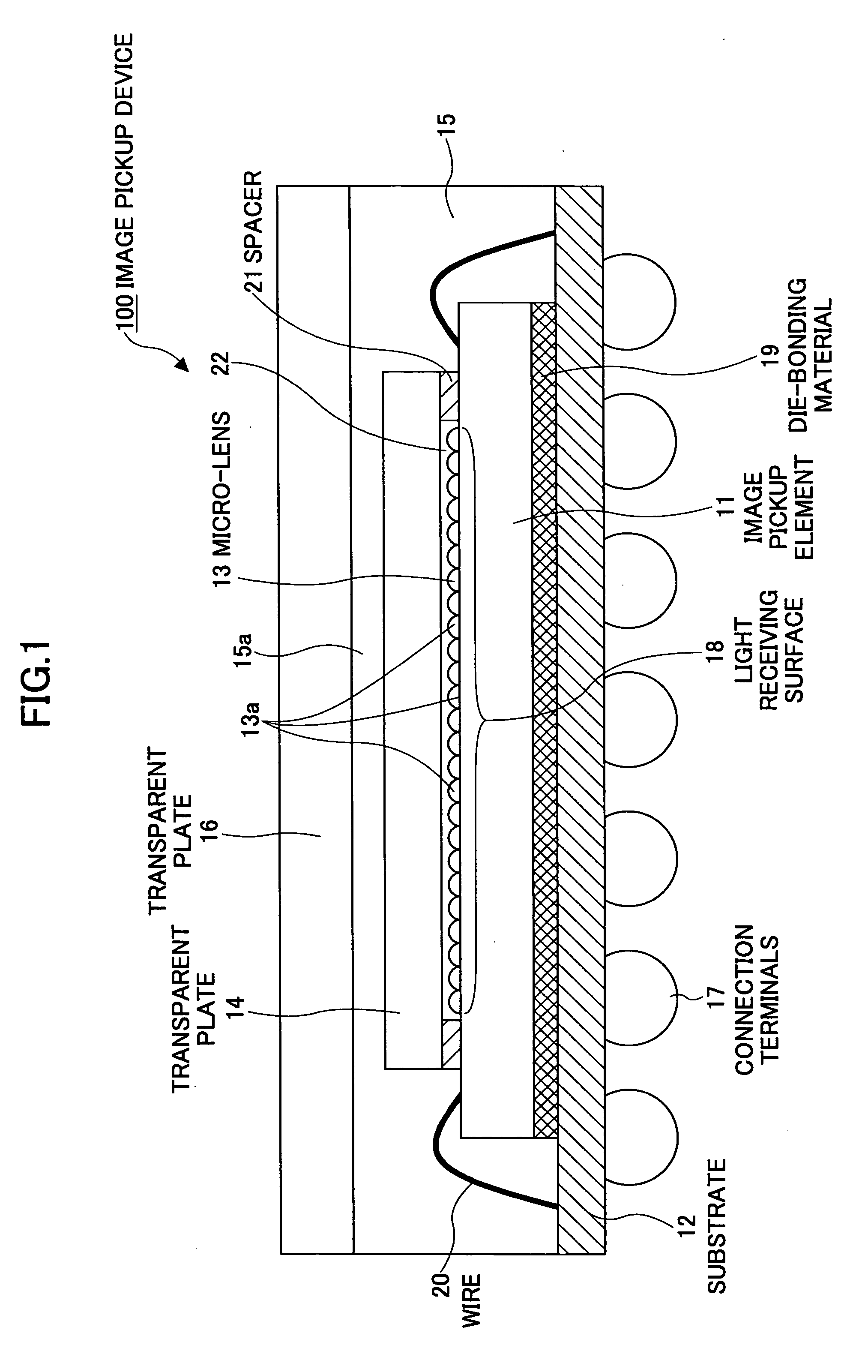
Image pickup device and production method thereof
InactiveUS20050275741A1Good lighting performanceSmall overall deformationTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal expansionComputer science
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Light emitting device
ActiveUS20090072257A1Improve light extraction efficiencyUniform heat generationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceBlocking layer
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Polymer resin composition, related method for forming a pattern, and related method for fabricating a capacitor
InactiveUS20070249117A1Reduce in quantityReduce processing timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-link(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same, circuit board and electronic instrument
InactiveUS6841849B2Not easily oxidizedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A depression is formed from a first surface of a semiconductor substrate on which is formed an integrated circuit. An insulating layer is provided on the inner surface of the depression. A first conductive portion is provided on the inside of the insulating layer. A second conductive portion is formed on the inside of the insulating layer and over the first conductive portion, of a different material from the first conductive portion. The first conductive portion is exposed from a second surface of the semiconductor substrate opposite to the first surface.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
Method of fabricating a semiconductor device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-Emitting Device and Display Device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
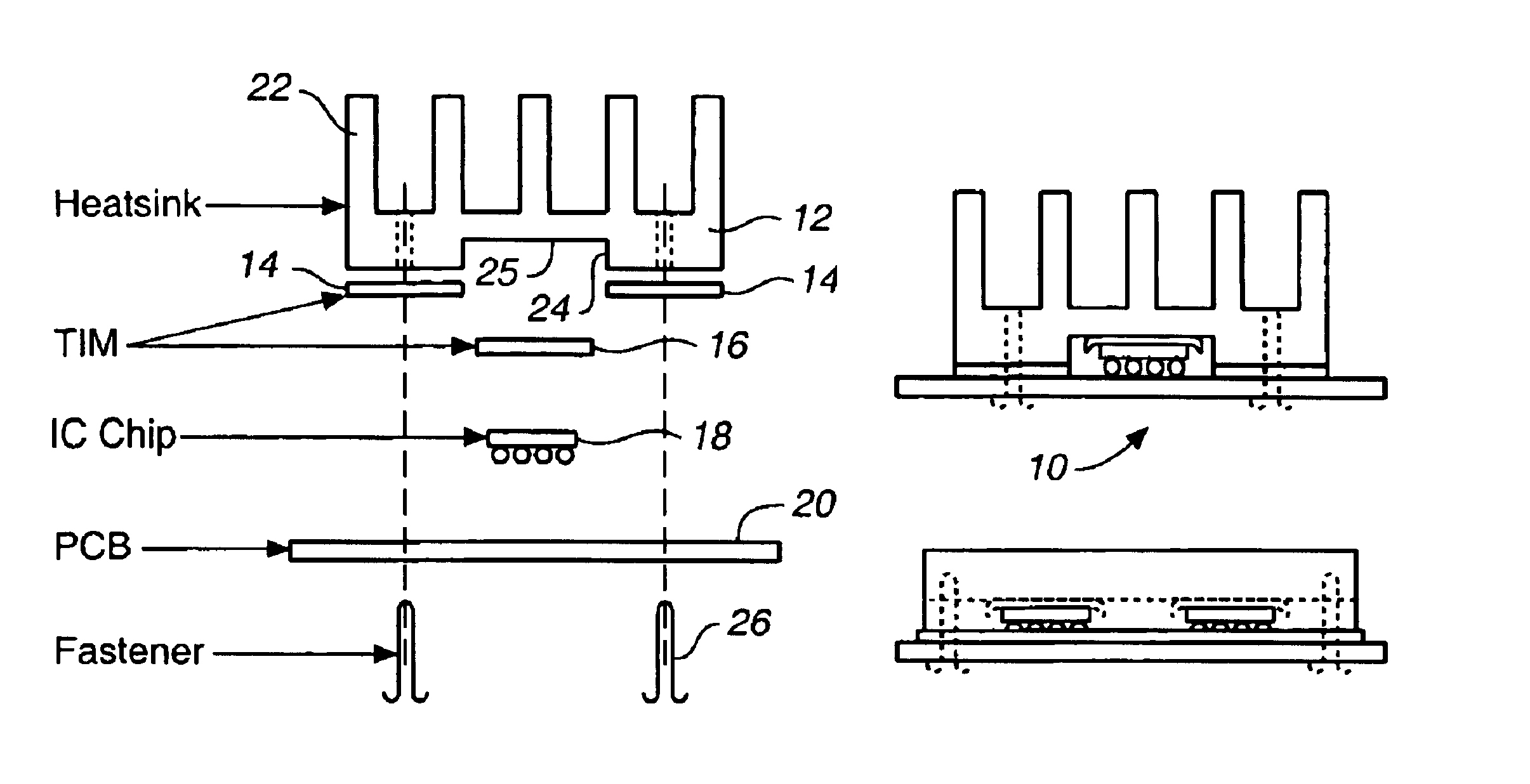
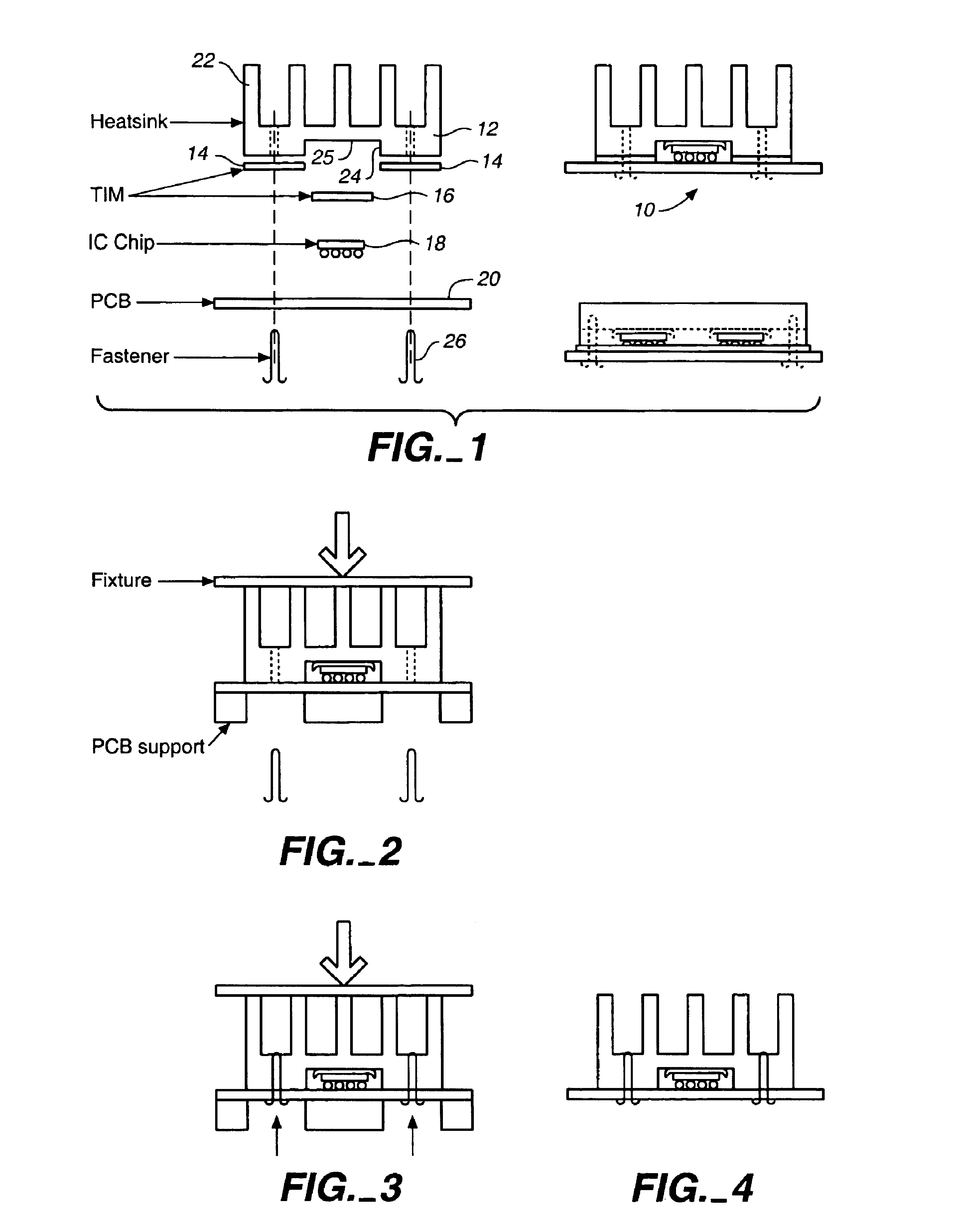
Heatsinking and packaging of integrated circuit chips
InactiveUS6853068B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitPrinted circuit board
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
Multilayer wiring board and power supply structure to be embedded in multilayer wiring board
InactiveUS20080149384A1Lower resistanceHigh currentPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringCopper
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
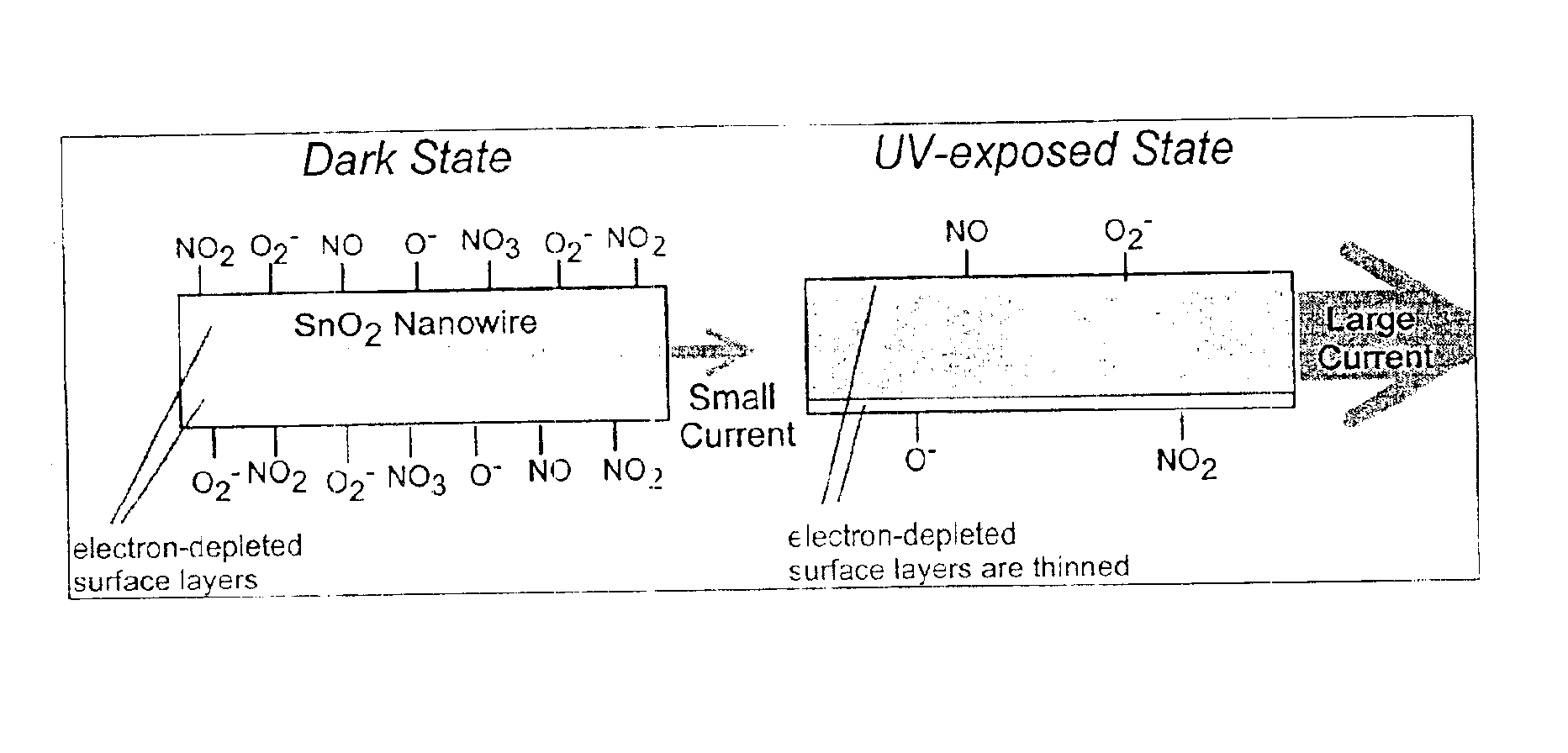
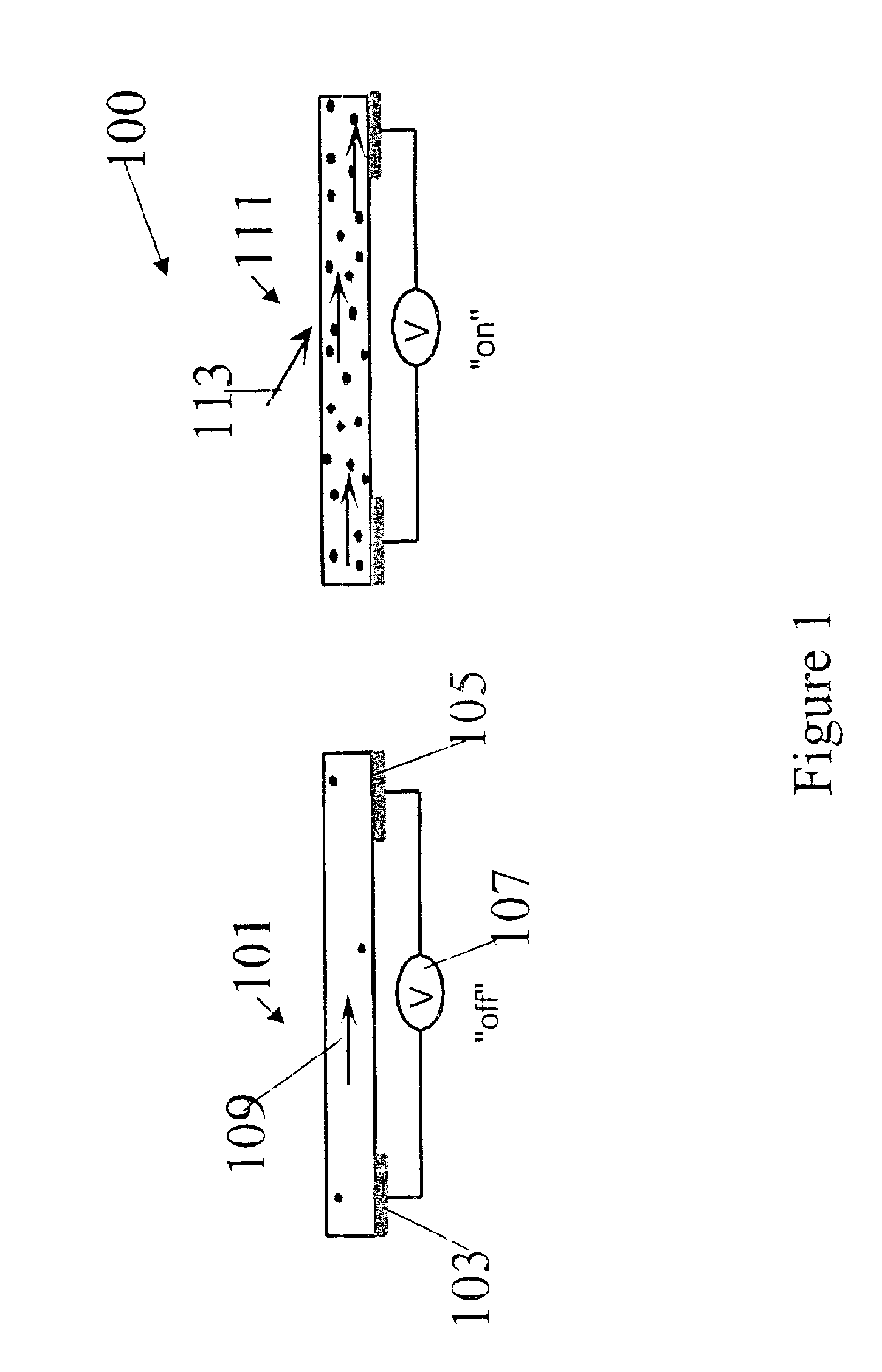
Nanowire optoelectric switching device and method
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Organic light emitting display panel and manufacturing method
ActiveCN106449702APrevent peelingImprove adhesionFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsSurface plate
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap