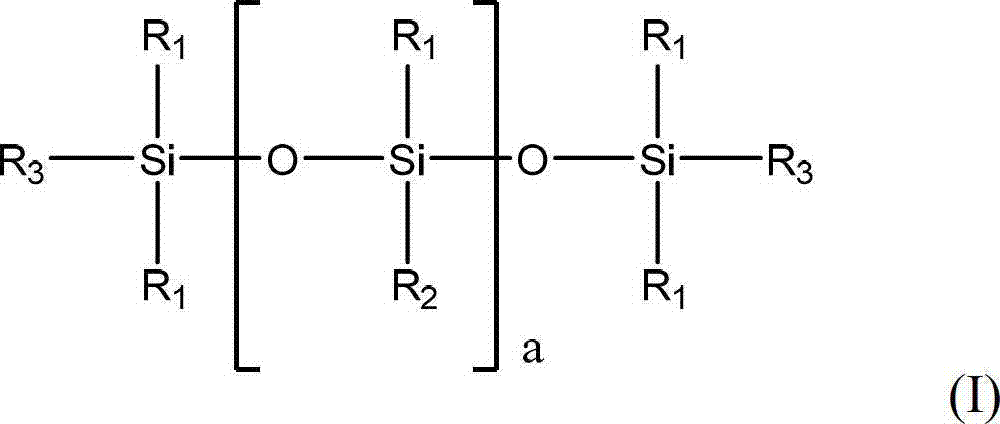
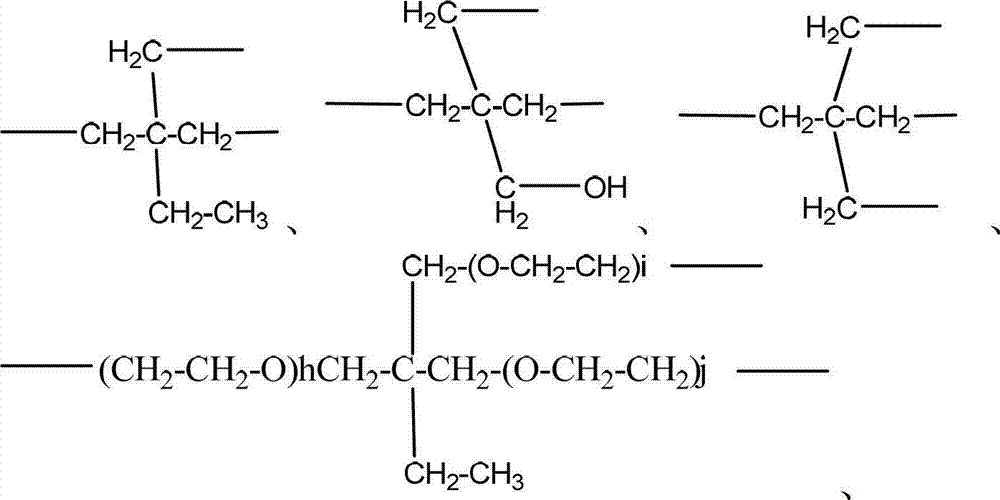
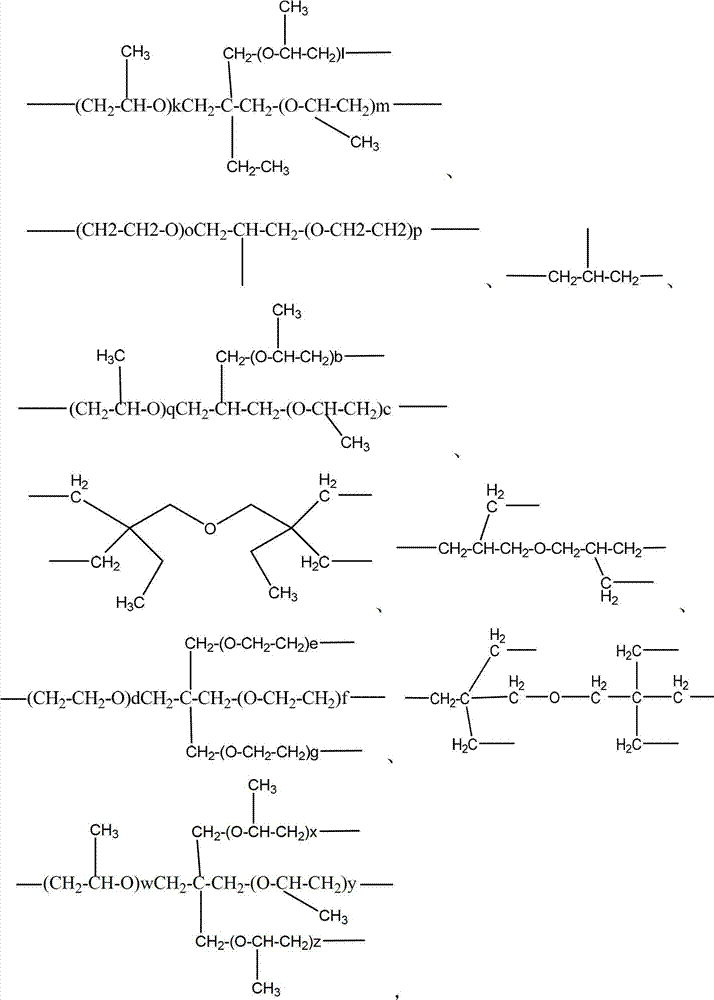
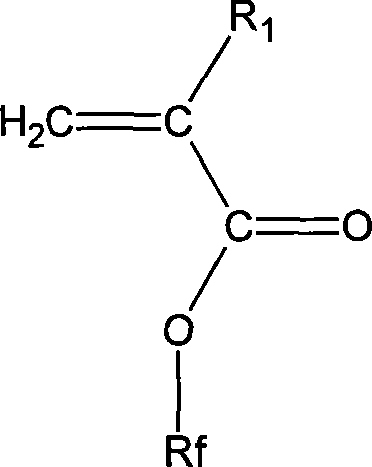
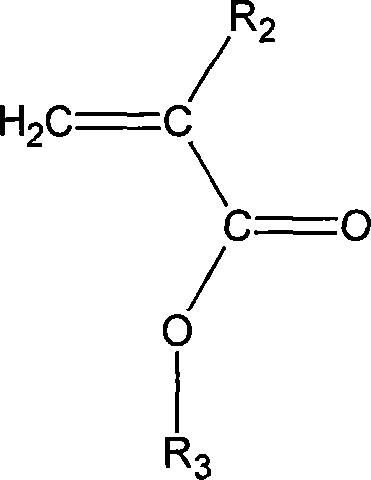
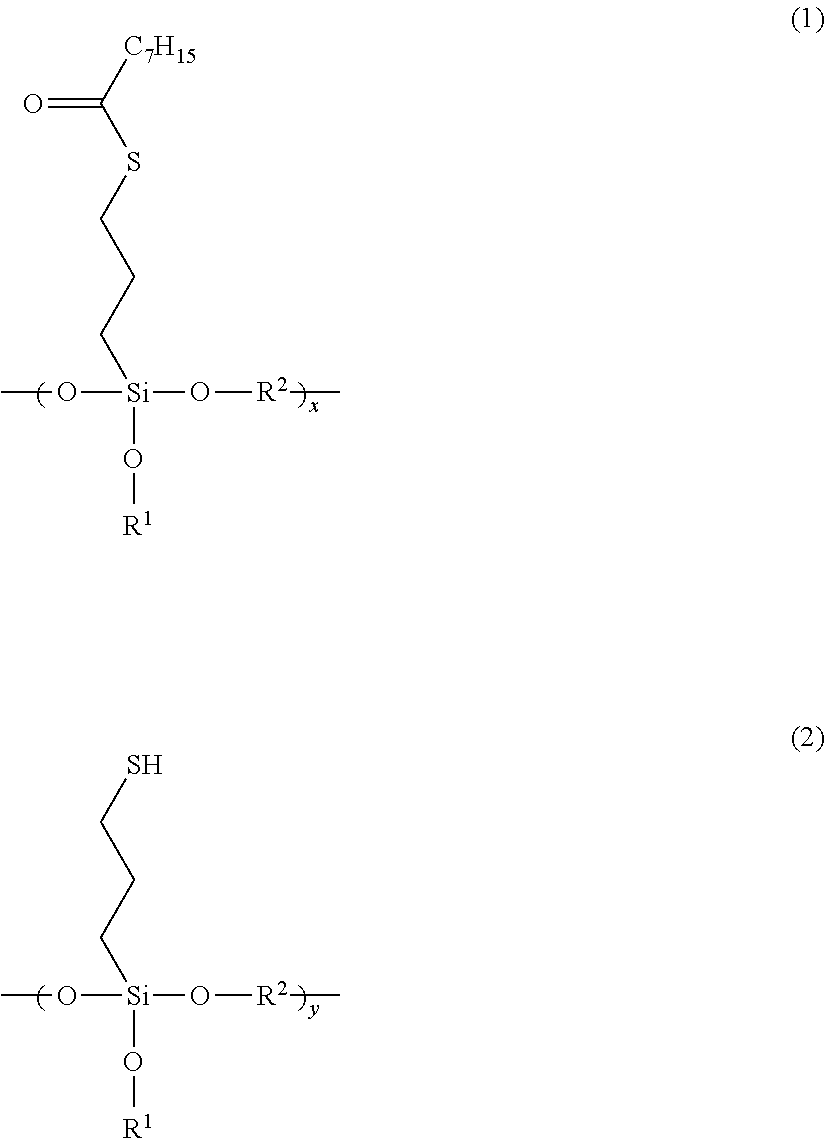
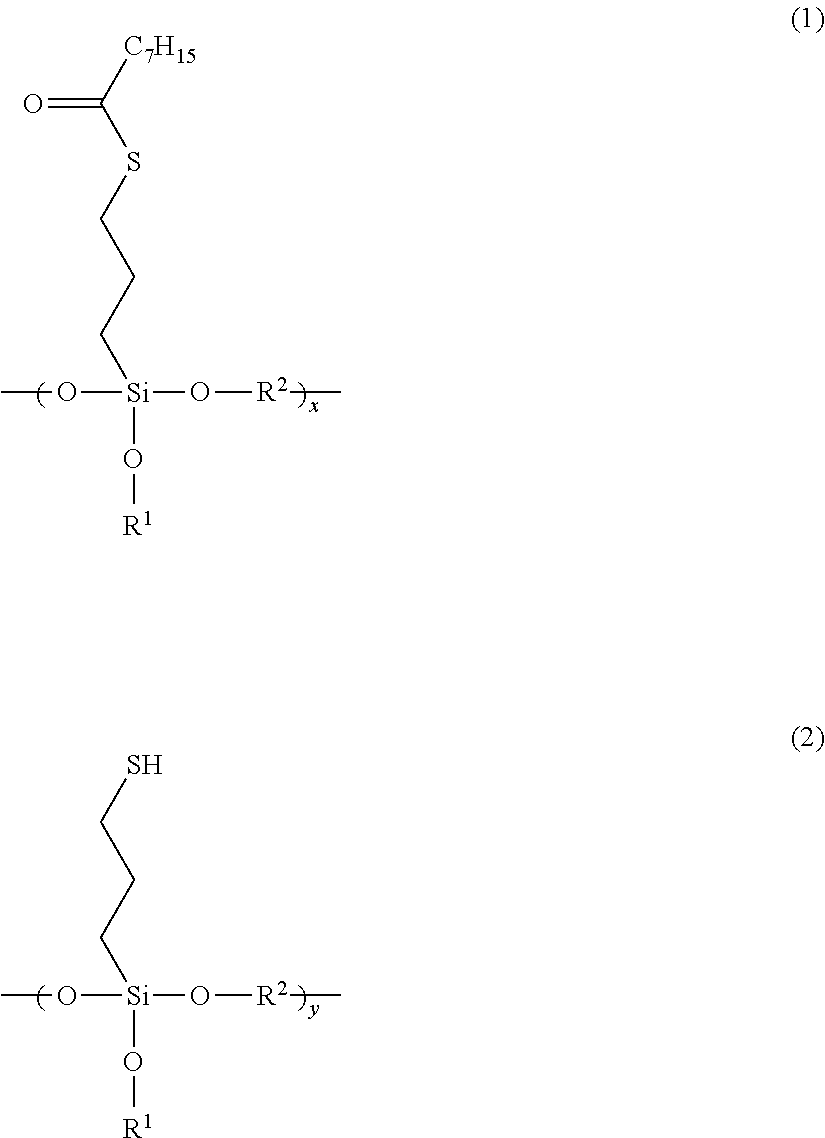
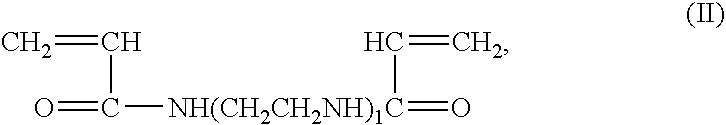Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409 results about "Polymer science" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer science or macromolecular science is a subfield of materials science concerned with polymers, primarily synthetic polymers such as plastics and elastomers. The field of polymer science includes researchers in multiple disciplines including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Method for depositing silicon-free carbon-containing film as gap-fill layer by pulse plasma-assisted deposition
ActiveUS20200013612A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPolymer scienceWafering
A film having filling capability is deposited by forming a viscous polymer in a gas phase by striking an Ar, He, or N2 plasma in a chamber filled with a volatile hydrocarbon precursor that can be polymerized within certain parameter ranges which define mainly partial pressure of precursor during a plasma strike, and wafer temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Process for the reduction of the relative permeability to water in oil-bearing formations
InactiveUS6474413B1Reducing possible extensionFluid removalDrilling compositionInjection pressurePolymer science
A process for the selective and controlled reduction of permeability to water in oil-bearing formations made up of sandstone or limestone, the process comprising the injection of a slug of polymer aqueous solutions having a polarity opposite to the polarity of the rock, followed by the injection of a spacing slug of alkaline halide and then a fresh slug of polymer aqueous solution, the polarity of which is opposite to the polarity of the first polymer slug, and then a slug of aqueous solution of trivalent metal crosslinking agent to effect the partial crosslinking of the polymer charges, the polymer layers being successively added until the injection pressure of the polymer aqueous solutions show that the desired Residual Resistance Factor RRF was attained, and well production may be resumed.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA PETROBRAS
Process for producing functionalized polymers
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer, the method comprising the steps of (a) polymerizing monomer in the presence of a coordination catalyst to form a polymer, (b) inhibiting said step of polymerizing with a Lewis base, and (c) reacting the polymer with a functionalizing agent.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Low Viscosity Liquid Polymeric Delivery System
InactiveUS20090181068A1Heavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderPolymer sciencePolymer solution
Owner:DUNN RES & CONSULTING
Graphene conductive polyester fibers and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104164707AOvercome cohesionOvercome uniformity issuesElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureSpinnerette packsPolyesterFiber
Owner:湖州市中磊化纤有限公司
Preparation method of superfine fiber high-imitation grain synthetic leather
ActiveCN102304858AImprove protectionImprove breathabilityLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsLow-density polyethylenePolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of superfine fiber high-imitation grain synthetic leather. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: spinning sea-island composite fibers by utilizing nylon 6 and low-density polythene as raw materials, manufacturing non-woven fabric by utilizing the sea-island composite fibers, coating one surface of the non-woven fabric by utilizing high-solid-concentration polyurethane slurry, infiltrating the non-woven fabric by utilizing low-solid-concentration polyurethane slurry, enabling the non-woven fabric to pass through an aqueous solution of dimethylformamide after infiltrating, solidifying polyurethane and forming a cellular structure to obtain synthetic leather semi-finished products, enabling the synthetic leather semi-finished products to pass through methylbenzene to separate sea-component low-density polythene out of the sea-island fibers, peeling off the sea-island composite fibers to be superfine fibers, washing away methylbenzene through boiling water, and drying to obtain the superfine fiber high-imitation grain synthetic leather. The product manufactured by the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of strong gradient, abundant hand feeling, fine and smooth surface wrinkles and strong toughness after being bent, and has the beneficial effects on aspects of pollution reduction, animal protection, ecological protection and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG TONGDA ISLAND NEW MATERIALS
Copolymer, process for producing the same, and resist composition
InactiveUS6706826B1Improve adhesionImprove solubilityOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusSolventResist
The present invention relates to a copolymer for use in paints, resists, and the like; a method for manufacturing the same; and a resist composition using the same. The copolymer according to the present invention is obtained by means of polymerizing at least one monomer containing an alicyclic structure and one monomer containing a lactone structure, and the distribution of the copolymer composition of said monomer containing a lactone structure in said copolymer is in the range of -10 to +10 mol % of the average copolymer composition of said monomer containing a lactone structure in said entire copolymer. In addition, the copolymer according to the present invention is obtained by means of polymerizing a monomer containing an alicyclic structure, a monomer containing a lactone structure, and another vinyl monomer comprising a higher polarity than said monomer containing an alicyclic structure, but a lower polarity than said monomer containing a lactone structure. The copolymer according to the present invention exhibits superior adhesion properties to surfaces possessing a high polarity, such as metal surfaces and the like, in addition to excellent hydrophobic and thermal resistance properties, and also displays a favorable solubility in solvents used for paints, resists, and the like.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Microcapsule composition
InactiveUS20050164116A1Lower resistanceGood workmanshipPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPolymer sciencePolystyrene
This invention relates to a composition comprising microcapsules suspended in an aqueous media, said microcapsules comprising a water immiscible material contained within an encapsulating wall of polymeric material, wherein the aqueous media contains a stabilizer comprising an anionic polymer mixture comprising a first sulfonated polystyrene polymer and a second sulfonated polystyrene polymer wherein the ratio of the weight average polymer molecular weight of the first polymer to the second polymer is greater than 2. It further relates to an imaging element comprising said microcapsules.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Phase change energy storage thermoplastic composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102070845AHas processing propertiesHigh elongation at breakHeat-exchange elementsPolymer scienceVulcanization
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +2
Industrially-applicable method for preparing polymer foamed material by using supercritical fluid technology
Owner:CHANGZHOU TIANSHENG NEW MATERIALS RES INST CO LTD
Use and composition of polysiloxane with modified acrylate radicals
ActiveCN102924993AImprove stain resistanceAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesOligomerPolymer science
Owner:ETERNAL CHINA INVESTMENT
Microrelief structural body, decorative sheet, decorative resin molded body, method for producing microrelief structural body, and method for producing decorative resin molded body
ActiveUS20160052227A1Increase flexibilityGood stretchabilitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storagePolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
A structural body which comprises a base and a microrelief structure layer having a microrelief structure. The microrelief structure layer is laminated on the base so as to form the surface layer of this structural body, and the microrelief structure layer has at least one physical property selected from the group consisting of (A) and (B) described below. (A) The elastic modulus at 25° C. is 50 MPa or more, and the elastic modulus at 80° C. is 30 MPa or less. (B) The tensile elongation at break at 80° C. is from 20% to 100% (inclusive).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Asphalt modified thermoplastic polyolefin water-proof coiled material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101550729AImproves UV resistanceExcellent ozone resistanceRoof covering using flexible materialsBuilding insulationsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Owner:胜利油田大明新型建筑防水材料有限责任公司
Method of amphipathic nature fluorine-contained copolymer modifying surface of polytetrafluoroethylene porous membrane
InactiveCN101108313AImprove anti-pollution performanceImprove hydrophilic abilitySemi-permeable membranesFiberTetrafluoroethylene
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method and application of high-strength oriented polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel
ActiveCN110229374AGuaranteed biocompatibilityReduce usageTissue regenerationProsthesisFreeze thawingPolymer science
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
Rubber compositions for oil seal of rubber framework and method for manufacturing same
Owner:青岛茂林橡胶制品有限公司
Tire rubber composition and pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110136962A1Improve wet grip performanceImprove balanceSilicon organic compoundsSpecial tyresPolymer scienceSilicon dioxide
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Spherical polybutylene-1 with high isotacticity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103288993AThe polymerization method is simpleSolve the difficulty of simultaneously controlling the isotacticity of polybuteneButenePolymer science
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inkjet recording ink set and ink cartridge, and recording device, image forming method, and image-formed article using such ink set
ActiveUS20120242741A1Desirable image densityImprove image qualityDuplicating/marking methodsInksPolymer scienceSURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:RICOH KK
Preparation method and application of water-soluble carbon fiber sizing agent
InactiveCN104975508AImprove protectionImprove smoothnessFibre treatmentFibre chemical featuresFiberCarbon fibers
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
High-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl alcohol fiber and melt spinning method of high-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl alcohol fiber
InactiveCN102776597AHigh strengthMeet toughnessFilament forming substance formingArtificial filament washing/dryingAlcoholPolymer science
Owner:SHANGHAI LUOYANG NEW MATERIAL TECH
Sulfonated aromatic copolyesters containing hydroxyalkanoic acid groups and shaped articles produced therefrom
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for compression moulding reinforced thermoplastic article
A method for manufacturing a polymeric article having an integrated reinforcing element. A thermoplastic material is introduced into a mould, after which reinforcing elements are inserted into the mould cavity. A second layer of the thermoplastic material is introduced into the mould, after which the mould is closed, pressing and heating the mould to melt the thermoplastic material and form the article. The thermoplastic layers may be provided in powder, sheet, or pellet form. The reinforcing elements may comprise reinforcing fibres or reinforcing fabrics. A polymeric track for a vehicle may be produced from this method.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC +1
Molded Article for Clean Room and Method for Producing Same
Owner:FUJI BAKELITE +2
Process for preparing halogen-free atrp products
The present invention relates to the in situ removal of terminal halogen atoms from polymer chains which have been prepared by means of atom transfer radical polymerization, and to the simultaneous removal of transition metals from polymer solutions.
Owner:EVONIK ROEHM GMBH
Vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion as electrostatic spinning adhesive and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN102030857AGood adhesionImprove water resistanceMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesLiquid surface applicatorsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion as an electrostatic spinning adhesive and a synthesis method thereof. Organic peroxides and zinc formaldehyde sulfate are taken as an initiator; vinyl acetate, ethylene, acrylic ester monomers and cross-linking monomer N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide are taken as comonomers; a nonionic emulsifier, and the synthetic emulsion and the protective colloid of an amphoteric emulsifier are matched to be taken as an emulsification system; and the copolymer emulsion is prepared through emulsion polymerization. Compared with the VAE (vinyl acetate-ethylene) emulsion prepared by the conventional preparation method, the product in the invention has the advantages of good water resistance, strong adhesion on low-surface-energy materials (polyethylene, polypropylene and the like), fine grain and the like. The vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion is suitable for being as the adhesive to be applied to the field of the electrostatic spinning in textile industry and the fields of waterproofing and packaging.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Tissue-adhesive materials
ActiveUS20090044895A1Improve adhesionEasy to useSurgical adhesivesCoatingsPolymer scienceContact layer
A multi-lamellar tissue-adhesive sheet comprises a structural layer or laminate conjoined to a tissue-contacting layer. The structural layer or laminate comprises one or more synthetic polymers having film-forming properties, and the tissue-contacting layer of material contains tissue-reactive groups. The synthetic polymers having film-forming properties are preferably biodegradable polyesters, and the tissue-reactive groups are most preferably NHS-ester groups.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Composite silicon-based flame-retardant viscose fiber and production method thereof
ActiveCN102409420AImprove adhesionIncrease contact surfaceMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentSpinning solutions preparationPolymer scienceSpinning
Owner:YIBIN GRACE +2
Terpene resin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102633919AEliminate quality impactEliminate the effects ofFood preparationTrimethylsilyl chloridePolymer science
The invention discloses a terpene resin and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: terpene substances are used as a raw material, AlCl3 in the presence of an aromatic solvent is used as a main catalyst, and a cocatalyst is used in the reaction; polymerization is carried out at low temperature to prepare the crude terpene resin product; and the crude terpene resin product is washed and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the terpene resin product. The cocatalyst is trimethylchlorosilane, triethylchlorosilane, tripropylchlorosilane or tributylchlorosilane, and accounts for 1-5% of the total mass of the terpene substance raw material; the main catalyst AlCl3 accounts for 4-12% of the total mass of the terpene substance raw material; the elemental chlorine content in the prepared terpene resin product is less than 100mg / kg, and the metallic aluminum content is less than 10mg / kg; the terpene resin product does not contain metallic antimony; and the residue level of the volatile solvent is less than 25mg / kg. The product reaches to the food level.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY +1
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap