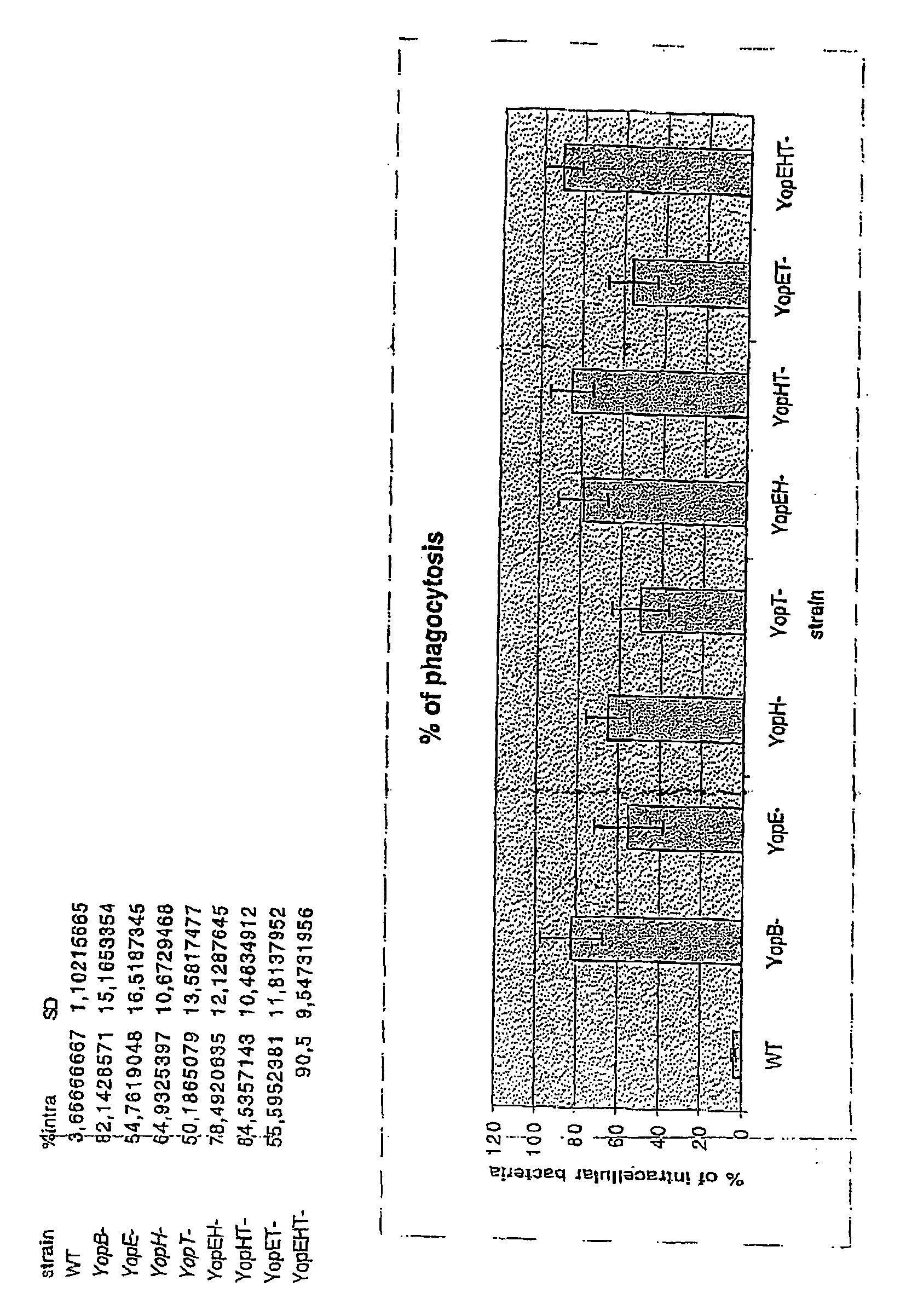
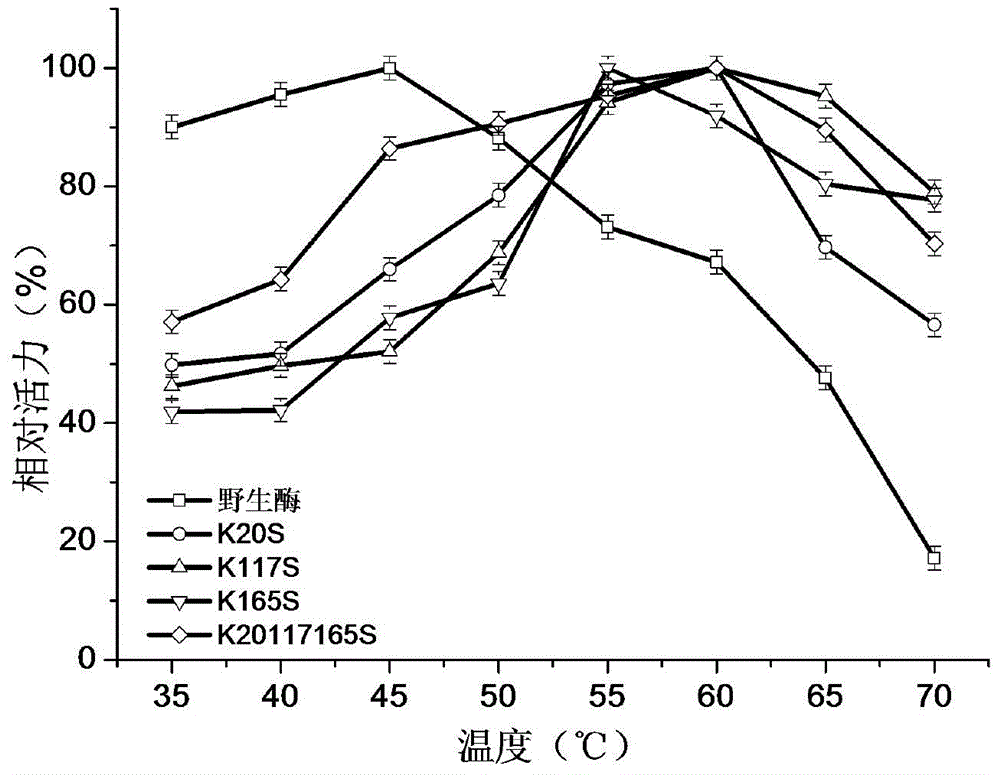
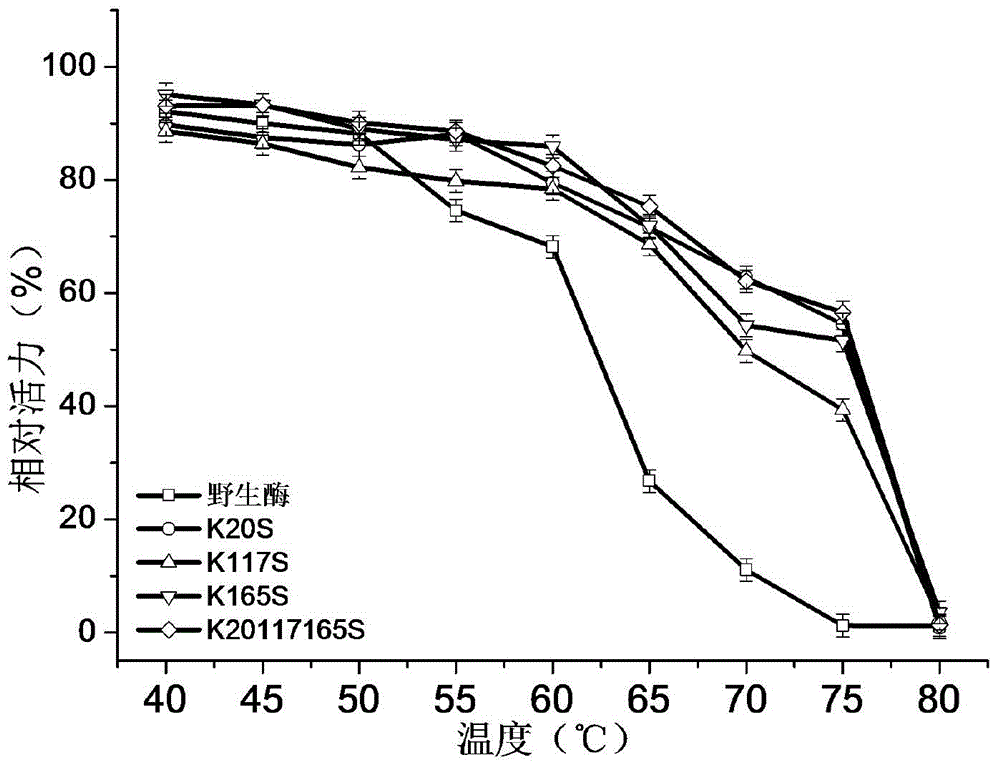
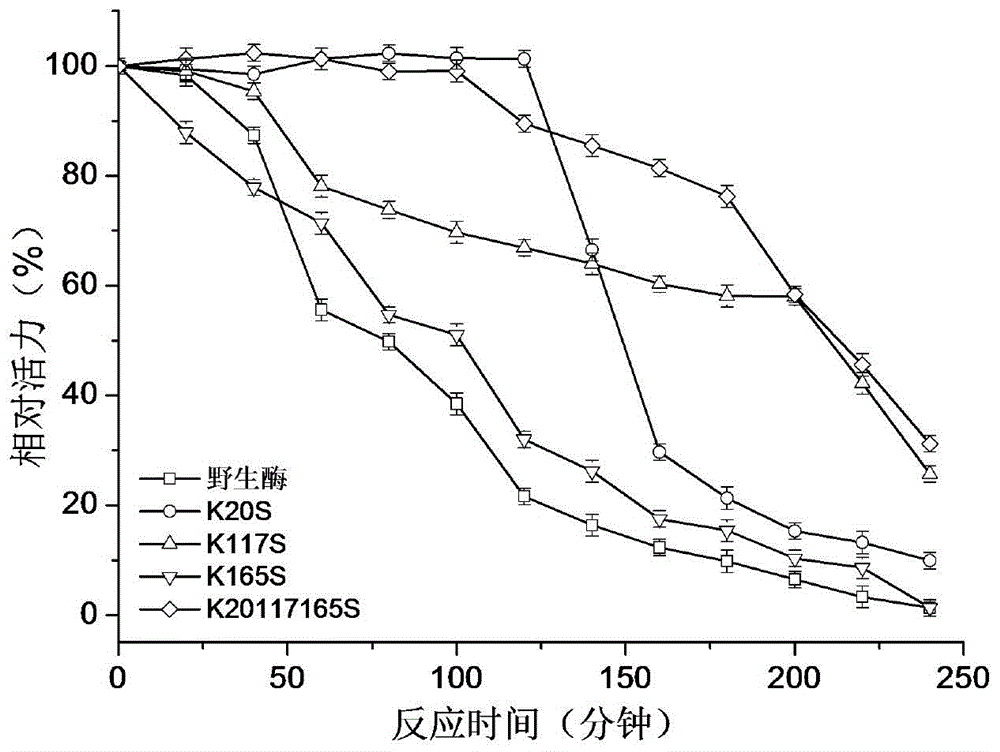
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
21 results about "Mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biology, a mutation is the alteration of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication (especially during meiosis) or other types of damage to DNA (such as may be caused by exposure to radiation or carcinogens), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), or cause an error during other forms of repair, or else may cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.
Protein variants having modified immunogenicity
InactiveUS20050181446A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityDough treatmentHydrolasesEpitopeBinding peptide
The present invention relates to a method of selecting a protein variant having modified immunogenicity as compared to the parent protein comprising the steps obtaining antibody binding peptide sequences, using the sequences to localise epitope sequences on the 3-dimensional structure of parent protein, defining an epitope area including amino acids situated within 5 Å from the epitope amino acids constituting the epitope sequence, changing one or more of the amino acids defining the epitope area of the parent protein by genetical engineering mutations of a DNA sequence encoding the parent protein, introducing the mutated DNA sequence into a suitable host, culturing said host and expressing the protein variant, and evaluating the immunogenicity of the protein variant using the parent protein as reference. The invention further relates to the protein variant and use thereof, as well as to a method for producing said protein variant.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Serum specificity metabolite spectrum for patient with lung cancer, and building method thereof
ActiveCN103616450AEasy to handleStrong qualitative analysis abilityComponent separationGas phaseOriginal data
Owner:HUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Method for predicting and sequencing neoantigens activity based on eigenvalues of tumor neoantigens
ActiveCN107704727AEfficient and accurate screeningSmooth changeProteomicsBiological testingAntigenScreening method
The present invention discloses a method for scoring and sequencing the neoantigens immunological activity based on eigenvalues of tumor neoantigens. The method comprises the following steps of: inputof WGS / WES and RNA-seq sequencing data of tumor-normal samples, prediction and annotation of tumor cellc mutation, and calculation of related eigenvalues; extraction of neoantigens related eigenvalues; setting of a scoring function of the neoantigen activity; and neoantigen sequencing based on the scoring function of the neoantigen activity. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the tumor cell mutation is analyzed and calculated, and the mutation annotation is completed to calculate the partial eigenvalue, and the MHC-I binding neoantigen is predicted to calculate the partial eigenvalue; all eigenvalues related to the tumor neoantigens are extracted so as to set the scoring function of the neoantigen activity, and finally through the scoring function of the neoantigen activity, the neoantigens are sequenced. Compared with the traditional screening method, the method is more efficient and precise, and has important application value for tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:王勇
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
1,3-1,4-Beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN104130988AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaWort preparationMutaseGlucanase
Owner:无锡正元生物科技有限公司
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bacterial strain for eliminating Listeria monocytogenes and application thereof
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
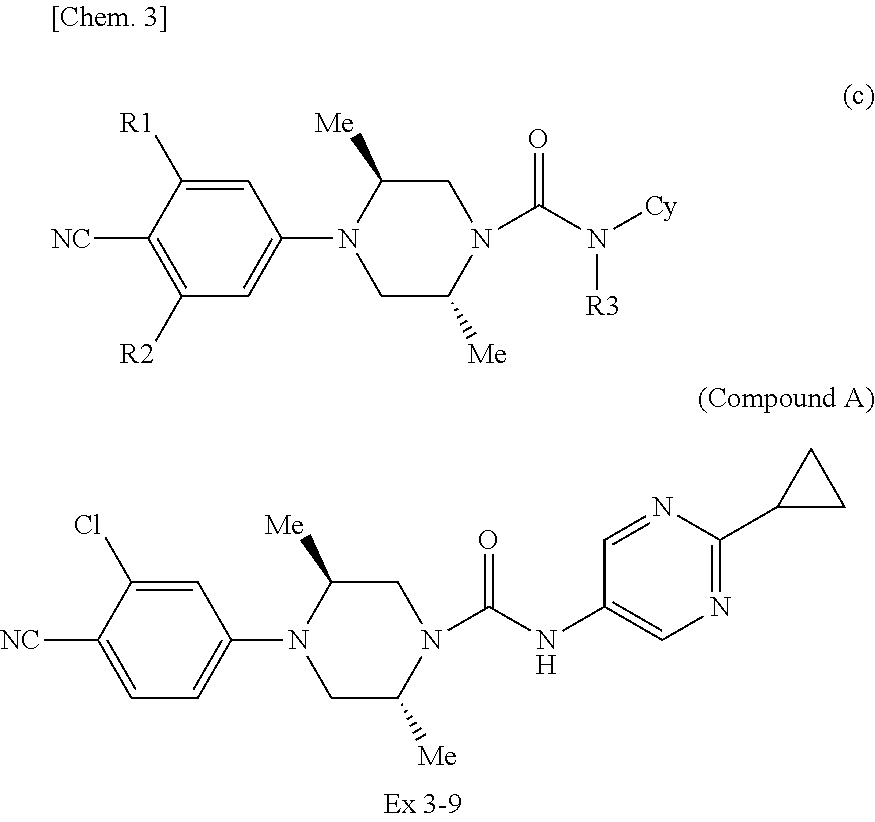
Antagonist for mutant androgen receptor
InactiveUS20130197009A1Excellent antitumor actionSuperior compositionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAntiandrogen AgentsMutation
[Problem] An object of the present invention is to provide a novel anticancer drug which is useful for treating prostate cancer accompanying androgen receptor mutation[Means for Solution] The present inventors conducted thorough research on mutant androgen-related diseases for which the traditional anti-androgen drugs become ineffective. As a result, they found that the compound, which is an active ingredient of the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention, exhibits an inhibitory action against transcriptional activation in a human mutant androgen receptor (AR), and has an excellent antitumor action in a human prostate cancer-bearing mouse, thereby completing the present invention. Accordingly, the compound, which is an active ingredient of the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention, is useful for a series of androgen receptor-related diseases including prostate cancer.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Artificial synthesised scorpion chloride ion neurotoxin gene-rBmK CTa
The invention makes 24-site mutation on natural scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin gene BmK CT according to the principle of Escherichia coli partial to codon, designs DNA sequence suitable to be expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), adopts PCR technique to complete artificial synthesis of recombinant scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin gene rBmK CTa. On this basis, it clones rBmK CTa into pEXSecI expression system to transfer in the BL21 (DE3), screens and obtains high-performance expressed bacterial strain, detects that the expressed product of the rBmK CTa accounts for 19.936% of the all-bacterium protein by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and by affinity chromatography, obtains purer protein with bioactivity, and can obtain 2.4mg protein from one liter culture liquor by purifying. The obtained modified recombinant scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin has inhibition effect on neuroglia cell and can be used in preparing medicines curing diseases by inhibiting neuroglia cell and also be used in research on the space structure and pharmacological activity of scorpion neurotoxin.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
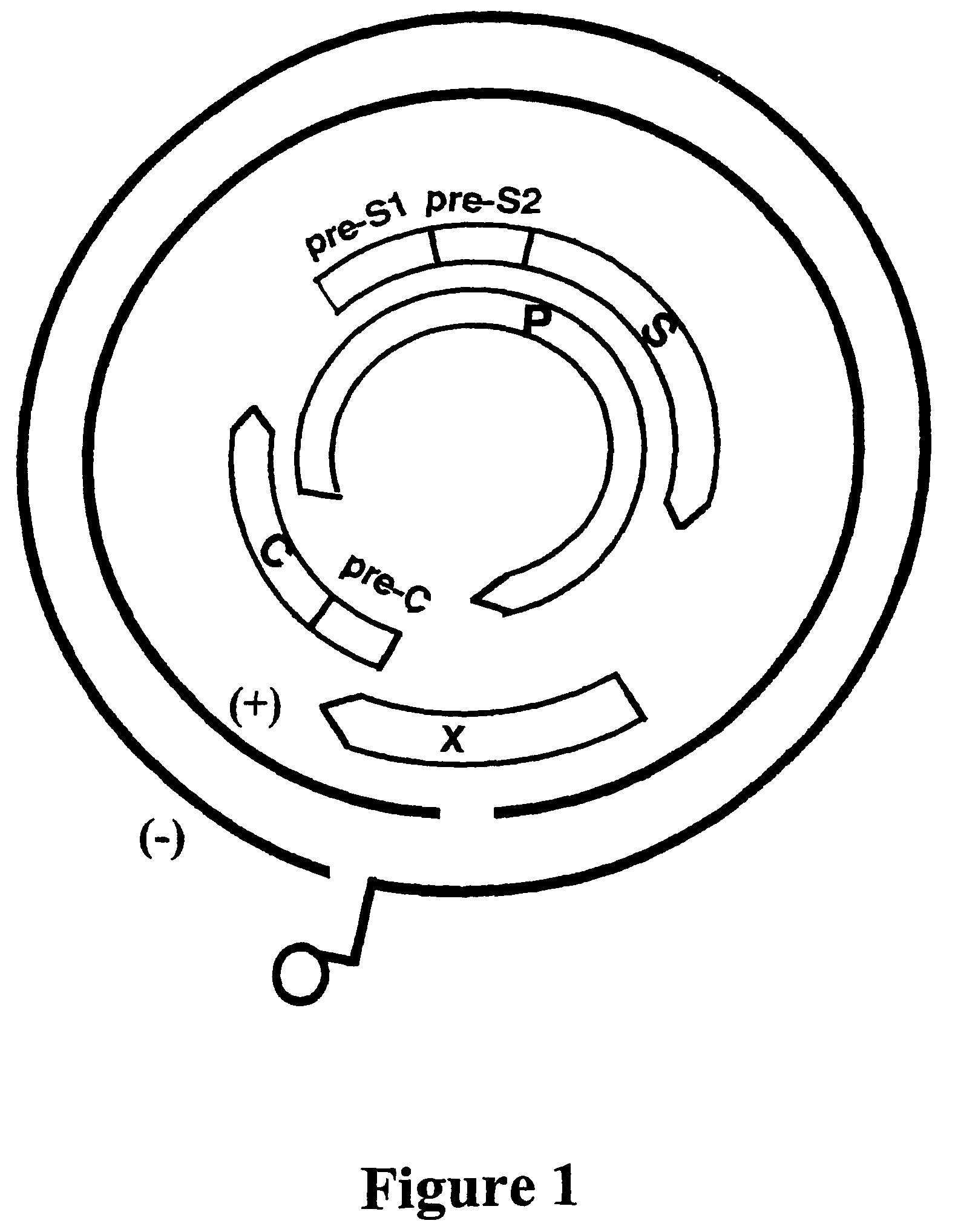
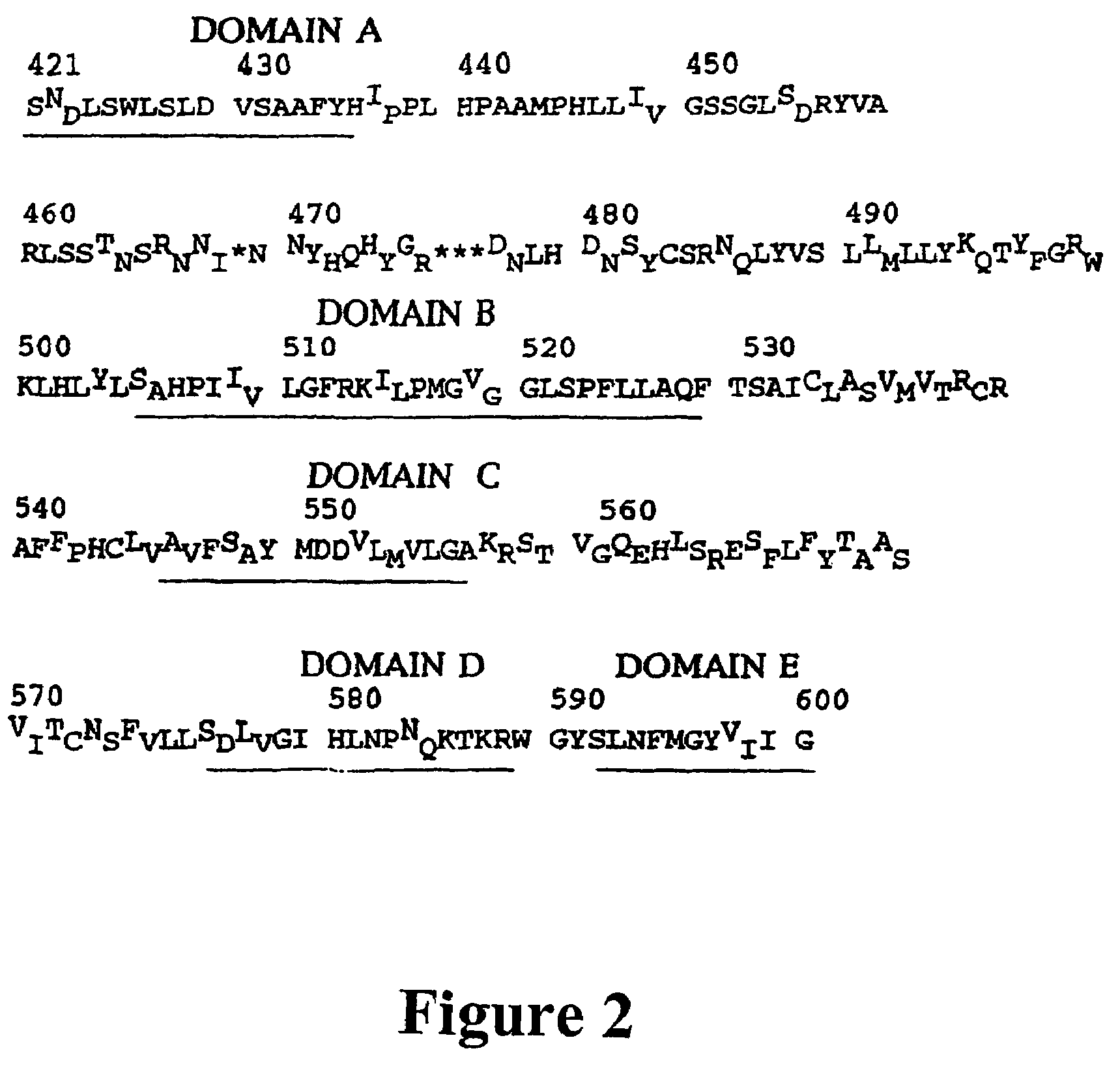
Hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase and surface antigen variants and methods of using same
Owner:ABL SA +2
Bacterium for stably producing 2,3-butanediol at high yield and method for compound mutation by using low-temperature plasma and diethyl sulfate
The invention discloses enterobacter cloacae for stably producing 2,3-butanediol at high yield and a method for compound mutation by using low-temperature plasma and diethyl sulfate. The enterobacter cloacae is classified and named as Enterobacter cloacae DLM and has the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 6053. The mutation method is characterized in that bacterium is suspended into physiological saline and pretreatment of diethyl sulfate and compound mutation of the low-temperature plasma and the diethyl sulfate are sequentially carried out. The strain can be used for producing the 2,3-butanediol by fermenting different effectively-utilized carbon sources, wherein the conversion rate of sugar is high and the concentration of the 2,3-butanediol is high; and when glucose or synanthrin is hydrolyzed into a carbon source, the concentrations of the 2,3-butanediol in a 5L fermentation tank respectively reach 125.2g / l and 120.2g / l. The mutation method used in the invention has the characteristics of simpleness and feasibility in operation, short treatment time in mutation and the like and provides a reliable method for mutation breeding of microorganisms.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and kit for detecting Helicobacter pylori drug resistance gene mutations
ActiveCN111996273AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenes mutationMultiplex
The invention provides a method and kit for detecting Helicobacter pylori drug resistance gene mutations. Specifically, the method detects drug resistance gene site mutations of five commonly used Helicobacter pylori antibiotics (including clarithromycin, metronidazole, quinolones, amoxicillin and tetracycline) based on multiplex PCR-Time-of-flight mass spectrometry, and matching primer and probecombinations and the kit are provided.
Owner:BEIJING JIANWEI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +1
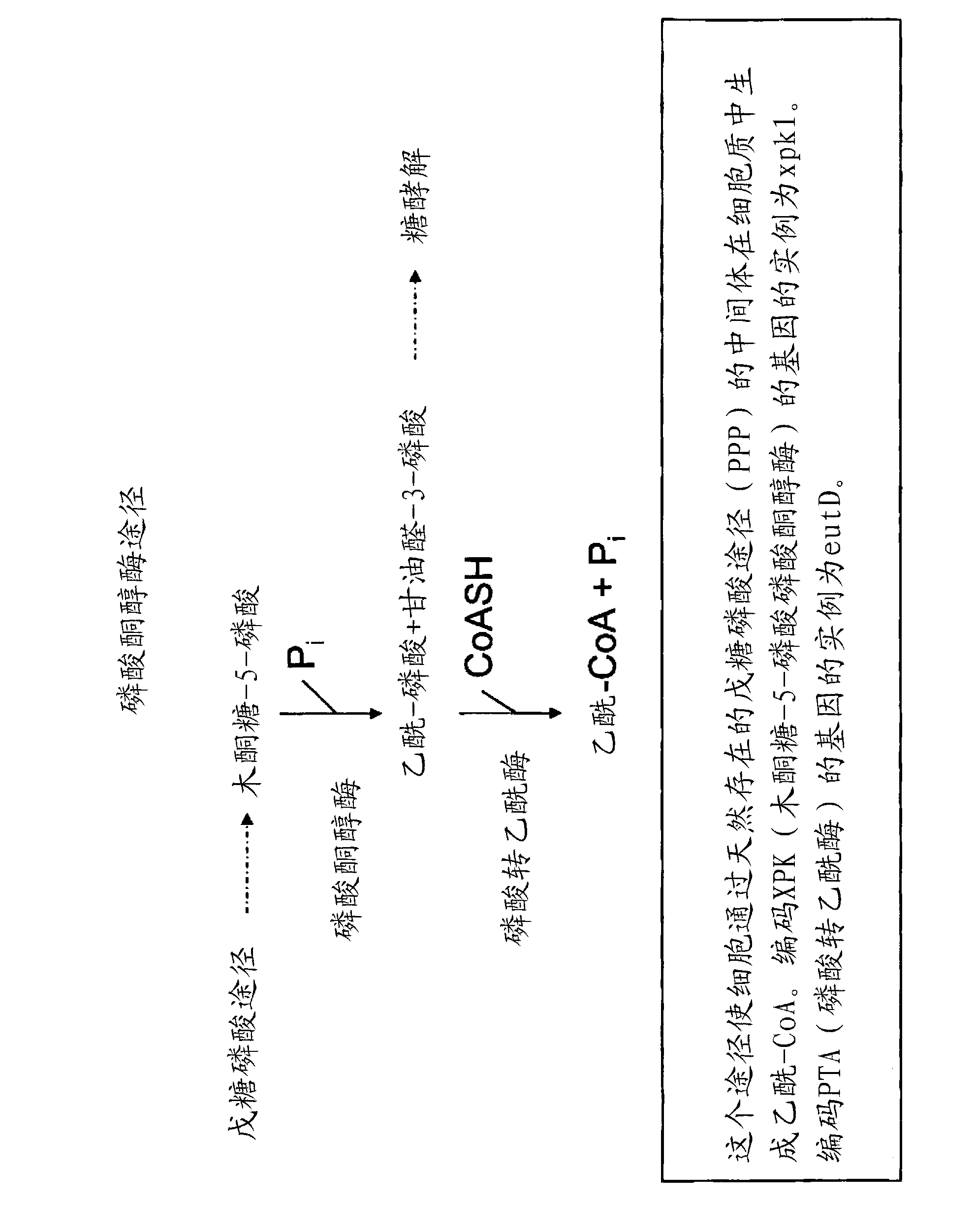
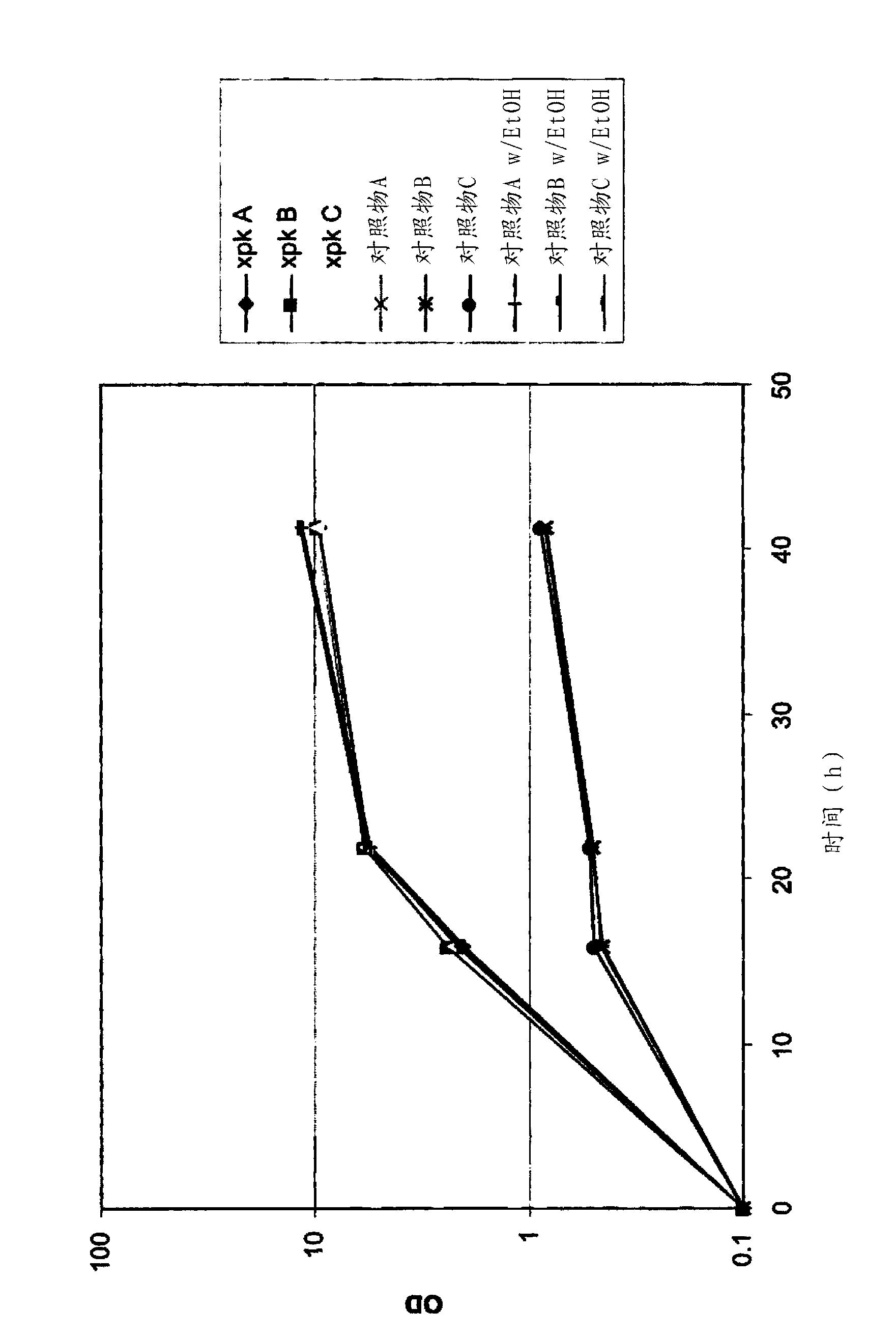
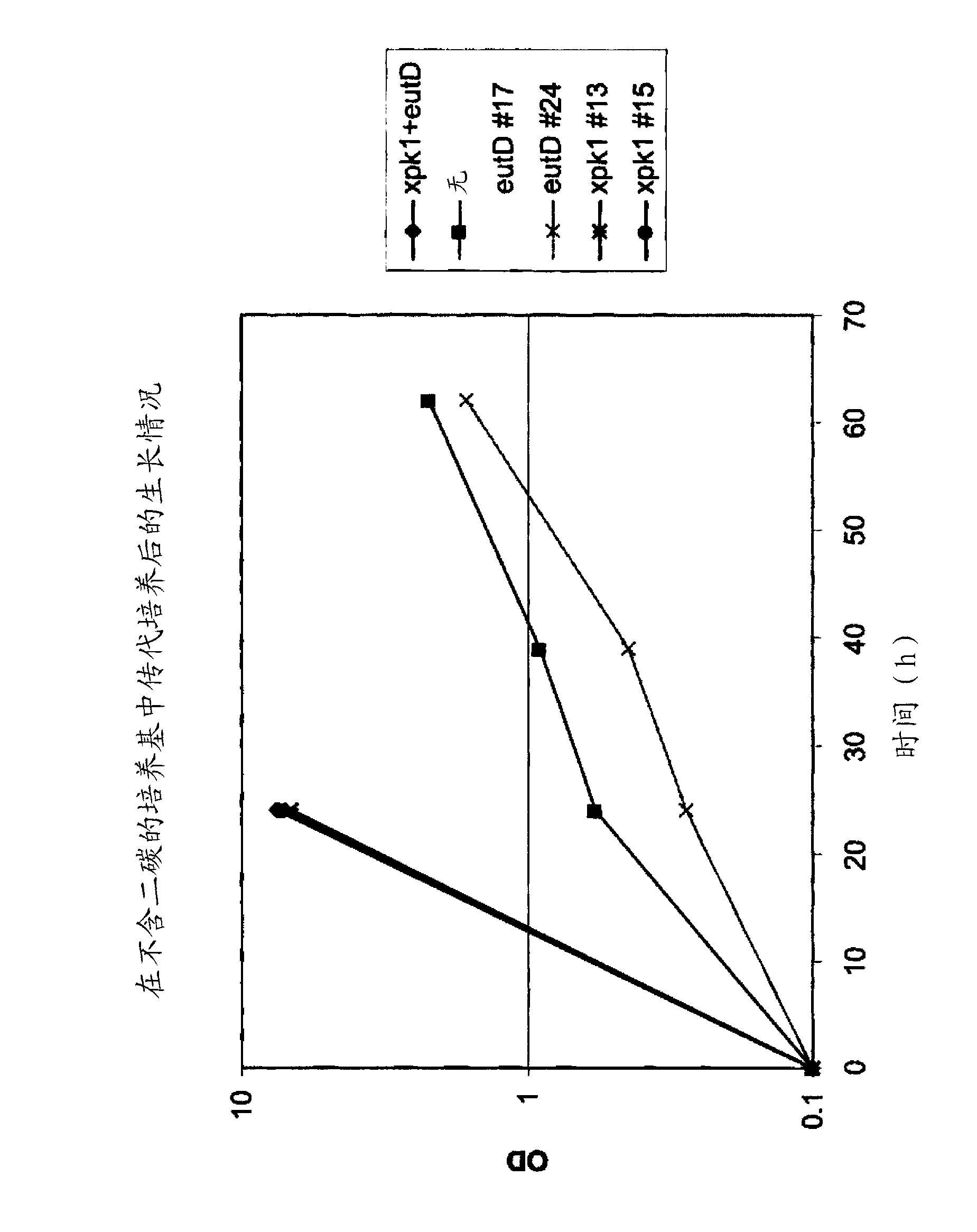
Recombinant host cells comprising phosphoketolases
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
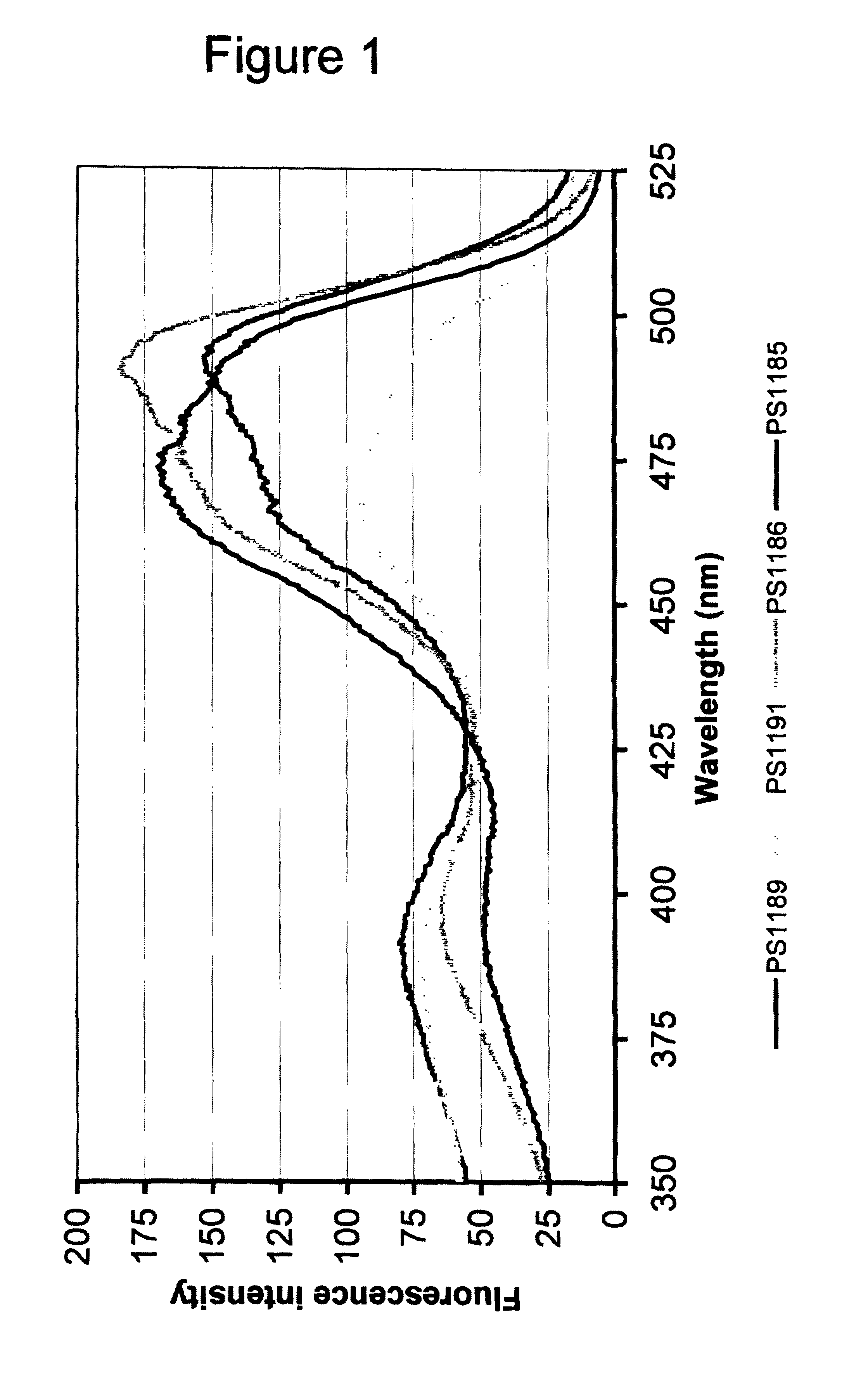
Fluorescent proteins
Owner:FISHER BIOIMAGE
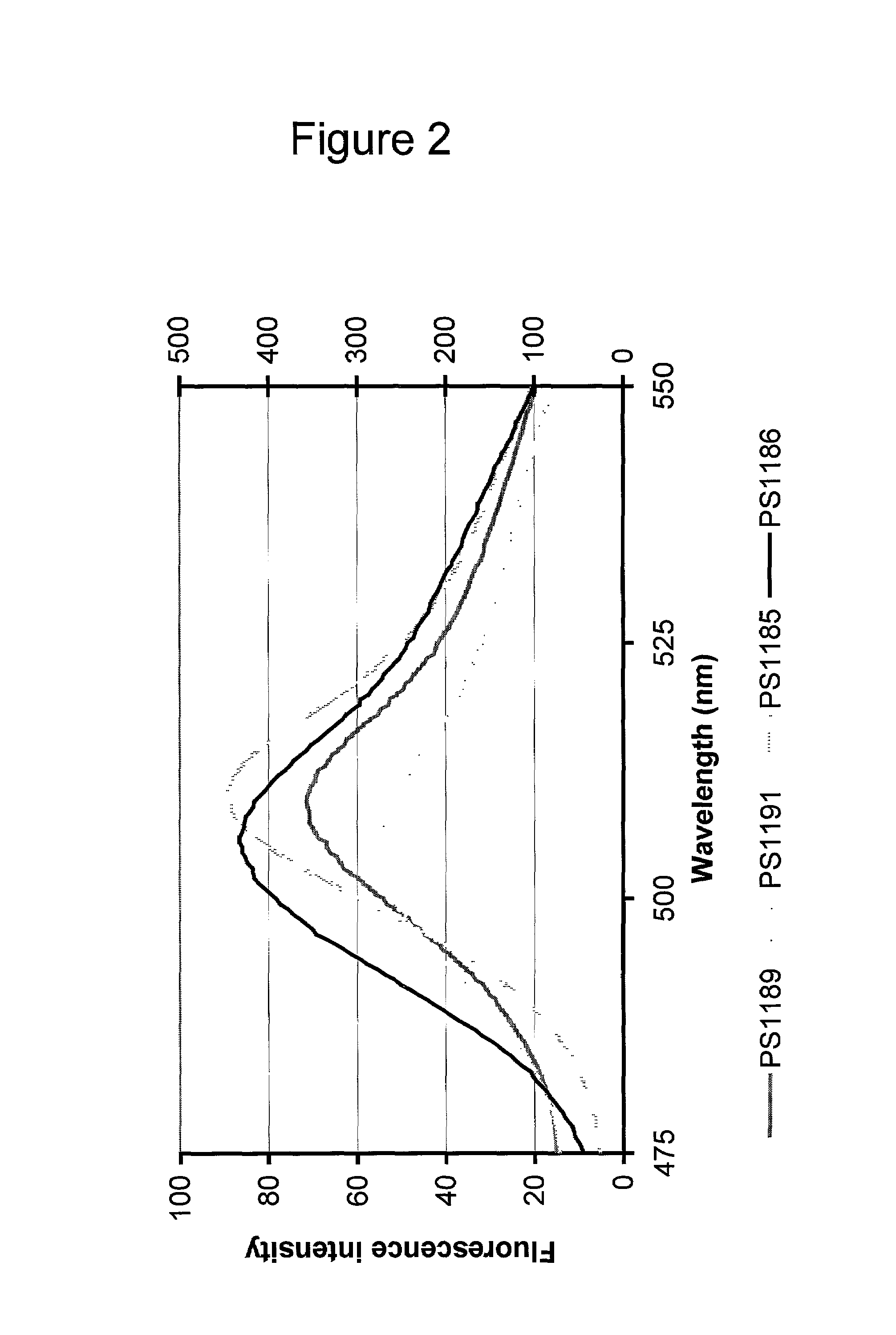
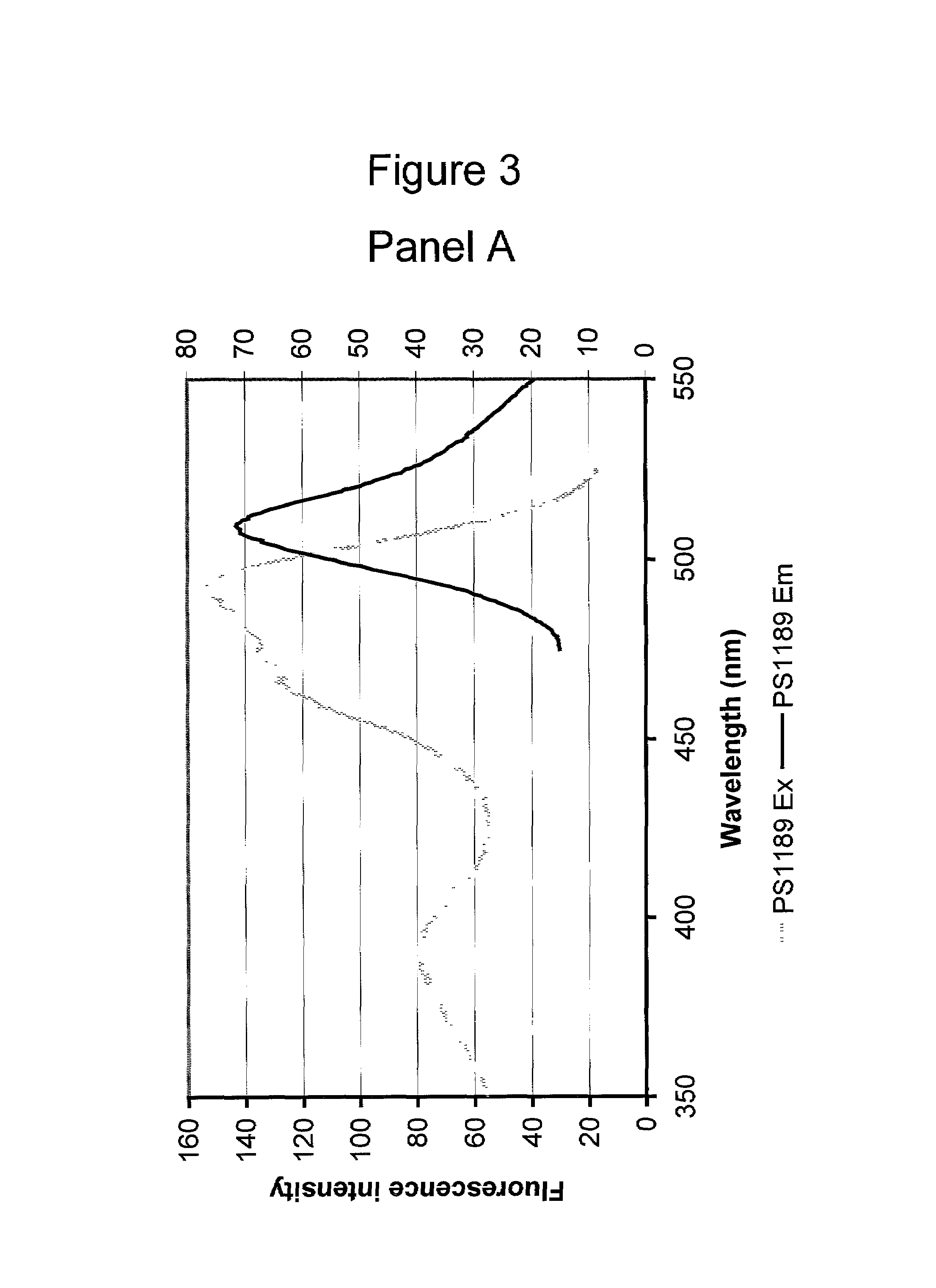
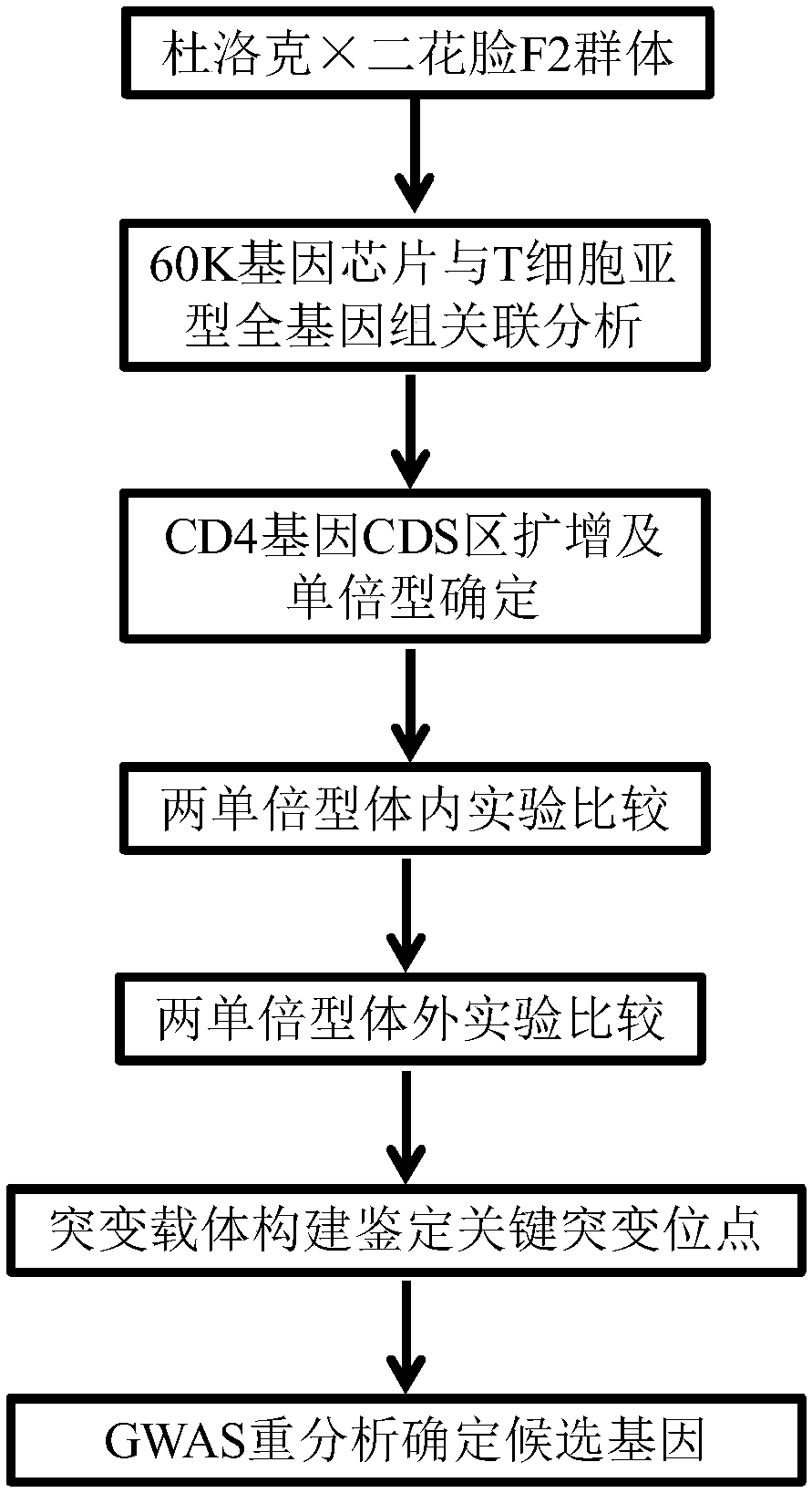
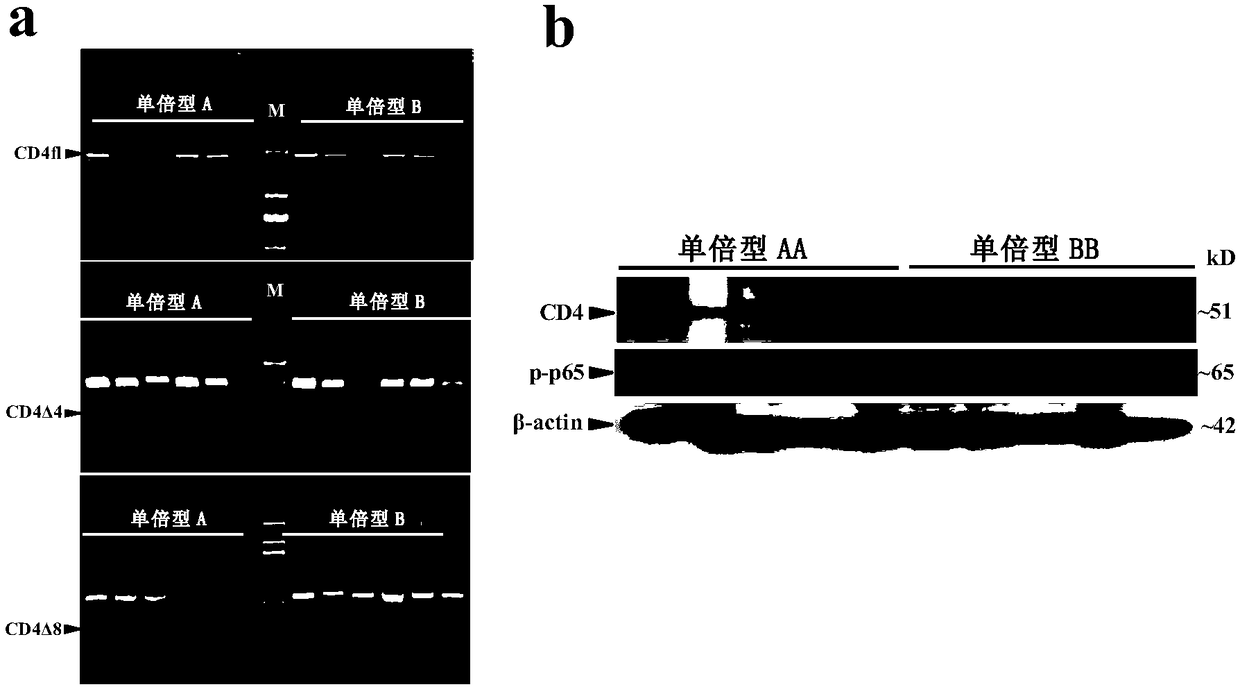
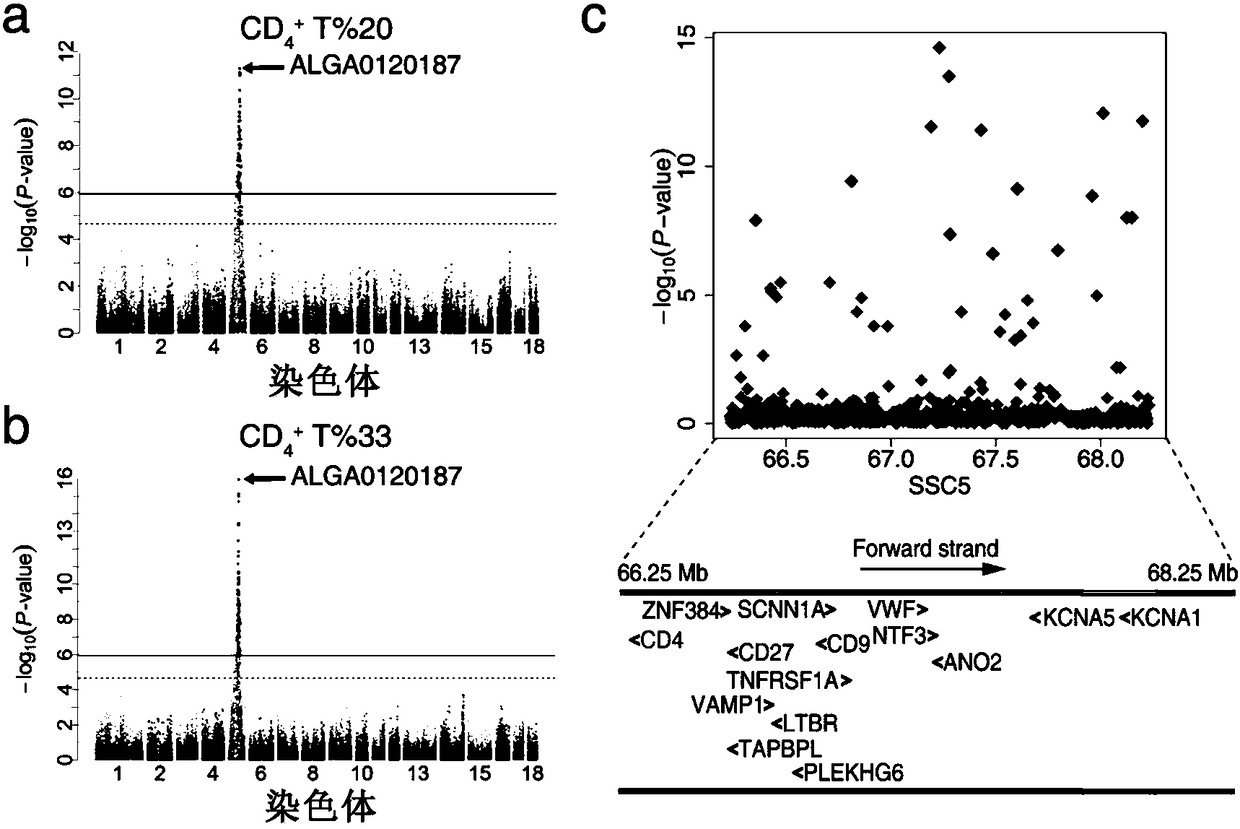
Identification and application of pig CD4 gene function mutation site molecular breeding marker
ActiveCN109423522AMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesMarker-assisted selectionMolecular breeding
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Acquiring method and device for mutation sites of genes corresponding to digestive system
InactiveCN106503488AIdentify base mutationsProteomicsGenomicsFile comparisonMULTIPLE VARIATIONS
The application provides an acquiring method and device for mutation sites of genes corresponding to digestive system, and relates to the technical filed of biological information. The method comprises the steps of conducting data comparison between a plurality of short sequences of the genes to be tested and the reference genome to obtain the preliminary variation site information of the genes to be tested; omitting the variation sites which don't meet the preset reservation requirements in the preliminary variation sites according to the preliminary variation site information, and taking the variation sites, obtained after omitted, in the genes to be tested as genes to be inspected; conducting comparison between the genes to be inspected and the multiple mutation sites of the genes corresponding to the digestive system in a digestive system gene pool; obtaining the site mutation conditions of the genes corresponding to the digestive system in the genes to be tested when the mutation sites which have the same positions and mutation basic groups as the mutation sites in the digestive system gene pool exist in the genes to be inspected. The acquiring method and device for the mutation sites of the genes corresponding to the digestive system can acquire the mutation conditions of multiple variation sites, in the variation sites of the genes to be tested, corresponding to the digestive system.
Owner:CHENGDU XINYUN DECODING TECH CO LTD
Protein SaCas9 antigen epitope and application thereof in gene editing
PendingCN114292830AAddresses immune response issuesNo cleavage effect on functional activityHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsAntigen epitopeDeimmunization
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a mutated Cas9 protein which has the activity of a cleavage gene, the mutation of the mutated Cas9 protein is an antigen epitope capable of reducing immunogenicity, and the mutated Cas9 protein is selected from A144G, E146G, E147G, D161G, G162A, R269G, D270A, E271G, N272G, E273G, P294A, T295A, D309A, P321A, E322G, A337G, R338G, T369A, E378G or short peptide 200-208 TYIDLLETR. The invention further discloses the antigen epitope of the SaCas9 protein and application of the SaCas9 protein in gene editing. The dominant antigen epitope has no influence on SaCas9 protein cleavage function activity, and the human body immune response problem possibly induced by a CRISPR-Cas9 system can be improved through deimmunization transformation of the Cas9 protein.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Detecting tumor mutation burden with RNA substrate
Owner:GENECENTRIC THERAPEUTICS INC +1
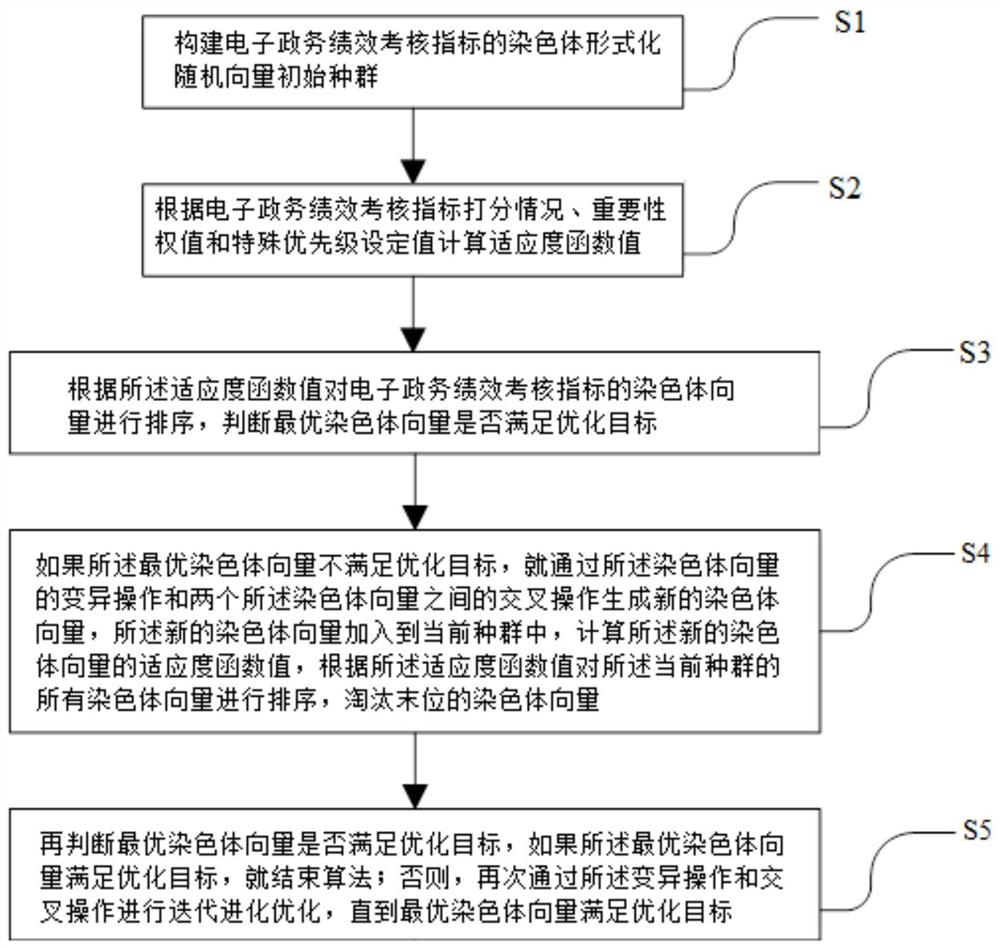
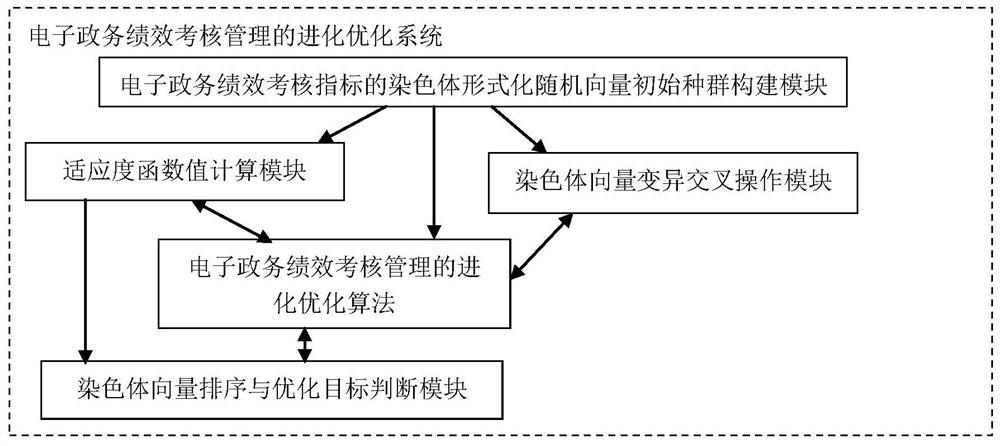
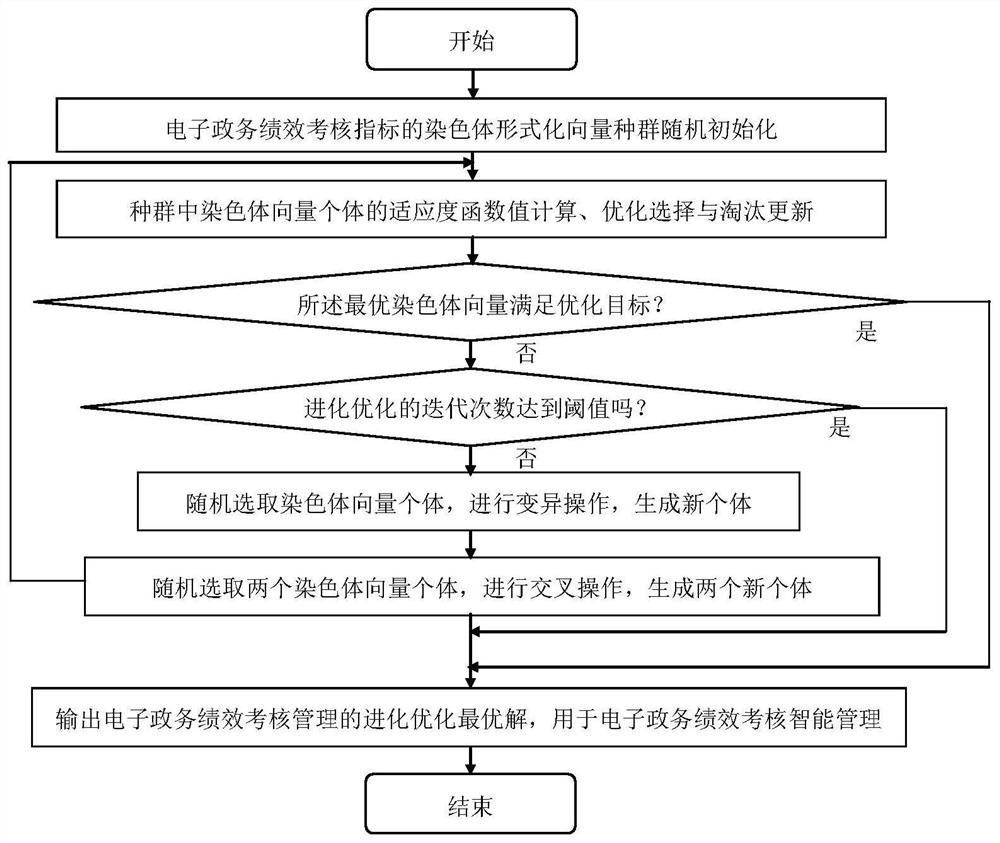
Evolutionary optimization method and system for e-government affair performance assessment management
Owner:昆山翦统智能科技有限公司
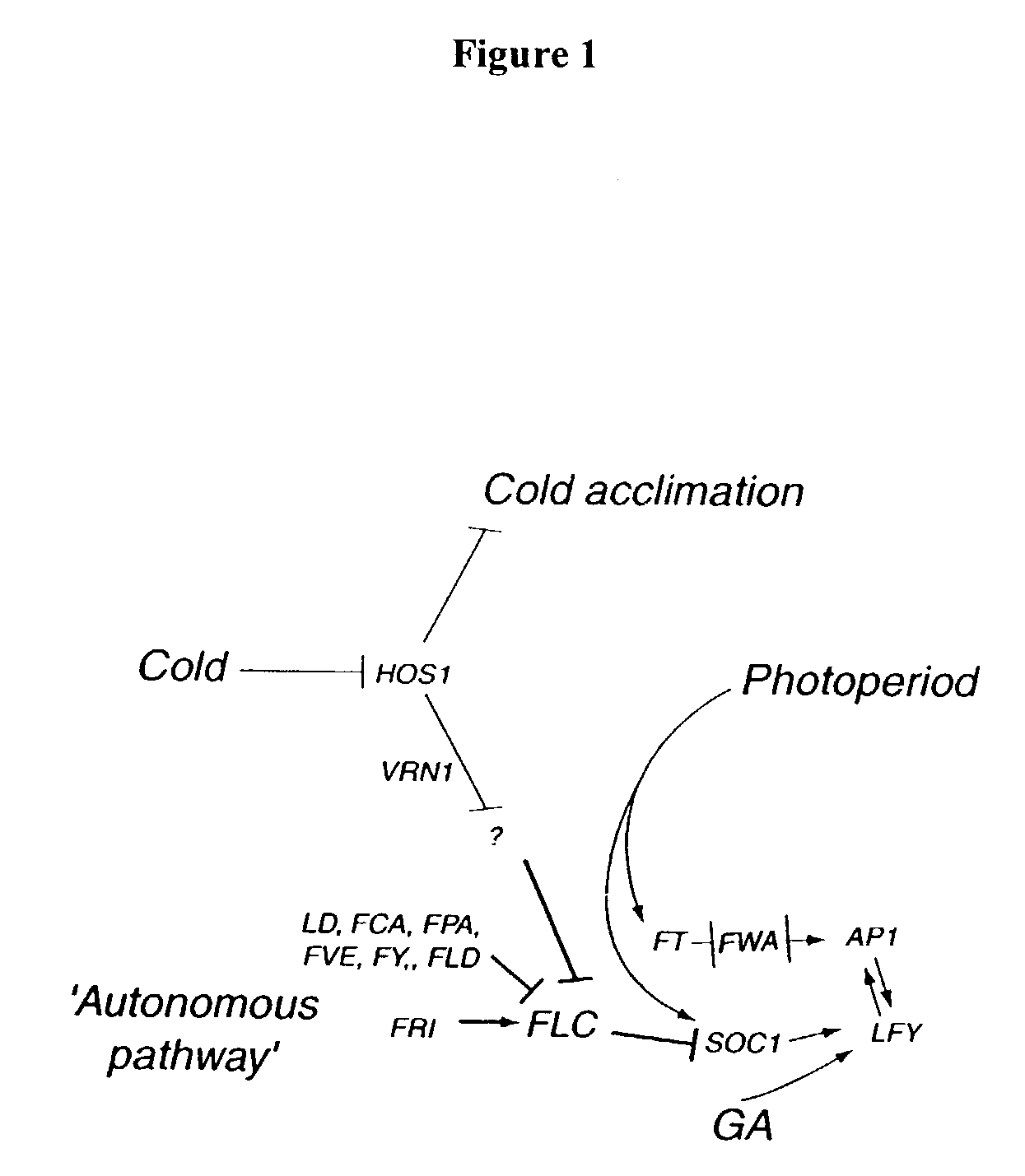
Plant vernalization independence (VIP) genes, proteins, and methods of use
InactiveUS7365182B2Decreased FLC RNA expressionEarly floweringSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesMutantVernalization
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
DNA library for detecting and diagnosing corneal dystrophy disease-causing genes as well as application of DNA library
PendingCN110714066AAccurate diagnosisAuxiliary clinical diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDescemets MembraneDisease
Owner:福州福瑞医学检验实验室有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap