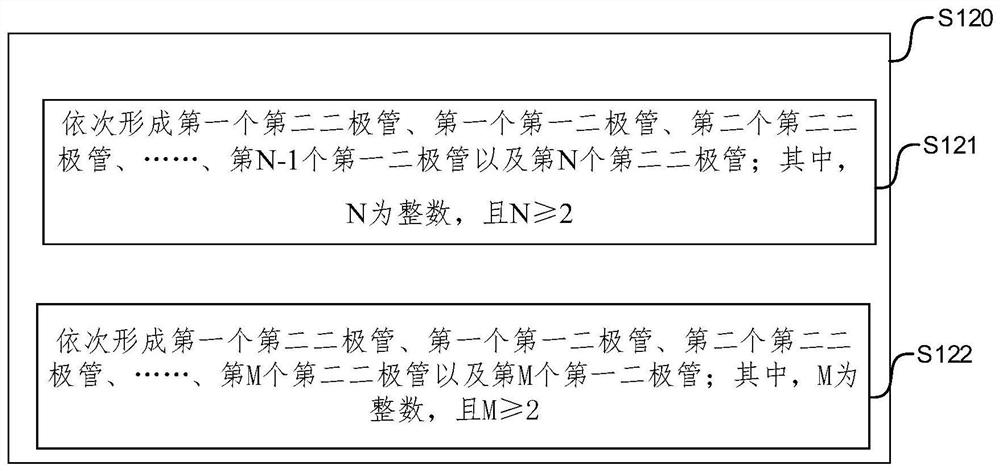
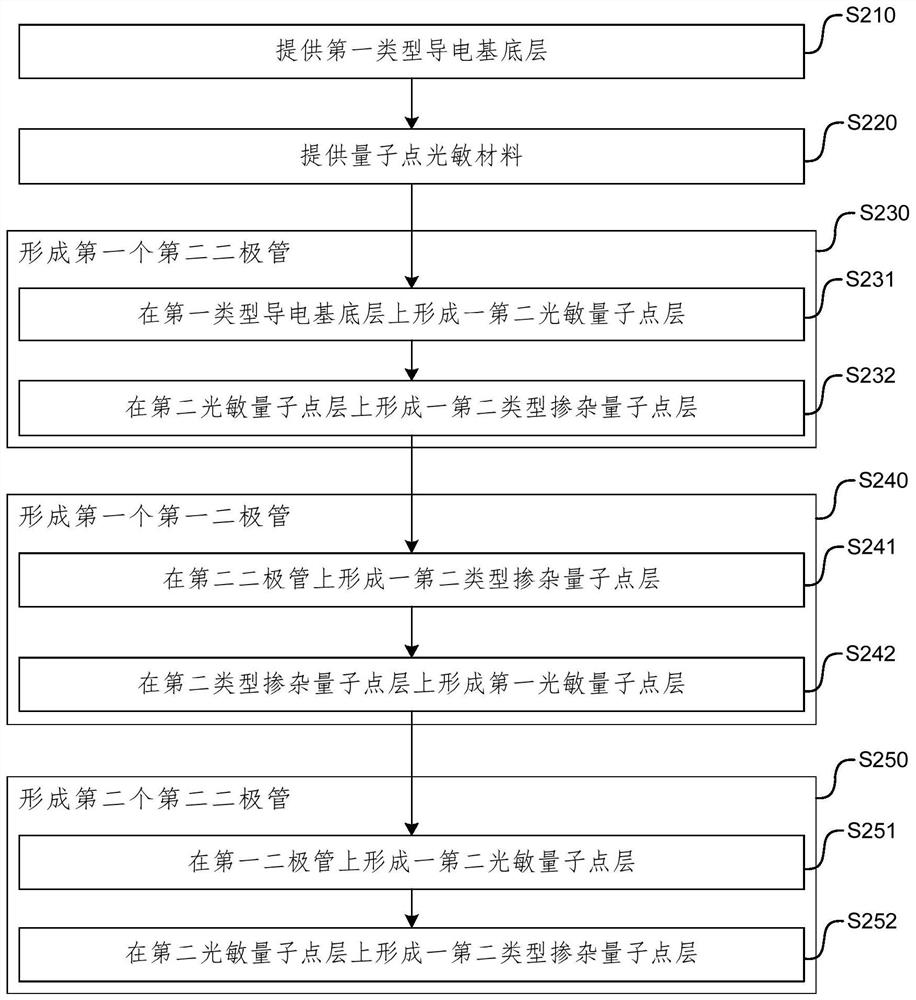
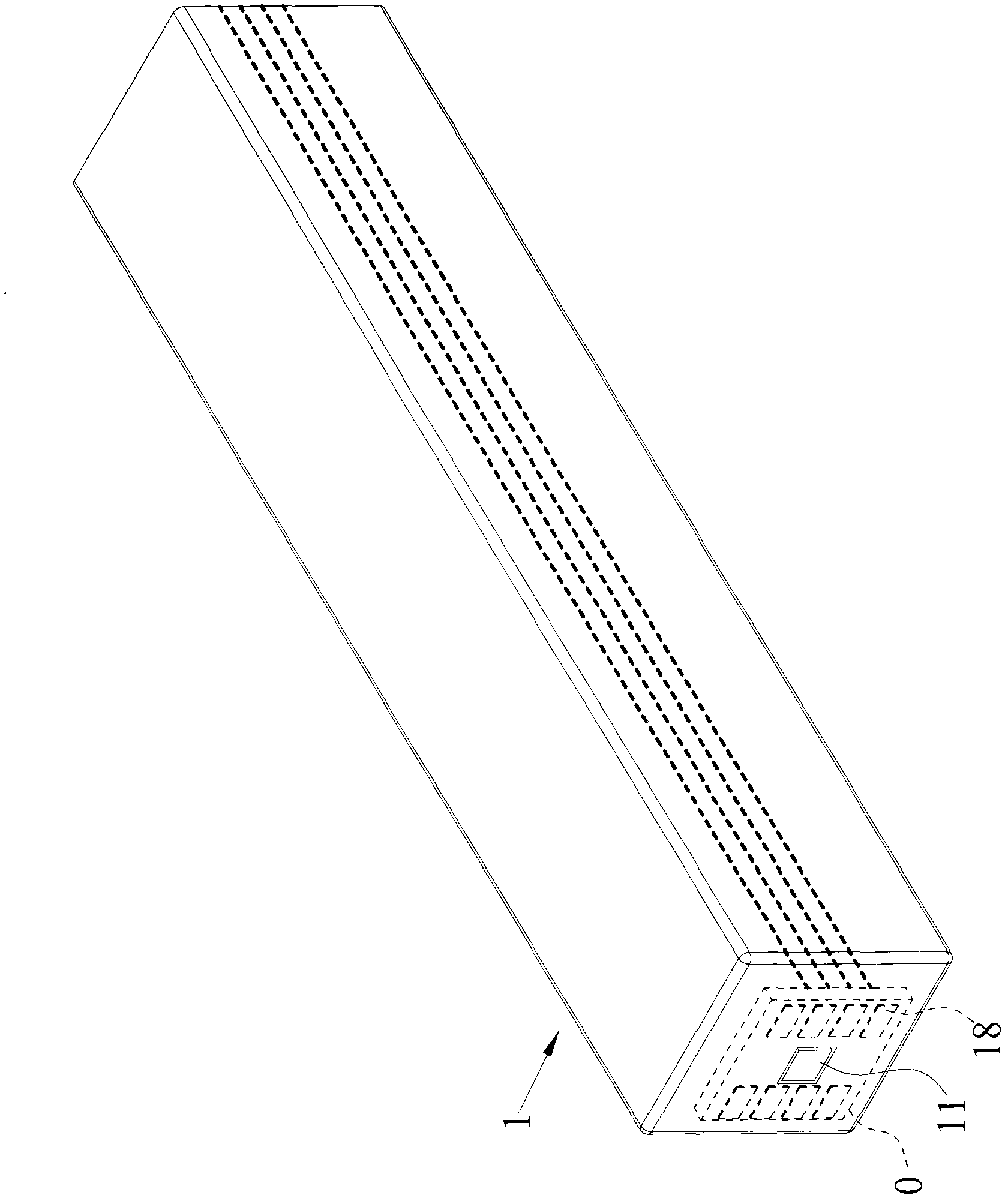
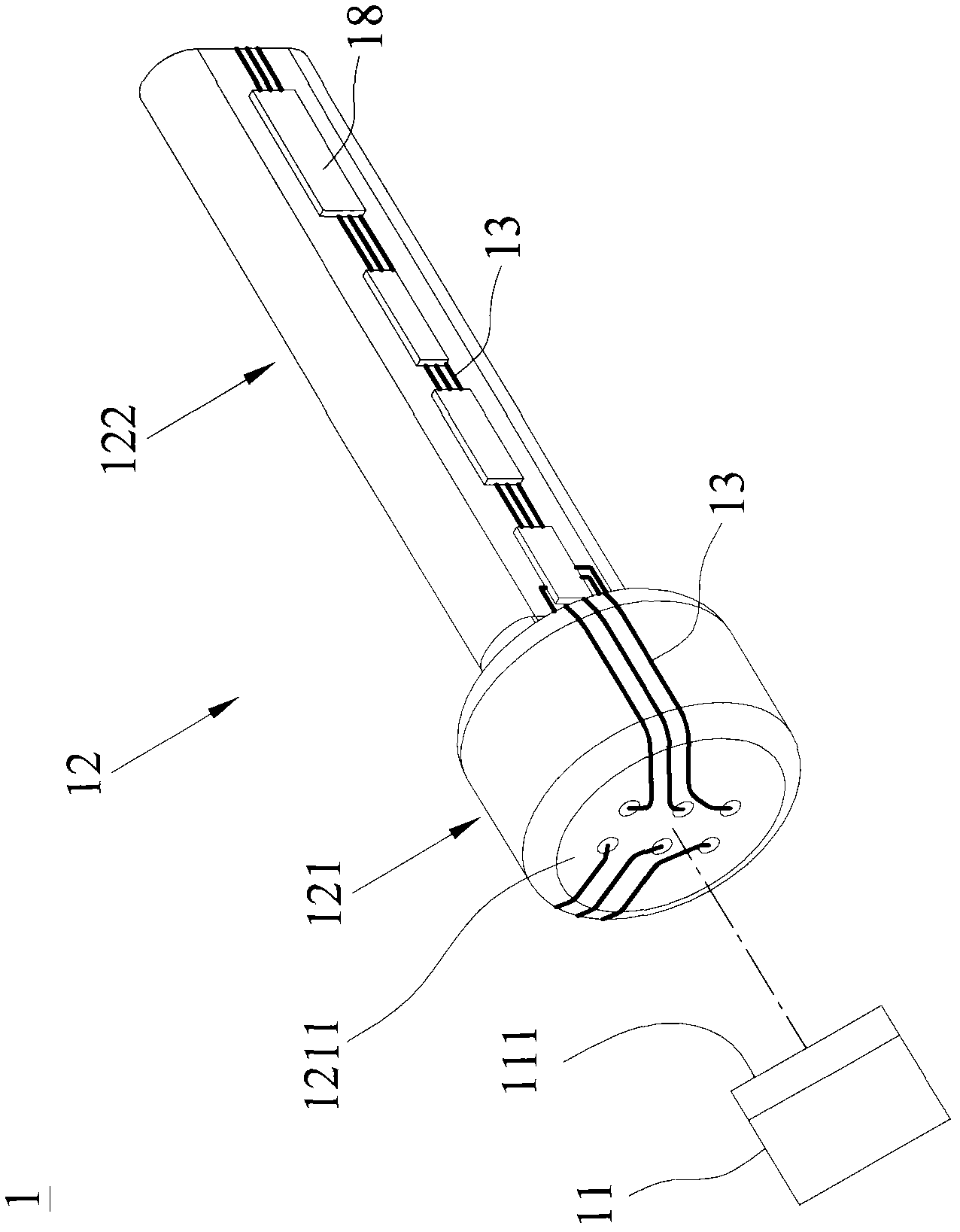
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about "Radiation controlled devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
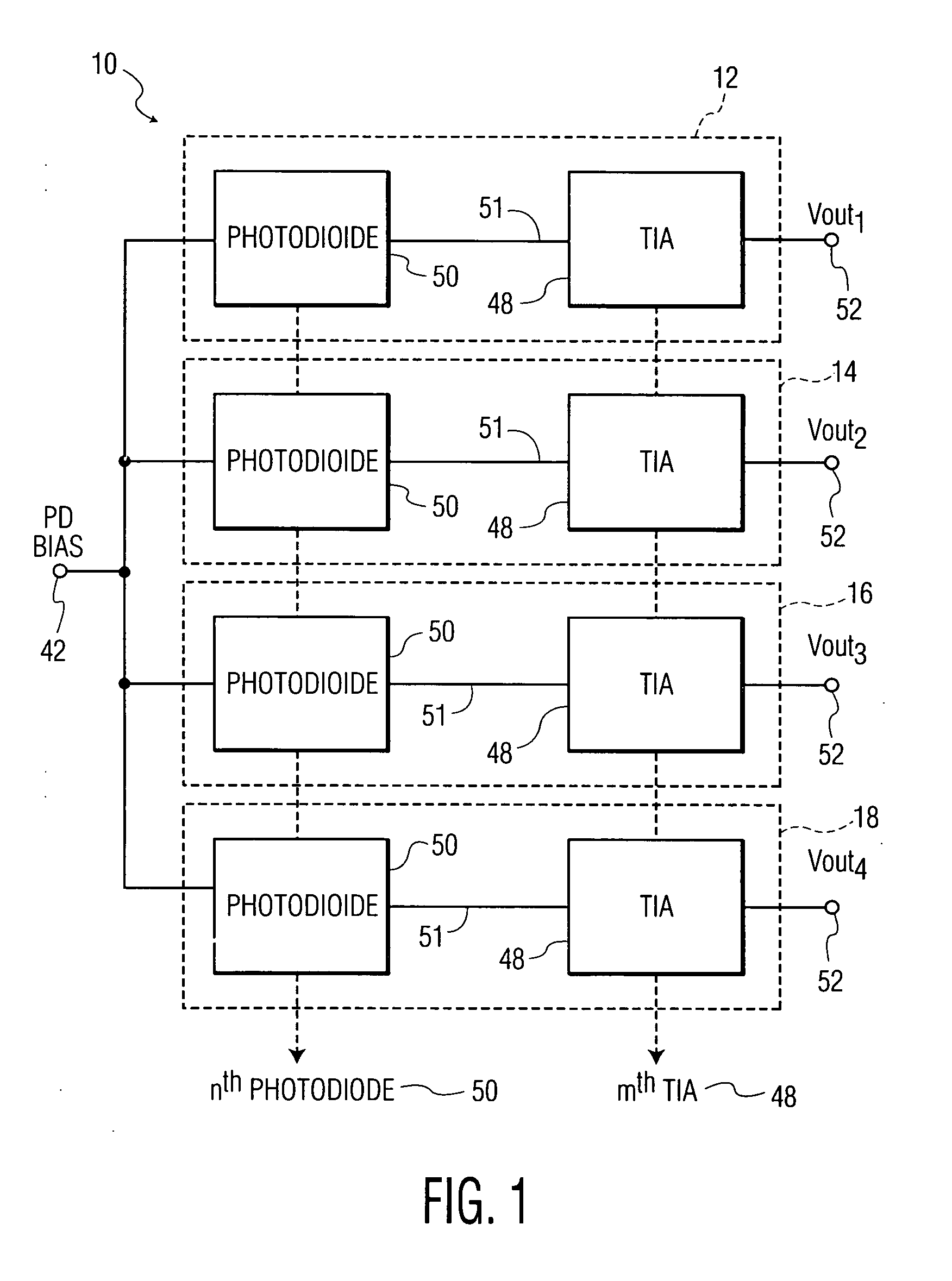
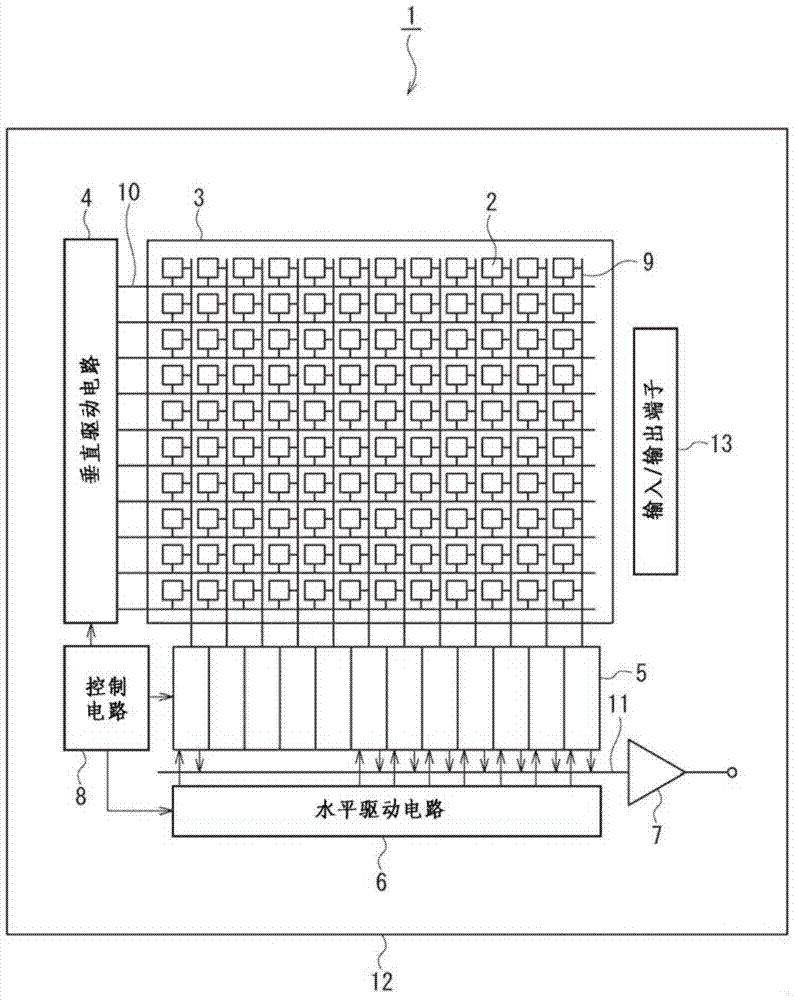
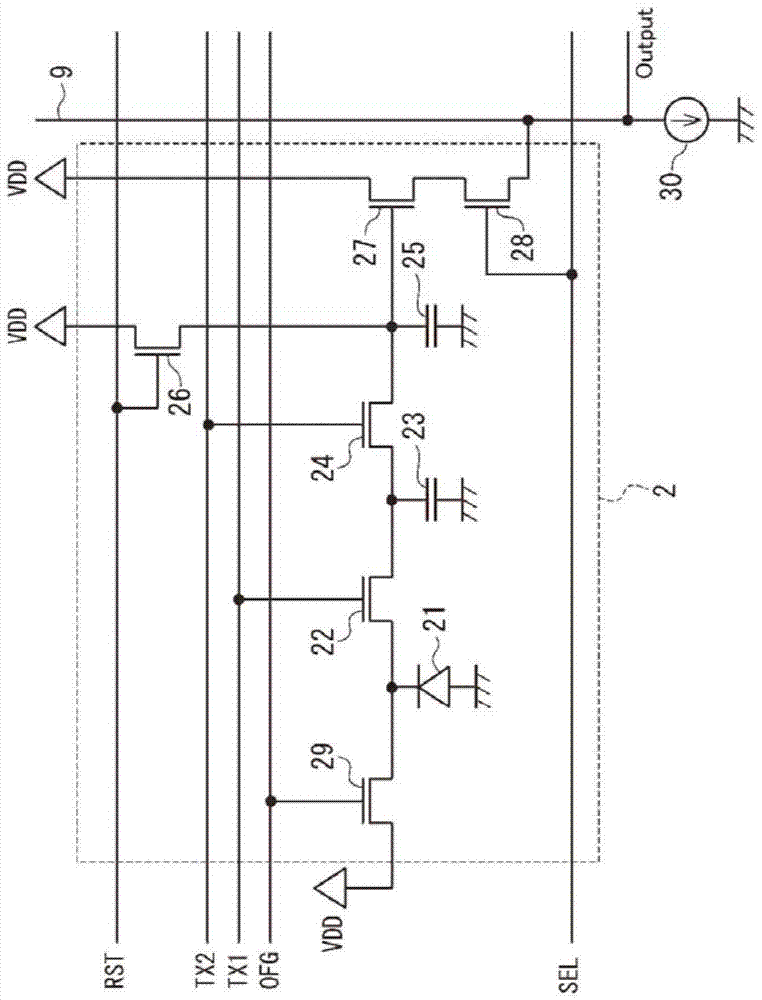
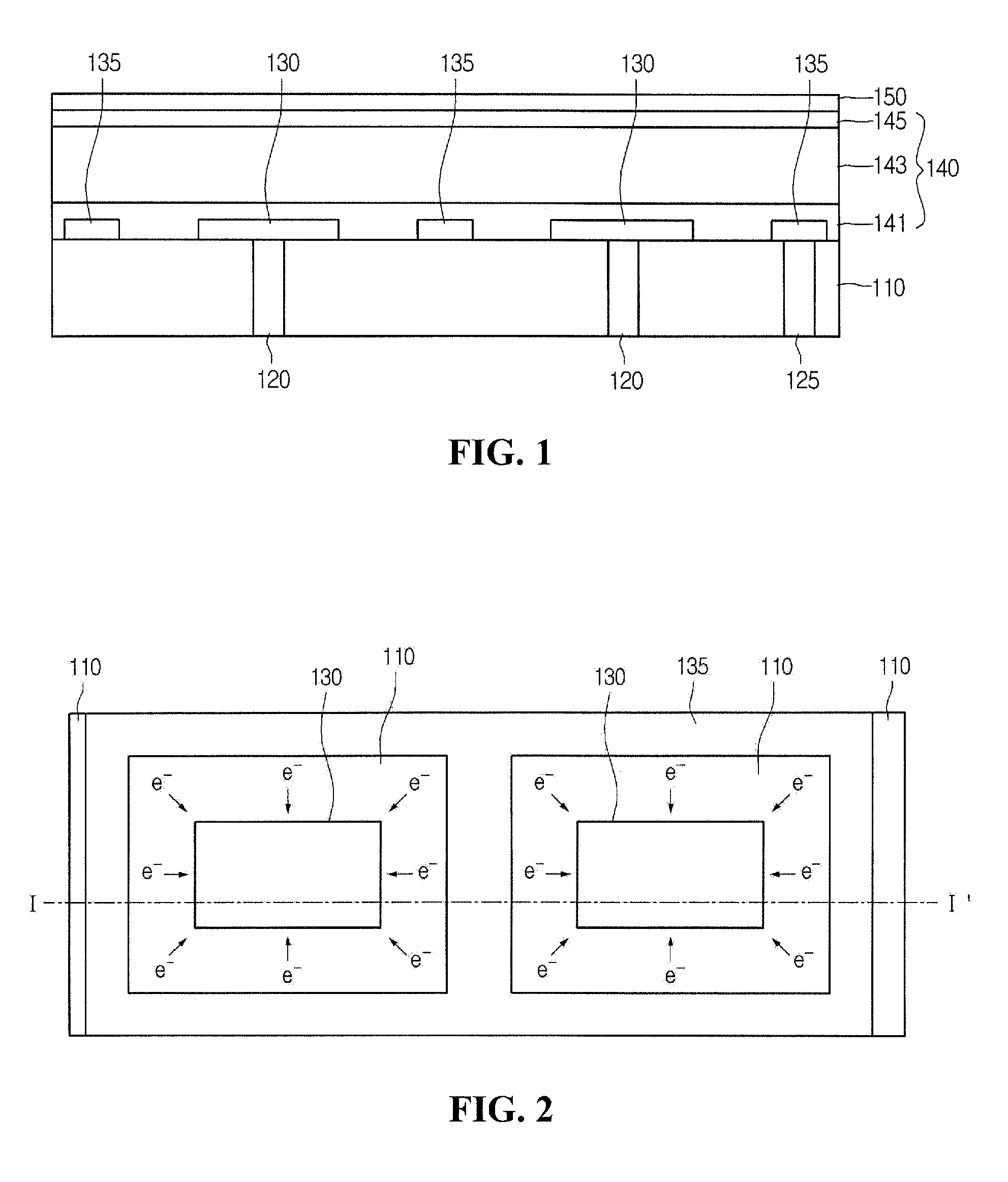
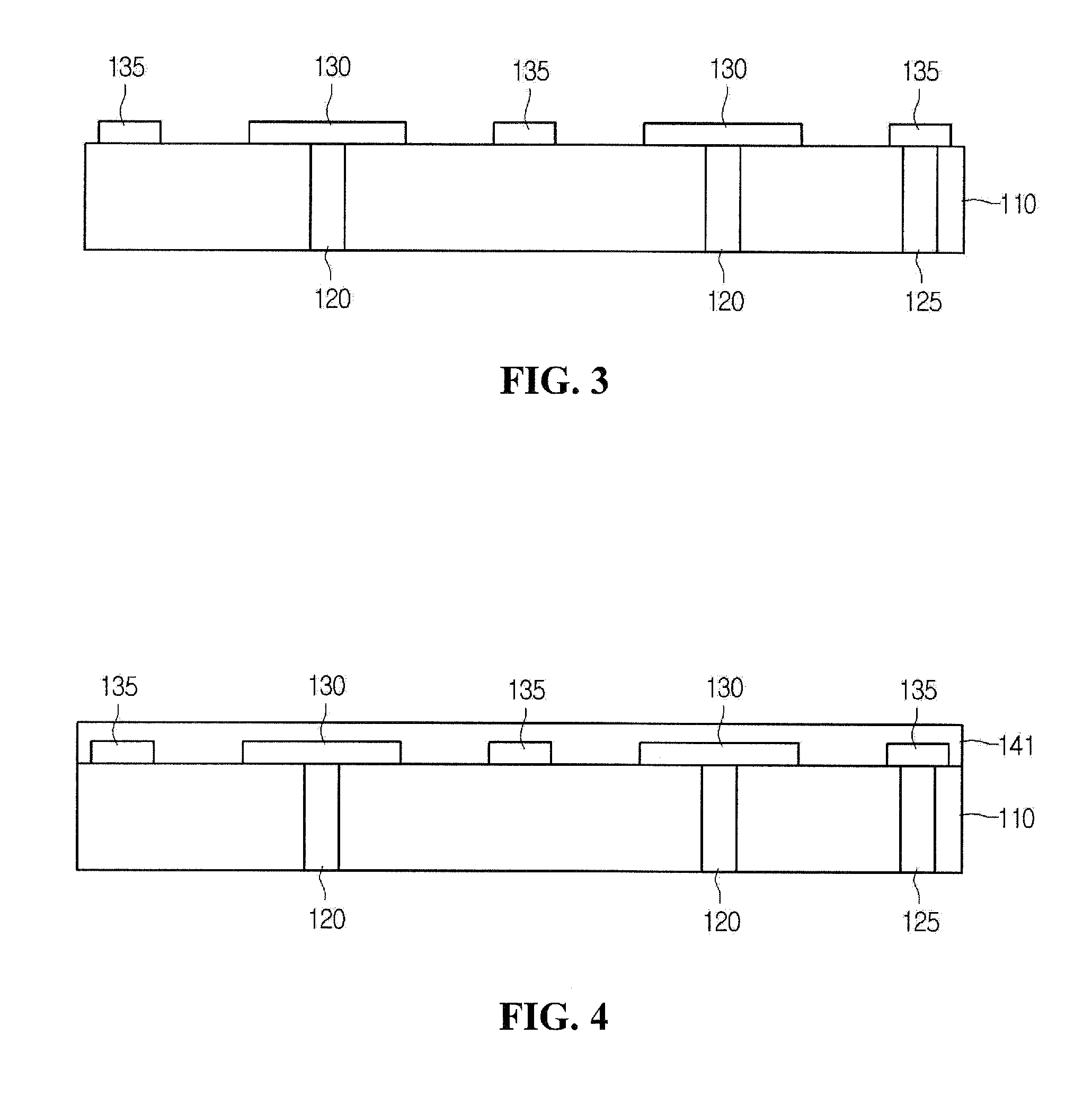
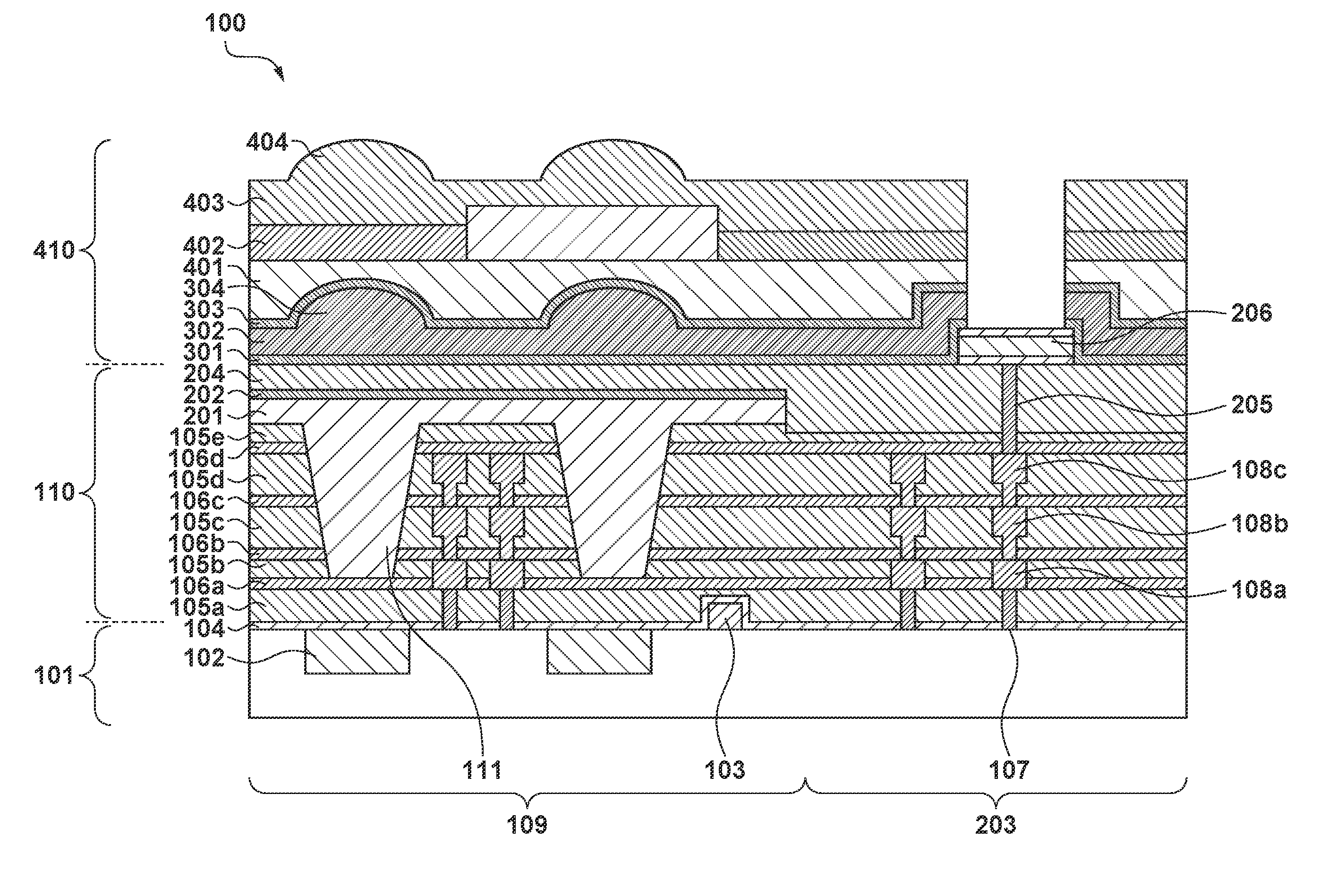
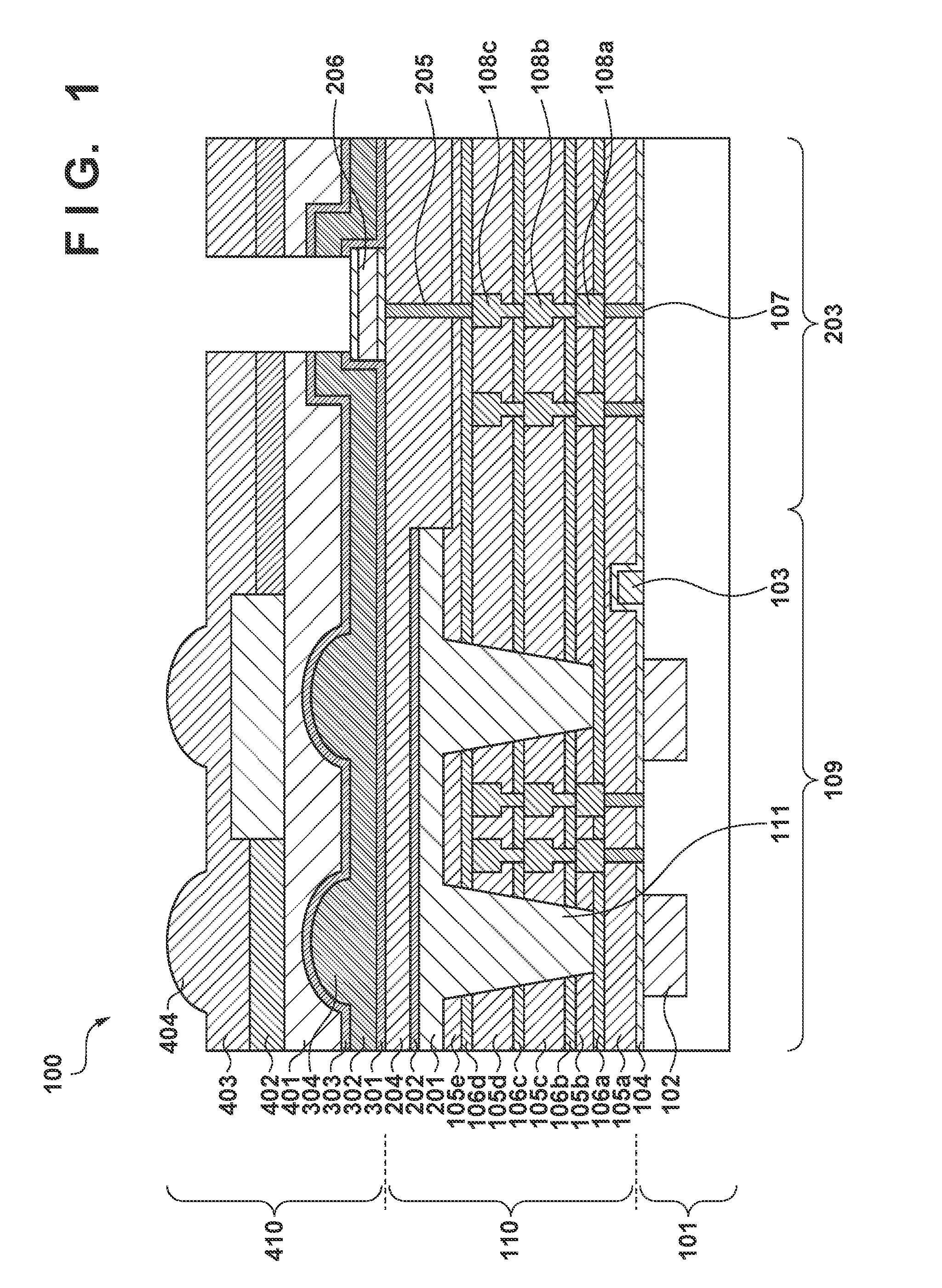
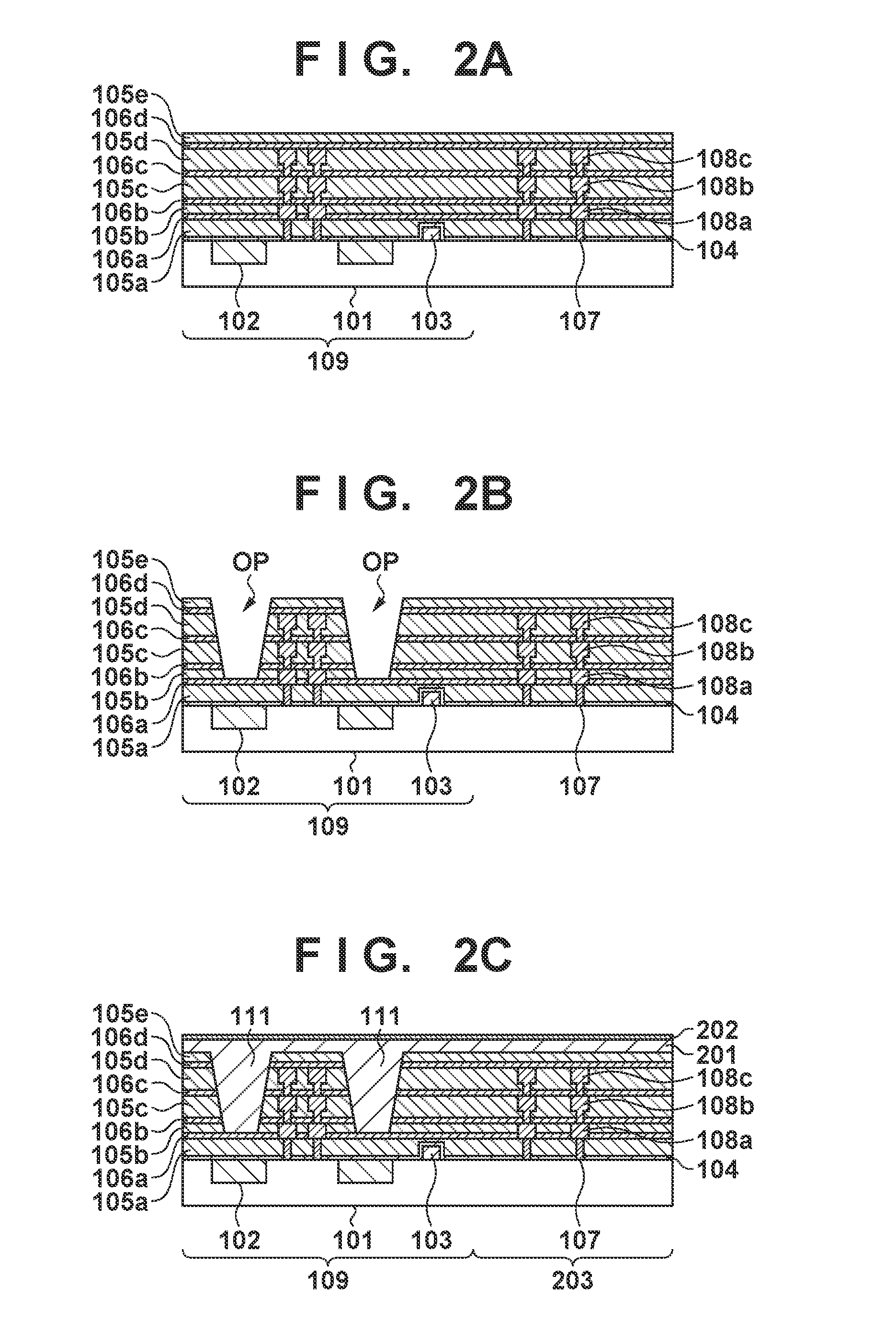
CMOS image sensor having wide dynamic range and sensing method thereof
ActiveUS20120033118A1Improve dynamic rangeWide dynamic range performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSProcessing element
Disclosed are a CMOS image sensor having a wide dynamic range and a sensing method thereof. Each unit pixel of the CMOS image sensor of the present invention includes multiple processing units, so that one shuttering section for the image generation of one image frame can be divided into multiple sections to separately shutter and sample the divided sections by each processing unit. Thus, the image sensor of the present invention enables many shuttering actions to be performed in the multiple processing units, respectively, and the multiple processing units to separately sample each floating diffusion voltage caused by the shuttering actions, thereby realizing a wide dynamic range.
Owner:ZEEANN
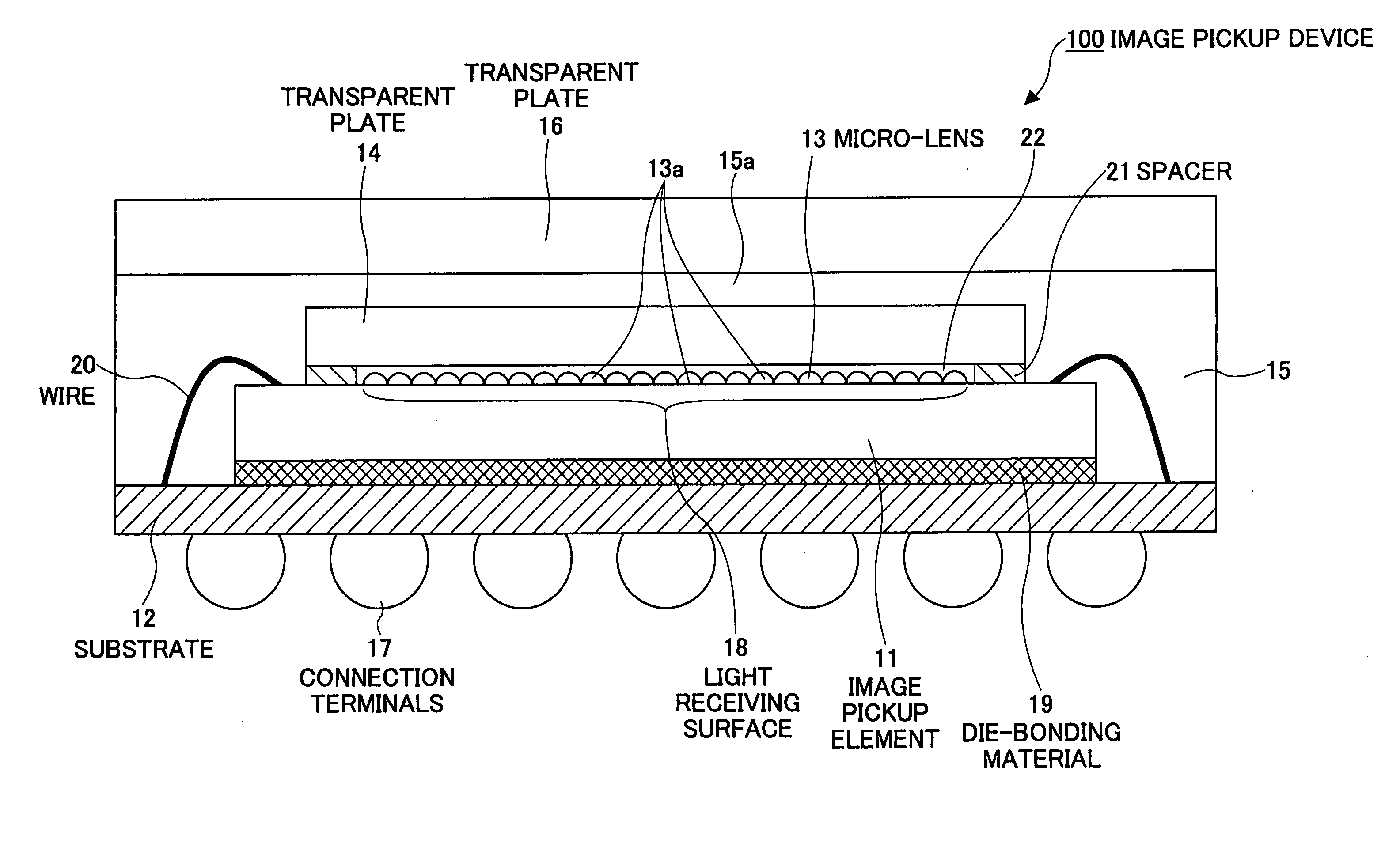
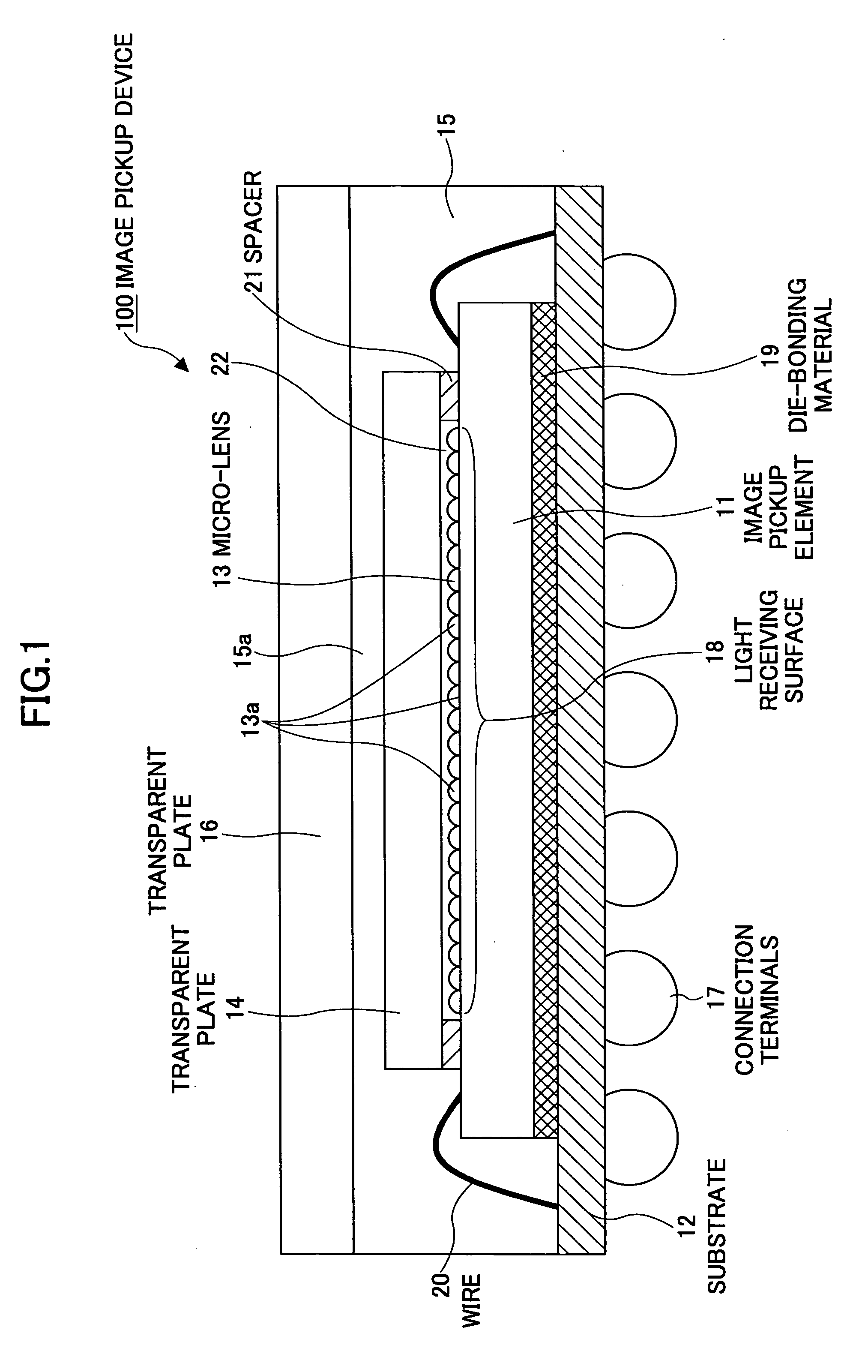
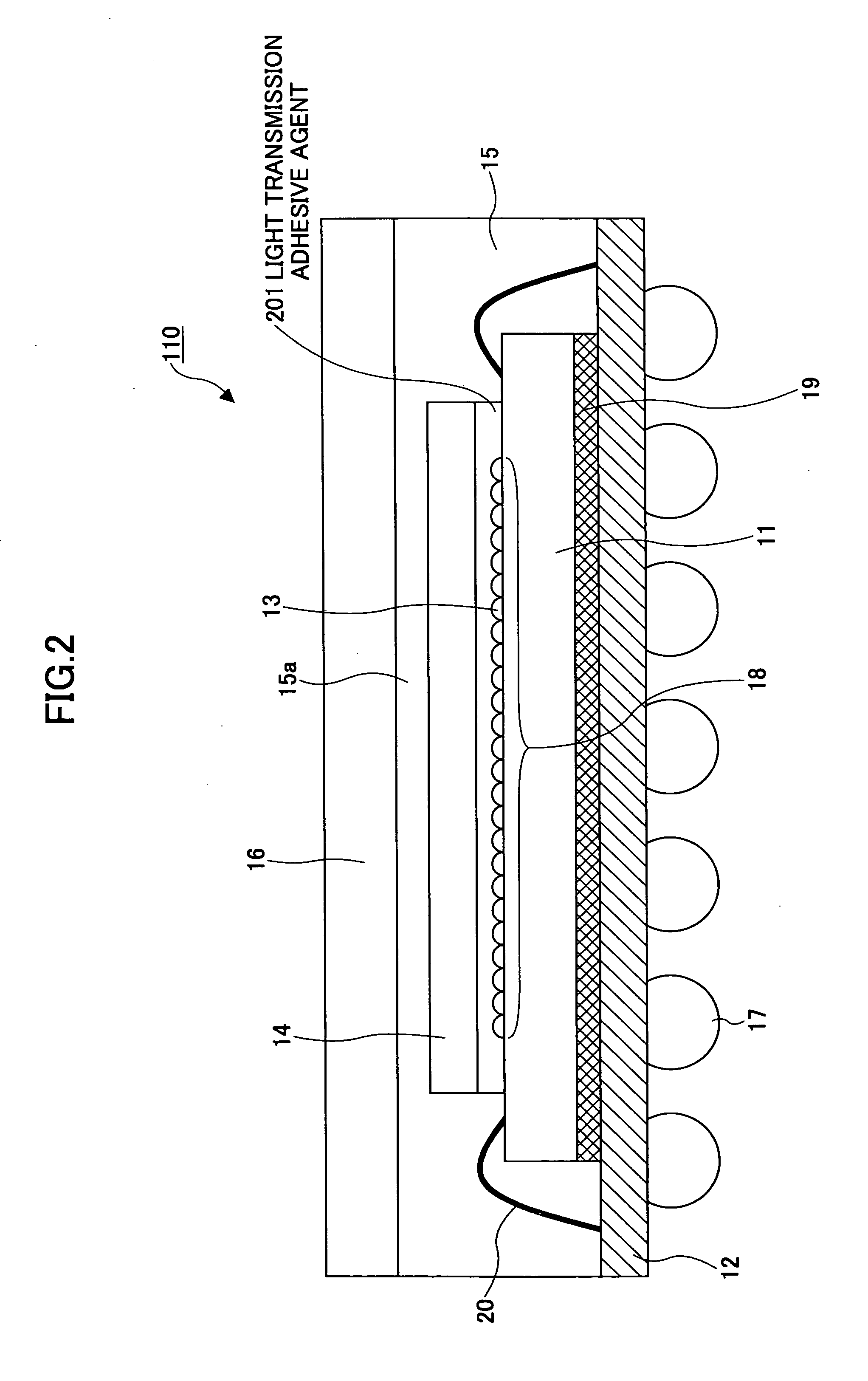
Image pickup device and production method thereof
InactiveUS20050275741A1Good lighting performanceSmall overall deformationTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal expansionComputer science
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
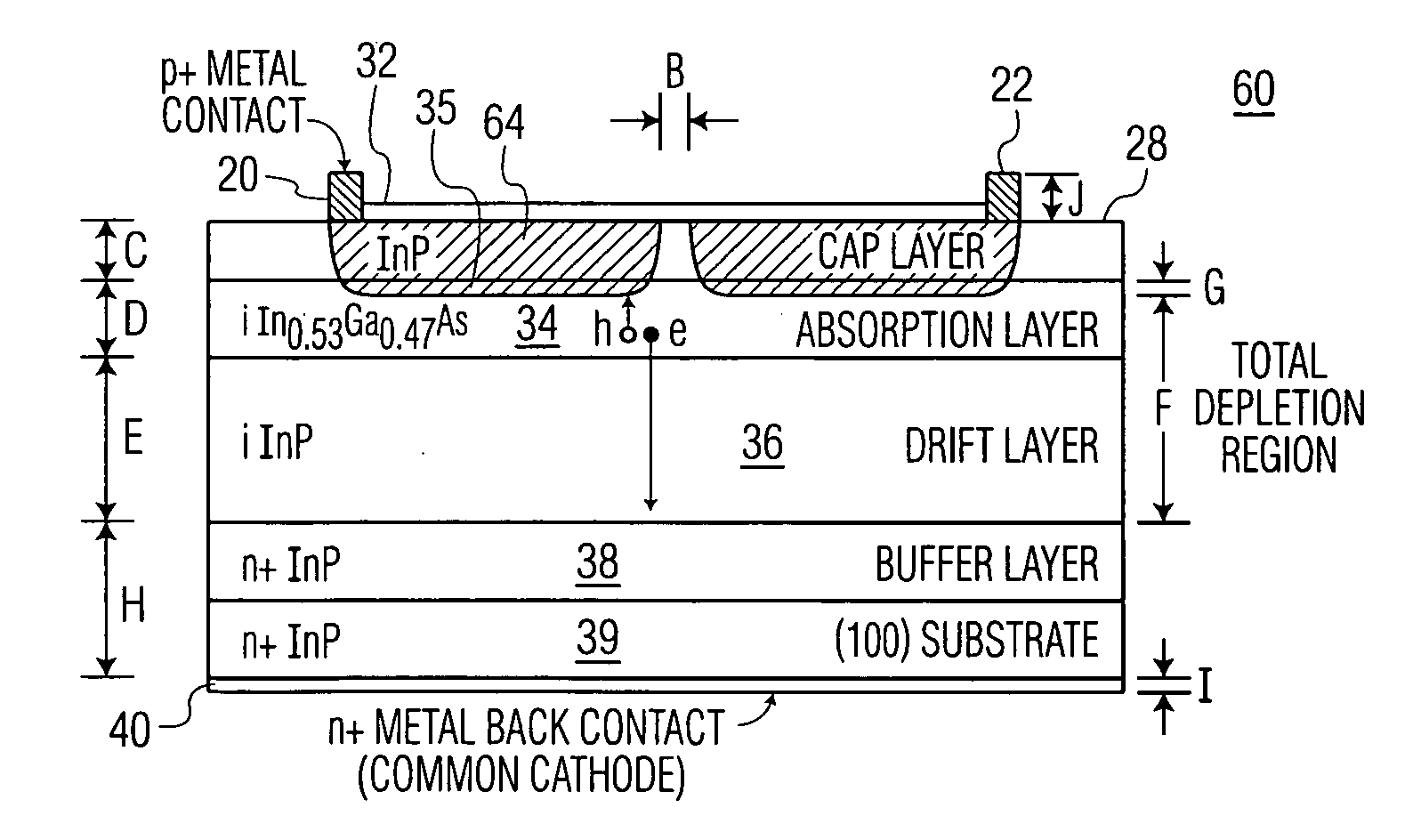
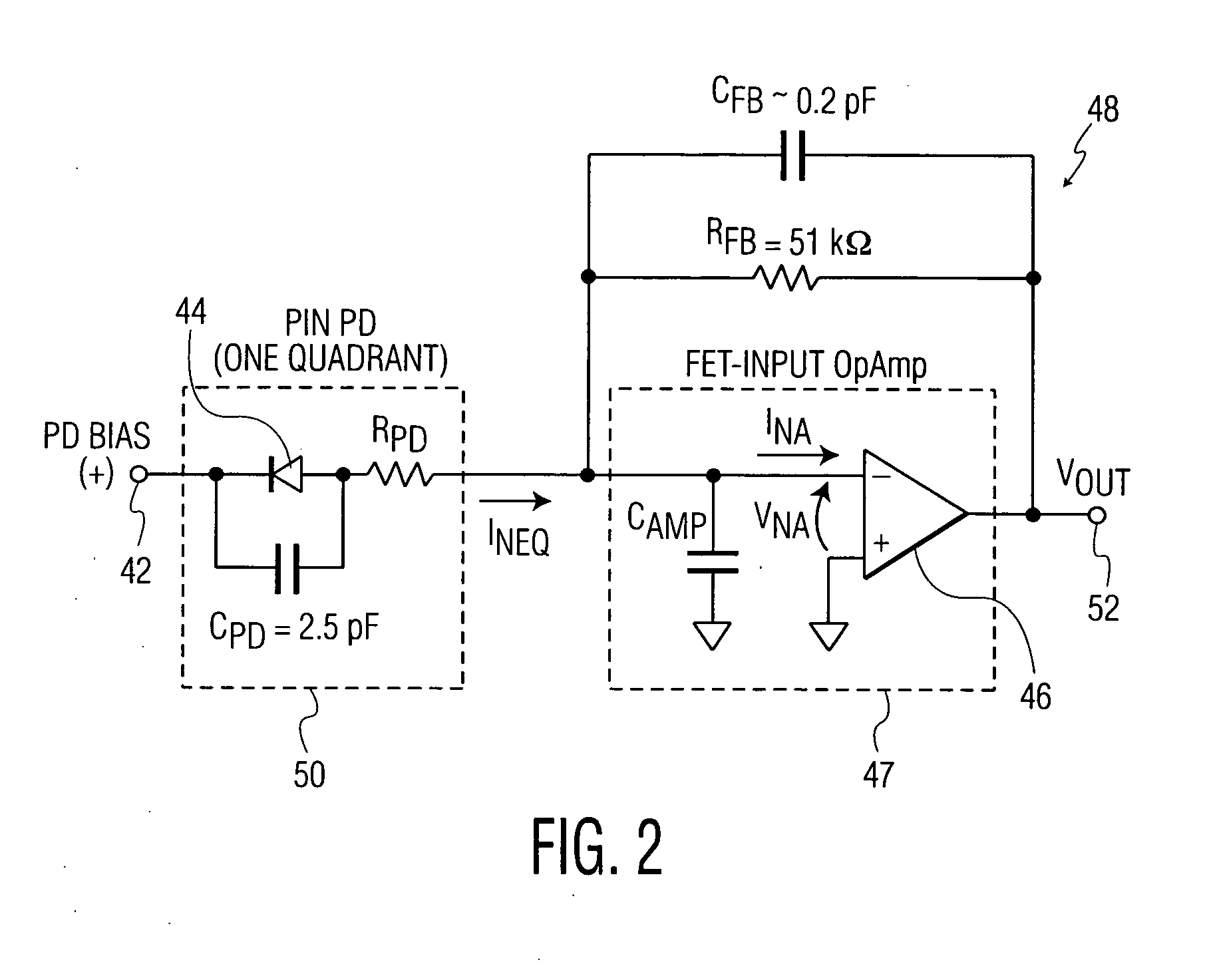
Low-noise large-area photoreceivers with low capacitance photodiodes
Owner:DISCOVERY SEMICON
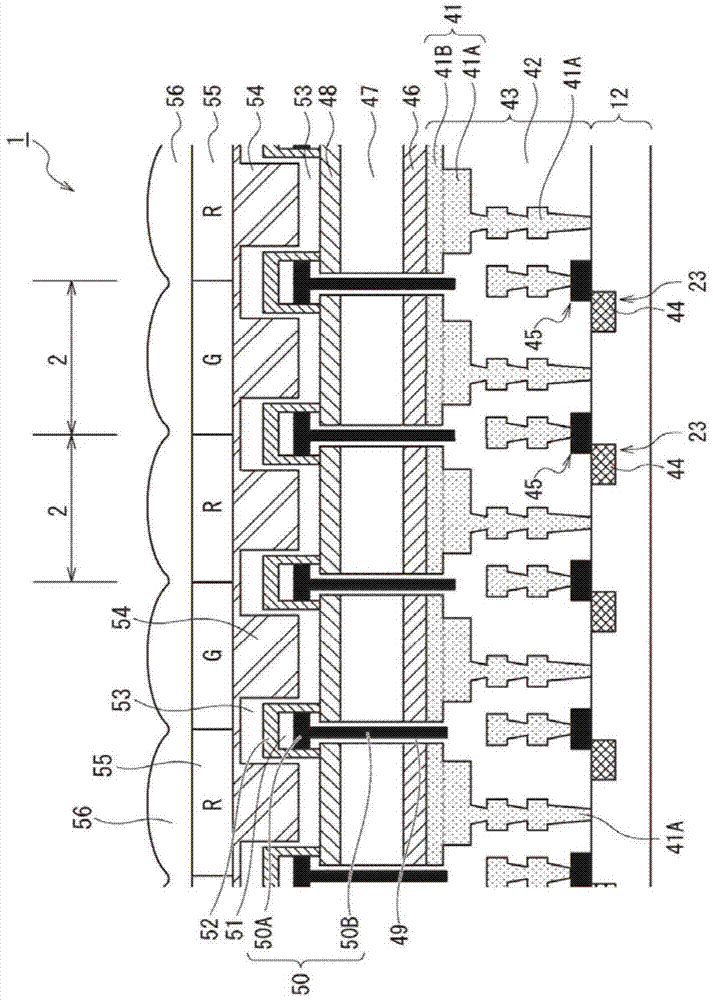
Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and electronic device
InactiveUS20090303359A1Improve machining accuracyInhibit coloringTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Amorphous silicon image sensor with storage capacitor structure
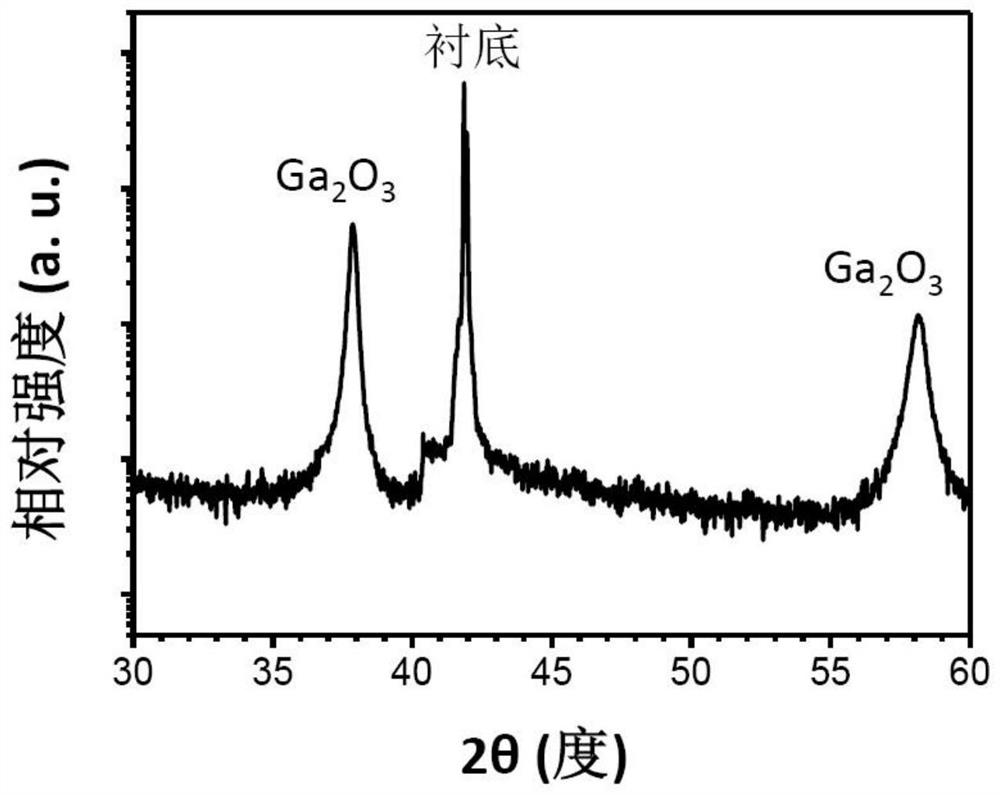
ActiveCN102157533AIncreased charge storage capacityImprove signal dynamic rangeRadiation controlled devicesCapacitanceDynamic range
Owner:CARERAY DIGITAL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Solid-state imaging device, drive method thereof and camera system
ActiveUS20110267522A1SpeedReduced settling timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionSlew rate
A solid-state imaging device includes: pixel signal reading lines; a pixel unit in which pixels including photoelectric conversion elements are arranged; and a pixel signal reading unit performing reading of pixel signals from the pixel unit through the pixel signal reading lines, wherein the pixel signal reading unit includes current source circuits each of which includes a load element as a current source connected to the pixel signal reading line forming a source follower, and the current source circuit includes a circuit generating electric current according to a slew rate of the pixel signal reading line and replicating electric current corresponding to the above electric current to flow in the current source.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solid state image pickup device, method of manufacturing the same, image pickup device, and electronic device
InactiveCN101853866AReduce the effects of chromatic aberrationReduce exposure timeSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesTransducerPhotoelectric conversion
The invention relates to a solid state image pickup device, a method of manufacturing the same, an image pickup device, and an electronic device. The solid state image pickup device includes a pixel section defined by unit pixels arrayed in line and row directions of a semiconductor substrate. Each of the unit pixels includes a photoelectric transducer that is formed on the semiconductor substrate and converts incident light into a signal charge, a waveguide that is formed above the photoelectric transducer and guides the incident light to the photoelectric transducer, and a microlens that is formed above the waveguide and guides the incident light to an end of light incident side of the waveguide. The waveguide has a columnar body with a constant cross section from the end of light incident side to an end of light exit side, and is arranged such that a center of rays of the incident light incident from the microlens on the end of light incident side of the waveguide is aligned with a central axis of the waveguide.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image sensor package
ActiveUS20060011811A1Ease can be packageReduce manufacturing costBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLower upperElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:KT IMAGING USA LLC
Radiological imaging apparatus and its detector unit
InactiveUS20050151087A1Improve shielding effectSuppresses superimposition of noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsSignal processing
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Solid-state image sensor, method of producing the same, and electronic apparatus
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Image Sensor and Method for Manufacturing The Same
InactiveUS20090115014A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSchottky barrierOptoelectronics
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Speckle reduction method and apparatus
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Image sensor package, optical glass therefor and processing method
InactiveCN1905140AEnsuring the ability to receive optical signalsPrevent intrusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFinal product manufactureRough surfaceOptoelectronics
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
Back-illuminated image sensor with three-dimensional transistor structure and forming method thereof
InactiveCN105185799AImprove fill rateImprove transconductanceSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesTransistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:GALAXYCORE SHANGHAI
Process for fabricating an array of germanium-based diodes with low dark current
ActiveUS20200176503A1Improve fill factorLower average currentFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesEngineeringPhotodiode
A process for fabricating an optoelectronic device including an array of germanium-based photodiodes including the following steps: producing a stack of semiconductor layers, made from germanium; producing trenches; depositing a passivation intrinsic semiconductor layer, made from silicon; annealing, ensuring, for each photodiode, an interdiffusion of the silicon of the passivation semiconductor layer and of the germanium of a semiconductor portion, thus forming a peripheral zone of the semiconductor portion, made from silicon-germanium.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
PendingUS20190363130A1Low heat resistancePrevent degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductorNon-volatile memory
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
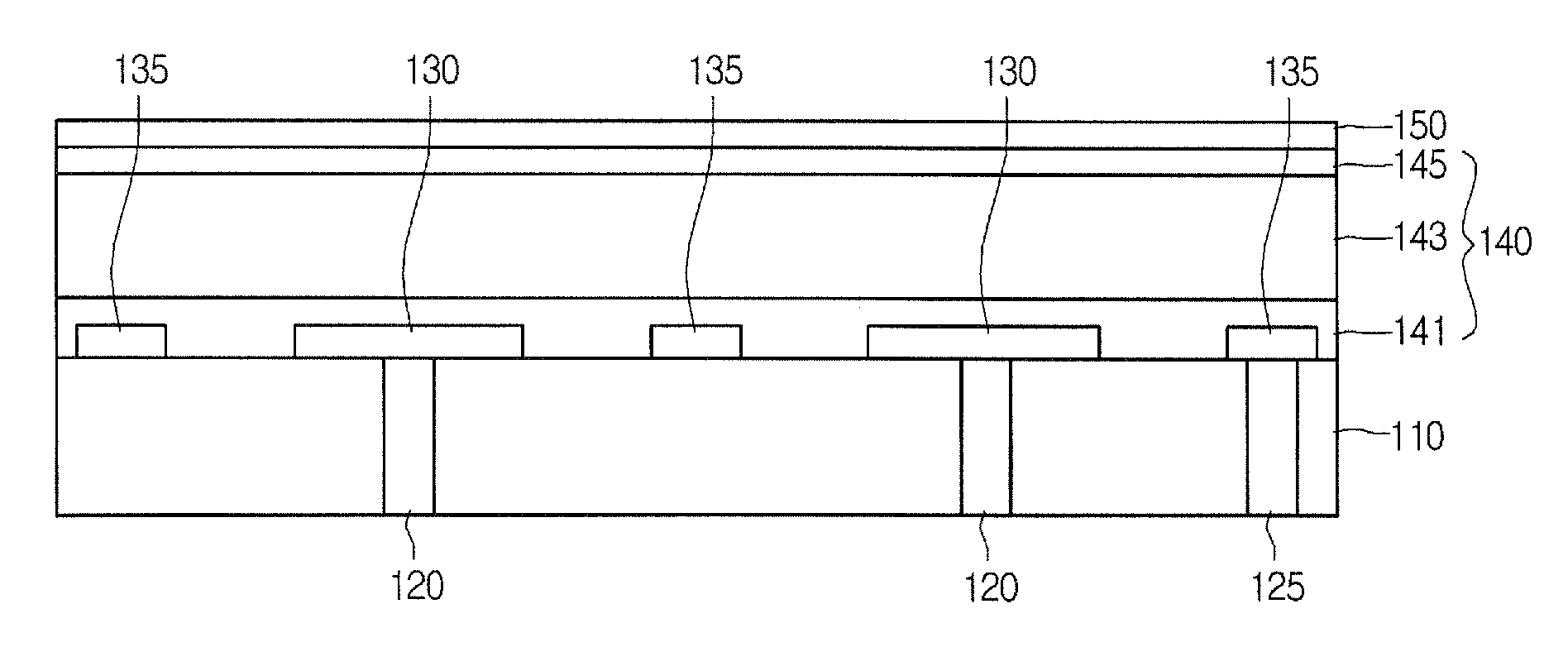
Method of fabricating semiconductor memory device and semiconductor memory device driver
Disclosed is a method of fabricating a semiconductor memory device including the step of irradiating ultraviolet rays on a metal interconnection at a bonding pad part, so that the metal interconnection can be prevented from being corroded because of a corrodent element in the process of erasing charges stored in a charge storage part. An oxide coating film is formed on the surface of the metal interconnection at the bonding pad part, and ultraviolet rays are irradiated onto the oxide coating film for erasing of charges from the floating gate.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
A sensing device and a sensing method
Owner:INTERFACE TECH CHENGDU CO LTD +2
Method for manufacturing solid-state image sensor
ActiveUS20160268332A1Quality improvementSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesImage sensorSolid-state
Owner:CANON KK
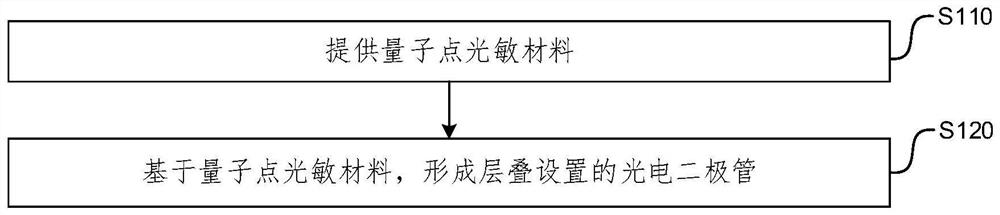
Imaging device, preparation method thereof, imaging array and preparation method thereof
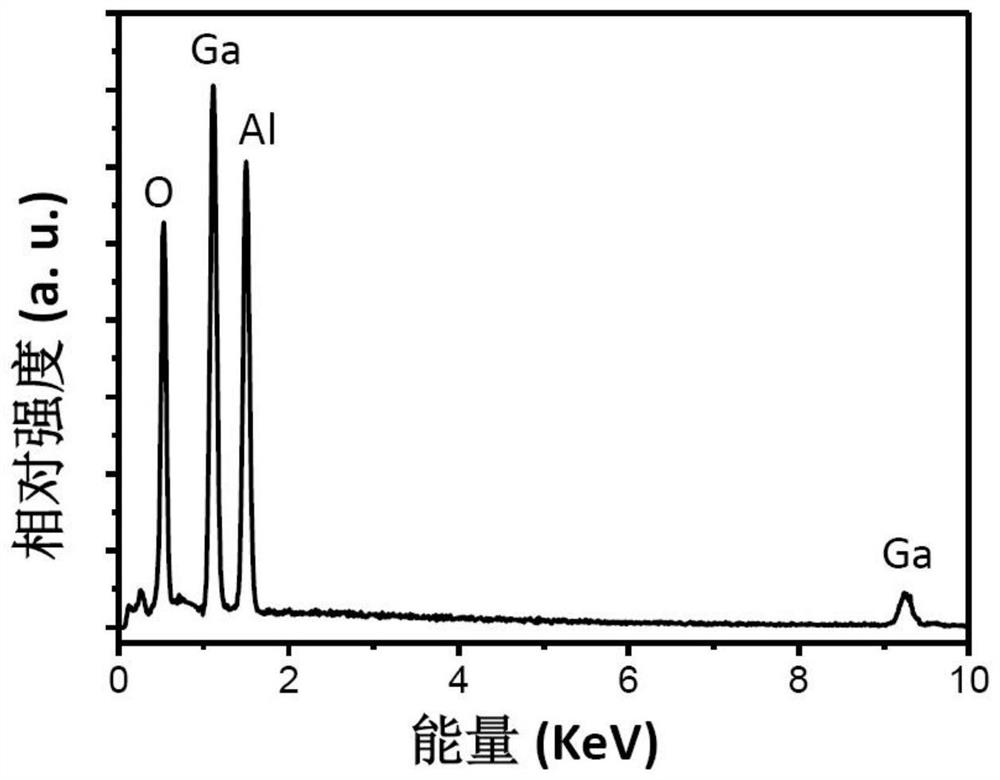
PendingCN114551486ASimple preparation processEasy to handleFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSignal responseQuantum dot
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Camera package, method for manufacturing camera package, and electronic device
PendingUS20220130880A1Increase in sizeReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesOptical articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present disclosure relates to a camera package, a method for manufacturing a camera package, and an electronic device with which it is possible to reduce manufacturing cost for lens formation.The camera package according to the present disclosure includes: a solid-state imaging element; and a lens formed above a transparent substrate that protects the solid-state imaging element. A lens formation region in which the lens is formed above the transparent substrate and a lens free region around the lens formation region differ in contact angle. The present disclosure can be applied to, for example, a camera package in which a lens is disposed above a solid-state imaging element, or the like.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Minisize sensing device
Owner:PIONEER MEDICAL INSTR
Solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20210358985A1Improve uniformitySolid-state devicesOptical filtersEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging device having a first area and a second area surrounding the first area is provided. The solid-state imaging device includes a substrate having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements. The solid-state imaging device also includes a color filter layer disposed on the substrate. The color filter layer includes a plurality of color filter segments corresponding to the plurality of photoelectric conversion elements. The solid-state imaging device further includes an optical waveguide layer over the color filter layer. The optical waveguide layer includes a waveguide partition grid, a waveguide material in spaces of the waveguide partition grid, and an anti-reflection film on the waveguide partition grid and the waveguide material. The width of the top of the waveguide partition grid is larger than the width of the bottom of the waveguide partition grid.
Owner:VISERA TECH CO LTD
Image pickup device and image pickup apparatus
An image pickup device includes a first pixel region including image pixels and phase difference pixels and a second pixel region including image pixels and including no pixel configured to output a valid phase difference pixel signal, wherein a part of the plurality of phase difference pixels in the first pixel region is arranged at a regular position at which a G filter is formed in a Bayer array and another part is arranged at an irregular position at which a filter that is other than the G filter is formed, and a basic arrangement pattern of filters in the second pixel region is equal to a basic arrangement pattern of filters in the first pixel region.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Image sensor device and method for forming same
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
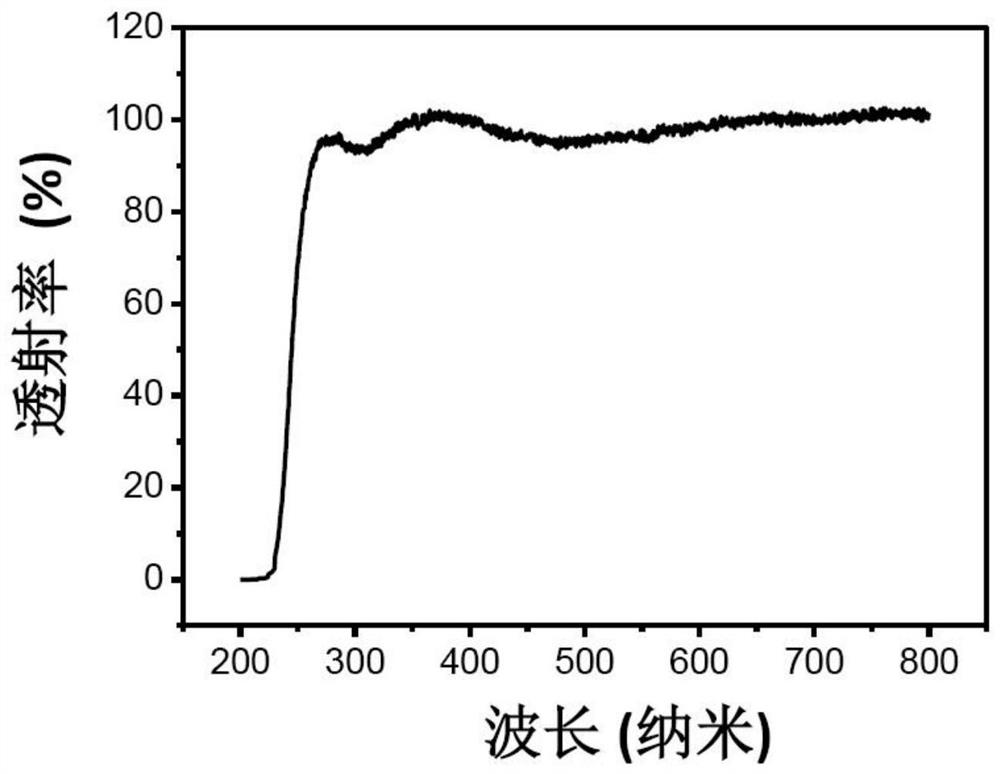
Ultraviolet detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113066876AAvoid damageConvenience guaranteedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesUltraviolet detectorsPhysical chemistry
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1531110APrevent Residual DefectsReduces the chance of junction leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerJunction leakage
To reduce a leakage current by suppressing the generation of a junction leakage. [Means to Solve the Problem]A semiconductor device comprises: a semiconductor region 103, in which an impurity of one conductivity type is doped; a gate insulation layer 105, formed on the semiconductor region 103; a gate electrode 106, formed on the gate insulation layer 105; a lightly doped layer 109a, formed in a region from the principal surface of the semiconductor region 103 to a first depth, in which a first impurity of the other conductivity type is implanted into the semiconductor region 103 with a first dose amount; and a heavily doped layer 109b, formed in a region from the principal surface of the semiconductor region 103 to a second depth, which is shallower than the first depth, in which a second impurity of the other conductivity type is implanted into the semiconductor region 103 with a second dose amount in a range of the first dose amount or more to 1x10E15 / cm<2 >or less.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Low power dual-sensitivity fg-mosfet sensor for a wireless radiation dosimeter
Owner:BEST THERATRONICS
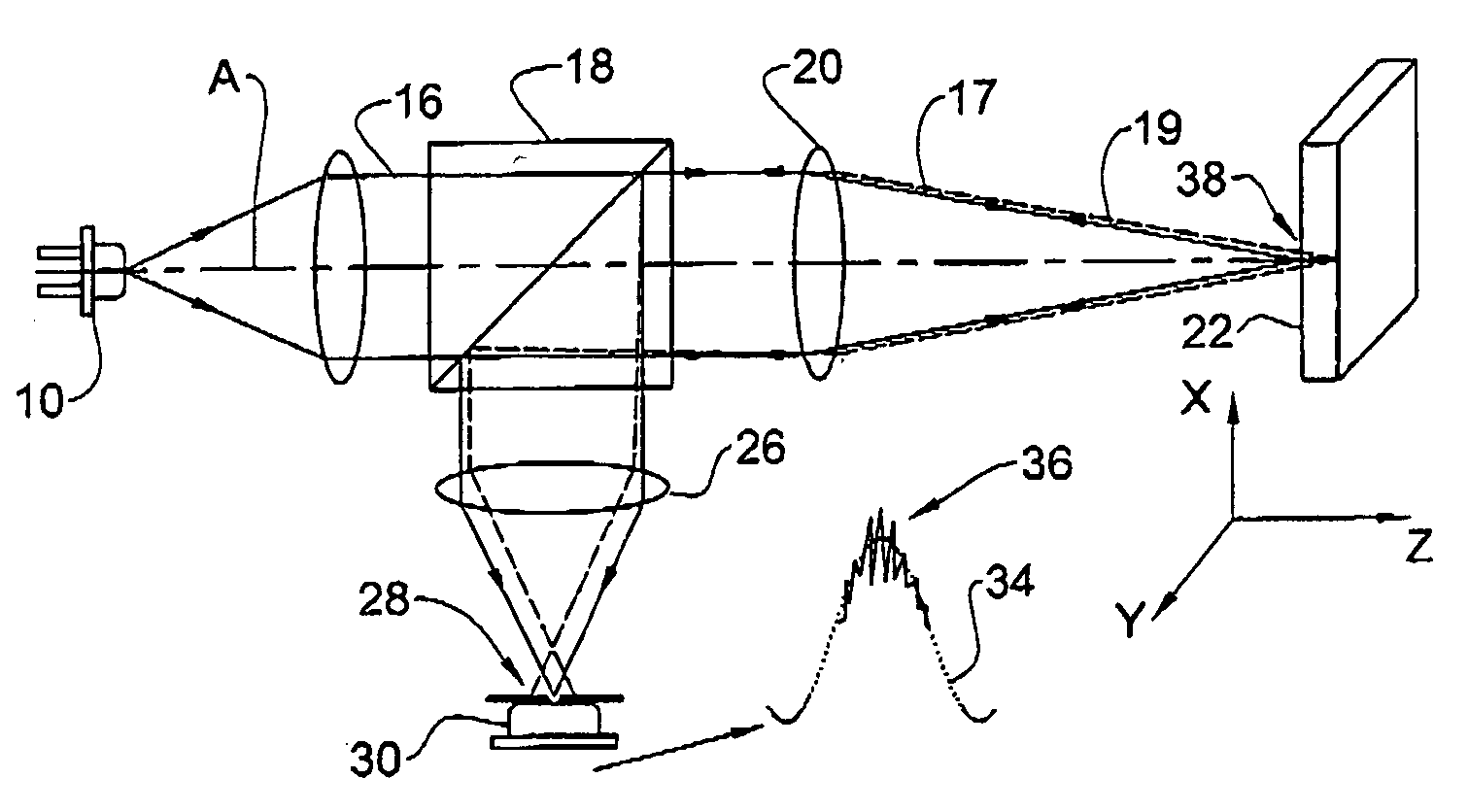
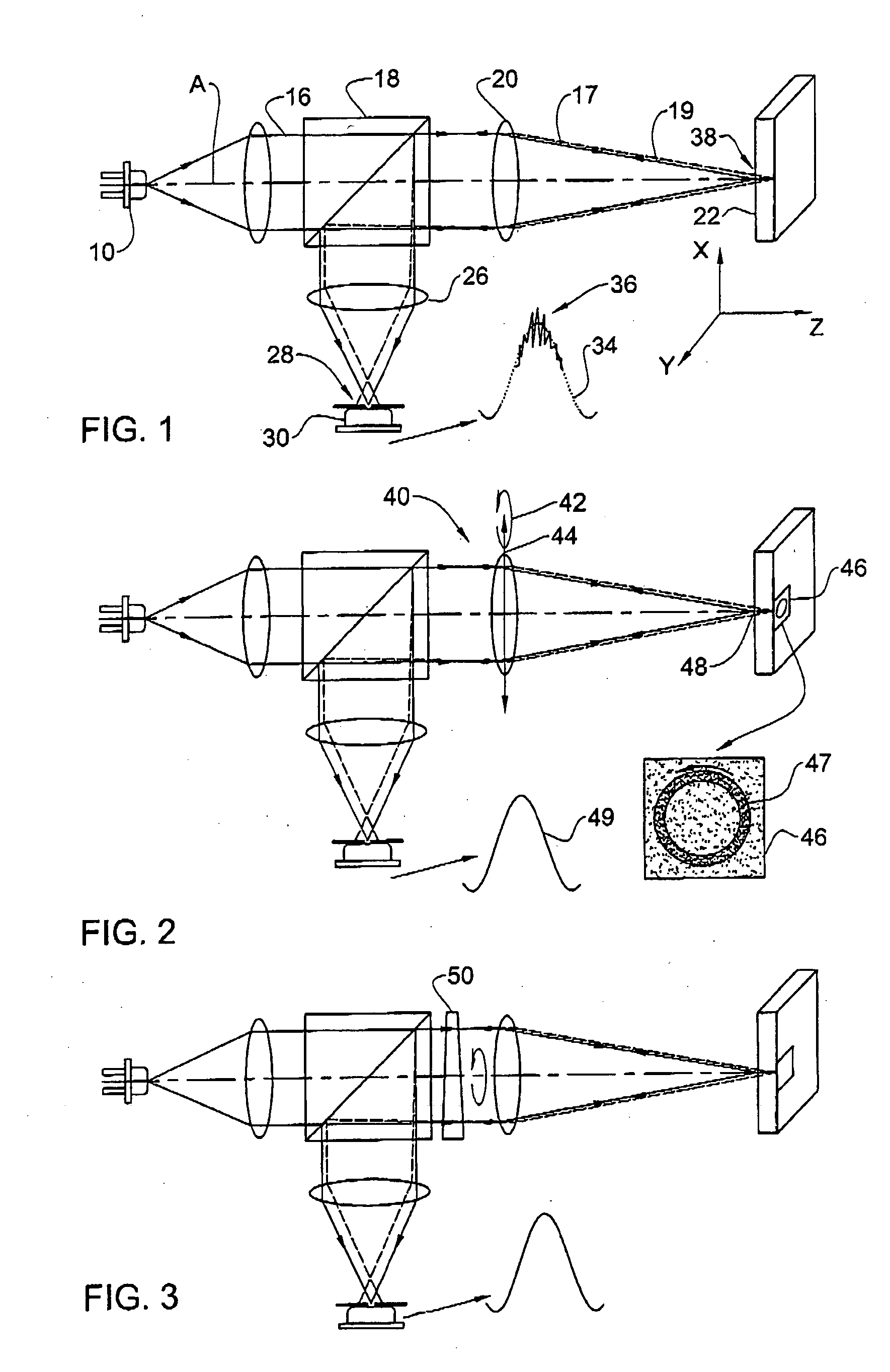
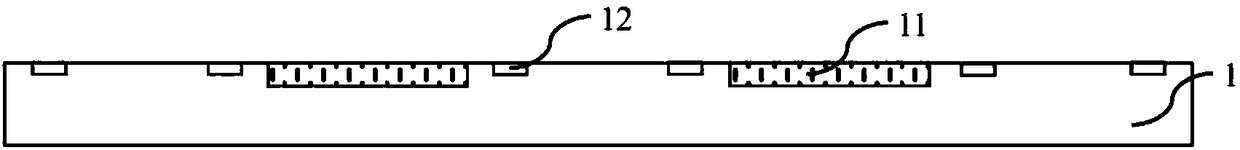
Sensor unit, radiation detector and method of manufacturing sensor unit
PendingCN112041704ASolid-state devicesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEngineeringMaterials science
A sensor unit (14) for a radiation detector (12), the sensor unit (14) comprising a conversion element (22) comprising a plurality of imaging pixels (30), wherein each imaging pixel (30) is configuredto directly convert radiation into an electrical charge and wherein each imaging pixel (30) comprises a charge collection electrode (28); and a readout substrate (24) comprising a plurality of readout pixels (32), wherein each readout pixel (32) is connected to an associated imaging pixel (30) by means of an interconnection (36) at a connection position on the charge collection electrode (28); wherein each readout pixel (32) has a smaller area than an associated imaging pixel (30) of the plurality of imaging pixels (30); and wherein the connection positions in relation to the charge collection electrodes (28) are varied with respect to a neighboring charge collection electrode (28). A radiation detector (12) and a method of manufacturing a sensor unit (14) are also provided.
Owner:XCOUNTER AB
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap