Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39results about "Hydrolases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
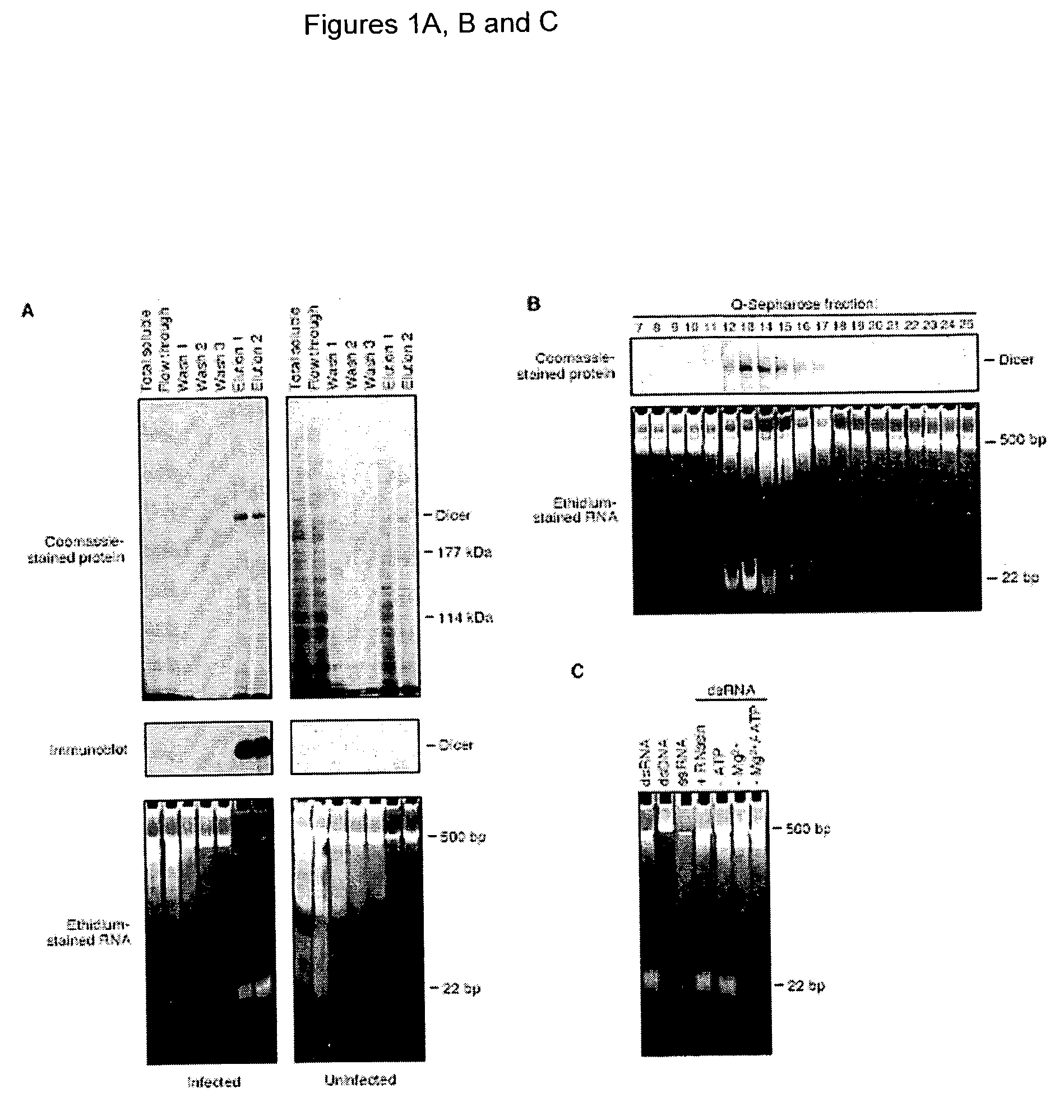
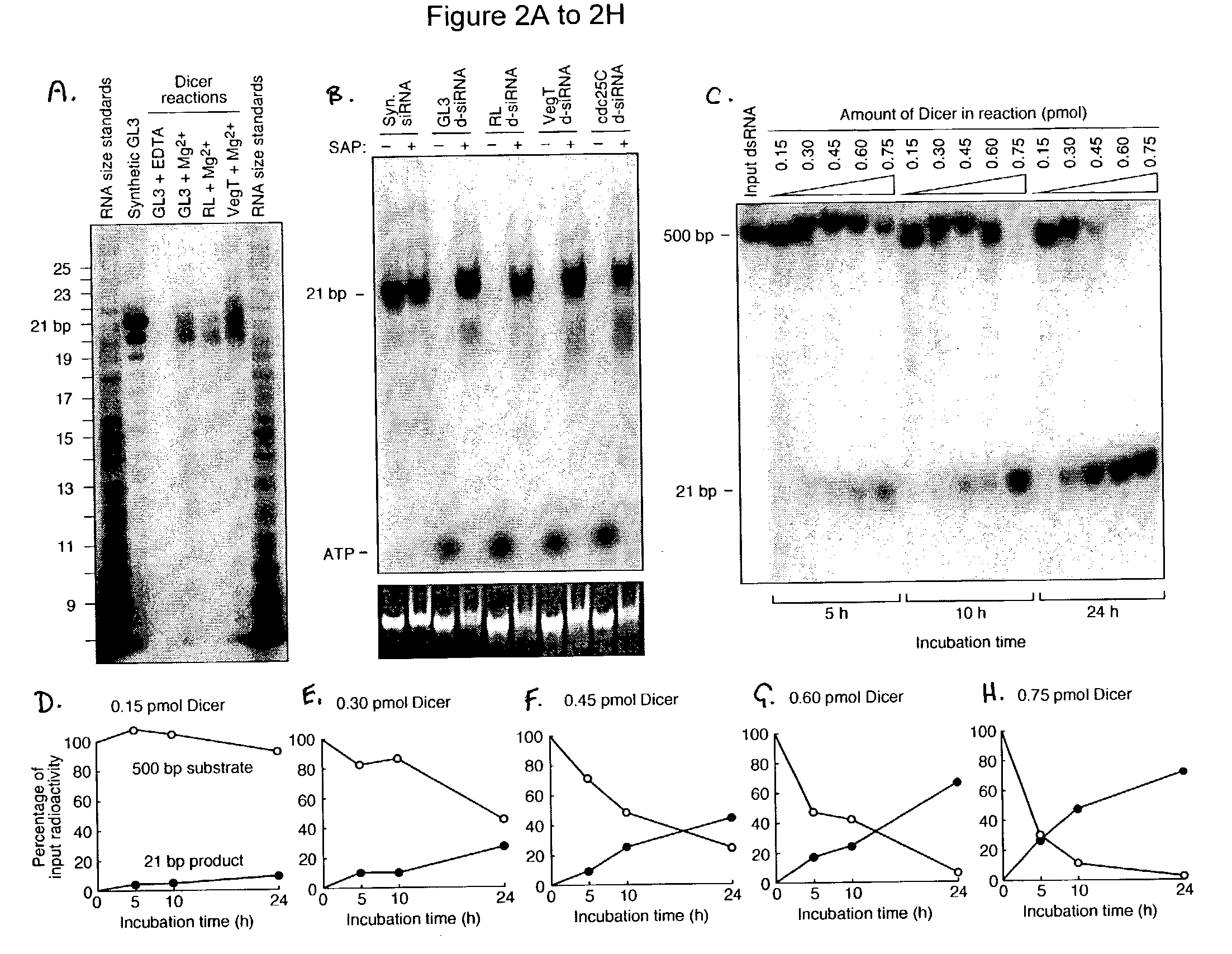
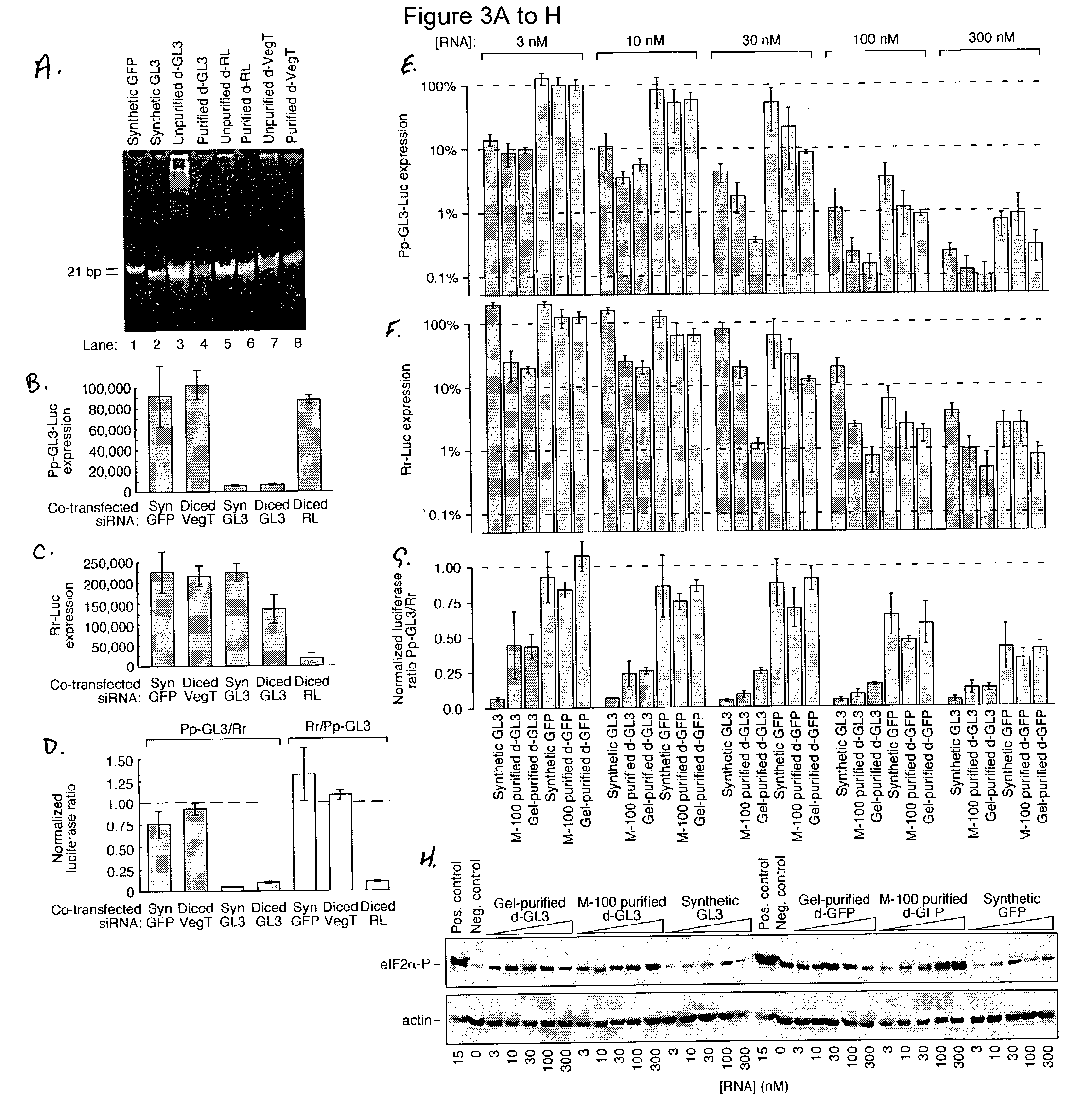
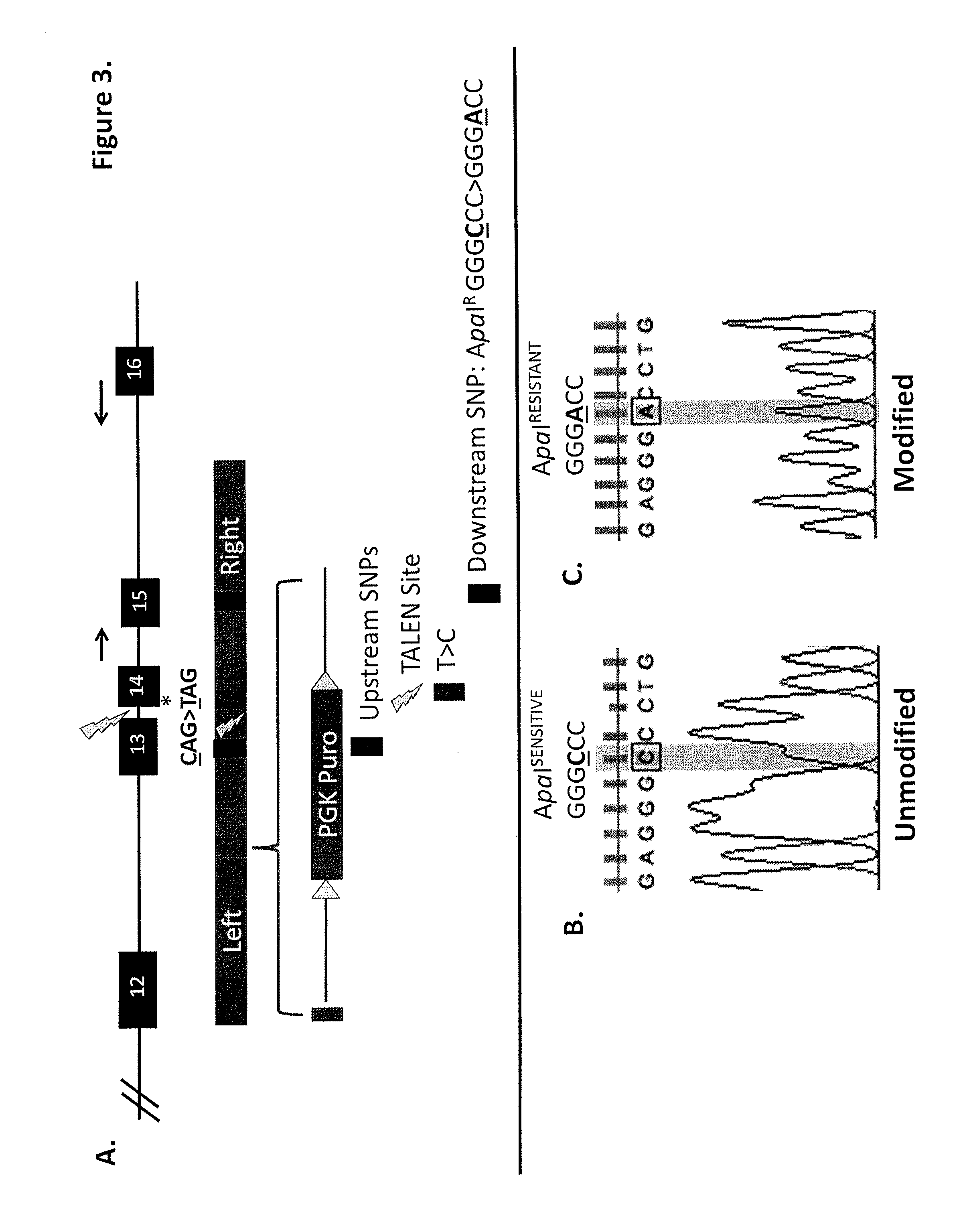
Methods and compositions for use in preparing siRNAs
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Protein variants having modified immunogenicity
InactiveUS20050181446A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityDough treatmentHydrolasesEpitopeBinding peptide
The present invention relates to a method of selecting a protein variant having modified immunogenicity as compared to the parent protein comprising the steps obtaining antibody binding peptide sequences, using the sequences to localise epitope sequences on the 3-dimensional structure of parent protein, defining an epitope area including amino acids situated within 5 Å from the epitope amino acids constituting the epitope sequence, changing one or more of the amino acids defining the epitope area of the parent protein by genetical engineering mutations of a DNA sequence encoding the parent protein, introducing the mutated DNA sequence into a suitable host, culturing said host and expressing the protein variant, and evaluating the immunogenicity of the protein variant using the parent protein as reference. The invention further relates to the protein variant and use thereof, as well as to a method for producing said protein variant.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
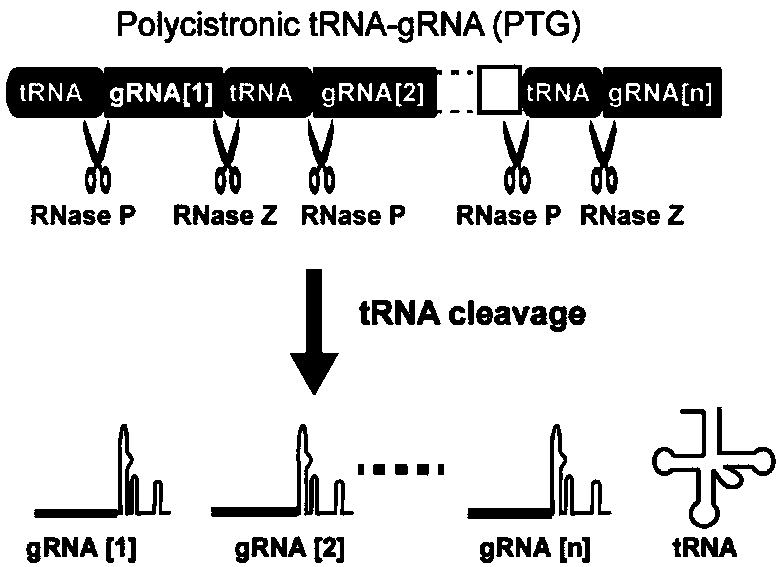
Genome editing method based on CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat) system and application thereof
ActiveCN107937432AImprove editing efficiencyImprove editing abilityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionInteinFusion gene
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Talen-based gene correction
ActiveUS20140256798A1Restores correct gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingHuman cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
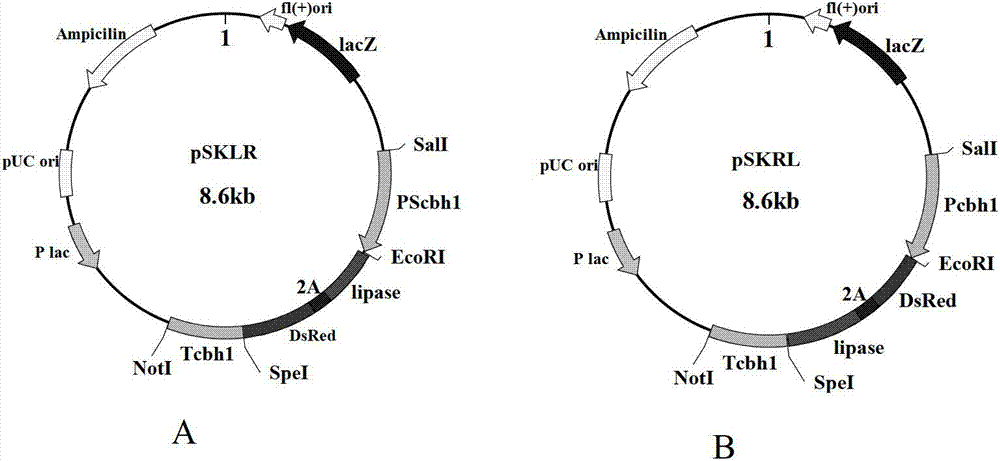
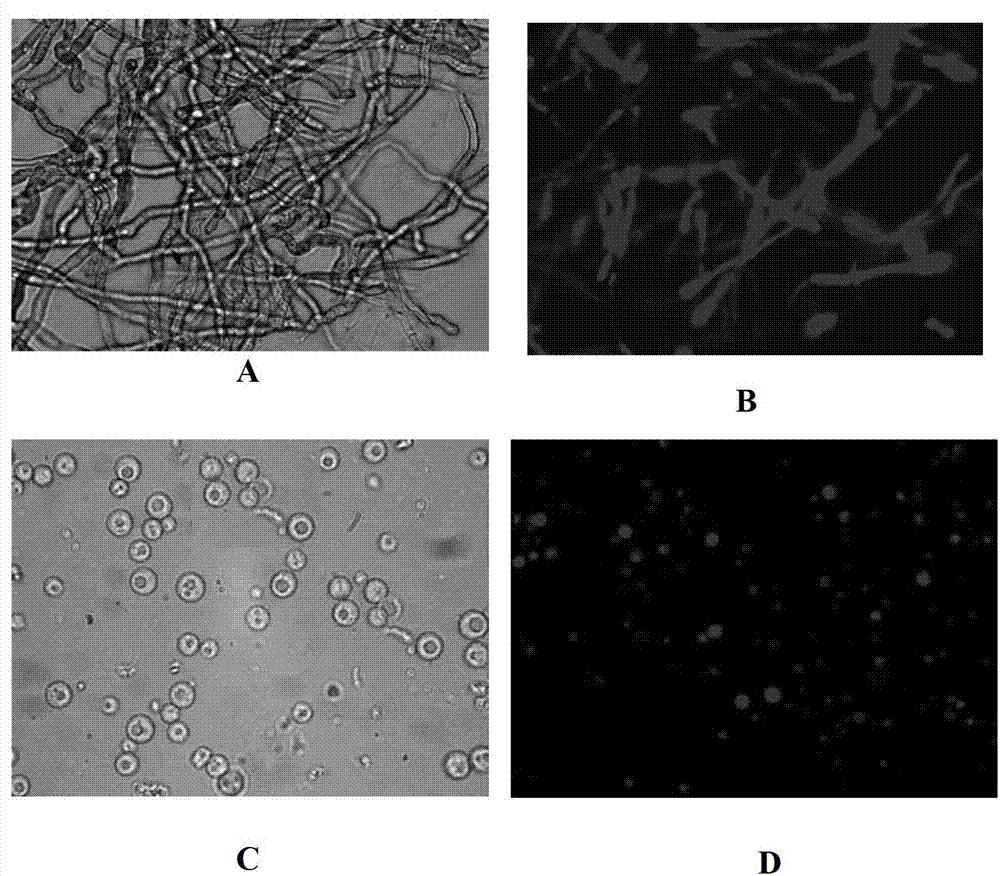
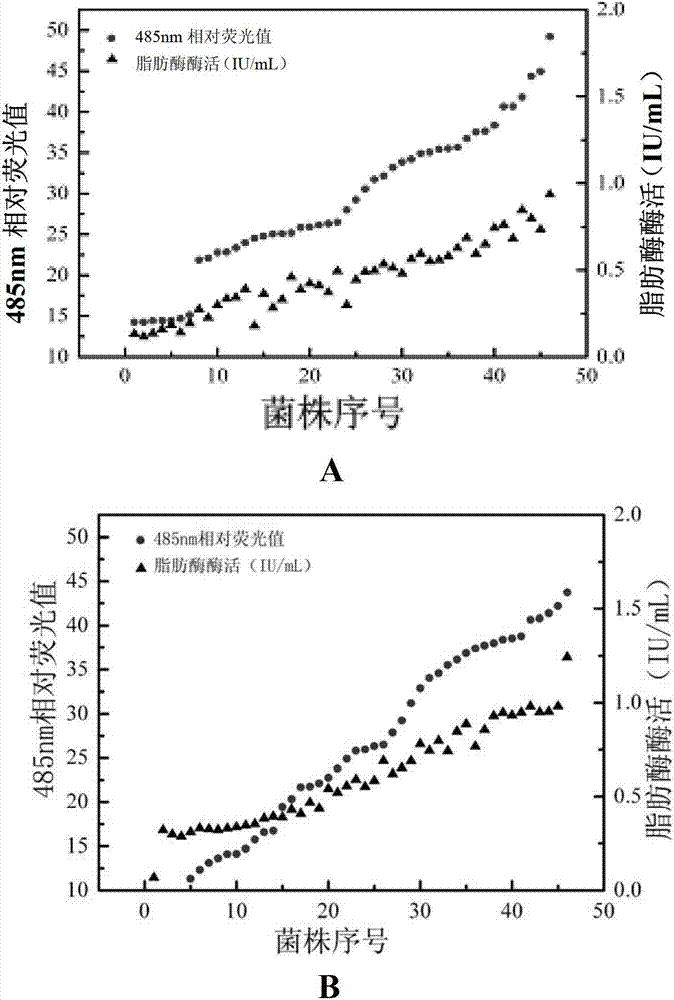
Method for high-throughput screening recombinant trichoderma reesei for efficiently expressing foreign protein
The invention discloses a method for high-throughput screening recombinant trichoderma reesei for efficiently expressing a foreign protein. The method comprises the steps as follows: comparing the red fluorescence intensity of recombinant trichoderma reesei for expressing the foreign protein identified by a flow cytometry meter(FCM); identifying the expressing ability of the foreign protein according to the red fluorescence intensity; and obtaining a result that the expressing ability of the foreign protein of the recombinant trichoderma reesei for expressing the foreign protein having higher red fluorescence intensity is strong. The gene of the foreign protein is led into the trichoderma reesei in a mode of a fusion gene, the fusion gene is formed by connecting a red fluorescence protein gene with the foreign protein gene through a connecting peptide 2A sequence; the foreign protein gene is positioned in the upstream or the downstream of the red fluorescence protein gene; a signal peptide sequence is formed at the 5' end of the foreign protein gene; and connecting peptides 2A are shown in 290th to 306th positions of the 8th sequence in the coding sequence list of the connecting peptide 2A sequence.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for retarding unhealth manifestations brought by ageing of human beings
InactiveUS20090053200A1Reduce functionReduced stress resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDna antibodyBlood plasma
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Pronucleus expression of epoxide hydrolase gene (EH-B) and preparation of chiral epichlorohydrin
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
GTP cyclohydrolase I gene folE and application
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nuclease inhibitors and methods for their use
ActiveUS20050214839A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligomerSulfate
A class of anionic oligomers and polymers that function for inhibition of nucleases, particularly RNase. Specific inhibitors include mixtures of oligomers of vinyl sulfate. Methods for inhibition or inactivation of one or more nucleases in vitro which comprises the step of contacting the one or more nucleases in a biological medium with one or more of the anionic oligomeric or polymeric inhibitors of this invention. Kits for carrying out a biological procedure, biological reaction and / or a biological assay containing one or more inhibitors of this invention. The use of oligomers and / or polymers of this invention as additives in buffers or reagents. The inhibitors of the invention can also be attached to surfaces to provide for removal of nucleases from media, solutions or other liquids in contact with the solid.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Recombinant vector and use in gene therapy
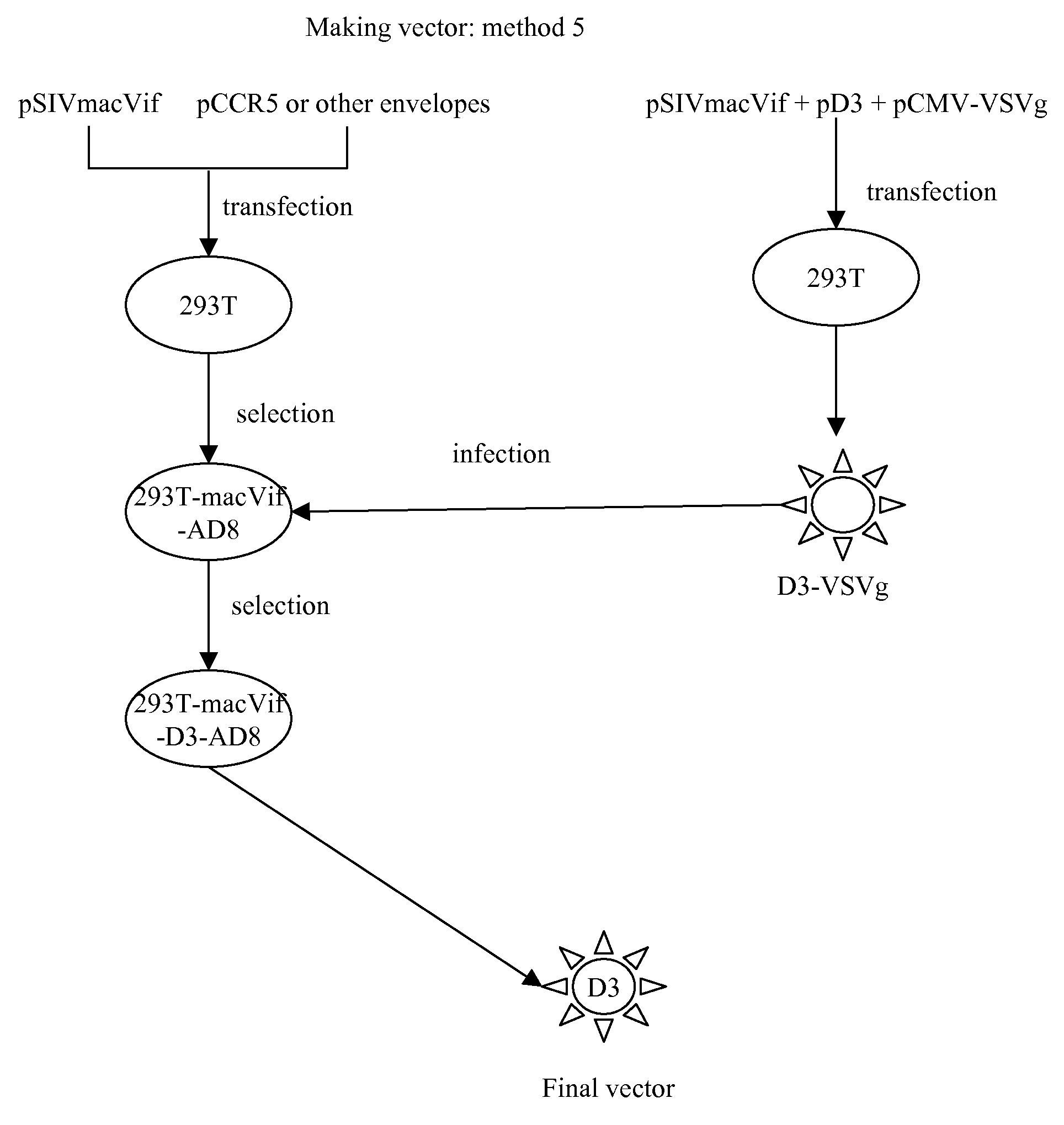
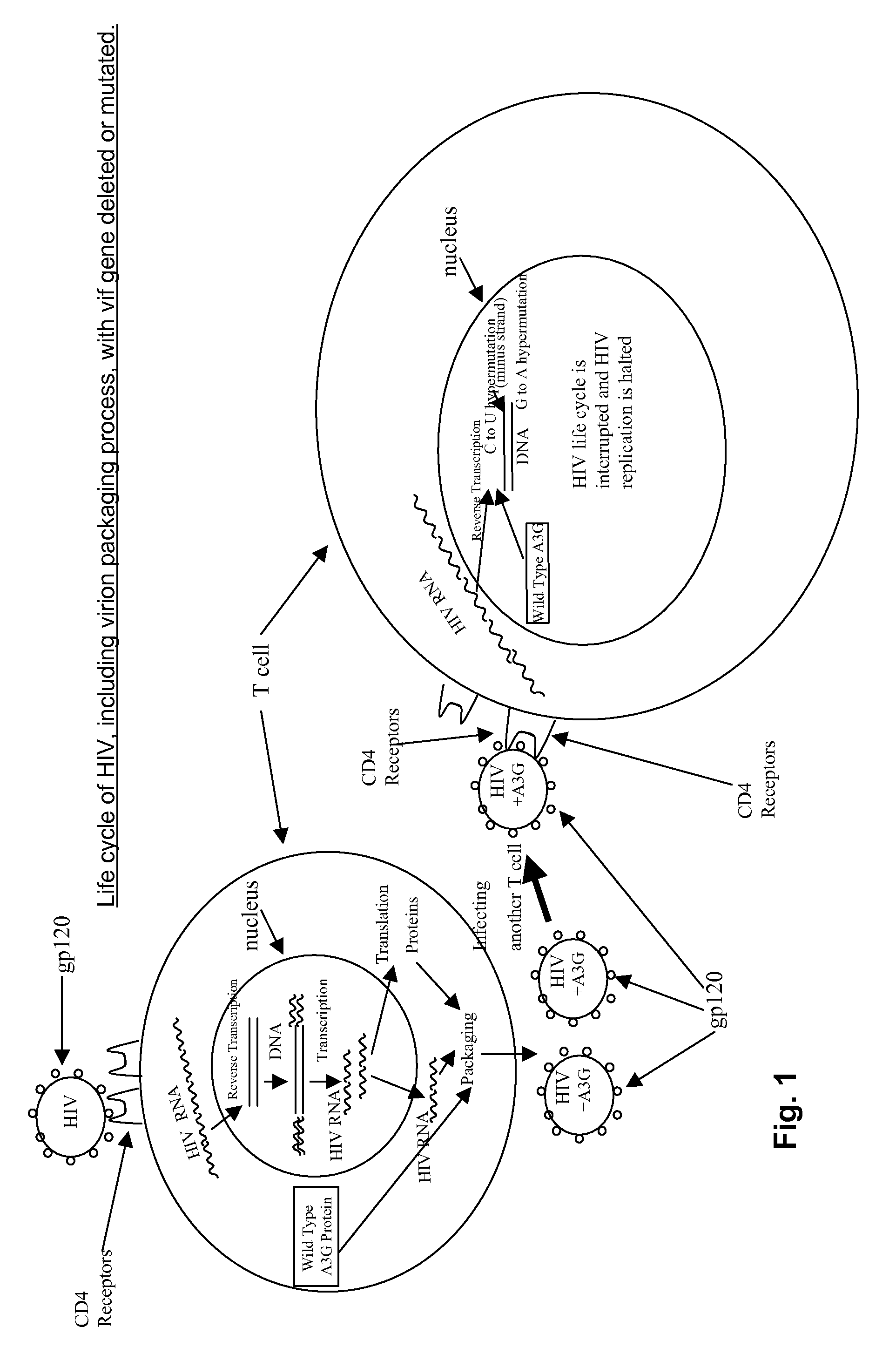
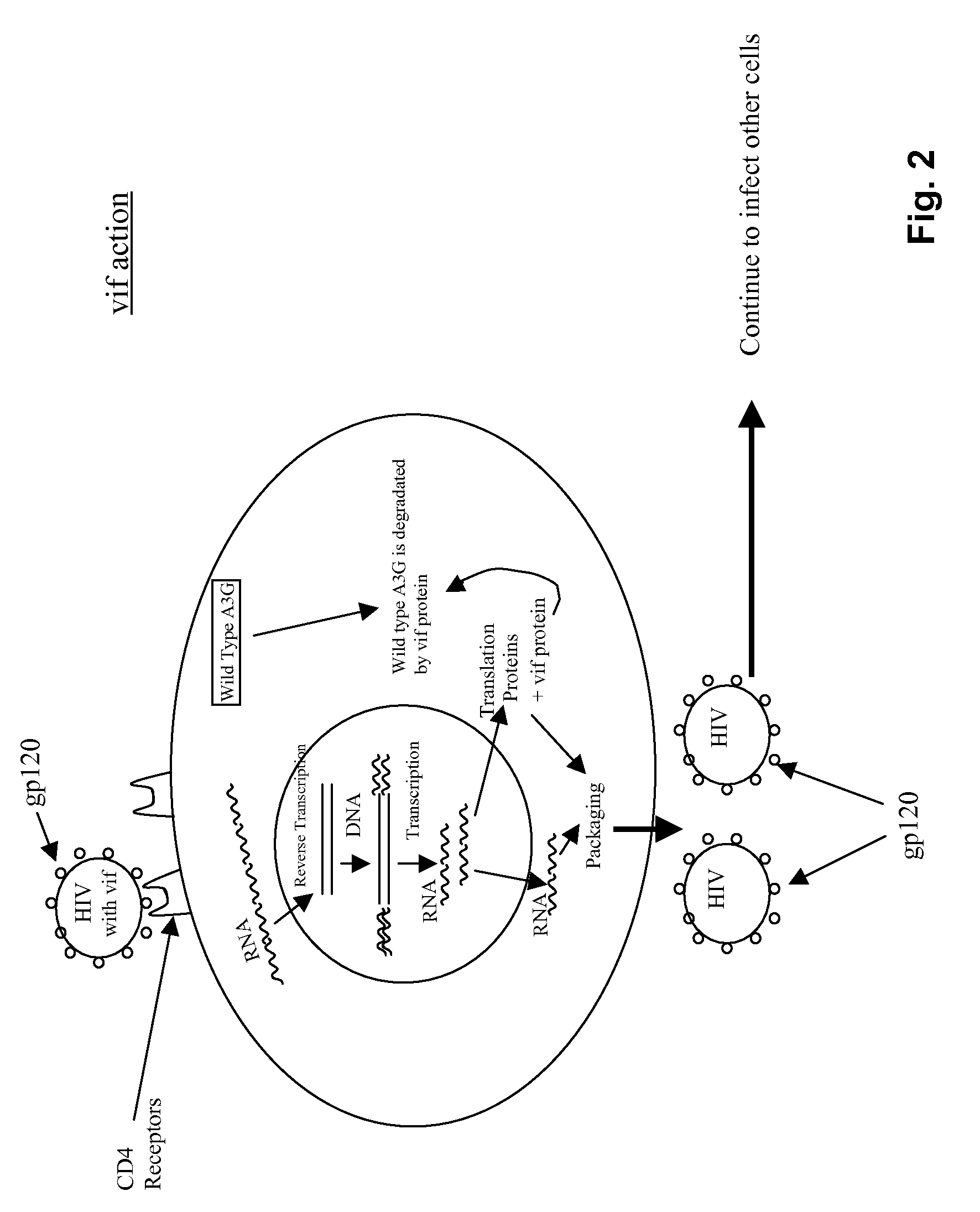
InactiveUS20080226675A1Preventing HIV infectionHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsWild typeHuman cell
Owner:XU HONGZHAN
Plant activation of insect toxin
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Method for isothermal amplification of nucleic acids
A method is disclosed for improved isothermal amplification of nucleic acids comprising the step of release of an essential component from a matrix under predetermined conditions. Furthermore, the invention relates to a kit comprising mesophilic enzyme and a matrix with embedded essential components for isothermal amplification. A composition comprising a matrix and a mesophilic enzyme and a method for embedding a mesophilic enzyme are disclosed as well.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Novel carbonyl reductase, gene thereof and method of using the same
InactiveUS20060035357A1Efficient productionReduce usageBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotideFiltration
The present invention provides a novel polypeptide efficiently forming (R)-N-benzyl-3-pyrrolidinol, a polynucleotide coding for said polypeptide, and use of the same. The present invention relates to a polypeptide having the following physical and chemical properties (1) to (4): (1) activity: acting on N-benzyl-3-pyrrolidinone with NADH or NADPH as a coenzyme, to form (R)-N-benzyl-3-pyrrolidinol; (2) optimum pH for activity: 5.5 to 6.0; (3) optimum temperature for activity: 50° C. to 55° C.; (4) molecular weight: about 55,000 as determined by gel filtration analysis, about 28,000 as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis. The present invention also relates to a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence shown under SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence listing, a polynucleotide coding for said polypeptide, and a transformant producing said polypeptide at high levels.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
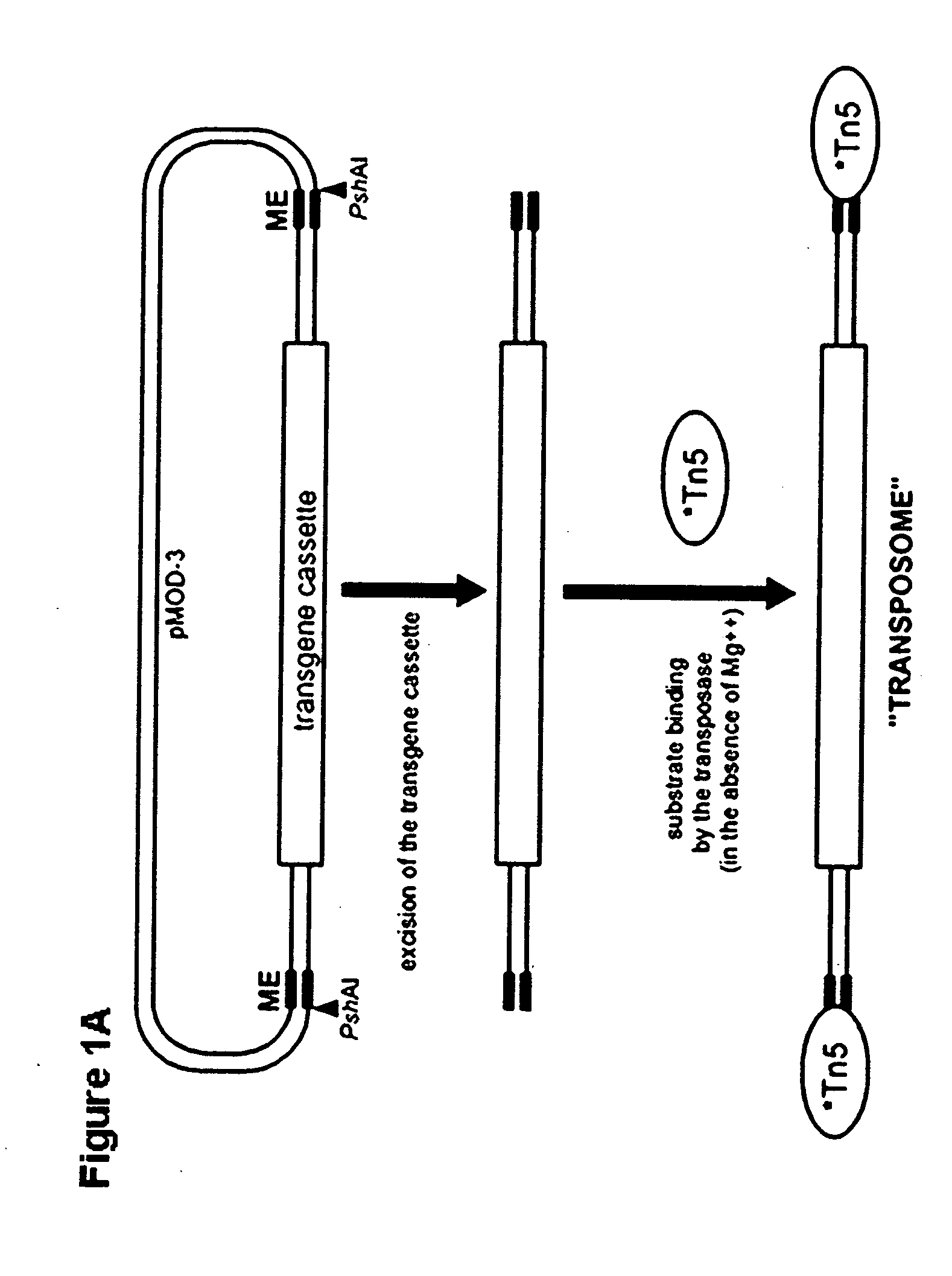
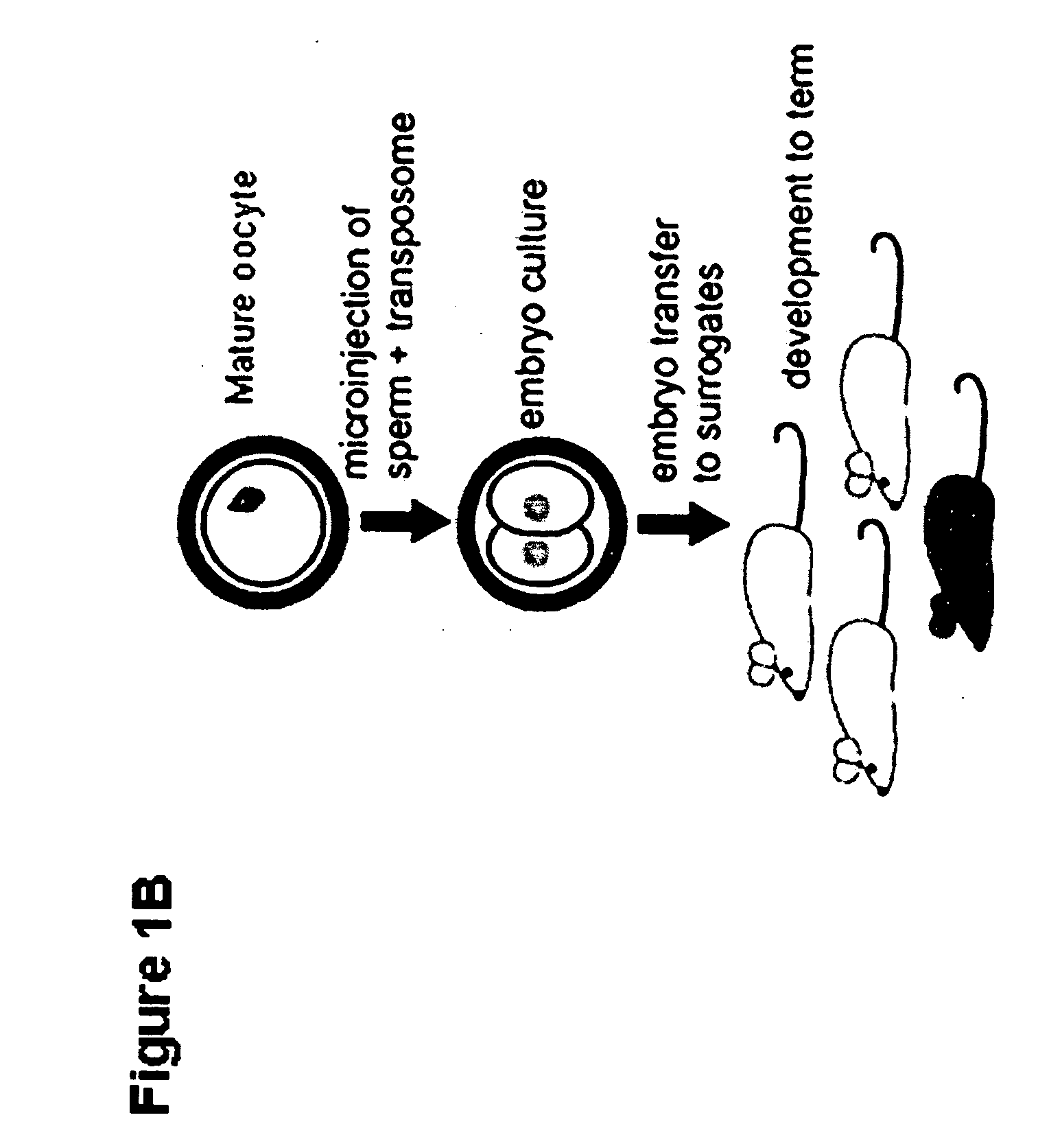
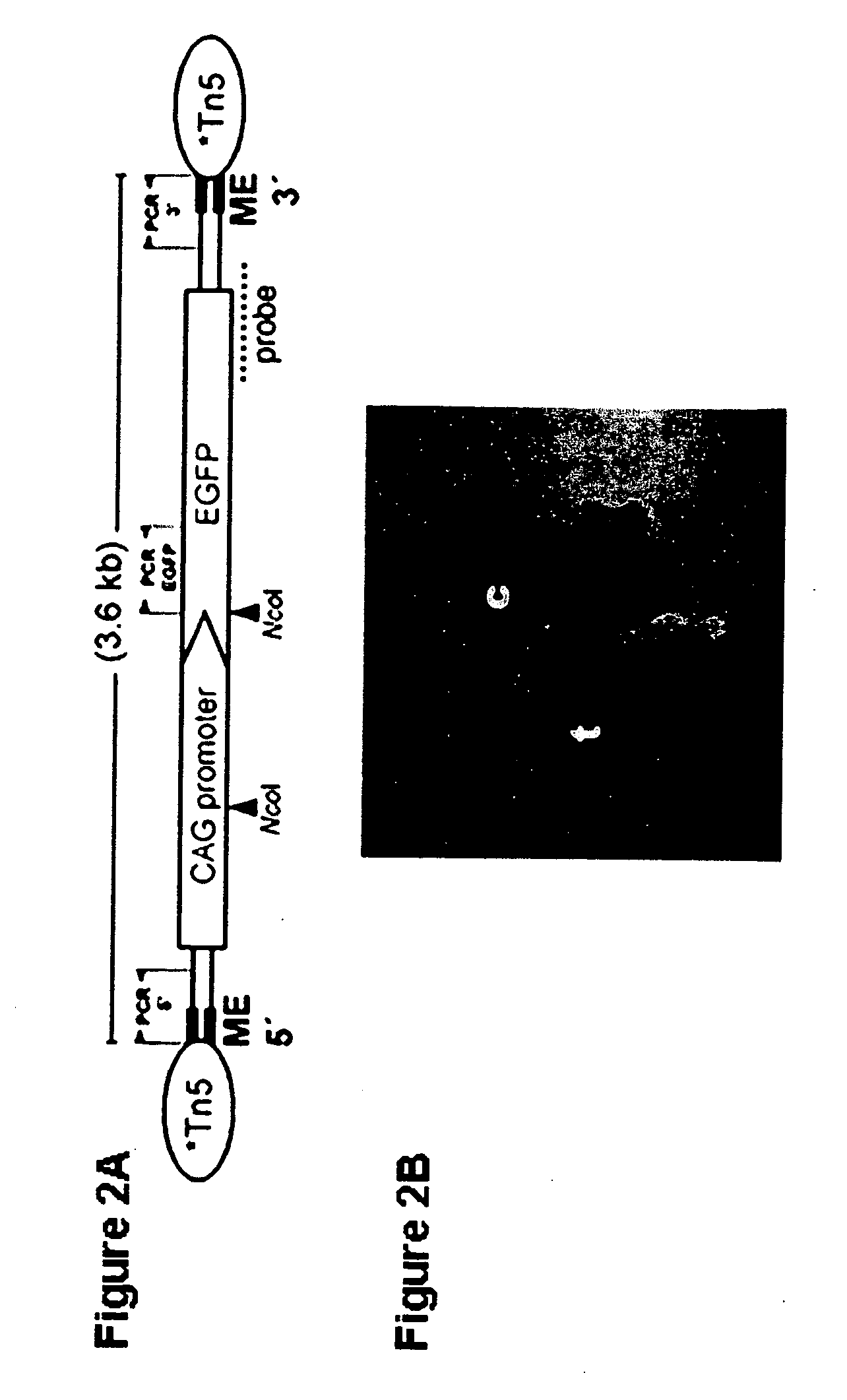
Tn5 transposase-mediated transgenesis
Owner:MOISYADI ISTEFO +2
Methods of preparing activated polymers having alpha nitrogen groups
InactiveUS20070166808A1Without costly column purificationHigh purityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPolymer scienceNucleophile
Methods for preparing substantially non-antigenic polymers having lone electron pair-containing moieties in high purity are disclosed. The polymers are useful as intermediates for synthesis of amine-based polymers and in the formation of activated polymers for conjugation with nucleophiles. Conjugates and methods of preparation and treatment with the conjugates are also disclosed. The resultant polymer-amines are of sufficient purity so that expensive and time consuming purification steps required for pharmaceutical grade polymers are avoided.
Owner:BELROSE PHARMA
Passivation of nerve agents by surface modified enzymes stabilized by non-covalent immobilization on robust, stable particles
InactiveUS6869784B2Easy accessLarge specific surface areaHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymeSurface modification
Enzymes are modified by incorporating anchor sites for linking the enzymes to a target surface without destroying the catalytic activity of the enzymes. A stable carrier to accommodate and bind the selected enzyme is constructed, and the enzyme is non-covalently linked to the carrier, generally through metal salts of iminodiacetate.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Extract of E. coli cells having mutation in ribosomal protein S12, and method for producing protein in cell-free system using the extract
InactiveUS20060008871A1Improve expression efficiencyExpression efficiency be lowBacteriaHydrolasesRibosomal protein E-L30Gene mutation
Owner:NAT FOOD RES INST +1
Pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases and a coding gene and application thereof. The pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases (TALEN) is obtained by merging a pair of DNA identifying proteins with two different source subunits of a Fok1 DNA incision enzyme respectively, and two adjacent locuses on a prion protein gene (PRNP) exon2 of a goat or a sheep can be identified in specificity mode. When the pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases is simultaneously transferred into a host cell, the nucleases can shoot targets of the exon2 locuses of a host cell PRNP gene and enable the target shooting locuses to have genic mutation so as to perform targeted modification on the PRNP gene of the goat or sheep. The nucleases have the advantages of being strong in specificity, high in target shooting efficiency and accuracy and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biosynthesis method and application of N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine
PendingCN114672525AEasy to implementSuitable for promoting industrial productionBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobiologyGenetic engineering
The invention provides a biological synthesis method of N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine and an application of the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine. The N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine is synthesized by using all the protein coding genes for synthesizing the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine or the recombinant genetic engineering bacteria capable of expressing and synthesizing all the protein coding genes of the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine. And separating the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine from the system to obtain the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine. The invention also discloses a recombinant vector containing a series of enzyme coding genes for synthesizing the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine and a recombinant gene engineering bacterium. A series of enzyme coding genes for coding the synthesized N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine in a recombinant vector and a series of enzymes for synthesizing the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine are expressed in a fermentation culture mode, the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine is synthesized, and the yield of the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine is high when the N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine is synthesized. The process is easy to implement, conditions are easy to control, and industrial production is suitable.
Owner:VDK NUTRITION BIOTECH CO LTD
Cas9 fused protein capable of improving gene knock in efficiency and exogenous gene knock in and integration system
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD
Sequence Specific and Organism Specific Antimicrobials and Related Materials and Methods
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
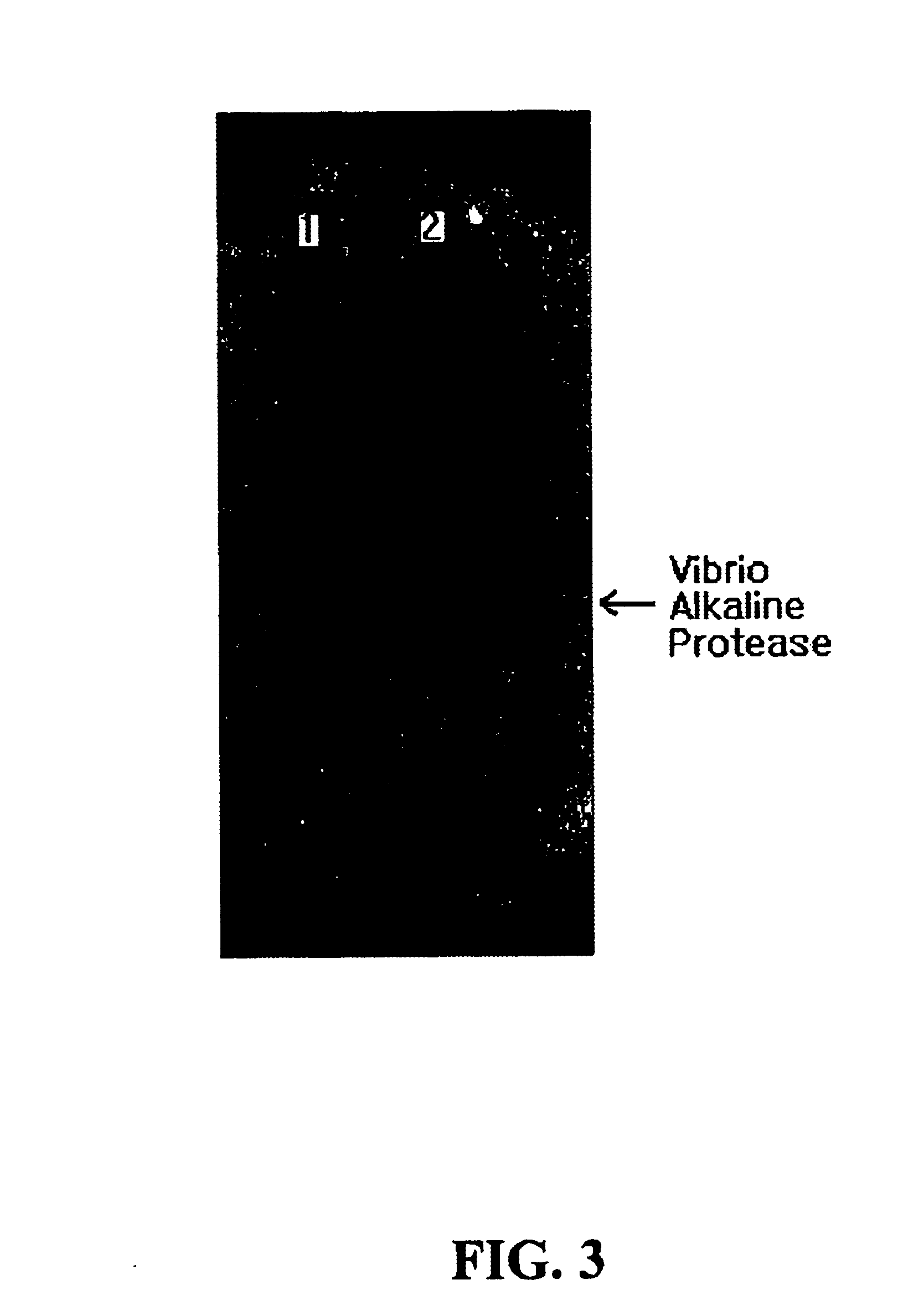
Recombinant plasmid pDSBCm, microorganisms transformed therewith, and method for producing an alkaline protease VapK
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Polynucleotide adapter design for reduced bias
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
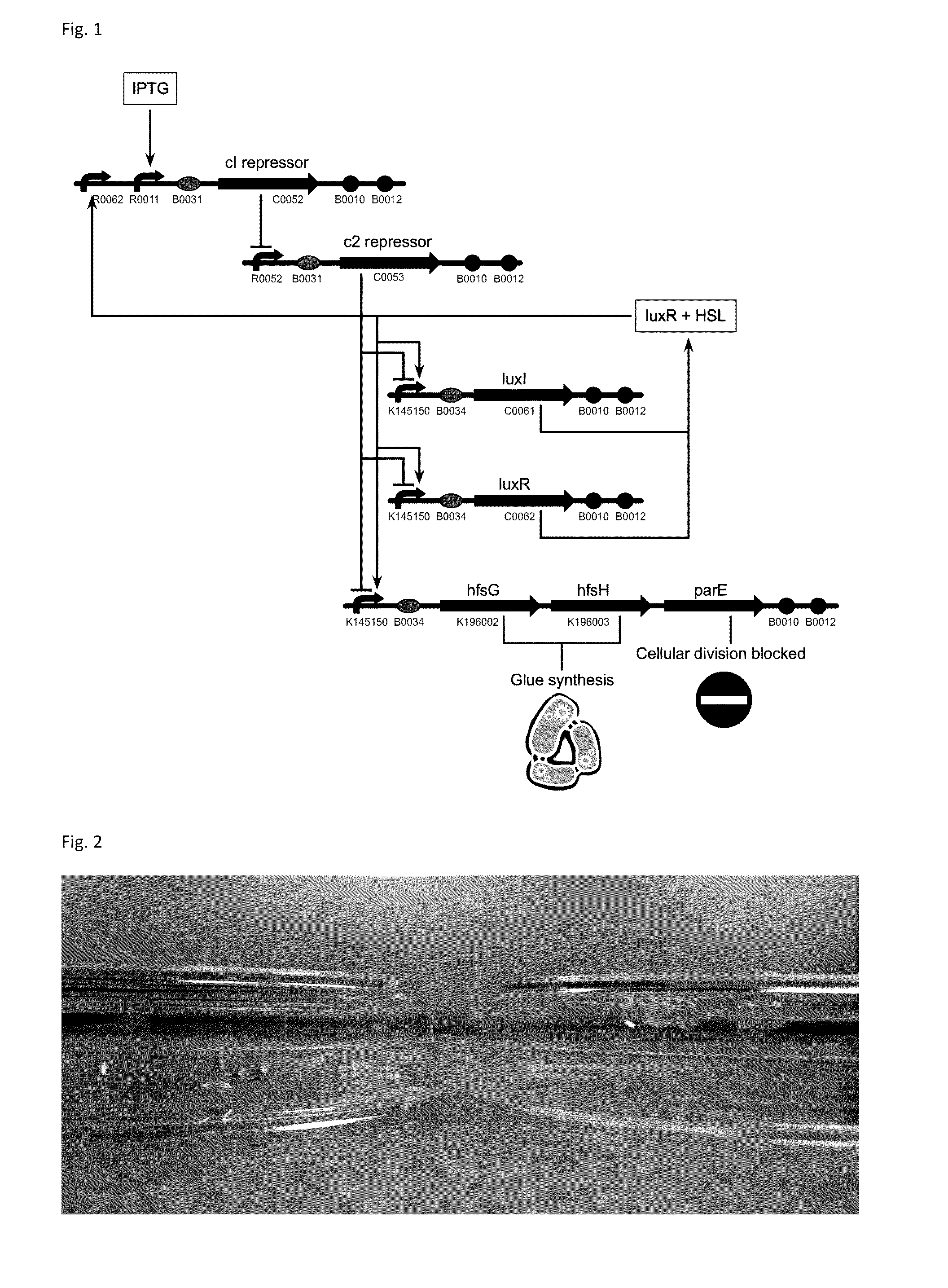
Biological glue and method for obtaining a biological glue
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Low-temperature lipase Lip1 as well as gene and application thereof
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
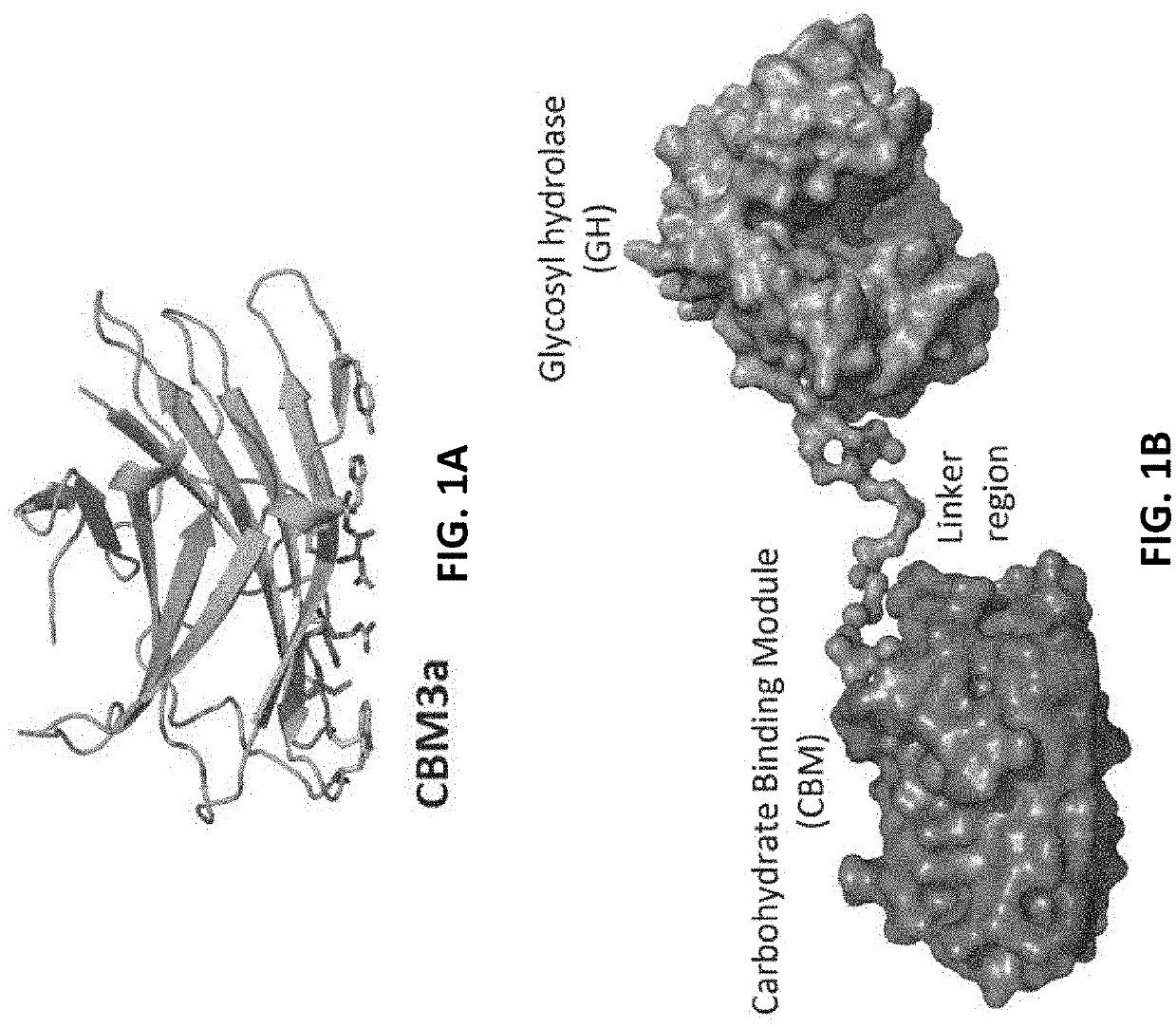
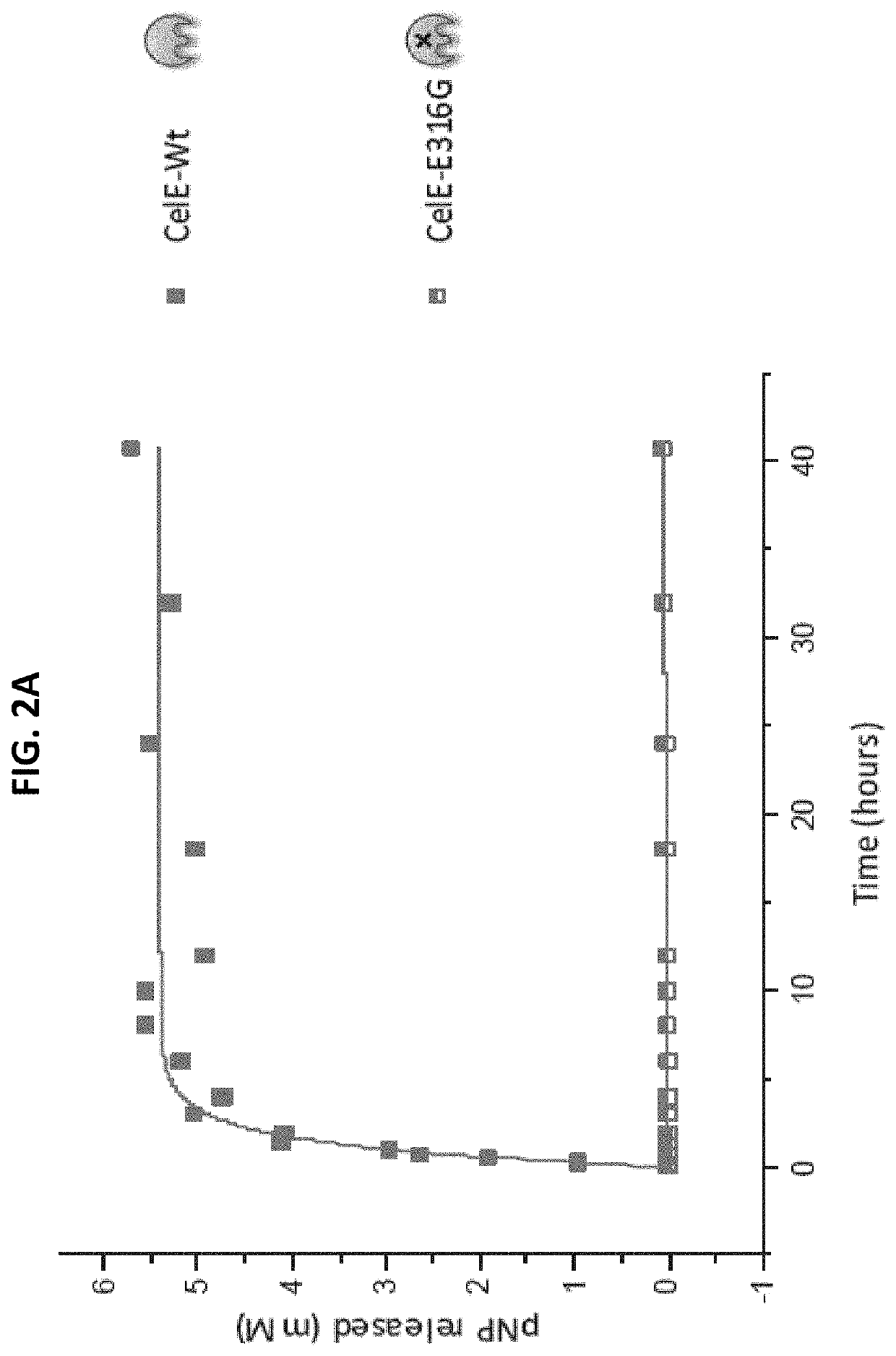
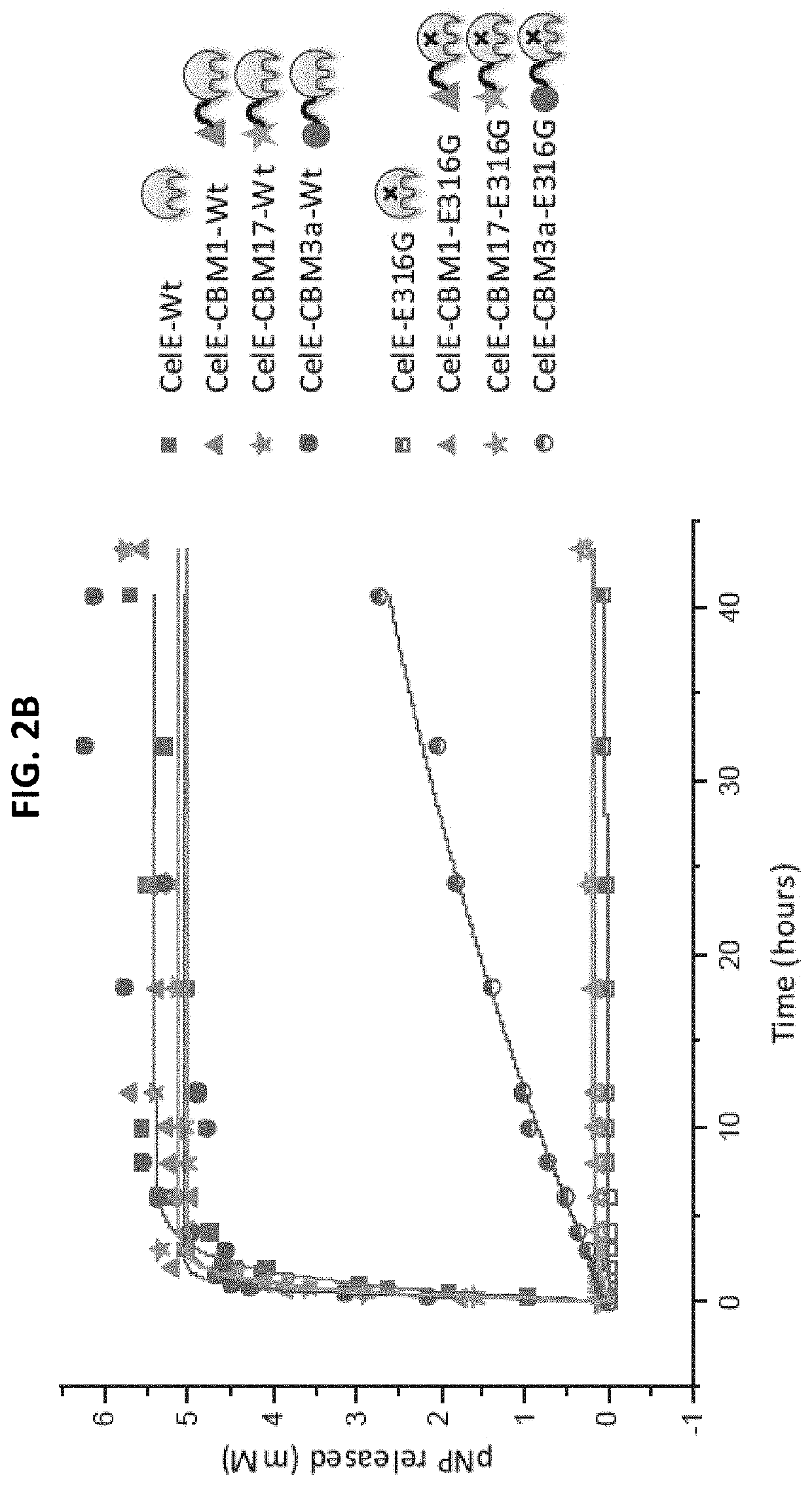
Engineered Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes for Glycan Polymers Synthesis
ActiveUS20200056215A1Promoting glycan polymer synthesisHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMolecular biologyPolymer
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
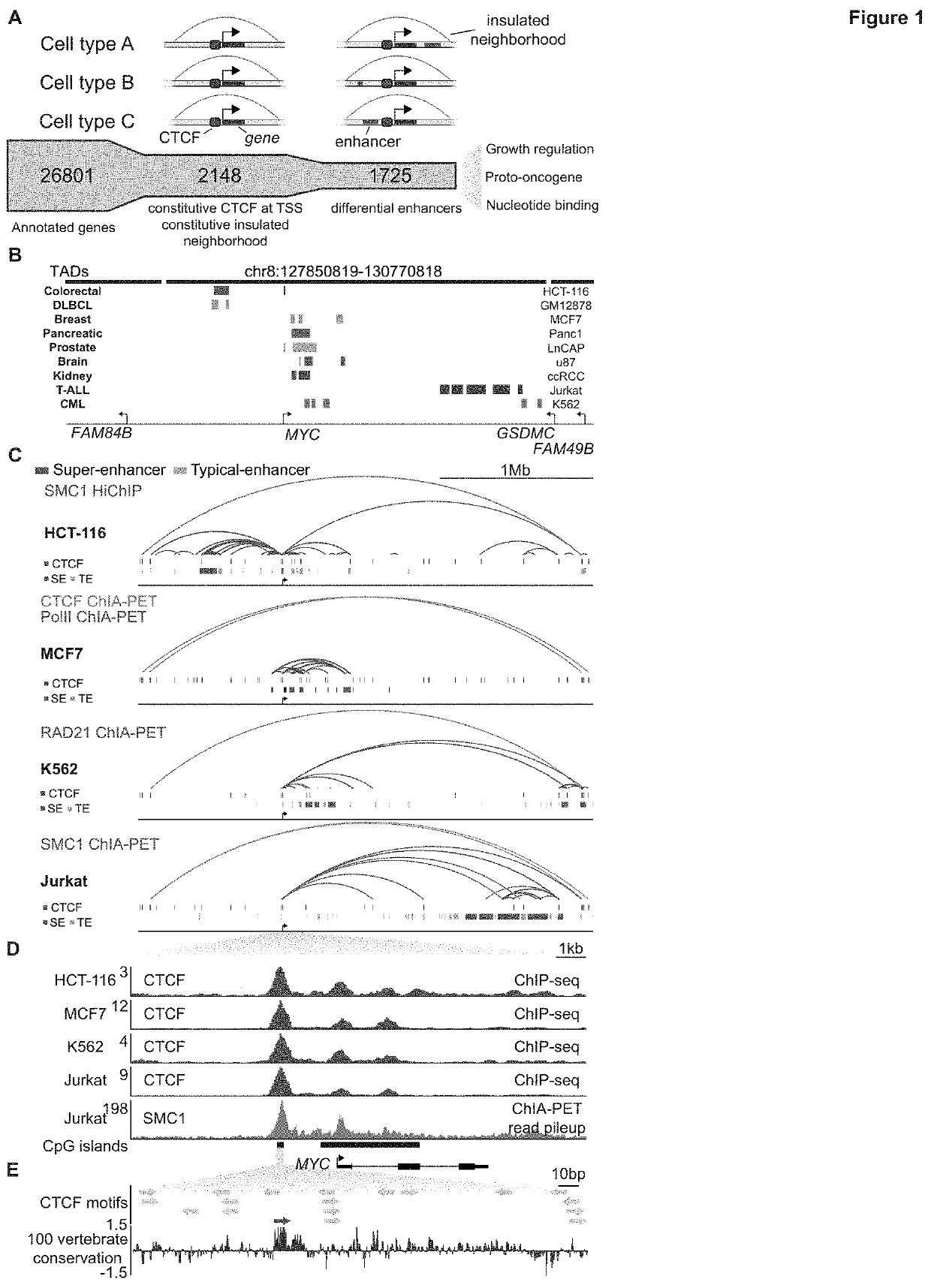
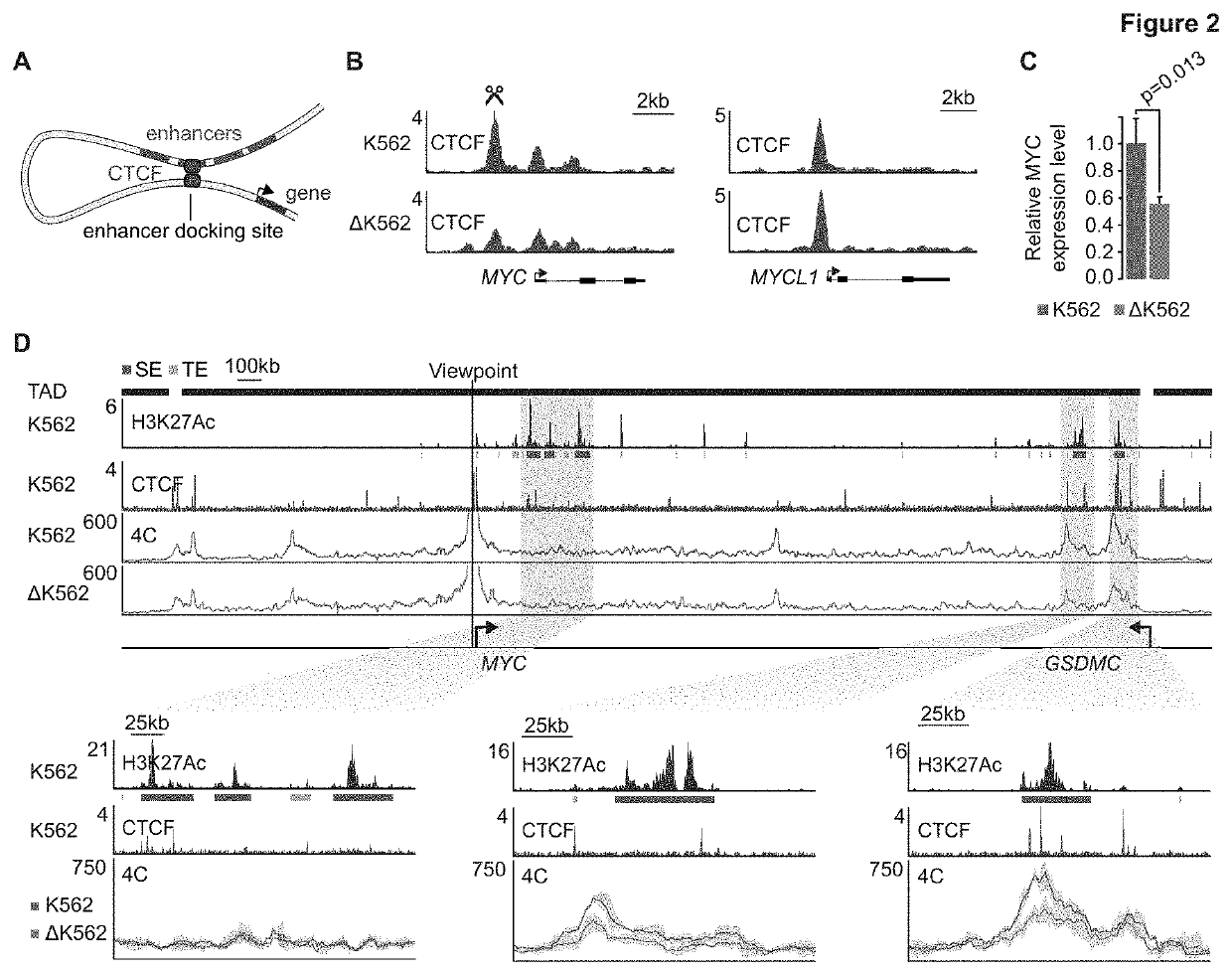
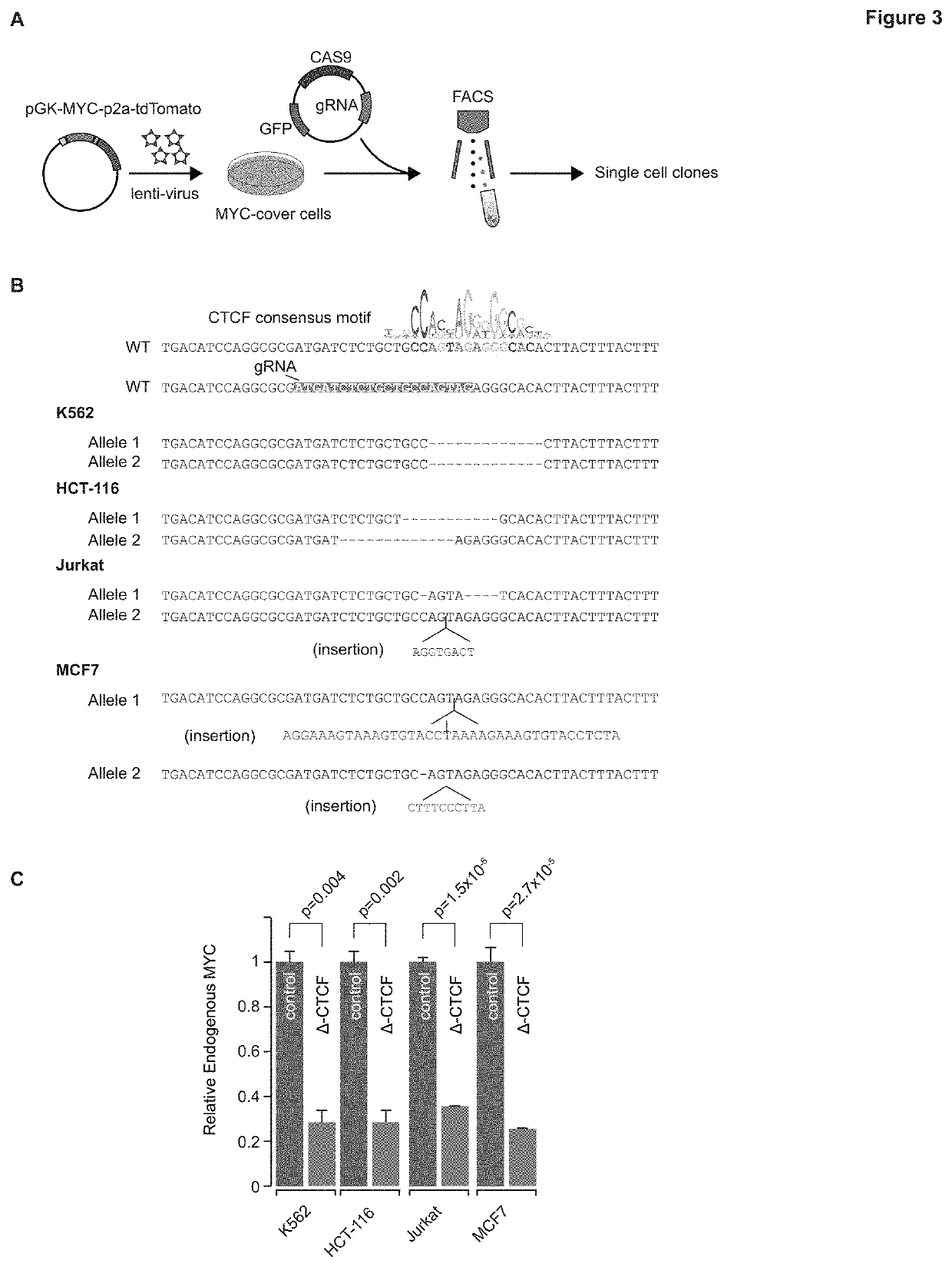
Regulation of transcription through ctcf loop anchors
PendingUS20200149039A1Facilitate oncogenic expression of geneHigh expressionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseBinding site
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Protein SaCas9 antigen epitope and application thereof in gene editing
PendingCN114292830AAddresses immune response issuesNo cleavage effect on functional activityHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsAntigen epitopeDeimmunization
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a mutated Cas9 protein which has the activity of a cleavage gene, the mutation of the mutated Cas9 protein is an antigen epitope capable of reducing immunogenicity, and the mutated Cas9 protein is selected from A144G, E146G, E147G, D161G, G162A, R269G, D270A, E271G, N272G, E273G, P294A, T295A, D309A, P321A, E322G, A337G, R338G, T369A, E378G or short peptide 200-208 TYIDLLETR. The invention further discloses the antigen epitope of the SaCas9 protein and application of the SaCas9 protein in gene editing. The dominant antigen epitope has no influence on SaCas9 protein cleavage function activity, and the human body immune response problem possibly induced by a CRISPR-Cas9 system can be improved through deimmunization transformation of the Cas9 protein.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
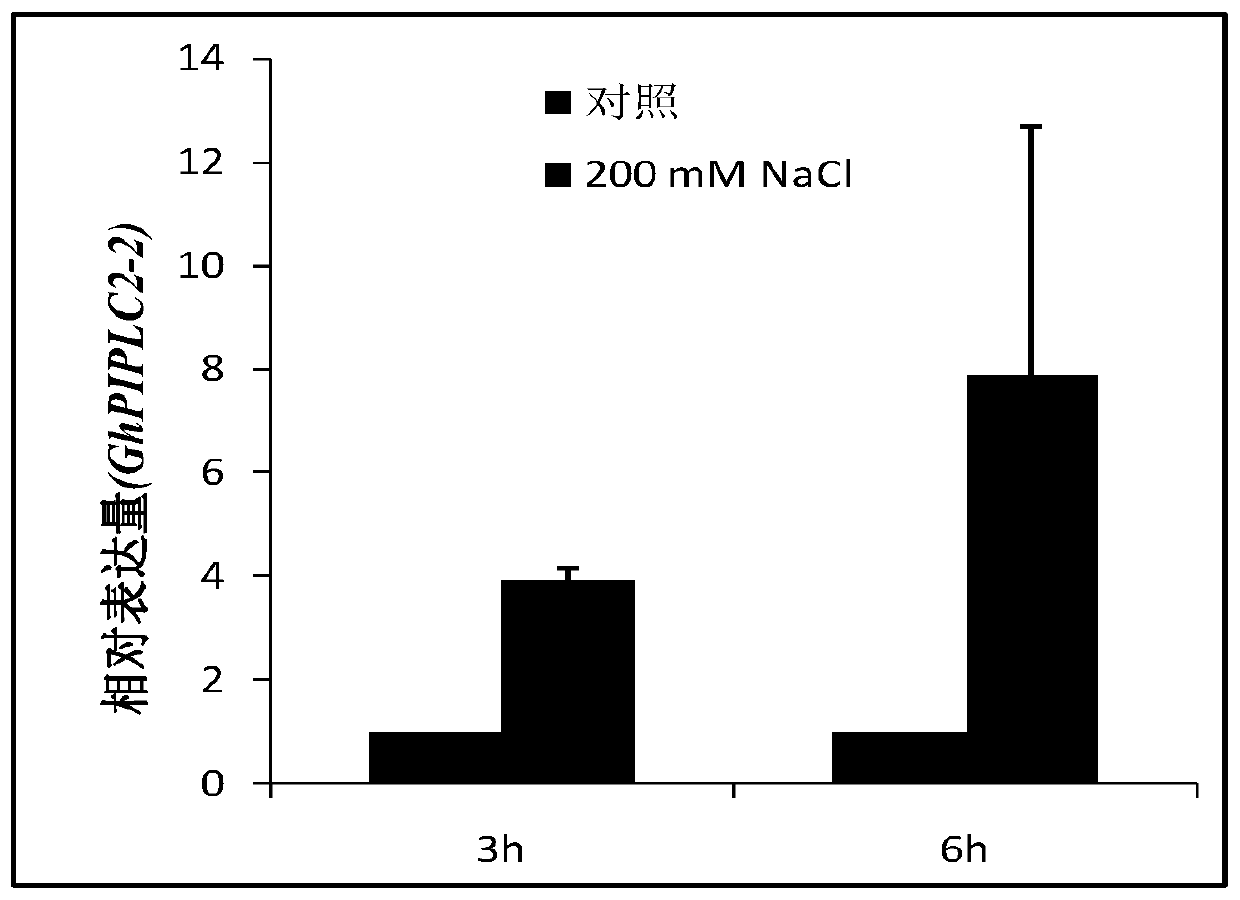
Upland cotton phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C gene GhPIPLC2-2 and application thereof
ActiveCN110804619AHydrolasesFermentationMolecular biologyPhosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Tag removal from proteins expressed in pro- and eukaryotic hosts
ActiveUS20180195056A1High expressionImprove solubilityHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsHost cell filopodiumProtease
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap