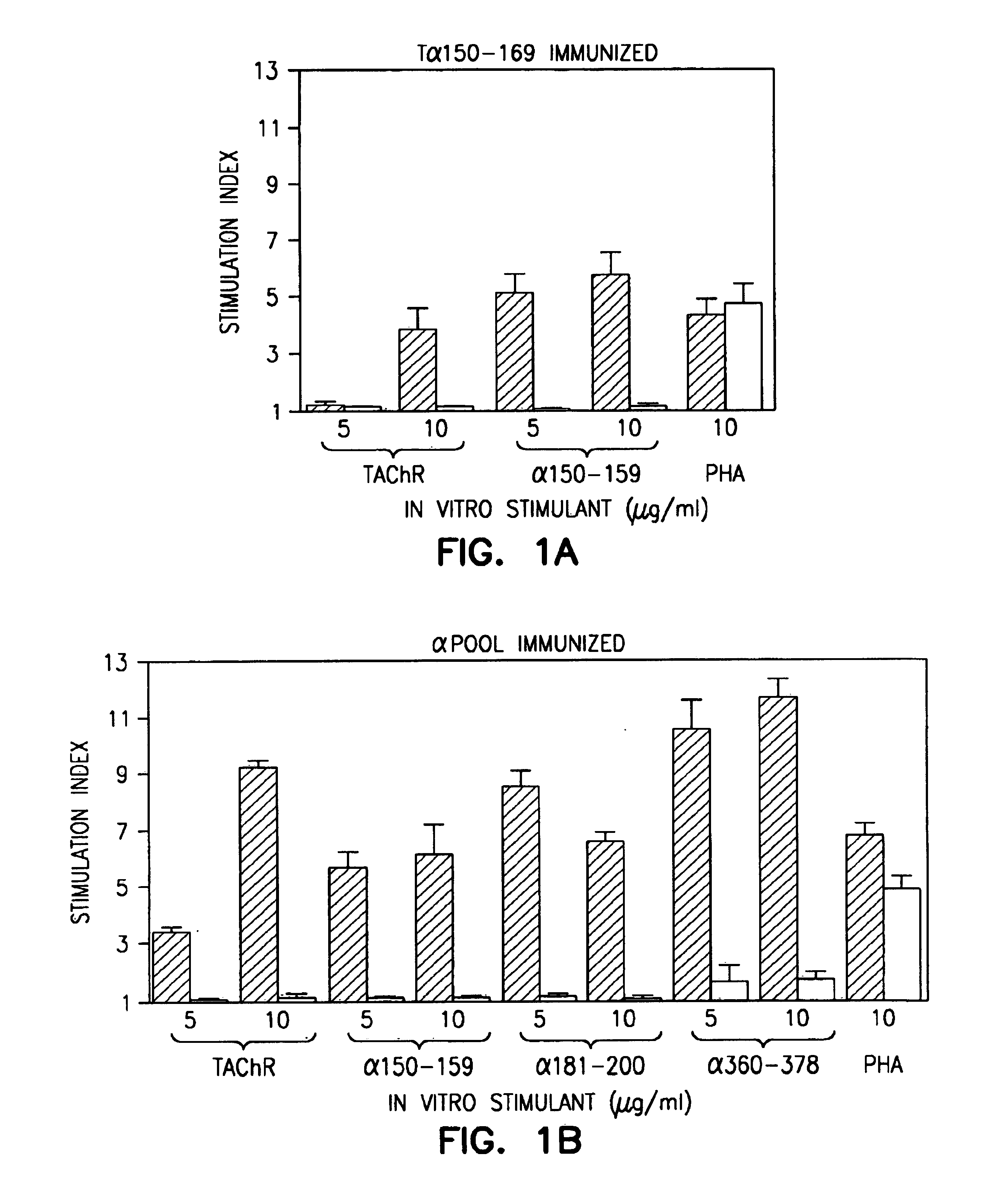
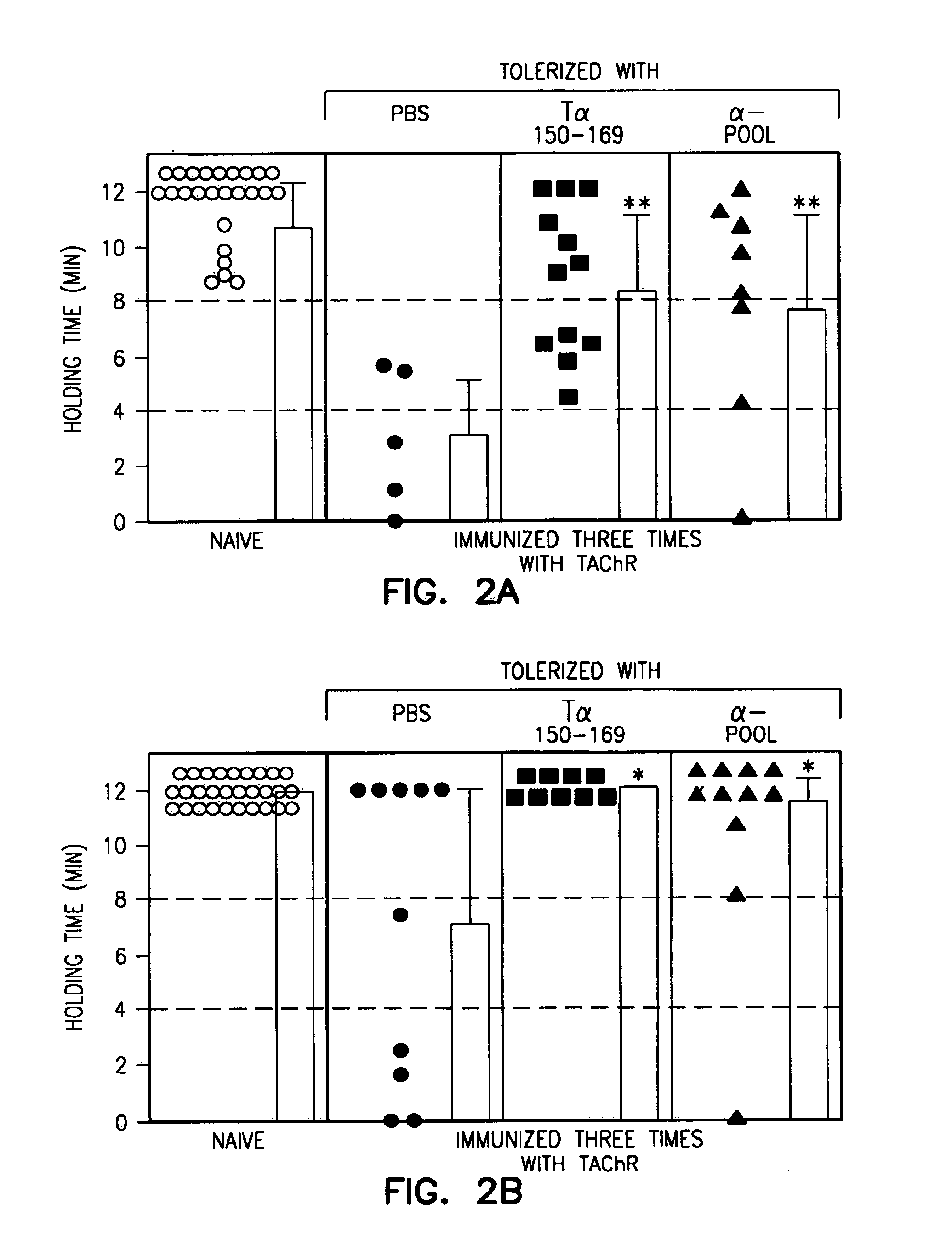
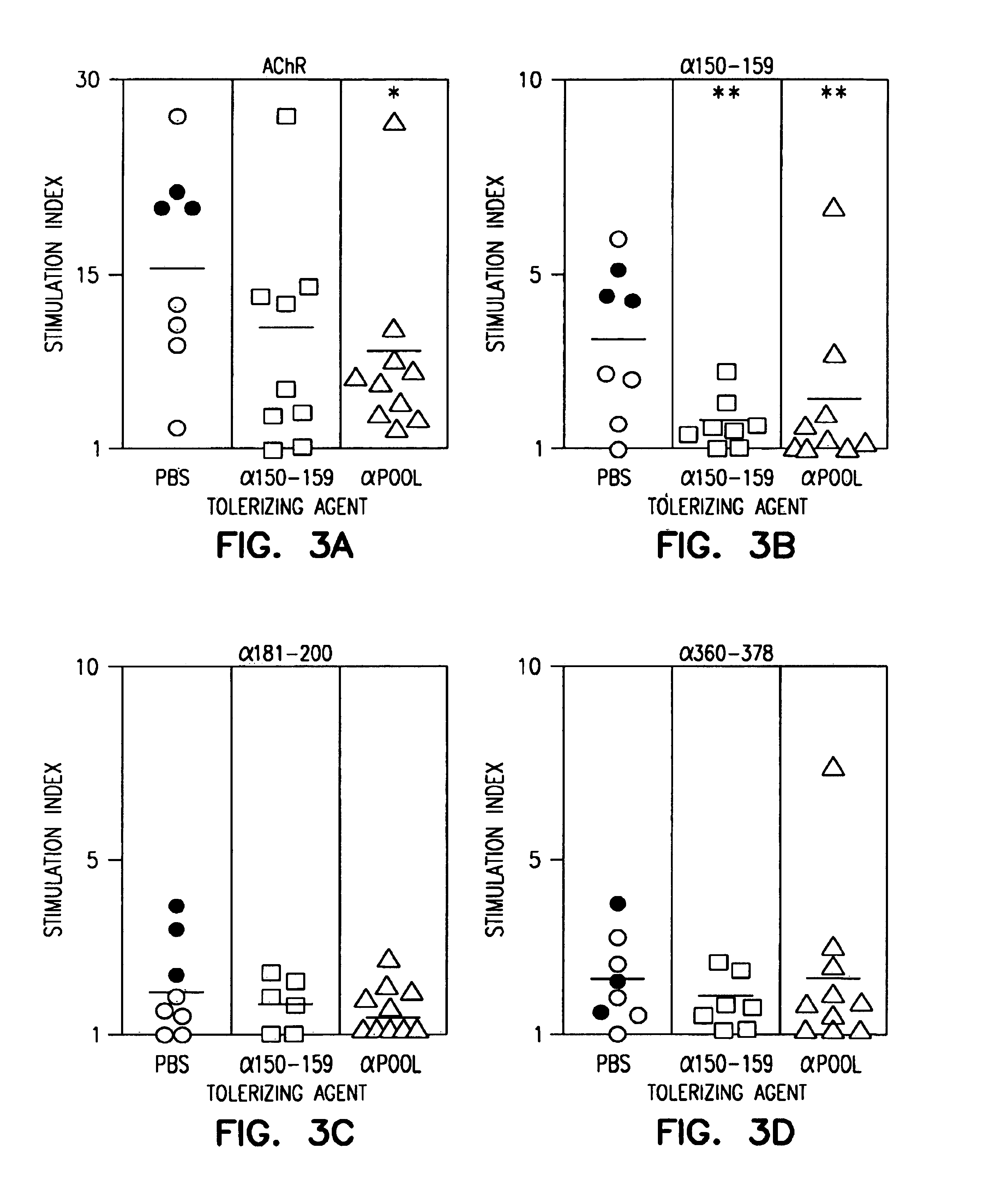
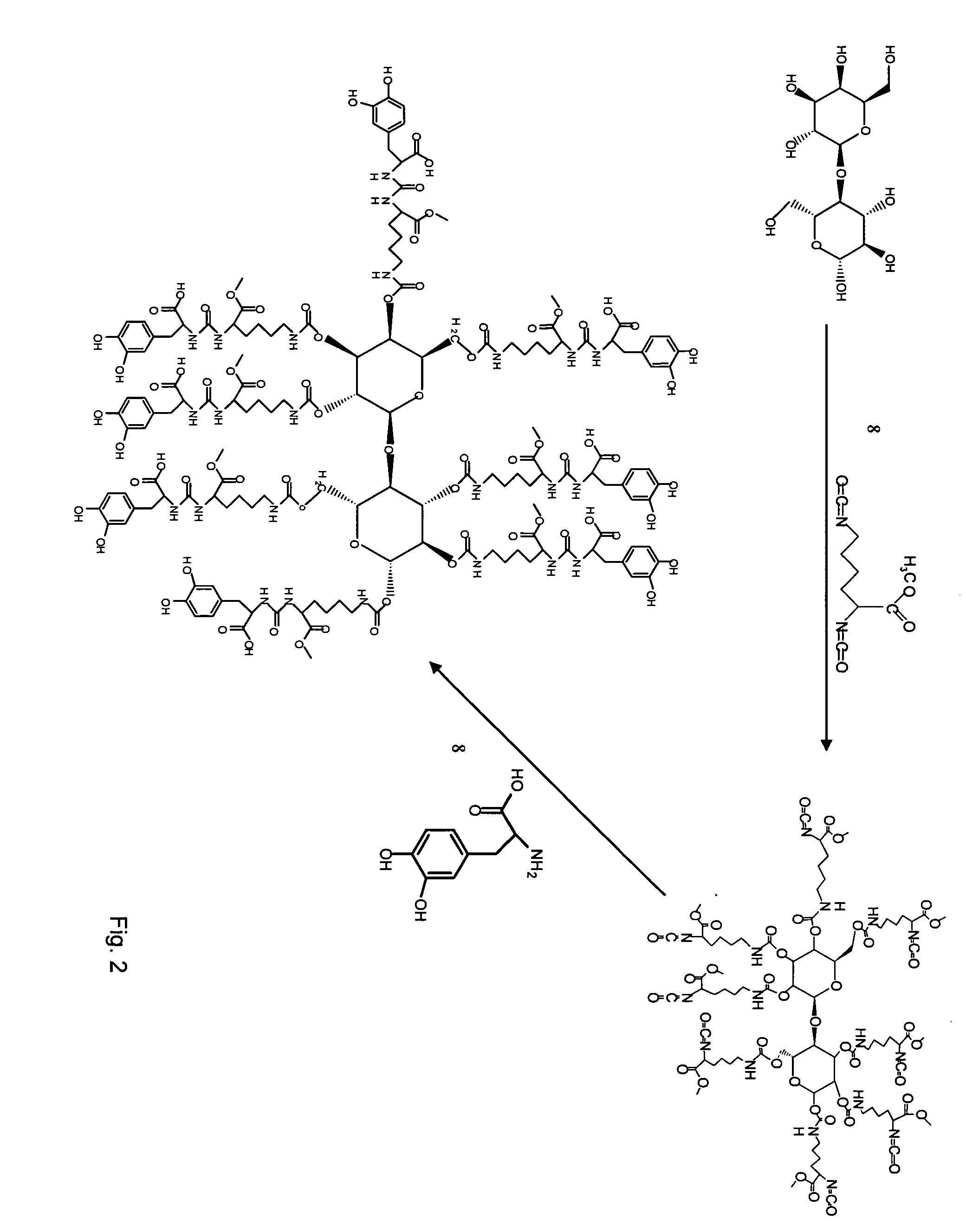
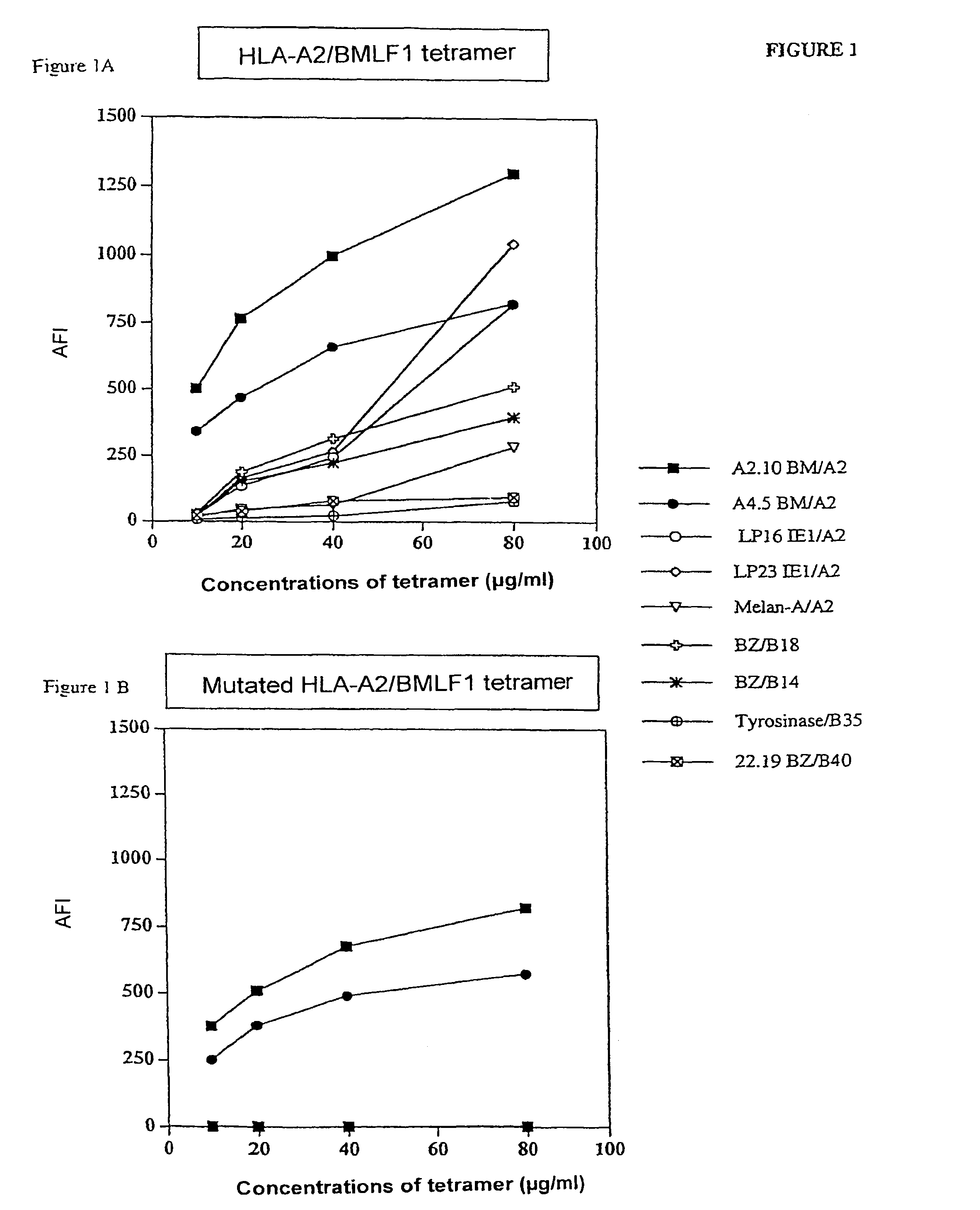
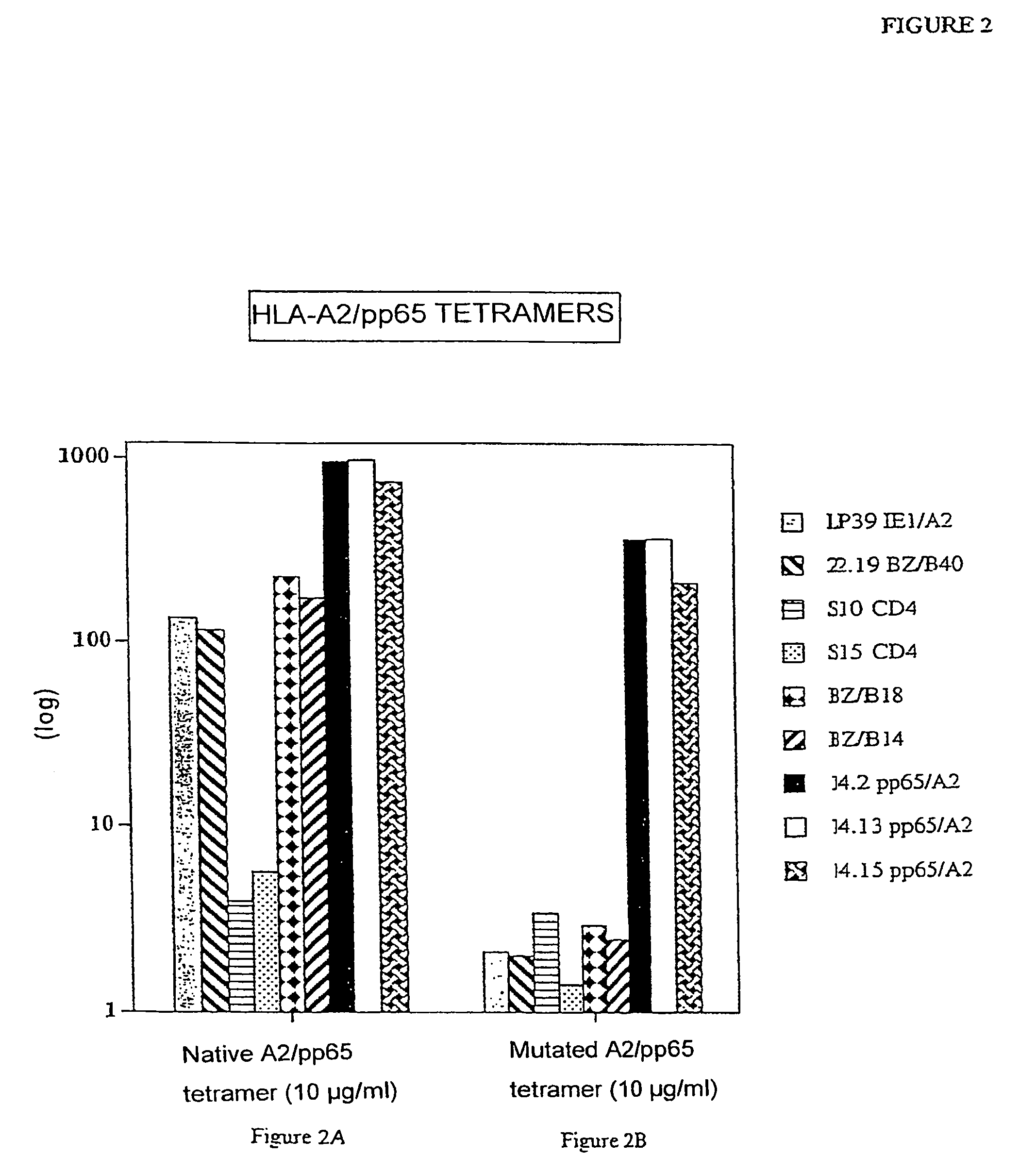
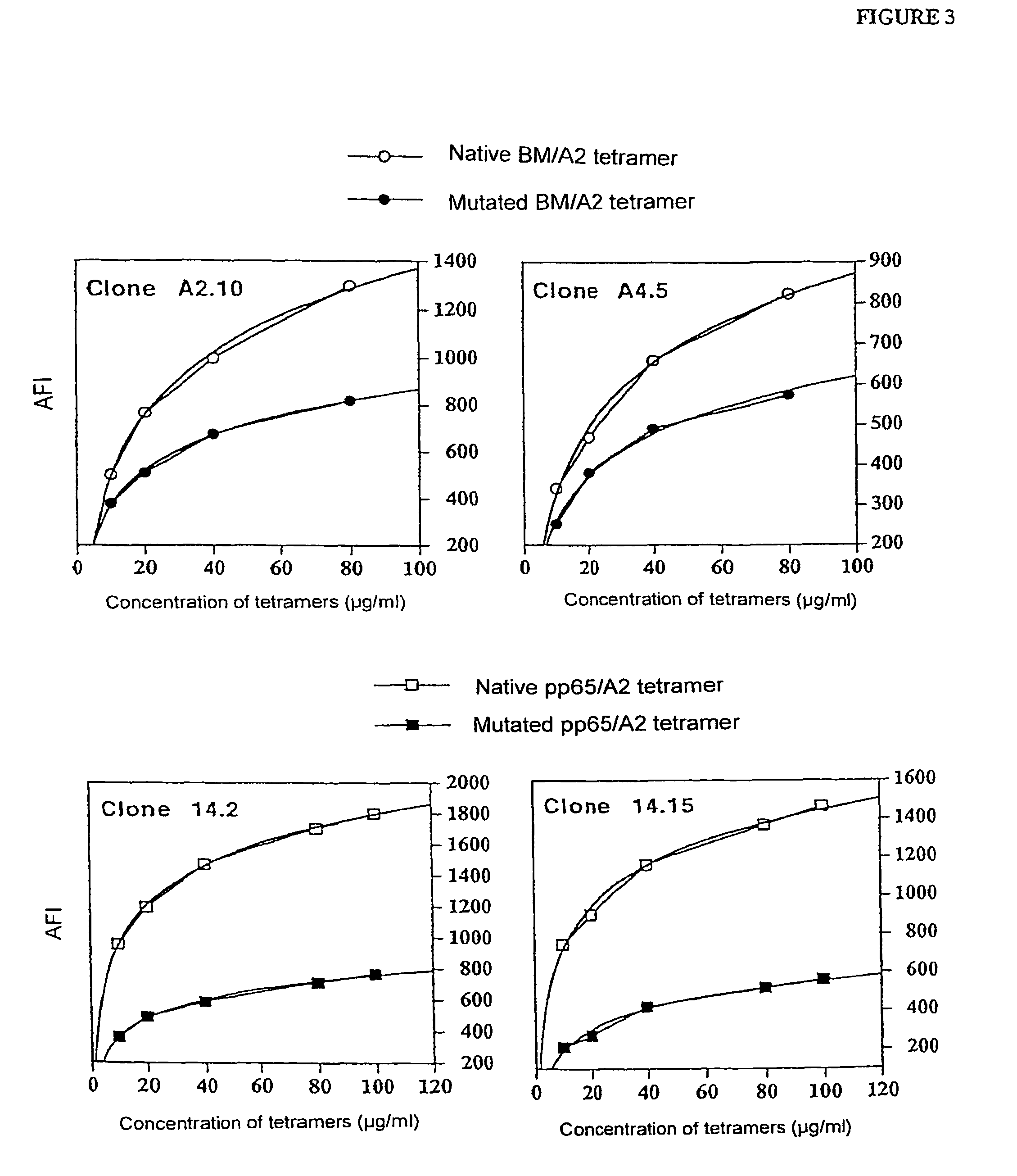
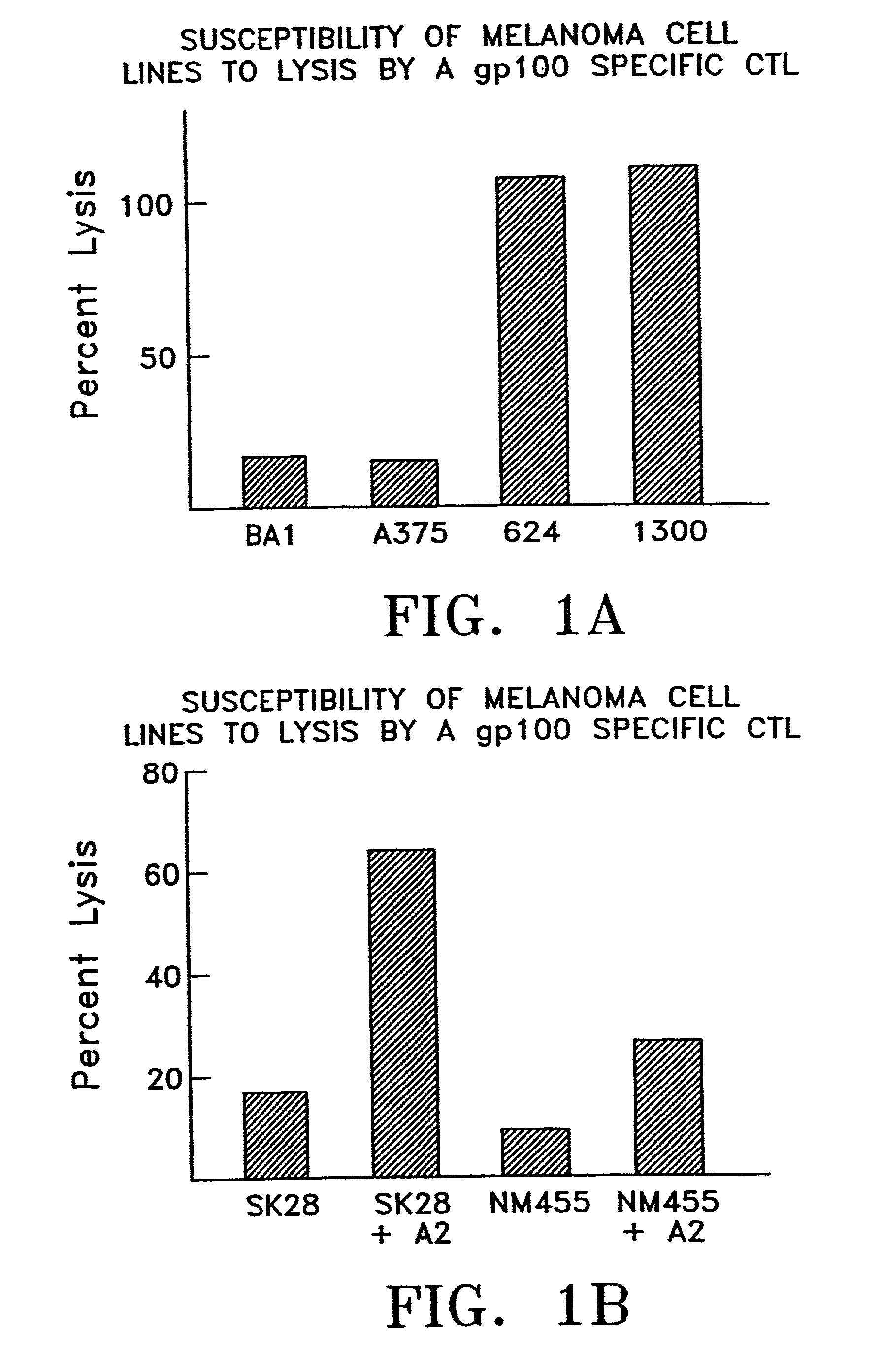
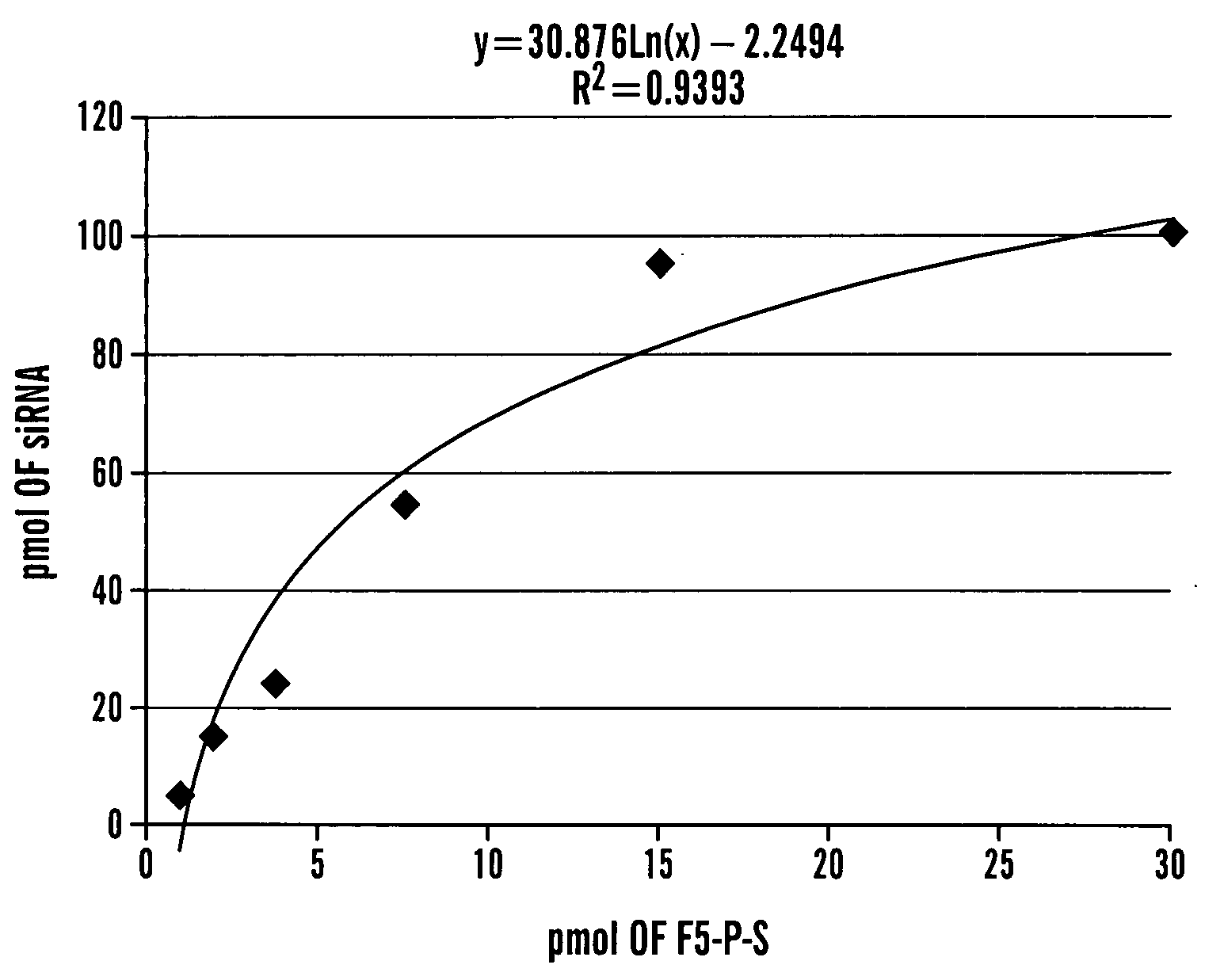
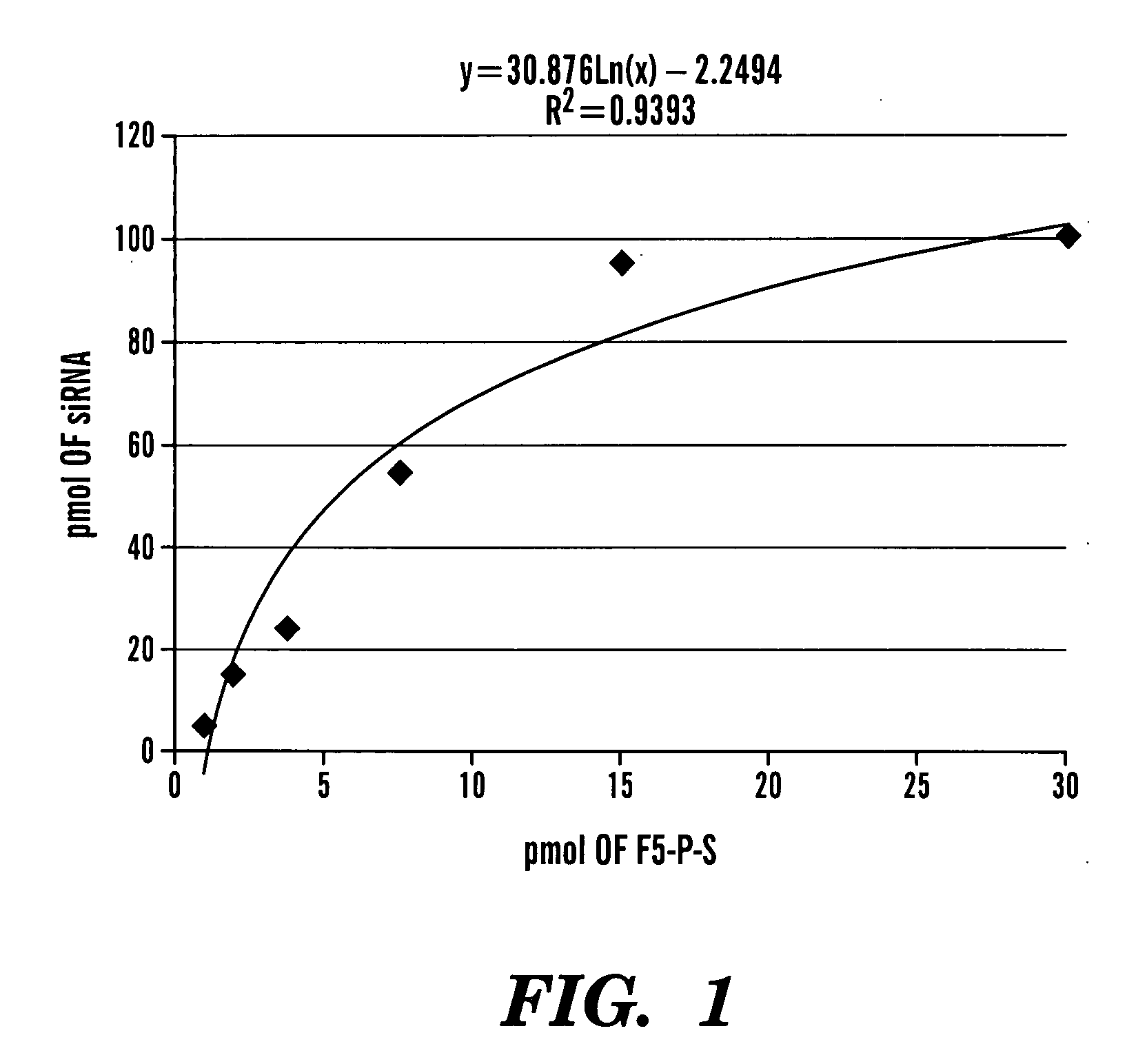
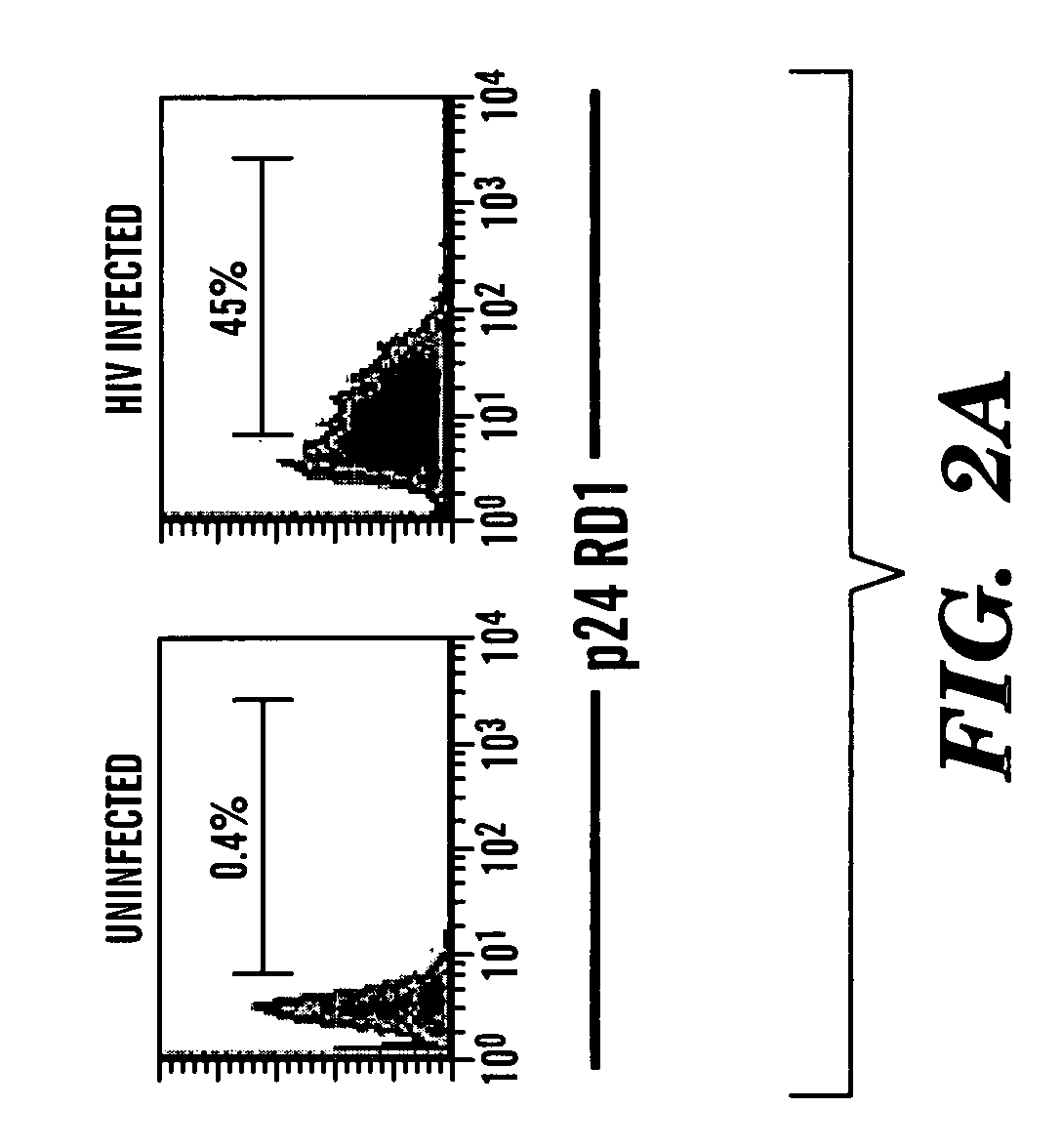
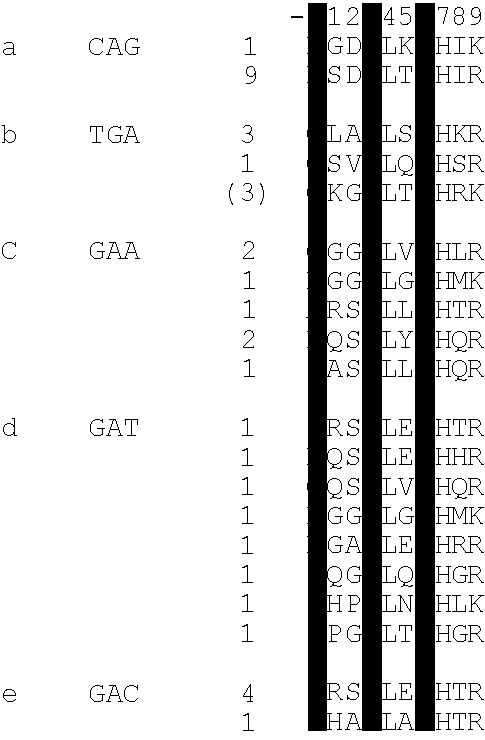
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
166results about "Peptide/protein ingredients" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for use of agent in combination with subatmospheric pressure tissue treatment
InactiveUS20070014837A1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBasic fibroblast growth factorWound healing agent
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Method for producing nucleic acid polymers
Owner:GENEART
Gastric retention controlled drug delivery system
ActiveUS20040180088A1Maintain physical integrityFast swellingOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderControlled drugsControl release
The present invention provides a gastric retention controlled drug delivery system comprising: (a) a controlled release core comprising a drug, a highly swellable polymer and a gas generating agent, said core being capable of swelling and achieving floatation rapidly while maintaining its physical integrity in gastrointestinal fluids for prolonged periods, and (b) a rapidly releasing coat composition comprising the same drug as in the core and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein the coating composition surrounds the core such that the system provides a biphasic release of the drug in gastrointestinal fluids.
Owner:SUN PHARMA INDS
Murine monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody 11D10 and methods of use thereof
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY
Beneficial effects of increasing local blood flow
InactiveUS20110028548A1Increase oxygenationImprove tissue nutritionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsArginineNitric oxide
Owner:STRATEGIC SCI & TECH
Child's cleaning implement comprising a biological extract
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Non-mammalian GnRH analogs and uses thereof in the immune system
InactiveUS20050043245A1Effective supervisionHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneDiseaseD-Arginine
Specially designed non-mammalian GnRH, its analogs, or biometics resistant to degradation by peptidase, are disclosed. The GnRH analogs are further defined as analogs of GnRH II or salmon GnRH. These non-mammalian analogs incorporate D-arginine, D-leucine, D-tBu-Serine, D-Trp or other active D amino acids at position 6 and ethylamide, aza-Gly-amide or other Gly amide at position 10. The D-Arg (6)—GnRH II-ethylamide, D-Arg (6)—GnRH II-aza-Gly (10)-amide, the D-Arg (6)—salmon GnRH ethylamide, and D-Arg (6)—salmon GnRH-aza-Gly (10)-amide analogs are also provided, and demonstrate preferential binding to immune system non-mammalian GnRH receptors. These non-mammalian GnRH or its analogs, or long-acting preparation, biometics or their antibodies may be used in pharmaceutical preparation, and specifically in treatment of various immune system disorders. The non-mammalian GnRH or its analogs are also provided in pharmaceutical preparations that may be used clinically for treating immune system disorders when used in very low doses and administered in pulsatile fashion. The aza-Gly (10) amide non-mammalian analogs are yet other embodiments of the non-mammalian GnRH or its analogs provided as a part of the invention. The use of agents that regulate the production or antibodies or In addition, the detection of non-mammalian GnRH or GnRH II or the non-mammalian GnRH receptors may be used as a diagnostic tool.
Owner:SILER KHODR THERESA
Methods to treat undesirable immune responses
InactiveUS6929796B1Reduced activityReduce the amount requiredBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsViral vectorGene replacement therapy
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
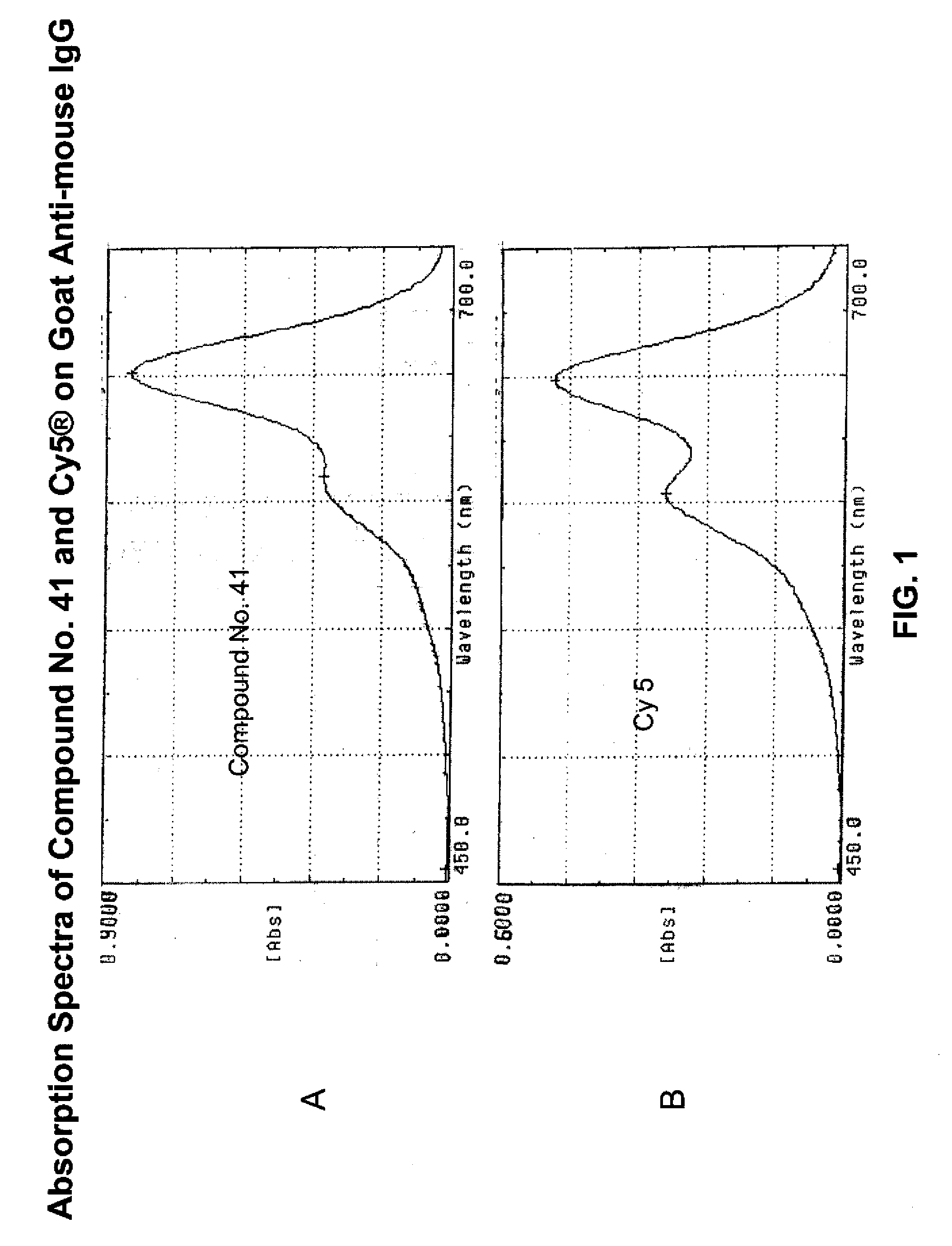
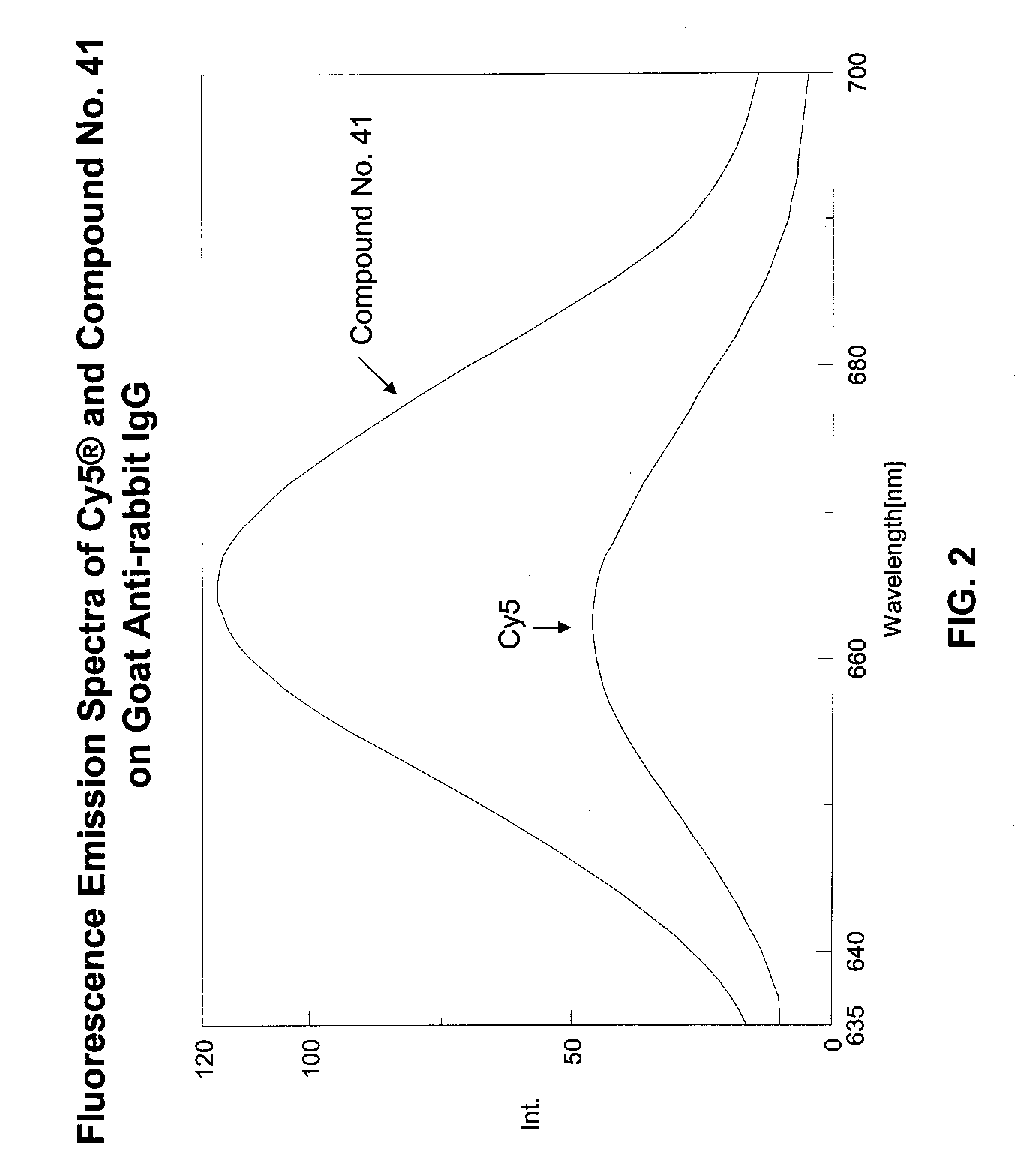
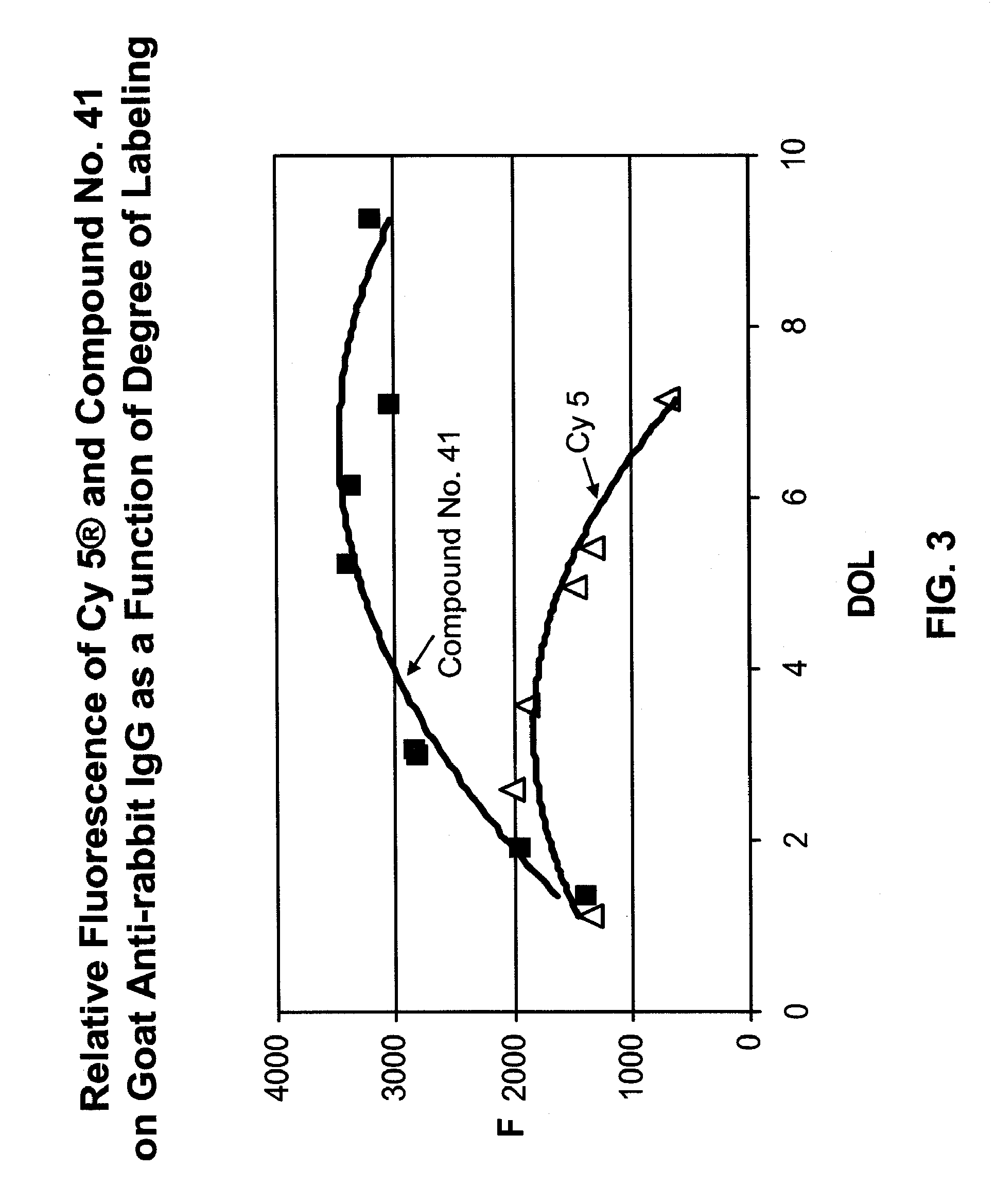
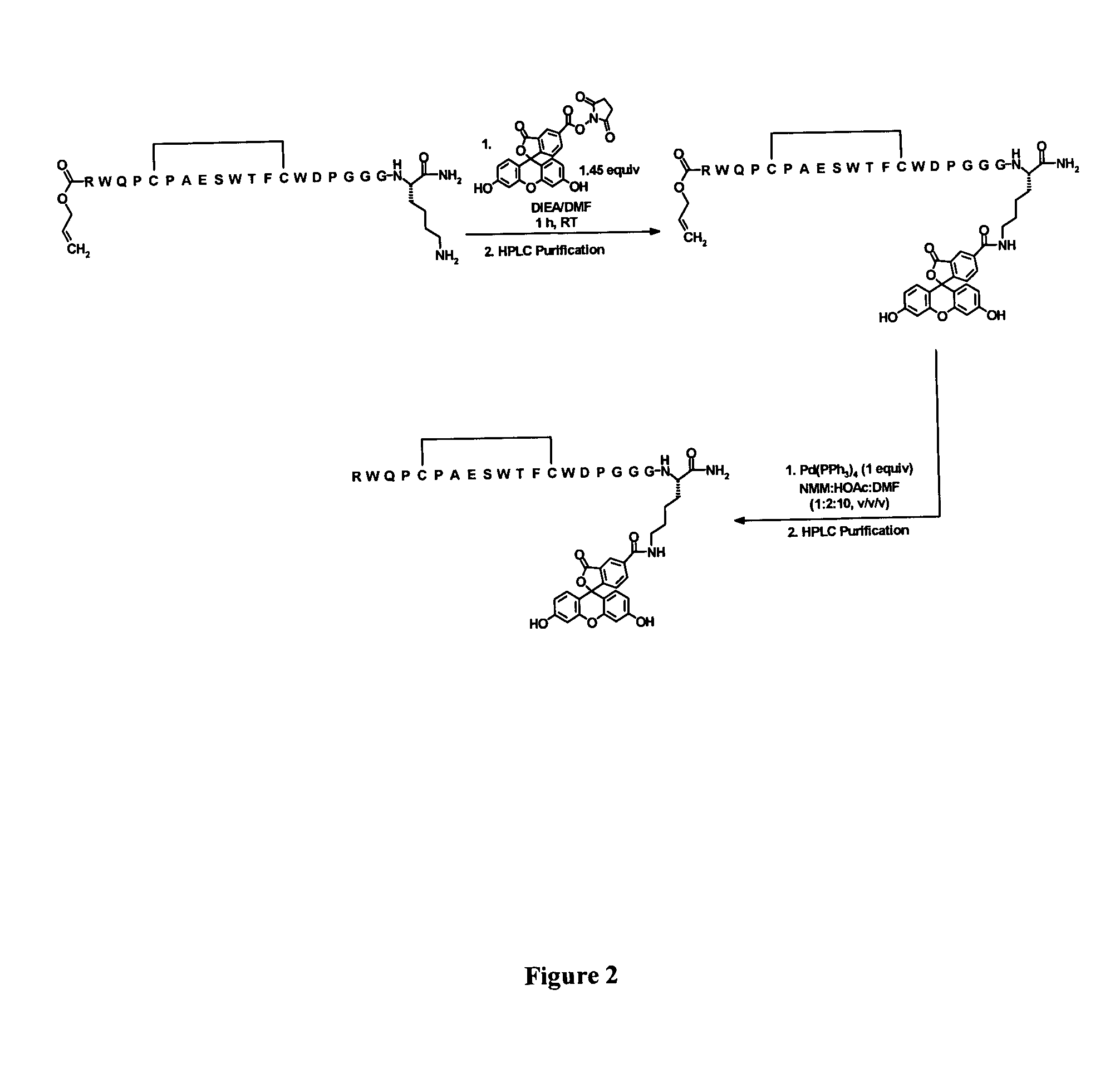
Fluorescent compounds
ActiveUS20090305410A1Convenient and effective labelingMethine/polymethine dyesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyDisease
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Methods for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of metabolic syndrome
InactiveUS20060211020A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphatidate cytidylyltransferaseGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides methods for detecting susceptibility to metabolic syndrome. In particular, the presence of differences in at least one of the following genes; microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), fatty acid binding protein 2 (FABP2), annexin A5 (ANXA5), pyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) alpha 2 (PDHA2), CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase) 1 (CDS 1), and glycerol kinase 2 (GK2) serves as a prognostic and diagnostic indicator of metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, metabolic syndrome can be treated by regulating the levels of MTP, FABP2, ANXA5, PDHA2, CDS1, and GK2.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
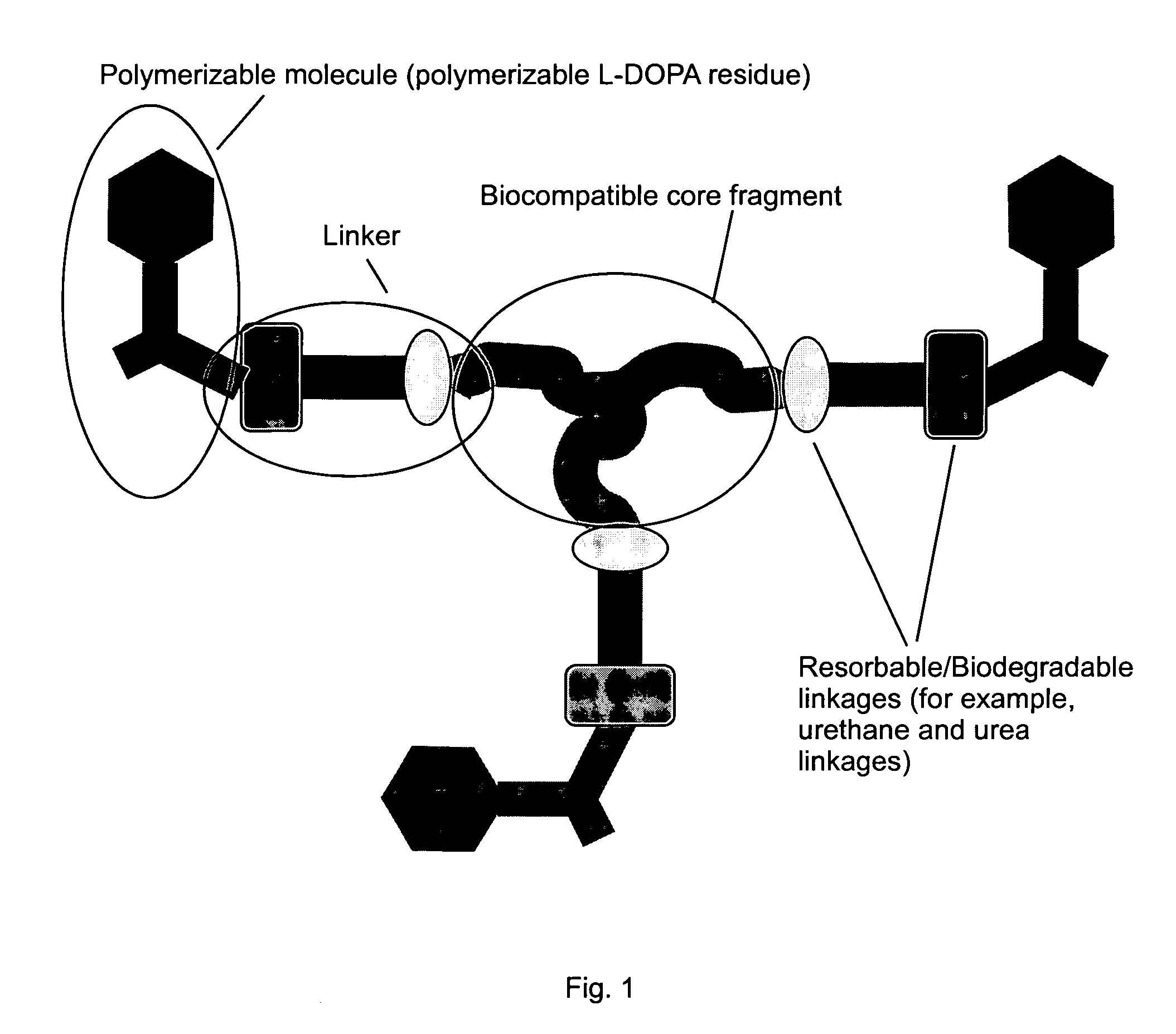
Wound healing polymeric networks
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
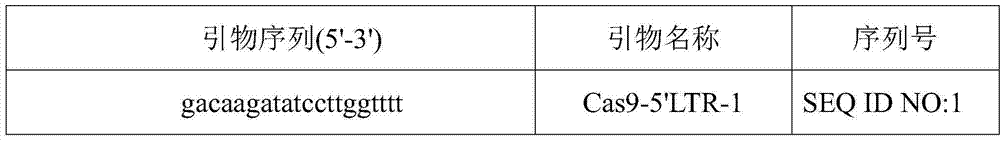
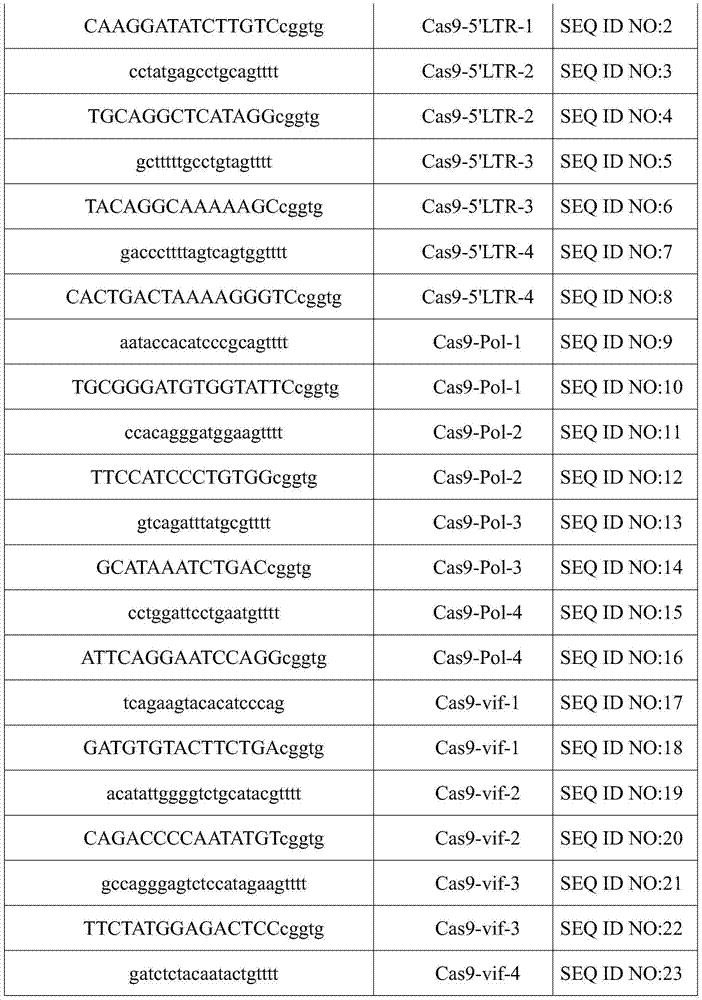
CRISPR-Cas9 system for preventing and/or treating HIV, as well as preparation method and application thereof
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Means for detection and purification of CD8+ T lymphocyte populations specific to peptides presented in the context of HLA
InactiveUS8309312B2Reduce background noiseEliminate needBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidePopulation specific
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Genes differentially expressed in cancer cells to design cancer vaccines
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method of Delivering Rna Interference and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080153737A1Limiting potential side effectQuantity minimizationFusion with RNA-binding domainAntibacterial agentsGeneticsDouble strand
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Binding proteins for recognition of DNA
InactiveUSRE39229E1Reduce the probability of occurrenceIncrease the number ofFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vitroZinc finger
Owner:GENDAQ +1
Use Of Dipyridamole For Treatment Of Resistance To Platelet Inhibitors
InactiveUS20090048173A1Reduce decreaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDipyridamolePlatelet inhibitor
Owner:EISERT WOLFGANG +1
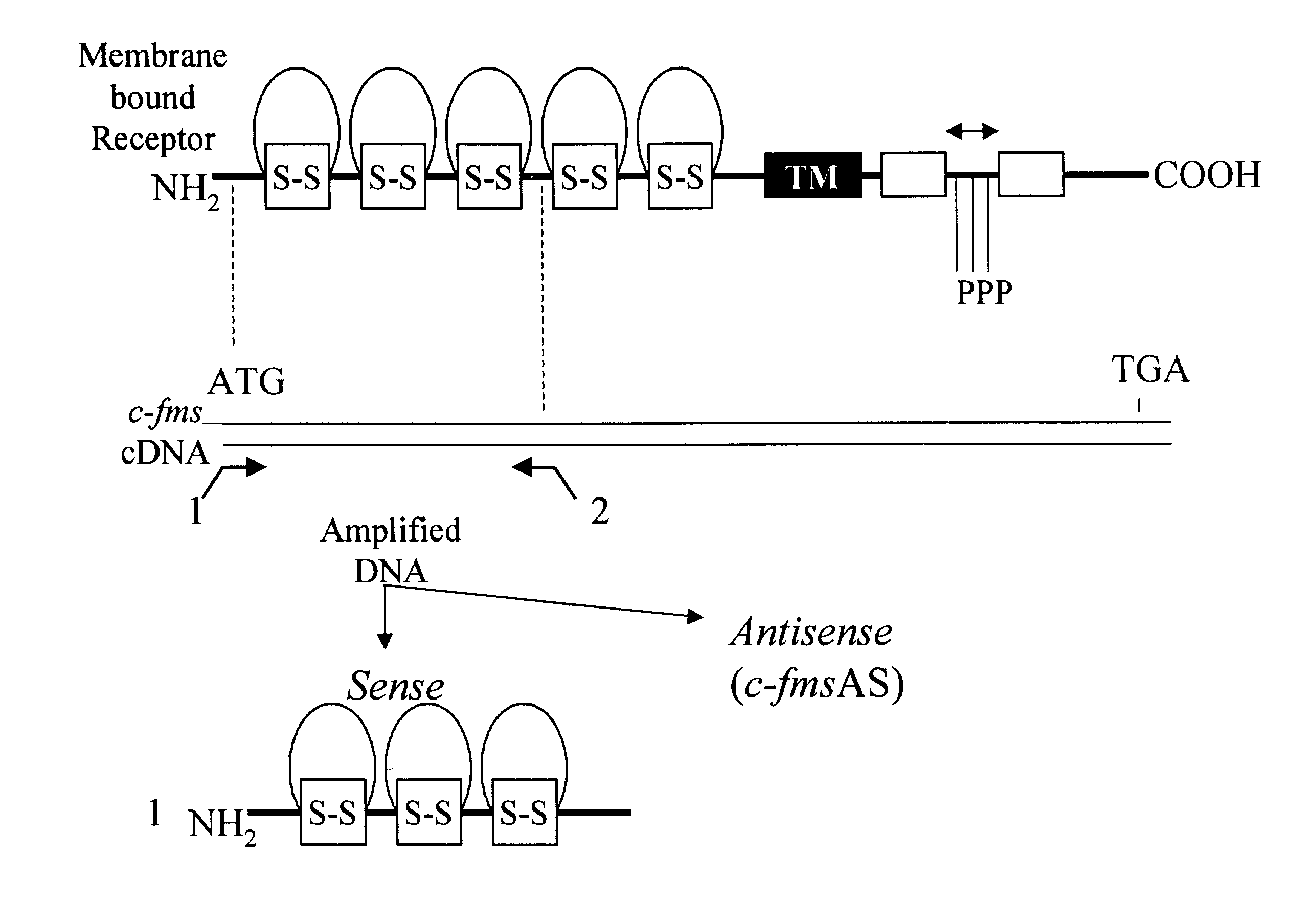
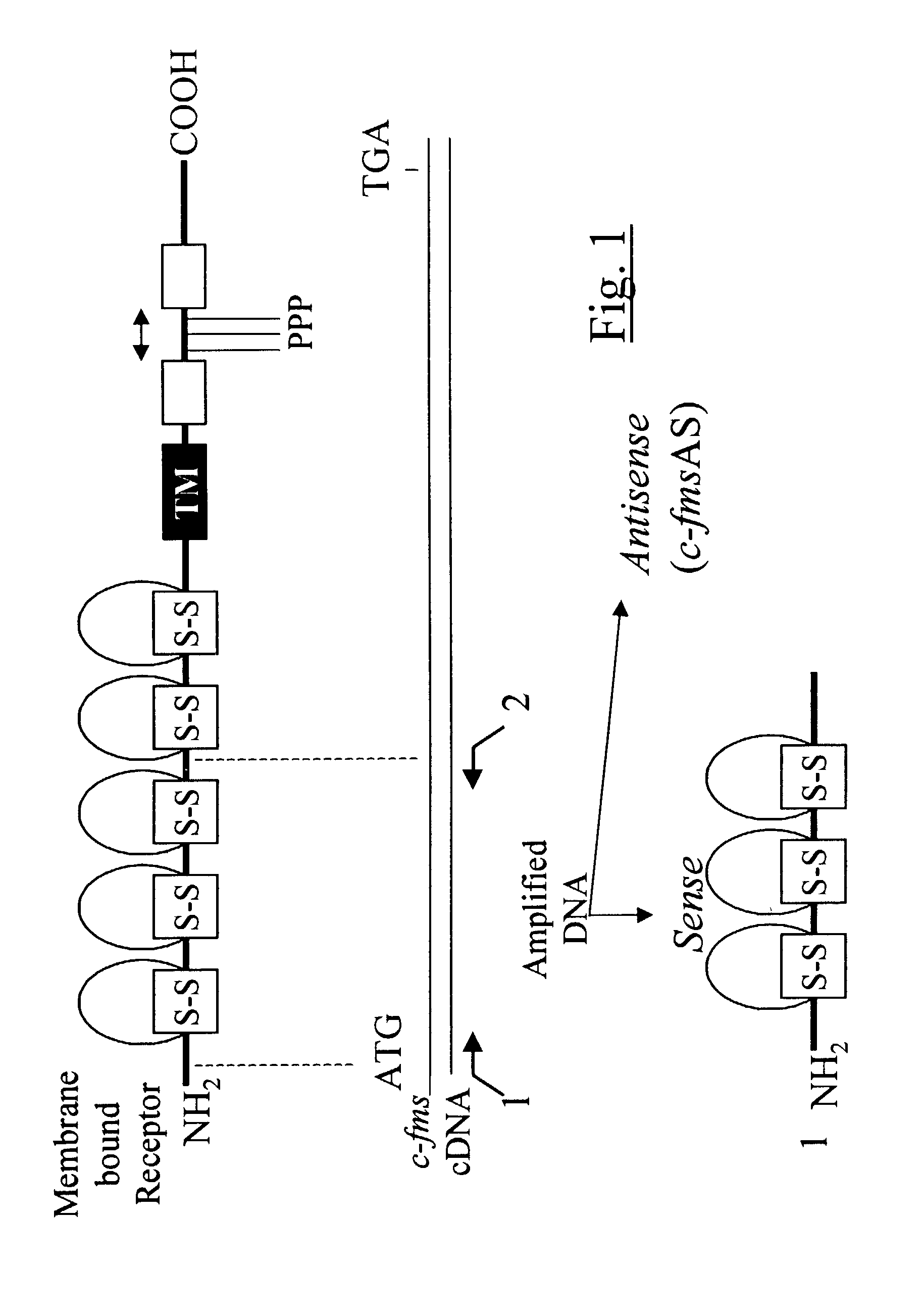
Methods for inhibiting macrophage colony stimulating factor and c-FMS-dependent cell signaling
Owner:RAJAVASHISTH TRIPATHI
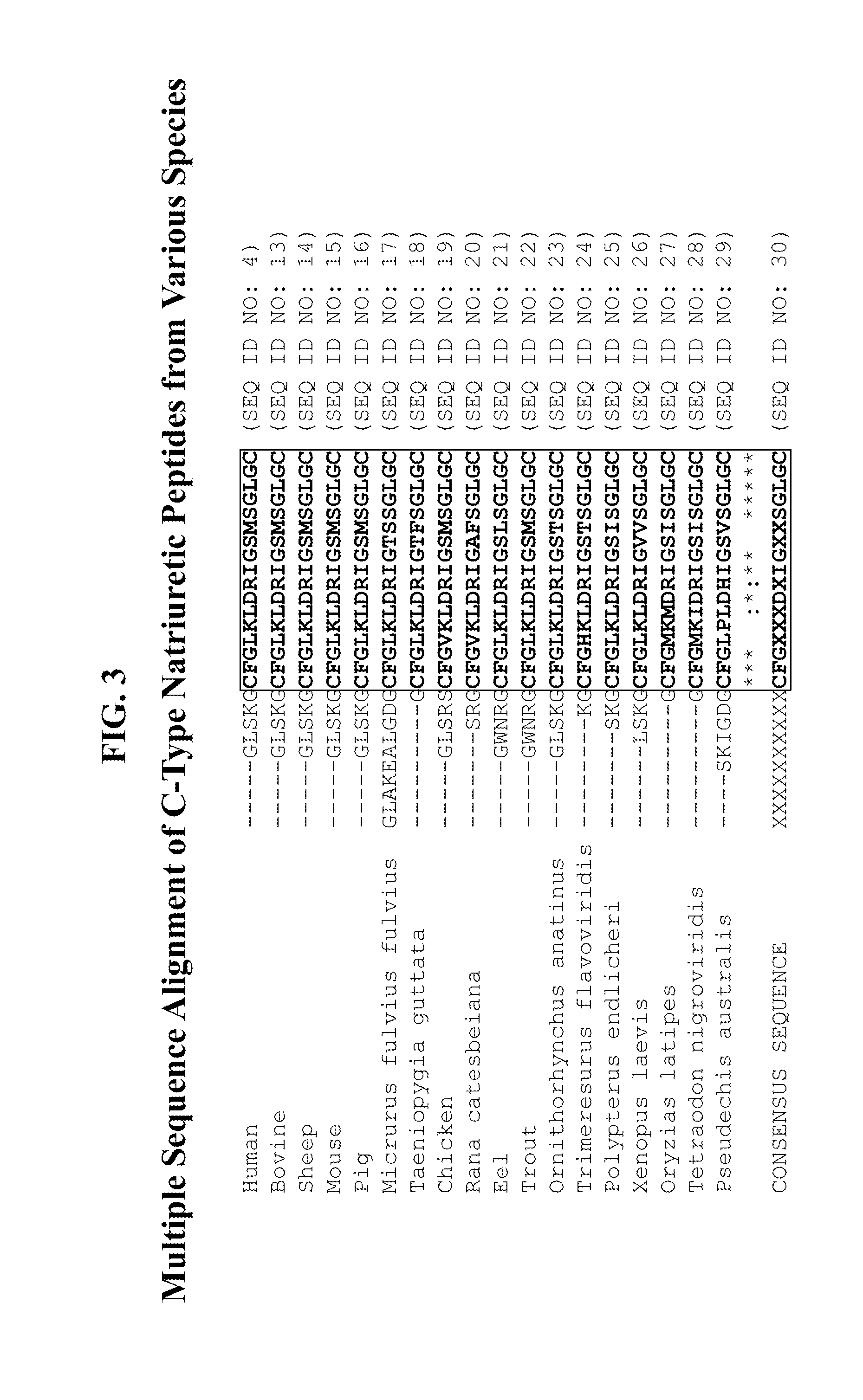
Compositions comprising natriuretic peptides and methods of use thereof
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
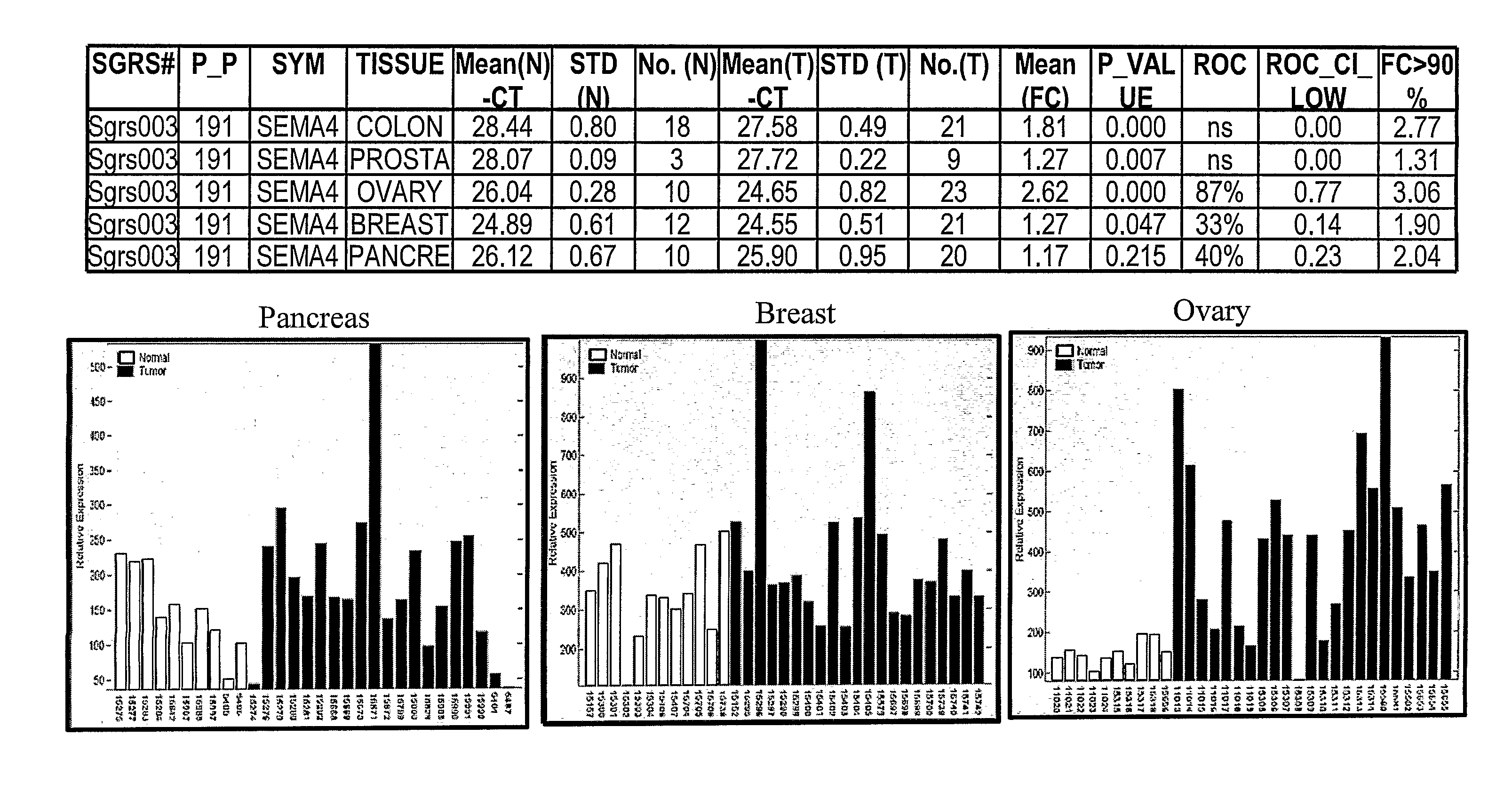
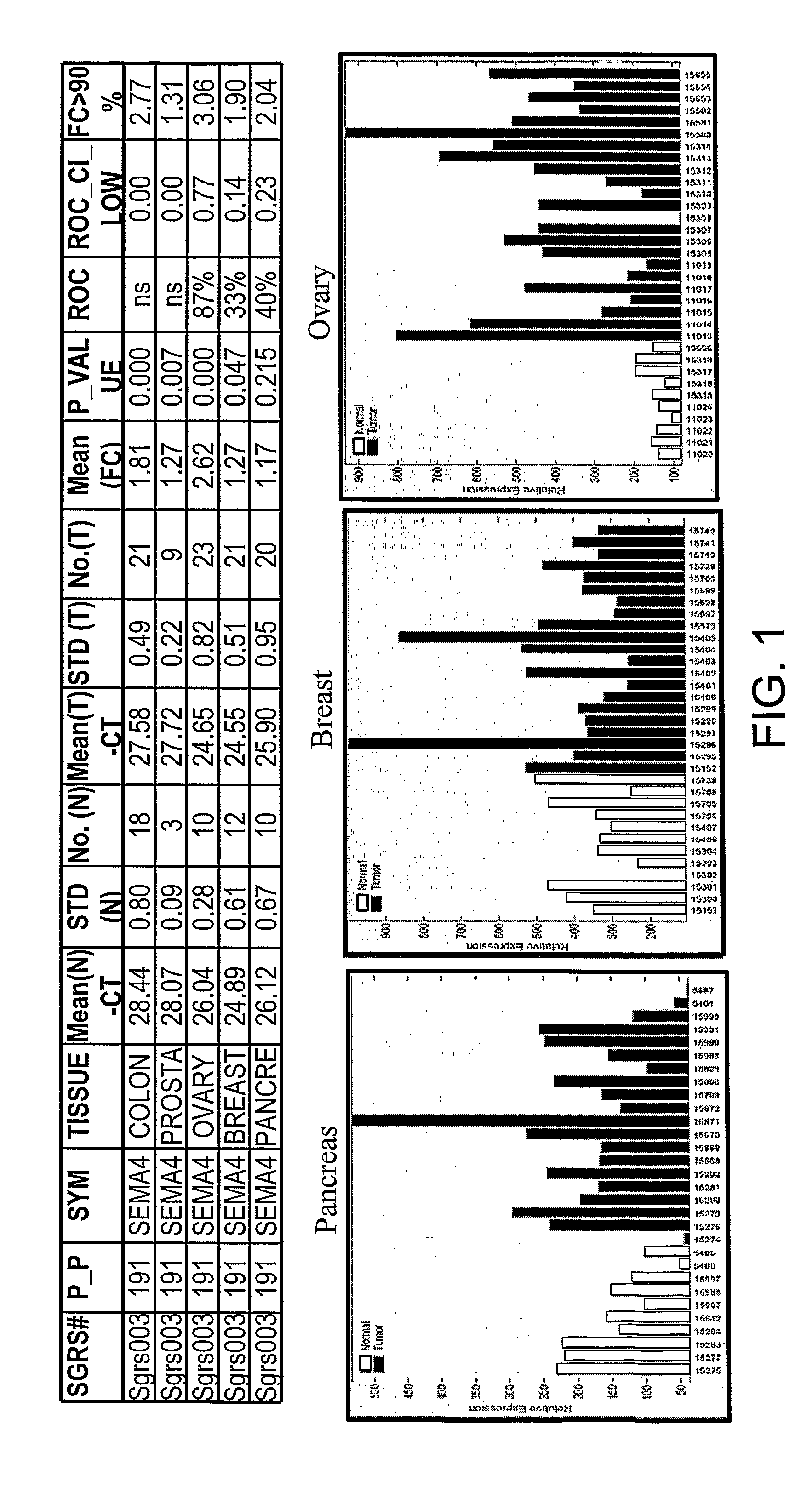
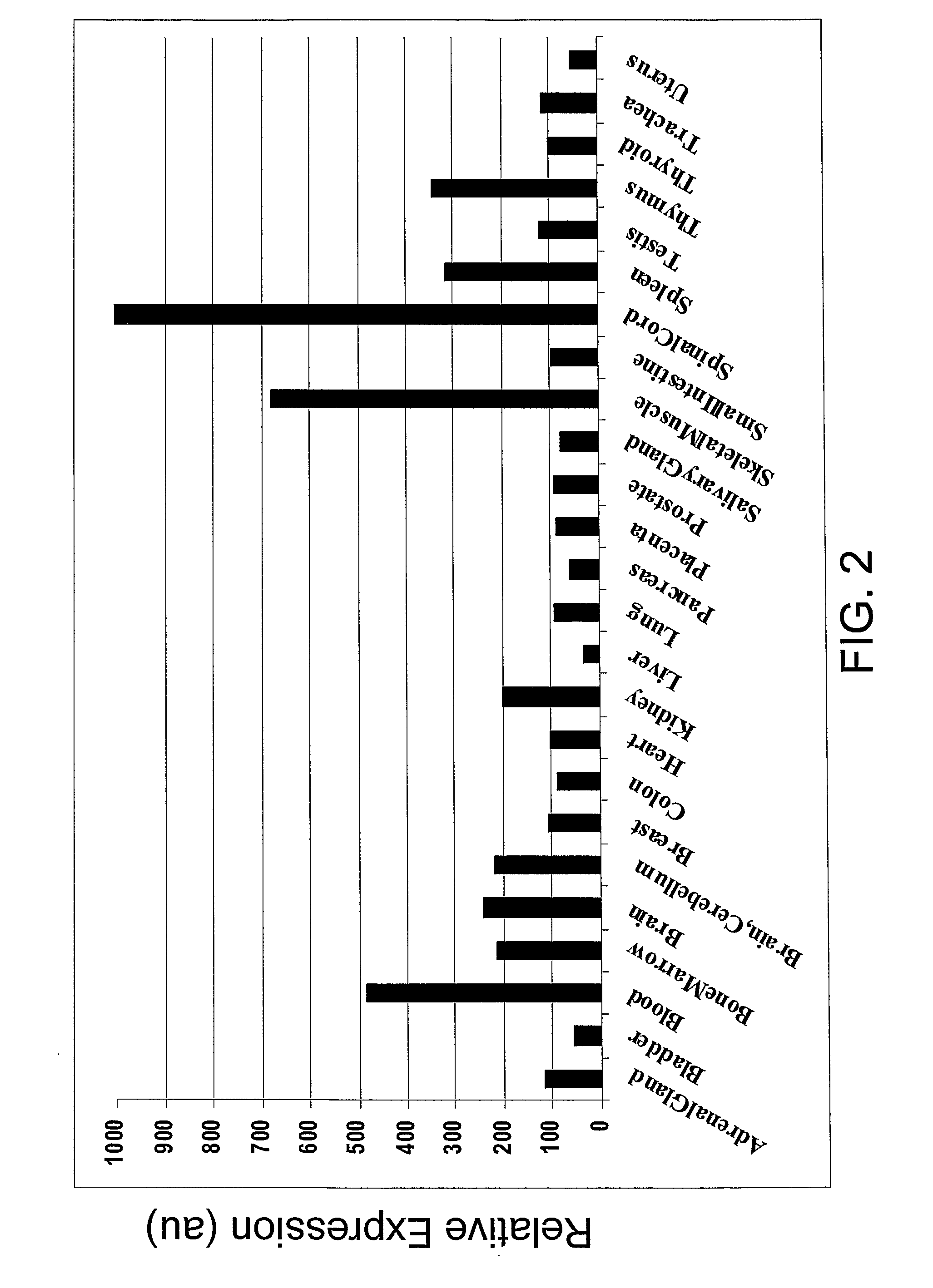
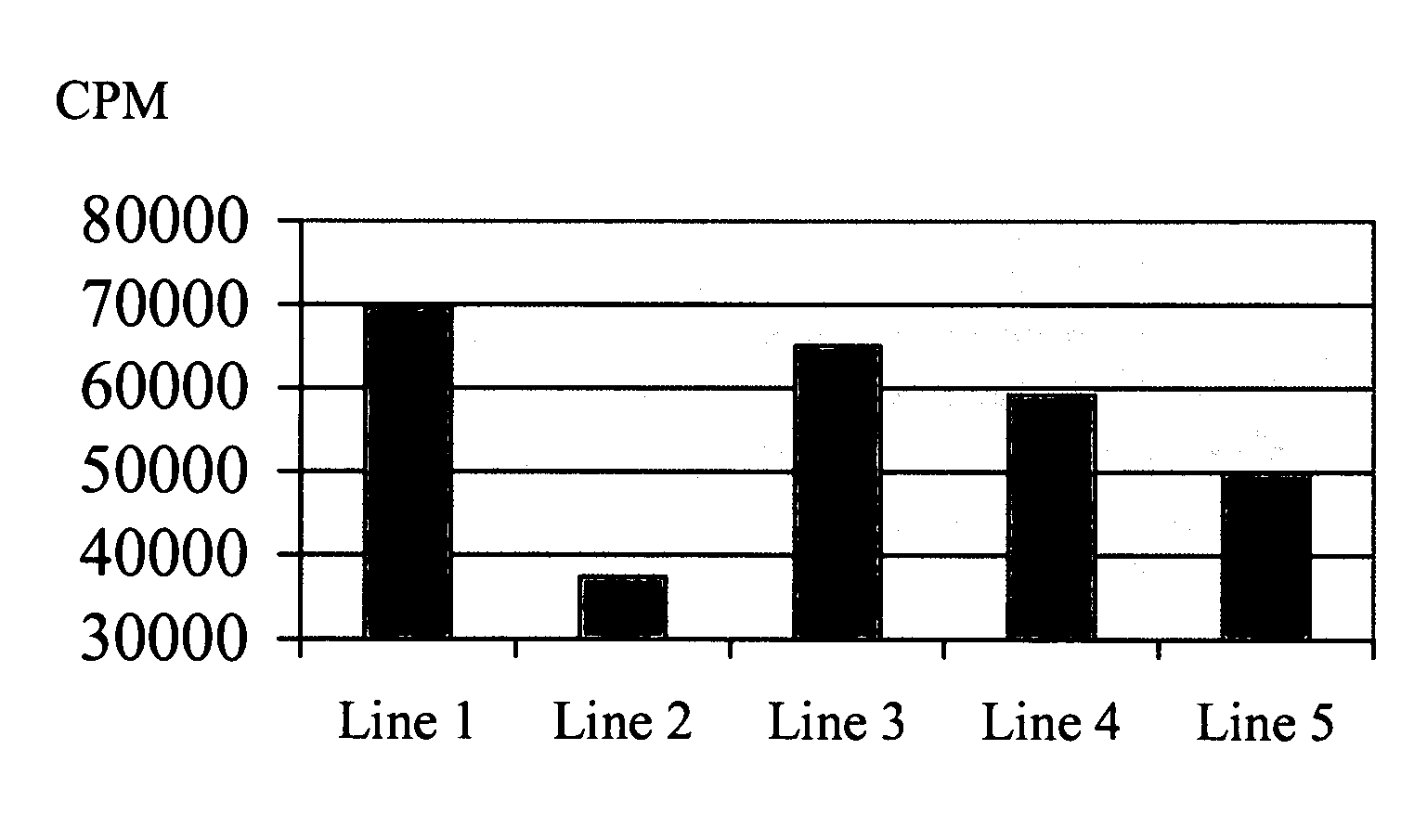
SEMA4D in Cancer Diagnosis, Detection and Treatment
InactiveUS20090104193A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancers diagnosisCancer research
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
Method for retarding unhealth manifestations brought by ageing of human beings
InactiveUS20090053200A1Reduce functionReduced stress resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDna antibodyBlood plasma
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Low protein infant formula with increased essential amino acids
ActiveUS20130079276A1Prevent adverse metabolic imprinting effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEssential amino acidBranched-chain amino acid
Owner:NUTRICIA
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Mucosal Bioadhesive SLow Release Carrier for Delivering Active Principles
A mucosal bioadhesive slow release carrier comprising an active principle and devoid of starch, lactose, which can release the active principal for a duration of longer than 20 hours. This bioadhesive carrier contains a diluent, an alkali metal alkylsulfate, a binding agent, at least one bioadhesive polymer and at least one sustained release polymer, as well as a method for its preparation.
Owner:ONXEO SA
Direct application of non-toxic crosslinking reagents to restabilize surgically destabilized intervertebral joints
InactiveUS20070202143A1Prevent spinal degenerationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeroxide active ingredientsIntervertebral jointSurgery procedure
Owner:ORTHOPEUTICS
Method of diagnosing breast cancer using nipple fluid
InactiveUS6905833B2Improve the level ofHigh riskPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisBreast cancerTest subject
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
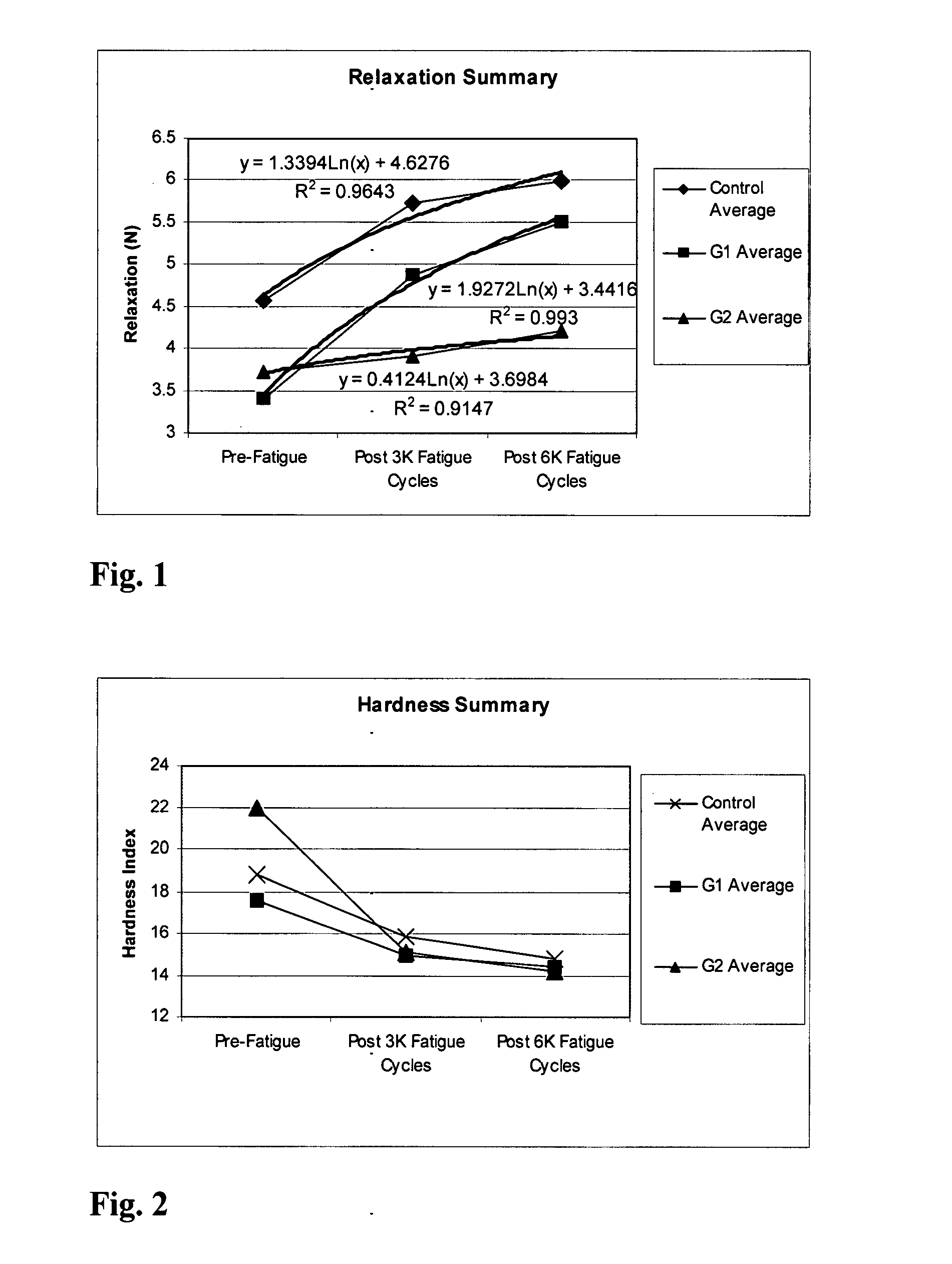
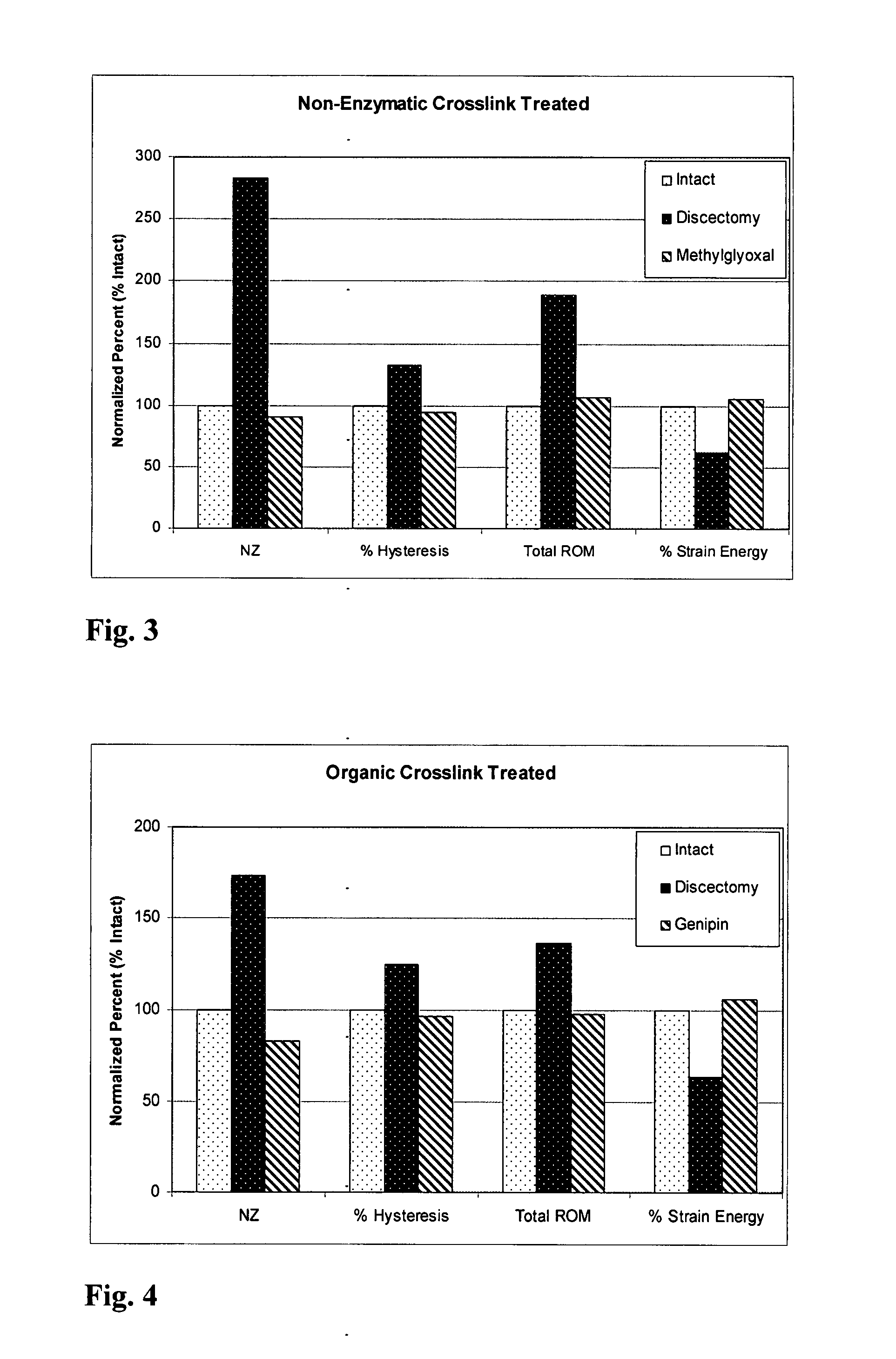
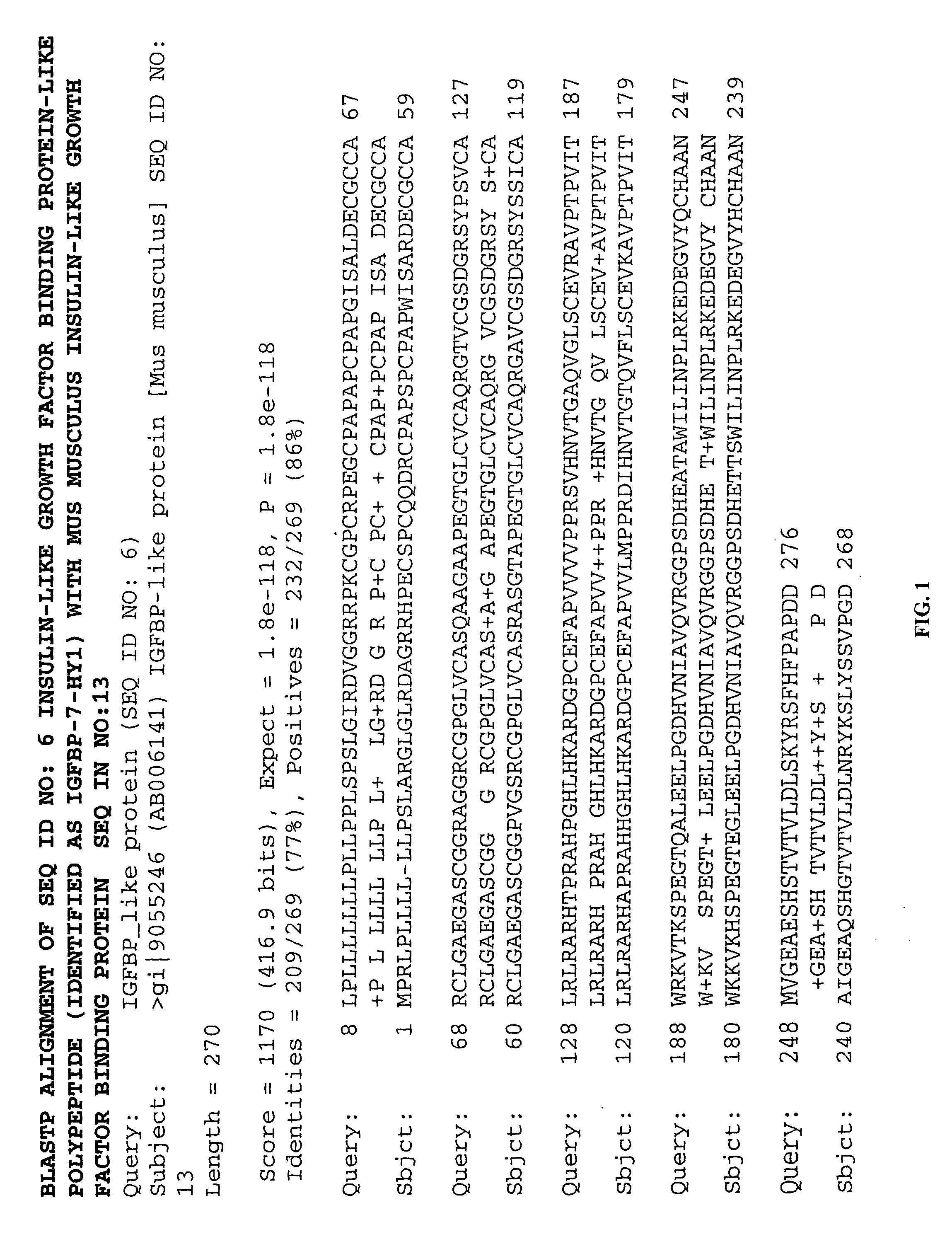
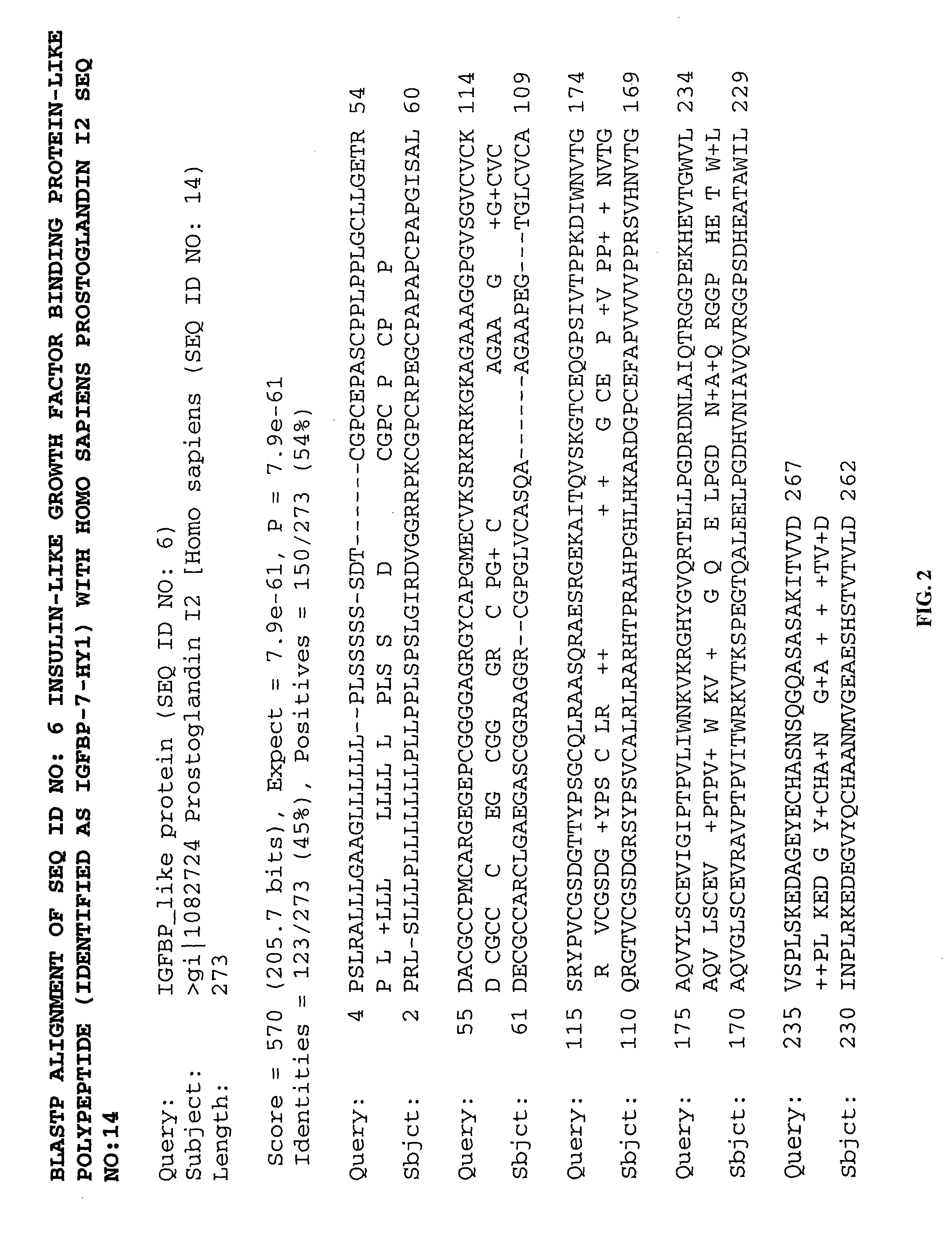
Methods of therapy and diagnosis using insulin-like growth factor binding protein-like polypeptides and polynucleotides
InactiveUS20060073514A1Promote wound healingReduced activityPeptide/protein ingredientsReceptors for hormonesNucleotideMutant
Owner:NUVELO INC
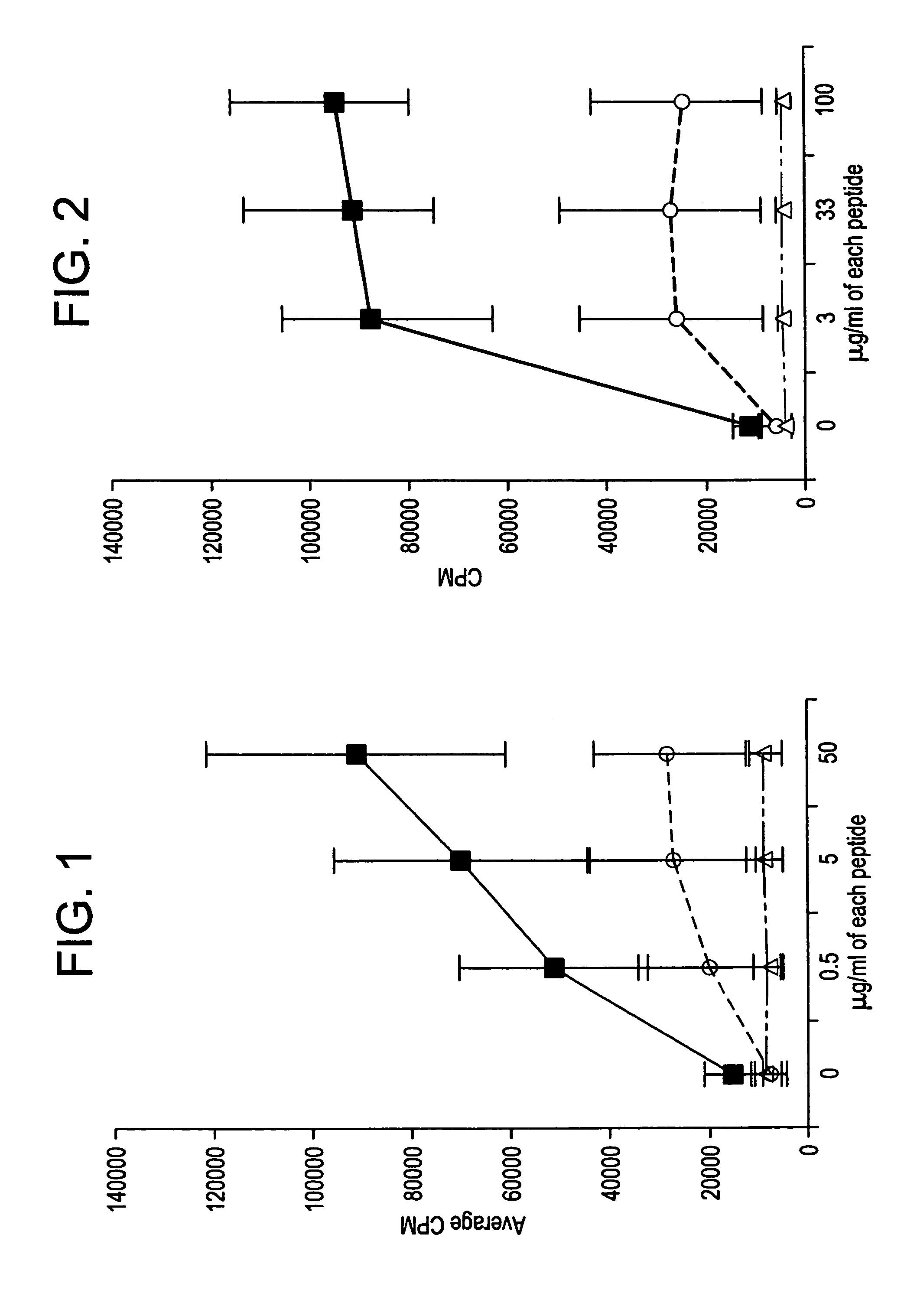
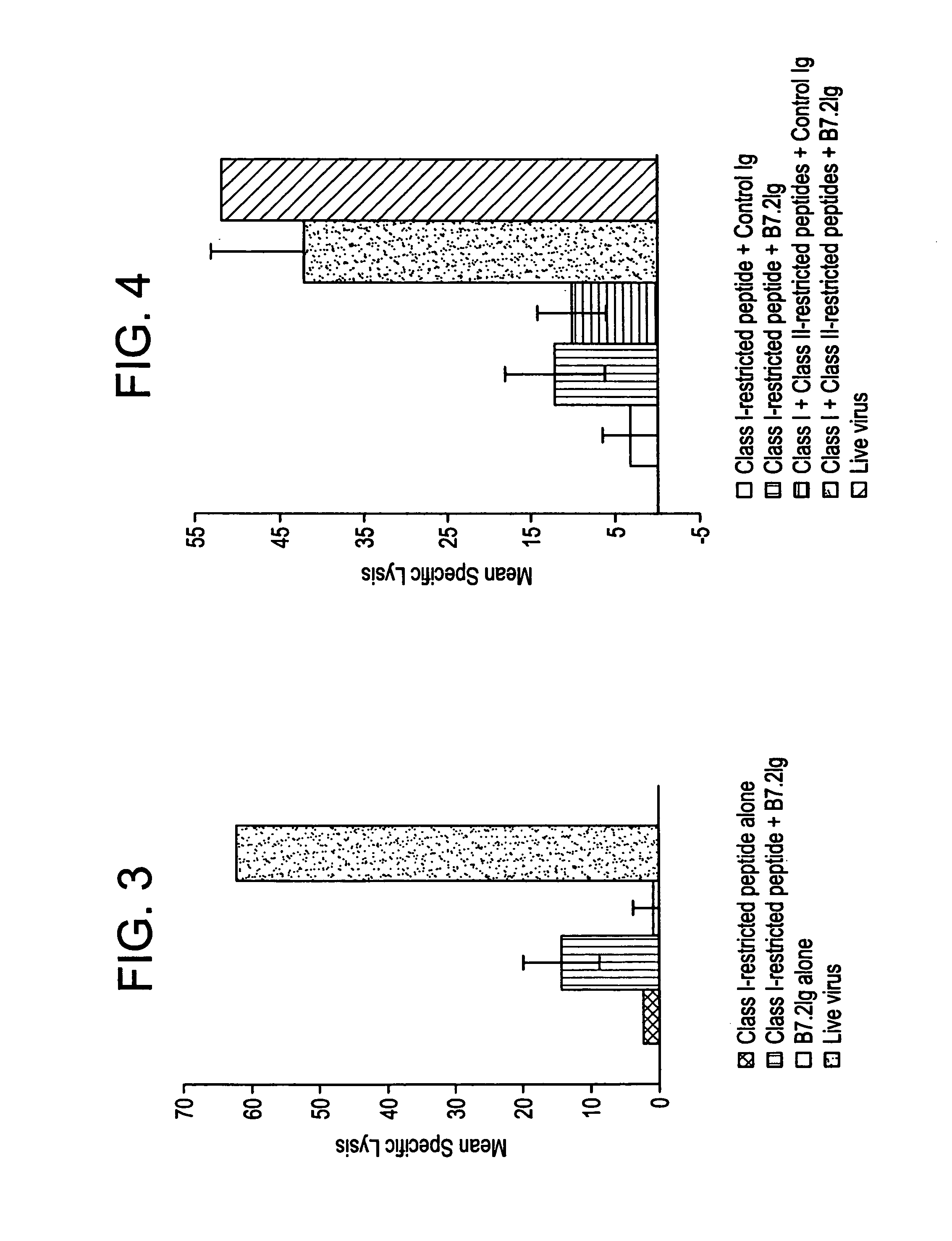
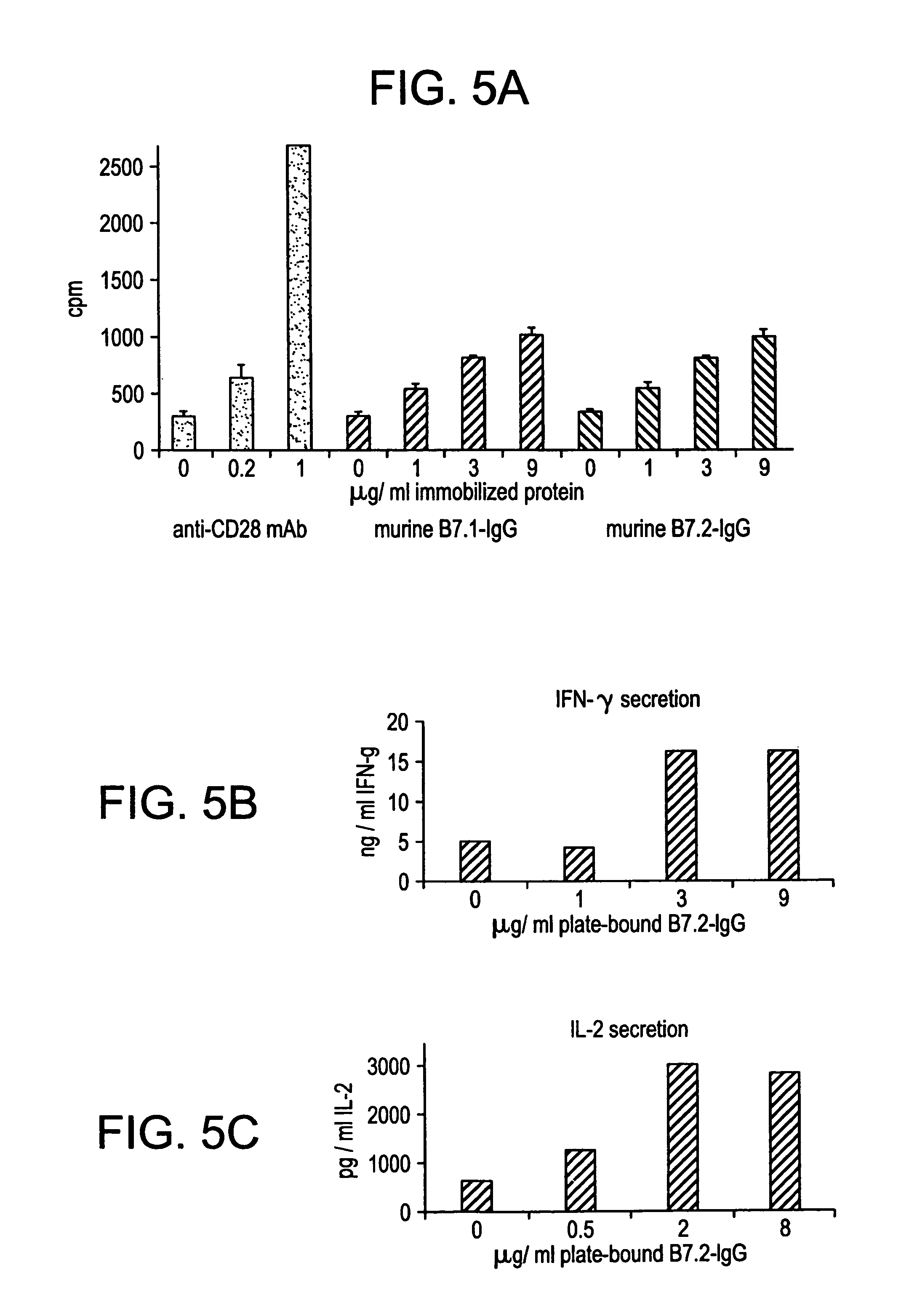
Enhancing immune responses with B7-1 or B7-2 in the absence of a crosslinking agent
InactiveUS7011833B1Enhance immune responseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenInfectious agent
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
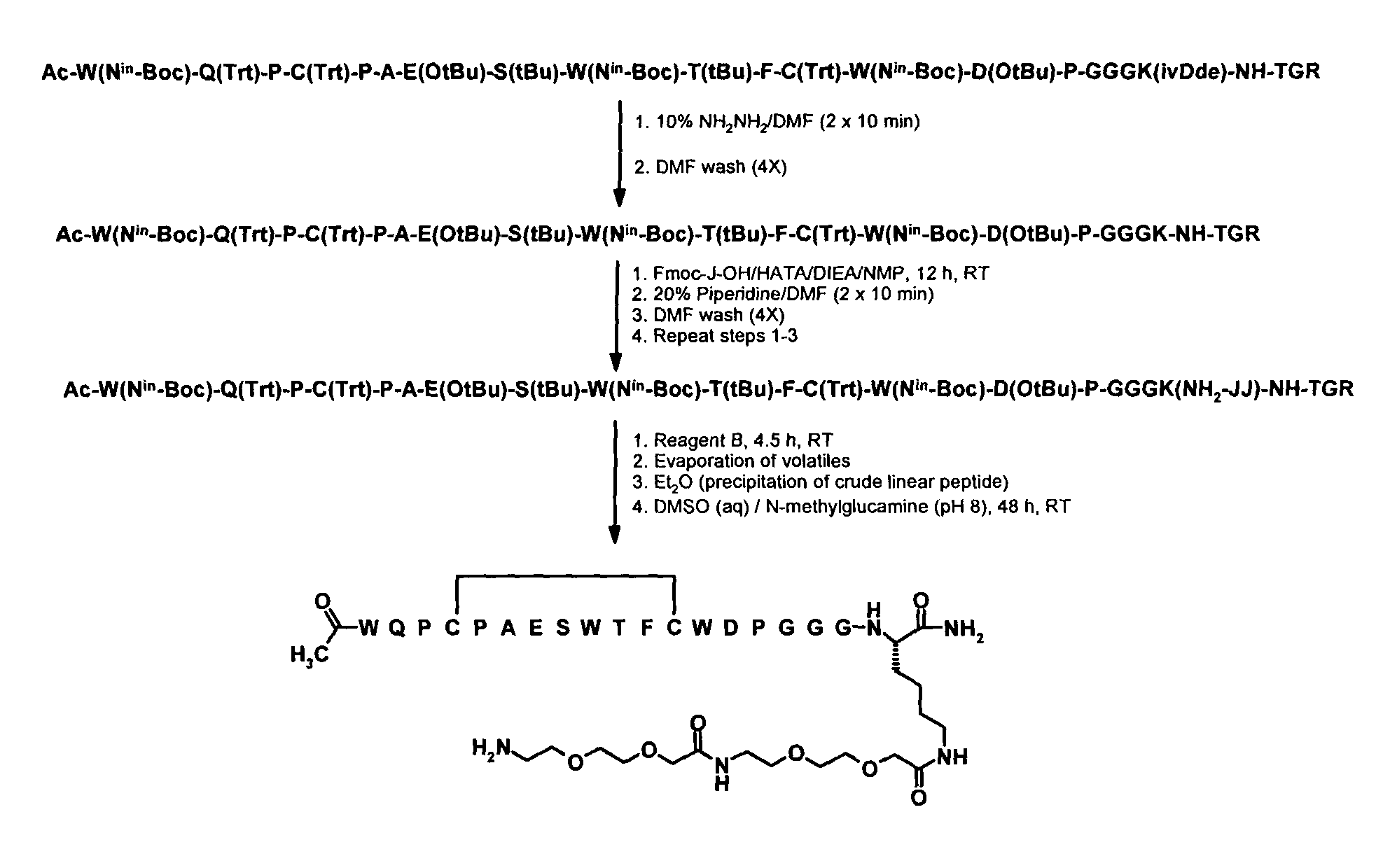
Fibrin-Binding Peptides and Conjugates Thereof
ActiveUS20100158814A1High degreeSuperior fibrin specific bindingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompound screeningBinding peptideCompanion animal
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
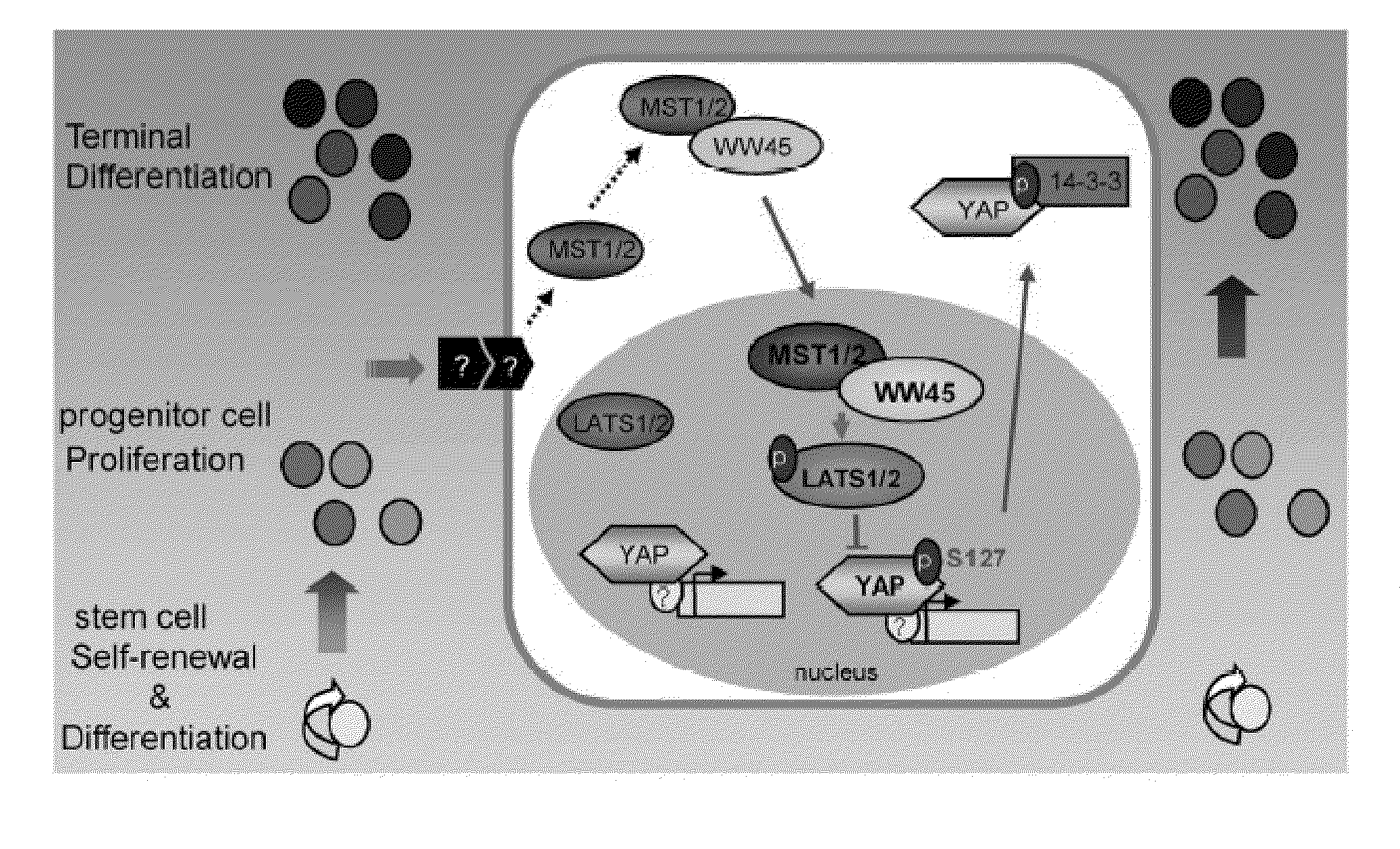
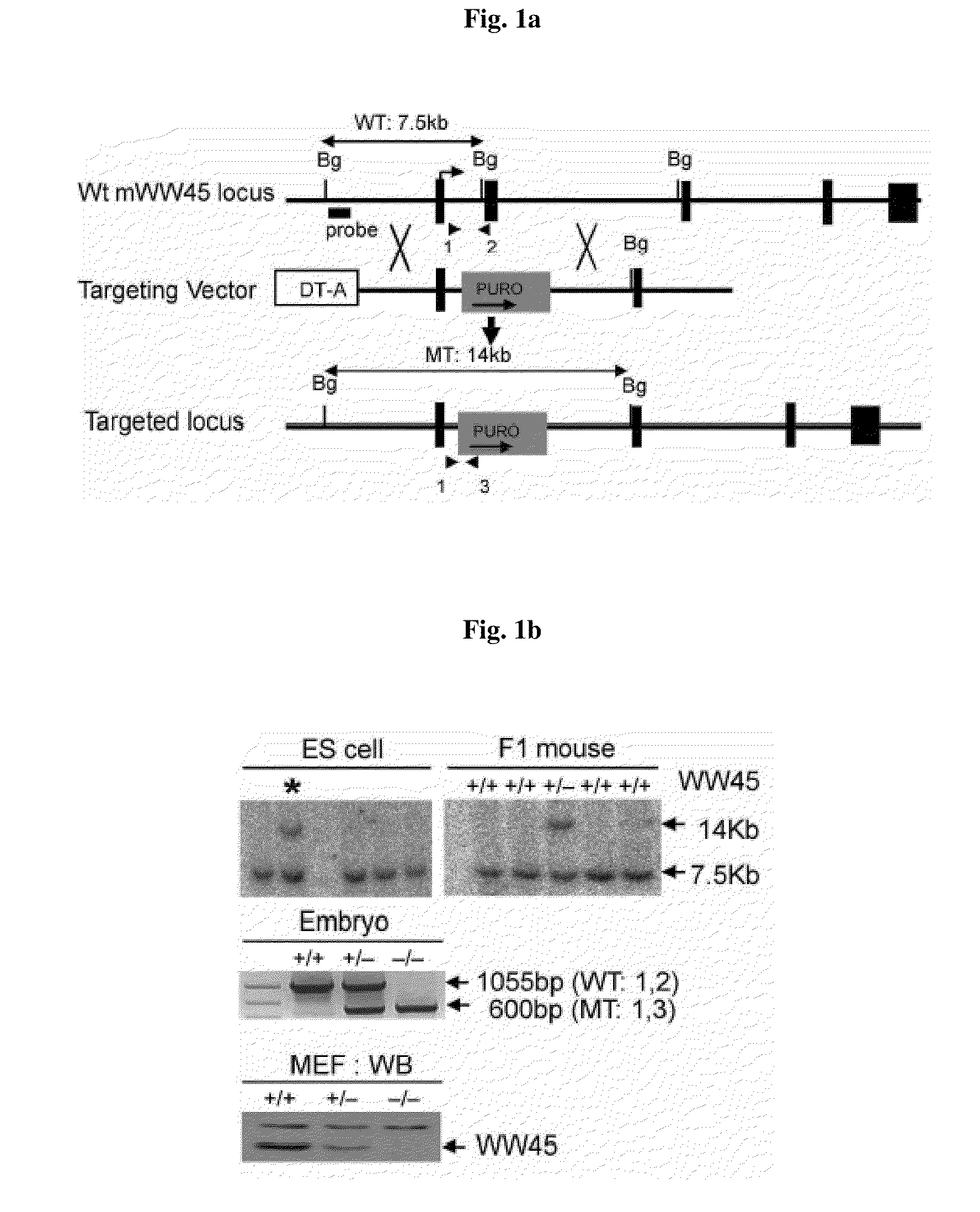
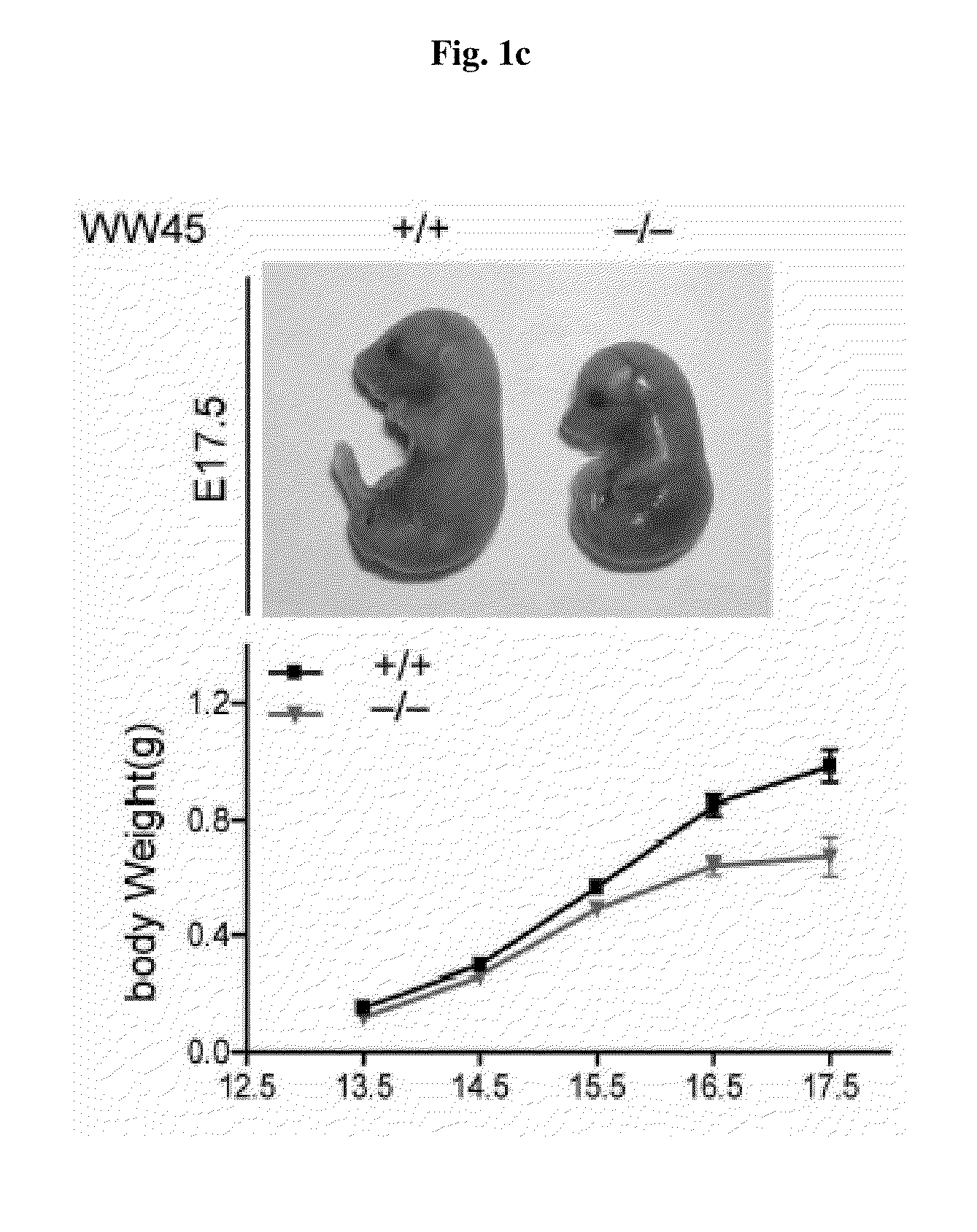
Methods of regulating differentiation in mammals
Mechanisms regulating cell proliferation stop and differentiation initiation during the development stage of mammalian embryo, and the proteins involved therein, are presented. Differentiation regulators, methods of regulating differentiation, transgenic organisms with loss of expression of the differentiation regulator, and methods of preparing the transgenic organisms, are provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap