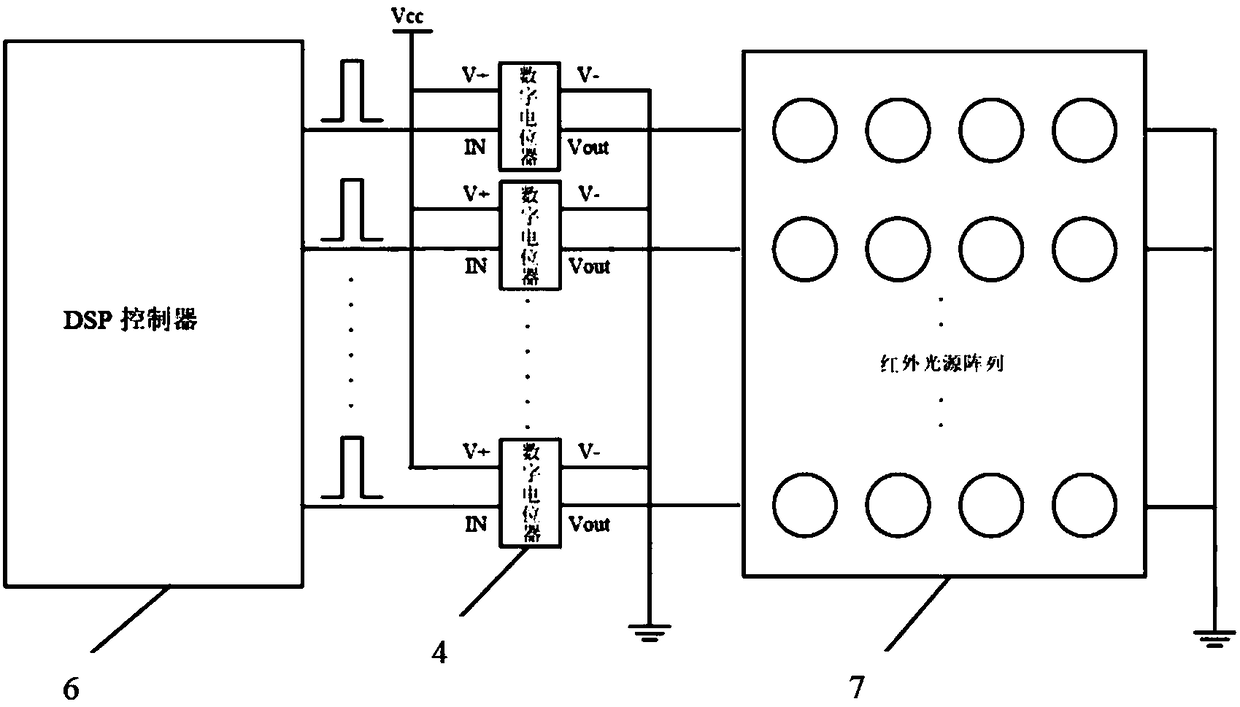
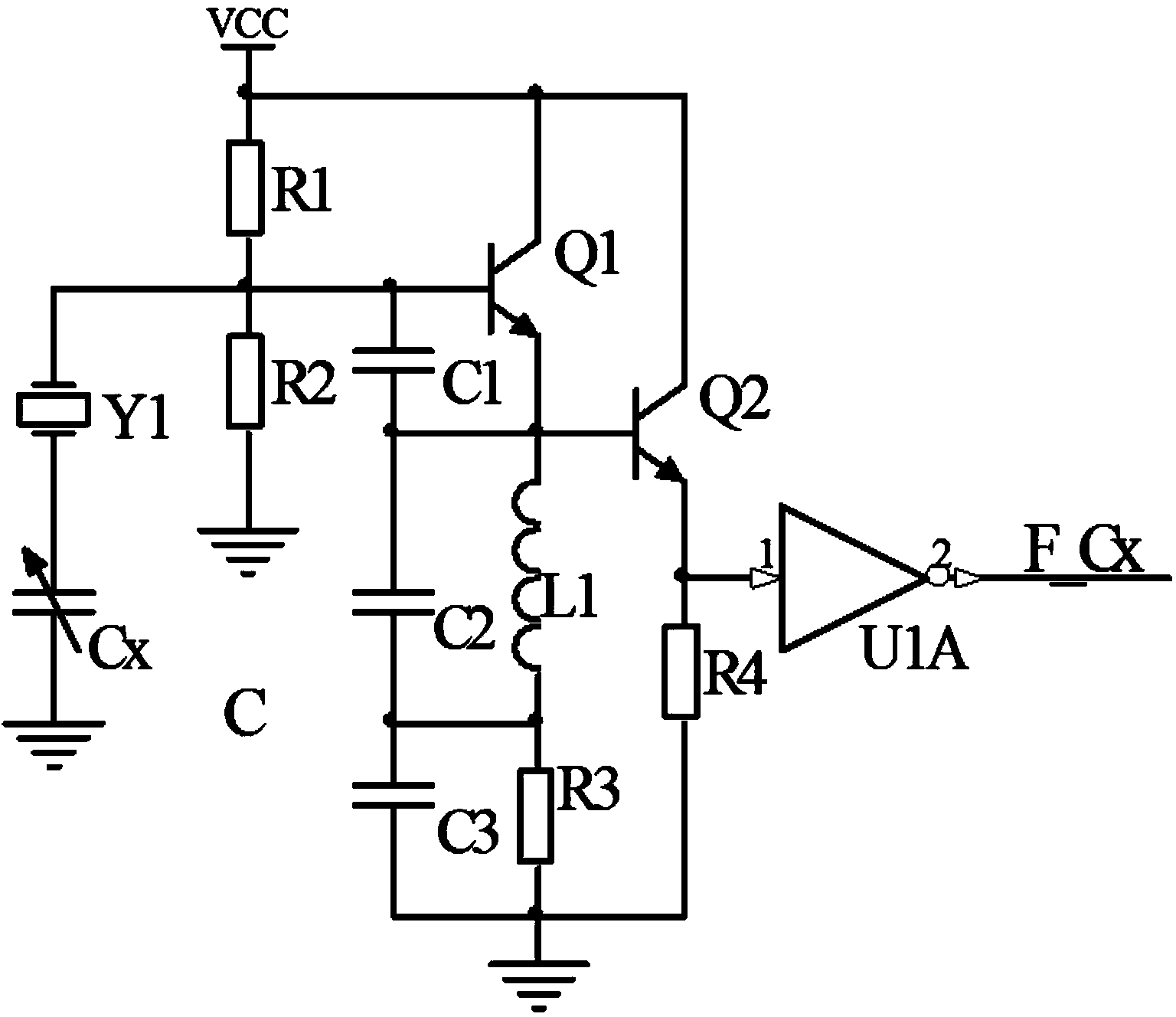
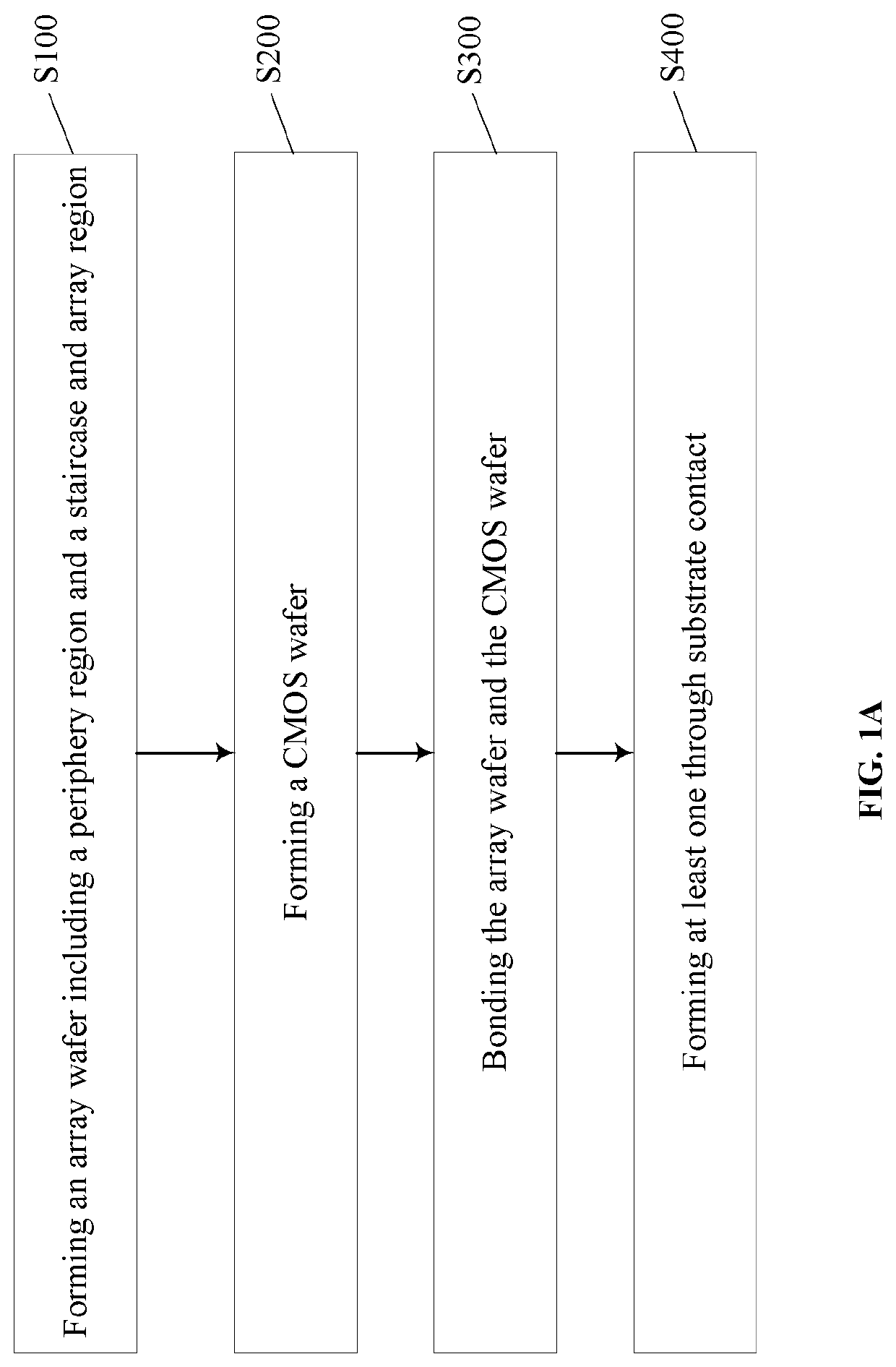
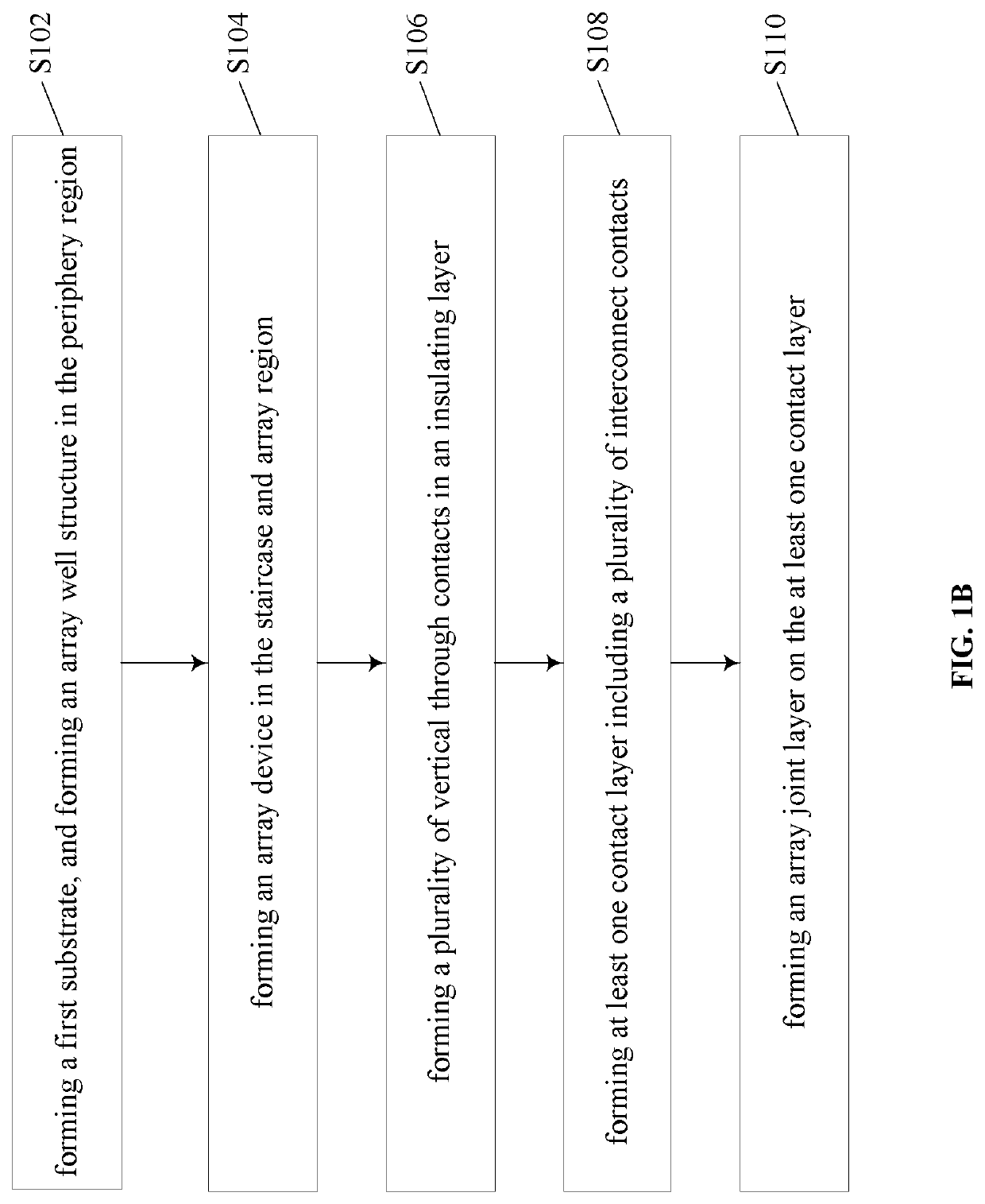
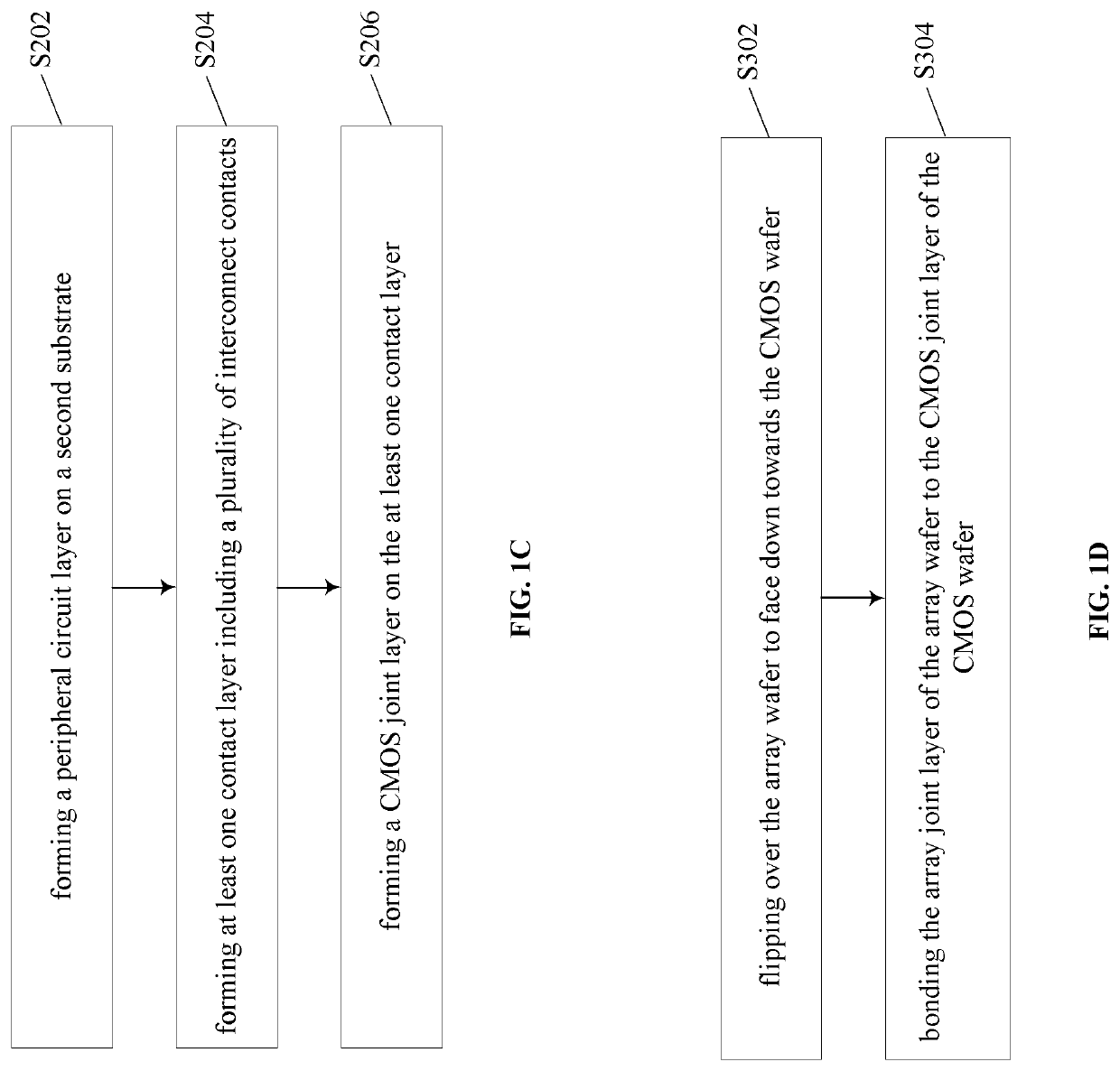
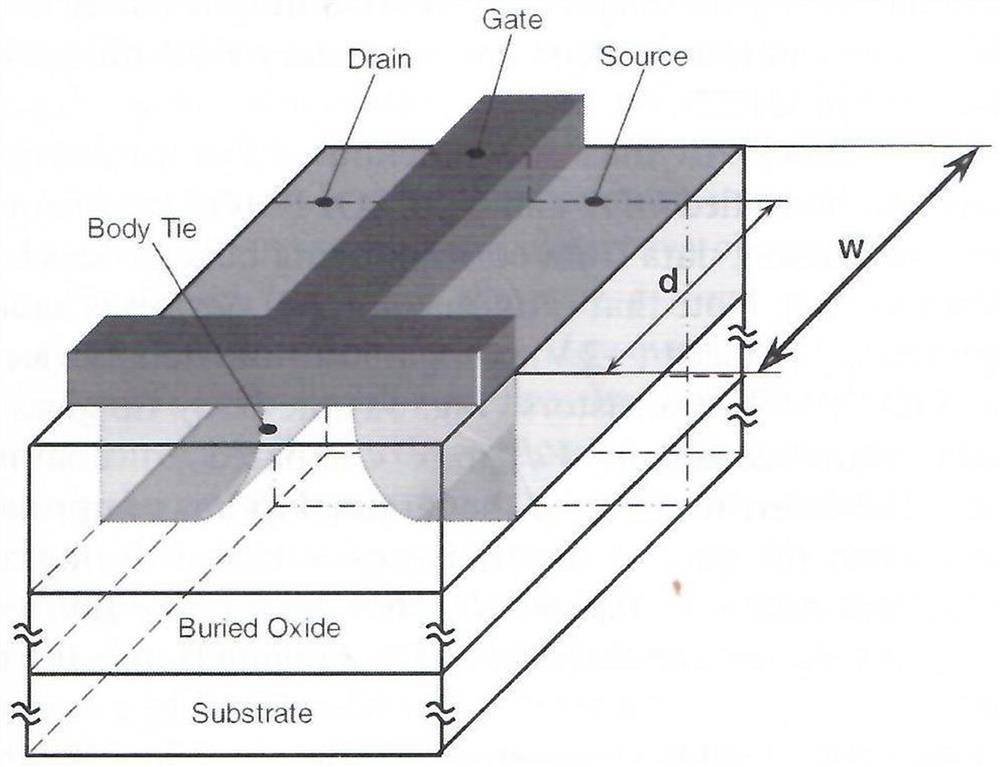
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
29 results about "CMOS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
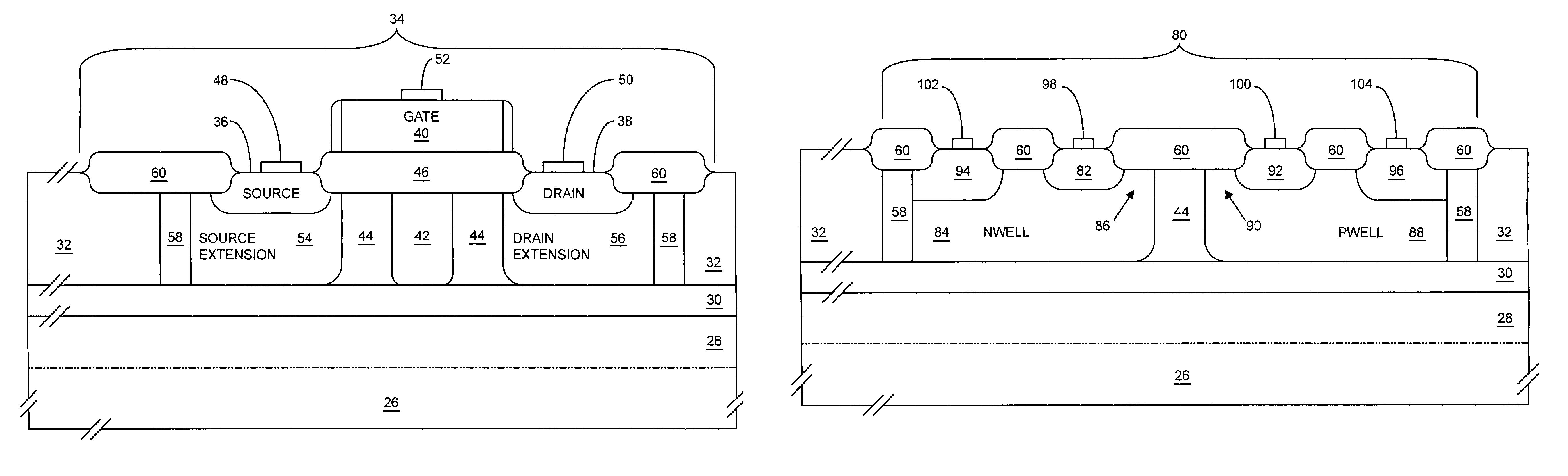
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS), also known as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (COS-MOS), is a type of MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuits (ICs), including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.
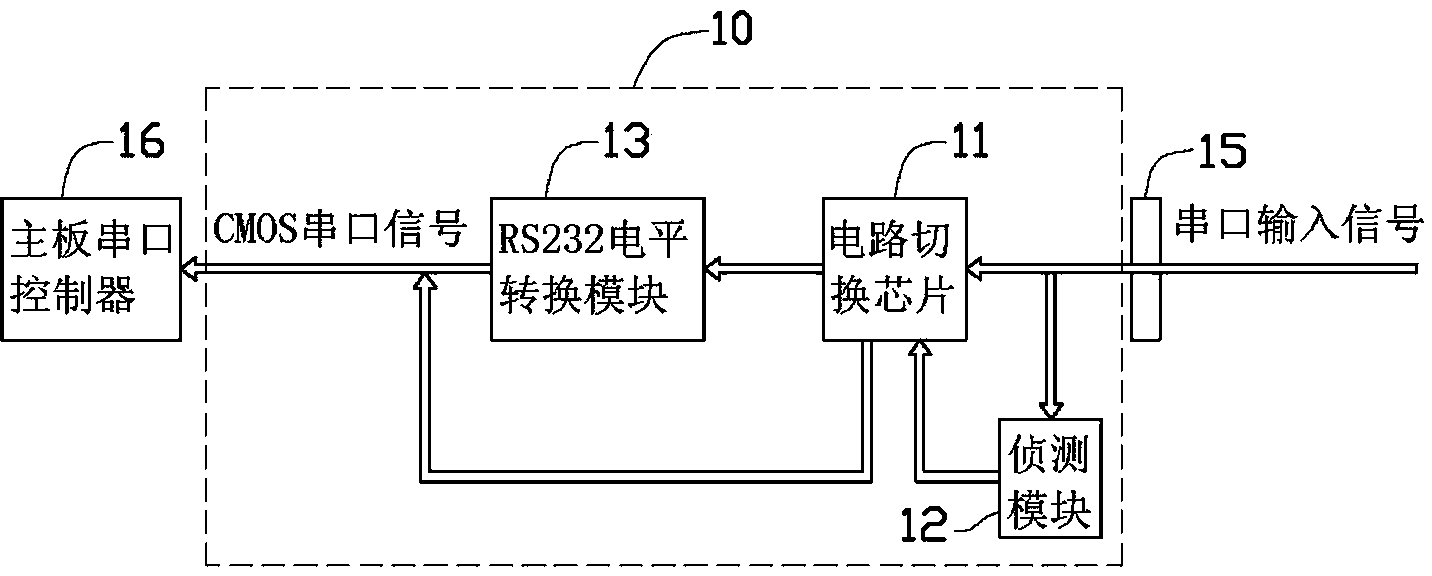
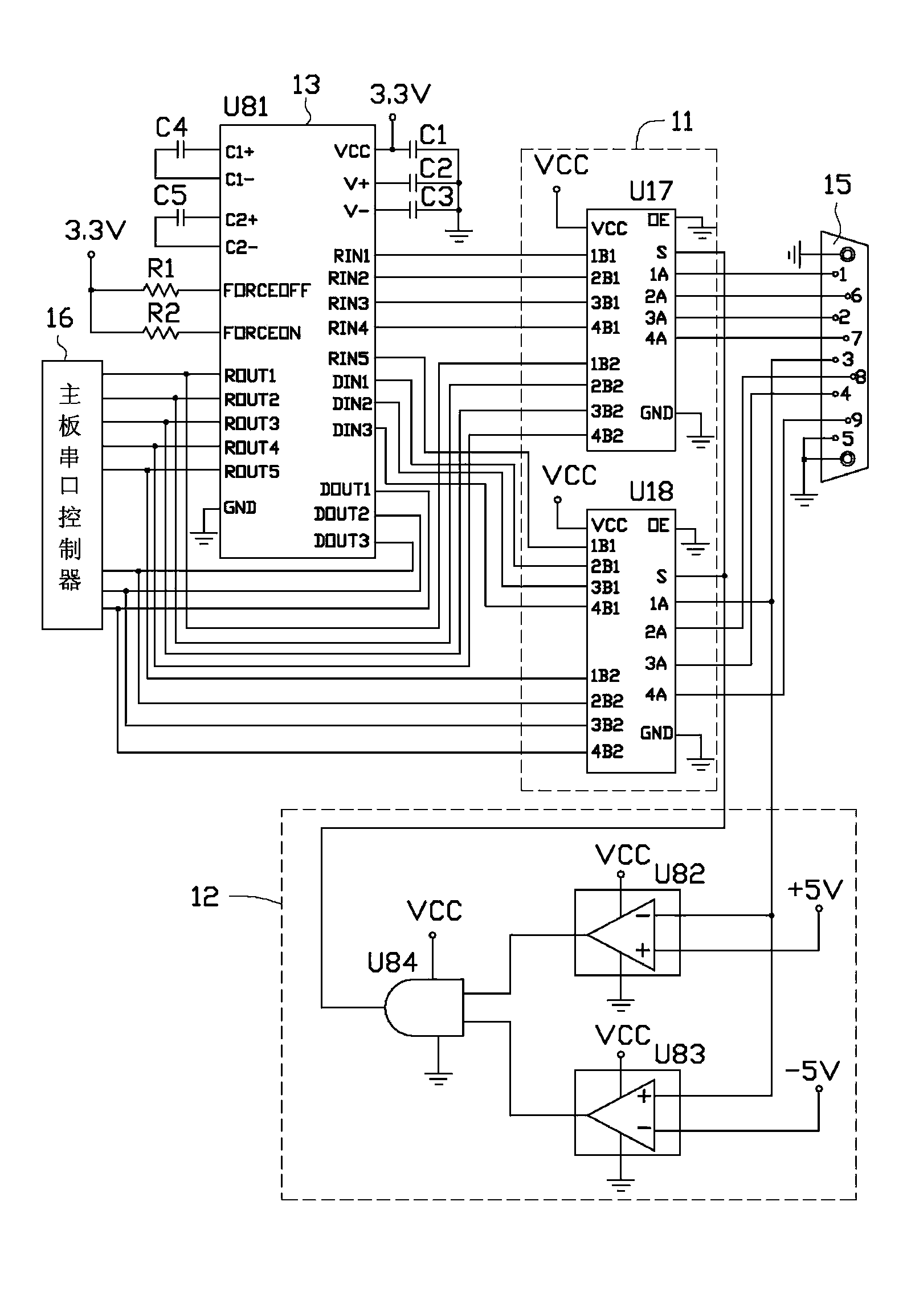
CMOS image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof
ActiveUS20120033118A1Improve dynamic rangeWide dynamic range performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSProcessing element
Disclosed are a CMOS image sensor having a wide dynamic range and a sensing method thereof. Each unit pixel of the CMOS image sensor of the present invention includes multiple processing units, so that one shuttering section for the image generation of one image frame can be divided into multiple sections to separately shutter and sample the divided sections by each processing unit. Thus, the image sensor of the present invention enables many shuttering actions to be performed in the multiple processing units, respectively, and the multiple processing units to separately sample each floating diffusion voltage caused by the shuttering actions, thereby realizing a wide dynamic range.
Owner:ZEEANN
Integration of high-voltage devices and other devices
Owner:QORVO US INC
Radiation tolerant combinational logic cell
InactiveUS20070109865A1Increase energy levelReduce sensitivityRead-only memoriesDigital storageCMOSData set
Owner:IDAHO UNIV OF +1
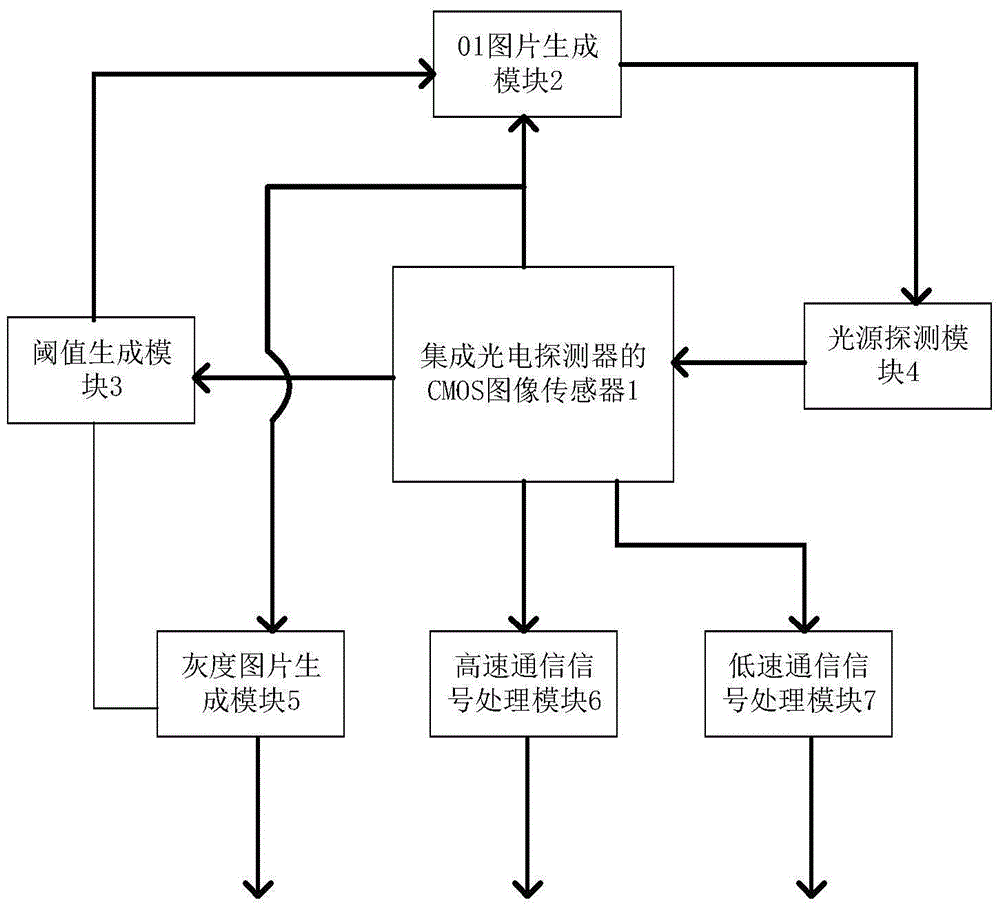
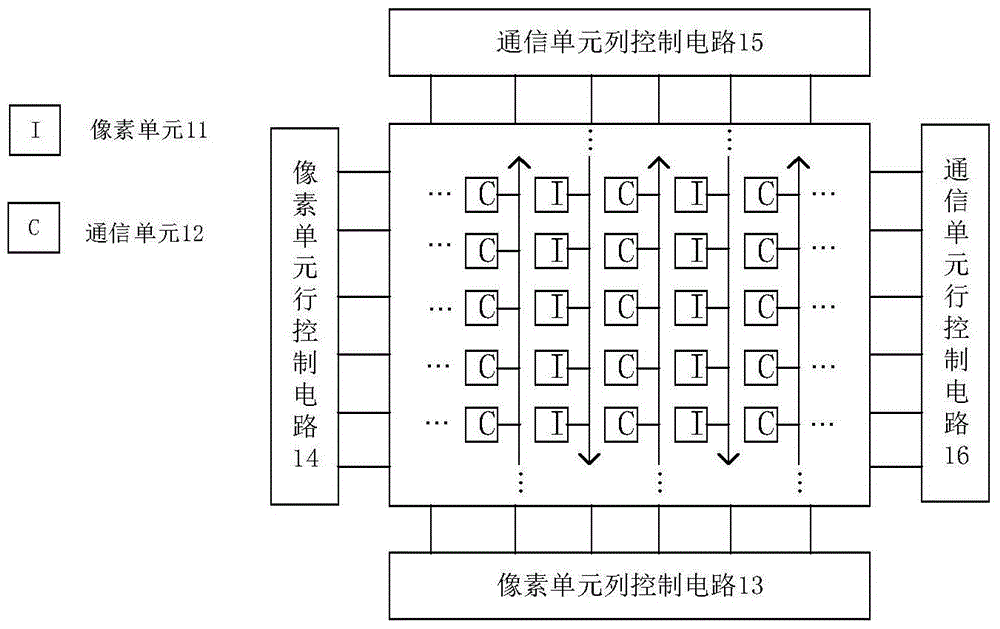
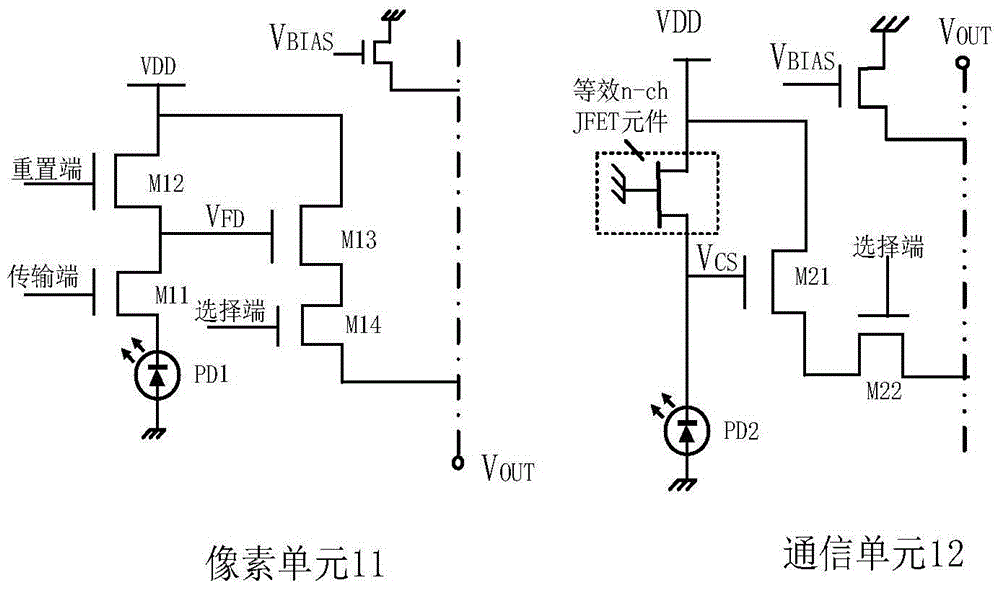
CMOS image sensor dual-mode communication receiving system of integrated photoelectric detector
ActiveCN105721801AAccurate detectionRemove background light noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow speedDual mode
Owner:西安仙农电子科技有限公司
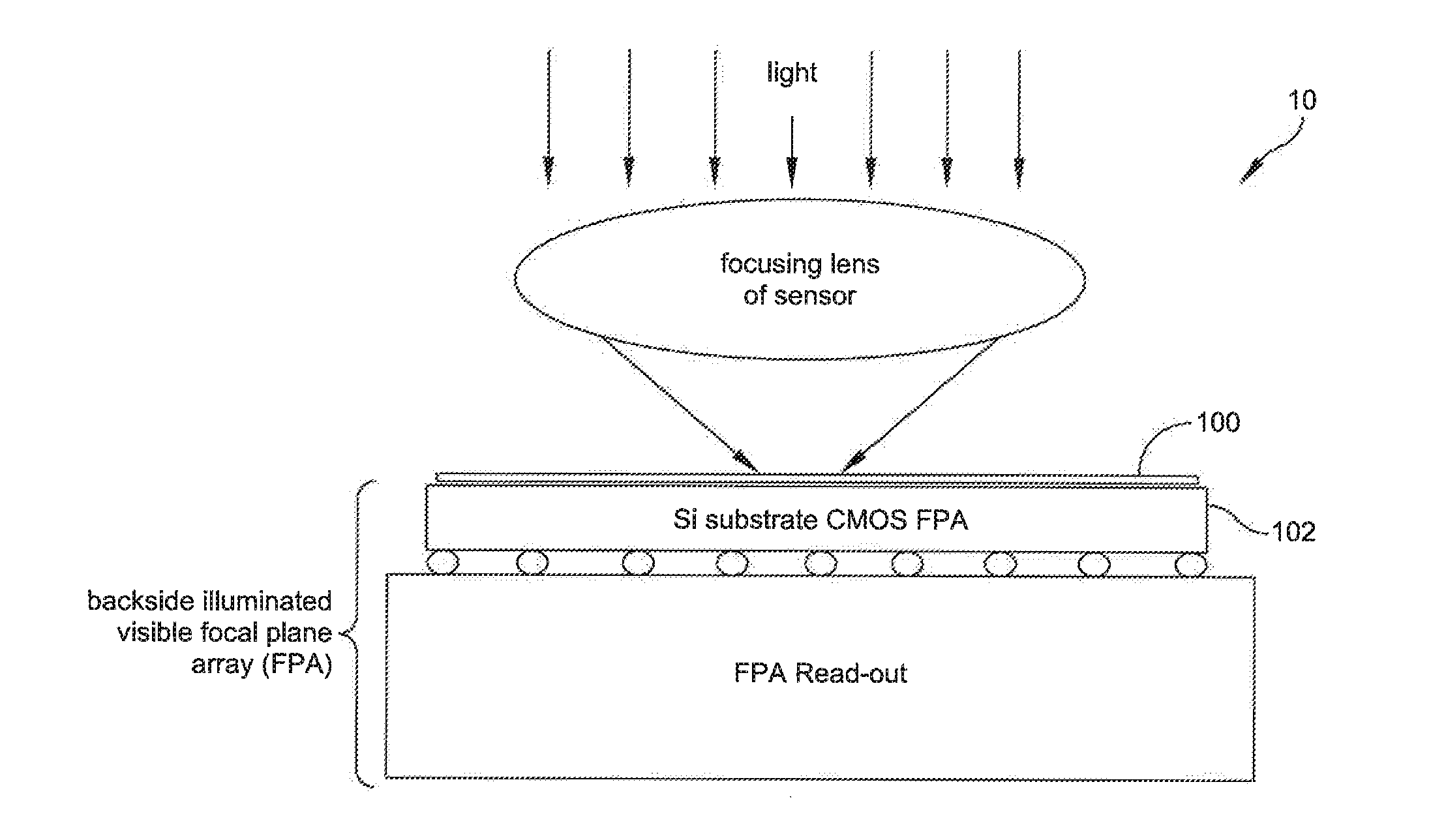
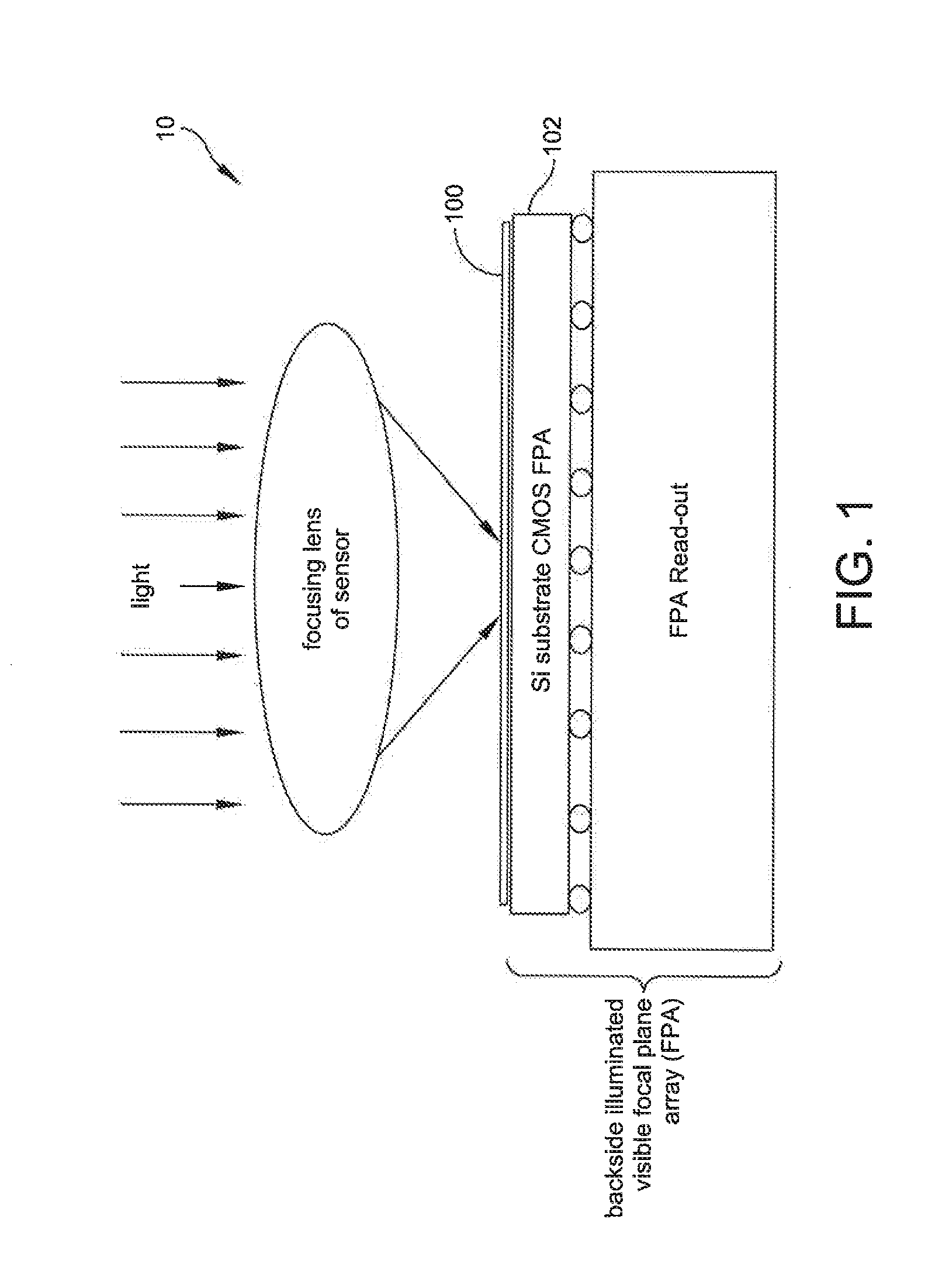
Broadband graphene-based optical limiter for the protection of backside illuminated CMOS detectors
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
TTL and CMOS compatible input buffer
ActiveCN101282114ALow costSimple and fast operationLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCMOSVoltage generator
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Low power consumption non-resistor full CMOS voltage reference circuit
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Universal CMOS device leakage characterization system
ActiveUS20070252613A1Marginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingCMOSGate dielectric
The invention provides a universal leakage monitoring system (ULMS) to measure a plurality of leakage macros during the development of a manufacturing process or a normal operation period. The ULMS characterizes the leakage of both n-type and p-type CMOS devices on the gate dielectric leakage, the sub-threshold leakage, and the reverse biased junction leakage, and the like. Testing is performed sequentially from the first test macro up to the last test macro using an on-chip algorithm. When the last test macro is tested, it scans the leakage data out.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Interface level switch device
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
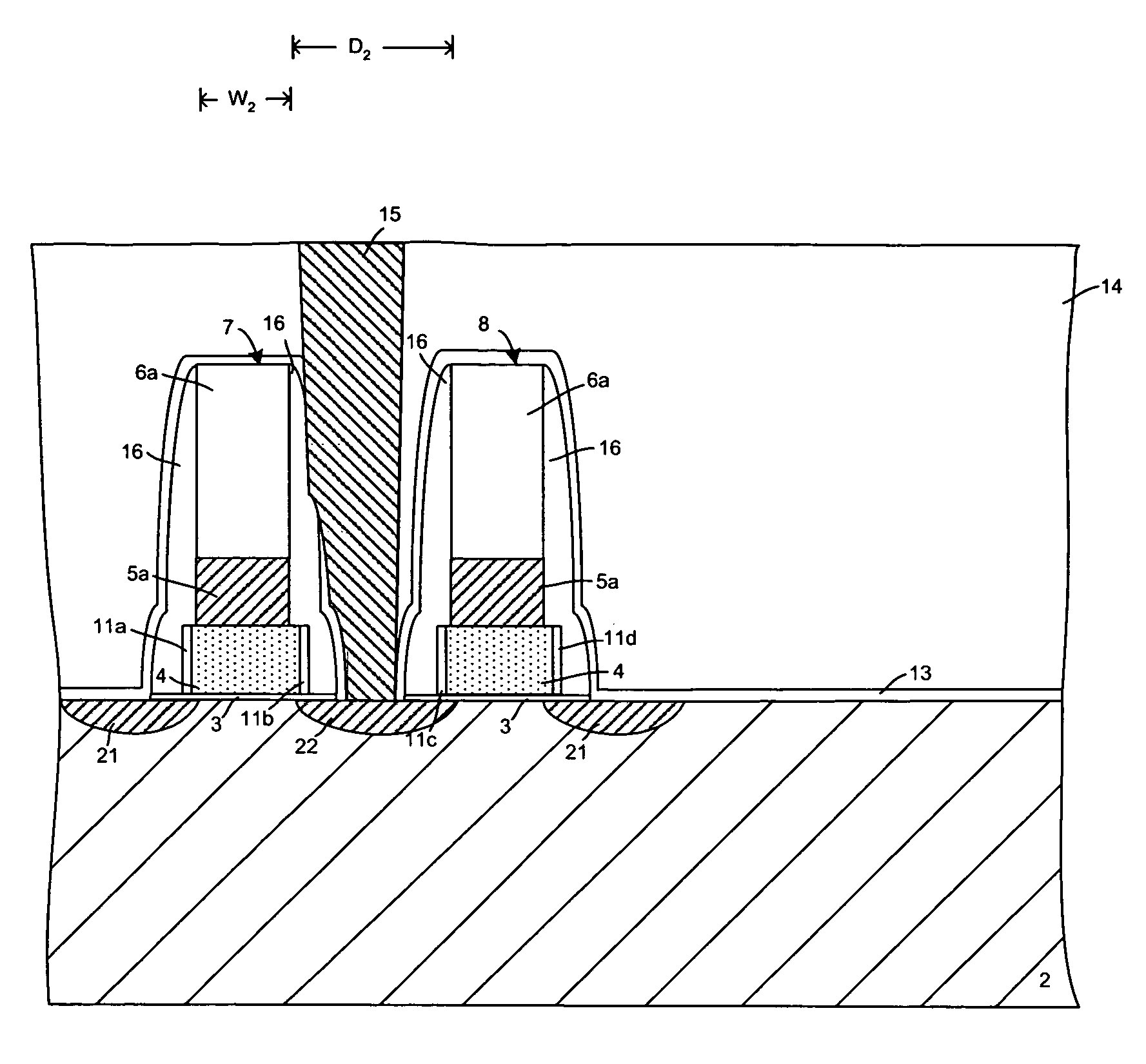
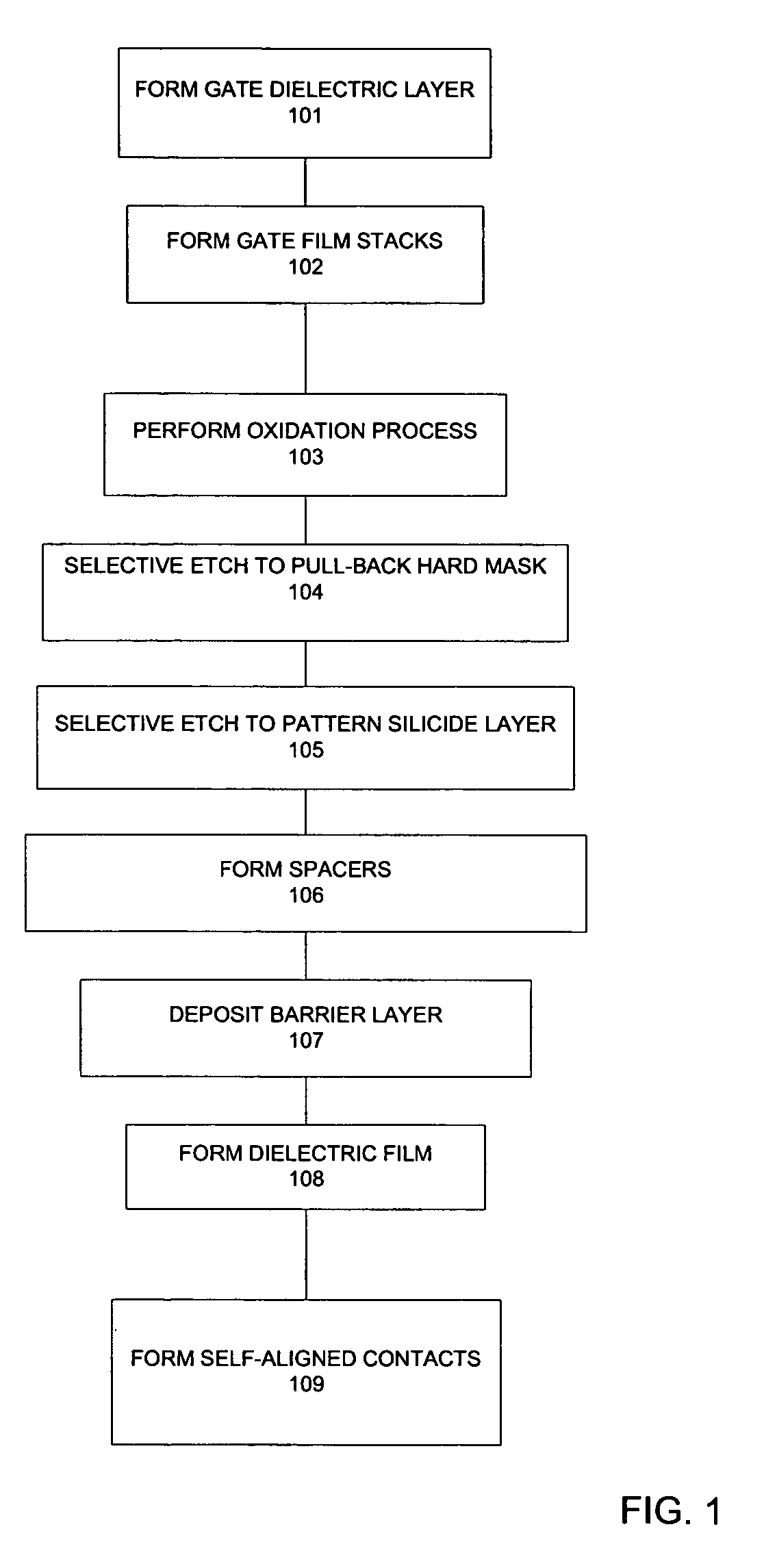
Method for forming CMOS structure with void-free dielectric film
InactiveUS7163881B1Reduce widthEasy to fillSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSDielectric layer
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
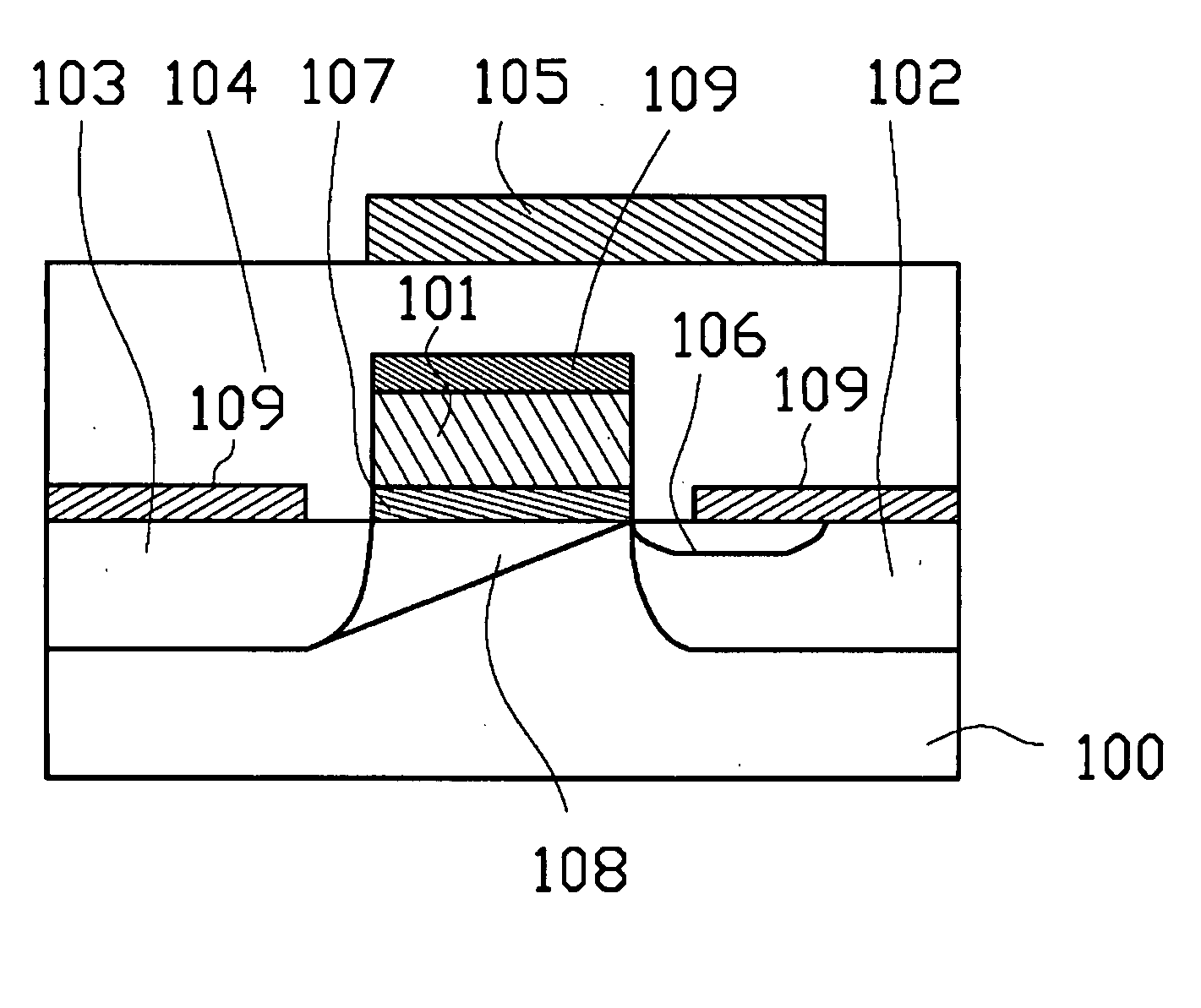
Semiconductor device structure and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN102456621ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOxide semiconductorCMOS
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Subthreshold latch
InactiveCN102075179AAvoid the problem of not saving data normallyGuaranteed to workLogic circuitsCMOSTransmission gate
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Manufacturing method of high-linearity and high-power CMOS structure
InactiveUS20080318372A1Improve linearityIncrease output powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSEngineering
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Power detection circuit in radio frequency front-end chip
Owner:RDA MICROELECTRONICS TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Portable Chinese-sensible code reading machine and reading method thereof
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI +1
Absolute capacitor and differential capacitor measuring circuit
Owner:JILIN UNIV
CMOS image sensor circuit and method of supplying initial charge thereof
Provided are a CIS circuit that does not increase an initial voltage charge time allocated by a CDS even if a pixel size is reduced and a method of providing an initial charge to the CIS circuit. The CIS circuit may include an APS block, a current source block and a charge supply block. The APS block may output APS signals from APS output terminals in response to sensed image transfer signals, pixel select signals and pixel reset signals. The current source block may control currents flowing from the APS output terminals to a power supply in response to a bias voltage. The charge supply block may provide a quantity of charges to the APS output terminals in response to a representative reset signal and a pre-resent signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
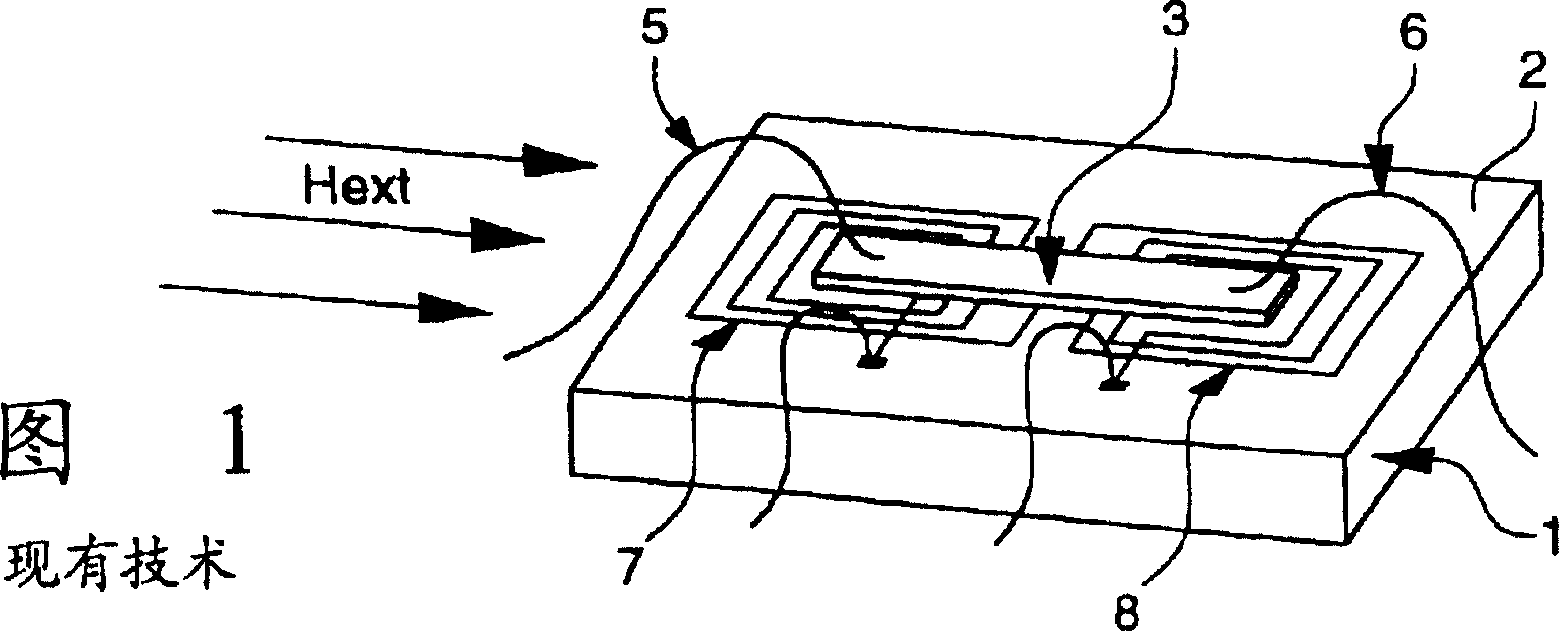
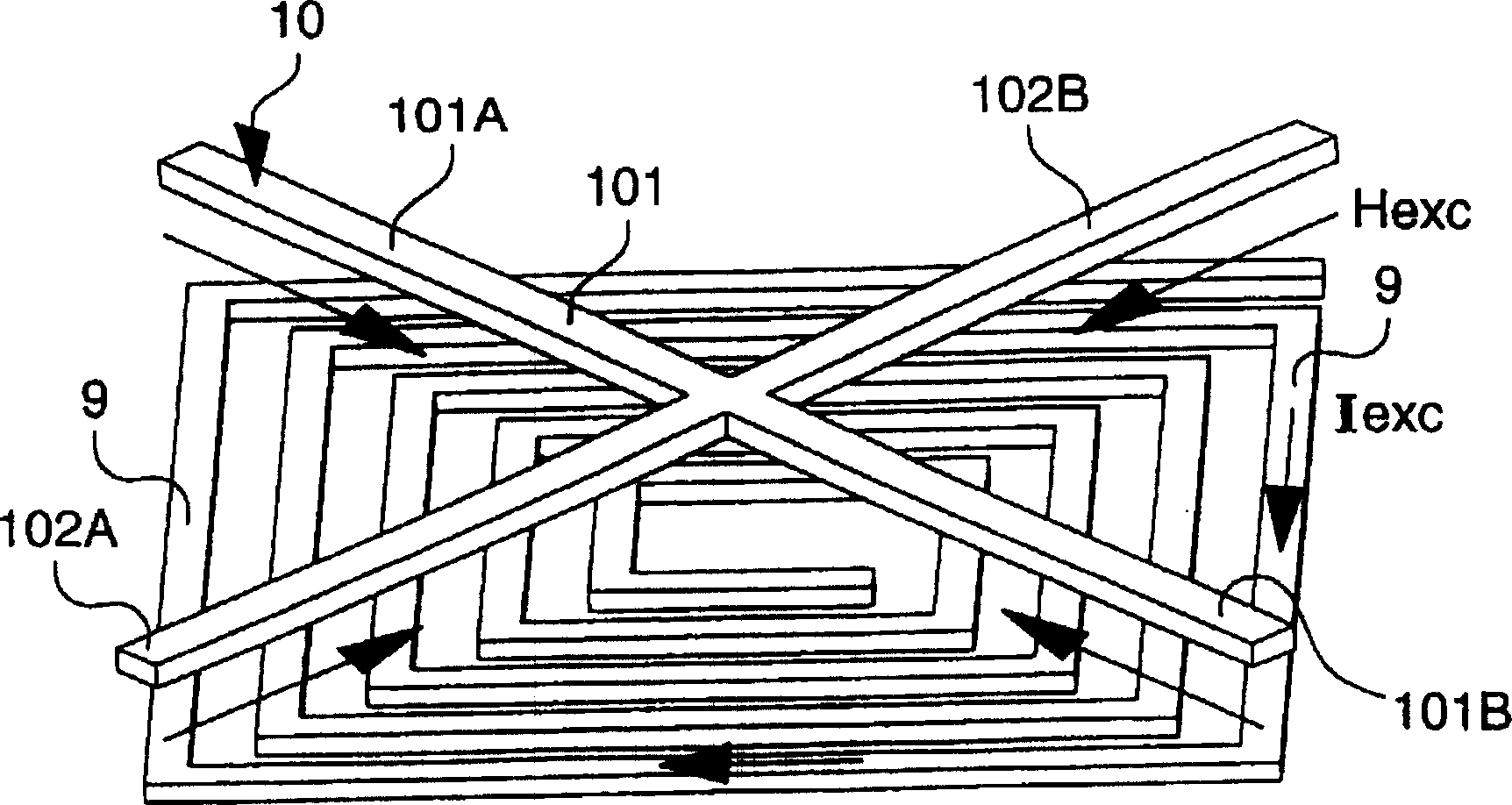
Magnetic sensor formed on semiconductor substrate
InactiveCN1153981CImprove performanceReduce current consumptionMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleSensorsCMOSMagnetic core
Planar magnetic sensor, made in particular via CMOS techniques on a semiconductor substrate (1) of for example parallelepiped shape. It includes an amorphous ferromagnetic core (10) in the shape of a Greek cross which occupies the two diagonals of the square defined by the outer contour (90) of the excitation coil (9), the latter being made in the form of a planar winding of square shape. One thus measures, via flat detection coils (70, 80 and 71, 81) which are mounted in series and in a differential arrangement, the two orthogonal components (H1, H2) of the external magnetic field (Hext).
Owner:ASULAB SA
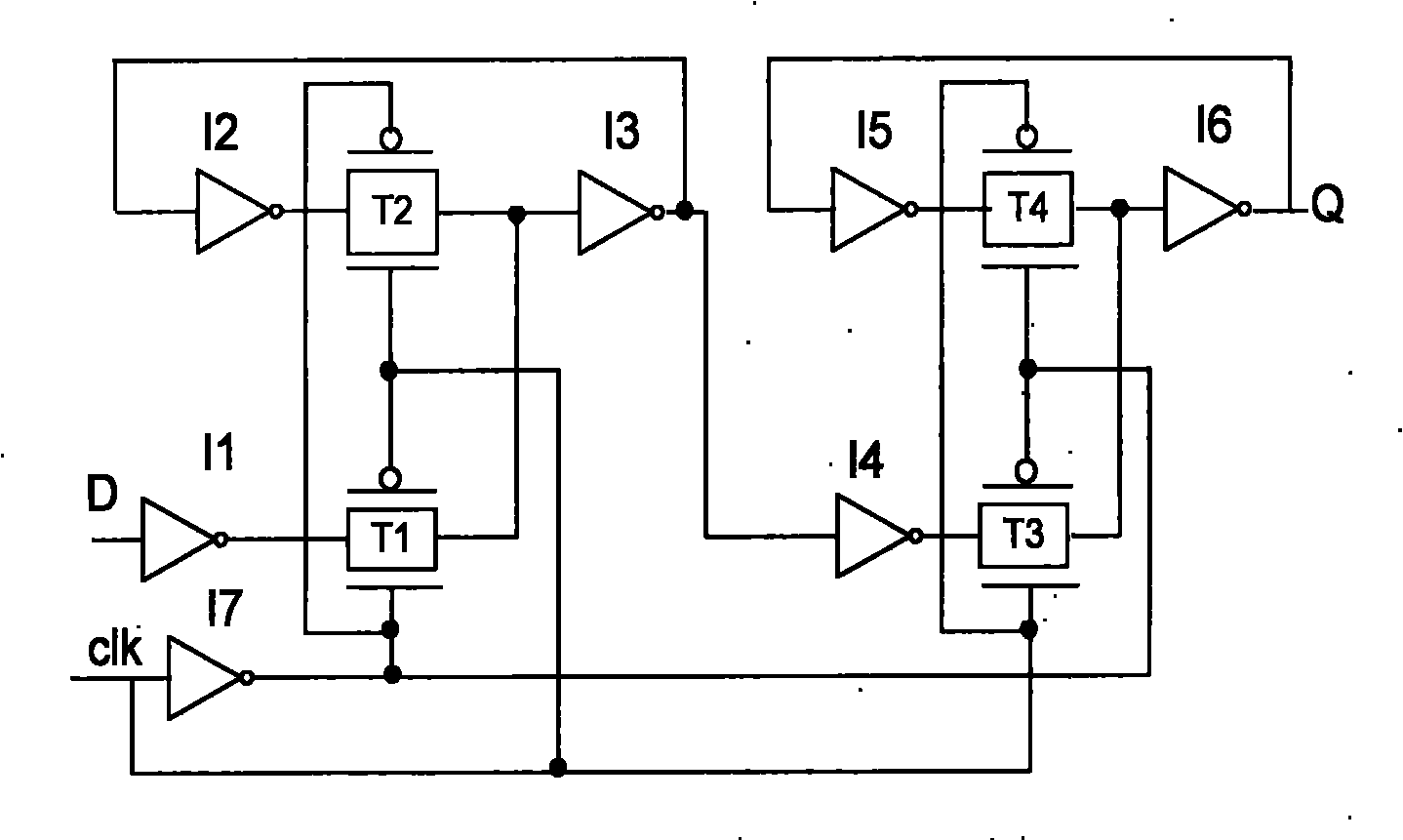
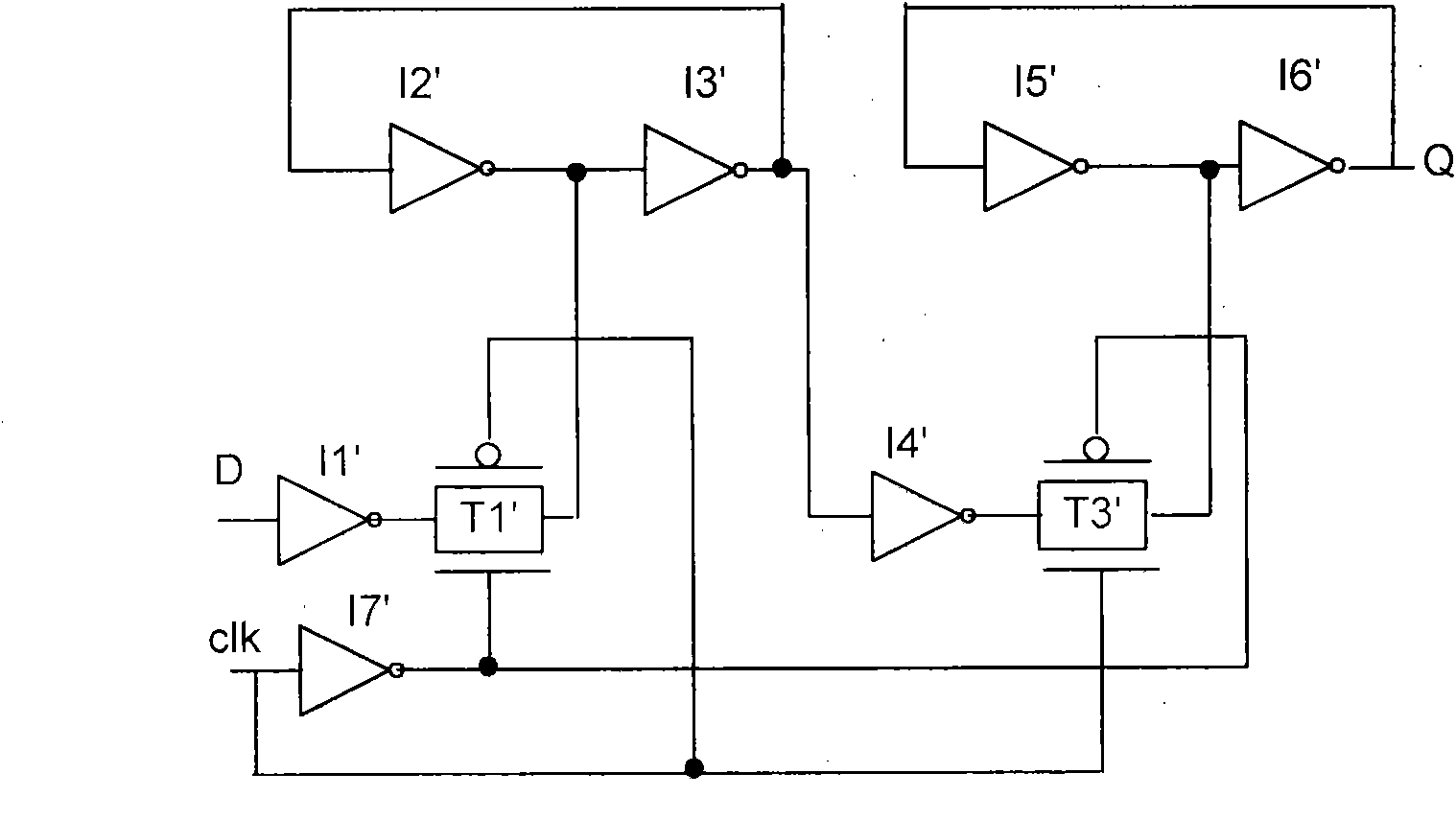
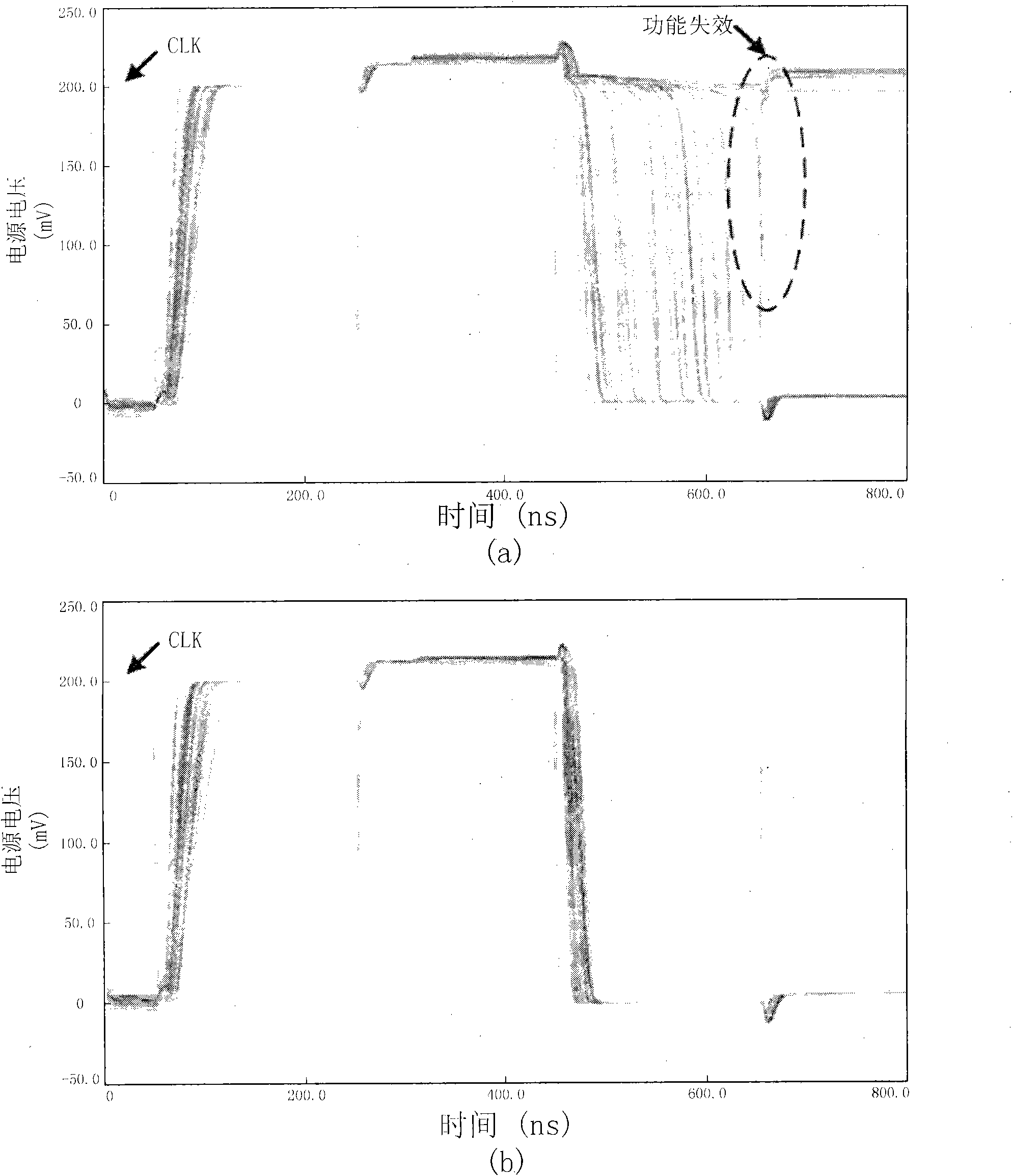
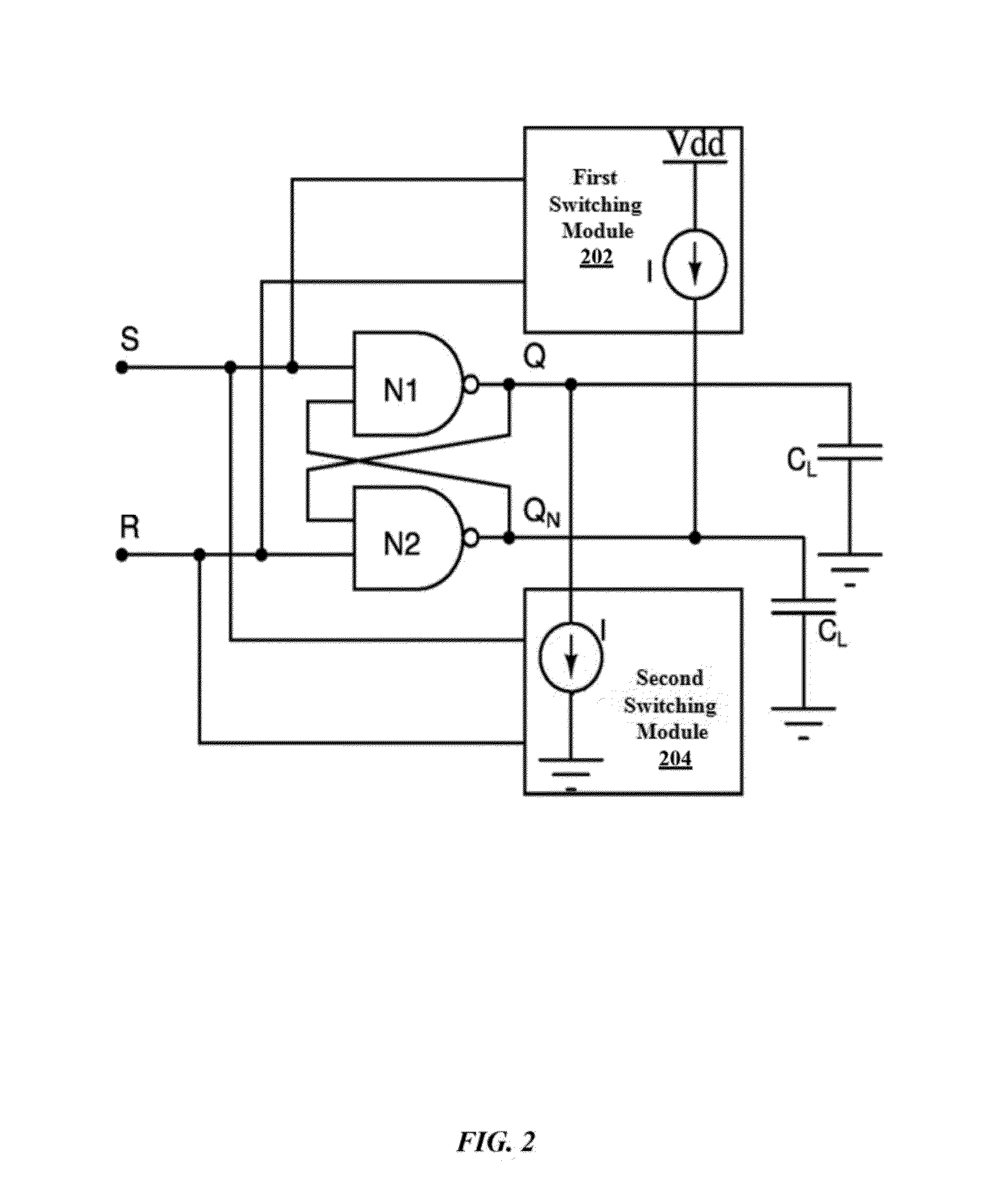
System and method for reducing metastability in CMOS flip-flops
ActiveUS20160164502A1Reducing metastabilityMetastability is reducedElectric pulse generatorCMOSMetastability
Owner:GOPALAN BHASKAR
Supply voltage and temperature independent receiver
ActiveUS10868537B1Threshold modification in field effect transistorsTransmissionOxide semiconductorCMOS
Owner:APPLE INC
Thermal infrared sensor array in wafer-level package
ActiveUS10788370B2Pyrometry using electric radation detectorsCMOSWafering
Owner:HEIMANN SENSOR GMBH
Ion implantation method of P-type well, P-type well structure and CMOS device manufacturing method
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI INTEGRATED CIRCUTE MFG CO LTD
Structure of planer phase change memory storage unit and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:SHANGHAI XINCHU INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Three-dimensional memory devices and fabricating methods thereof
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
ESD protection transistor and ESD protection method of CMOS device
Owner:SHENZHEN HORB TECH CORP LTD
CMOS making method
ActiveCN106558552AImprove mobilityImprove driving abilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSCharge carrier mobility
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Diffuse reflection structure of scientific-grade CMOS camera and processing method and equipment thereof
PendingCN114488654APrevent reflections from spotting lightMeet the needs of diffuse reflectionTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsCMOSRough surface
Owner:福州鑫图光电有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap