Memory cell that includes a carbon nano-tube reversible resistance-switching element and methods of forming the same
A technology of memory cells and carbon nanotubes, used in electrical components, static memory, digital memory information, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
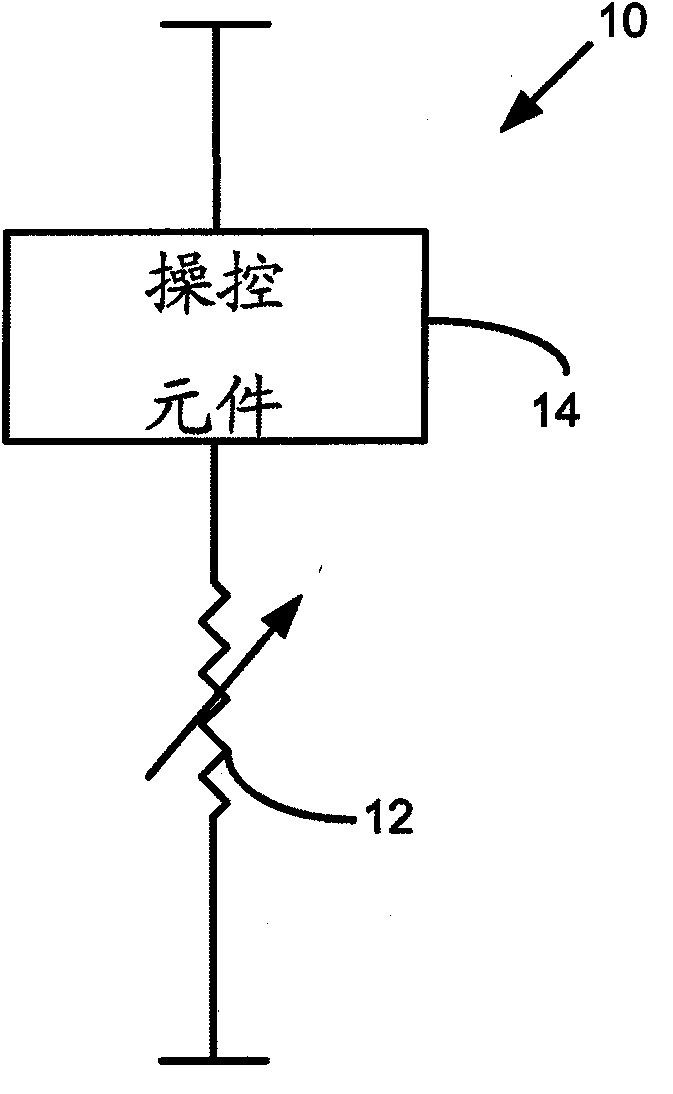
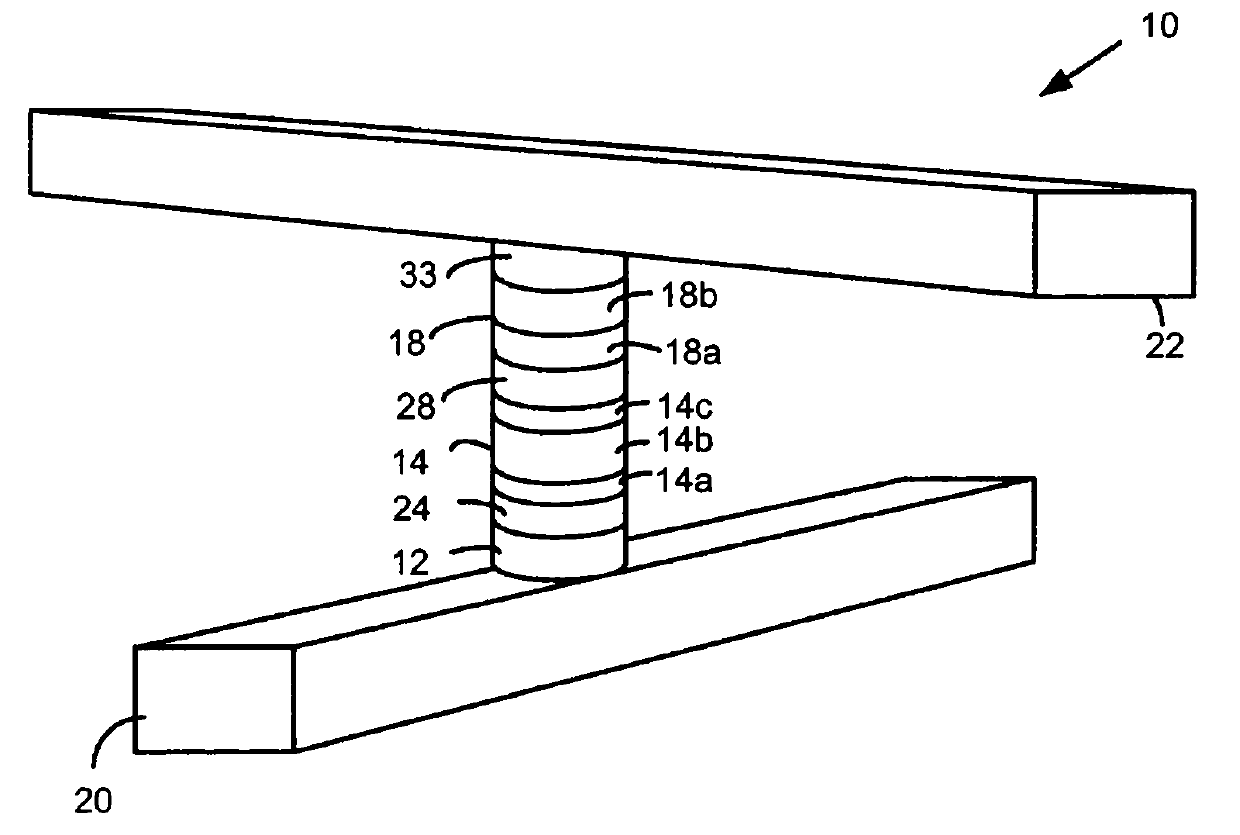
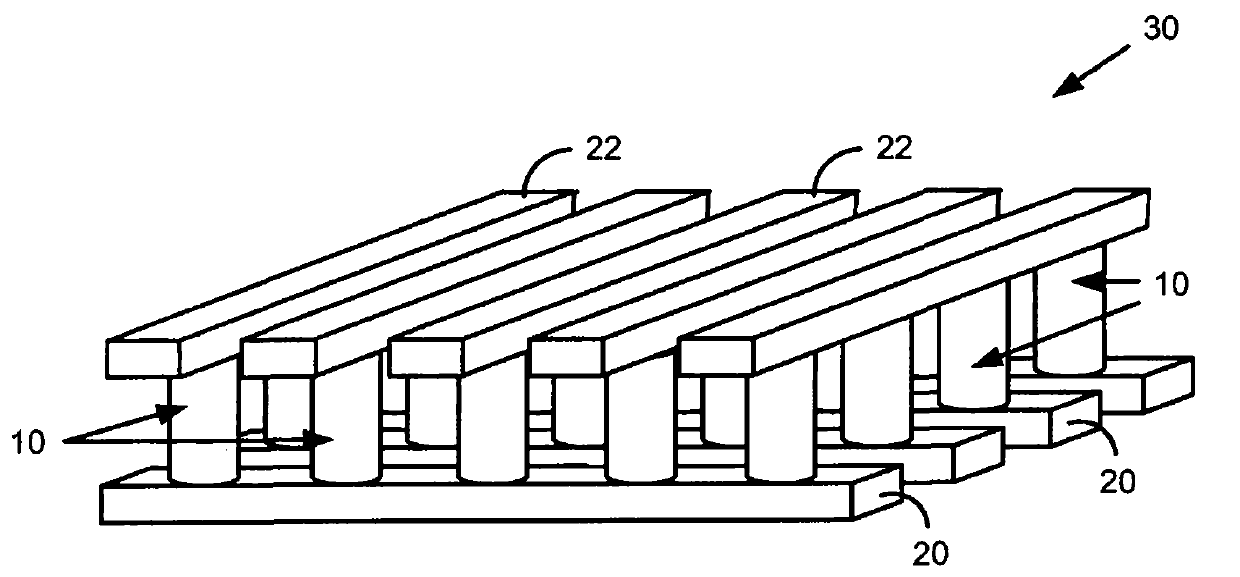
[0018] Some CNT materials have been shown to exhibit reversible resistance-switching properties that may be suitable for use in non-volatile memory. However, when CNT materials are used in forming memory cells, the deposited or grown CNT materials typically have rough surface topography, and significant thickness variations, such as many peaks and valleys. The rough surface topography of CNT material can cause difficulties in forming memory cells. For example, the rough surface topography of CNT materials may make the CNT materials difficult to etch without overetching the underlying substrate, increasing manufacturing costs and complexity associated with their use in integrated circuits. Additionally, voids in the surface of the CNT material may be penetrated by conductive material deposited over the CNT material and cause vertical shorts to occur. Although the peaks on the surface of the CNT material can be removed by planarization, any valleys or voids that remain after plana
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap