Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Solid-state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
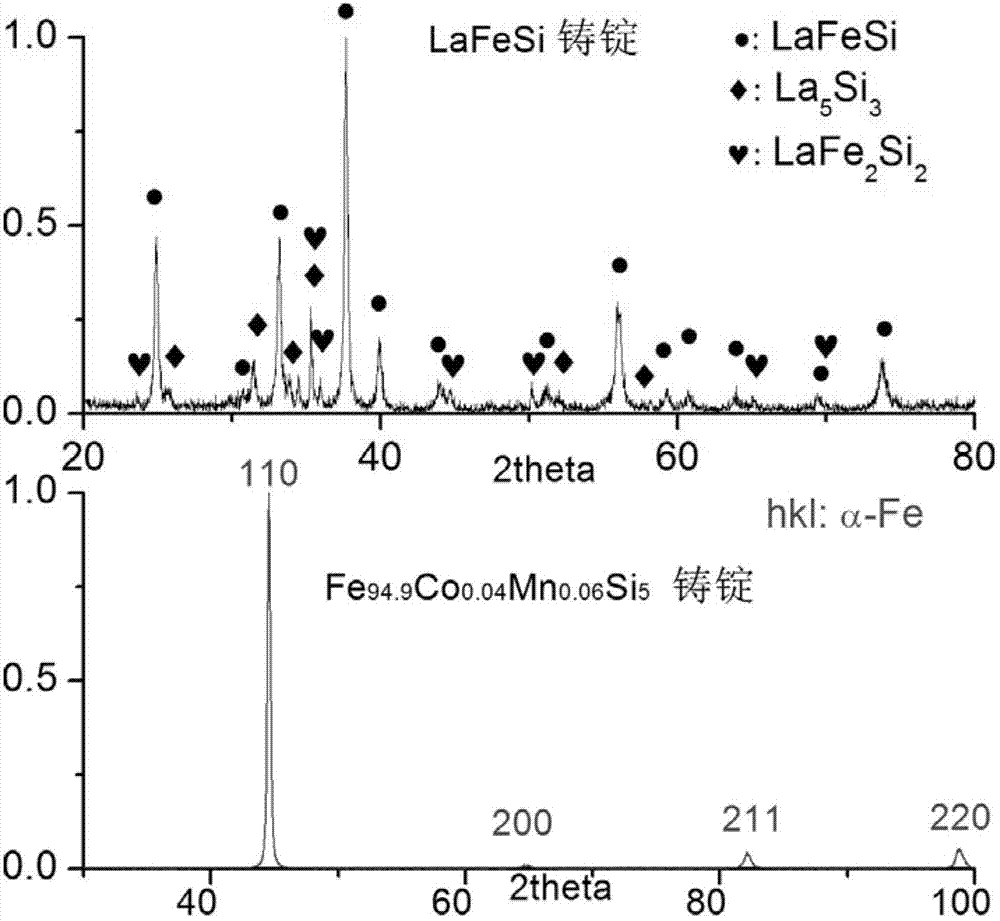
Solid-state electronics means semiconductor electronics; electronic equipment using semiconductor devices such as semiconductor diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used for devices in which semiconductor electronics which have no moving parts replace devices with moving parts, such as the solid-state relay in which transistor switches are used in place of a moving-arm electromechanical relay, or the solid-state drive (SSD) a type of semiconductor memory used in computers to replace hard disk drives, which store data on a rotating disk.
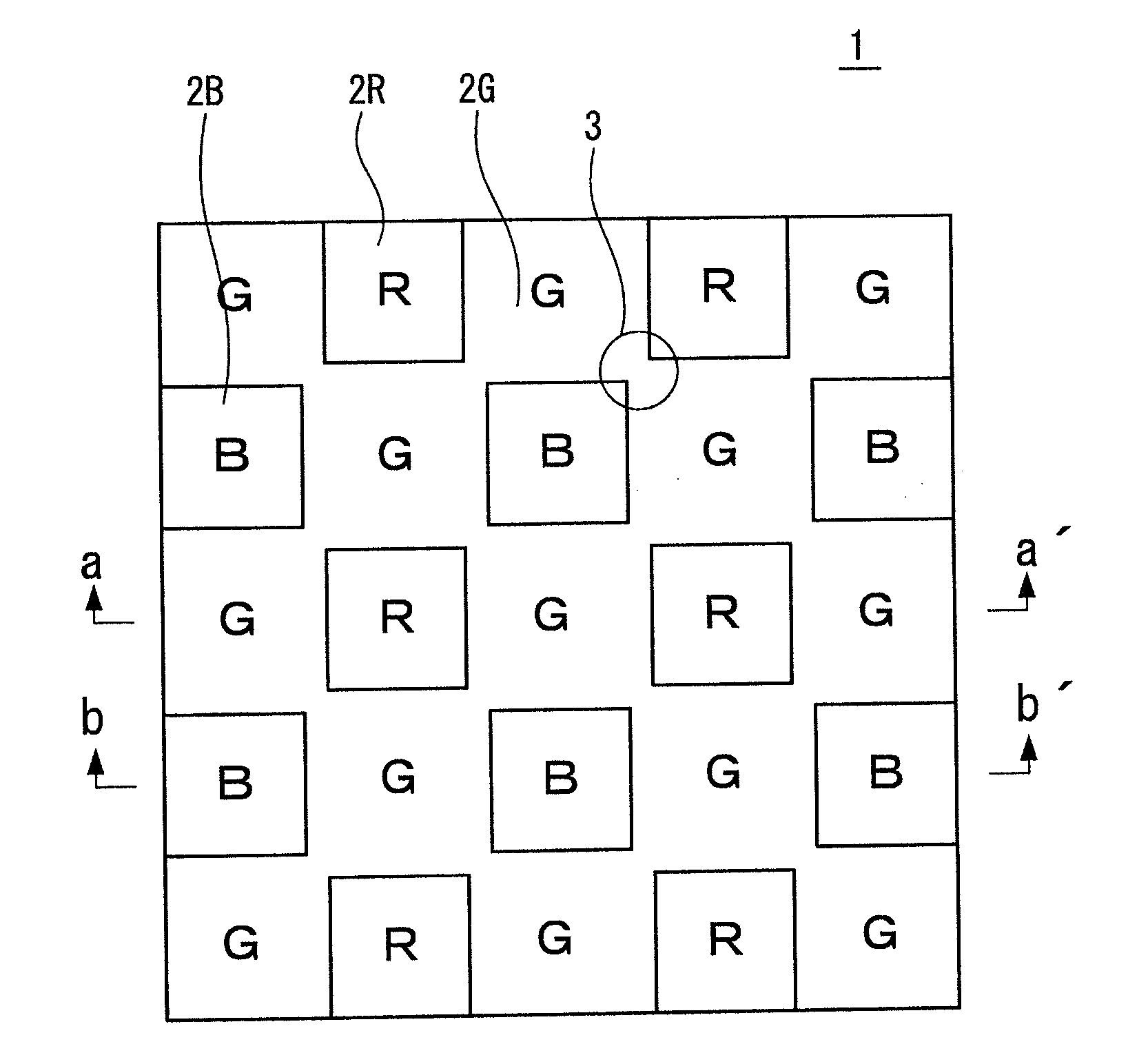
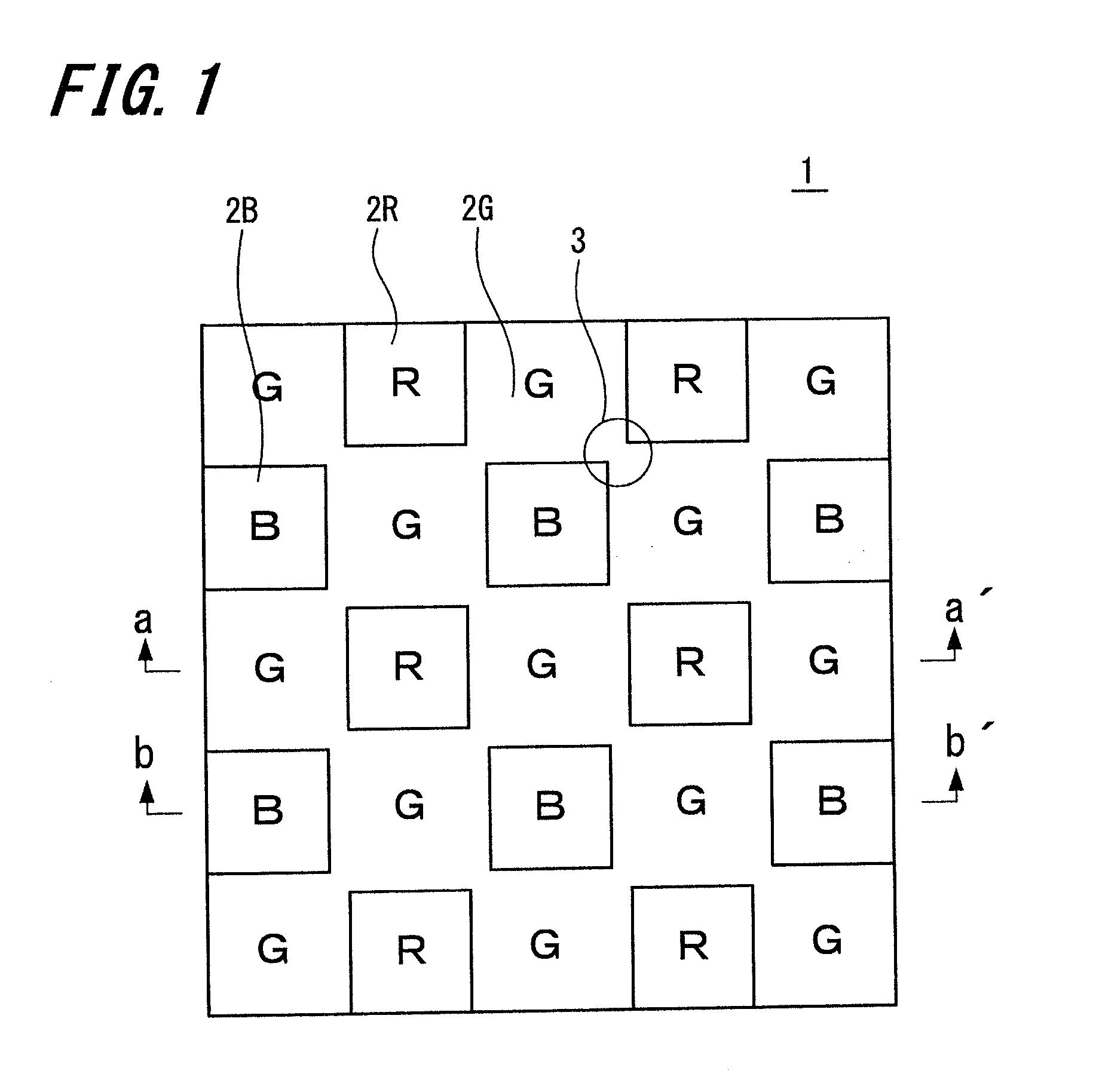
Lighting device having first, second and third groups of solid state light emitters, and lighting arrangement
ActiveUS20110031894A1Sharp contrastPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsLength waveLight emitter
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
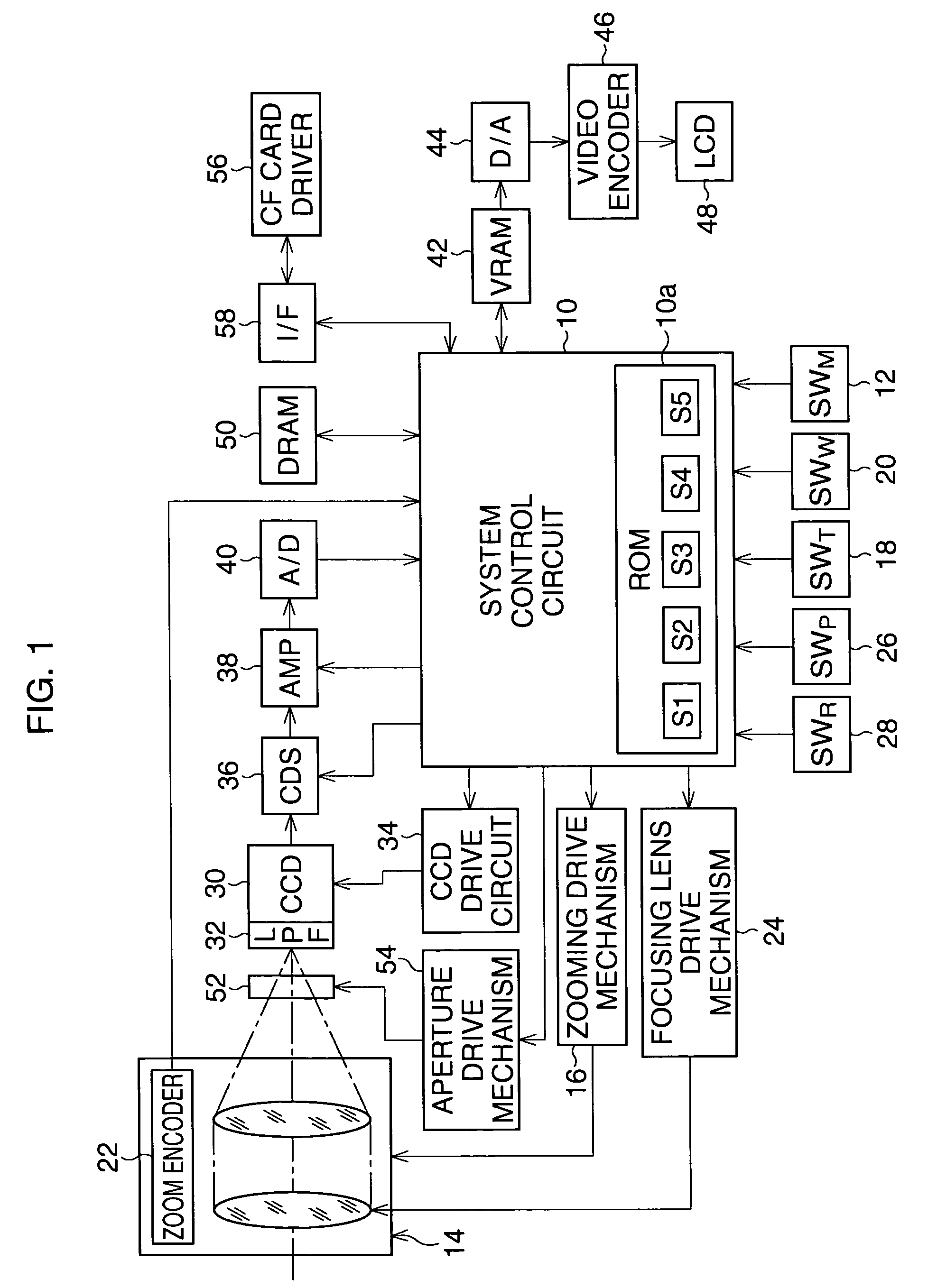
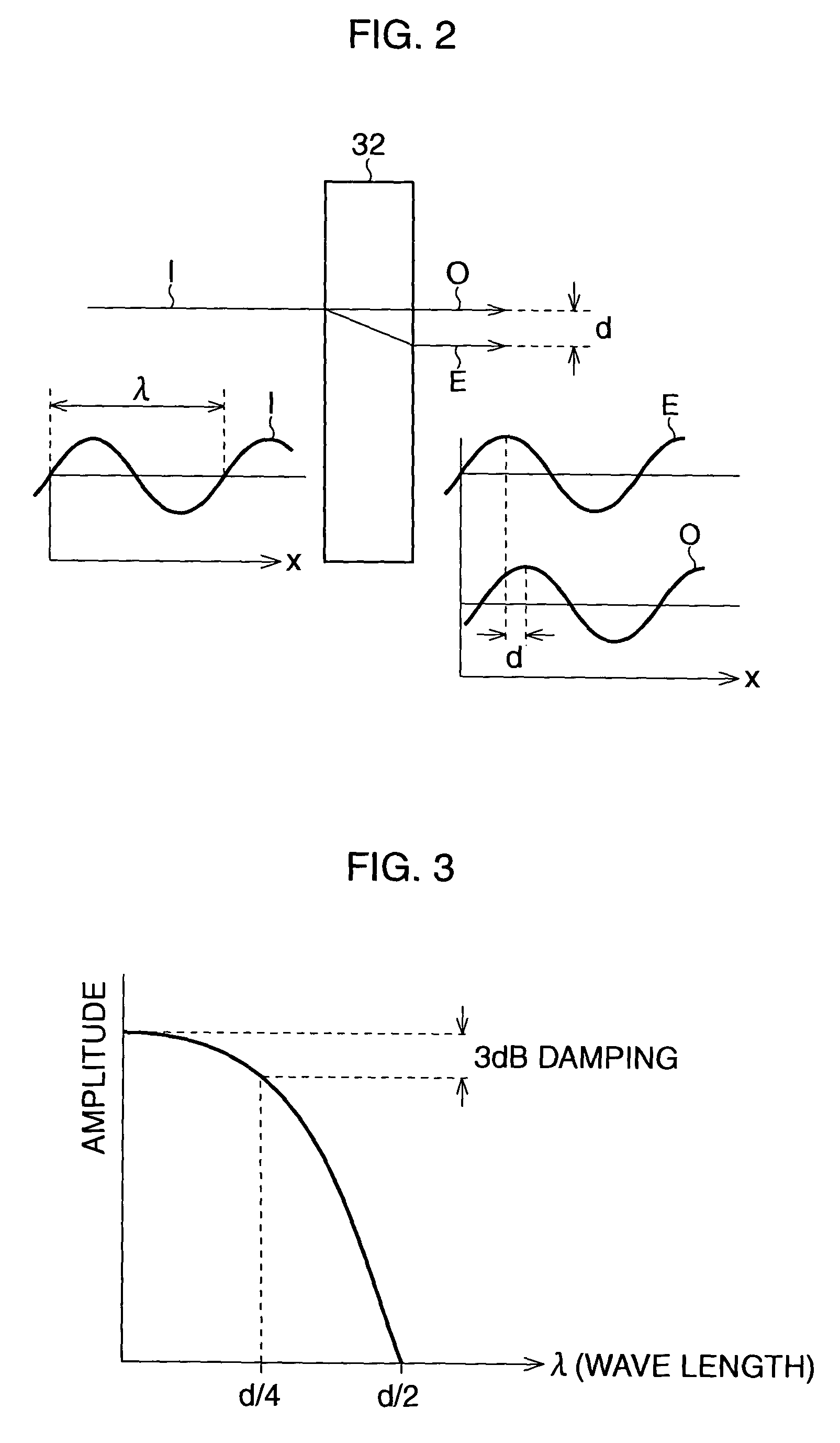
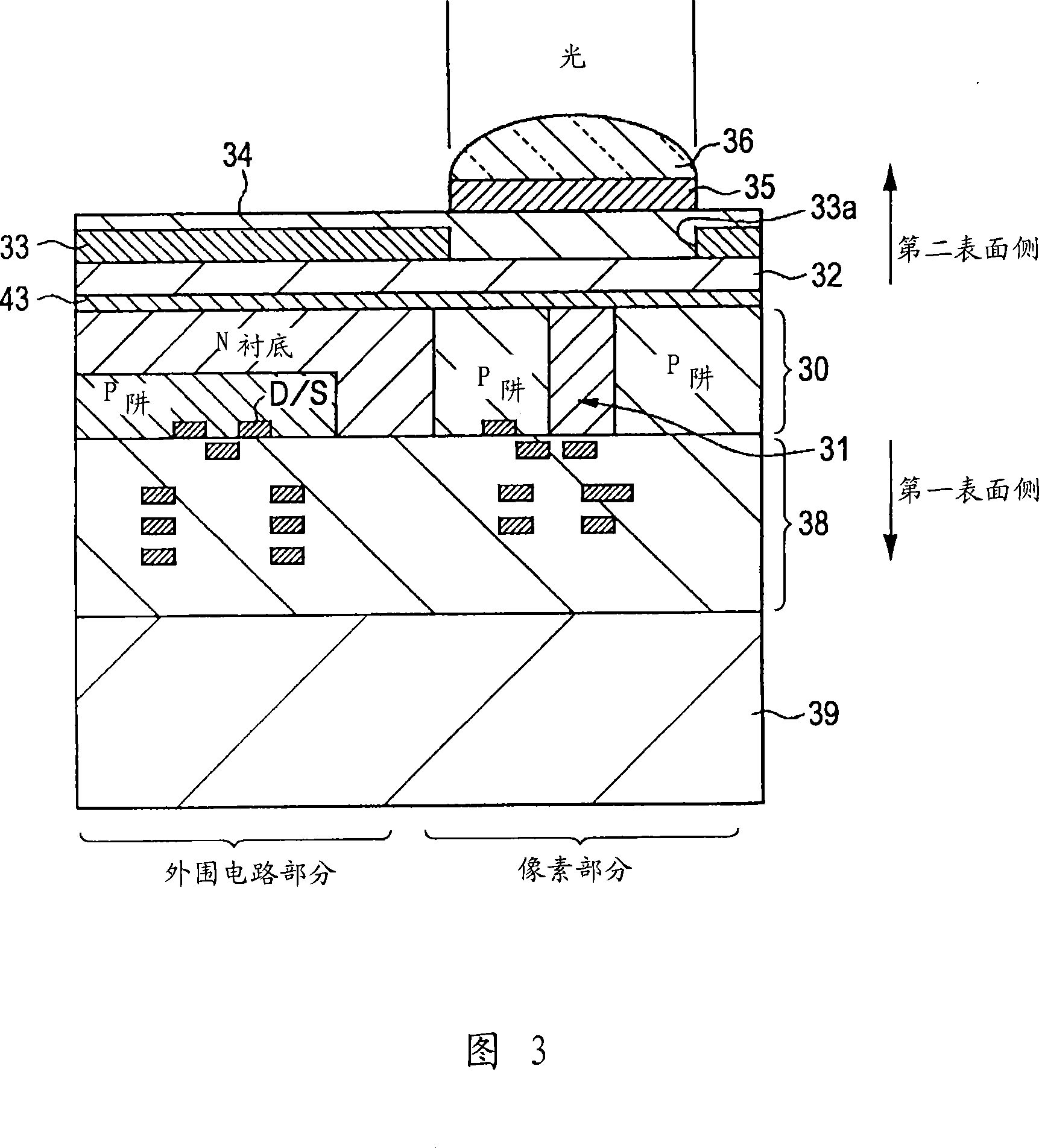
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing the same, and camera
InactiveUS20090147101A1Reduce probabilityReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPhotoelectric conversionTransistor
A solid-state imaging device is provided. The solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of arrayed pixels, an optical inner filter layer, and an inner-layer lens. Each of the plurality of arrayed pixels includes a photoelectric conversion portion and a pixel transistor. The optical inner filter layer is configured to block infrared light and faces a light-receiving surface of the photoelectric conversion portion of a desired pixel among the arrayed pixels. The inner-layer lens is formed below the optical inner filter layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Digital camera
InactiveUS7221394B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsBand-pass filterTime control
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Solid-state imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080030605A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDifferential signalingPhotoelectric conversion
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Solid-state light sources for curing and surface modification
InactiveUS20060274421A1Improve stabilityExtended service lifePoint-like light sourcePretreated surfacesMultiwavelength spectroscopyLight beam
Owner:HERAEUS NOBLELIGHT AMERICA
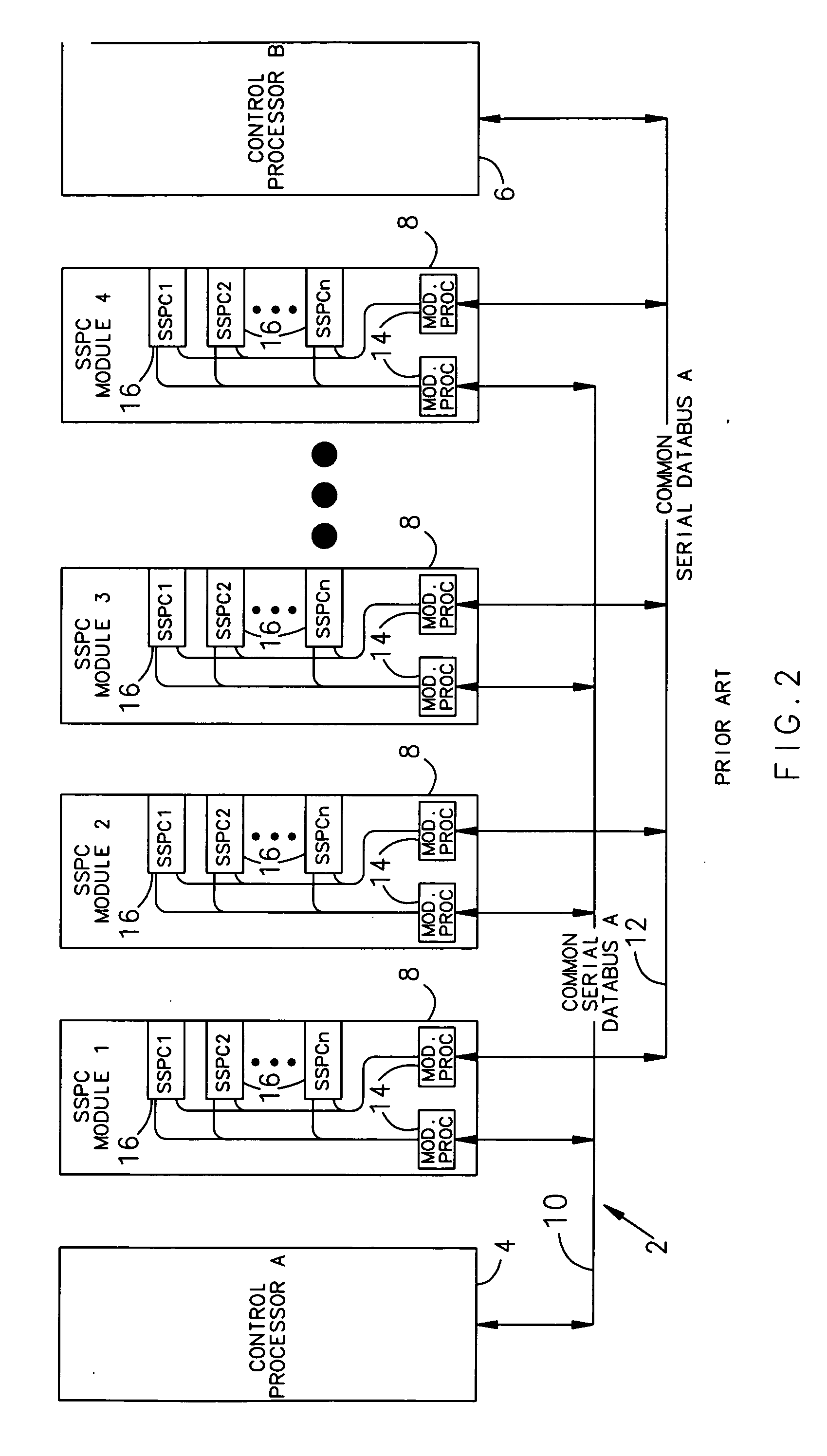
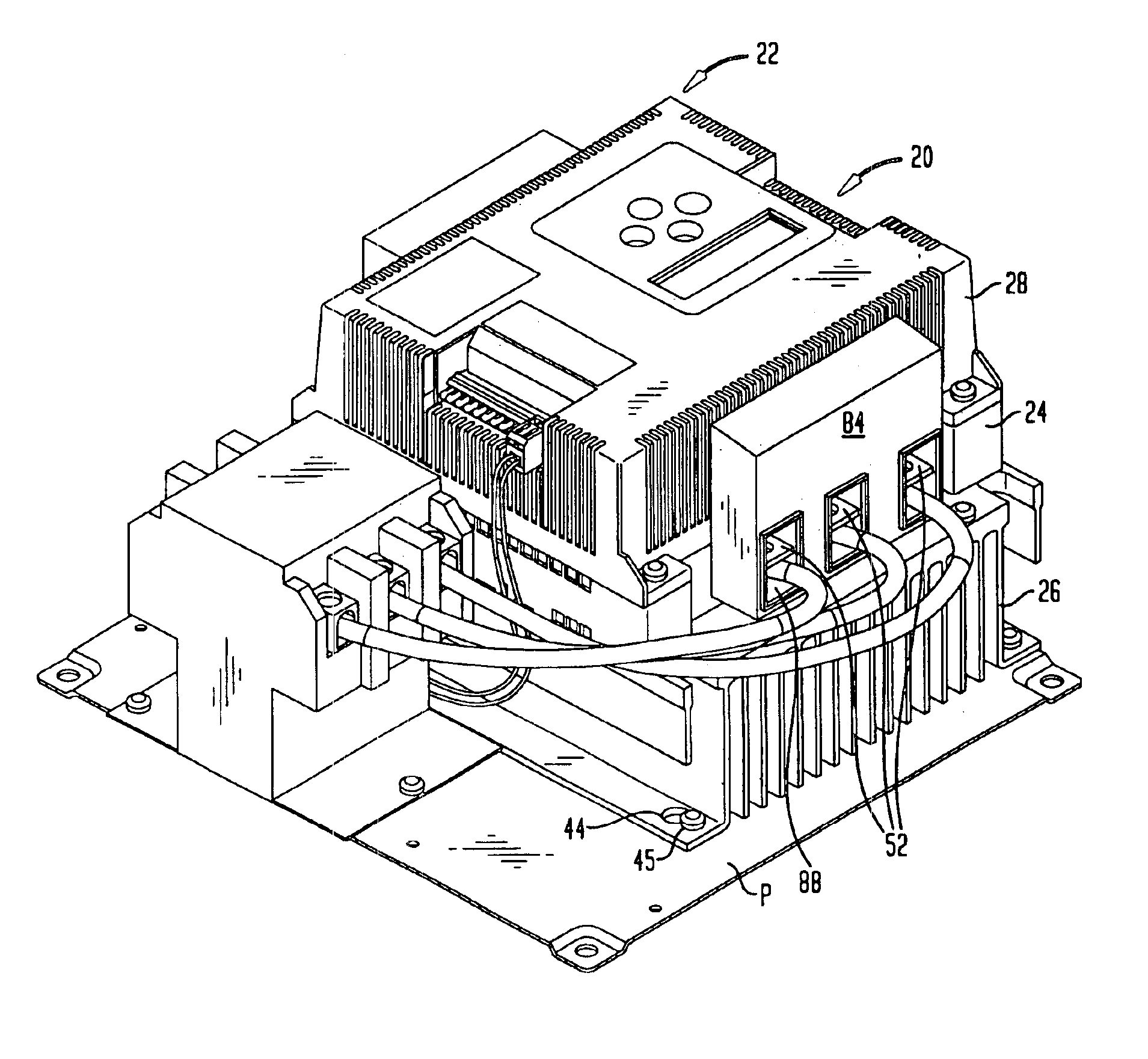
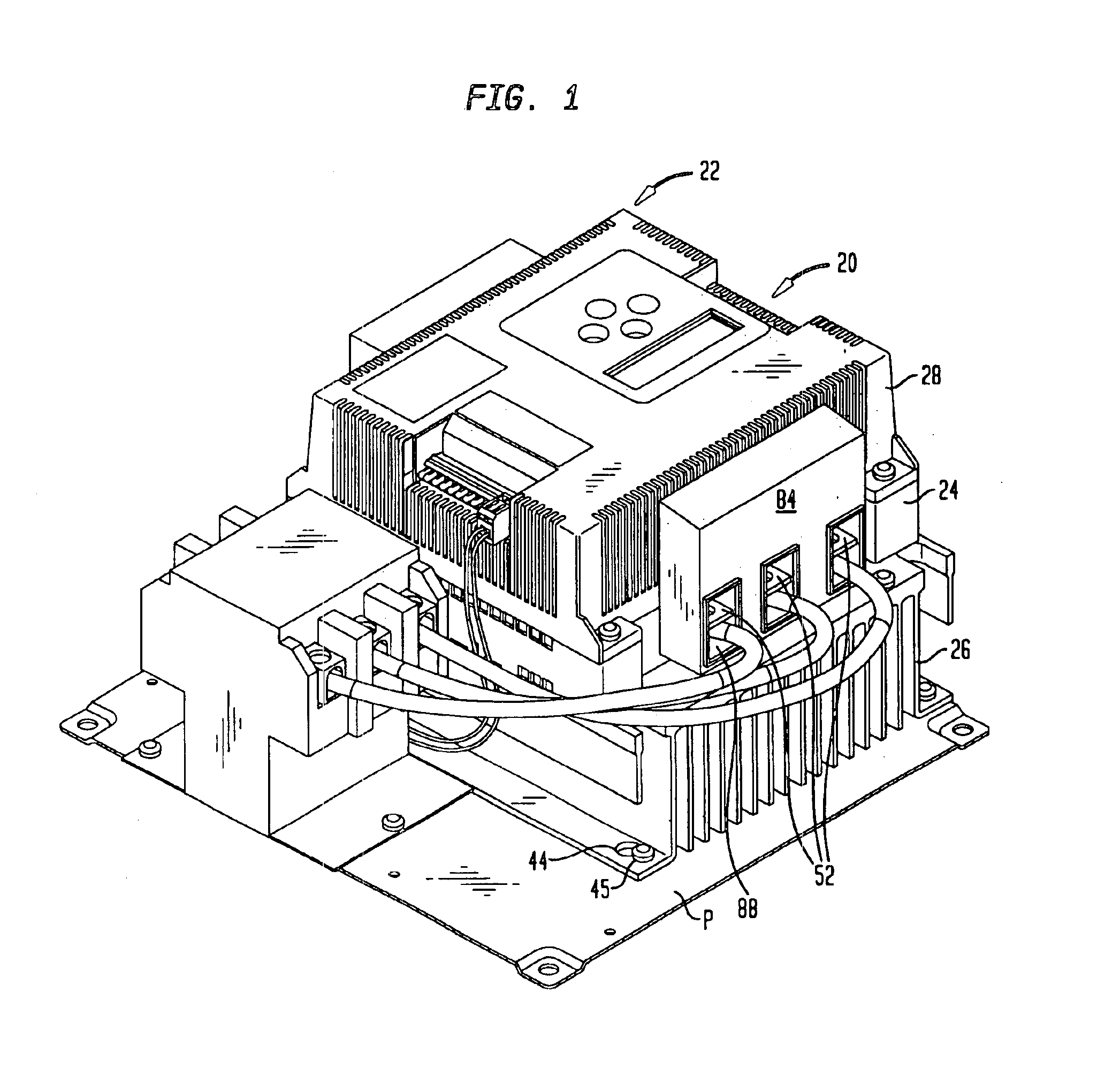
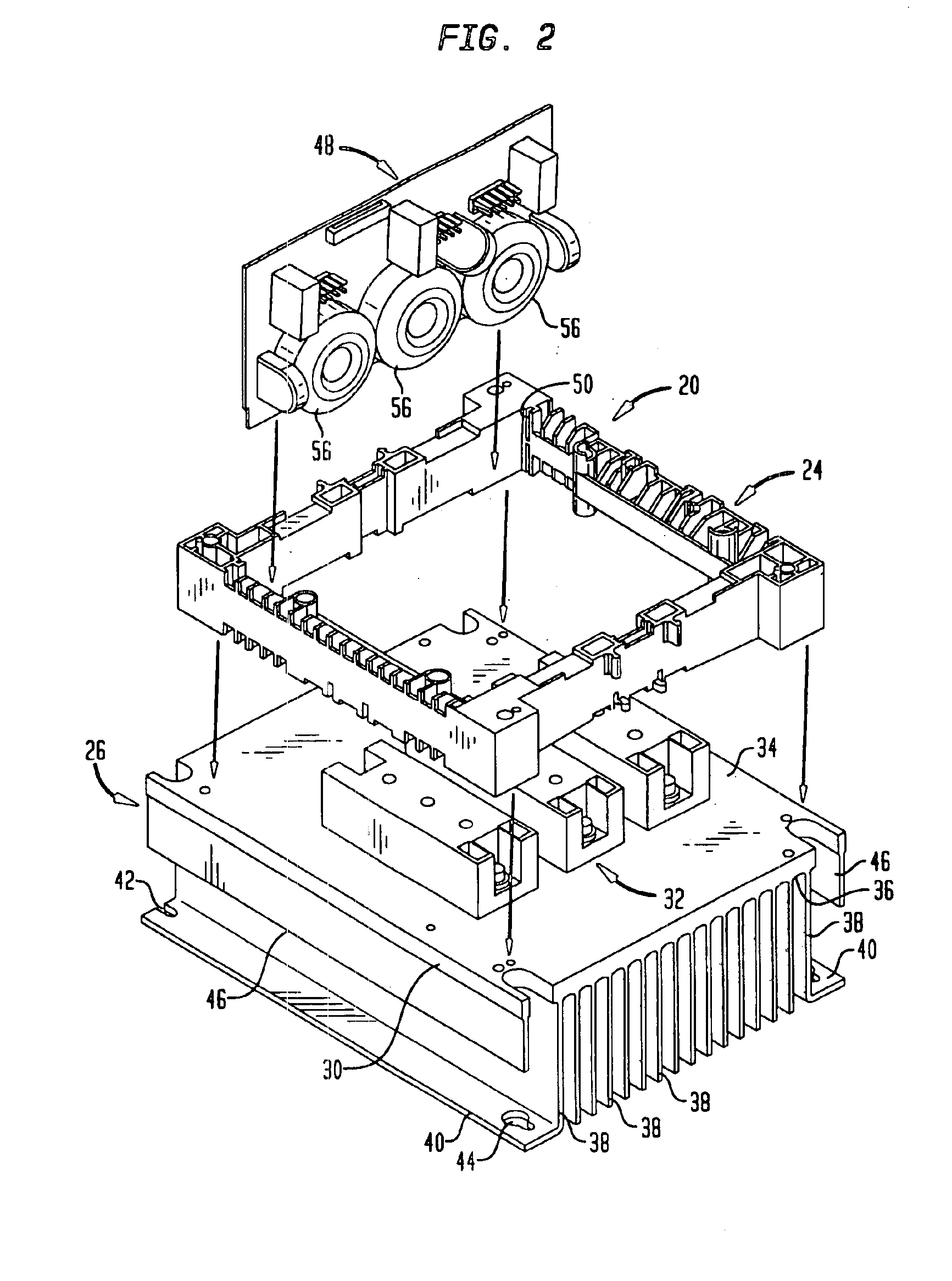
Individually and redundantly addressable solid-state power controllers on multiple modules in a power distribution assembly
InactiveUS20060071559A1Digital data processing detailsPower network operation systems integrationSolid-statePower module
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Downhole Well Communications Cable
ActiveUS20120031607A1High service temperaturePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCommunication cablesVinyl etherTetrafluoroethylene
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
System and method for improved motor controller
InactiveUS6891725B2Reduce manufacturing costDecrease stockSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlCurrent rangeModularity
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY & AUTOMATION INC
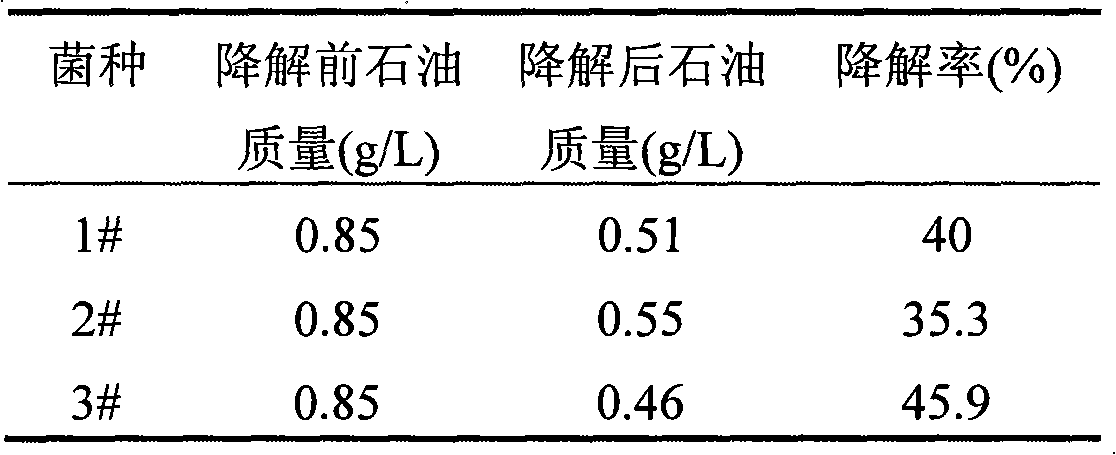
Solid microbial agent to remedy soil contaminated by petroleum, preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN101597576AHigh organic contentImprove micro-ecological environmentBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismEcological environment
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
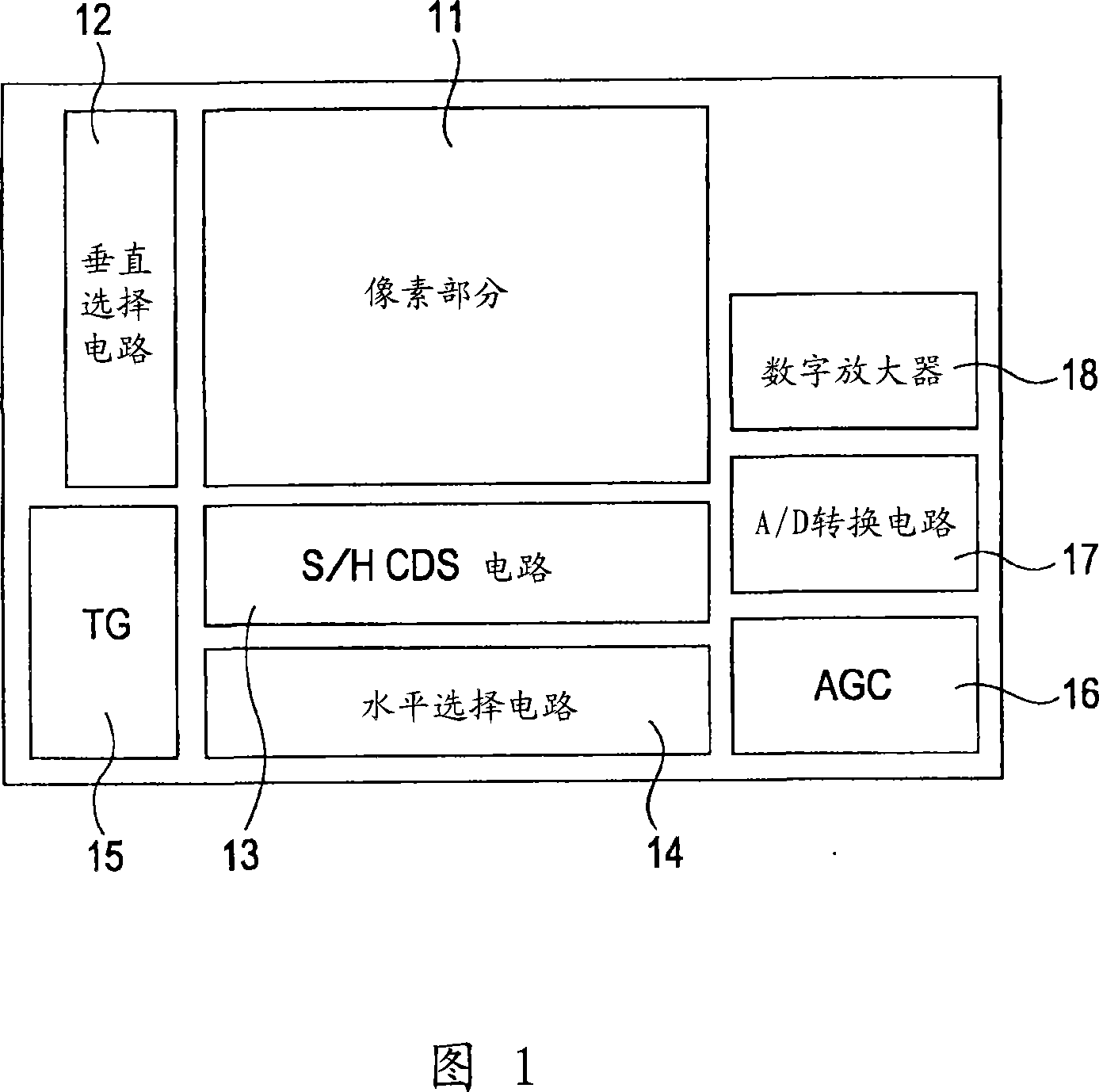
Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and electronic device
InactiveUS20090303359A1Improve machining accuracyInhibit coloringTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
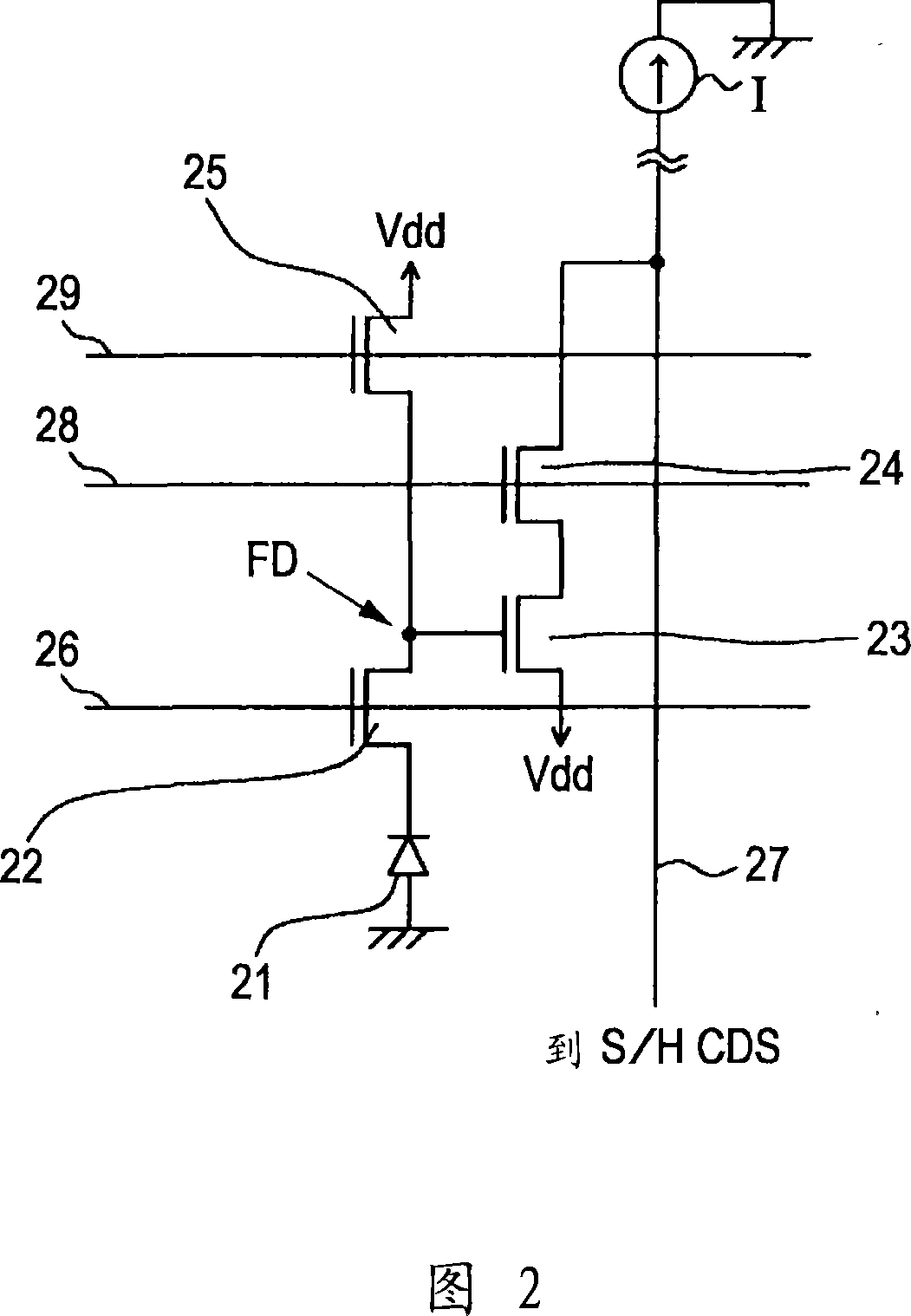
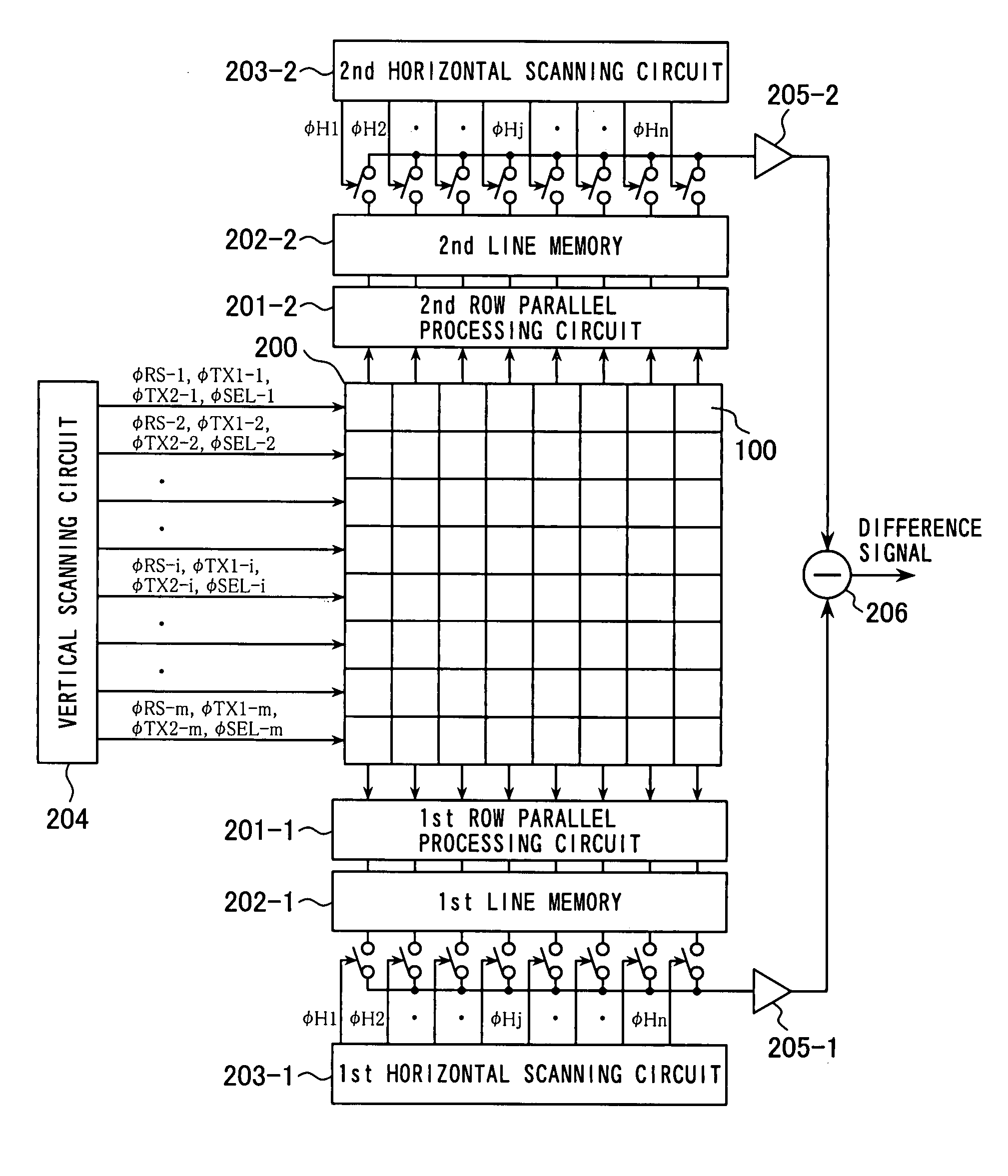
Solid-state imaging device, drive method thereof and camera system
ActiveUS20110267522A1SpeedReduced settling timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionSlew rate
A solid-state imaging device includes: pixel signal reading lines; a pixel unit in which pixels including photoelectric conversion elements are arranged; and a pixel signal reading unit performing reading of pixel signals from the pixel unit through the pixel signal reading lines, wherein the pixel signal reading unit includes current source circuits each of which includes a load element as a current source connected to the pixel signal reading line forming a source follower, and the current source circuit includes a circuit generating electric current according to a slew rate of the pixel signal reading line and replicating electric current corresponding to the above electric current to flow in the current source.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solid state image pickup device, method of manufacturing the same, image pickup device, and electronic device
InactiveCN101853866AReduce the effects of chromatic aberrationReduce exposure timeSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesTransducerPhotoelectric conversion
The invention relates to a solid state image pickup device, a method of manufacturing the same, an image pickup device, and an electronic device. The solid state image pickup device includes a pixel section defined by unit pixels arrayed in line and row directions of a semiconductor substrate. Each of the unit pixels includes a photoelectric transducer that is formed on the semiconductor substrate and converts incident light into a signal charge, a waveguide that is formed above the photoelectric transducer and guides the incident light to the photoelectric transducer, and a microlens that is formed above the waveguide and guides the incident light to an end of light incident side of the waveguide. The waveguide has a columnar body with a constant cross section from the end of light incident side to an end of light exit side, and is arranged such that a center of rays of the incident light incident from the microlens on the end of light incident side of the waveguide is aligned with a central axis of the waveguide.
Owner:SONY CORP
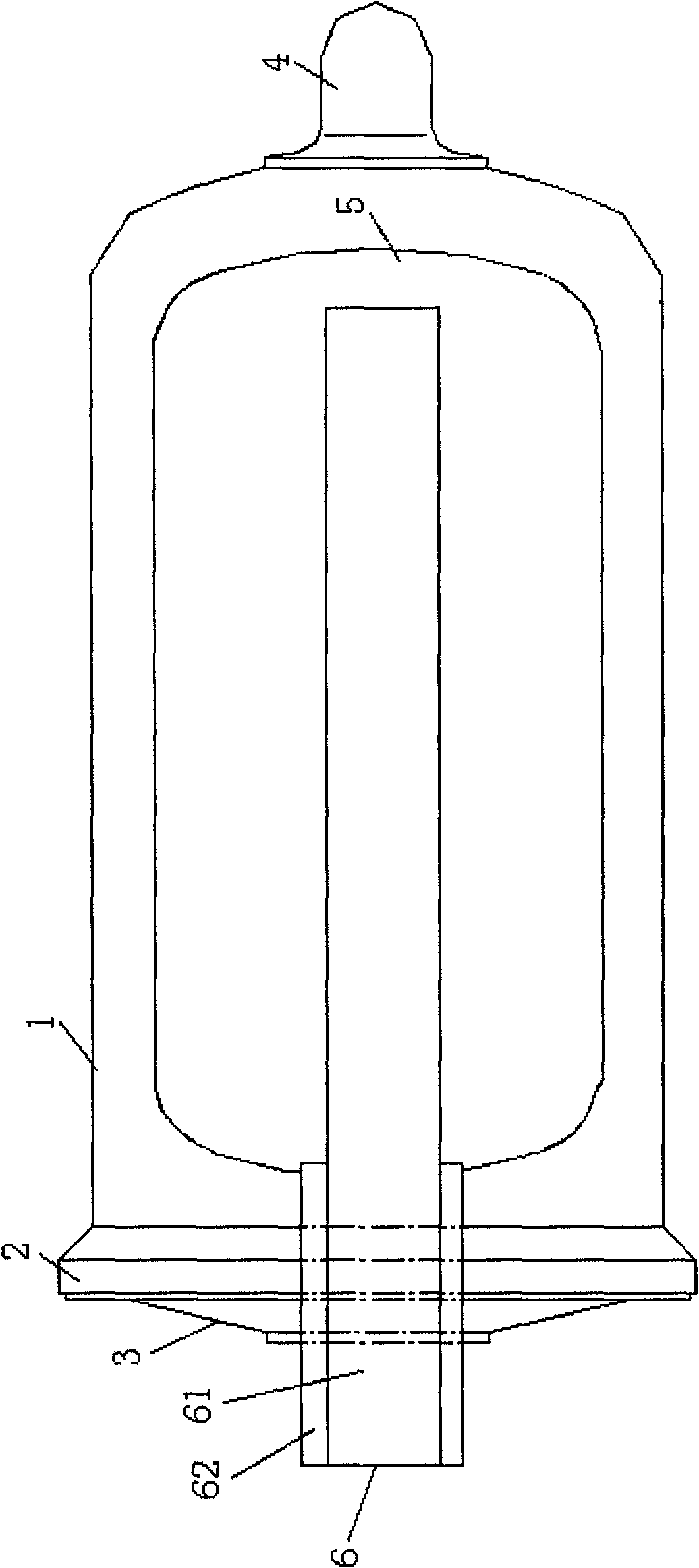
Thermal storage type vacuum tube
InactiveCN101639296AExtended service lifeIncrease the heat exchange areaHeat storage plantsSolar heat devicesSolar waterMetallic materials
Owner:北京桑达太阳能技术有限公司
Solid state radiation detector
InactiveUS6191465B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStructural principleSolid-state
Owner:INTERFACE STUDIES
Solid state image pickup device, driving method thereof and camera
InactiveUS6980244B1Increase shutter speedExtension of timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSolid-stateElectronic shutter
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Electrochemical pipeline erosion corrosion testing device
ActiveCN109444236AEnables electrochemical measurementsEasy to analyzeMaterial electrochemical variablesTest efficiencyMaterial Erosion
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
A design method of a page-level flash memory conversion layer of a solid-state hard disk
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
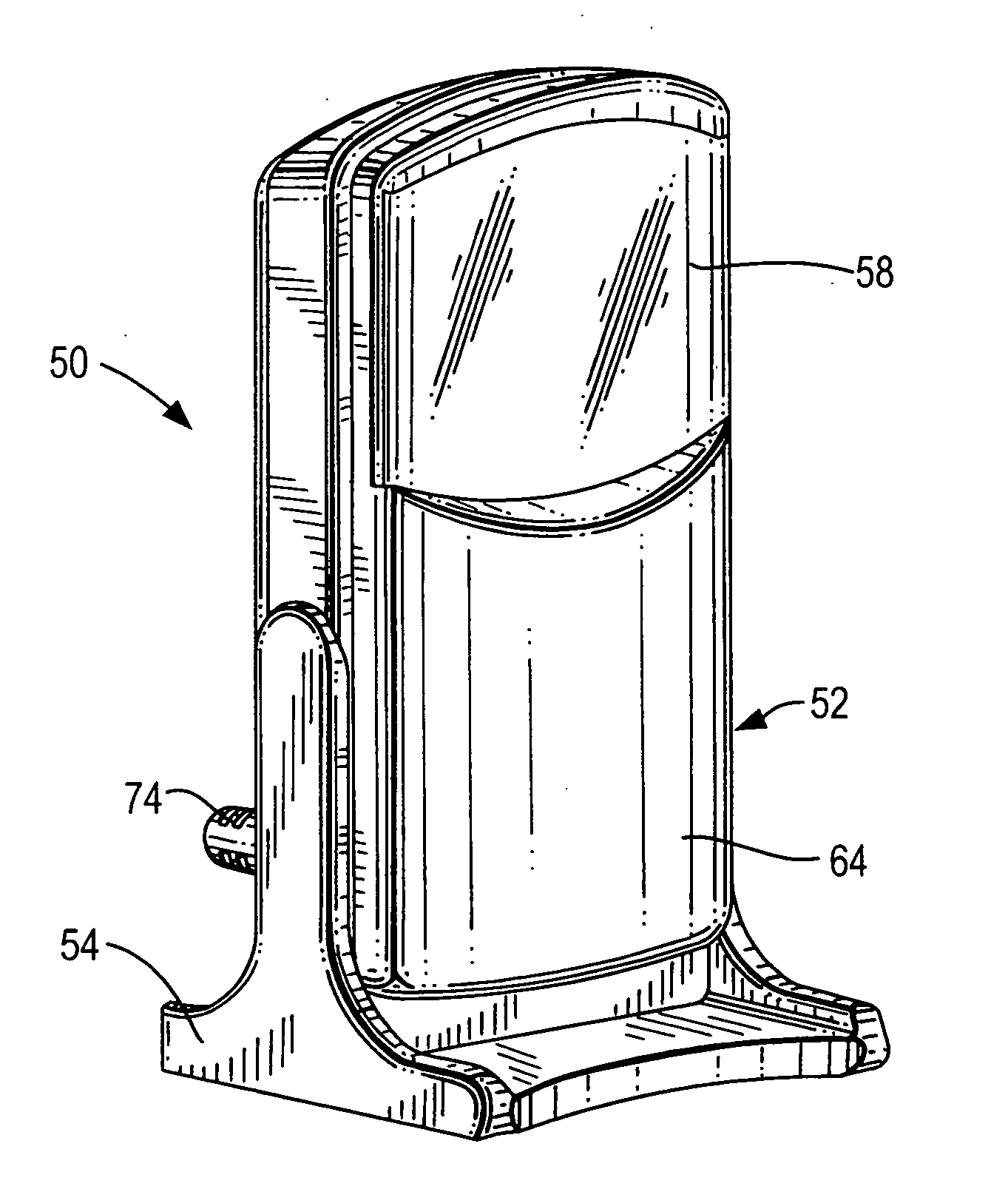
Compact, ergonomic imaging reader and method
InactiveUS20080296388A1Reduce chanceIncrease vertical heightSensing by electromagnetic radiationField of viewComputer science
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
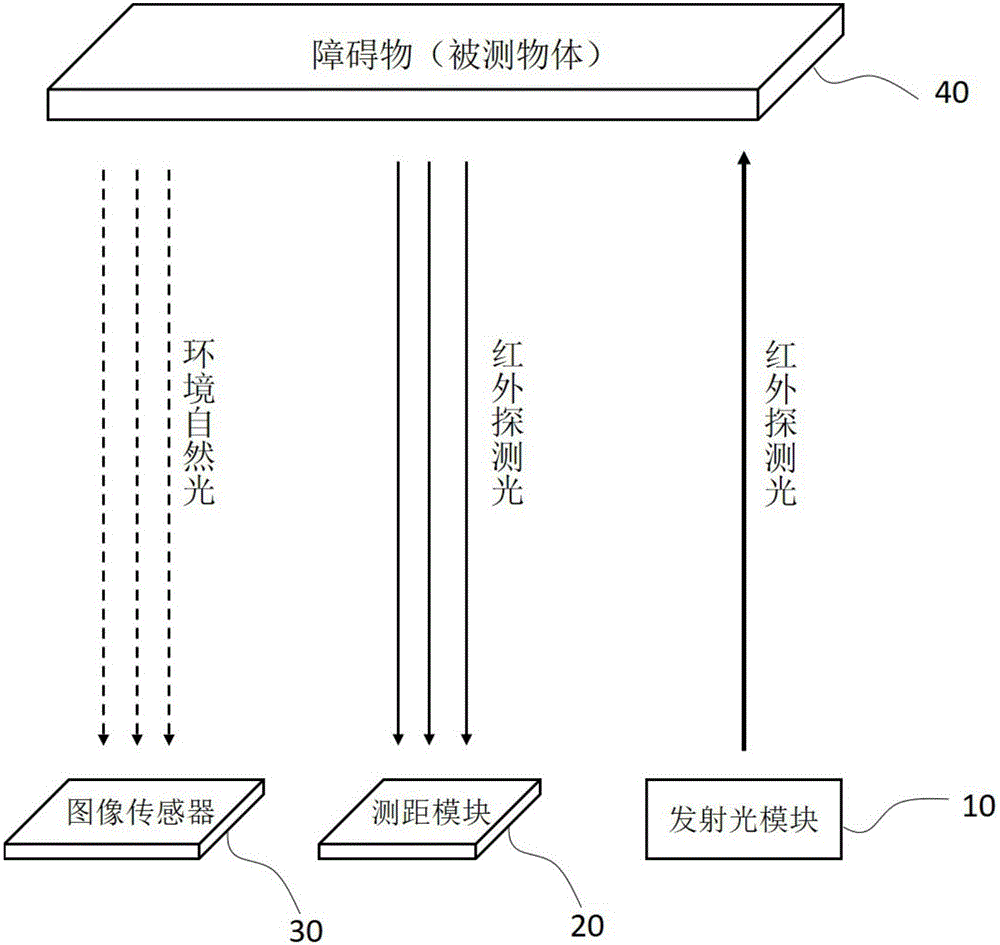
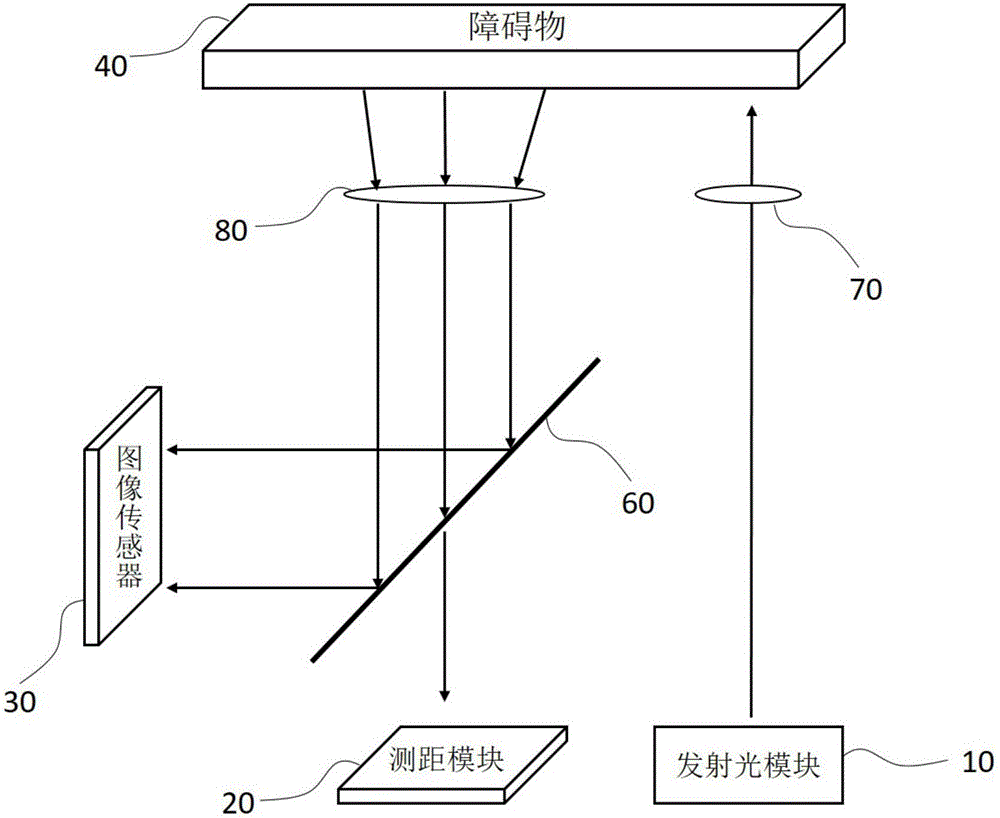
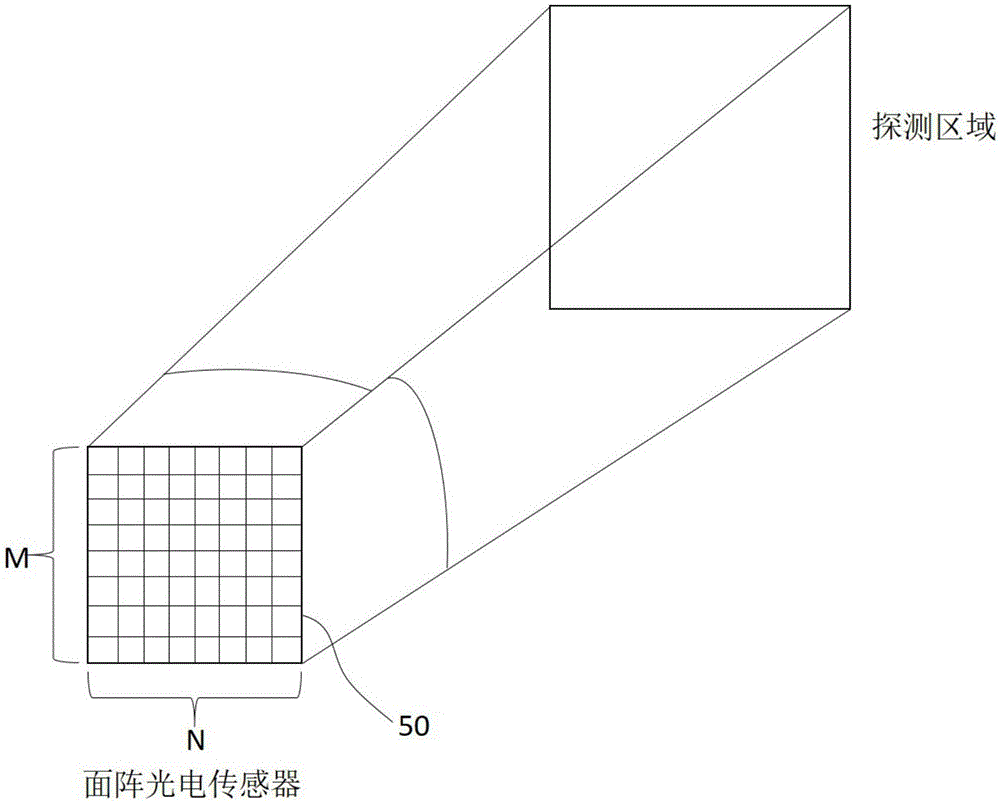
Solid-state multi-line ranging device and ranging method
PendingCN106526573AImprove stabilityExtend your lifeElectromagnetic wave reradiationObject basedTime of flight
Owner:BENEWAKE BEIJING TECH CO LTD
Thermal Energy Management of Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20070152674A1Reduce energy consumptionAccurate placementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal energyElectricity
Owner:HUBBELL DAVID ALLEN
High-temperature fermentation method of Chinese herbal medicines
Owner:湛江银恒生物科技有限公司
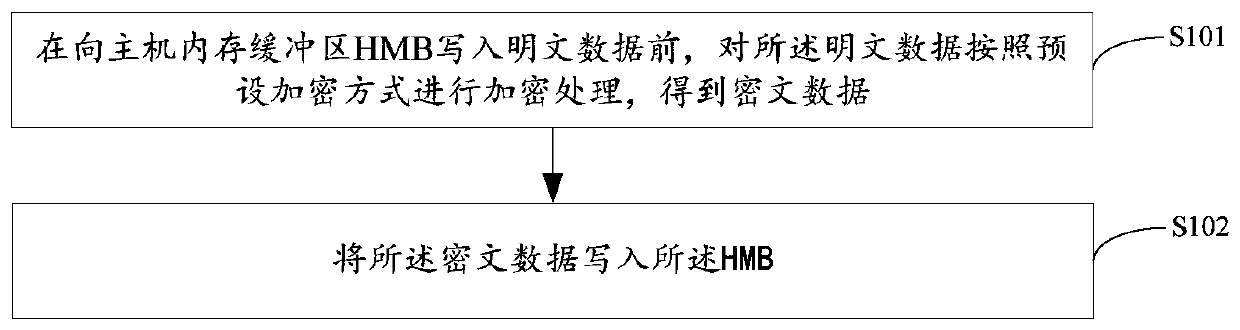
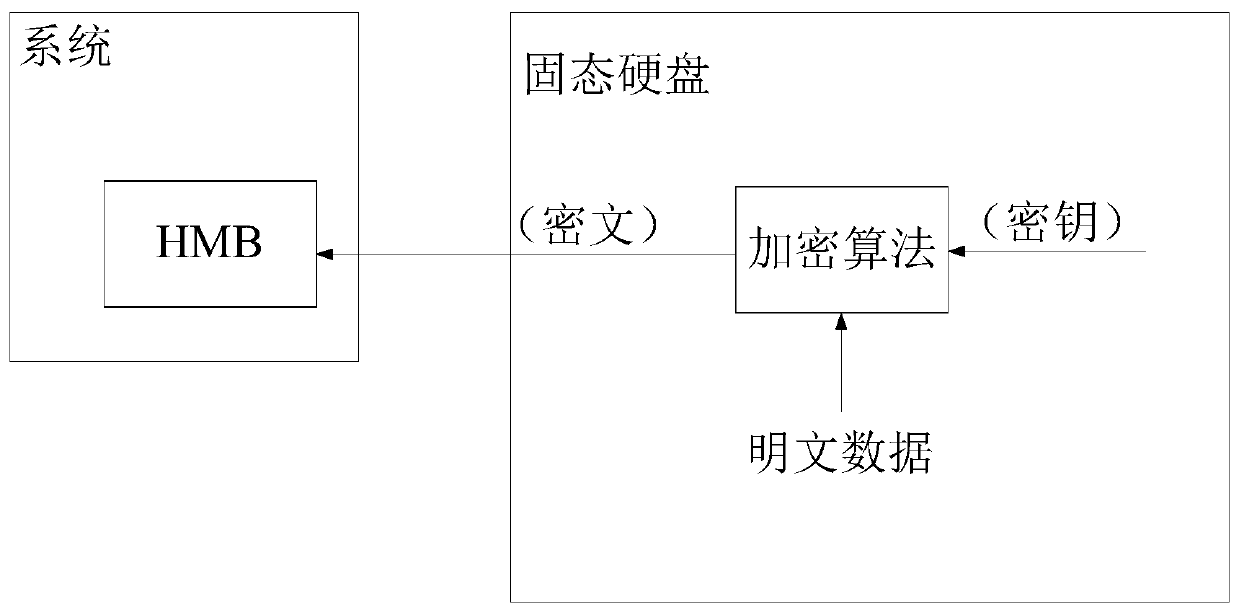
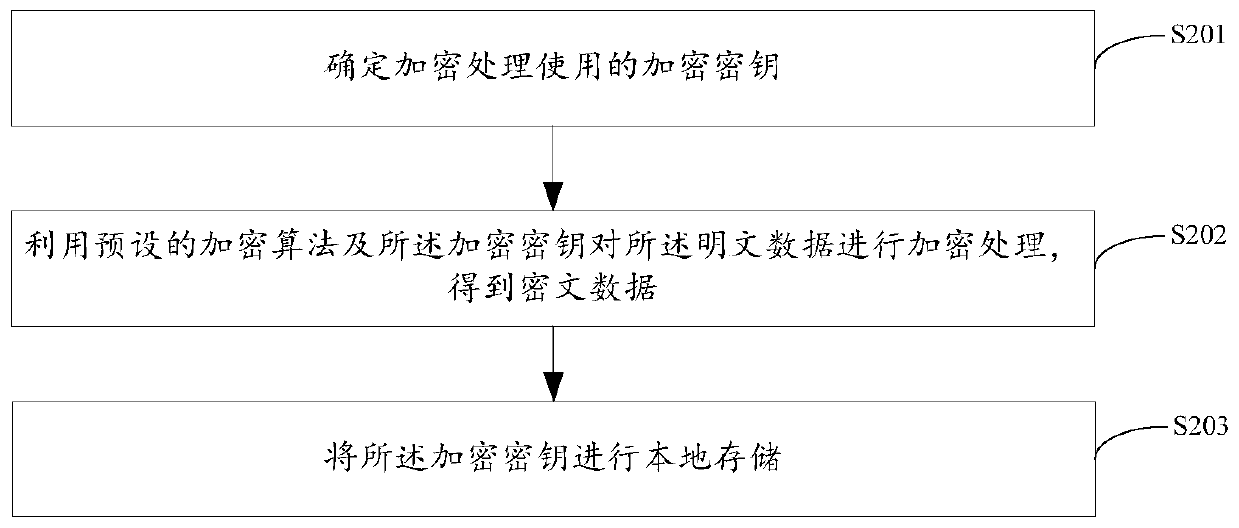
Data protection method and device, solid state disk and storage medium
PendingCN110472445AEnsure safetyDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionPlaintextCiphertext
Owner:SHENZHEN TIGO SEMICON
Method for preparing rare-earth compound with NaZn13 structure by solid state diffusion
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High-temperature thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103107279AThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsDecompositionSolid-state
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
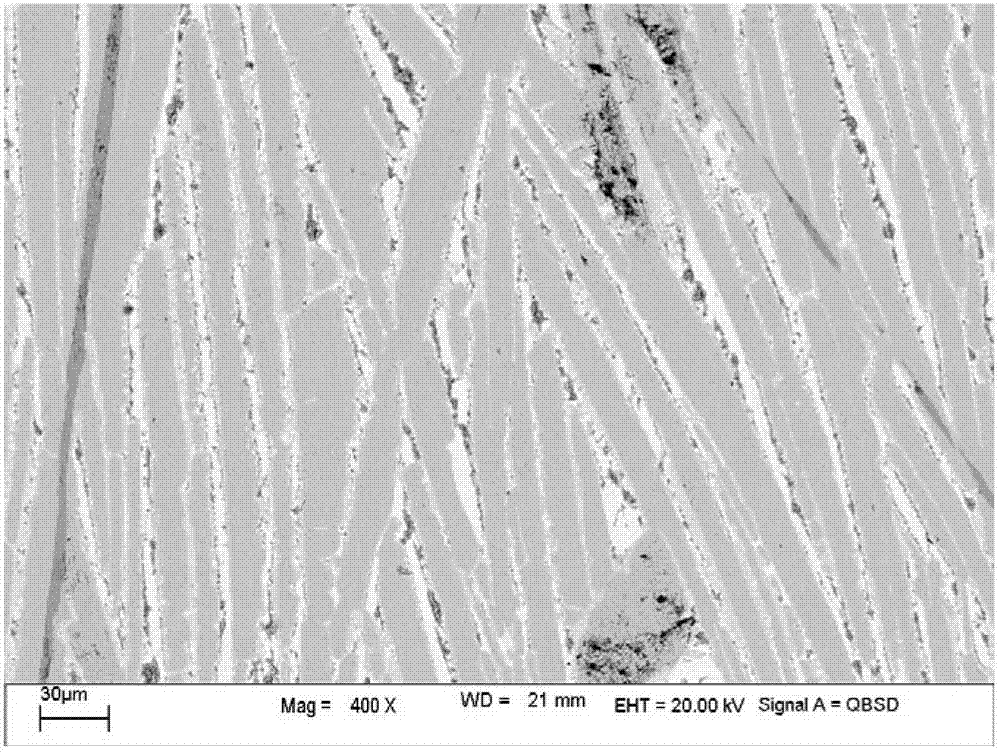
Al-Co-W alloy with alternating lamellar microstructure characteristics and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an Al-Co-W alloy with alternating lamellar microstructure characteristics and a preparation method thereof, relates to preparation of novel materials and in particular relates to an alloy with alternating lamellar microstructure characteristics and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the alloy comprises an alternating lamellar structure, and the lamellar pairs occur periodically. In the Al-Co-W alloy system, Al component can diffuse quickly, Co component can diffuse slowly and W component is immovable basically. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a CoxWy type intermetallic compound or a (Co-W) solid solution by using components Co and W of which the diffusion rates are different, and grinding the intermetallic compound or solid solution into small particles; controlling the heating temperature and reaction mode in a protective atmosphere so that the component Al in solid state, liquid state or gas state reacts with the CoxWy type intermetallic compound or the (Co-W) solid solution; reacting for a proper period of time, rapidly cooling to room temperature, thereby obtaining the alloy with alternating lamellar microstructure characteristics. According to the invention, a novel path is provided for preparation of novel composite materials and connection of out-phase materials.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
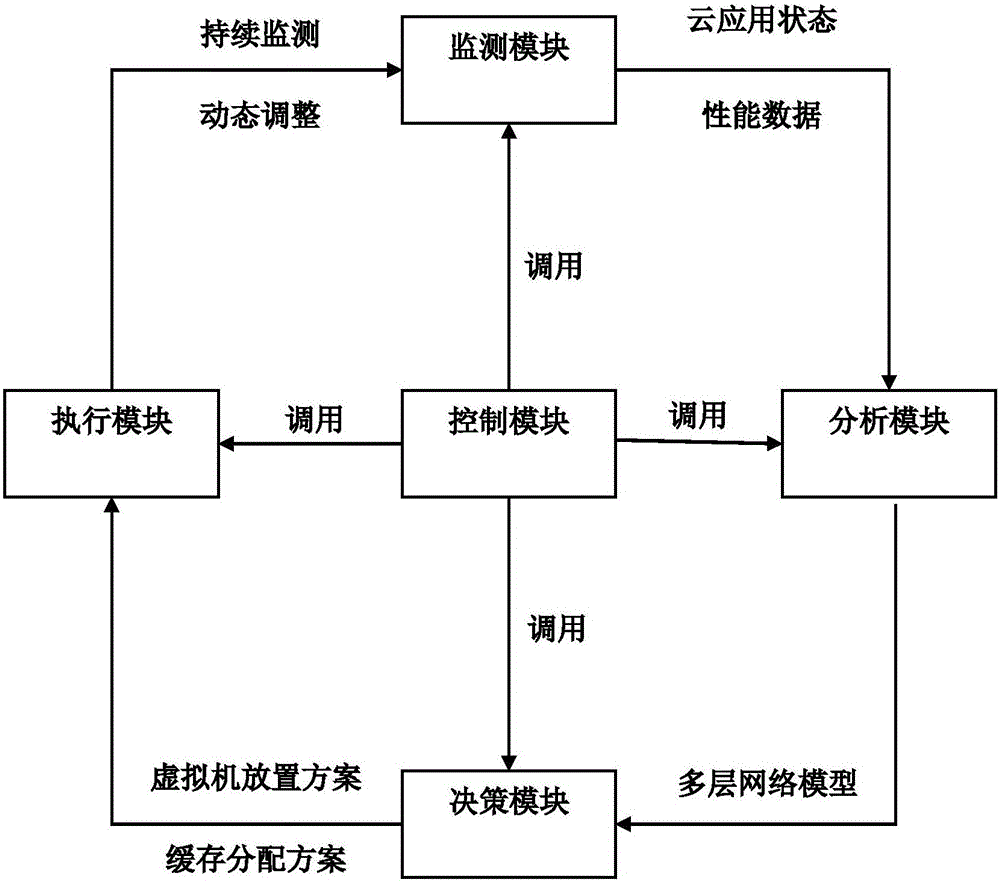
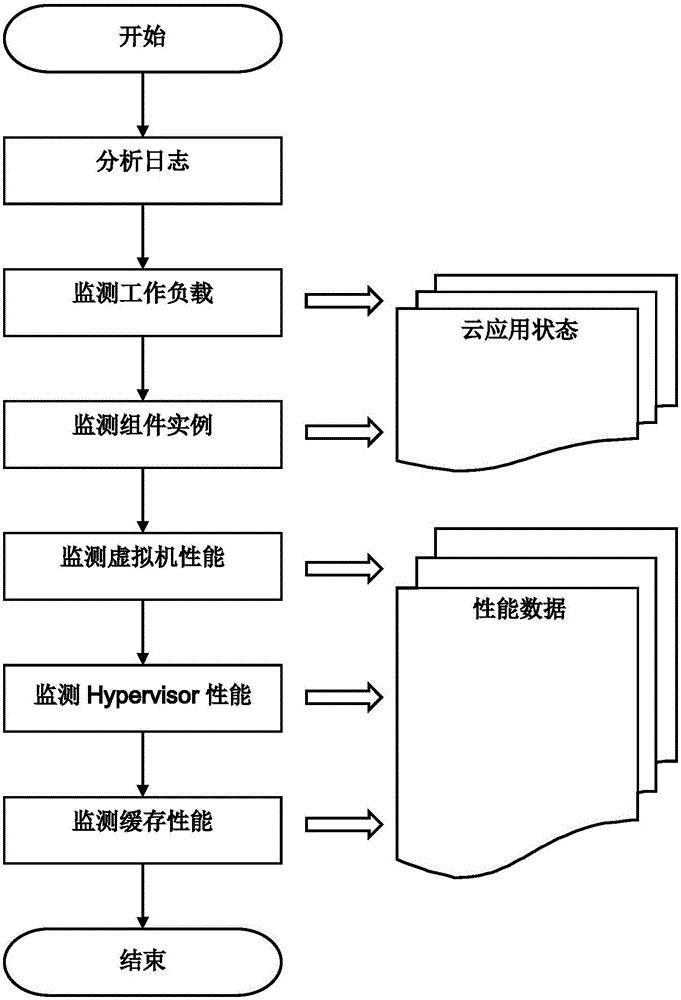
Cloud application-guided solid state disk cache management system and method
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photosensitive coloring resin composition, colored pattern or black matrix, color filter, liquid crystal display device or solid-state imaging element, and method for producing color filter
InactiveCN107615167AExcellent developabilityExcellent adhesionOptical filtersPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid-crystal displayHydrogen atom
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
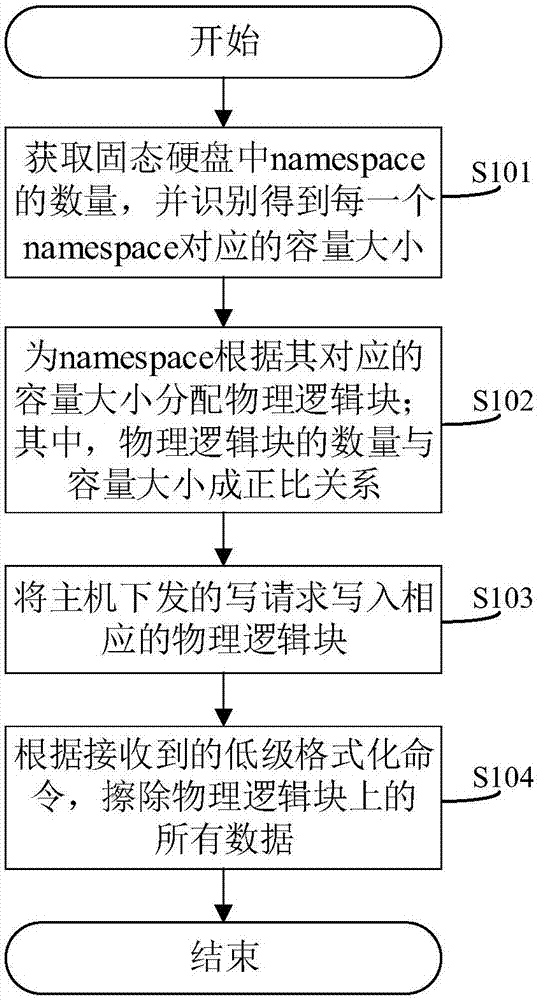
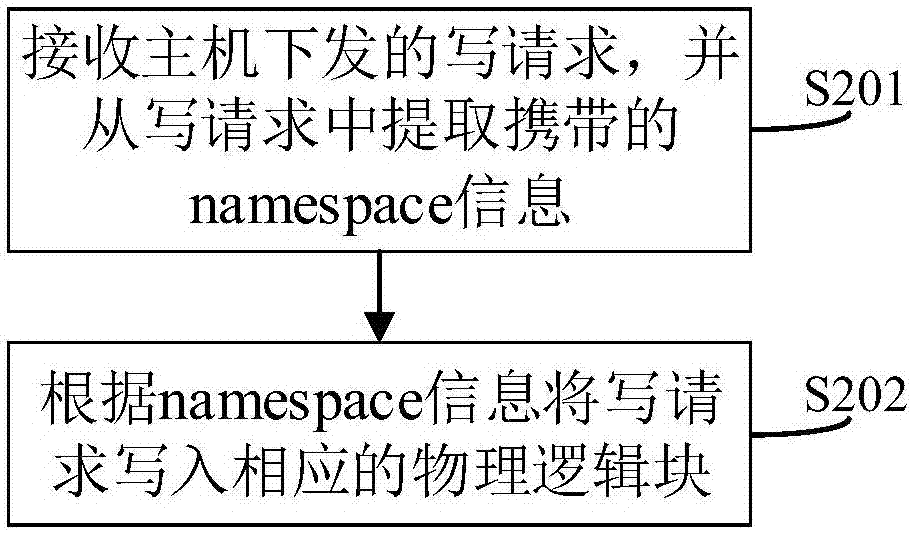
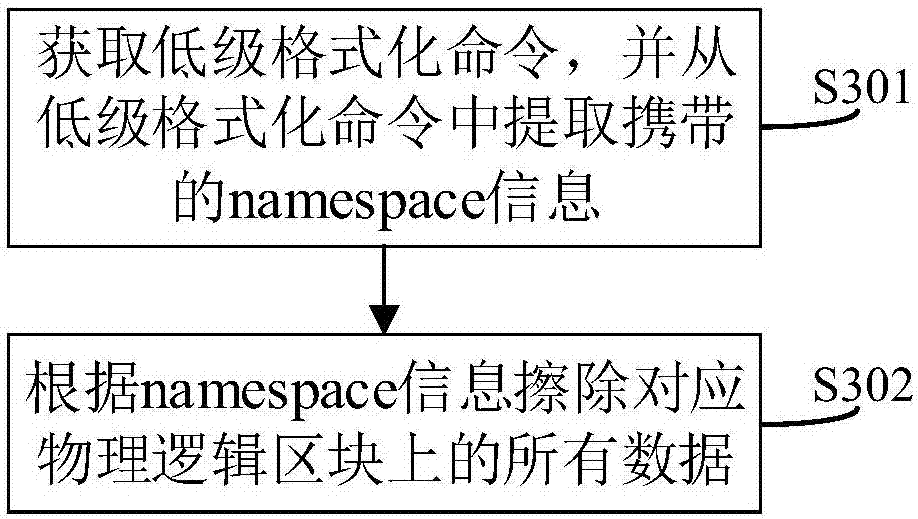
Method and system for low-level formatting of solid-state disk
InactiveCN107315546ASimple processSimple stepsInput/output to record carriersSolid-state driveNamespace
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
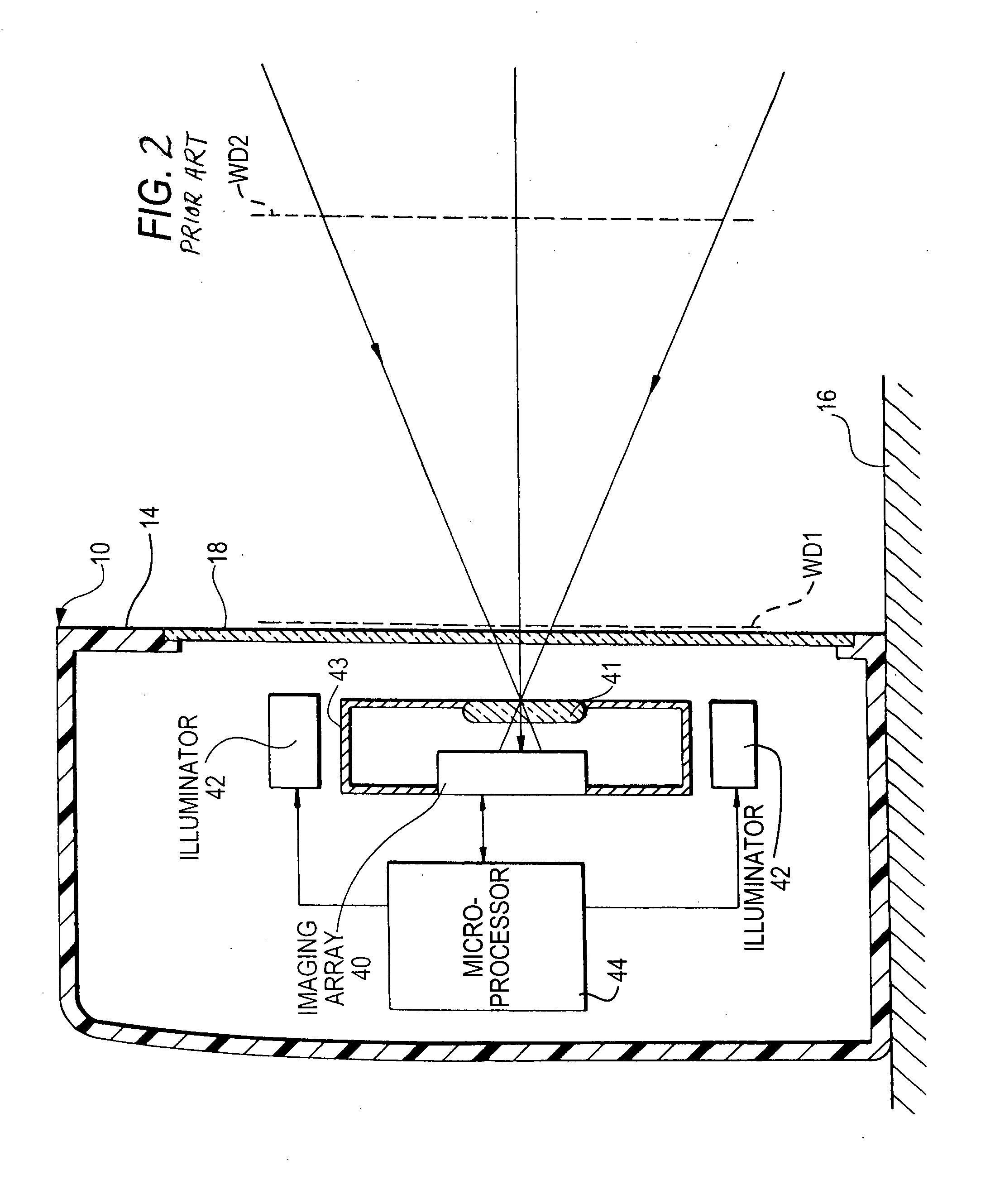
Method for the compensation of image disturbances in the course of radiation image recordings and radiation image recording apparatus
ActiveUS7070328B2Television system detailsAdditive manufacturing apparatusUltrasound attenuationAntiscatter grid
A method is for the compensation of image disturbances in the course of a radiation image recording caused by a defocusing of an antiscatter grid, arranged in the beam path between a beam source and a digital radiation image receiver and focused with respect to a specific distance from the focus of the beam source. Such image disturbances are caused by a defocusing-dictated attenuation of the primary radiation incident on the radiation image receiver. A solid-state image detector includes radiation-sensitive pixels arranged in matrix form and a device for pixelwise amplification of the radiation-dependent signals. In the method, at least some of the signals supplied in pixelwise fashion are amplified by an amplifying device in a manner dependent on the actual distance of the antiscatter grid from the focus.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS AG
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap