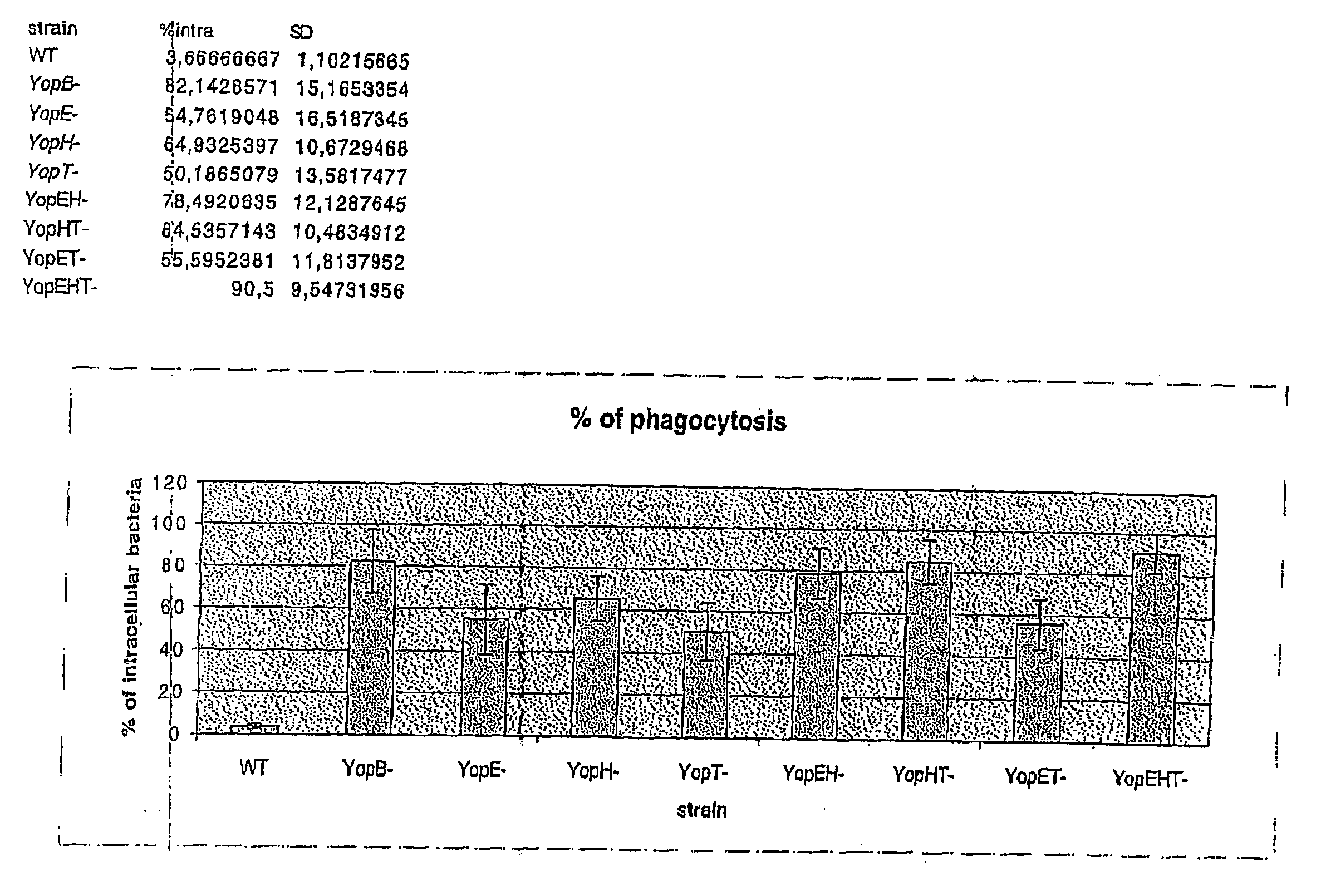
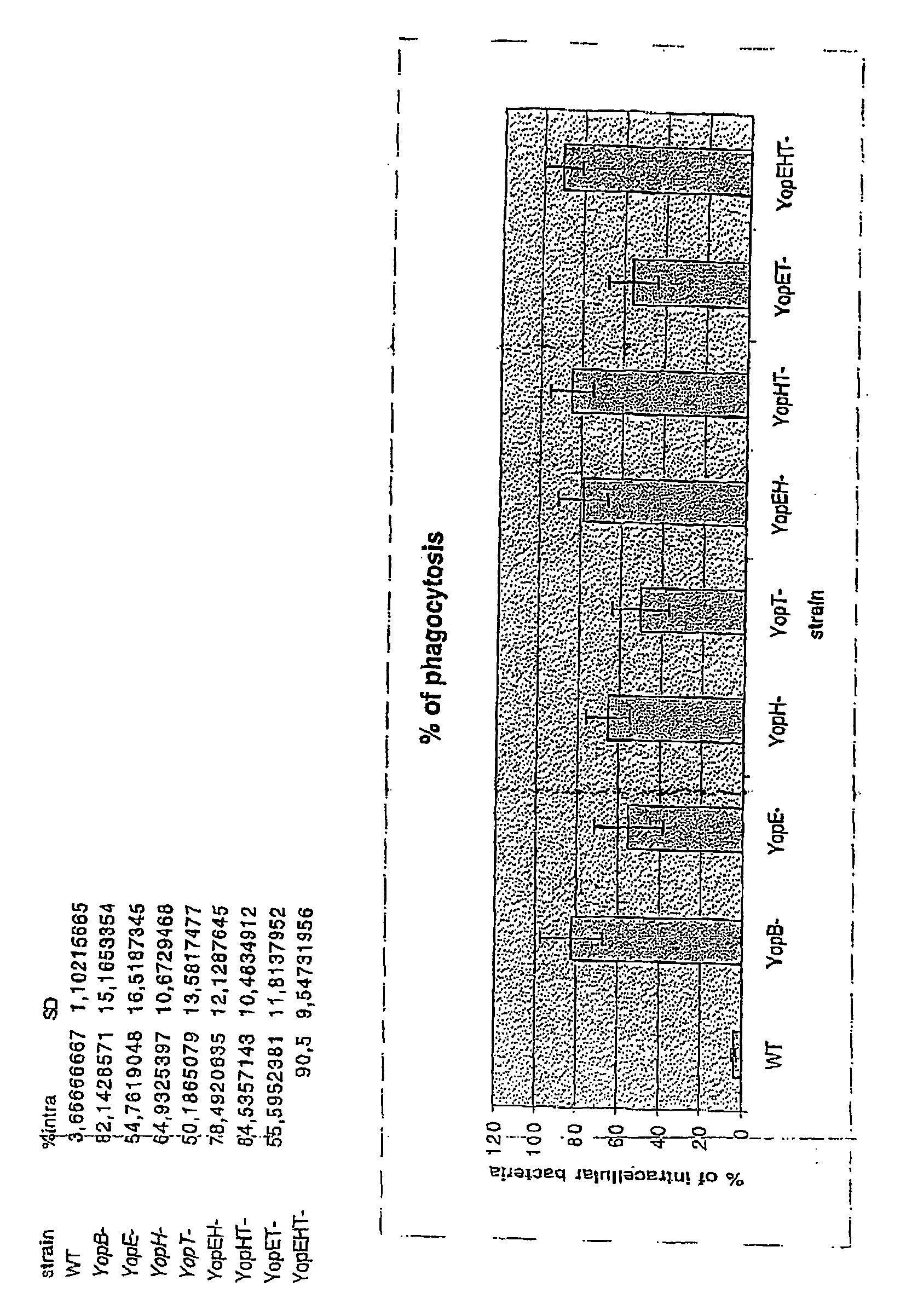
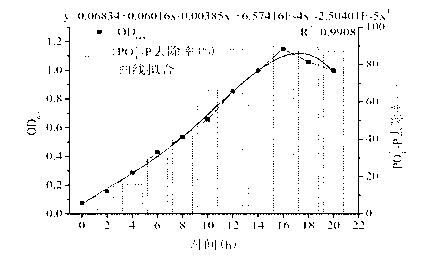
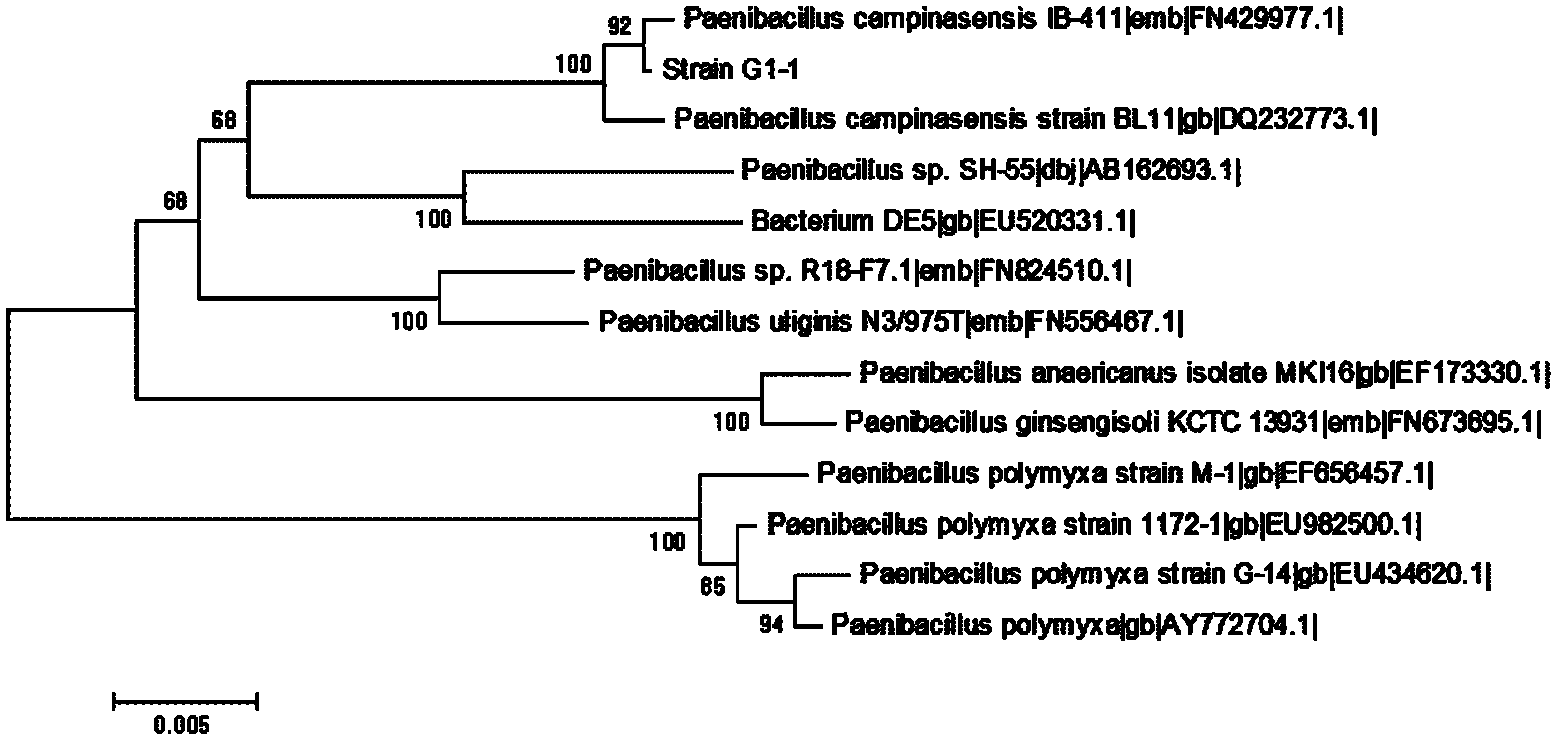
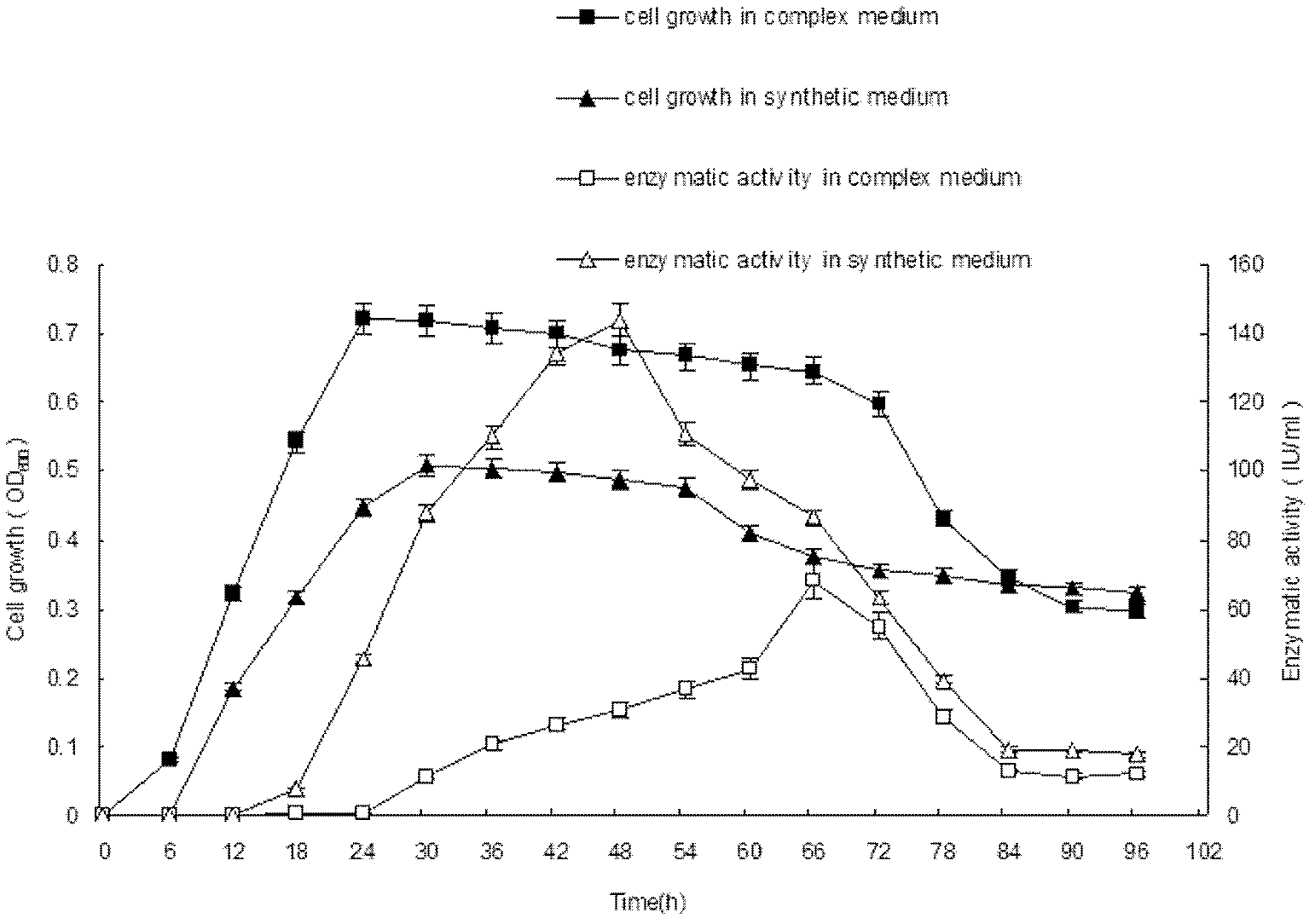
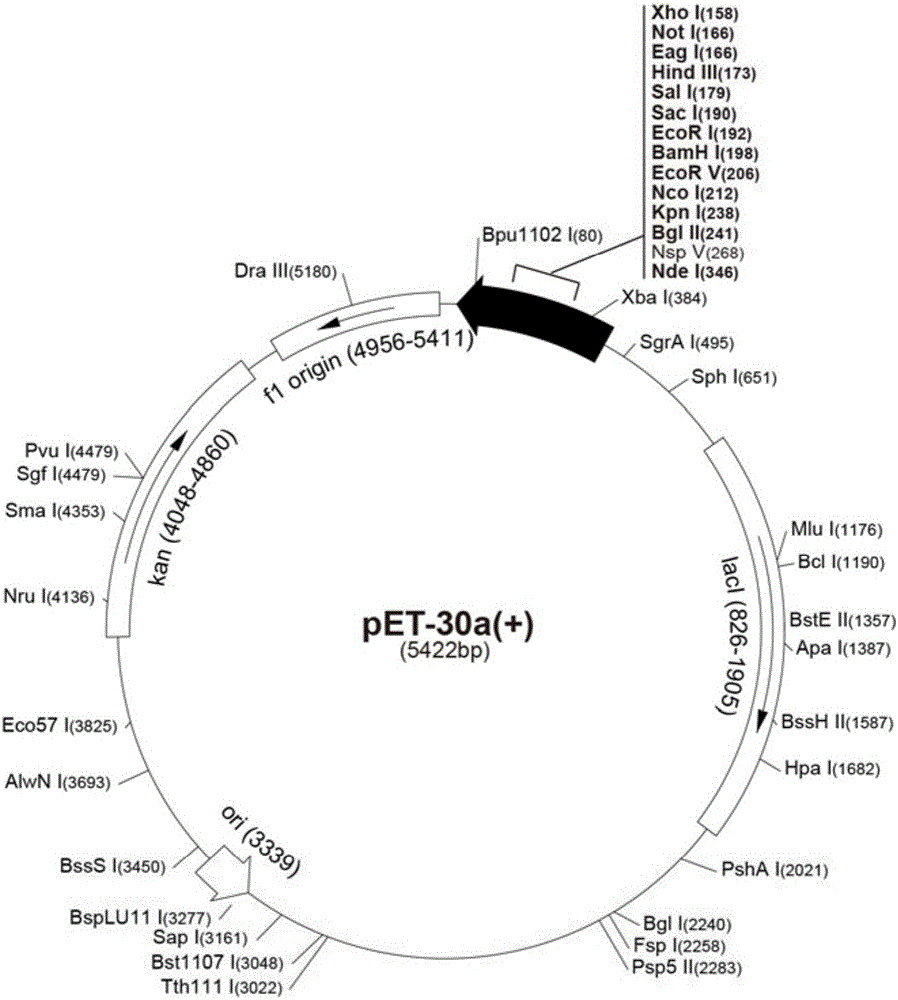
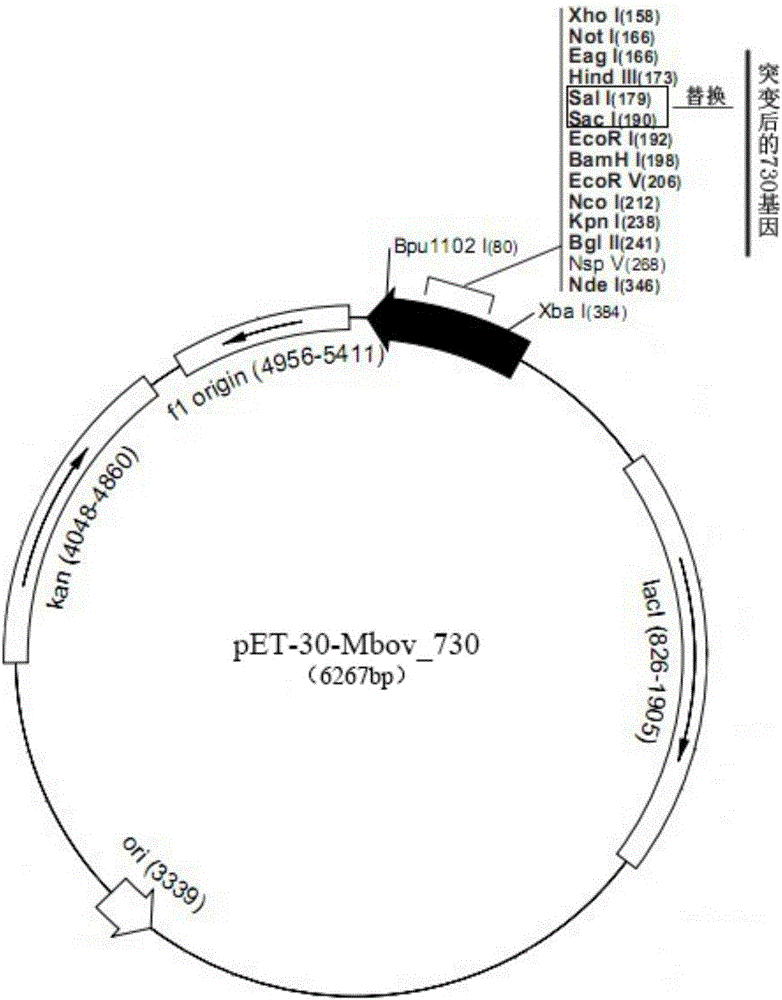
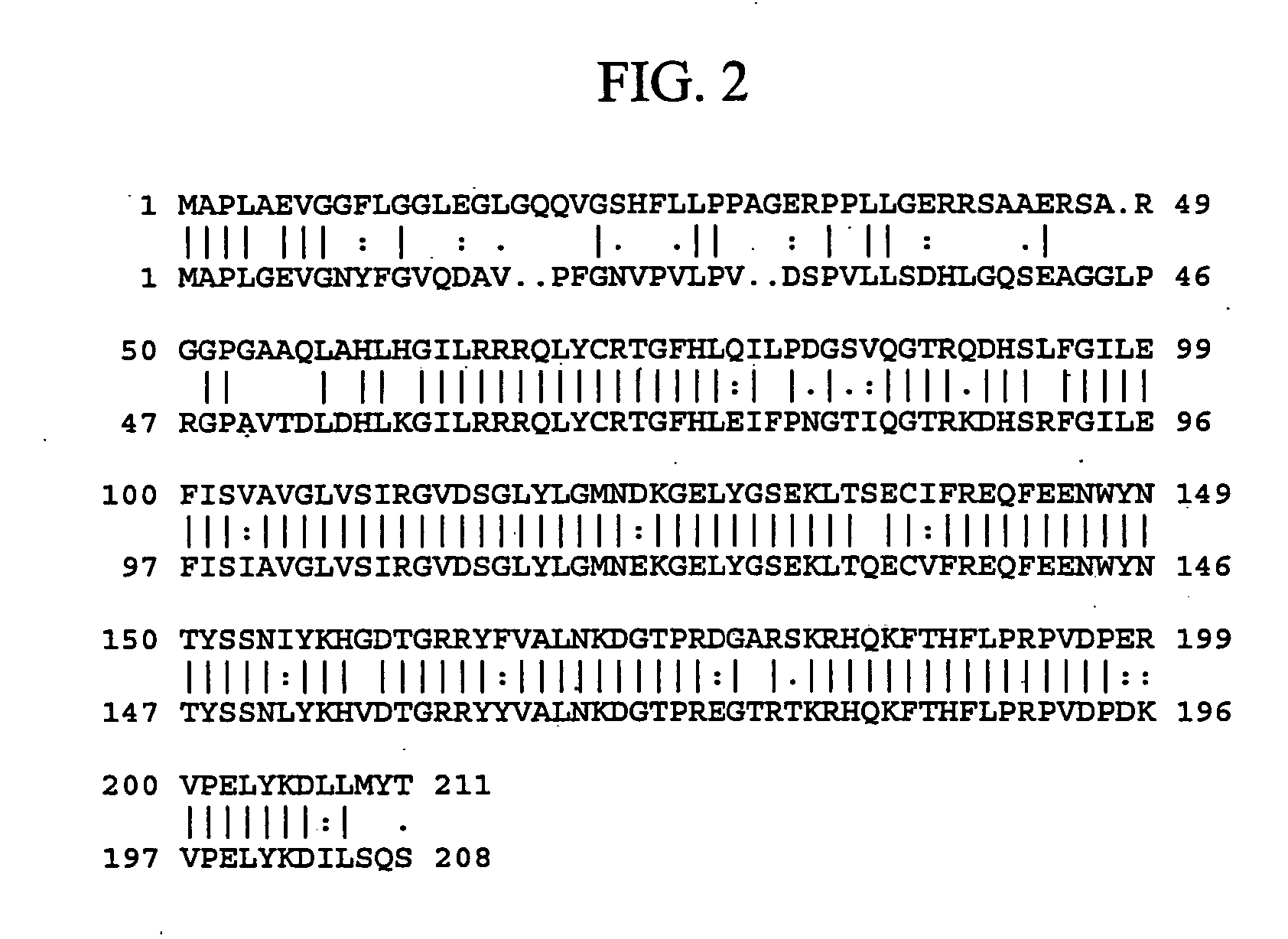
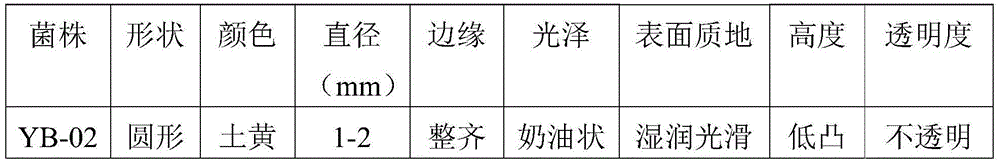
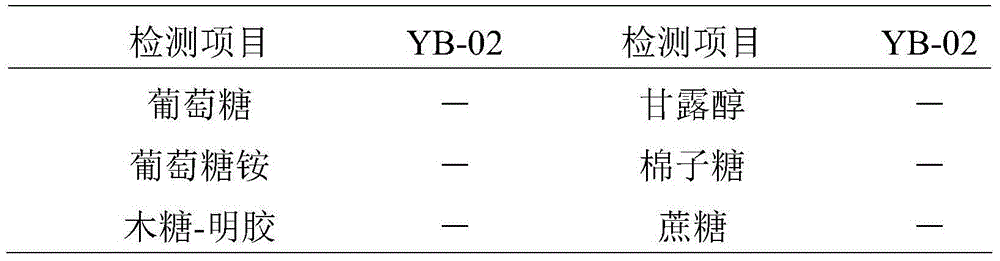
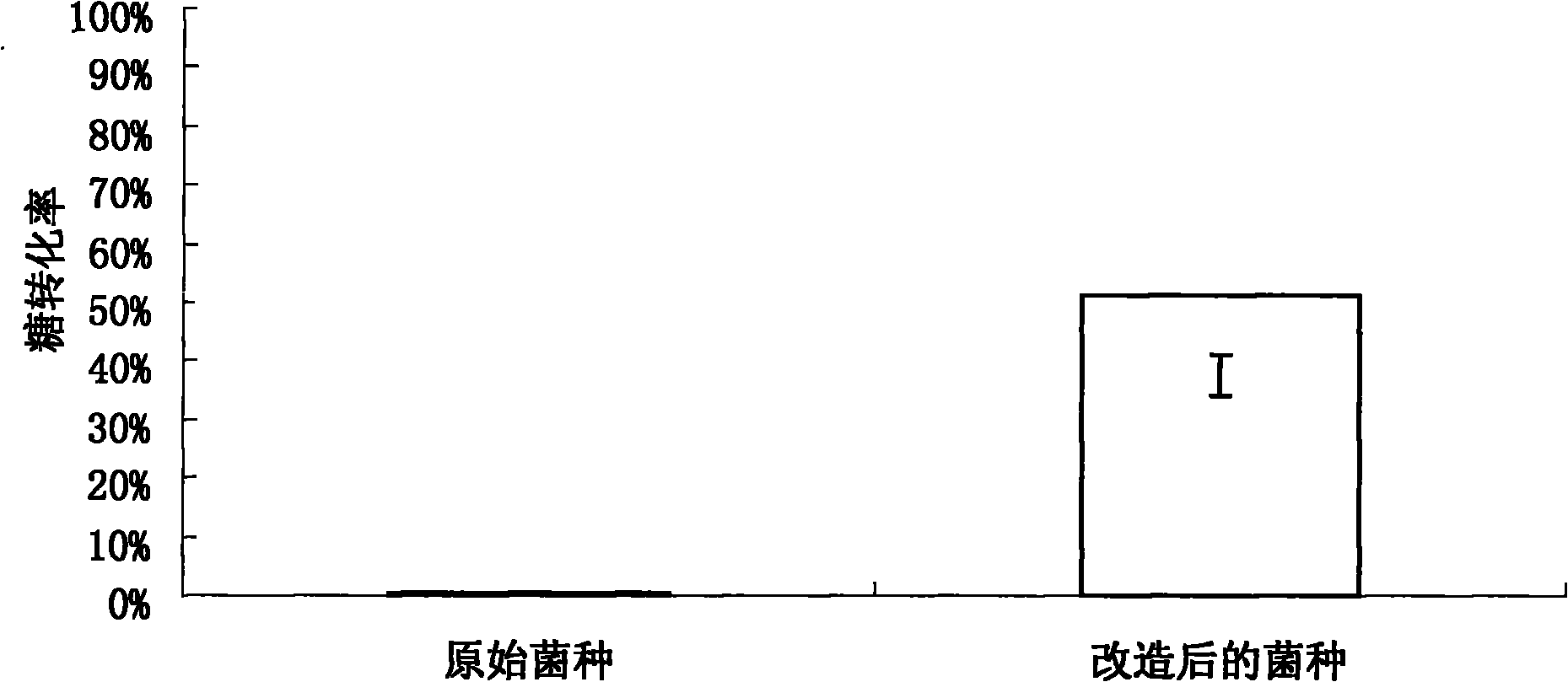
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149results about "Bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
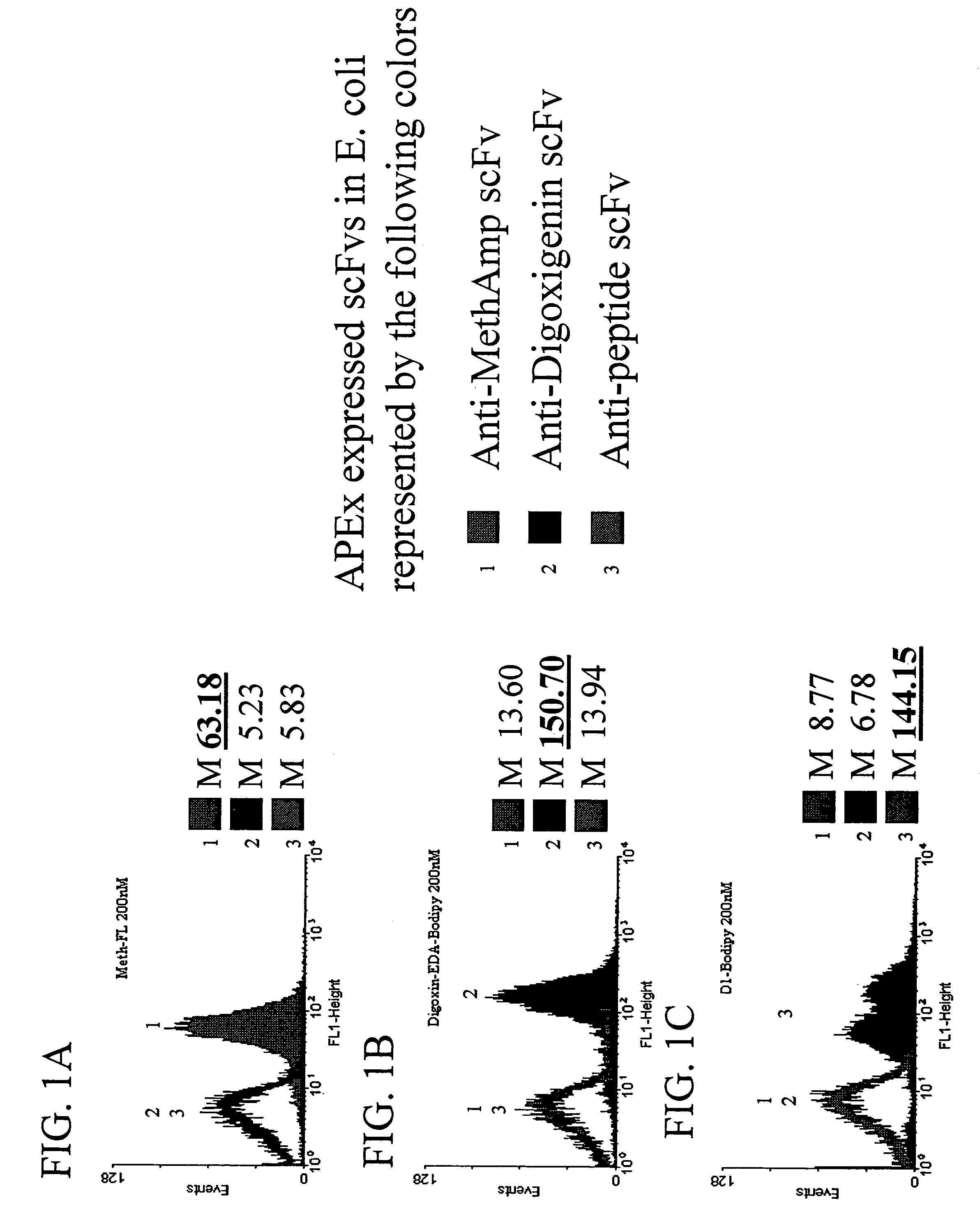
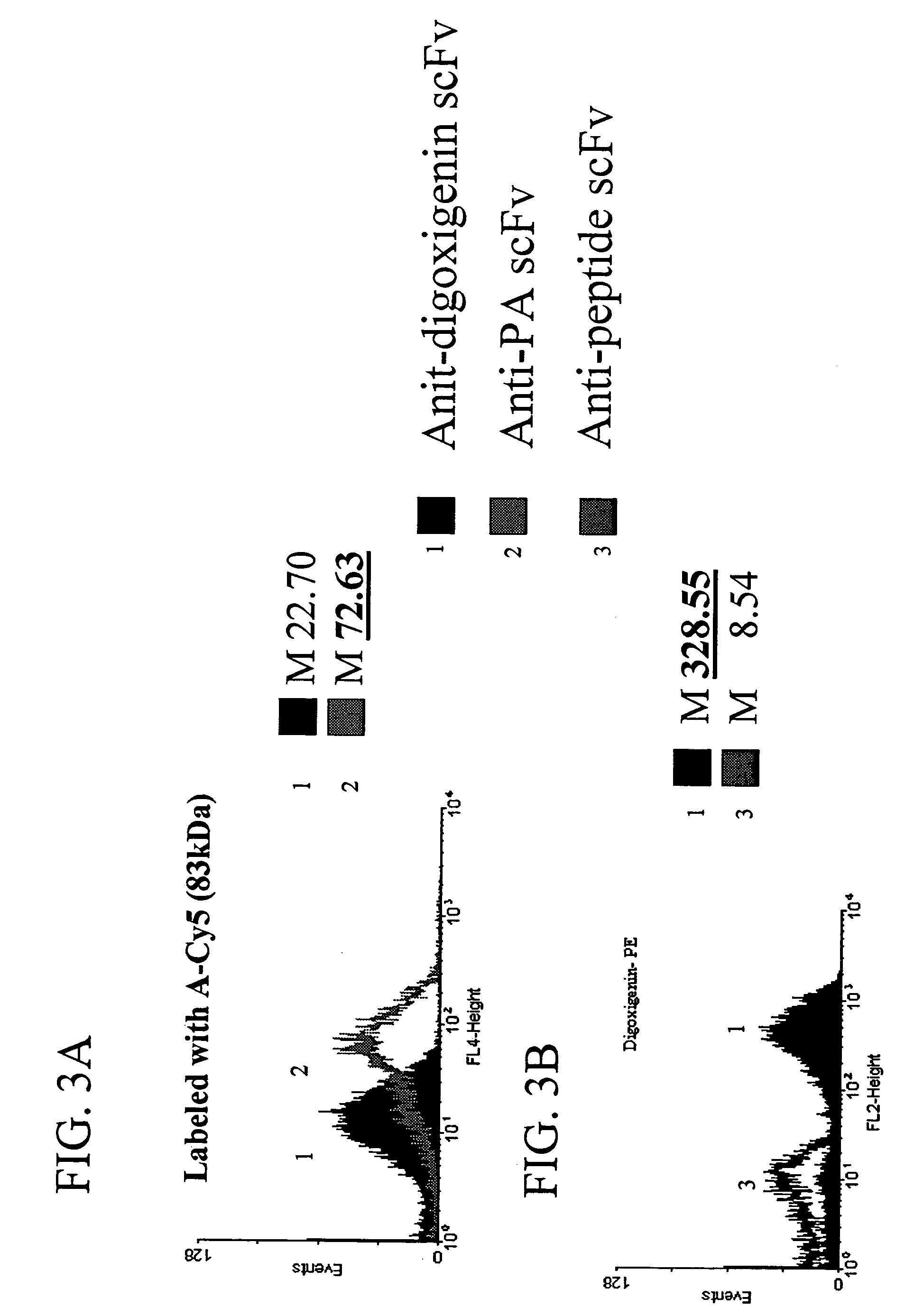
Combinatorial protein library screening by periplasmic expression
InactiveUS7094571B2Improve breathabilityPeptide librariesBacteriaFluorescence-Activated Cell SortingFluorescent labelling
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Composite preparation microbiological, and preparation method
InactiveCN101050423AReduce pollutant contentQuick removalFungiBacteriaFermentationPhotosynthetic bacteria
This invention relates to a composite microbe preparation, which is composed of: photosynthetic bacteria group 2-3.8 wt.%, lactic acid bacteria group 0.6-1.8 wt.%, Saccharomyces cerevisiae 1-1.8 wt.%, Gram-positive bacteria group 1-3.8 wt.%, filamentous bacteria group 1-3.8 wt.%, culture medium 10-38 wt.%, and deionized water 65-80 wt.%. The preparation method comprises: performing amplification culture on the above bacteria separately to obtain production bacteria solutions, sealing in a stainless steel fermentation tank, adding deionized water and culture medium, inoculating the production bacteria solutions, fermenting until the pH is 3.8-4 and the living bacteria number is not less than 2X10 to the power 9, then packaging and storing. The composite microbe preparation can rapidly and effectively remove inorganic and organic pollutants in wastewater, denitrify, dephosphorize and inhibit algae growth by oxidation, reduction and fermentation.
Owner:ZHENMEI TECH DEV SHANGHAI
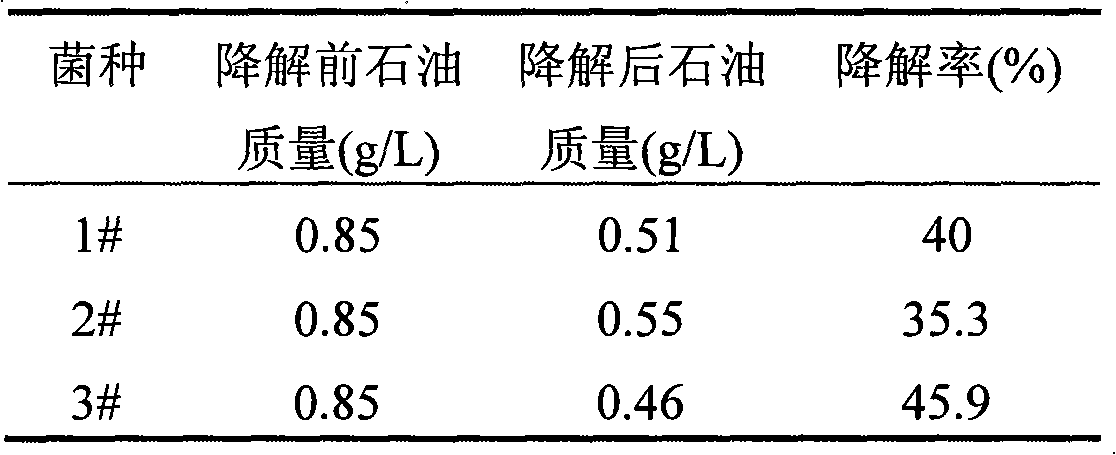
Solid microbial agent to remedy soil contaminated by petroleum, preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN101597576AHigh organic contentImprove micro-ecological environmentBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismEcological environment
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
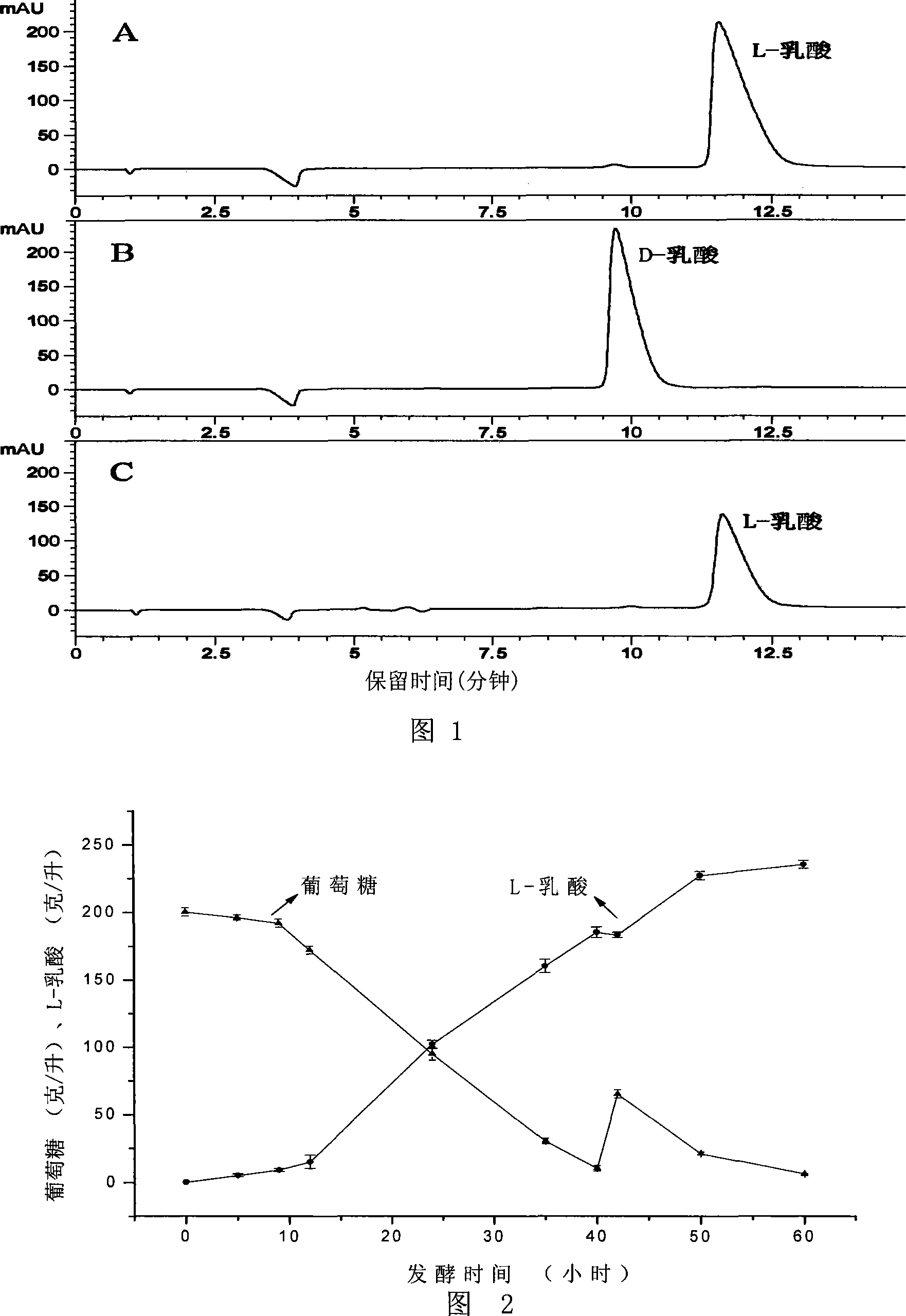
Method for producing L-lactic acid and isoduicitol lactobacillus special for the same
ActiveCN101173241AImprove utilization efficiencySimplify raw material handlingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon sourceHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method producing L-lactic acid and a special lactobacillus rhamnosus which is Lactobacillus rhamnosus CASL CGMCC No.2183. The L-lactic acid can be obtained by cultivating the Lactobacillus rhamnosus CASL CGMCC No.2183. The fermentation culture medium of the strains is provided with a carbon source, a nitrogen source and the neutralizer used for controlling the fermentation liquid pH; the carbon source is glucose of 150 to 200g / L (the initial fermentation concentration); the nitrogen source is soybean meal hydrolysate, soybean meal hydrolysate and corn steep liquor, or soybean cake powder, and can comprise protease by 0.05 to 0.1g / L when the nitrogen source is soybean cake powder; the neutralizer is the calcium carbonate of 75 to 100g / L, the rest is water and the pH of the fermentation culture medium is 5.5 to 7. With glucose as substrate and a transformation rate of 94.5% to 96.5%, the Lactobacillus rhamnosus CASL CGMCC No.2183 produces the L-lactic acid with an optical purity of 97.6% to 98.7% under the condition of 35 DEG C-45 DEG C, with a highest concentration of 235g / L.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alcaligenes faecalis and application thereof
InactiveCN103289939AEfficient removalReduced footprintBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismWastewater
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
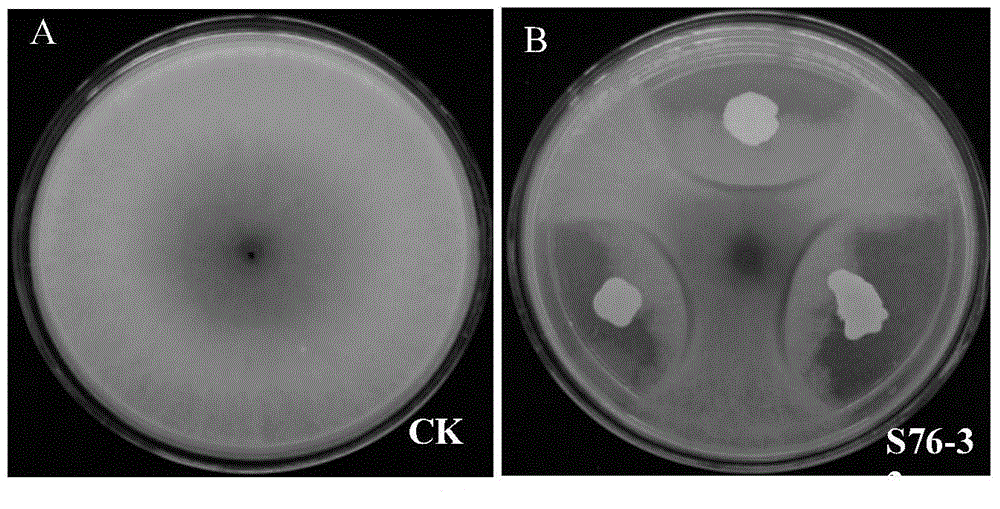
Biological control strain capable of preventing and curing root knot nematode disease for greenhouse vegetable
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
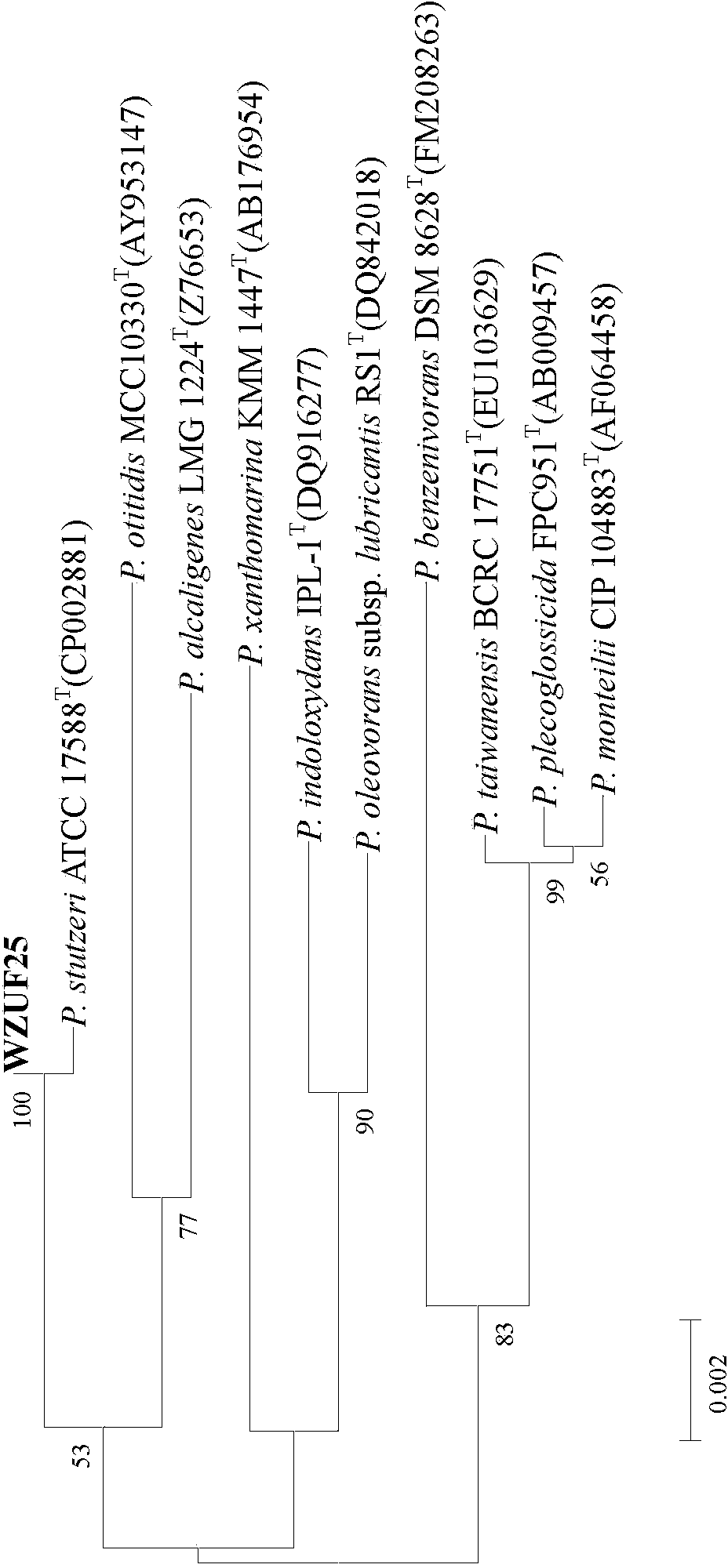
Pseudomonas stutzeri and its culture, immobilization and use
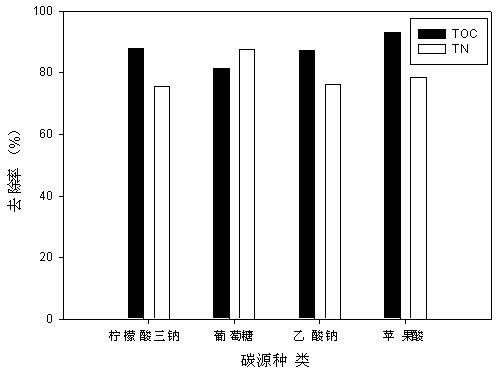
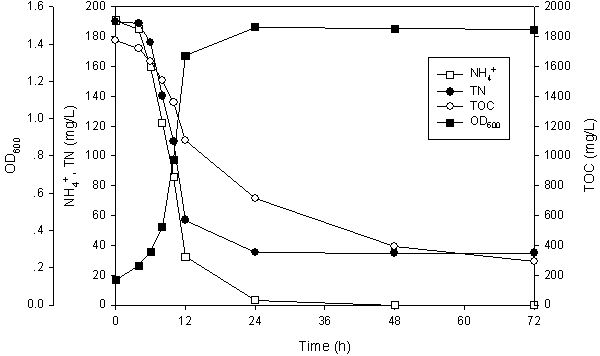
InactiveCN103497908AHigh removal rateWide pH rangeBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobiological cultureDenitrification
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
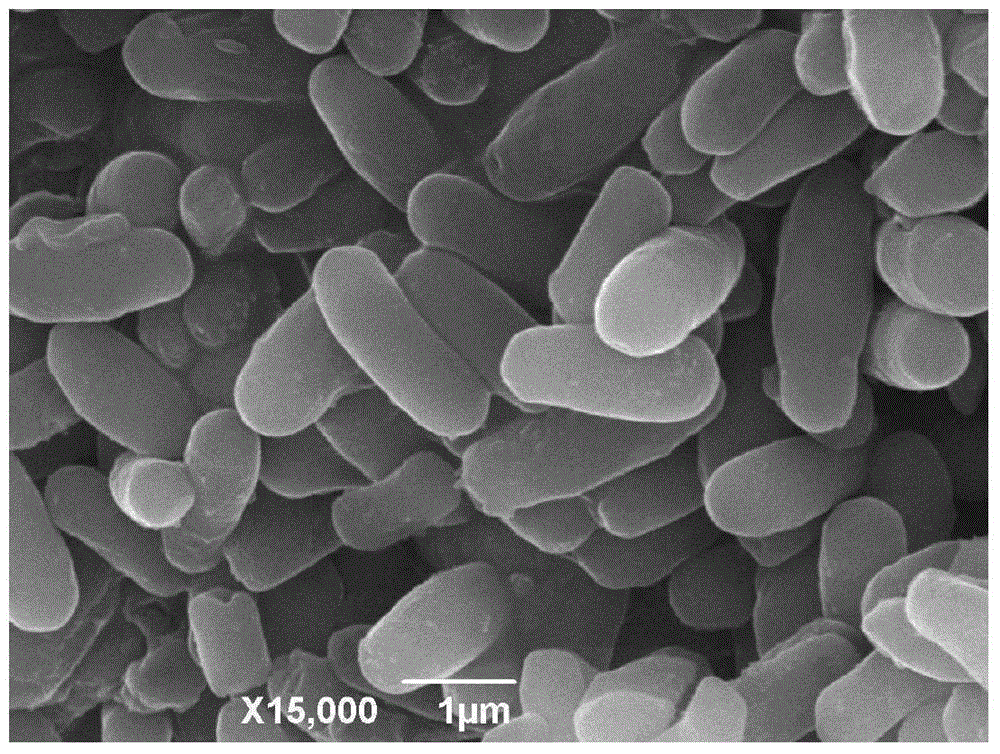
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
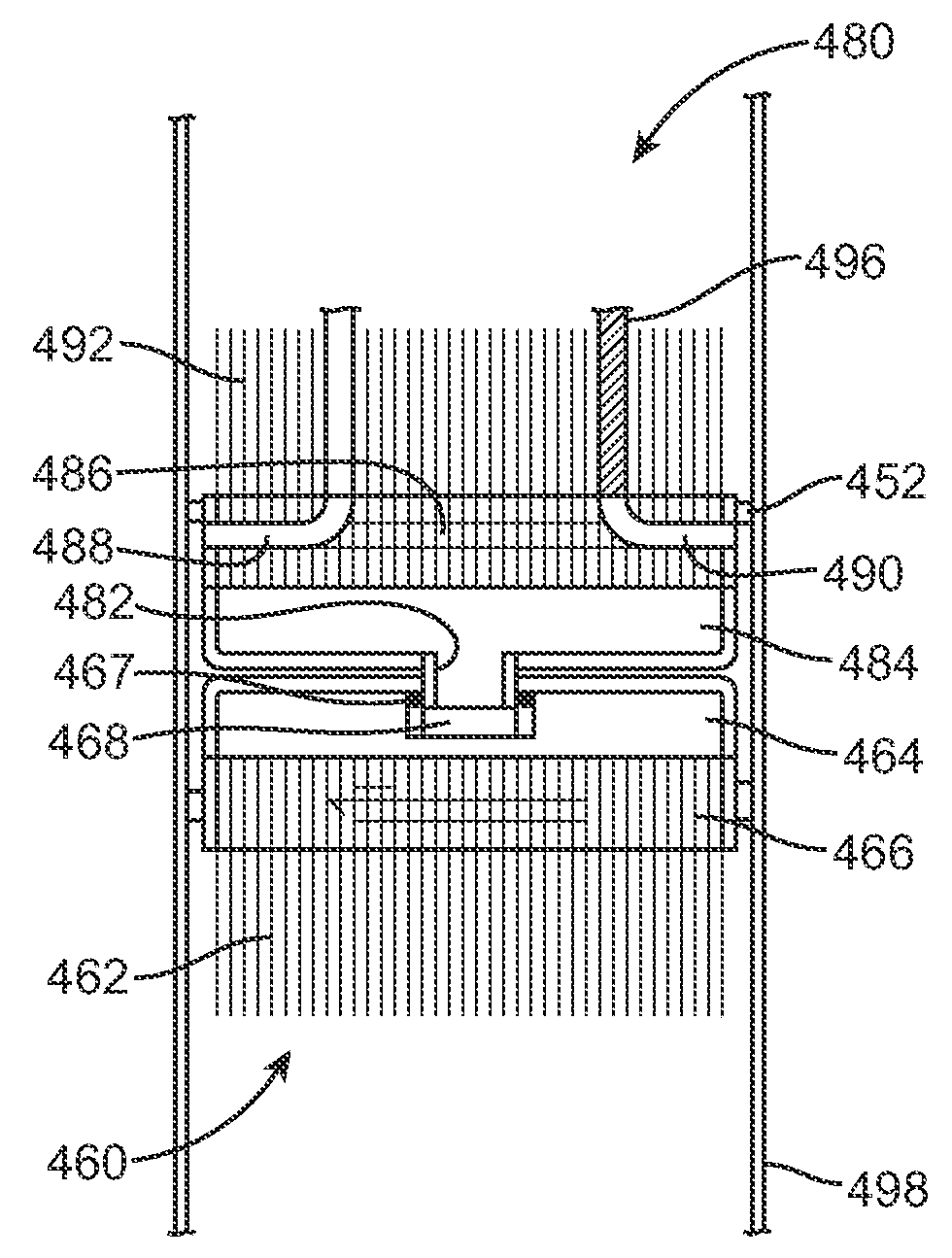
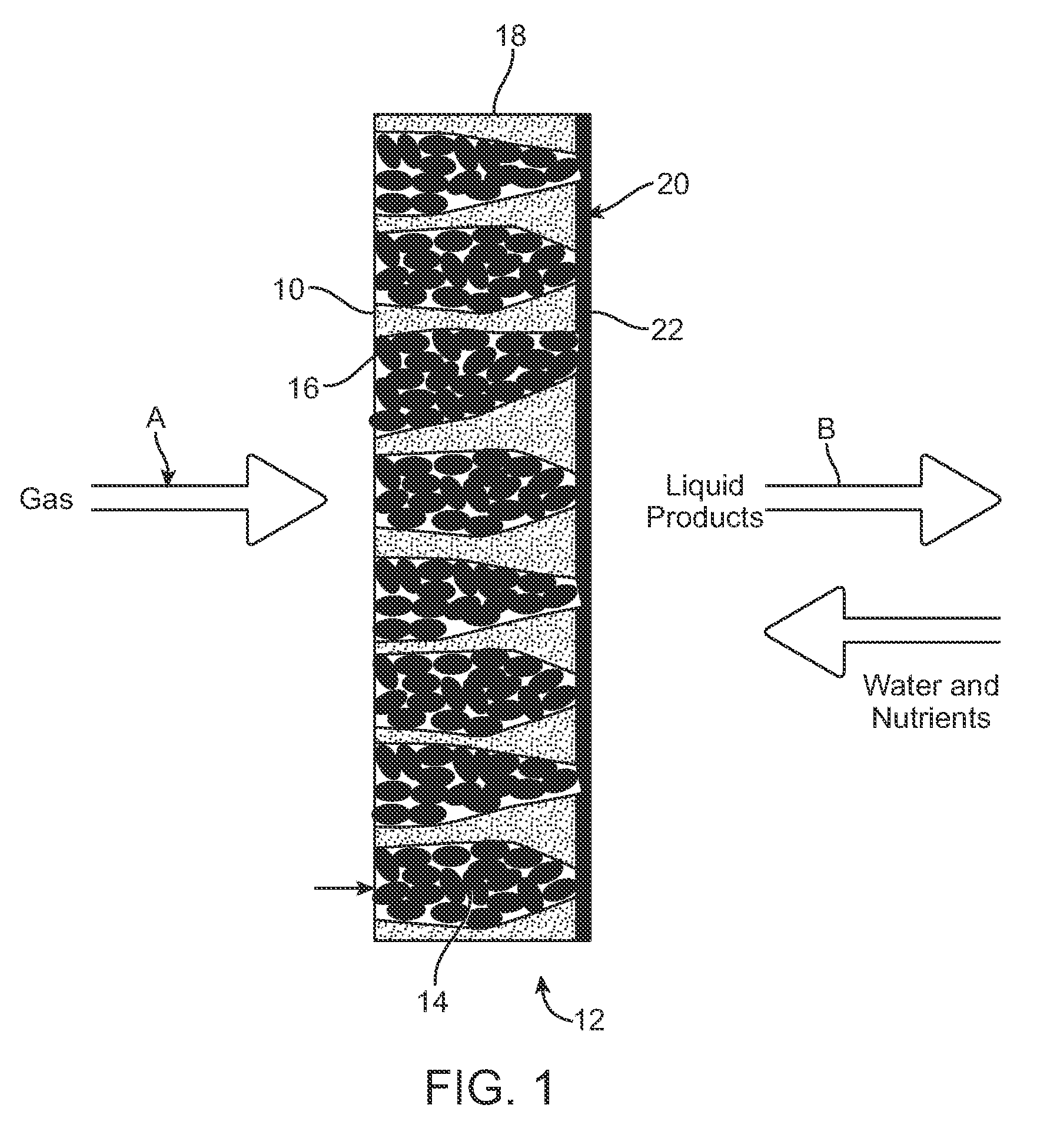
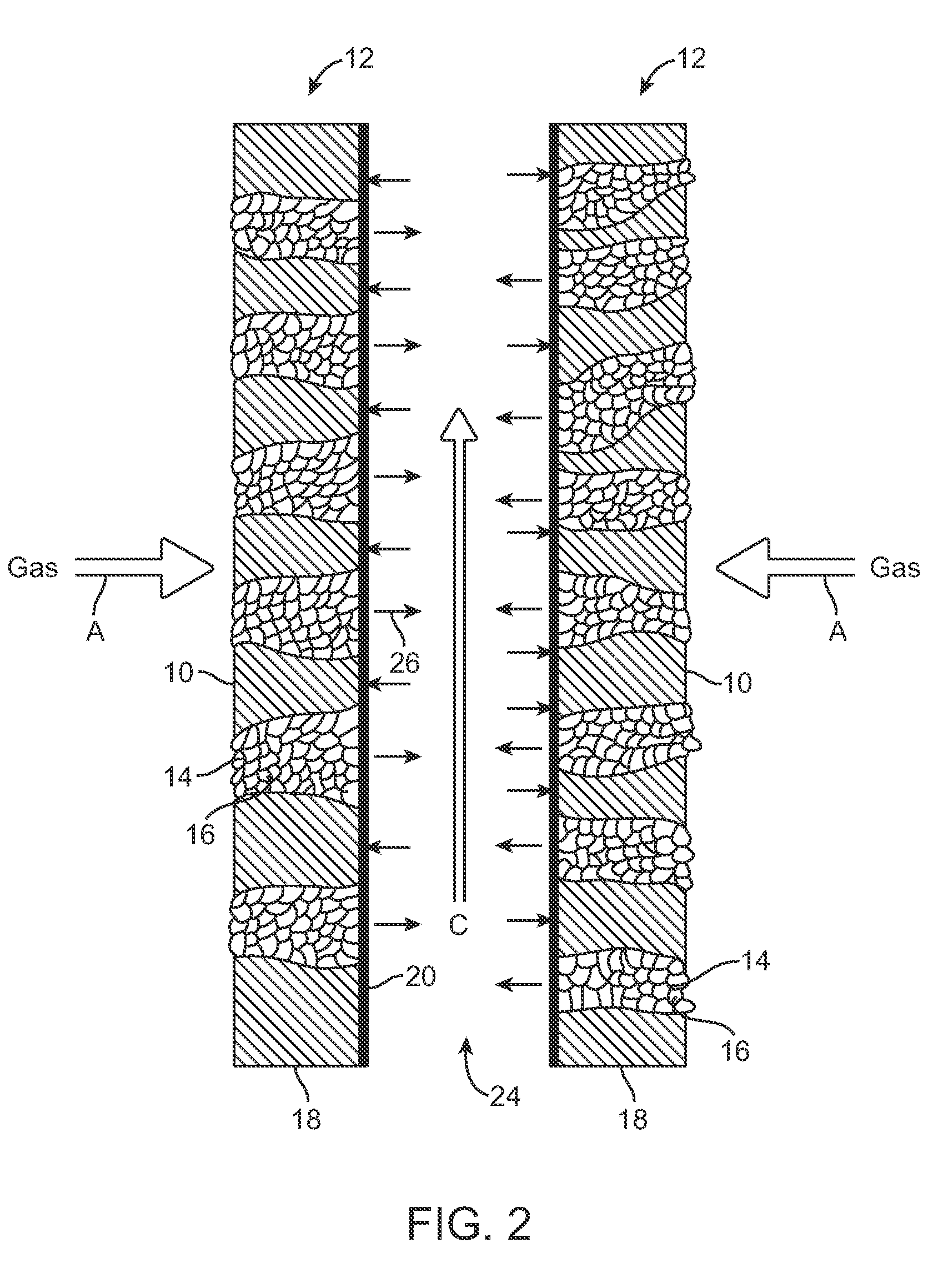
Stacked Array Bioreactor for Conversion of Syngas Components to Liquid Products
InactiveUS20090215153A1Promote and controlLess permeabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid productFiber
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
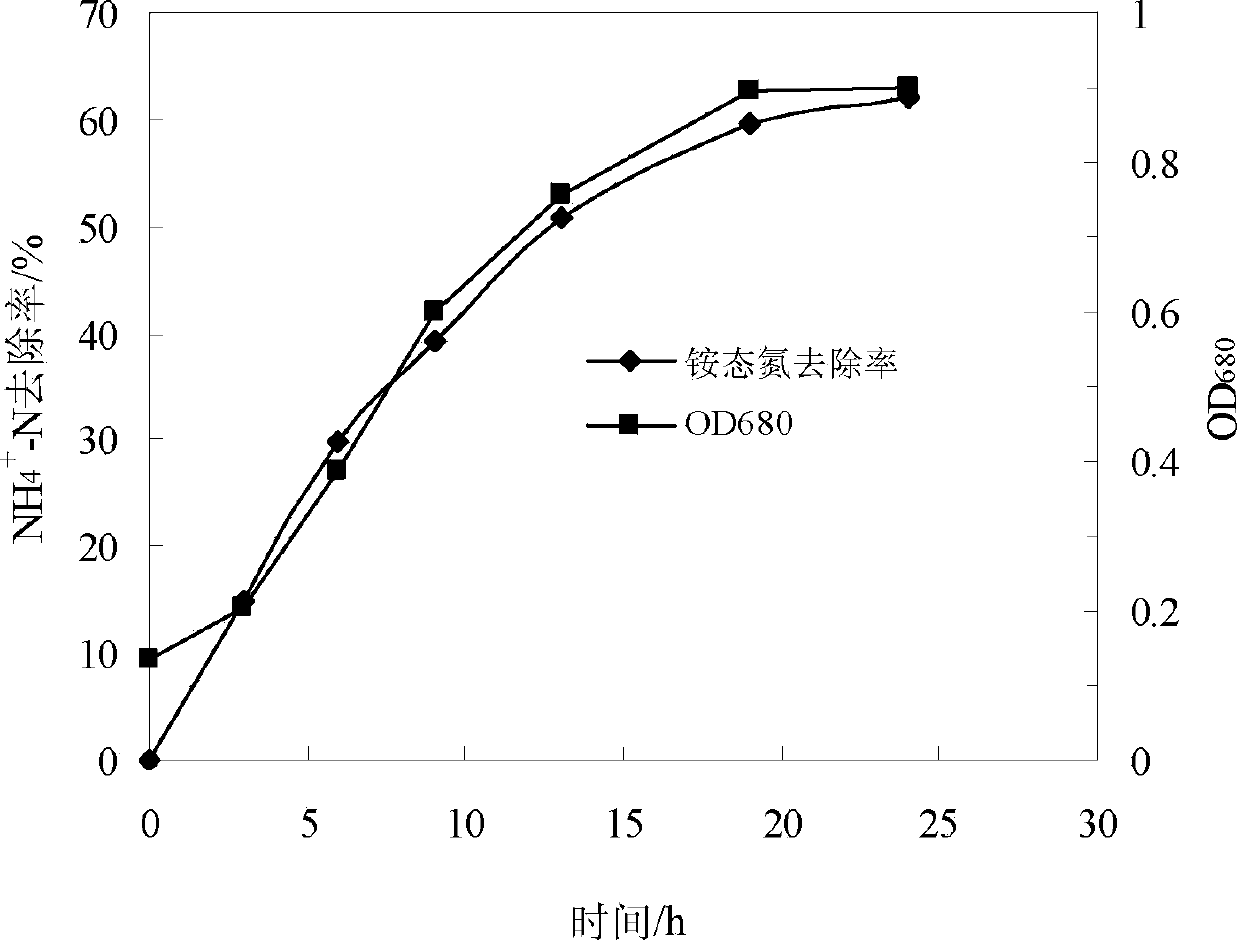
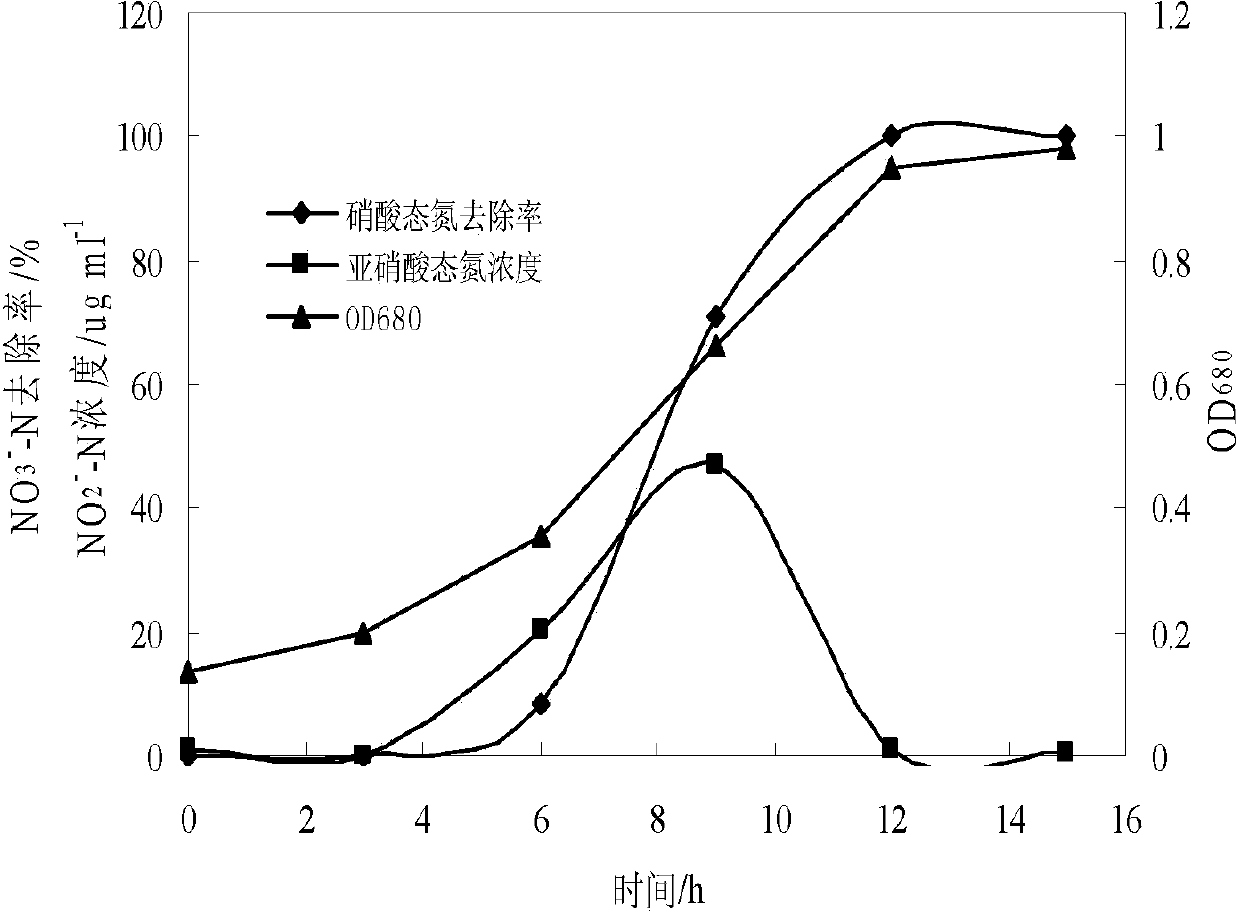
Denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria bacillus cereus H-hrb01 and screening method and application
ActiveCN102827787AEasy to waterExcellent water indicatorsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChemical oxygen demand
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
High-yield strain of high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase, method for producing high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase through fermentation of high-yield strain, and high temperature resistant 1,4-beta-D-xylanase
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Application of mycoplasma bovis MbovP730 protein in natural infection and vaccine immunity identification
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Fibroblast growth factor-like molecules and uses thereof
Owner:AMGEN INC
Brevibacillus laterosporu with function in quickly decomposing nitrite nitrogen and bacteriostasis function and application thereof
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
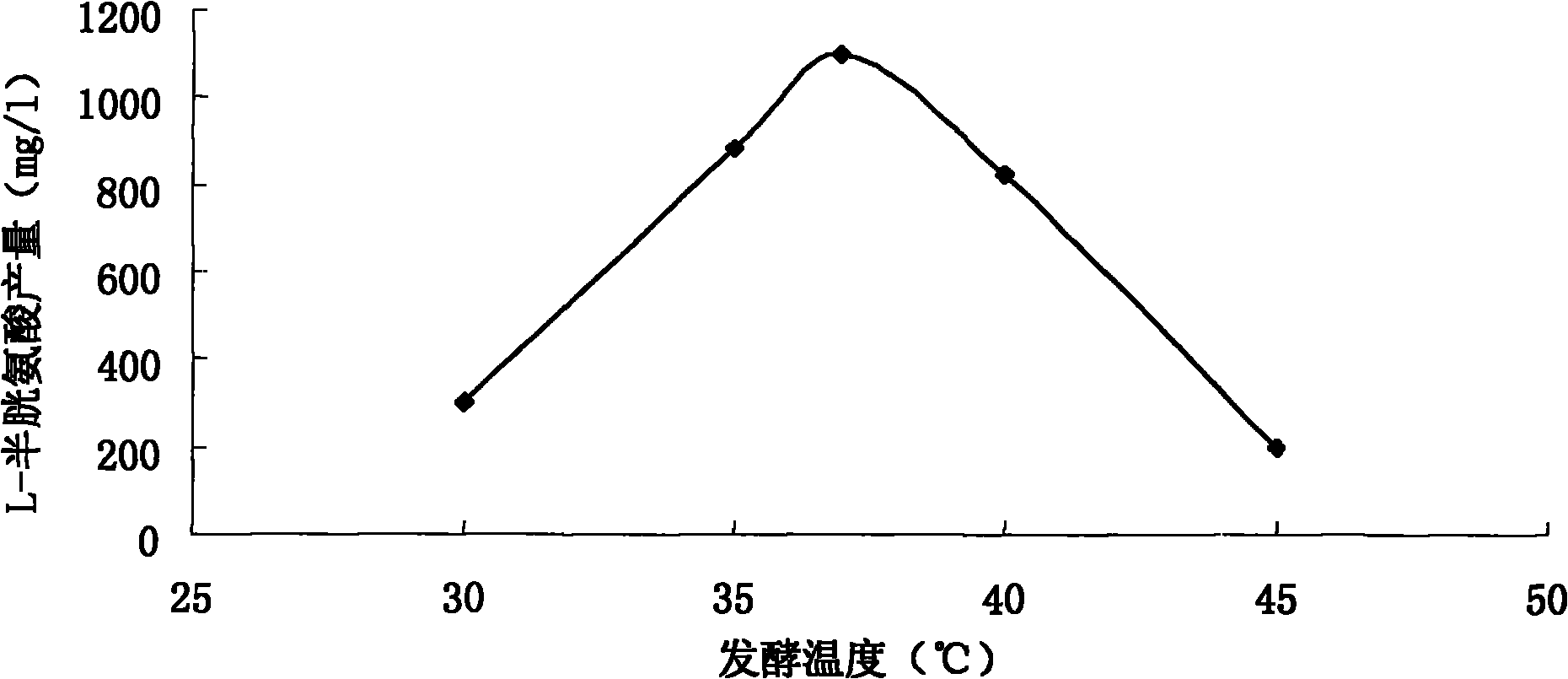
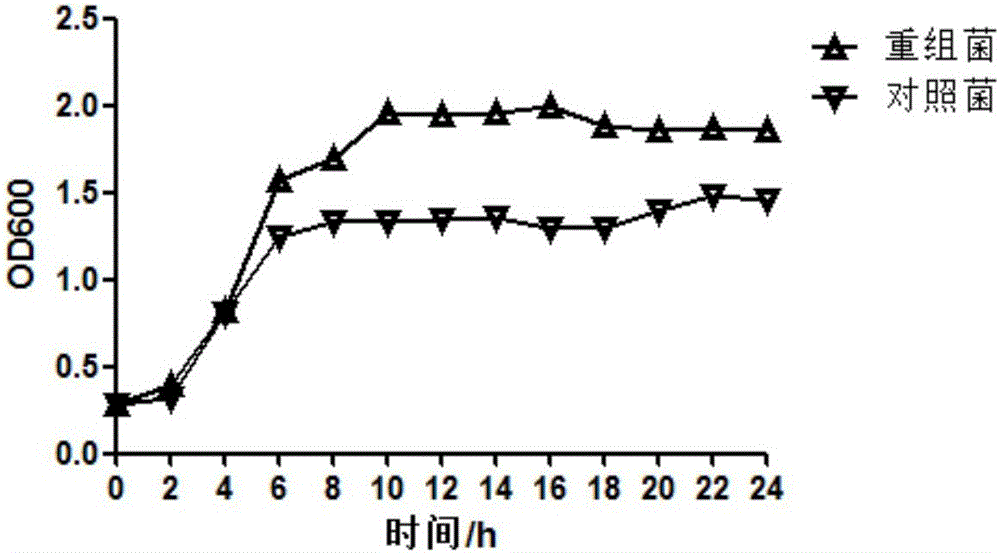
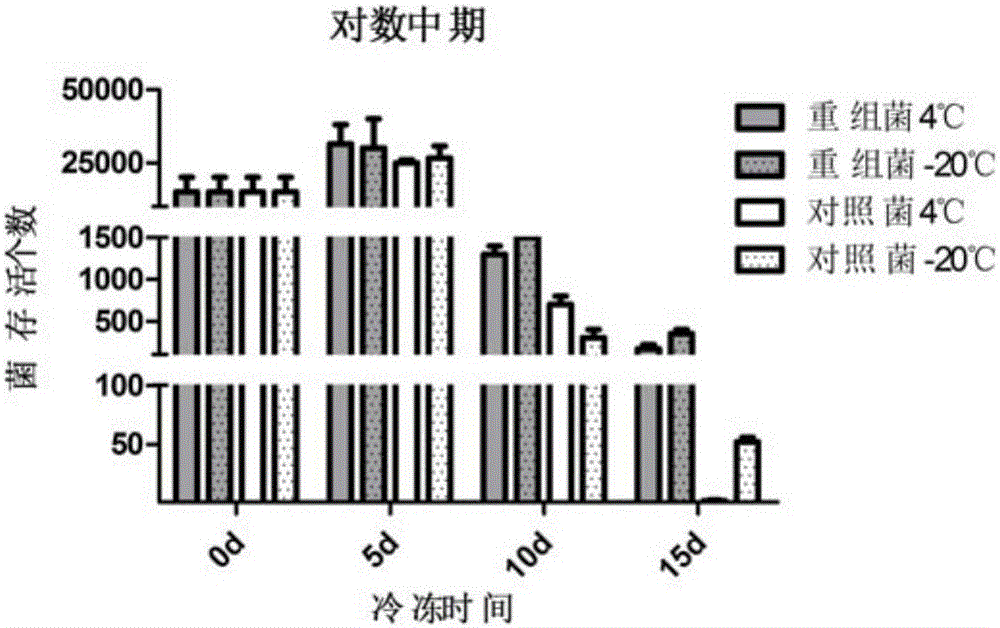
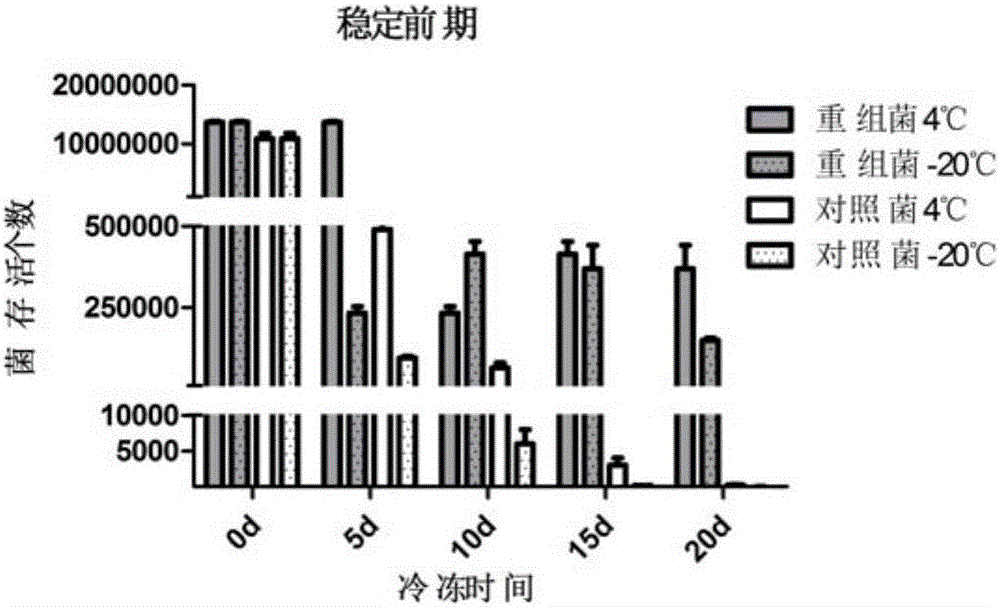
Escherichia coli and method for preparing L-cysteine by using same
ActiveCN101831397APromote accumulationHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSerine acetyltransferase
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
GAD gene for increasing stress tolerance of lactic acid bacteria and application thereof
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cell isolation method
InactiveCN1395620AUniversal binding ability is beneficialAdvantages FlexibilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
Owner:挪威诊断联合股份有限公司
Recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103773729AAbundant resourcesGood synthesis effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLycopene
The invention relates to a recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Particularly, an escherichia coli endogenous 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphoric acid (MEP) precursor pathway is reconstructed; the reconstructed escherichia coli base cell is utilized to perform the efficient biological synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds; the reconstruction of the precursor pathway mainly comprises the steps of fully digging the MEP precursor pathway gene modules of the sources of other natural microorganisms, screening gene modules with excellent characteristics to be expressed in the escherichia coli, and at the same time, performing the downstream synthesis pathway for integrally assembling the colibacillus chemical compounds in the reconstructed base cell, wherein the colibacillus chemical compounds include sesquiterpene chemical compounds such as amorphadiene, diterpene chemical compounds such as shell alkene, tetraterpenes chemical compounds such as lycopene, polyterpene chemical compounds, other terpene alkaloid chemical compounds and the like. The escherichia coli base cell can remarkably facilitate the synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
1,3-1,4-Beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN104130988AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaWort preparationMutaseGlucanase
Owner:无锡正元生物科技有限公司
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof for degrading o-aminobenzoic acid
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bacterial strain for eliminating Listeria monocytogenes and application thereof
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multipath composite neuraminic acid producing bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394292AHigh catalytic activityReduce synthetic pressureBacteriaTransferasesO-Phosphoric AcidGlucosaminephosphate isomerase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pseudomonas putida WP07, preparation method and purpose
ActiveCN110438030ASimplify the screening processLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismResource utilization
The invention discloses pseudomonas putida WP07, a preparation method and purpose. The pseudomonas putida WP07 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.17760. By a microbiological method, pigwash oil is converted into biodegradable plastic PHA which has environment affinity, so that resource utilization and innocent treatment of the pigwash oil can be realized, the preparation cost of the PHA can also be reduced, and the pseudomonas putida WP07 has favorable application prospects.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound microbial agent for treating dye waste water as well as preparation and application of compound microbial agent
InactiveCN102080057AStrong broad spectrumGood decolorization and degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcinetobacter haemolyticusMicroorganism
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens capable of preventing and treating wheat scab and application thereof
ActiveCN104673705AImprove environmental safetyGood inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaTriticeaePlant disease
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
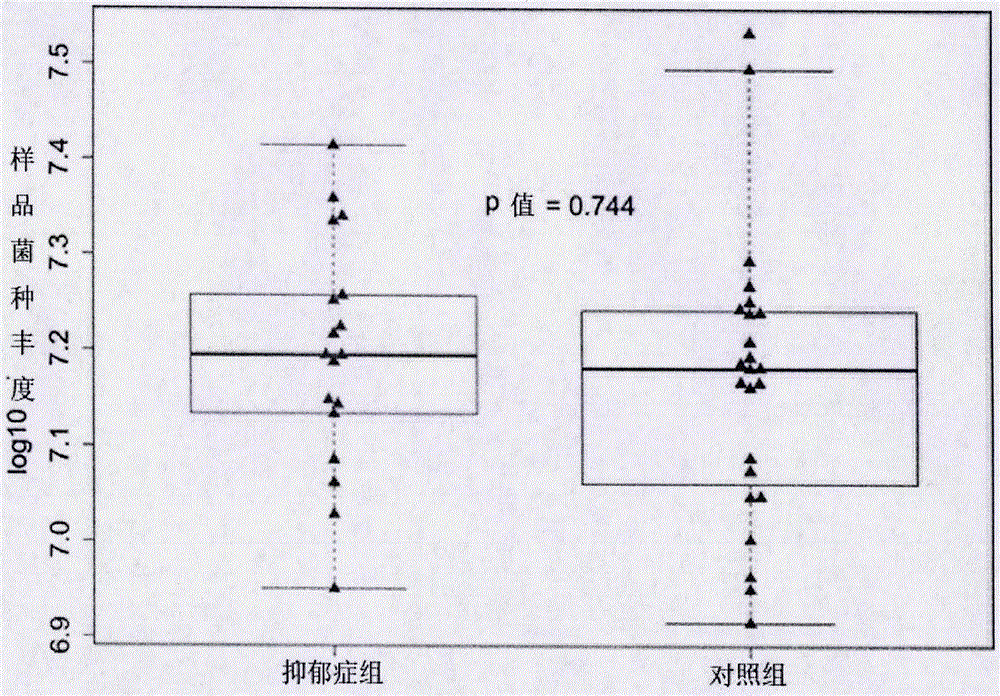
Depressive disorder biomarker and use thereof
InactiveCN106554998AImprove diagnostic accuracySimplify the diagnostic processBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsScreening methodSaccharomonospora viridis
Owner:SHENZHEN KANGNING HOSPITAL SHENZHEN MENTAL HEALTH INST SHENZHEN MENTAL HEALTH CENT
Lactobacillus paracasei as well as strain domestication method and culture method thereof
Owner:ENSHI QINGJIANG BIO ENG
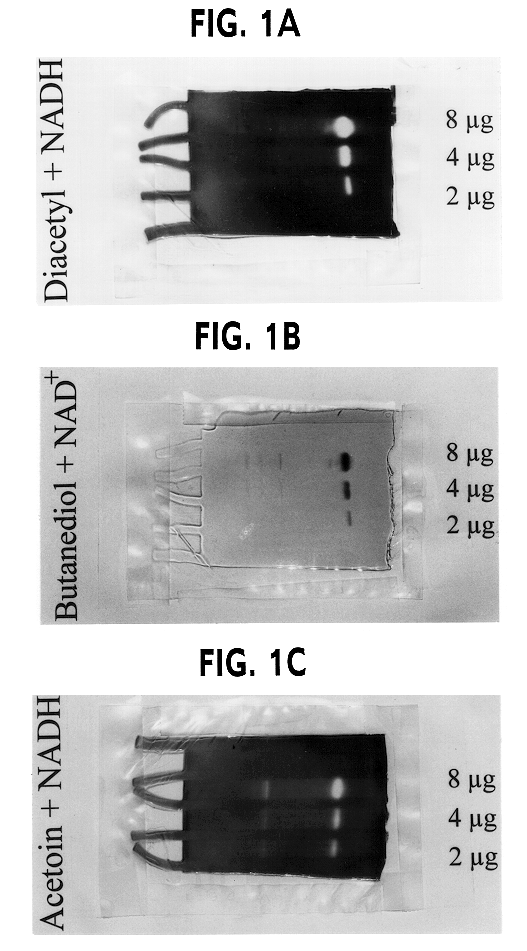
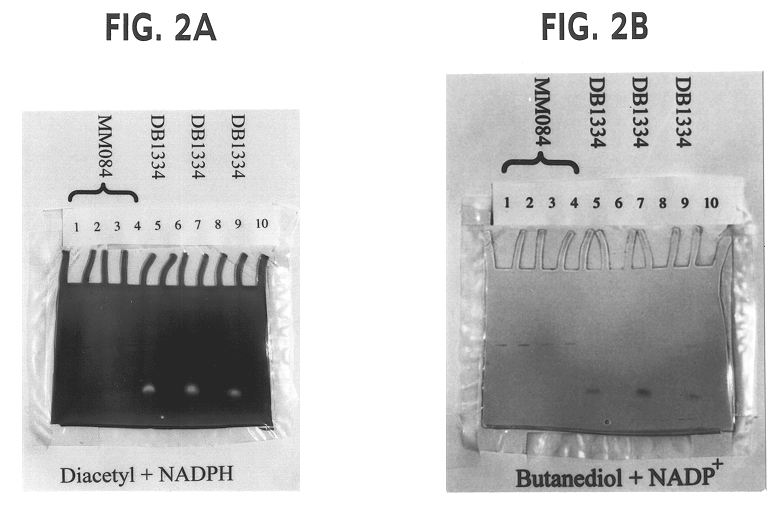
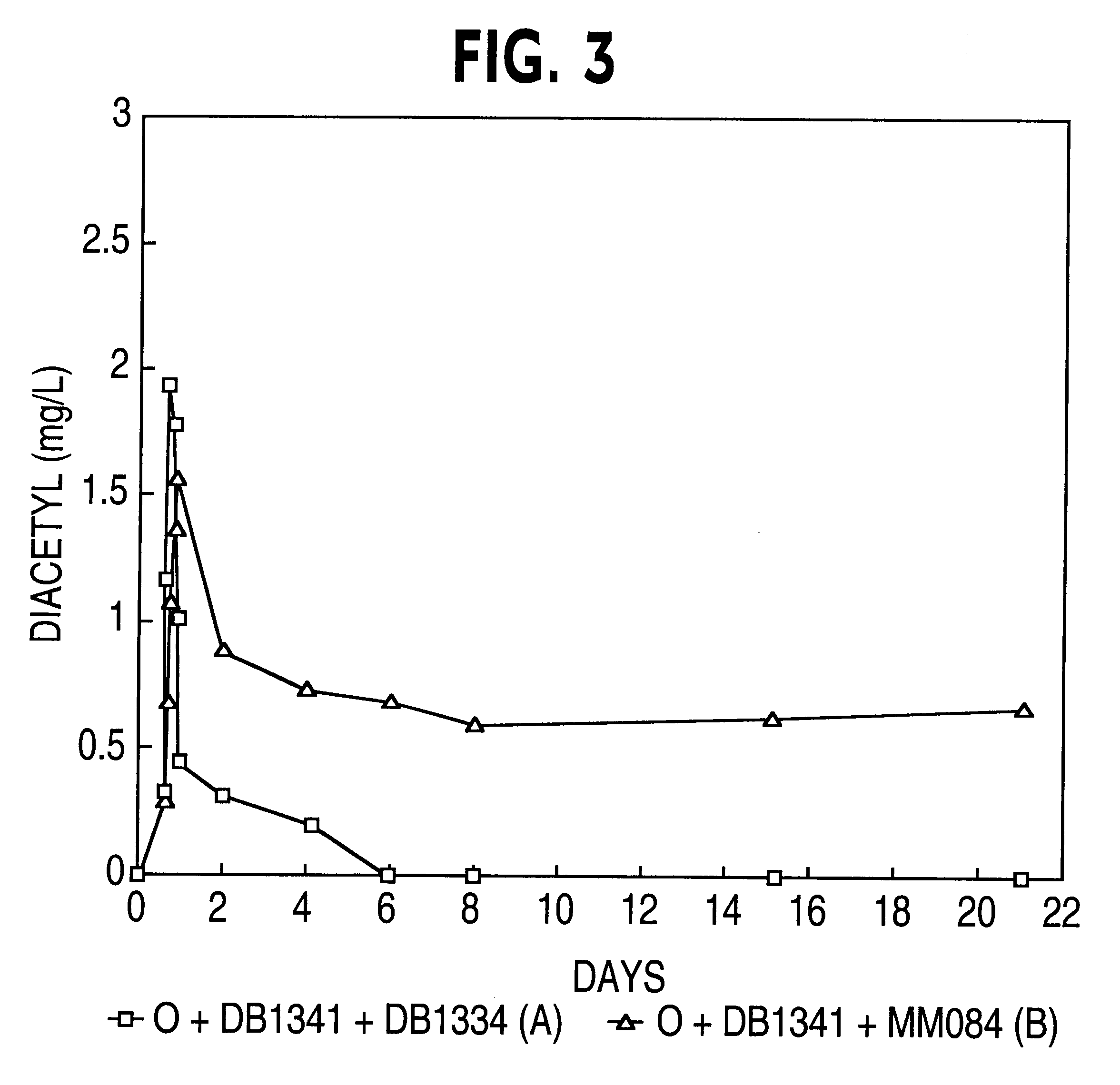
Genetically modified lactic acid bacteria having modified diacetyl reductase activities
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Protein, DNA coding for same and method of producing the protein
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap