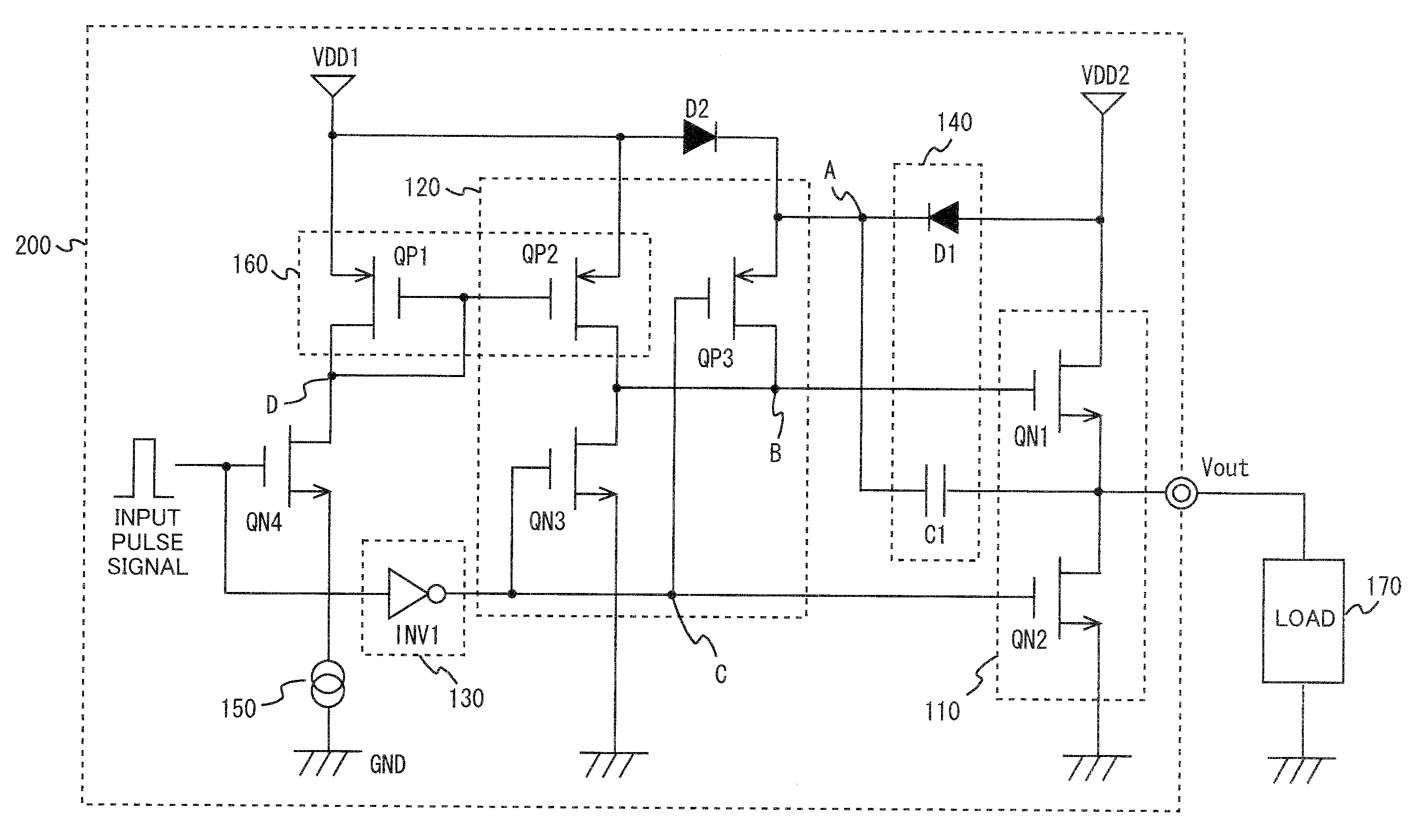
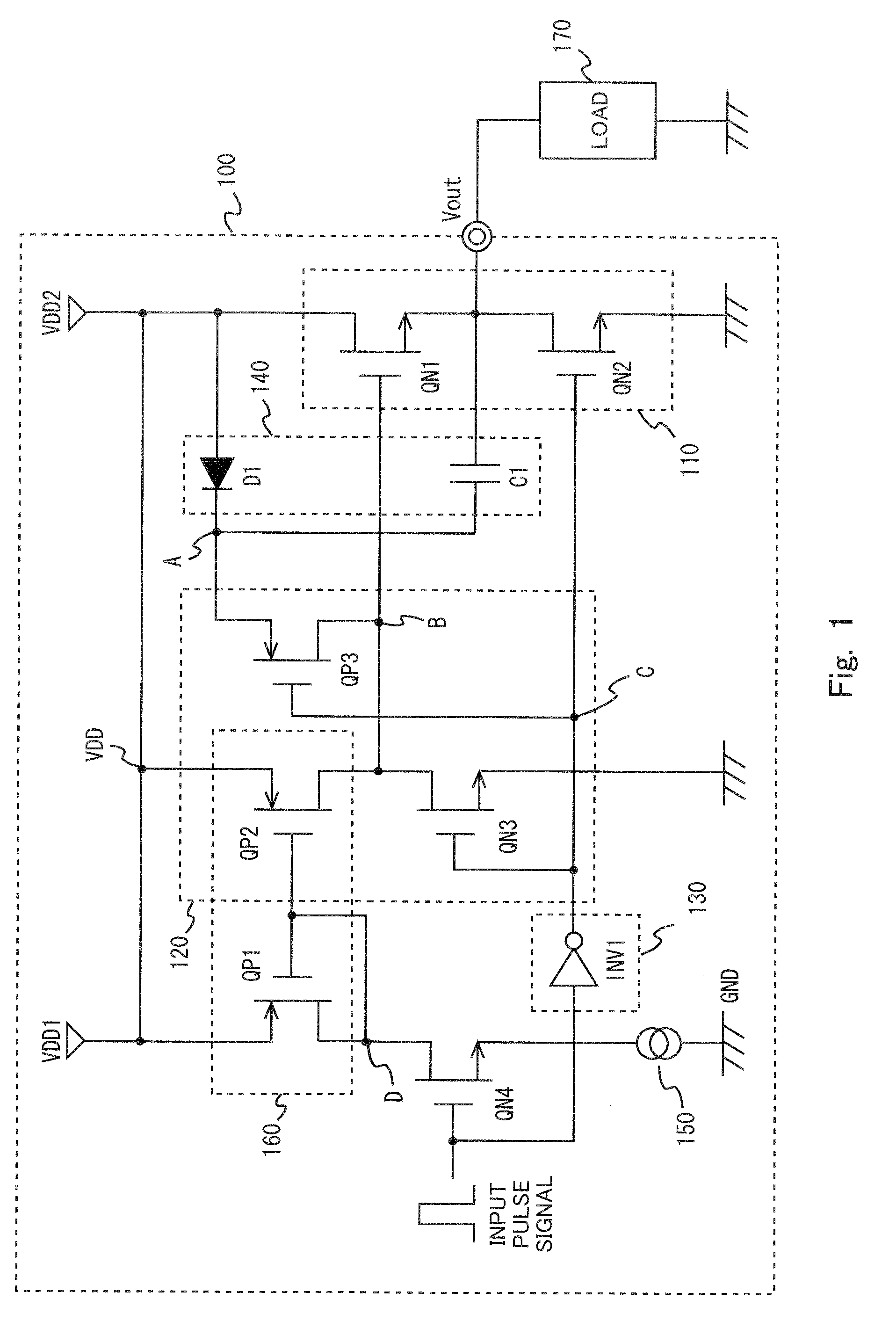
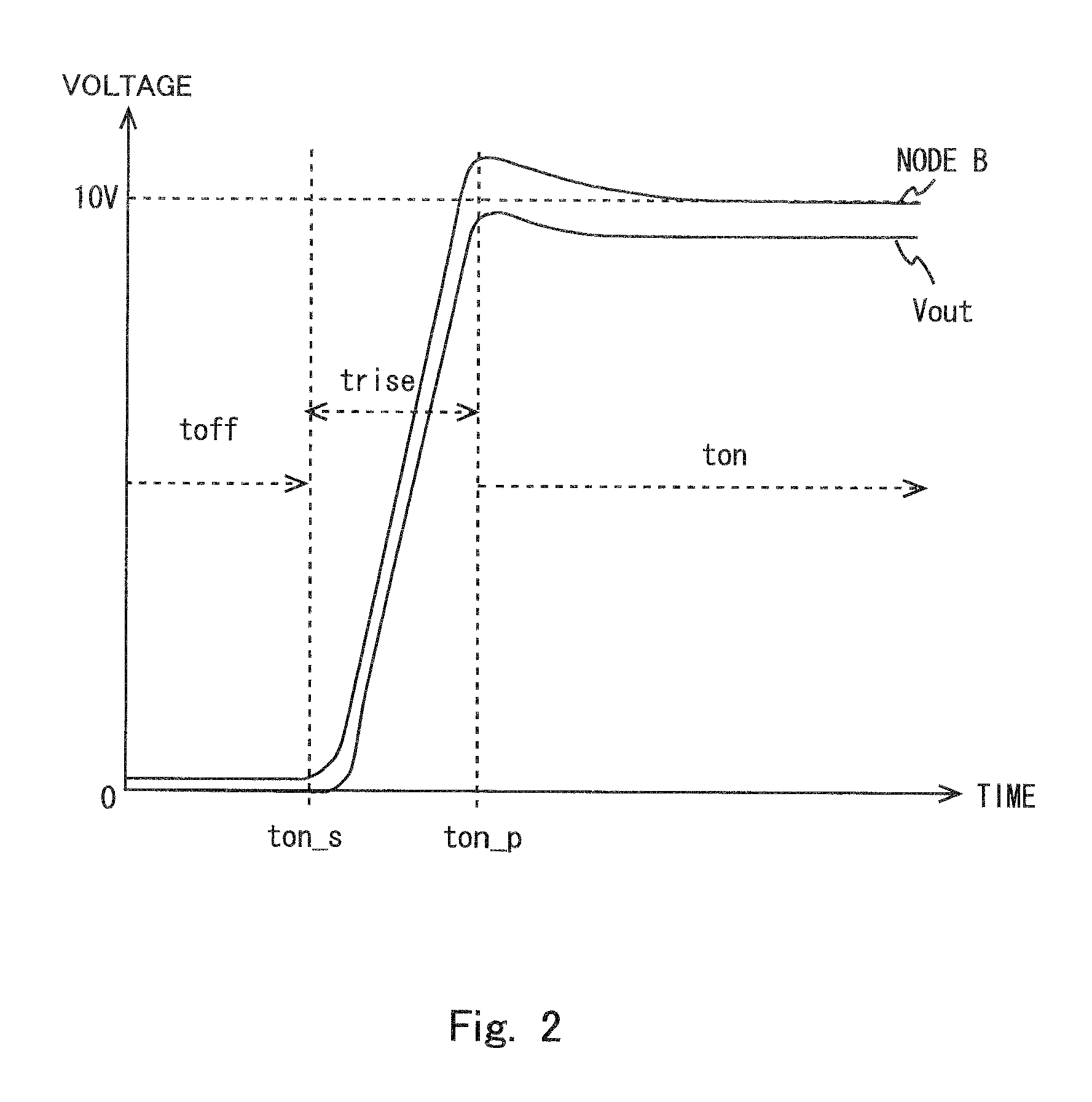
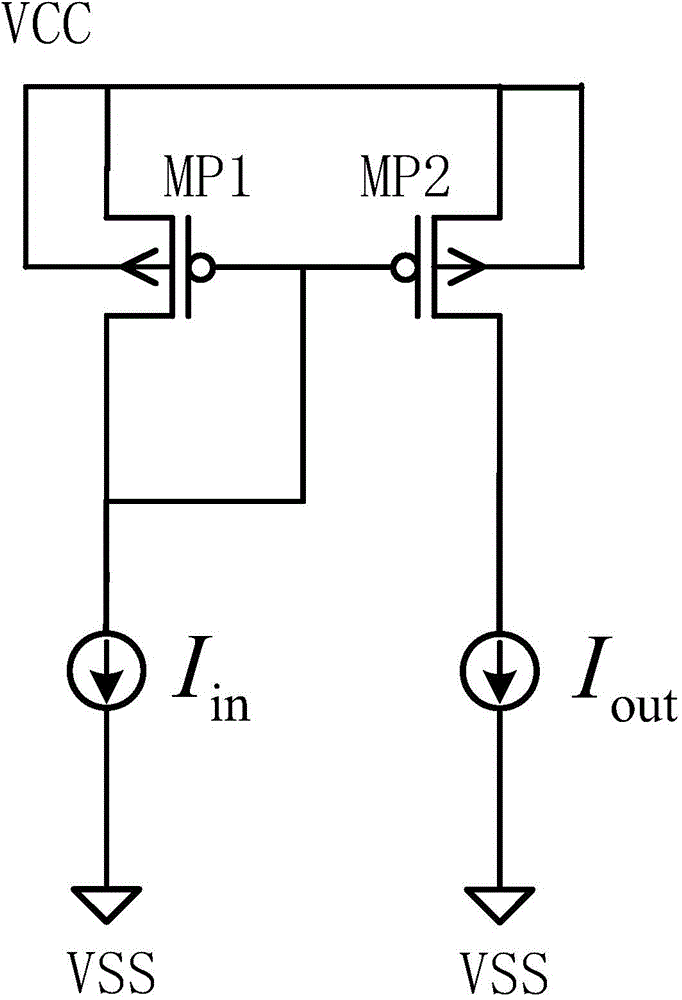
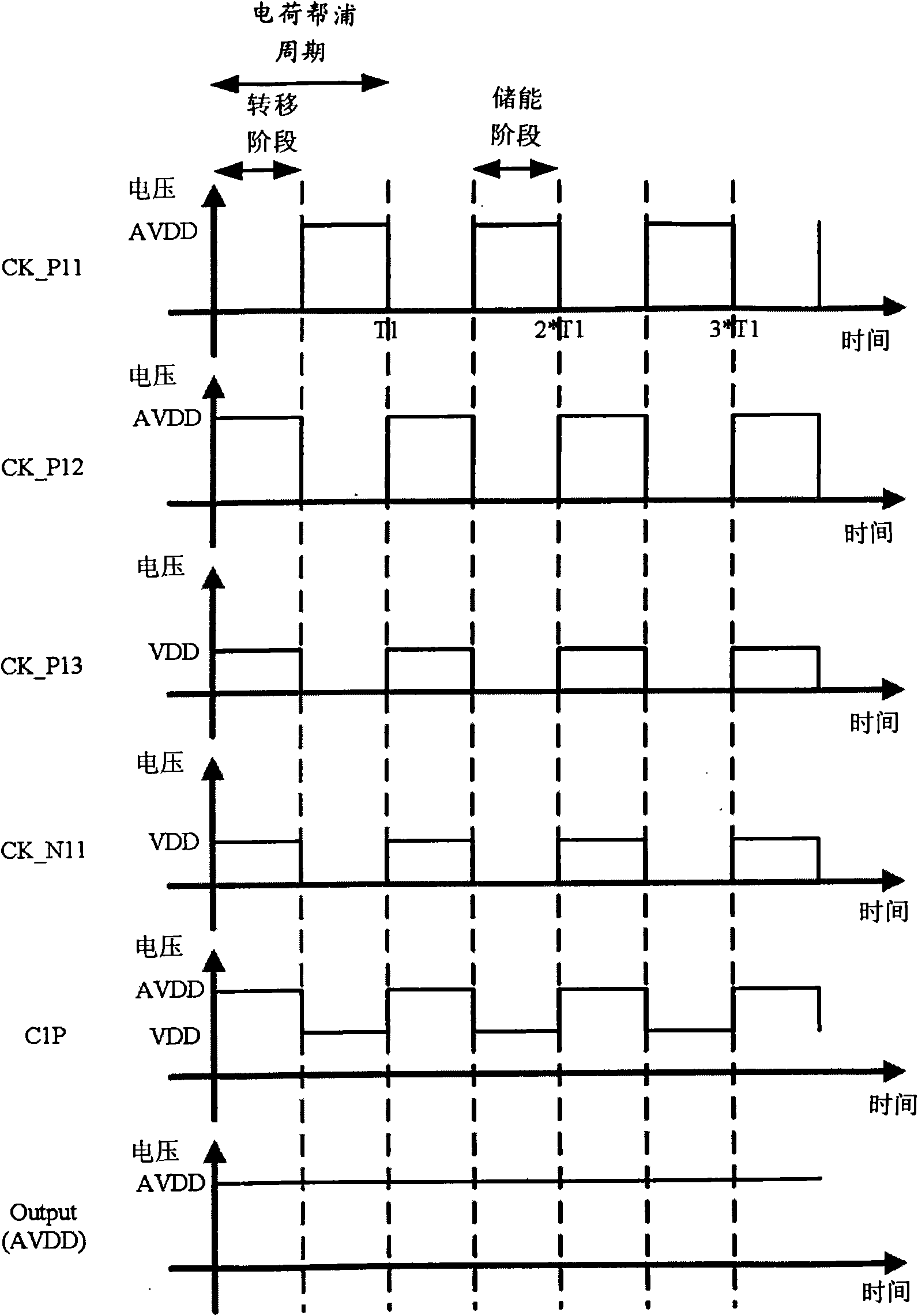
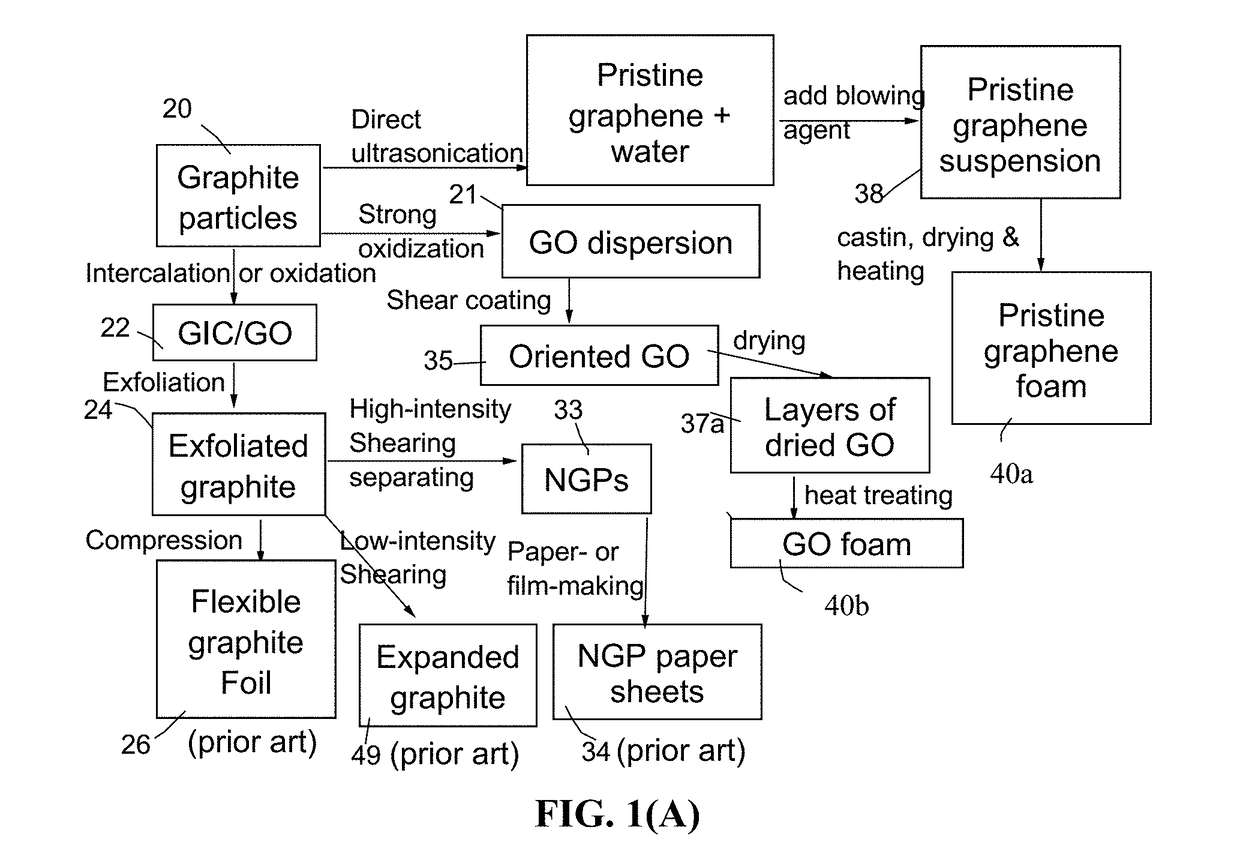
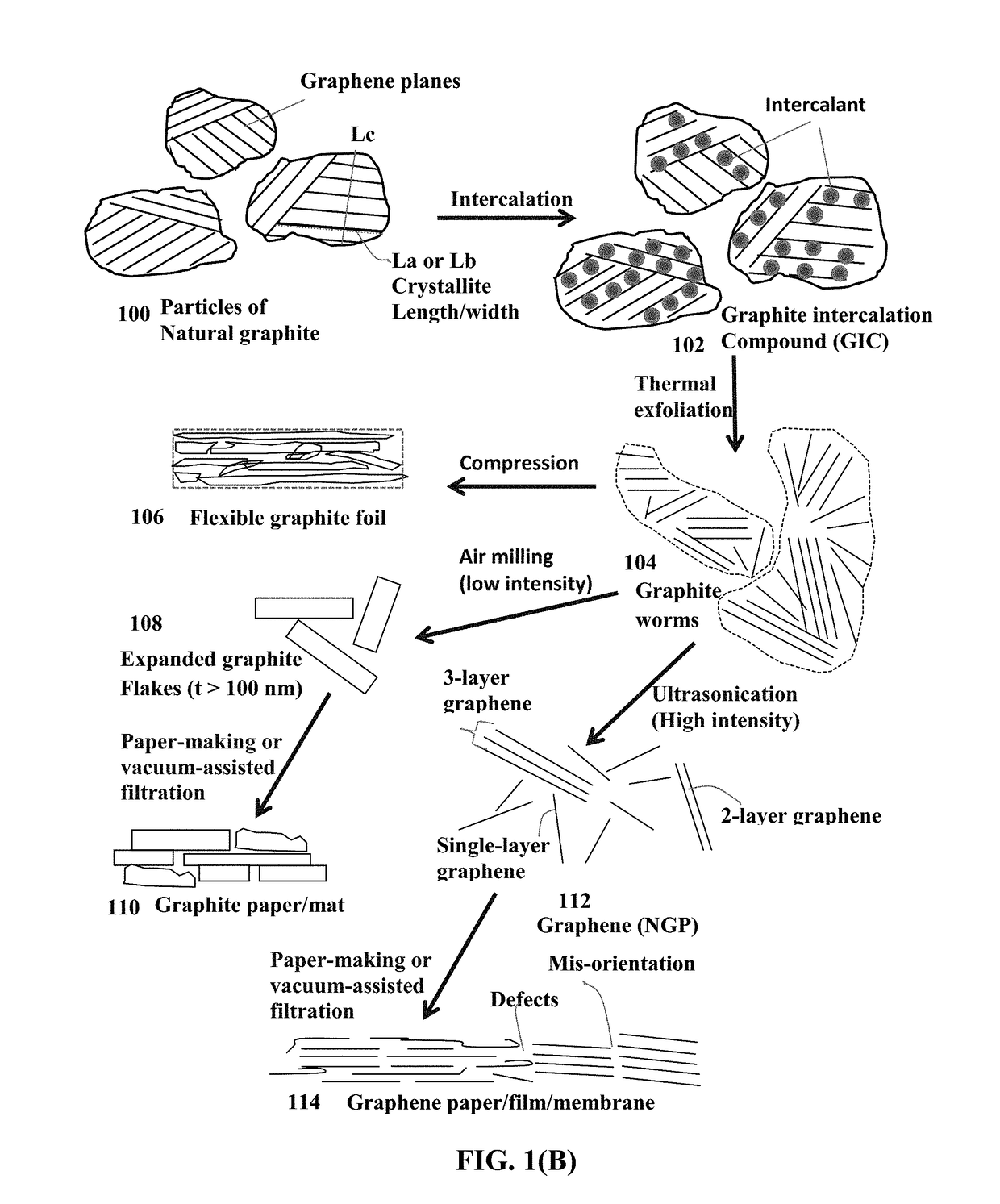
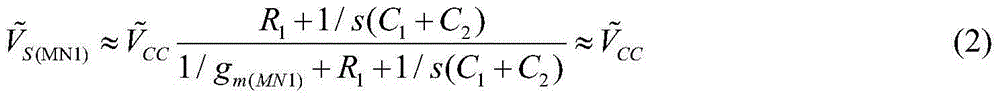Patents
Literature
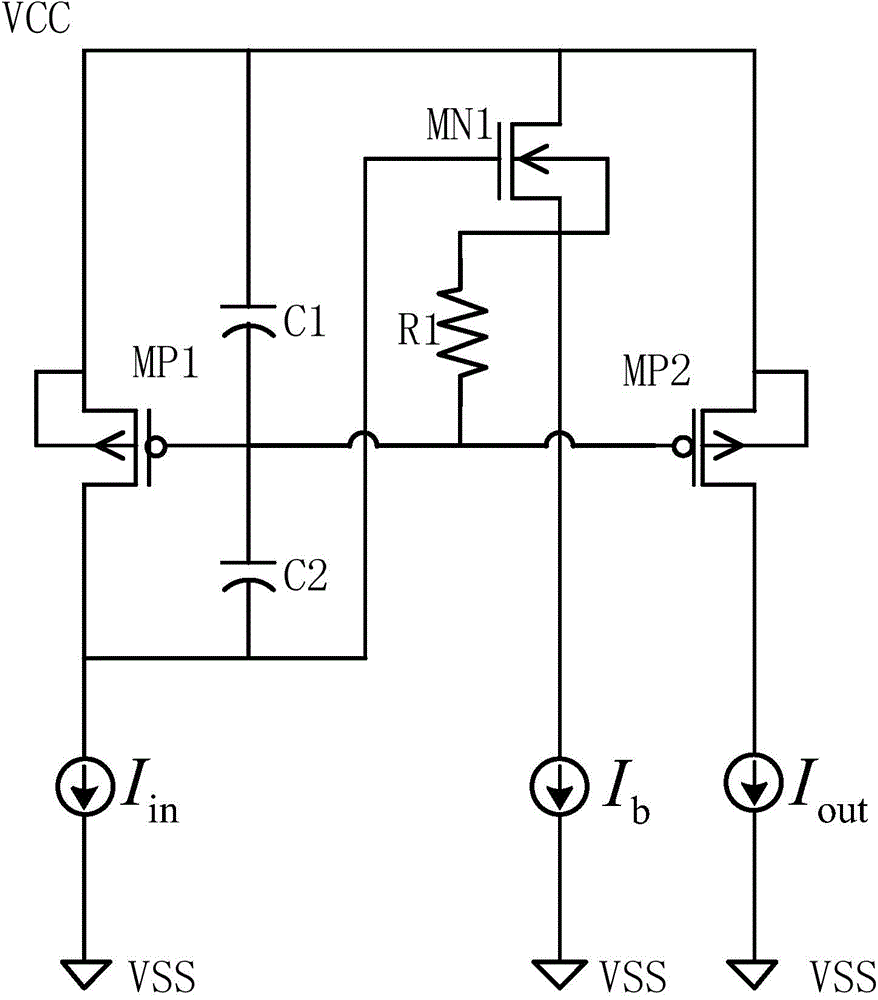
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
140 results about "Capacitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
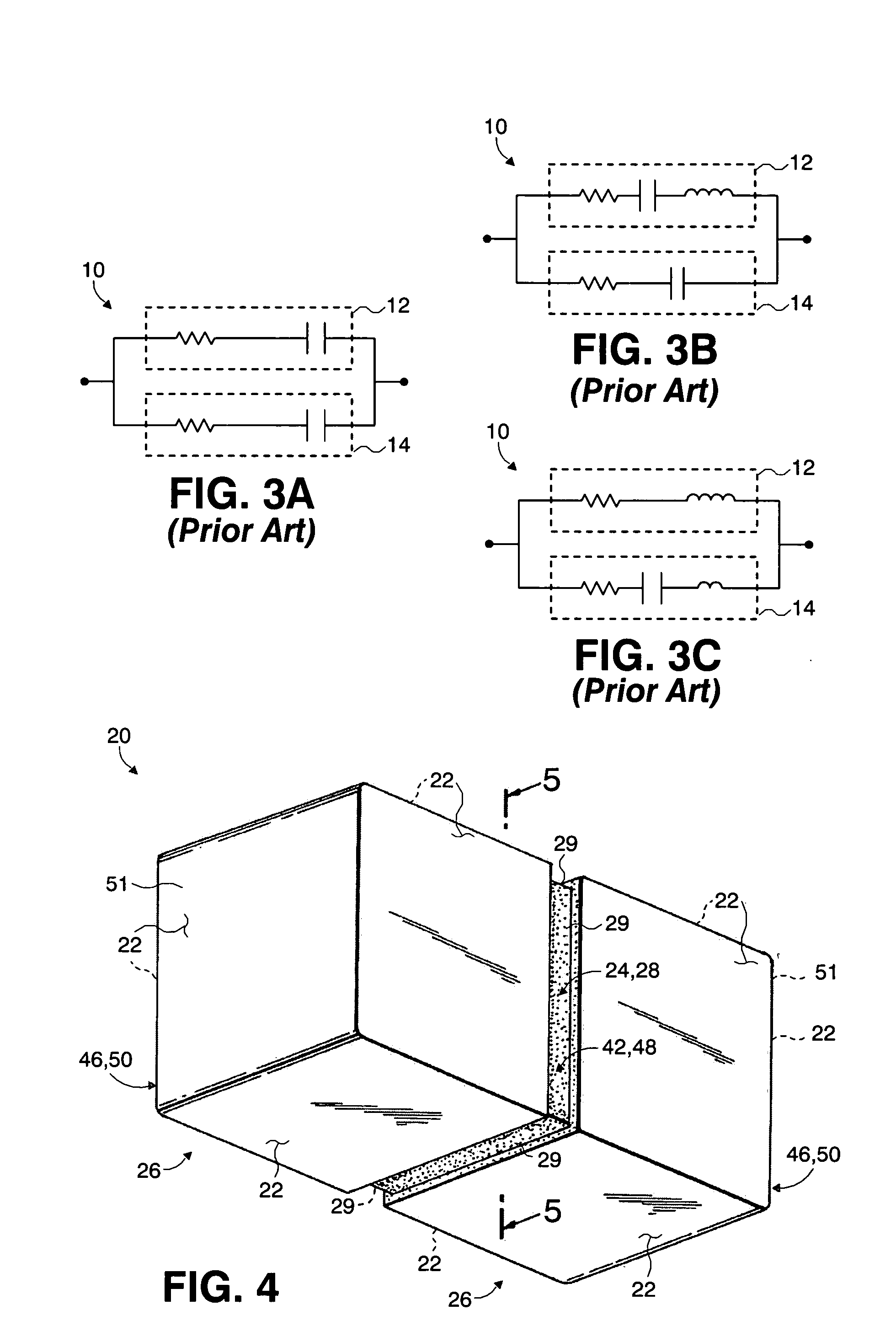
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as a condenser or condensator. The original name is still widely used in many languages, but not commonly in English.
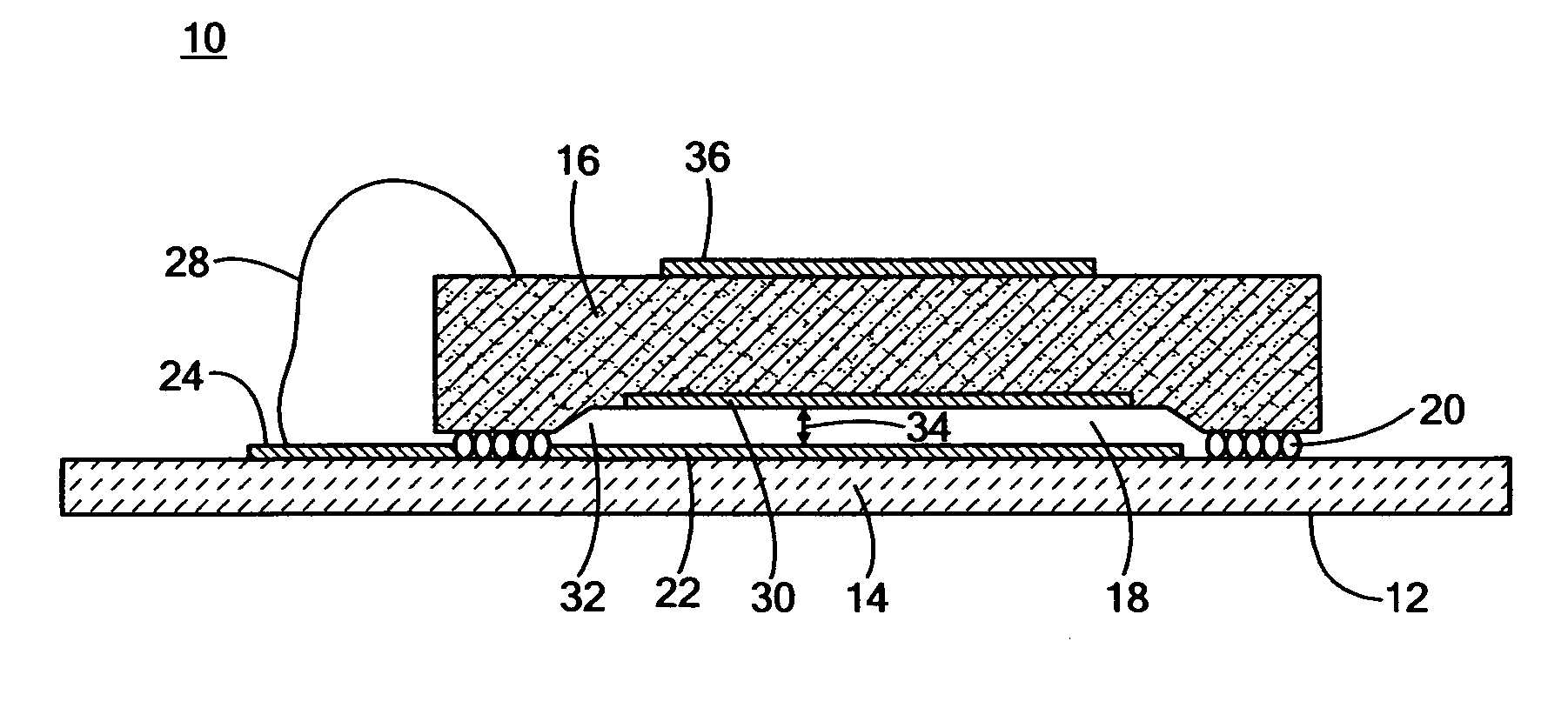
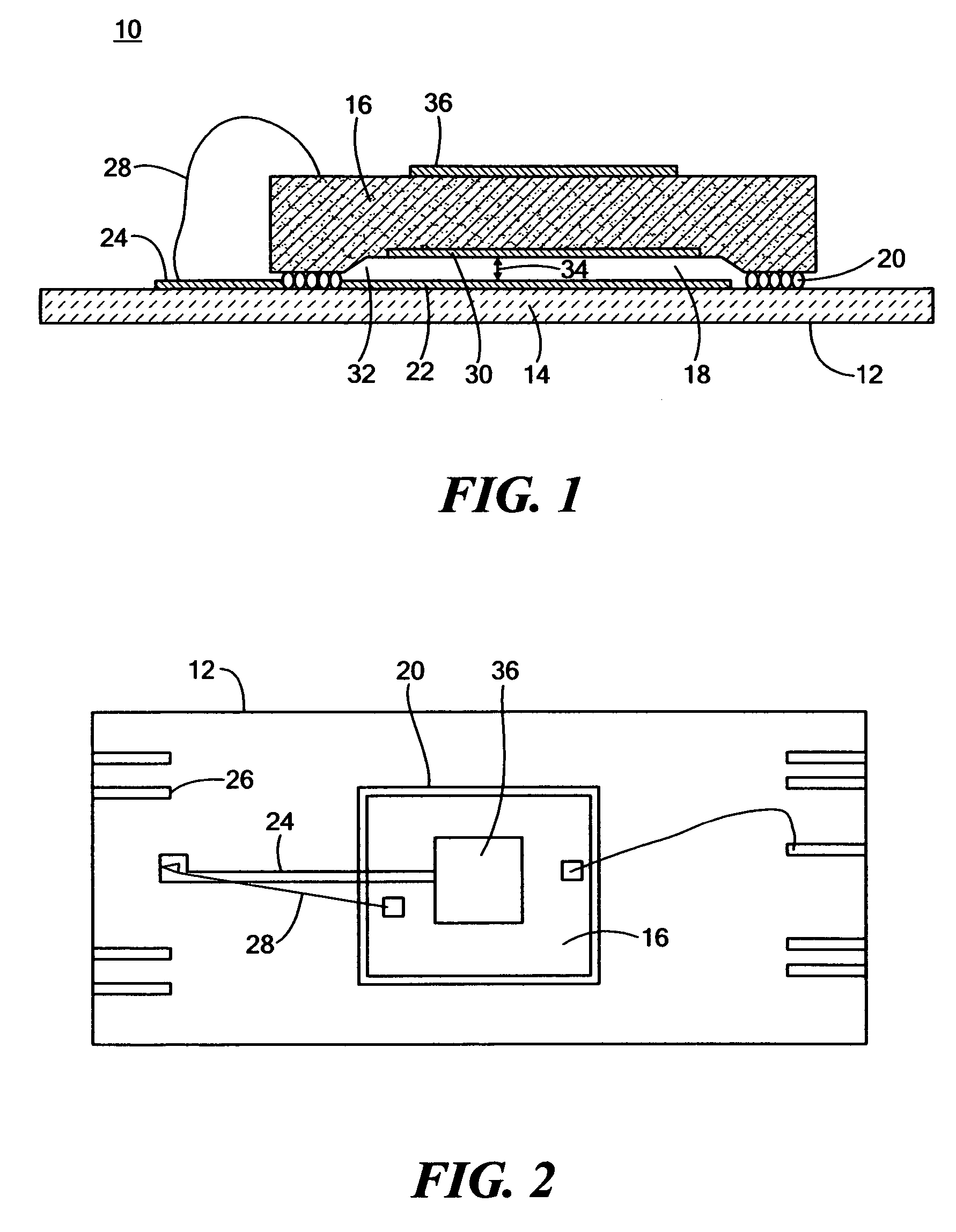
Capacitive measurement system
InactiveUS20050099188A1Reduce and eliminate effectResistance/reactance/impedenceConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringCapacitive measurement
Sensor circuits for the measurement of small variations in the value of a sensing capacitor. An alternating voltage excites the sensing capacitor a predetermined frequency whereby the voltage on the sensing capacitor reverses polarity. This voltage on the sensing capacitor is sampled each time the voltage reverses polarity. An accumulator accumulates the sampled charges from the sensing capacitor. An output signal that represents the charge in the charge accumulating means indicates the measured capacitance.
Owner:BAXTER LARRY K
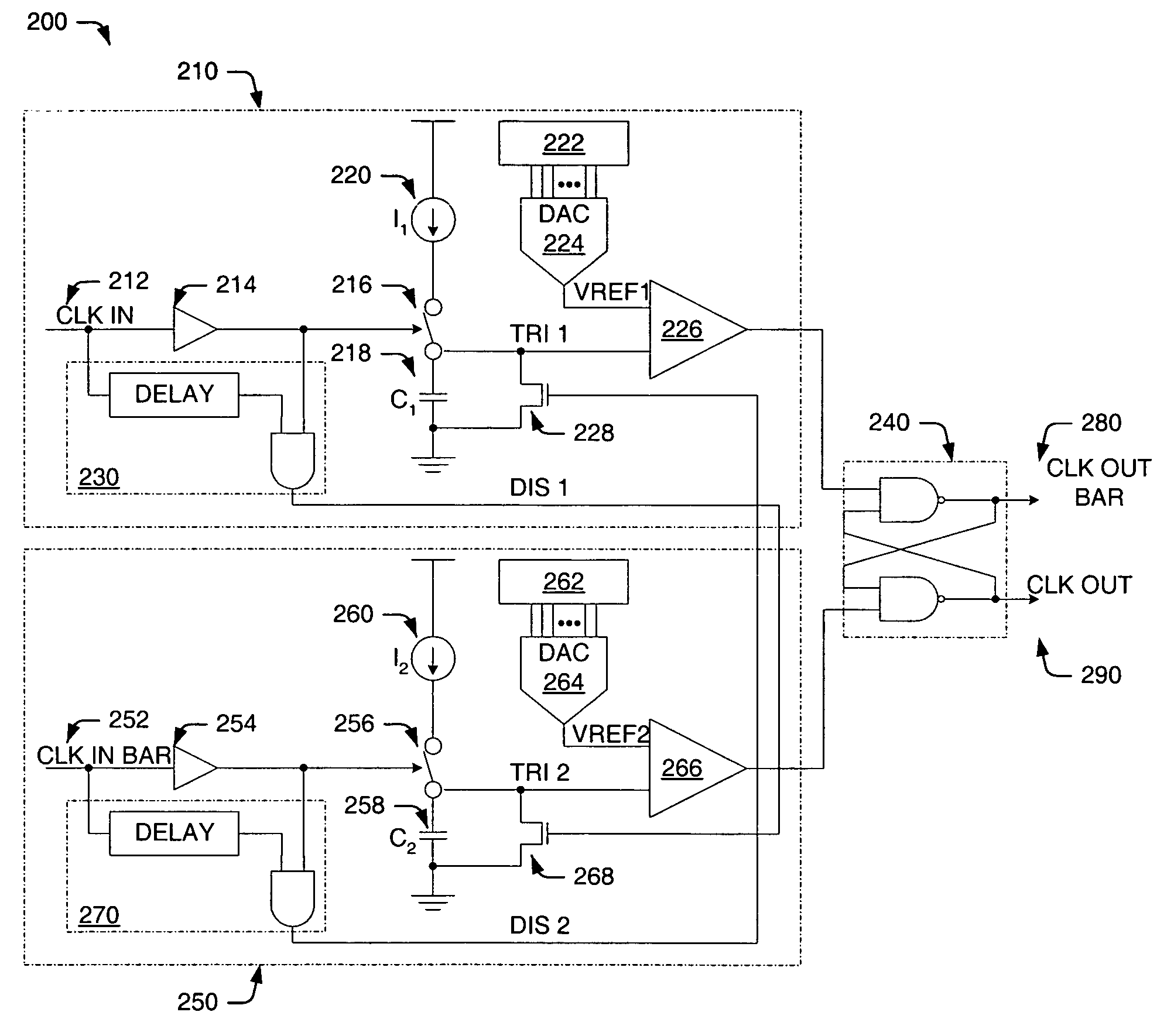
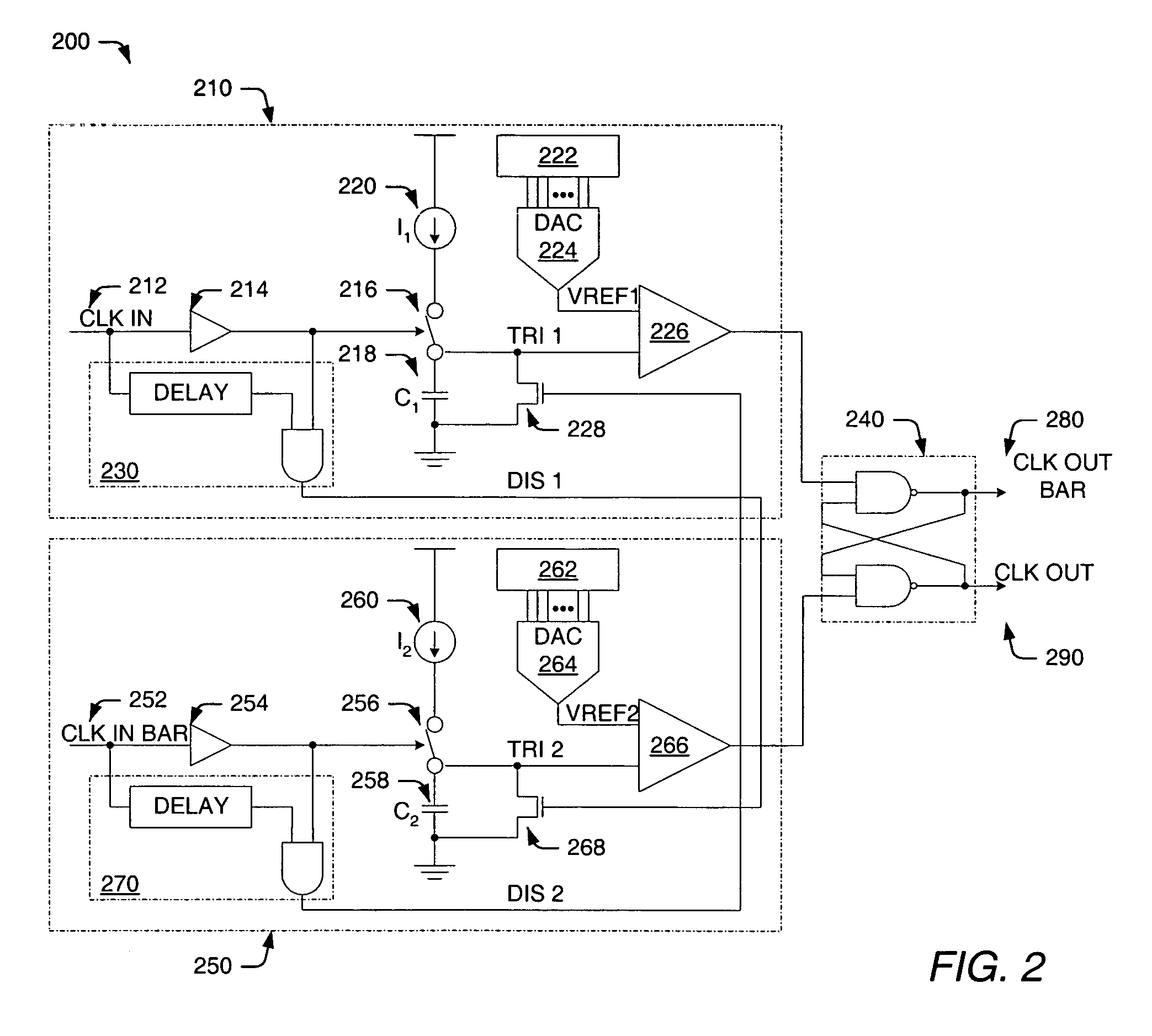
Programmable phase shift and duty cycle correction circuit and method
ActiveUS7138841B1Manipulation where pulse delivered at different timesElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitPhase shifted
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
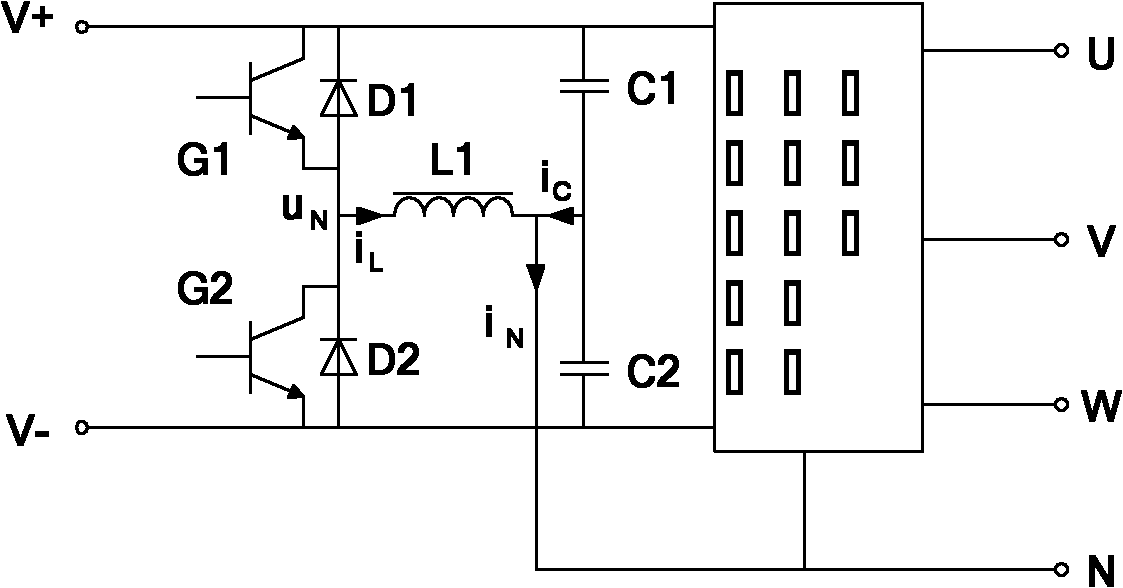
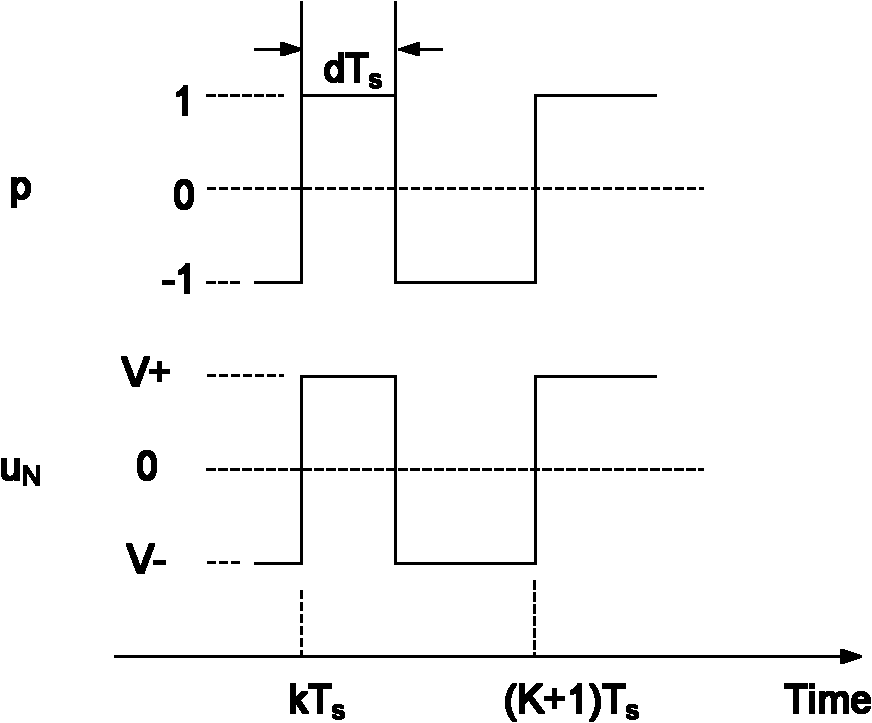
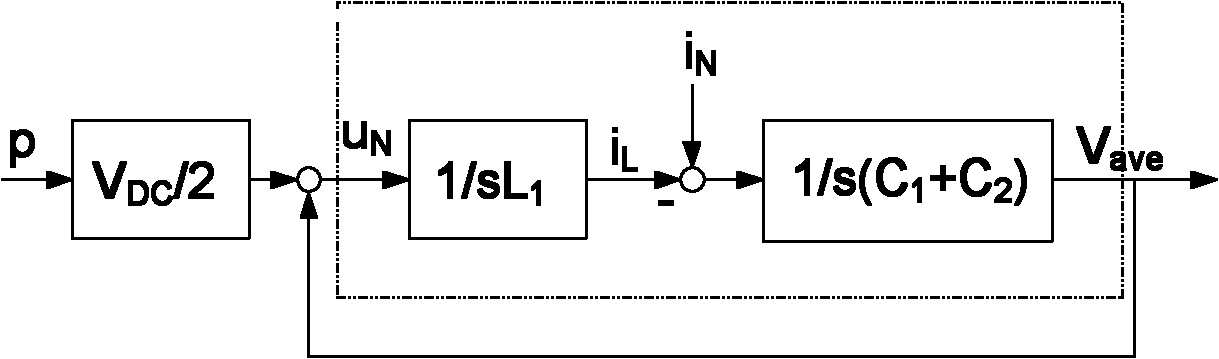
AC-to-ac power converter without a dc link capacitor
InactiveUS6839249B2Easy to switchConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric power transfer ac networkCurrent modeAC power
An ac-to-ac power converter includes a source-side inverter that is operated in current mode and a drive side inverter that is operated in commutation mode. The source side inverter performs current regulation during a first portion of each modulating cycle and space vector modulation during a second portion of each modulating cycle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Polymer resin composition, related method for forming a pattern, and related method for fabricating a capacitor
InactiveUS20070249117A1Reduce in quantityReduce processing timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-link(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Differential pipelined analog to digital converter with successive approximation register subconverter stages
InactiveUS6879277B1Improve conversion speedReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAnalog-to-digital converterCapacitor
Pipelined analog to digital conversion systems are provided having cascaded multi-bit successive approximation register subconverter stages. Capacitor arrays are provided in the subconverter stages, where switching logic selectively couples the capacitors to operate in sample, conversion, and residue amplification modes for generating multi-bit subconverter digital outputs and analog subconverter residue outputs. In one implementation, the capacitors are switched according to a thermometer code to reduce differential converter non-linearity, and the first subconverter stage gain is reduced to improve the conversion system bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and circuit for controlling an electric power plant
InactiveUS20060132103A1High precisionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlCapacitancePower station
A control circuit is for an electric power plant including an asynchronous generator of an AC voltage, a motor to rotate a rotor of the asynchronous generator as a function of a first control signal of a developed motor torque, and a bank of capacitors coupled to the asynchronous generator and having a total capacitance varying as function of a second control signal. The control circuit may include a monitor circuit to monitor at least one parameter of the AC voltage, and a control signal generator circuit cooperating with the monitor circuit to generate the first and second control signals by soft-computing techniques both as a function of the frequency and of a representative value of an amplitude of the AC voltage to make the AC voltage have a desired amplitude and frequency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Amorphous silicon image sensor with storage capacitor structure
ActiveCN102157533AIncreased charge storage capacityImprove signal dynamic rangeRadiation controlled devicesCapacitanceDynamic range
Owner:CARERAY DIGITAL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Rain sensor with sigma-delta modulation and/or footprinting comparison(s)
InactiveUS20070157721A1Hazard reductionReduce distractionsDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
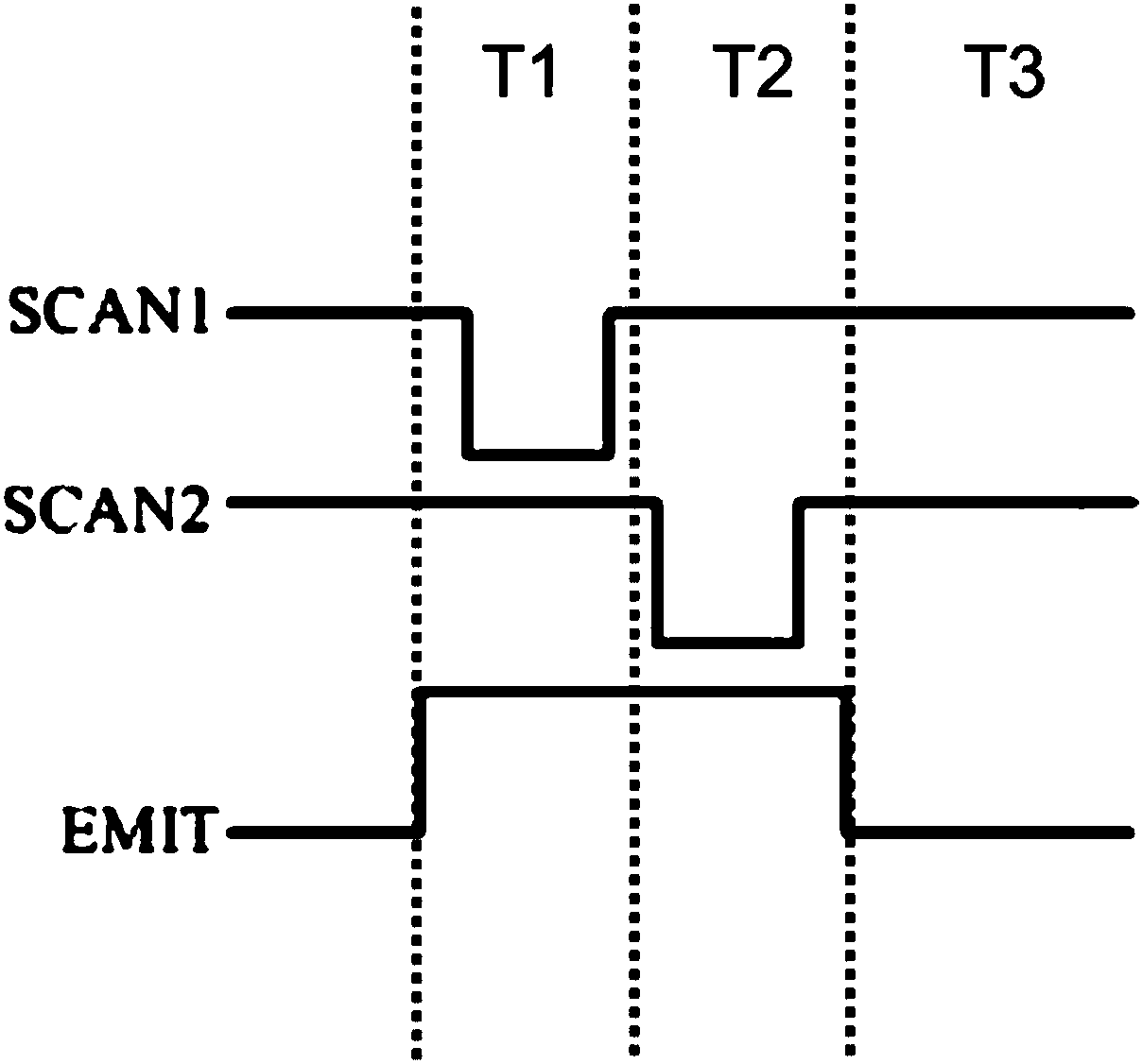
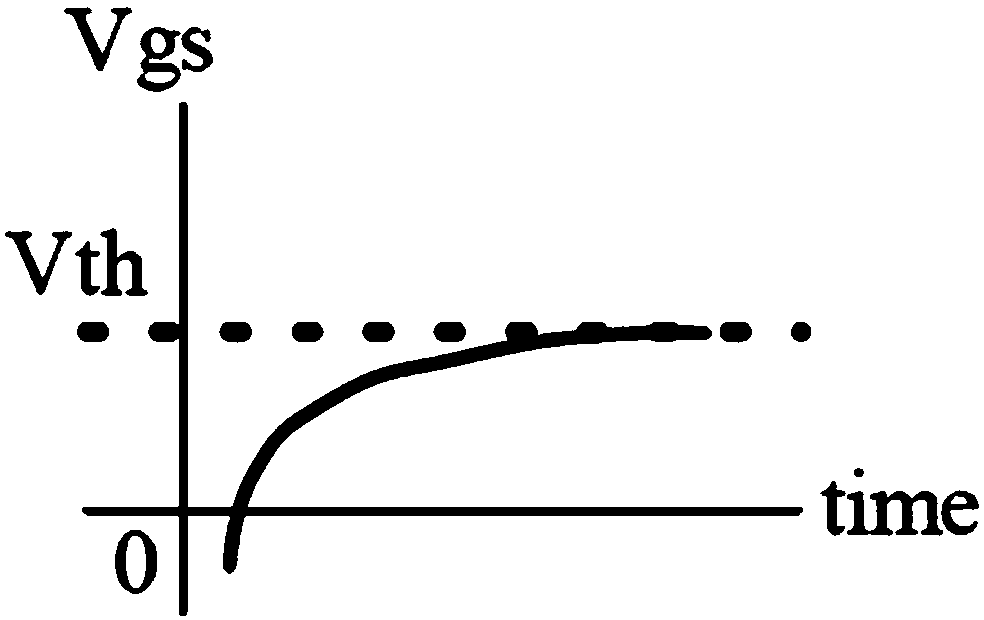
Pixel circuit, driving method of pixel circuit, display panel, and driving method of display panel
ActiveCN108389549AReduce the number of timesImprove the compensation effectStatic indicating devicesElectricityControl signal
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sealed capacitive sensor
InactiveUS20060191351A1Low costRobust and reliable and accurateFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCapacitor
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Capacitive liquid level detector for direct methanol fuel cell systems
InactiveUS20080282795A1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementReactant parameters controlMachines/enginesFuel cellsDielectric layer
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Pixel driving circuit, pixel driving method and light emitting display device
ActiveUS20110304593A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentDisplay device
A pixel driving circuit, a pixel driving method and a light emitting display device are provided in the present invention. The pixel driving circuit includes first through fifth transistors and a capacitor and is for driving a light emitting diode. The third transistor forms a diode connection to make information of the threshold voltages of both the third transistor and the light emitting diode be stored in the capacitor in a data writing period. In a light emitting period, the second transistor compensates drift variation of the threshold voltages of the third transistor and the light emitting diode according to the information stored in the capacitor to provide a stable driving current for driving the light emitting diode.
Owner:E INK HLDG INC
Output drive circuit
InactiveUS20090315595A1Stable output voltageStable outputTransistorElectric pulse generatorEngineeringCapacitor
An output drive circuit includes: a totem-pole output including: a high-side transistor (HST) with drain and source, an output stage power supply voltage applied to the drain, the source connected to the first node (N1); and a low-side transistor with source and drain, a ground voltage applied to the source, the drain connected to N1; and a bootstrap part including a capacitor supplying charge to a gate of HST when on, the charge being charged when HST is off, and one terminal of the bootstrap part connected to N1, the output drive circuit further including: a first transistor (T1) that conducts when HST is to be on, T1 connected between a drive circuit power supply voltage and the gate of HST; and a second transistor conducting when HST is to be turned on, the second transistor connected between the other terminal of the capacitor and HST gate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Current mirror for low supply voltage
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High surface area and low structure carbon blacks for energy storage applications
ActiveUS20120214000A1Increase capacitanceEfficient separationPigmenting treatmentCapacitor and primary/secondary cellsApparent densityElectrochemical double layer capacitor
The present invention, in part, relates to a carbon black having a) a nitrogen BET surface area (BET) of from about 600 m2 / g to about 2100 m2 / g, b) a CDBP value in mL / 100 g of from about (−2.8+(b*BET)) to about (108+(b*BET)), where b is 0.087 and BET is expressed in m2 / g, and c) an apparent density (p, g / cm3) of at least about 0.820+q*BET, where q=−2.5×10−4, as determined at a compressive force (P) of 200 kgf / cm2 on dry carbon black powder. Energy storage devices, such as electrochemical double layer capacitors (EDLC's), containing the carbon black are also disclosed. Methods for making the carbon blacks and EDLC's made with them are also provided.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Orientation-insensitive ultra-wideband coupling capacitor and method of making
ActiveUS20050057886A1Avoid disadvantagesMultiple fixed capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesUltra-widebandCoupling
Owner:AMERICAN TECH CERAMICS CORP
Sampling hold circuit
InactiveCN103036569ALeak won'tImprove linearityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceLinearity
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
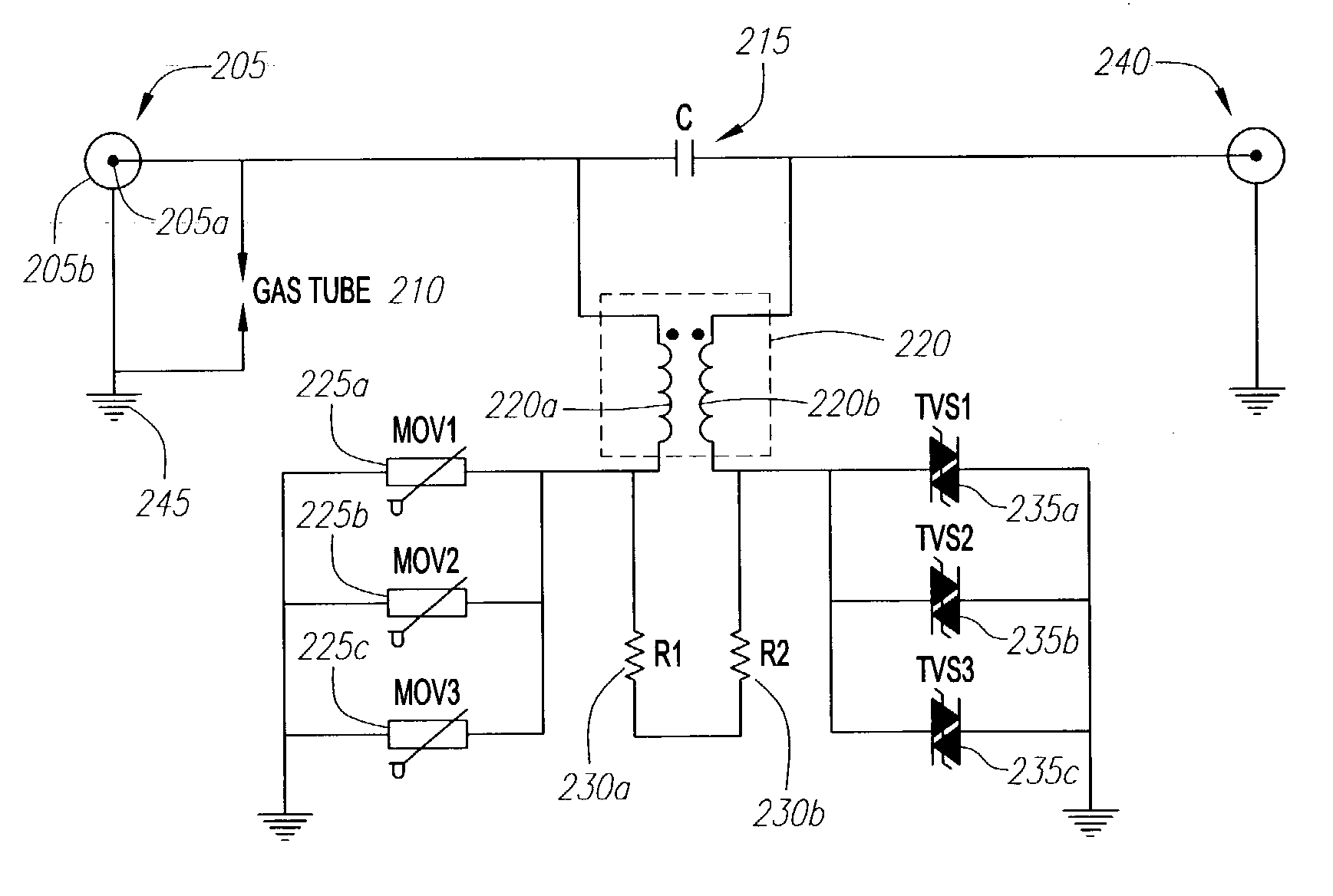
Circuit for diverting surges and transient impulses
InactiveUS20050259376A1High bandwidthSmall sizeCoupling device detailsEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectrical conductorTransformer
Owner:INFINITE ELECTRONICS INT INC
Non-volatile ferroelectric memory with high read current and operation method thereof
ActiveCN107230676AImprove read and write speedLarge read currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesIn planeA domain
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
DC-DC converter
InactiveCN103490631ANo charge and dischargeHigh speedDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterInductor
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Module combined power quality conditioning system for tractive power supply network
InactiveCN101574935ASmall footprintReduce lossPower supply linesPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPower qualityCapacitance
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Component assembly
ActiveUS20130242517A1Well formedDistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFinal product manufactureThermal deformationEngineering
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Apparatus for deriving a plasma display panel
InactiveUS20060152448A1Reduce switching lossesReduced transient timeStatic indicating devicesWing accessoriesCapacitanceHigh concentration
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Pulse generator and continuous-time sigma-delta modulator
ActiveUS20100156686A1Avoid SNR DegradationAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Organic light emitting diode pixel compensation circuit, and display panel and display device containing the same
An Organic Light Emitting Diode pixel compensation circuit is disclosed. The circuit includes first through fifth transistors, and a storage capacitor. The first transistor is coupled to a first scan signal, a power supply voltage, and a first electrode of the storage capacitor. In addition, the second transistor is coupled to the first scan signal, a data signal, and the third transistor. The third transistor is coupled to the power supply voltage, and the fifth transistor. Furthermore, the fourth transistor is coupled to a second scan signal, the third transistor, and the storage capacitor, and fifth transistor is coupled to a light emitting signal, and the OLED. In addition, the storage capacitor is coupled to the fifth transistor, and a low-level signal and emits light based on a drive current generated by the third transistor.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Charge pump
ActiveCN101567685AImprove power efficiencyShorten rise timeReliability increasing modificationsStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceComputer module
Owner:SITRONIX TECH CORP
Rolled Supercapacitor and Production Process
ActiveUS20180330893A1Reduce electrolyte layer thicknessImprove directionHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrodesSupercapacitorOptoelectronics
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
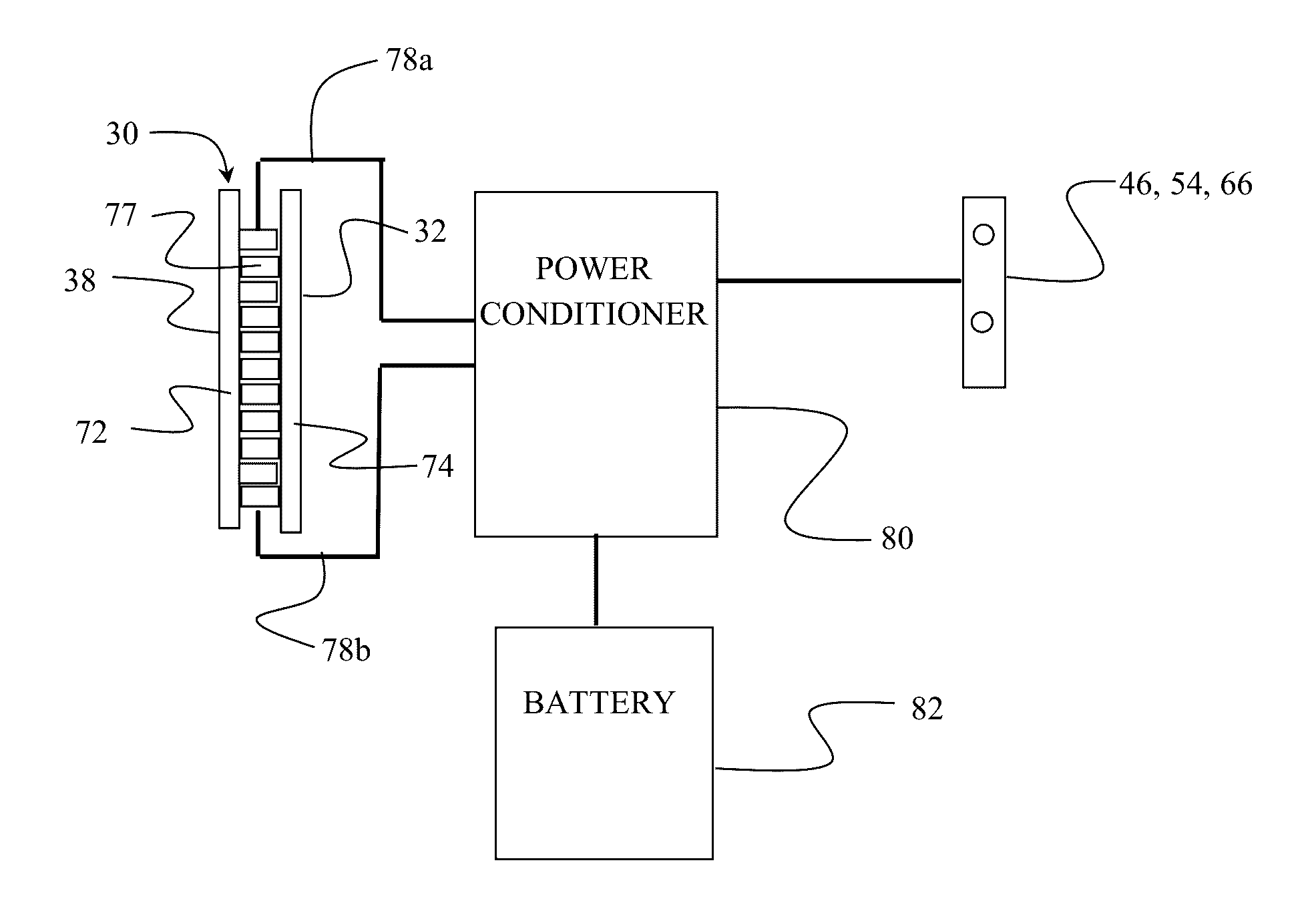
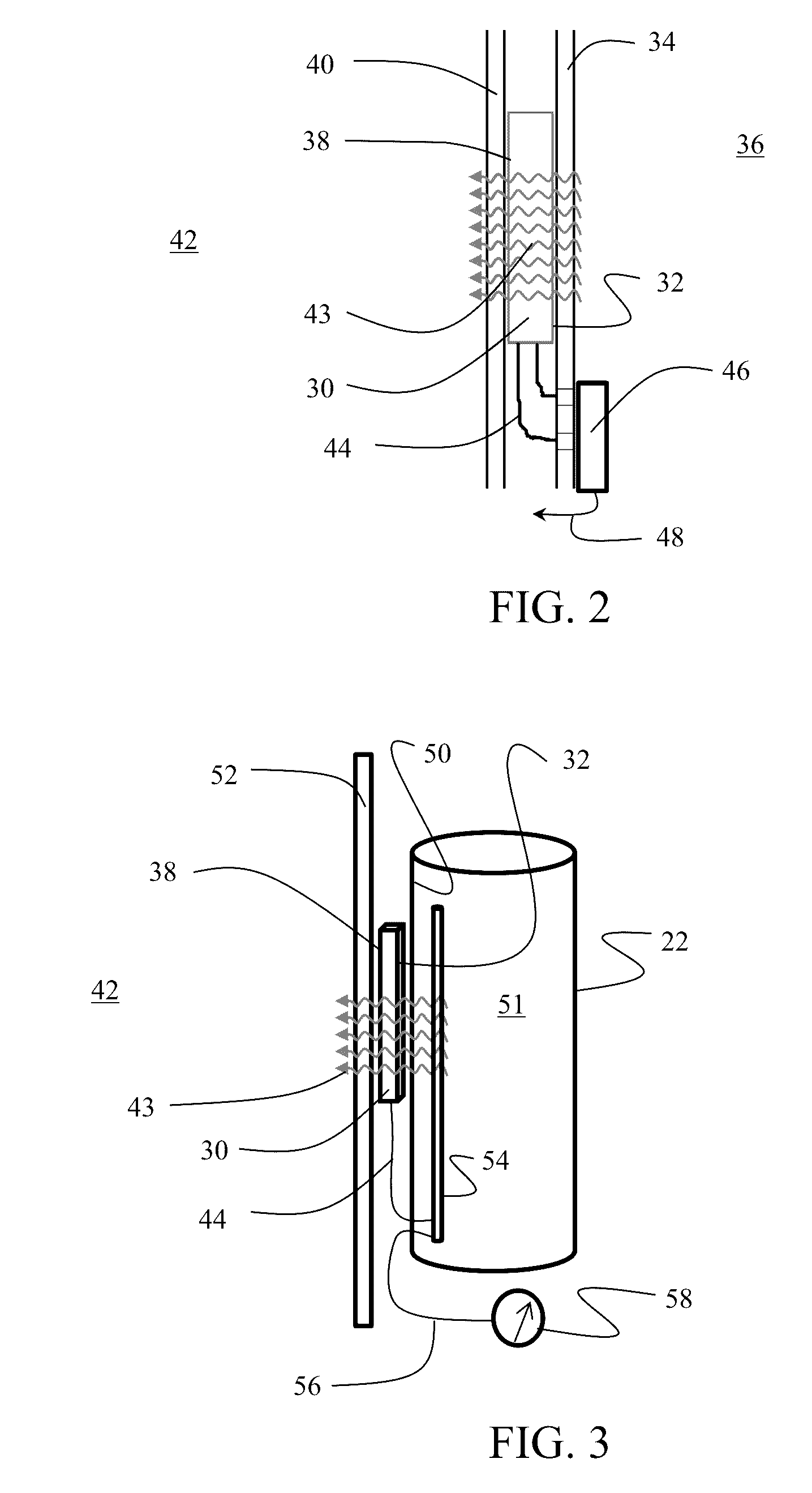
Powering aircraft sensors using thermal capacitors
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Fabrication Process Using Circuit-on-Wire
ActiveUS20150221671A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive matrixElectrical connection
A method is provided for forming a circuit-on-wire (CoW) assembly. The method forms a flexible line with a plurality of periodic alignment marks used as a guide to place CoW devices overlying a surface of the flexible line. The CoW devices may be LEDs, capacitors, diodes, photodiodes, resistors, thin-film transistors, or combinations of the above-listed elements. The flexible line may be a conductive material, such as a metal wire, and the periodic alignment marks may be vias formed through the wire. If the flexible line is electrically conductive, an electrically conductive adhesive may be applied to the electrically conductive line, so that an electrical connection is formed between the CoW devices and the electrically conductive line. Subsequent to placing the CON devices, processes may be formed on the flexible line and CoW devices such as lithographic etching and thin-film deposition. An active matrix array using CoW devices is also presented.
Owner:SHARP KK
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap