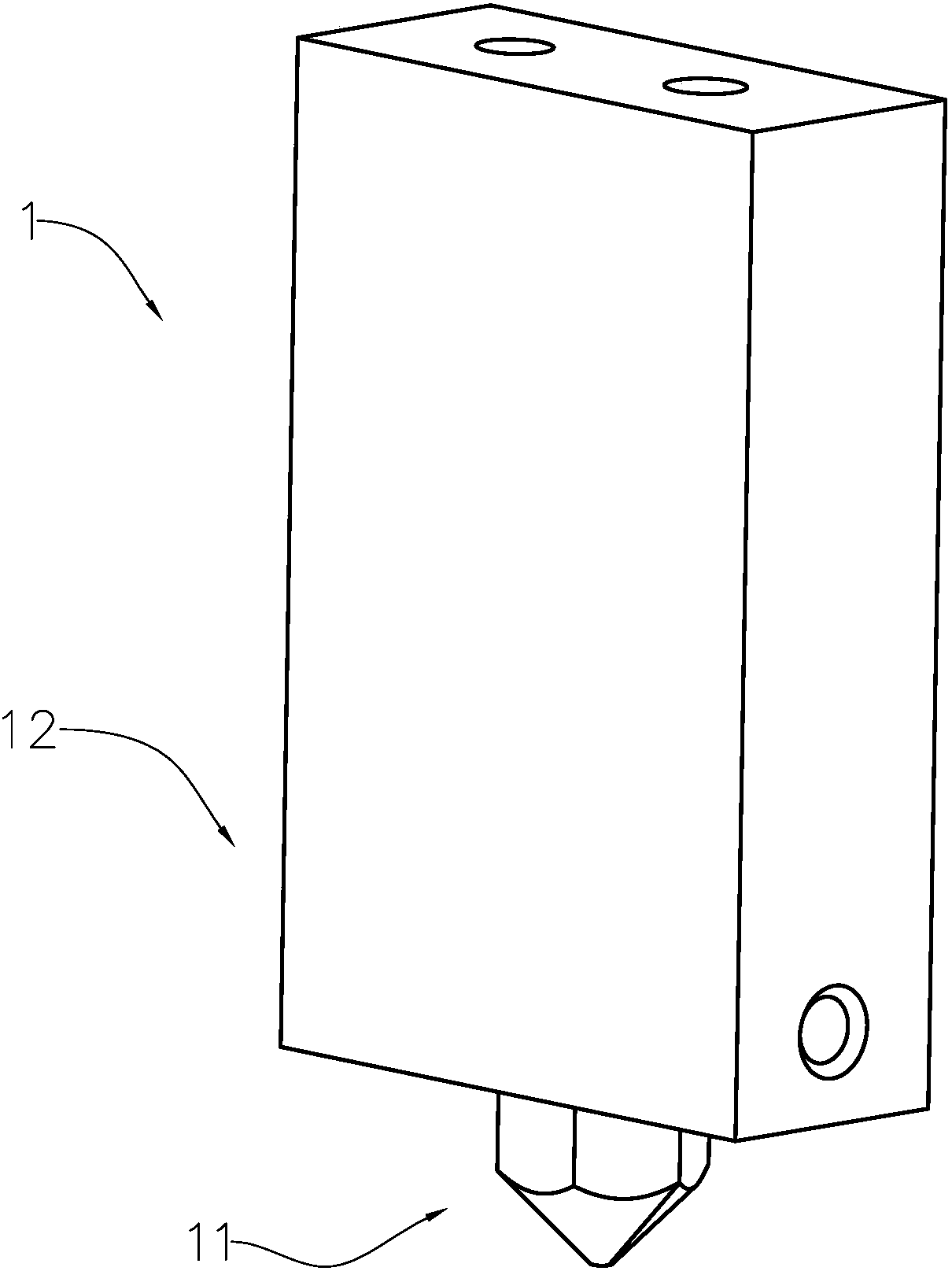
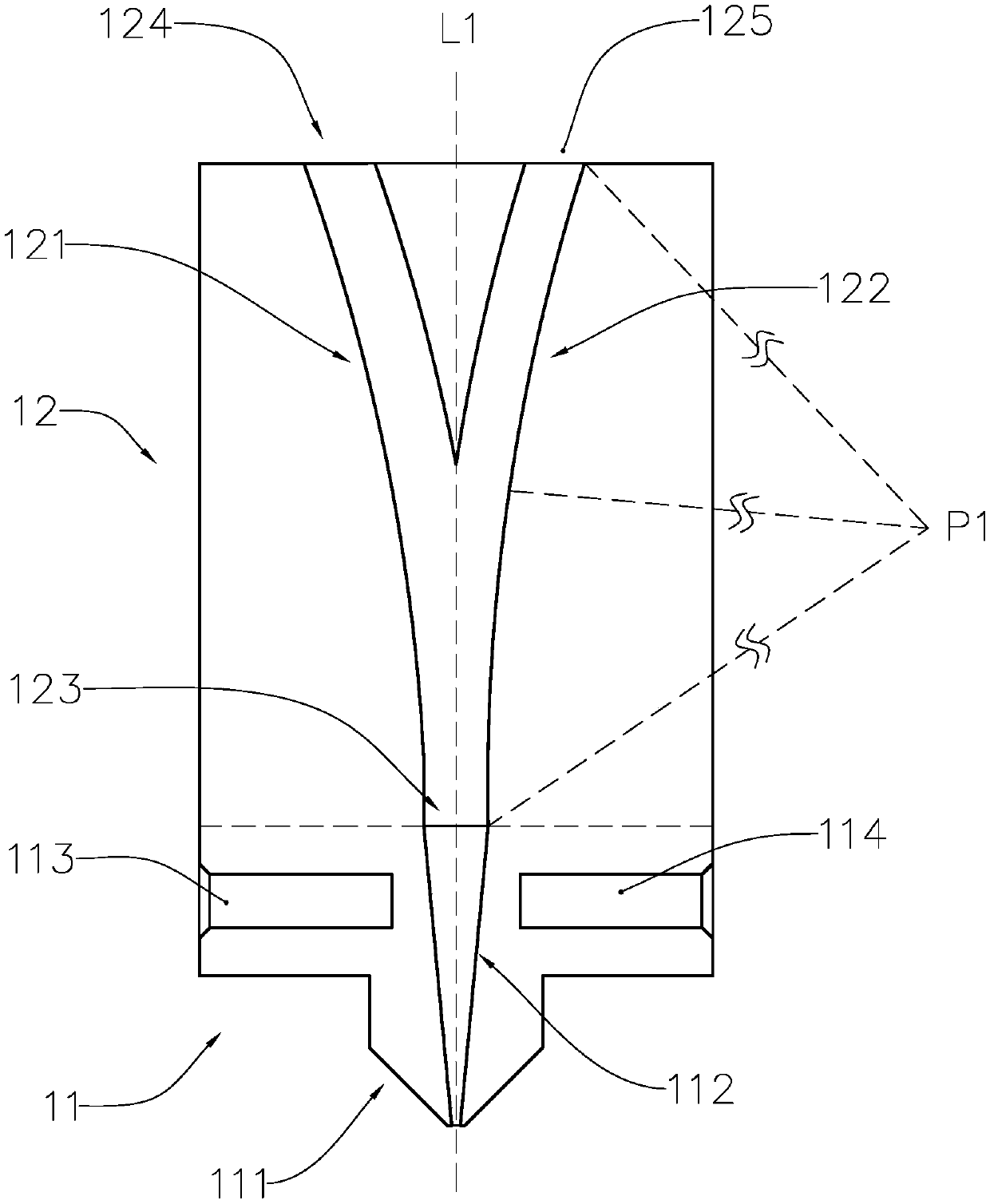
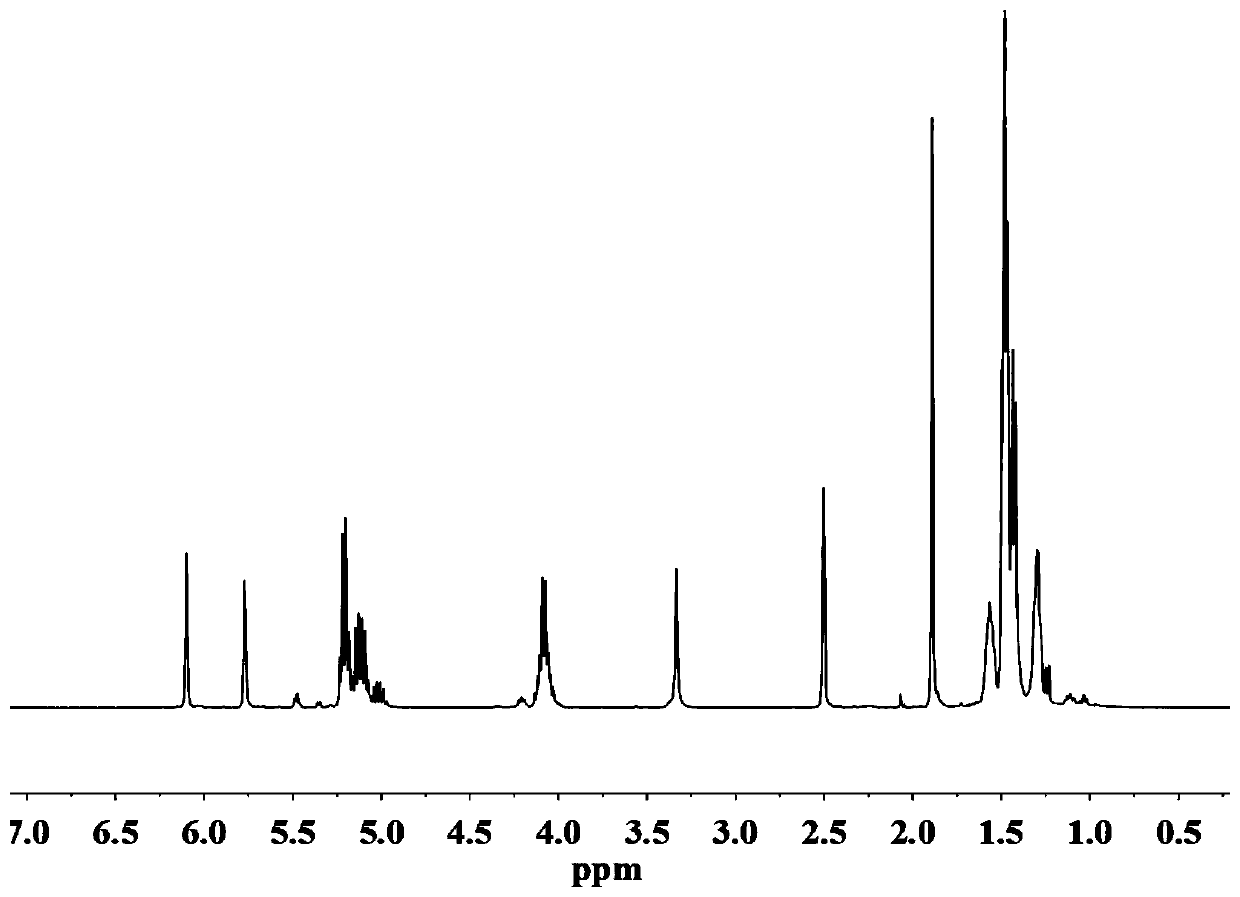
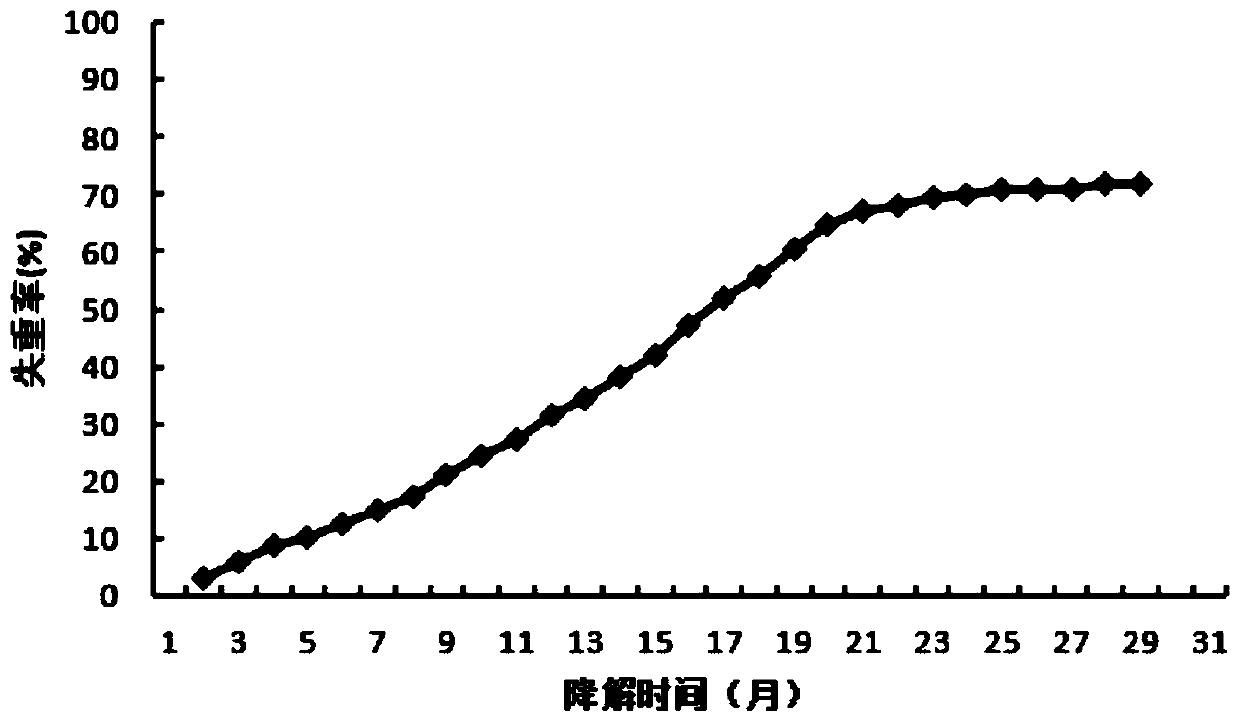
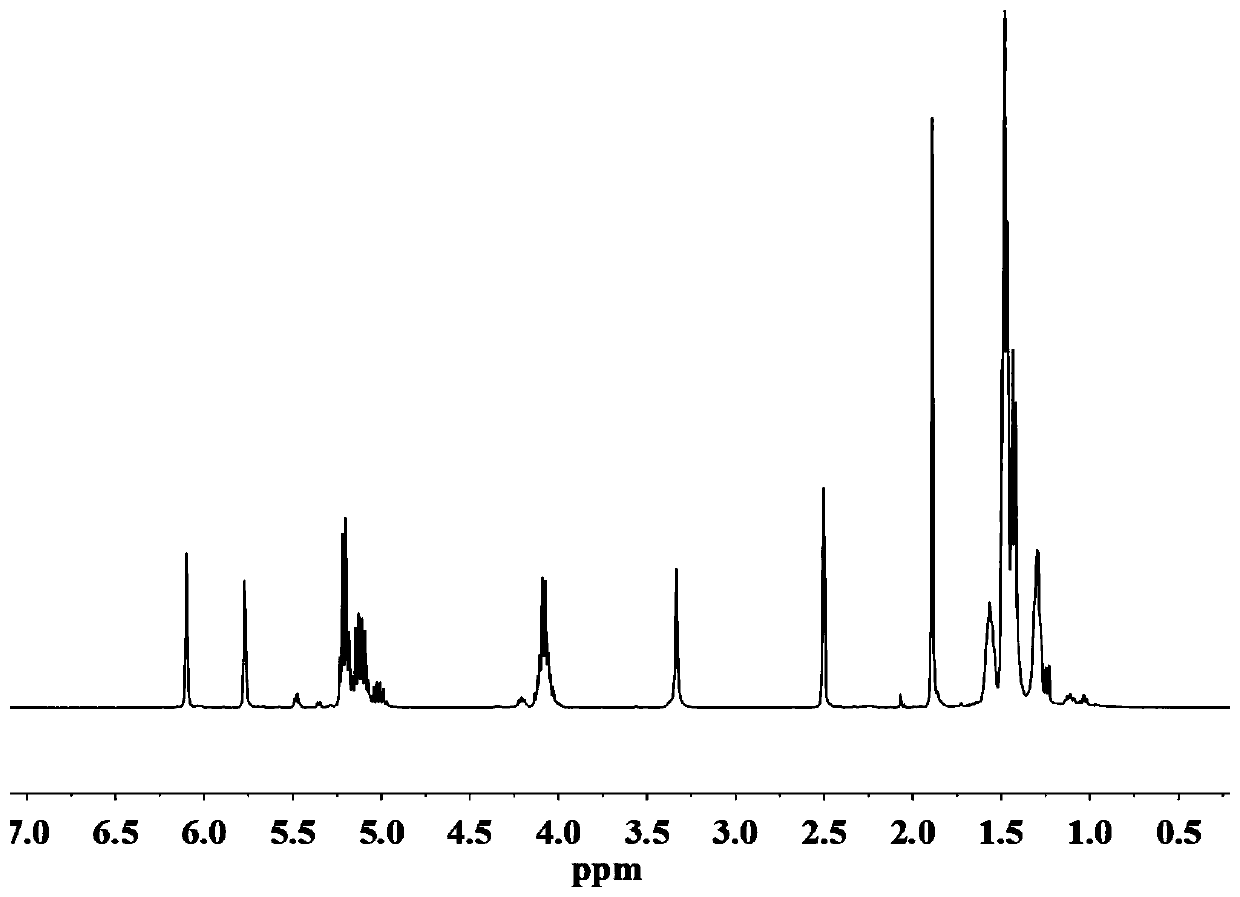
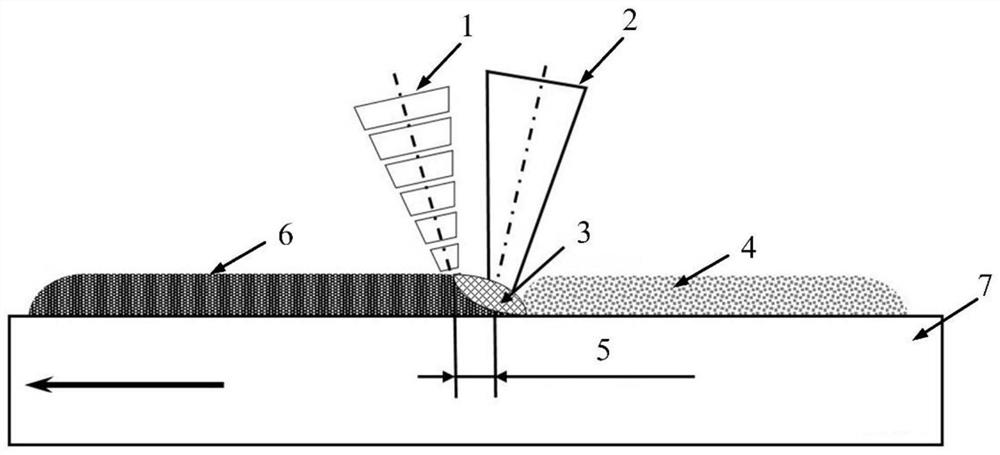
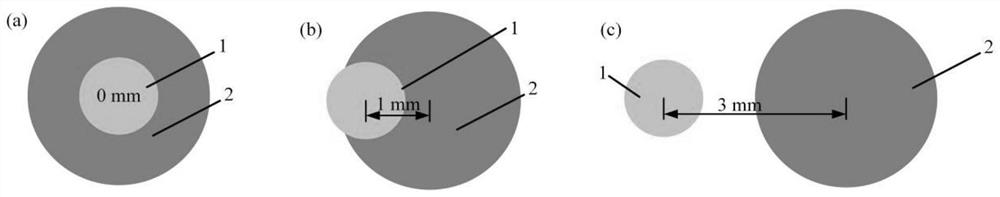
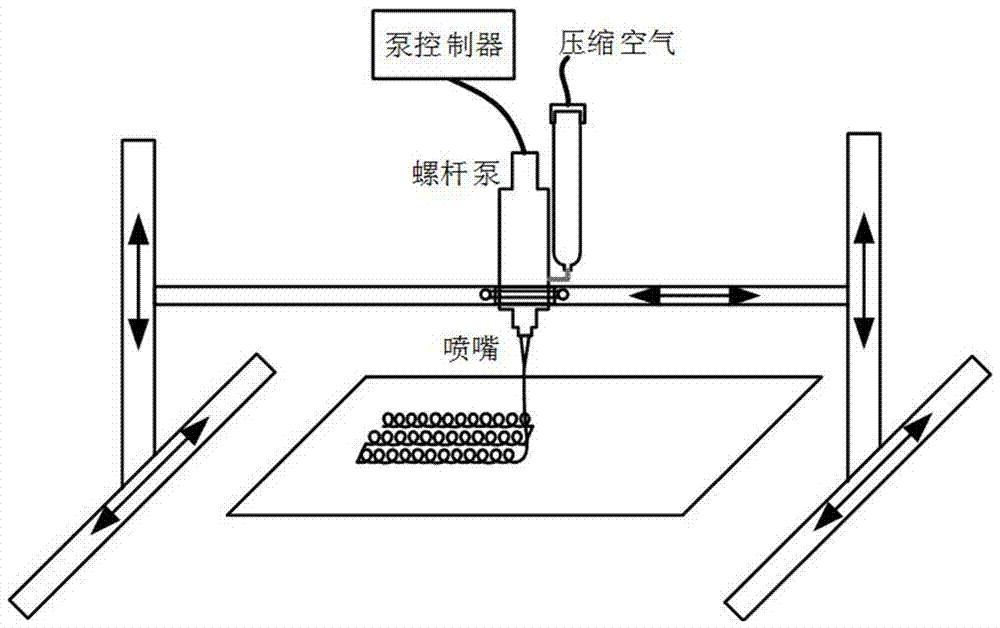
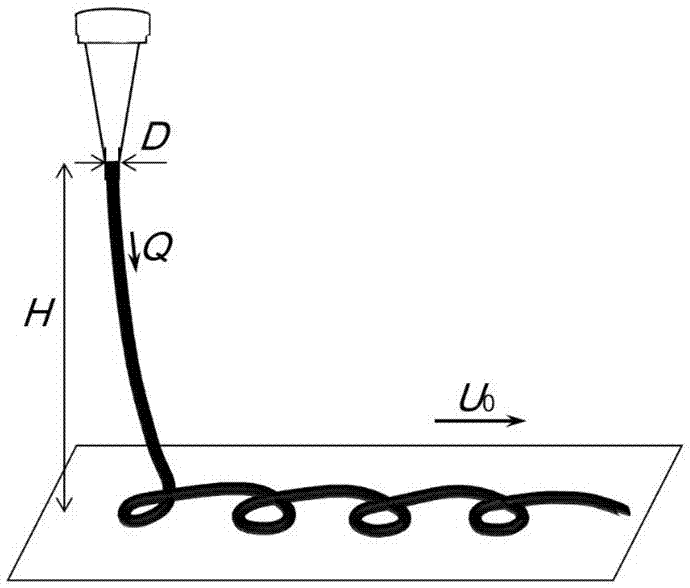
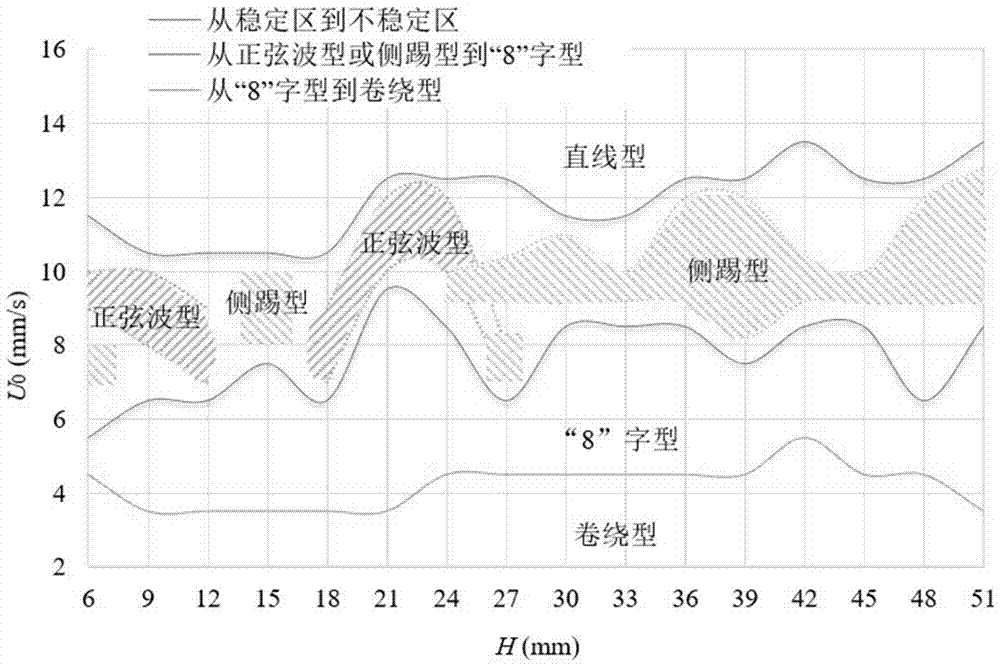
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117results about "Additive manufacturing apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
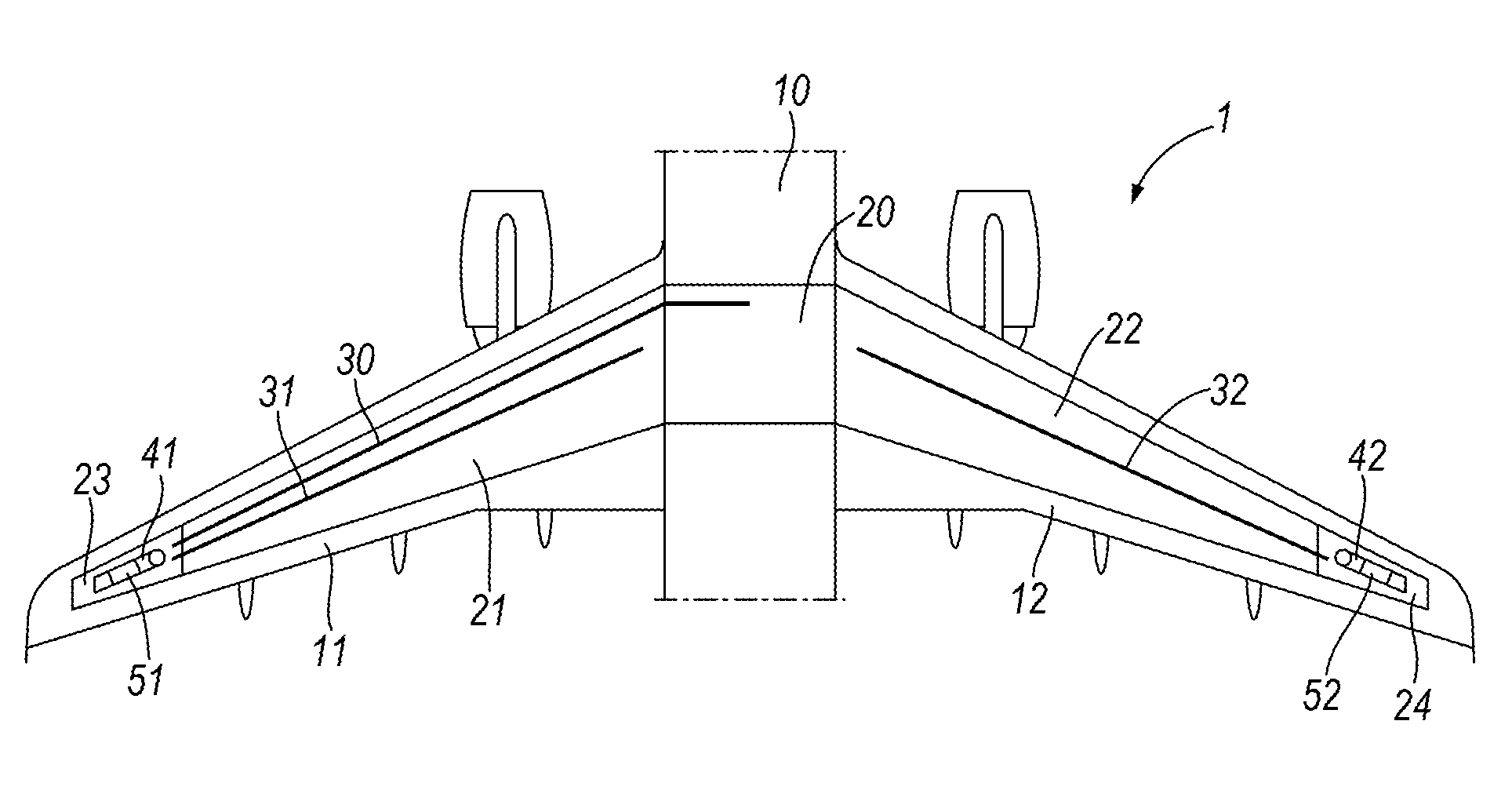
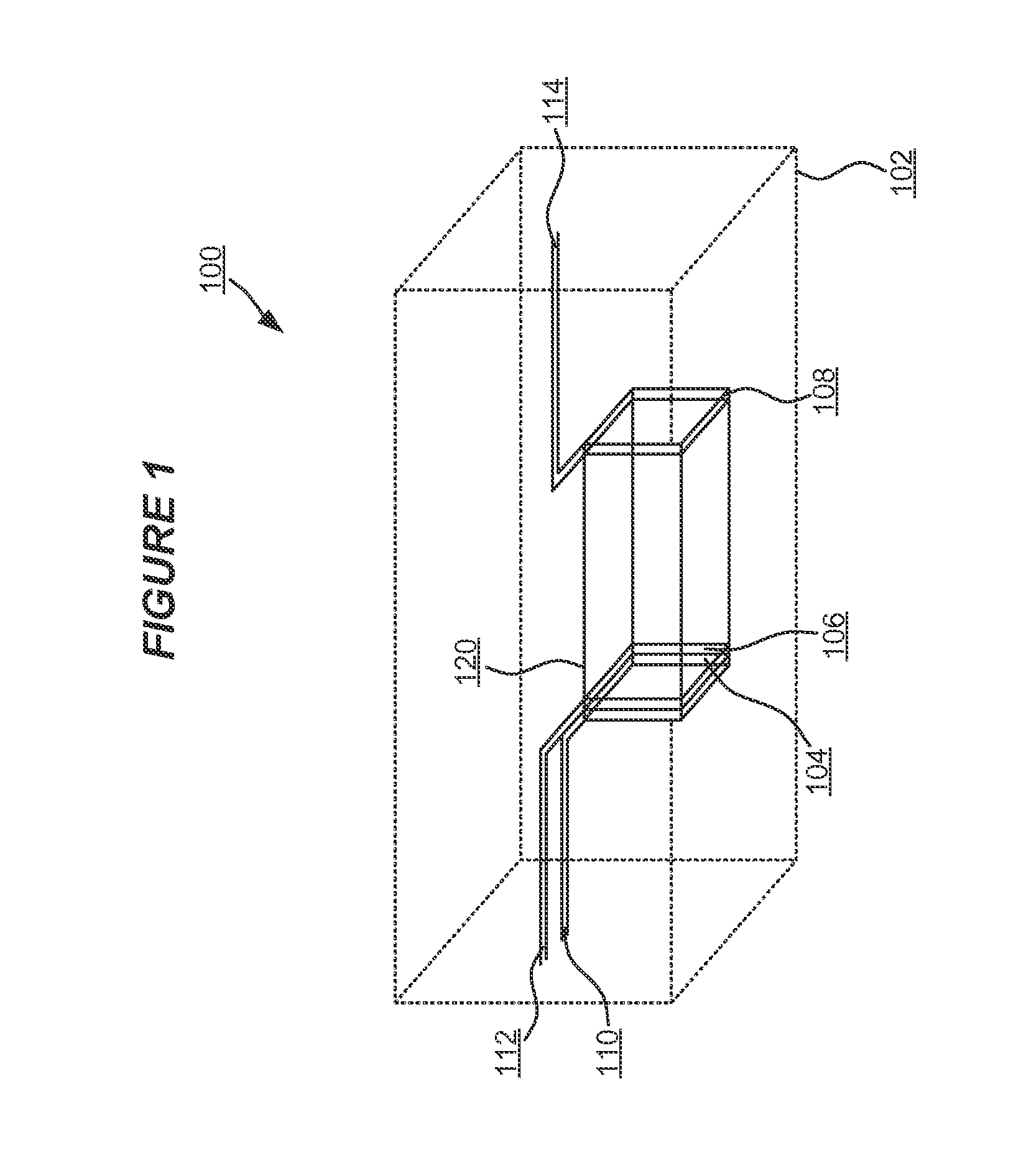
Flame trap cartridge, flame arrestor, method of preventing flame propagation into a fuel tank and method of operating an aircraft
InactiveUS20120273239A1Improve flame retardant performanceProlong foaming timeLiquid fuel feeder/distributionAdditive manufacturing apparatusAirplaneEngineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Printed active device
ActiveUS20150270089A1Reduce manufacturing costLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusControl electrodesElement spaceElectrical connection
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
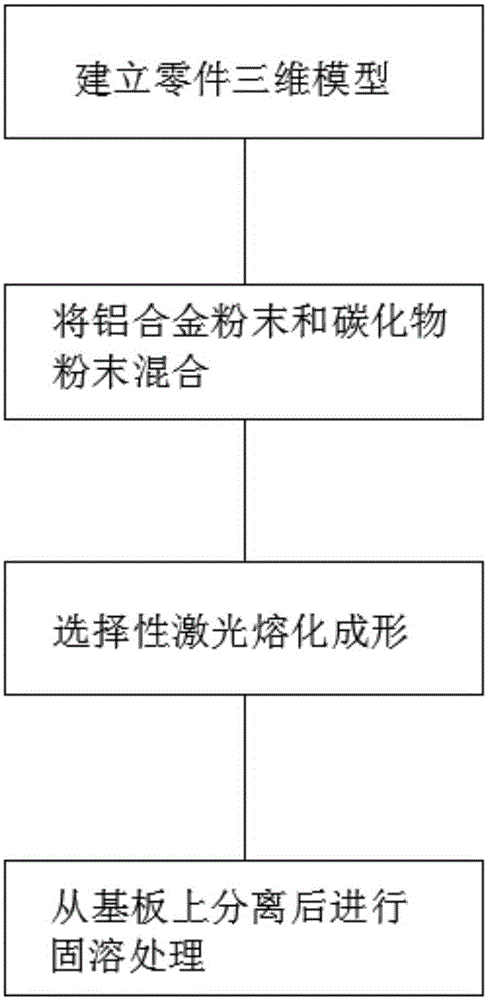
Rapid manufacturing method for laser remelting scanning carbide dispersion strengthened aluminum alloy
ActiveCN105112708AFast preparationMade preciselyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyThree dimensional modelMuffle furnace
The invention discloses a rapid manufacturing method for laser remelting scanning carbide dispersion strengthened aluminum alloy. The method includes the following steps that (1) a three-dimensional part model is established on a computer, and then the three-dimensional part model is converted to be in an STL format and imported into selective area laser melting forming equipment; (2) aluminum alloy powder and carbide powder are mixed, and then are ball-milled through a ball grinder to be evenly mixed; (3) the ball-milled mixed powder is transferred into the selective area laser melting forming equipment, and the mixed powder is formed according to three-dimensional model data under the protection of inert gases; and (4) a formed part is separated from a substrate by the adoption of the wire-electrode cutting technology, and then is subjected to solution treatment in a muffle furnace, afterwards, quenching is carried out, ceramic bead sand blasting treatment is conducted, and accordingly a finished product is obtained. By the adoption of the method, dispersion strengthening phases can be evenly distributed, and therefore the purposes of obtaining the ceramic phase dispersion strengthened aluminum alloy and improving the high-temperature performance of the aluminum alloy are achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional printer, three-dimensional printing method and preparation method for metal slurry
InactiveCN105108152AGuaranteed printing accuracySimple structureAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpray nozzleSlurry
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method and device for layered buildup of a shaped element
Owner:SCHWARZLER KLAUS
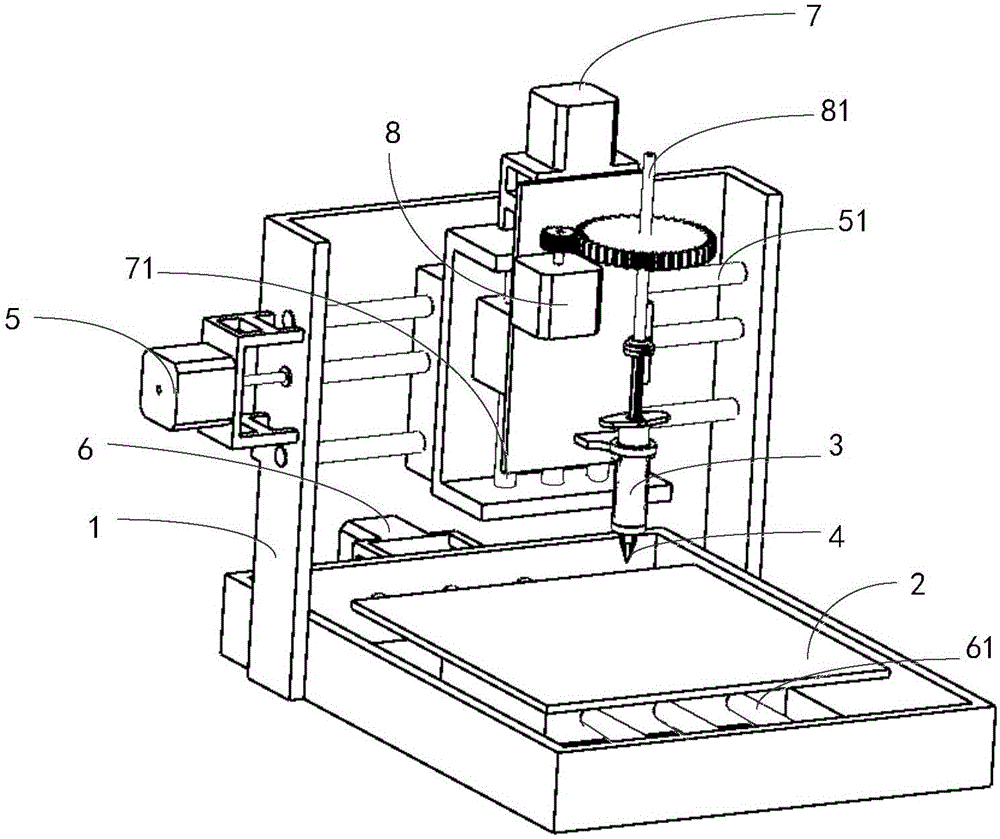
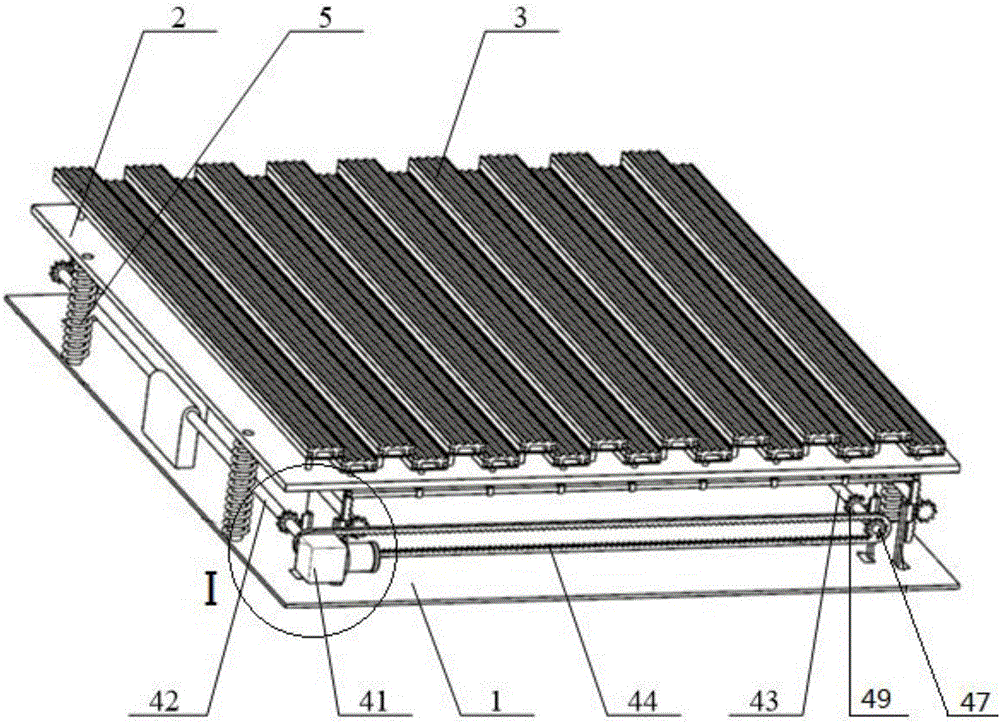
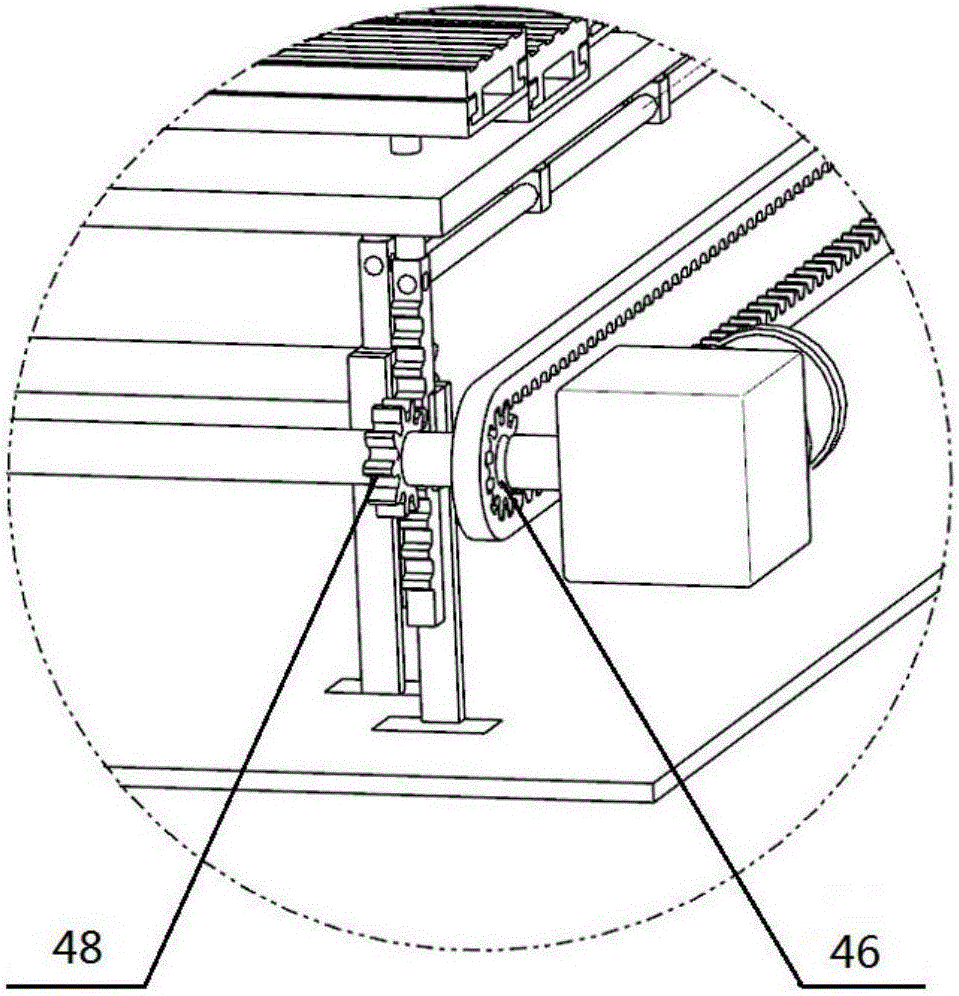
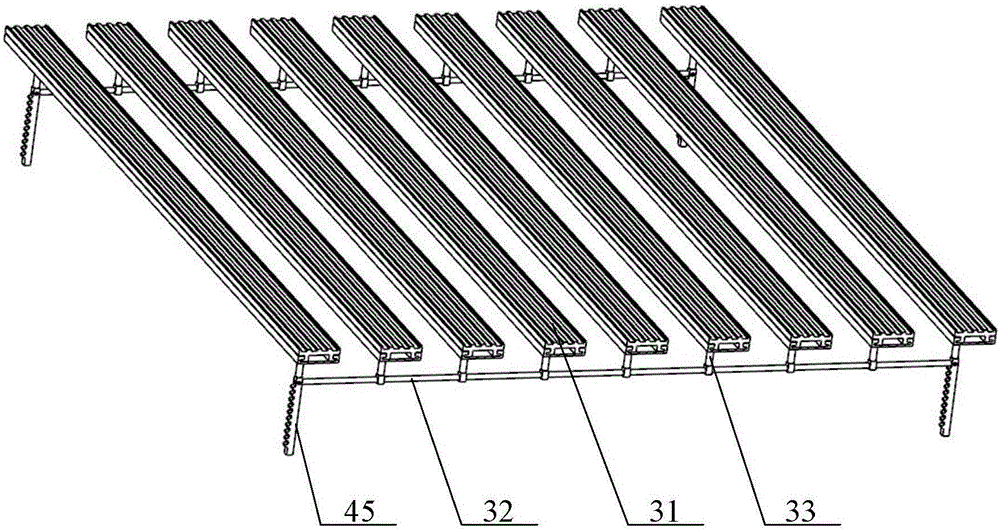
Multi-knife automatic knife changing type powder laying scraper knife device of 3D printer
InactiveCN105172145AGuaranteed normal operationReduce manufacturing costAdditive manufacturing apparatusControl systemReciprocating motion
Owner:党金行
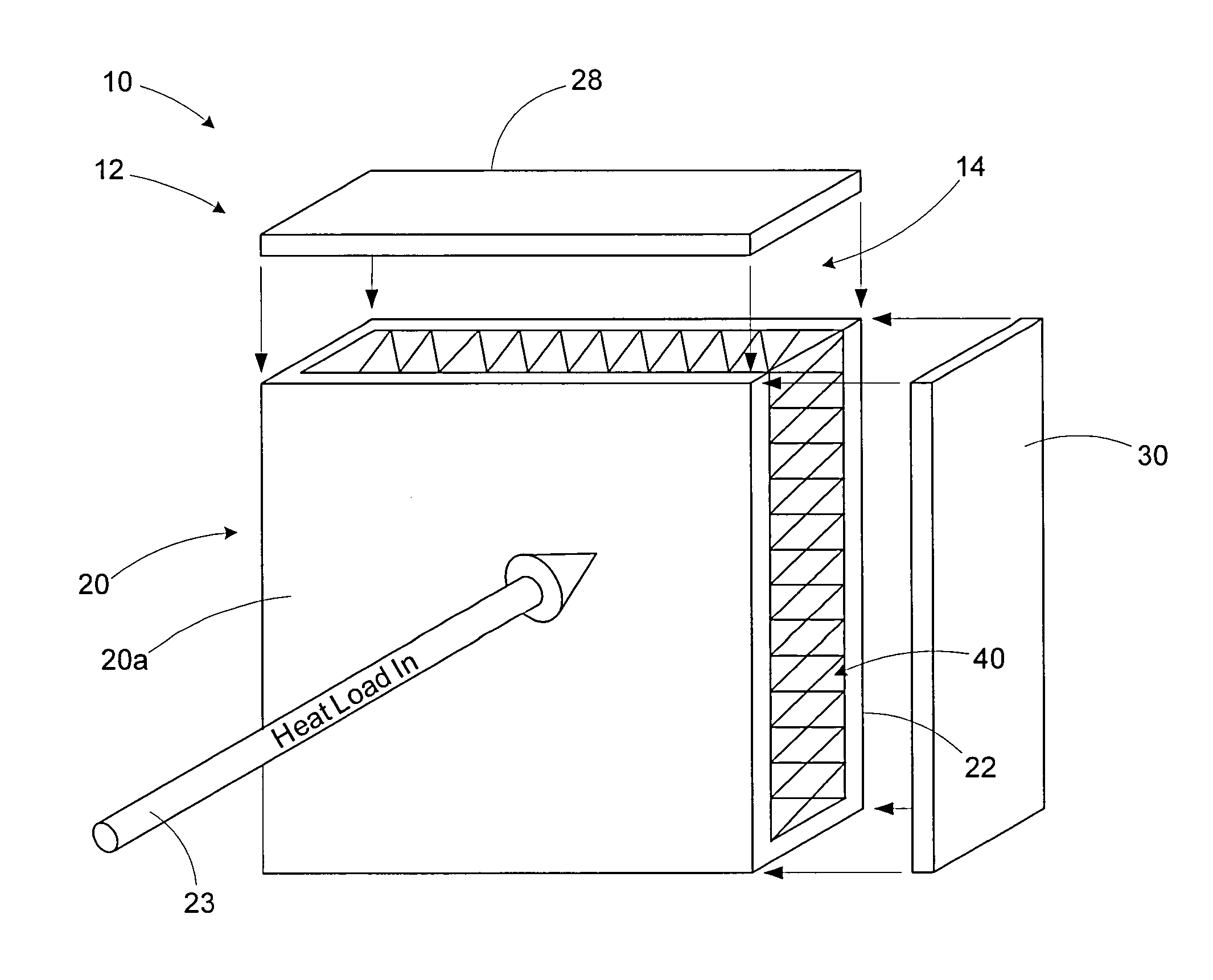
Heat-absorbing structural material
InactiveUS20120061065A1Envelopes/bags making machineryAdditive manufacturing apparatusWaxInterior space
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
System and method for additive fabrication using laminated sheets
ActiveUS9550349B1Fast formingImprove developmentAdditive manufacturing apparatusLamination ancillary operationsComputer generationThermal energy harvesting
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Laser wire fusing additive manufacturing titanium alloy component structure refining and isometric crystal converting method
ActiveCN111451504AEffectively compatibleRelease residual stressAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyManufacturing technologyMetallurgy
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Patient-specific intraluminal implants
ActiveUS20140088698A1Increase opportunitiesPrecise positioningStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisPatient specific
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
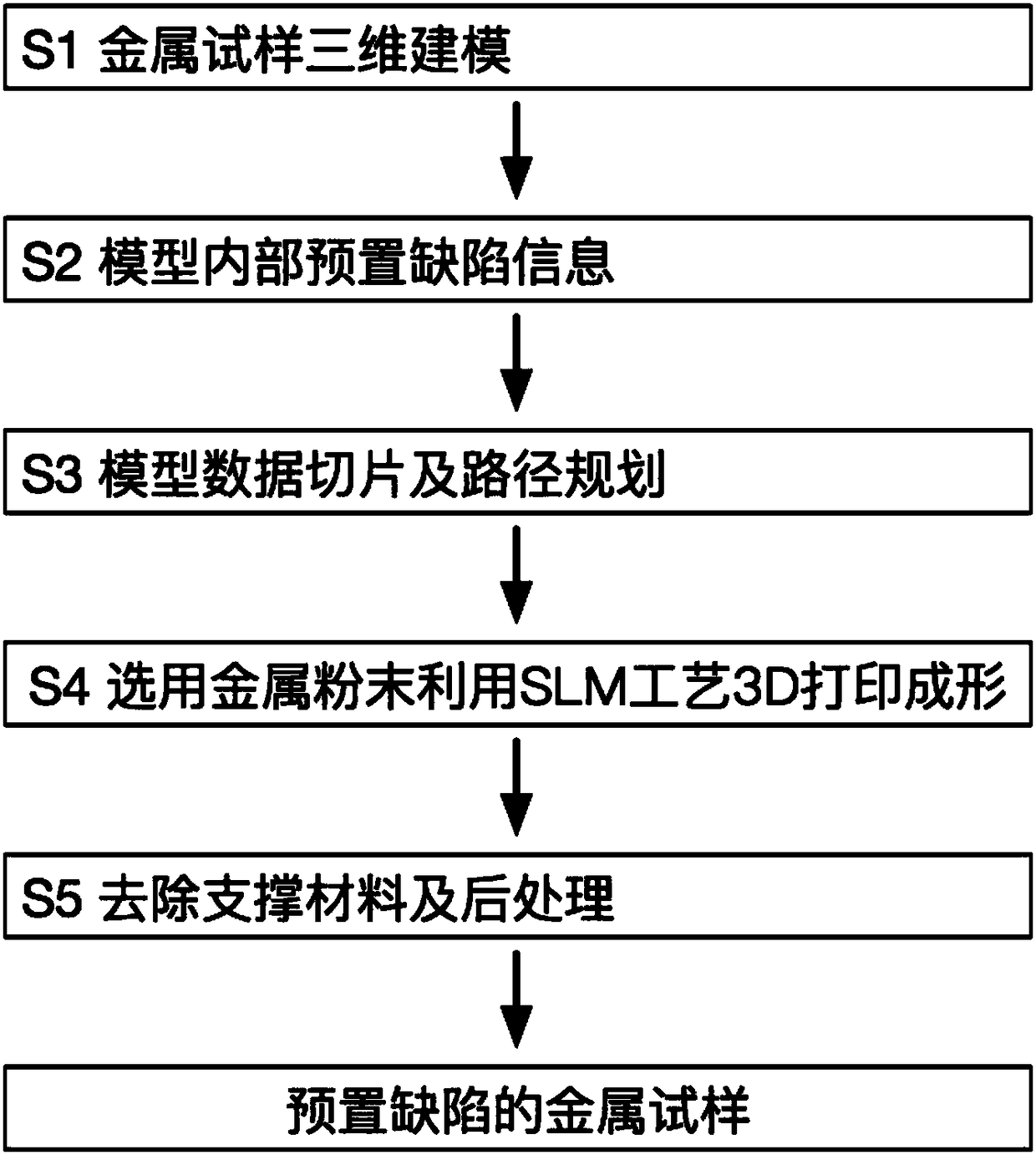
Metal sample 3D printing forming method with defect presetting process
InactiveCN108436081AAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyThree dimensional modelData model
Owner:无锡市产品质量监督检验院
Static shaft shoulder device of static shaft shoulder friction stir welding and additive manufacturing method
InactiveCN107160030ASmooth rotationIncrease stiffnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Alloying component and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110592411AImprove distributionFull play formAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyHigh entropy alloysCarbon nanotube
Owner:INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
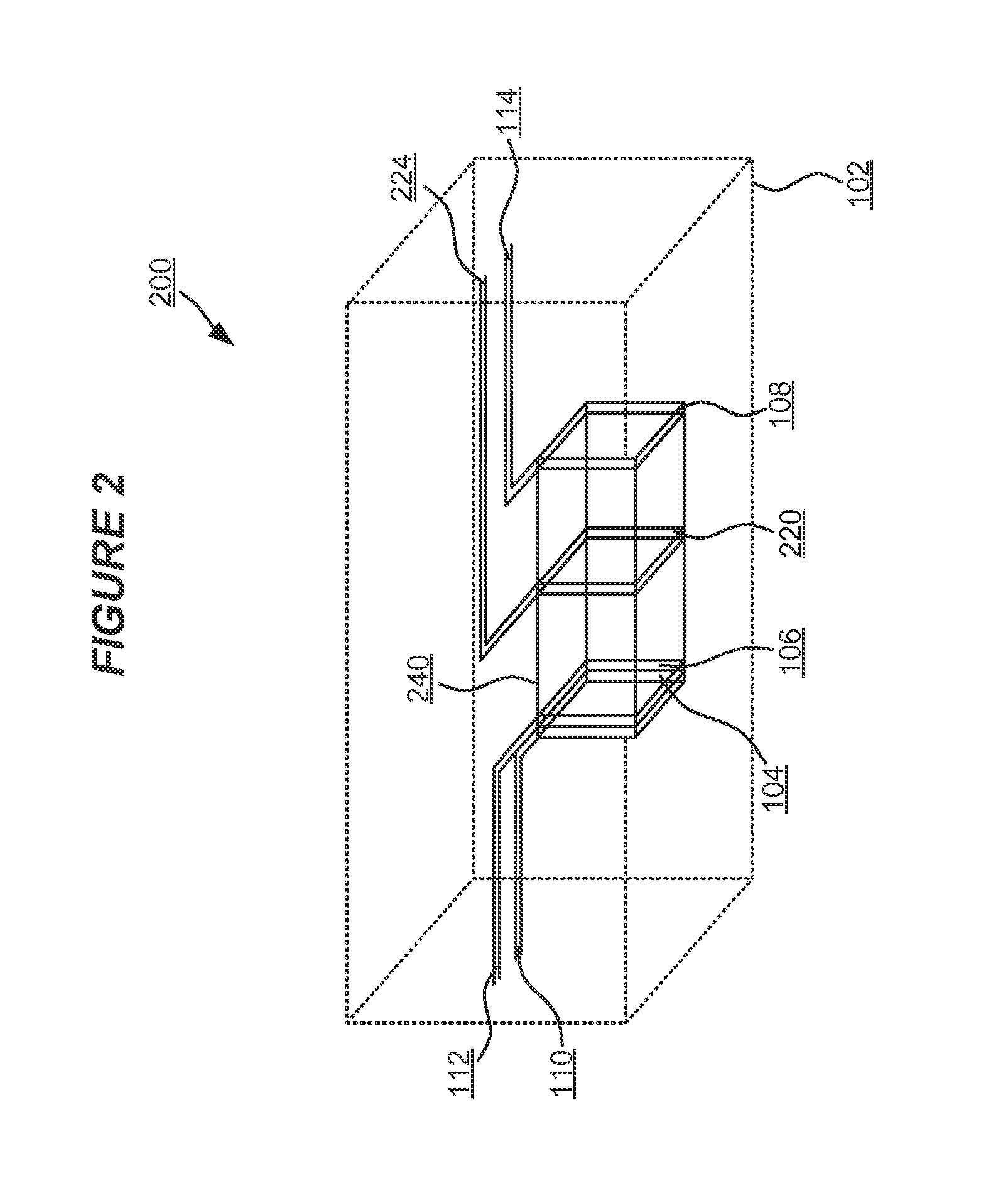
Methods and systems for producing a desired apparent coloring in an object produced through rapid prototyping
A method of producing a desired apparent coloring in an object (200) produced through rapid prototyping includes varying a color of successive layers (201,202,203,204) that are nested inwardly from a surface of the object (200).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Device for easily peeling forming parts obtained by additive manufacturing on printing table
InactiveCN105690766APeel off effortEffective shearAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringMachine tool
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
3D printed cerebral hemorrhage puncture drainage path positioning device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109893223AAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical needlesMedical equipmentCerebral hemorrhages
Owner:成都真实维度科技有限公司 +1
Noise suppression apparatus and methods of manufacturing the same
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Laser-assisted graphene tooth 3D printing process
Owner:GUANGZHOU FENGSHANG ELECTRIC APPLIANCE
3D (three-dimensional) printing extruder, 3D printer and manufacturing method of 3D printing extruder
PendingCN107855530ASmooth and easy feedingNo cloggingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineering3d printer
Owner:PRINT RITE UNICORN IMAGE PROD CO LTD
Method for improving durability of GH3536 alloy manufactured by selective laser melting technology
PendingCN111390180AAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyHeat treatingAnisotropy
Owner:南京国重新金属材料研究院有限公司
Photocurable polyester oligomer for 3D printing as well as preparation method and application thereof
Owner:BMF NANO MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Laser composite additive manufacturing method for controlling flowing of molten pool based on pulse laser
ActiveCN112692304AThe control method is simple and effectiveImprove flatnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusMetallic material coating processesEngineeringPulsed laser beam
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Copolymerized nylon powder material used for selective laser sintering, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107337793AControl melting pointEasy to separateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSelective laser sinteringAntioxidant
Owner:HUNAN FARSOON HIGH TECH CO LTD
3D printer
InactiveCN105856569AIncrease profitImprove reliabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer printingEngineering
The invention relates to a printer. A 3D printer comprises a cylinder body, a curing starting switch, a spraying device, a DLP (Digital Light Processing) projector, a piston type worktable and a computer, wherein a storing box of which the upper end is opened is formed between the upper surface of the piston type worktable and the inner surface of the cylinder body; the spraying device comprises a spraying head provided with a spraying port, scrappers, and a driving mechanism which is controlled by a computer and can be used for driving the spraying head to move synchronous with the scrapers; the spraying head and the scrapers are positioned above the piston type worktable; the DLP projector can be used for directly projecting into the storing box from the top of the projecting box; the DLP projector is provided with a light outlet, a light outlet cover, a cover closing spring which can drive the light outlet cover to close the light outlet, and an electromagnet which can drive the light outlet cover to open; the curing starting switch can be triggered when the spraying head moves to an end point of a travel so as to enable the electromagnet to be electrified to generate magnetism. The 3D printer has the advantage that the ultraviolet rays can be directly projected on a resin layer, so that the problem of low utilization rate of the ultraviolet rays of an existing 3D printer can be solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU YANZHI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Smoothing of 3D printed lenses
ActiveUS20170100903A1Improved additive processSimple processAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical articlesPolymer sciencePolymer coatings
Systems and methods for smoothing a lens are disclosed herein. A monomer used to make or augment the lens according to an additive method is deposited on the lens surface to be smoothed. A film or membrane with certain elastic properties is pressed against the layered (stepped) surface, with the monomer in between the lens and the membrane. The pressure of the membrane spreads the monomer over the surface of the lens, filling the spaces between the layered (stepped) surface and the membrane. A curing agent is applied to transition the monomer into a polymer coating matching the curve of the membrane. The membrane is removed, leaving a clean, smooth lens surface.
Owner:INDIZEN OPTICAL TECH OF AMERICA LLC
Polypropylene composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109627581AGood 3D printing qualityImprove performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusPolypropylene compositesPolymer science
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUPER DRAGON ENG PLASTICS +1
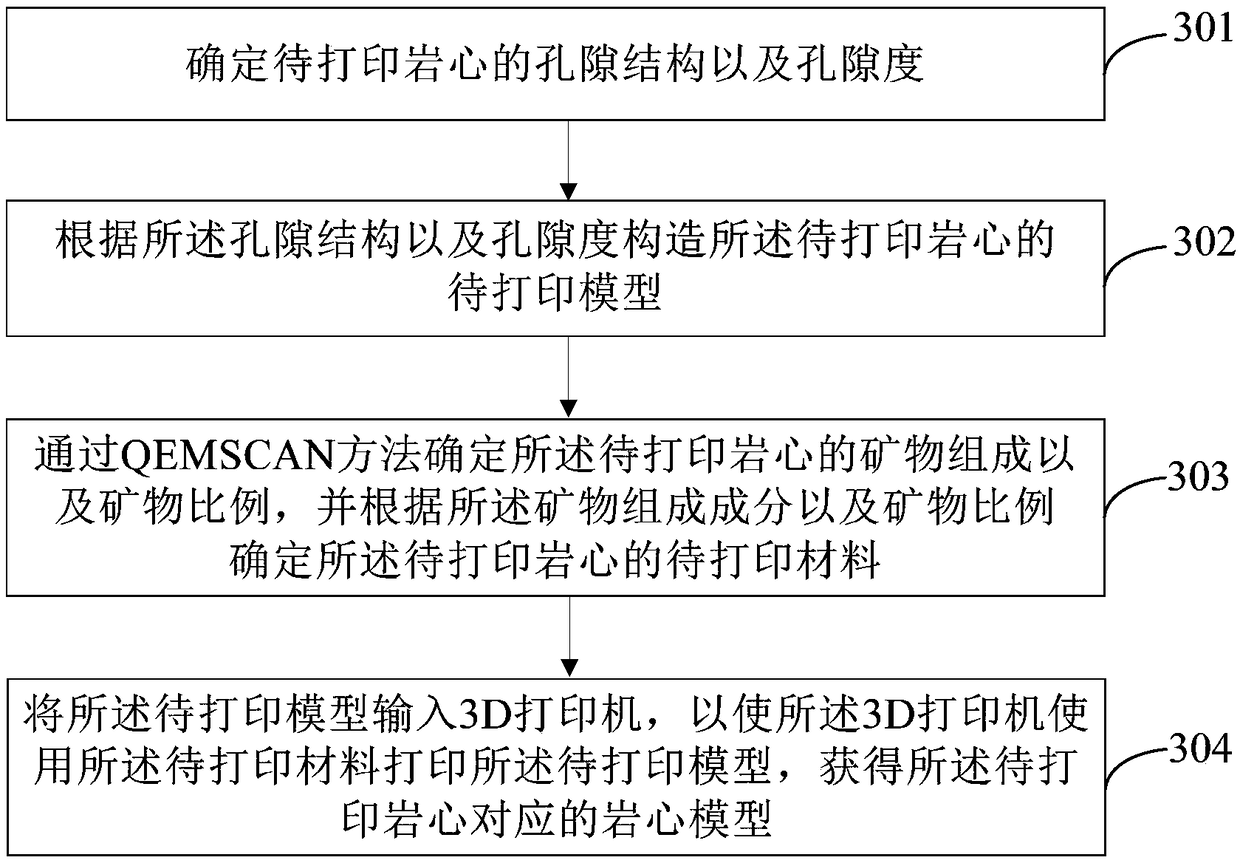
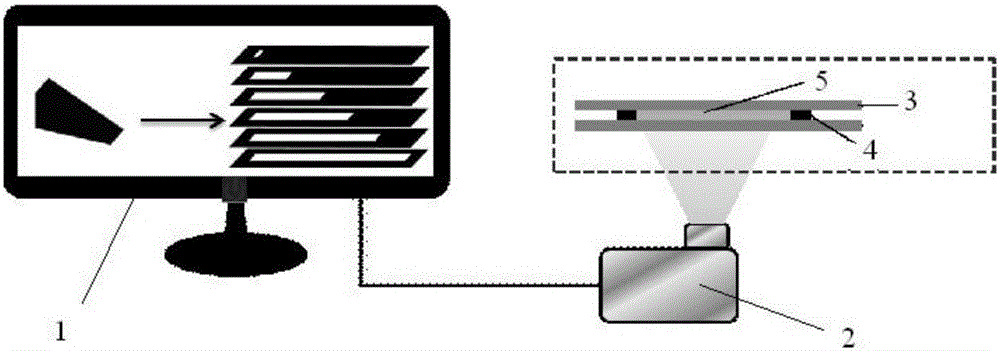
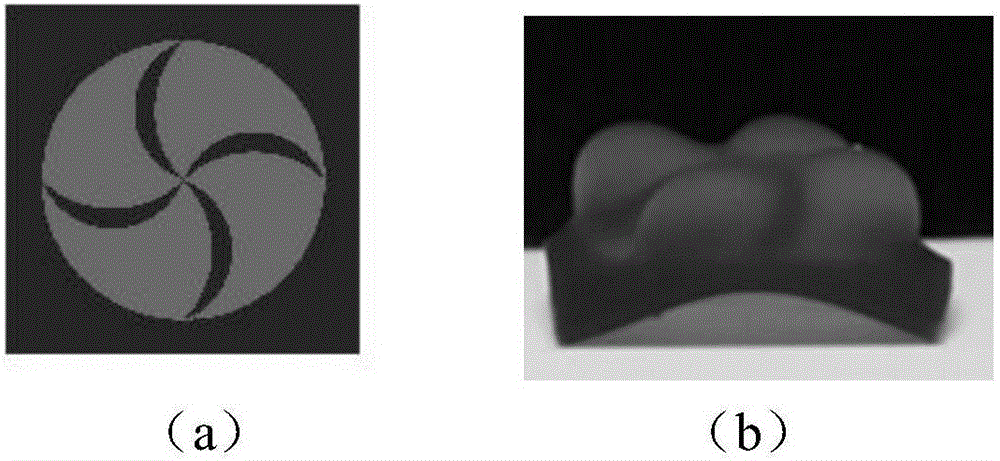
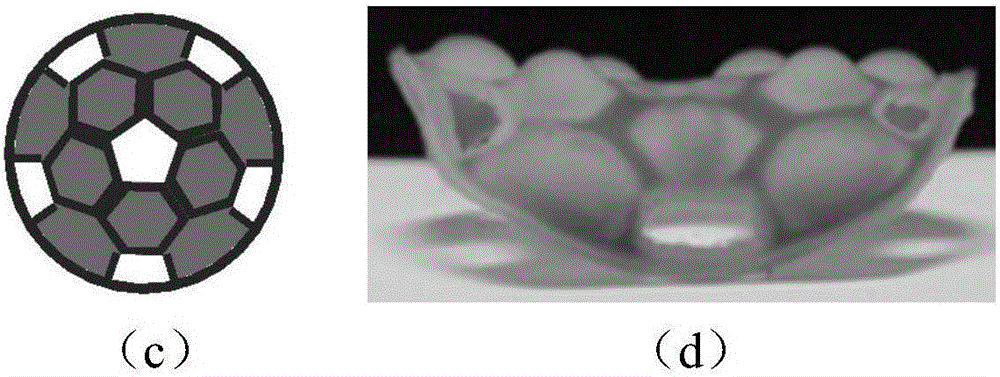
High-precision 3D printing method and device for unconventional rock model
InactiveCN108819215AAdditive manufacturing apparatusPreparing sample for investigationPetrologyPetroleum
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method for constructing three-dimensional structure based on digital light processing
ActiveCN105818382AHigh precisionBuild fastAdditive manufacturing apparatusDigital signal processingSolvent
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Porous elastic foam production method based on 3D printing of wet cured silica gel
ActiveCN107379516AAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsElastic modulusMoving speed
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap