A design method of a page-level flash memory conversion layer of a solid-state hard disk
A flash memory conversion layer and design method technology, applied in computing, memory systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the lifespan of NAND flash memory, limited service life, and not supporting in-place updates, etc., to improve overall performance and service life, reduce The effect of write times and good system response time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Embodiment 1: The write request does not hit in W-CMT and R-CMT.
[0084] Suppose the initial state of the mapped buffer is as Figure 5 As shown in the "initial state" in the figure, there is a request "access data page LPN=1280, write access request, request size 1" arrives, and the processing process is as follows:
[0085] C1, when an access request arrives (LPN=1280), first query the W-CMT, and the request mapping item is not found in the W-CMT, and then query in the R-CMT, and the request mapping item is also not found. At this point, the mapping information of the access request needs to be loaded into the W-CMT.
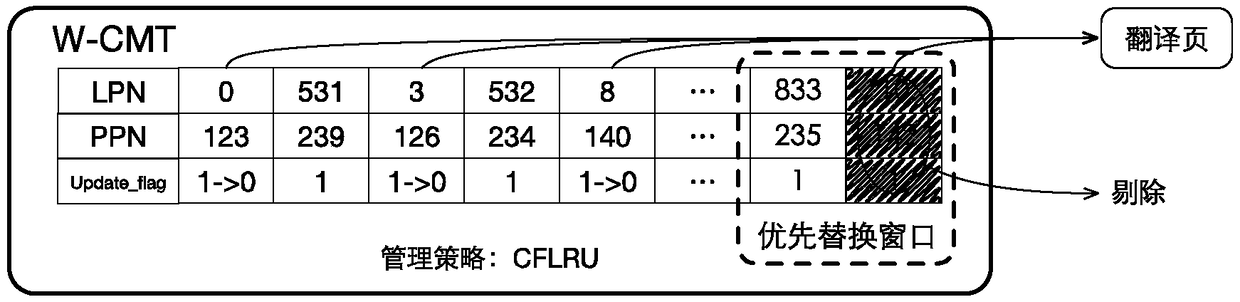
[0086] C2. At this time, the W-CMT is in a full state, and a mapping item needs to be selected for removal. Since there is no clean mapping information in the priority replacement area, the mapping information (LPN=6) at the LRU position is selected as the victim item (ie, the item to be eliminated).
[0087] C3, through the LPN of the victim item, cal
Embodiment 2
[0096] Embodiment 2: The write request hits in the R-CMT.
[0097] Suppose the initial state of the mapped buffer is as Figure 6 As shown in the "initial state" in "Initial State", there is an existing "access data page LPN=1280, write access request, request size is 1" request arrives, and its processing process is as follows: C1, when an access request arrives (LPN= 1280), query W-CMT first, no request mapping item is found in W-CMT,
[0098] C2 then inquires in the R-CMT, and finds the mapping information corresponding to the request in the R-CMT.
[0099] C3, W-CMT is full at this time, query whether there is a clean mapping item in the priority replacement area, and get a clean mapping item of LPN=833, then remove it as a victim item.
[0100] C4, and then migrate the mapping information from the R-CMT to the MRU position of the W-CMT.
[0101] C5, assuming that the newly allocated data page of the flash memory is PPN=661, update the mapping information, and set the upda
Embodiment 3
[0103] Embodiment 3: The write request hits in the W-CMT.
[0104] Suppose the initial state of the mapped buffer is as Figure 7 As shown in the "initial state" in the figure, there is a request "access data page LPN=1280, write access request, request size 1" arrives, and the processing process is as follows:
[0105] C1, when an access request arrives (LPN=1280), first query the W-CMT, and query the request mapping information in the W-CMT.
[0106] C2. Migrate the mapping information to the MRU position of the W-CMT.
[0107] C3, assuming that the newly allocated data page of the flash memory is PPN=661, update the mapping information, and set the update bit to dirty (Update_flag=1).
[0108] To sum up, the status of the mapping buffer after processing is as follows Figure 7 shown in "End State".
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap