Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
29 results about "Dielectric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dielectric (or dielectric material) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example if the field is moving in the positive x-axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative x-axis). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.
Semiconductor memory device comprising memory cells with floating gate electrode and method of production
InactiveUS20060038220A1Improve compatibilityLower Level RequirementsTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricSemiconductor materials
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Solid Electrolytic Capacitor Containing a Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Quaternary Onium Salt
ActiveUS20120147529A1Highly solubleEasily and cost-effectively formedMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesDielectricElectrolysis
A solid electrolytic capacitor a solid electrolytic capacitor that includes an anode body, a dielectric overlying the anode body, and a solid electrolyte overlying the dielectric is provided. The capacitor also comprises a conductive polymer coating that overlies the solid electrolyte and includes nanoparticles formed from a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) quaternary onium salt.
Owner:CENT FOR ORGANIC CHEM +1
Waveguided laser channels for a gas laser
Owner:EPILOG CORP
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device package using the same
ActiveUS20150243657A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceDielectric
Owner:ANCORA SEMICON INC
Quartz type pressure sensor, and production method therefor
InactiveCN1813179AEasy to strictly manage the thicknessLittle change over the yearsFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationDielectricCapacitance
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Dielectric anti-reflective coating surface treatment to prevent defect generation in associated wet clean
InactiveUS7125783B2Reduce silicon contentDensifying layerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricResist
A method for preventing the formation of watermark defects includes the steps of forming a pad oxide, a silicon nitride layer and a silicon oxynitride layer over a semiconductor substrate. A photoresist mask is formed over the resulting structure, with the silicon oxynitride layer being used as an anti-reflective coating during exposure of the photoresist material. An etch is performed through the photoresist mask, thereby forming a trench in the substrate. The photoresist mask is stripped, and the silicon oxynitride layer is conditioned. For example, the silicon oxynitride layer may be conditioned by a rapid thermal anneal in the presence of oxygen or nitrogen. A wet clean step is subsequently performed to remove a native oxide layer in the trench. The conditioned silicon oxynitride layer prevents the formation of watermarks during the wet clean process.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Photosensitive polysilazane composition, method of forming pattern therefrom, and method of burning coating film thereof
InactiveUS6902875B2High resolutionIncrease resistancePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsDielectricInter layer
A finely patterned silica type ceramic film suitable as an inter-layer dielectric is formed in a short time by applying, onto a substrate, a positive working radiation sensitive polysilazane composition comprising a modified poly(sil sesquiazane) having a number average molecular weight of 100 to 100,000 and containing a basic constituent unit represented by the general formula: —[SiR6(NR7)1.5]— and other constituent units represented by the general formula: —[SiR62NR7]— and / or —[SiR63(NR7)0.5]— (R6 and R7 independently represent a hydrogen atom, a C1-3 alkyl group or a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group) in a ratio of 0.1 to 100 mol-% to said basic constituent unit, a photo acid generator and preferably a water-soluble compound as a shape stabilizer, then patternwise exposing the resultant coating film, subjecting the exposed part of the coating film to moistening treatment, developing it with an aqueous alkali solution, wholly exposing the coating film to light and moistening treatment again, followed by burning treatment.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Mulitlayer film reflecting type high precision round metal grating and making method thereof
InactiveCN1790068AAvoid deformationHigh precisionDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDielectricTitanium alloy
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
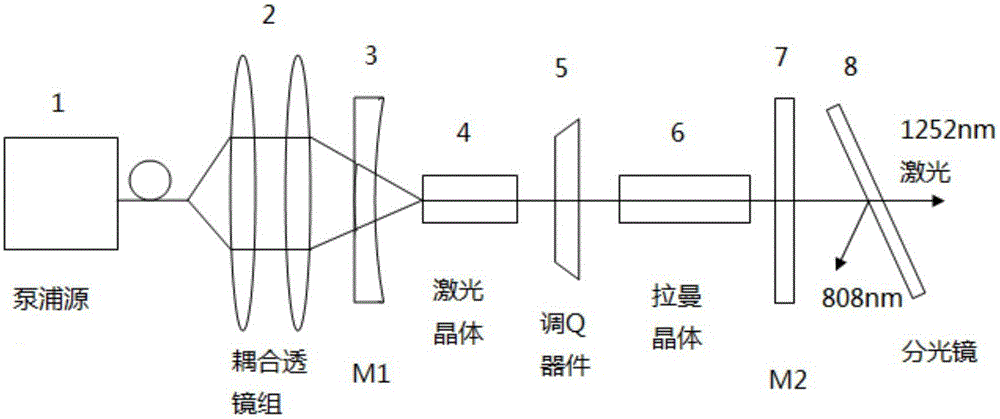
1.2 micron wavelength all-solid-state raman laser
InactiveCN105140775ACompact structureEasy to useLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialDielectricRaman amplifiers
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Microwave Device For Tissue Ablation
ActiveUS20150038956A1Good mechanical resistanceIncreased mechanical toughnessSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingDielectricElectrical conductor
Owner:H S HOSPITAL SERVICE
Electric discharge machine and electric discharge machining method
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
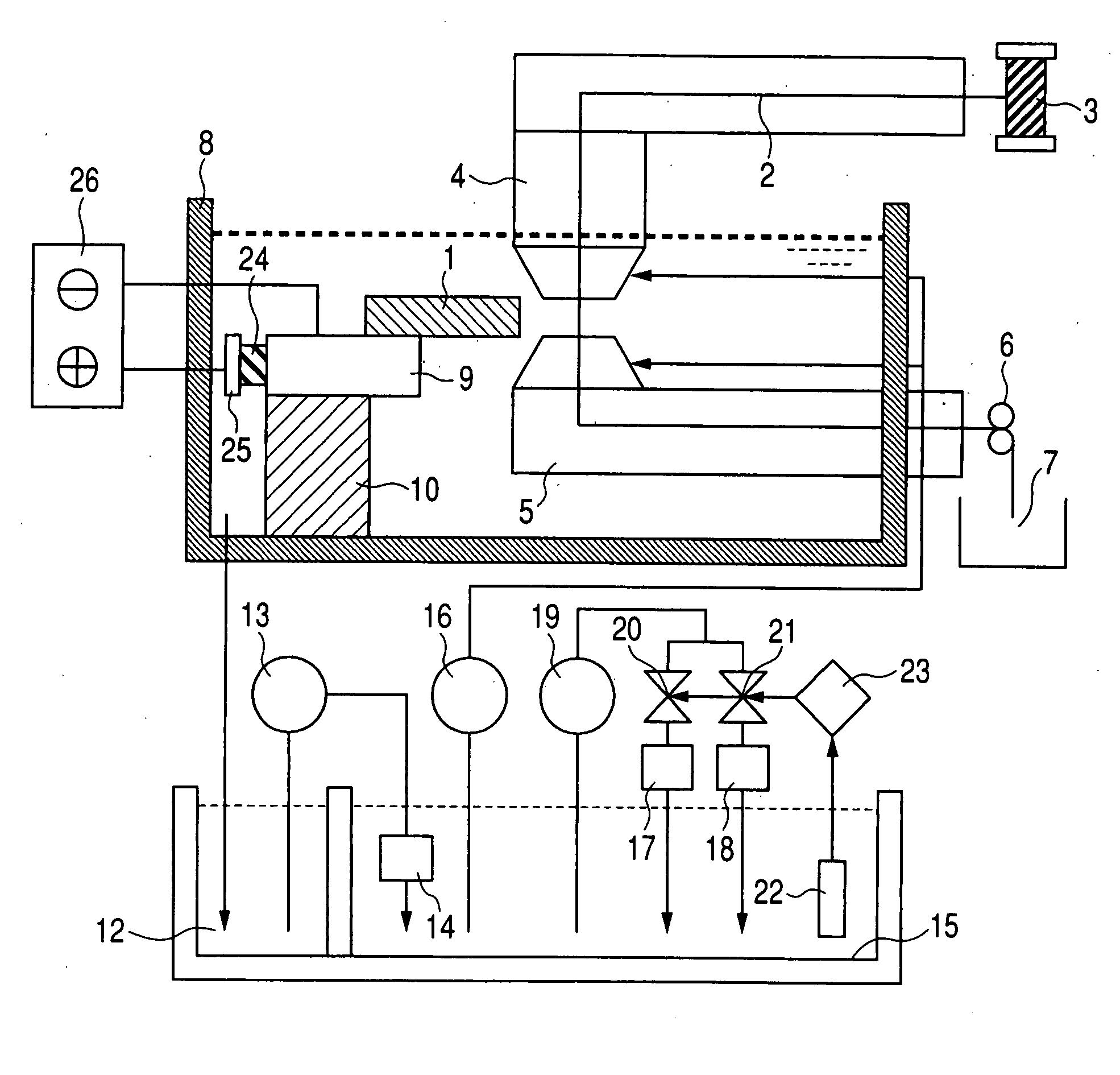
Dielectric fluid for electric discharge machining a non electrically conductive material
InactiveCN101410214ARapid Ablation ProcessingPromote rapid formationDielectricElectric discharge
The invention relates to a dielectric fluid (5) for electrical discharge machining an electrically non-conductive material, characterised in that it is of an aqueous solution or an aqueous suspension of at least one carbonaceous substance.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Organic silicon electronic potting adhesive for PCB circuit board with stable dielectric insulation performance
InactiveCN106634810AHigh tensile strengthHigh hardnessNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesDielectricAdhesive
The invention discloses an organic silicon electronic potting adhesive for a PCB circuit board with stable dielectric insulation performance. The organic silicon electronic potting adhesive is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 to 50 parts of vinyl-terminated silicone oil-1, 50 to 60 parts of vinyl-terminated silicone oil-2, 0.38 to 0.5 part of 12% of a platinum catalyst, 0.02 to 0.04 part of acetenyl cyclohexanol, 25 to 30 parts of vinyl silicon resin, 14.8 to 16.8 parts of 1-allyloxy-2,3-epoxypropane, 23 to 25 parts of 1,3,5,7-tetramethyl cyclotetrasiloxane, 2.7 to 3.6 parts of a silane coupling agent A171, an appropriate amount of silicon-containing silicon oil, 2.6 to 3 parts of mica powder, 1.8 to 3 parts of porcelain powder, 0.2 to 0.3 part of dimethyl silicone polymer, 4.6 to 5 parts of carboxylated latex, 1.1 to 1.6 parts of polyvinyl alcohol and an appropriate amount of deionized water. The potting adhesive disclosed by the invention has high heat conduction, dielectric insulation, impact resistance and adhesive performance, is high in fluidity, and is extremely suitable for potting electronic products.
Owner:TONGLING ONBOLE PCB CO LTD
FinFET and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103855026AReduce adverse effectsReduce usageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The invention discloses a FinFET and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method of the FinFET comprises the steps of forming a semiconductor fin with a trapezoidal cross section, forming one of a source region and a drain region, forming a sacrifice side wall, using the sacrifice side wall as a mask, forming the other one of the source region and the drain region, removing the sacrifice side wall, and using a gate stack for replacing the sacrifice side wall, wherein the gate stack comprises a gate conductor and gate dielectric media, and the gate dielectric media partition the gate conductor and the semiconductor fin.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Connection structure of semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20190081000A1Improve coverageImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricPower semiconductor device
A connection structure of a semiconductor device is provided in the present invention. The connection structure includes an interlayer dielectric, a top metal structure, and a passivation layer. The interlayer dielectric is disposed on a substrate. The top metal structure is disposed on the interlayer dielectric. The top metal structure includes a bottom portion and a top portion disposed on the bottom portion. The bottom portion includes a first sidewall, and the top portion includes a second sidewall. A slope of the first sidewall is larger than a slope of the second sidewall. The passivation layer is conformally disposed on the second sidewall, the first sidewall, and a top surface of the interlayer dielectric.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
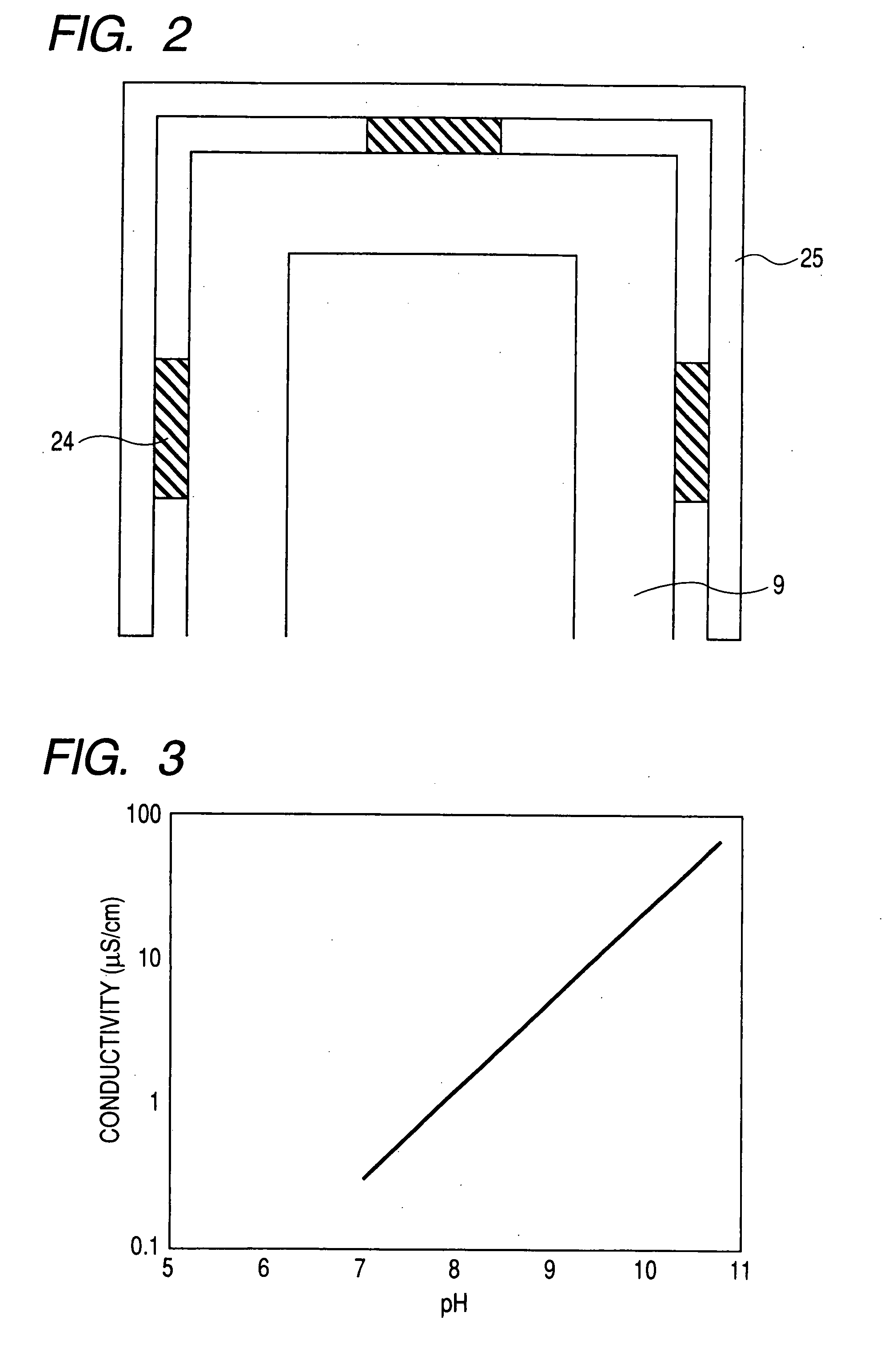
Dielectric constant measuring jig and method based on parallel plate capacitance method
ActiveCN112540234AExperiment operation is simpleLow costResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricCapacitance
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Printed circuit board having DC blocking dielectric waveguide vias
InactiveUS20140097918A1High frequency circuit adaptationsPrinted circuit aspectsDielectricDielectric permittivity
A printed circuit board is disclosed. The printed circuit board includes a first signal transmission layer, a via and a second signal transmission layer. The via connects the first signal transmission layer to the second signal transmission layer. The via includes a first region made of a first dielectric material having a first dielectric constant, and a second region made of a second dielectric material having a second dielectric constant lower than the first dielectric constant. The via allows AC Component of an electro-magnetic signal to be transmitted from the first signal transmission layer to the second signal transmission layer while blocking any DC component of the electromagnetic signal.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for integrating multi-beam-frequency-invariant conformal array
ActiveCN112818289ASimple processIncrease flexibilityComplex mathematical operationsDielectricPhysical space
The invention discloses a method for integrating a multi-beam-frequency-invariant conformal array, and relates to an artificial electromagnetic device. The method comprises the following steps: integrating three beams by using an EGMPM algorithm to obtain a linear antenna array system with frequency invariance, thereby obtaining point source excitation and point source spacing of the linear antenna array system in a virtual space; obtaining a mapping relation from a virtual space to a physical space by setting a Laplacian equation and boundary conditions, the mapping relation being represented by a Jacobian matrix J, mapping each point source position to an actual conformal lens through conformal transformation, and keeping the amplitude of the point source unchanged; setting a relative dielectric constant of the conformal lens through a Jacobian matrix mapped between the virtual space and the physical space; according to the antenna reflection theory, setting a foam layer at the bottom end of a bottom array element placement position of an antenna array, and adjusting the relative dielectric constant of the area, so that a multi-beam-frequency-invariable conformal array is realized. The cost is saved, and the flexibility and applicability of the antenna array are improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
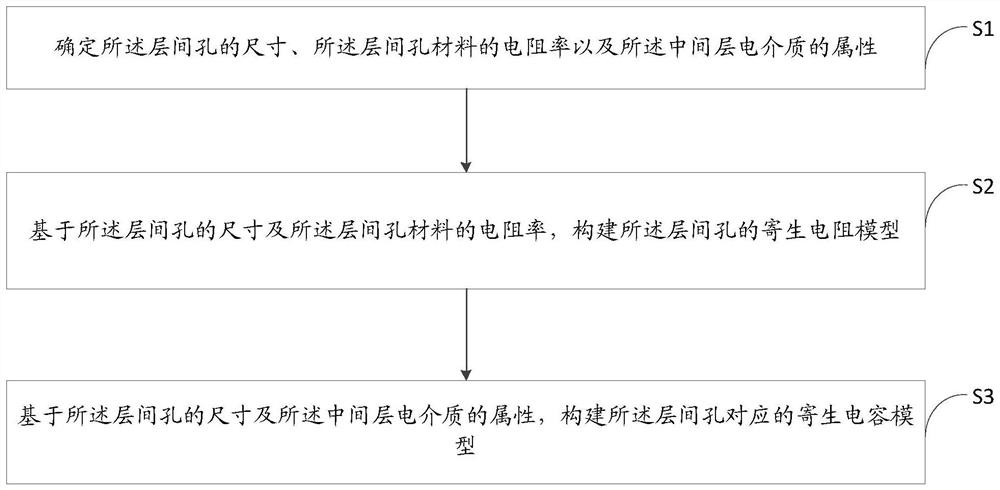
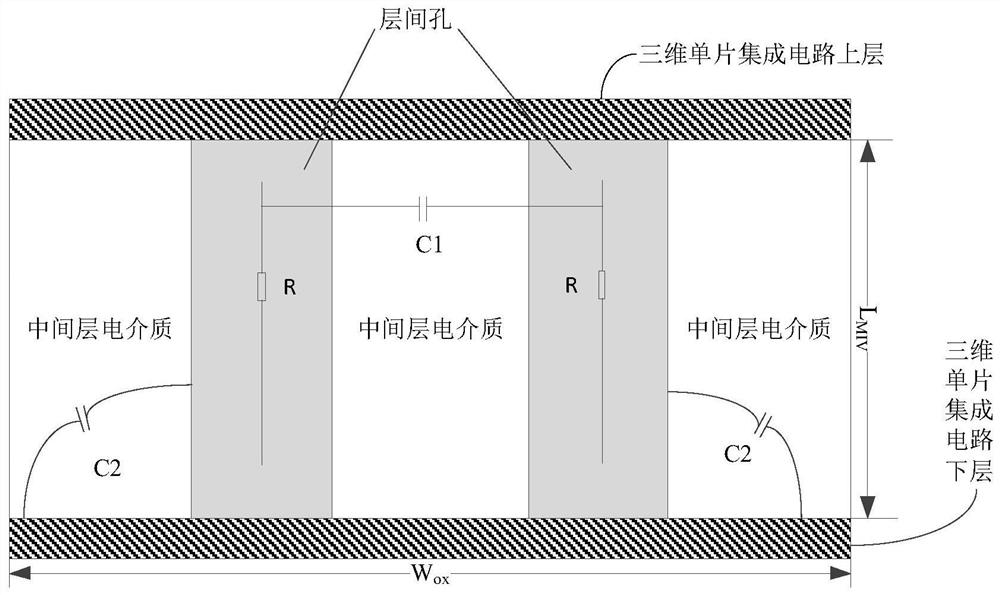
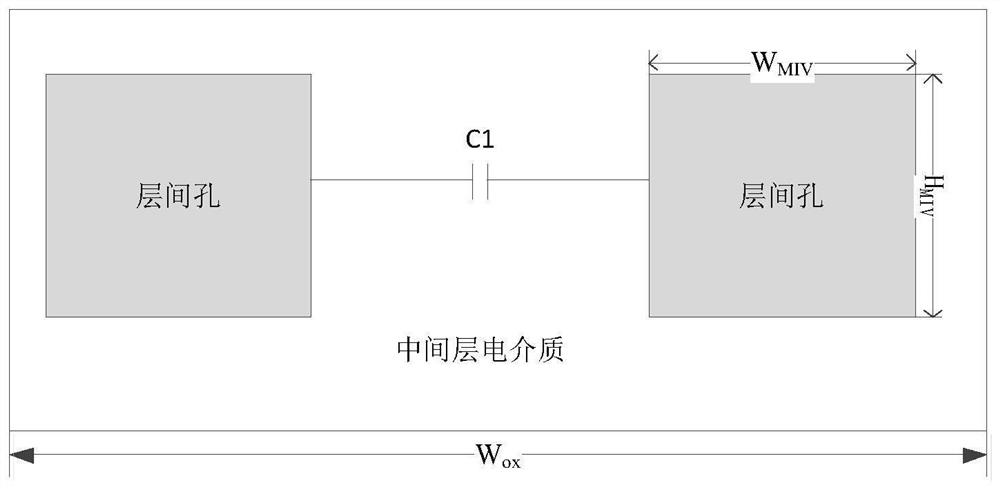
Interlayer hole modeling method, anti-single event effect analysis method and device
PendingCN114818237ADesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designDielectricElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveCN104183472AAvoid short-circuiting problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricManufacturing technology
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Filling medium compression section rectangular waveguide for fracturing rock
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Memory cell that includes a carbon nano-tube reversible resistance-switching element and methods of forming the same
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Combinable circuit structure
PendingCN108513437ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePrinted circuits structural associationsDielectricLiquid metal
Owner:BEIJING DREAM INK TECH CO LTD
Radio frequency (RF) connector pin assembly
ActiveCN110622362ALine/current collector detailsTwo-part coupling devicesDielectricMechanical engineering
A radio frequency (RF) connector pin assembly is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the RF connector pin assembly includes a first dielectric, a second dielectric, and a contact pin positioned in ahousing. The contact pin has a first pin section, a second pin section, and an annular collar. Axial movement of the contact pin is limited by the annular collar moving in a gap between the first andsecond dielectrics. The first pin section is adapted to provide electrical continuity with an external component, for example, a connector, and the second pin section terminates distally in a connection feature, which may be connected to an external structure, for example, a printed circuit board (PCB). The contact pin axially moves, or floats, in response to movement of the connection feature byengagement with the external structure. Multiple housings may be independently removably mounted in a block with independently movable contact pins.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Organic optoelectronic devices based on a single-crystal pt complex
PendingUS20220359837A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMetallic electrode
A photodetection device is configured to detect light and the photodetection device includes a substrate having a largest surface; a dielectric formed over the largest surface of the substrate; a first metallic electrode formed on the dielectric; a second metallic electrode formed on the dielectric, at a given distance from the first metallic electrode, to form a channel; and a single-crystal linear-chain polyfluorinated dibromo-platinum(II) diimine complex located in the channel.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-channel broadband coaxial rotary hinge and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN112201913AReduce radial sizeIncrease working frequencyWaveguide type devicesDielectricHigh bandwidth
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Micro-electromechanical switch fabricated by simultaneous formation of a resistor and bottom electrode
The present invention provides a method and product-by-method of integrating a bias resistor in circuit with a bottom electrode of a micro-electromechanical switch on a silicon substrate. The resistor and bottom electrode are formed simultaneously by first sequentially depositing a layer of a resistor material (320), a hard mask material (330) and a metal material (340) on a silicon substrate forming a stack. The bottom electrode and resistor lengths are subsequently patterned and etched (350) followed by a second etching (360) process to remove the hard mask and metal materials from the defined resistor length. Finally, in a preferred embodiment, the bottom electrode and resistor structure is encapsulated with a layer of dielectric which is patterned and etched (370) to correspond to the defined bottom electrode and resistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap