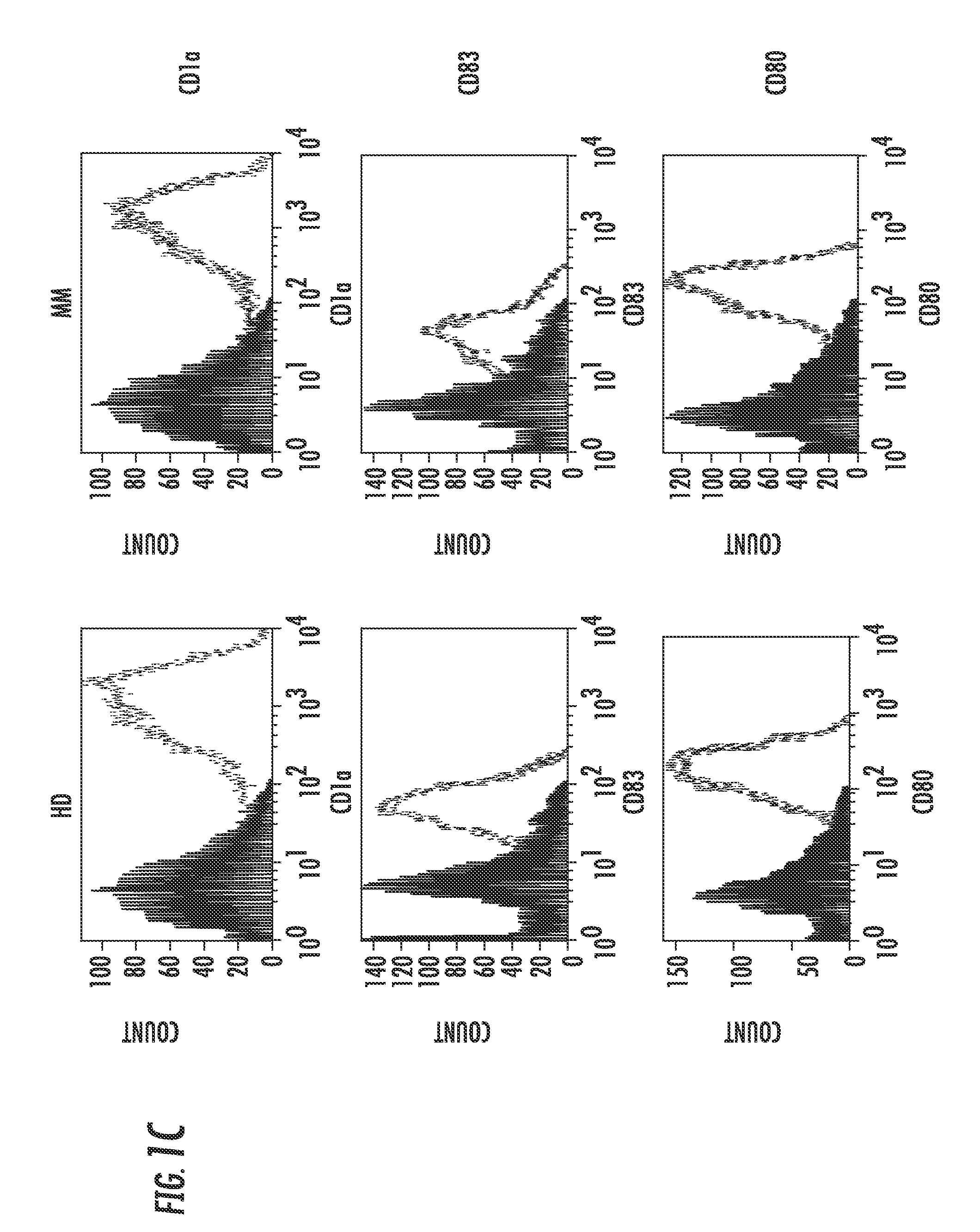
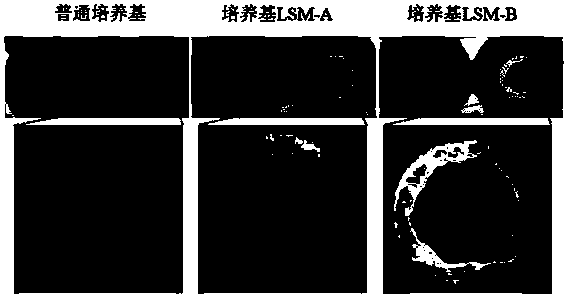
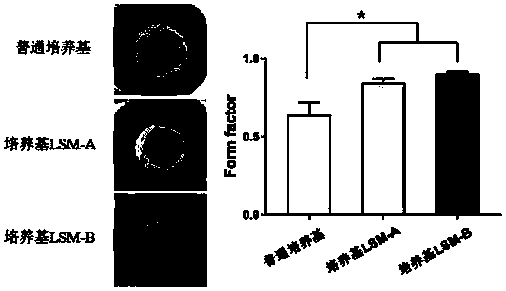
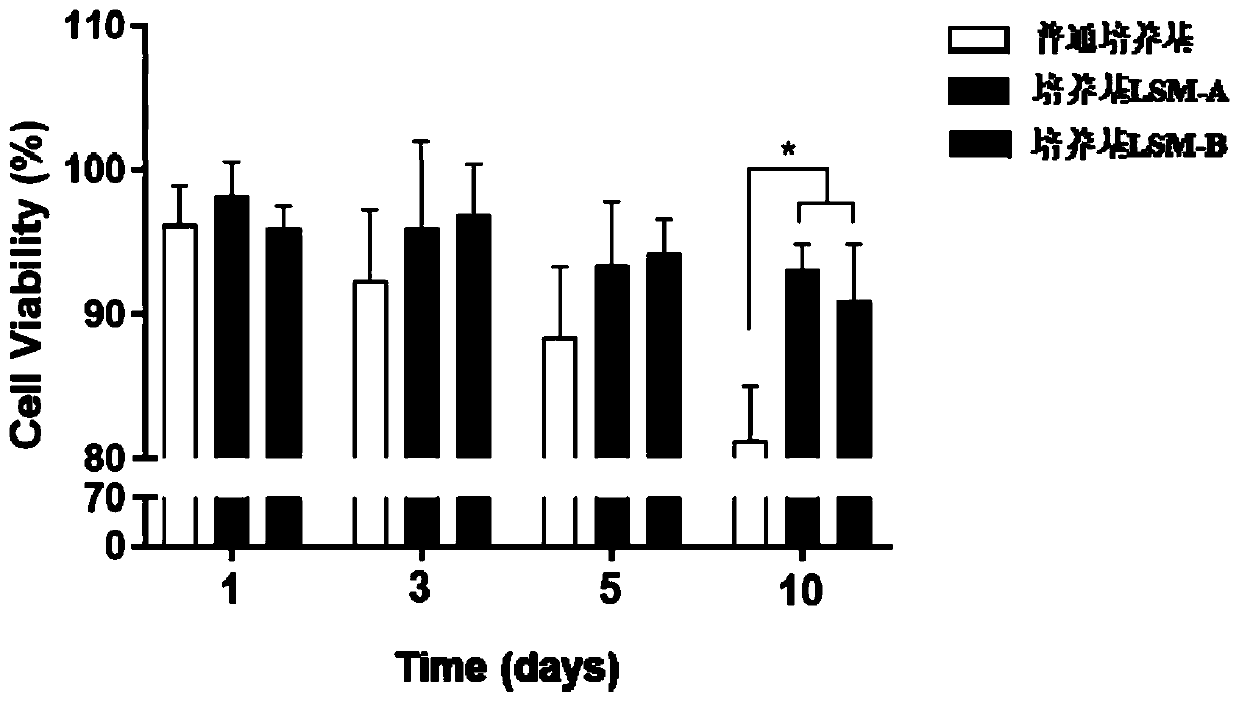
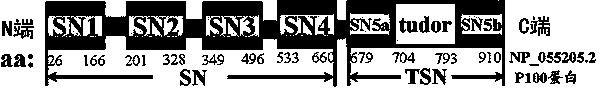Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171 results about "Molecular biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular biology /məˈlɛkjʊlər/ is a branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity between biomolecules in the various systems of a cell, including the interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins and their biosynthesis, as well as the regulation of these interactions.
Methods and compositions related to peptides and proteins with c-terminal elements
ActiveUS20090226372A1Powder deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementCell selectivityPeptide sequence
Disclosed are compositions and methods useful for targeting and internalizing molecules into cells of interest and for penetration by molecules of tissues of interest. The compositions and methods are based on peptide sequences that are selectively internalized by a cell, penetrate tissue, or both. The disclosed internalization and tissue penetration is useful for delivering therapeutic and detectable agents to cells and tissues of interest.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
Selective Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Derived Protein Profiles for Cancer and other Pathologic Entities
InactiveUS20130288233A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein profilingDiagnostic test
The invention relates to a method of detecting and quantifying small peptides derived from proteins from a range of different clinical samples using the Selective Reaction Monitoring (SRM) profiling technique. By targeting these unique peptides which specifically identify particular proteins, the present invention enables multiple samples to be run in a multiplexed fashion in order to identify, diagnose, quantitate and profile a full range of benign and pathologic entities, including but not limited to, the complete range of cancers and the spectrum of inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory cell typing and bone marrow cell typing. The SRM assay is capable of performing clinical blood typing and it can also act as a diagnostic test to identify women at highest risk for cervical cancer base on Human Papillomavirus (HPV) testing.
Owner:MAP DIAGNOSTICS PTY LTD
Serum-free culture system for efficiently culturing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro
InactiveCN104164405AGood repeatabilityImprove passaging stabilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntioxidantCytokine
The invention relates to a serum-free culture system for efficiently culturing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. The serum-free culture system comprises the following components: a basal culture medium a-MEM, cell factors, hormones and proteins, unsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, energy substances, an amino acid additive, vitamins and metal additives. The serum-free culture system comprises simple and clear components, is free from harms of pathogens, does not have difference between batches, has good repeatability, can obtain plenty of high-quality human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a short time and has high passage stability, so that the serum-free culture system can be applied to scientific researches and can provide high-purity vibrant cells for cell therapy as a mating system in cell therapy.
Owner:CYAGEN BIOSCI INC
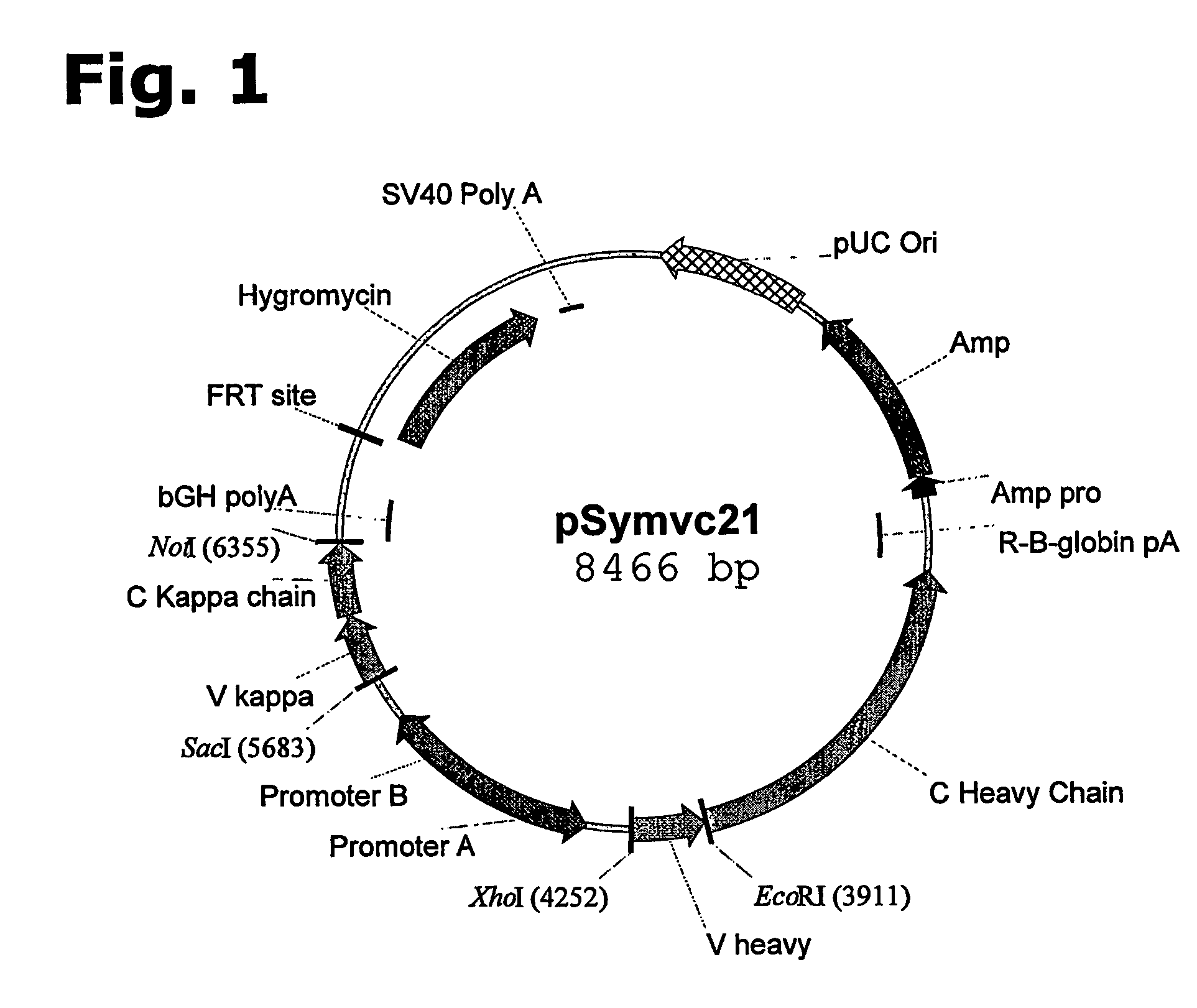
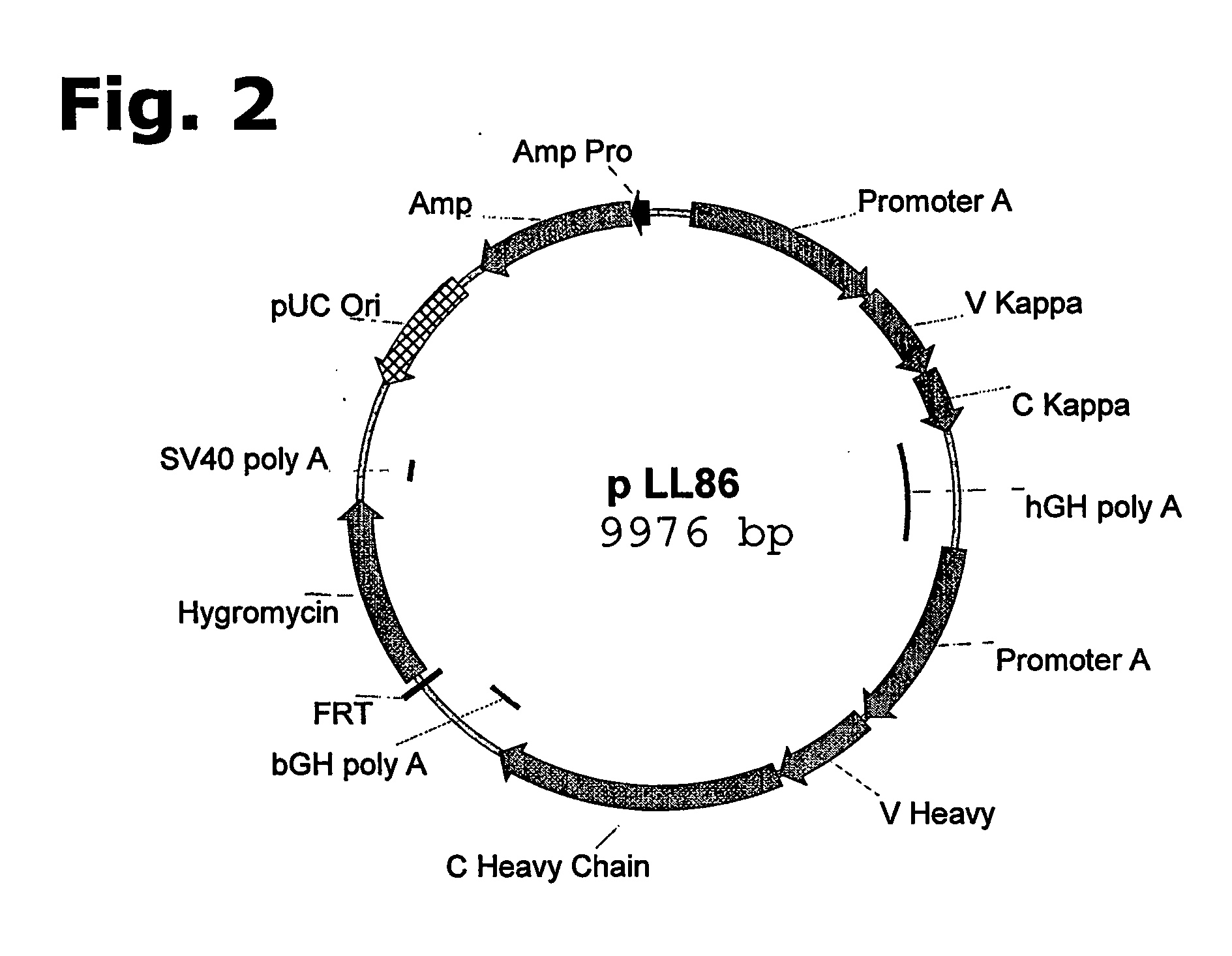
Method for manufacturing recombinant polyclonal proteins
InactiveUS20060275766A1Minimizing unwanted batch-to-batch variationPeptide librariesImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPresent methodPlasma derived
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
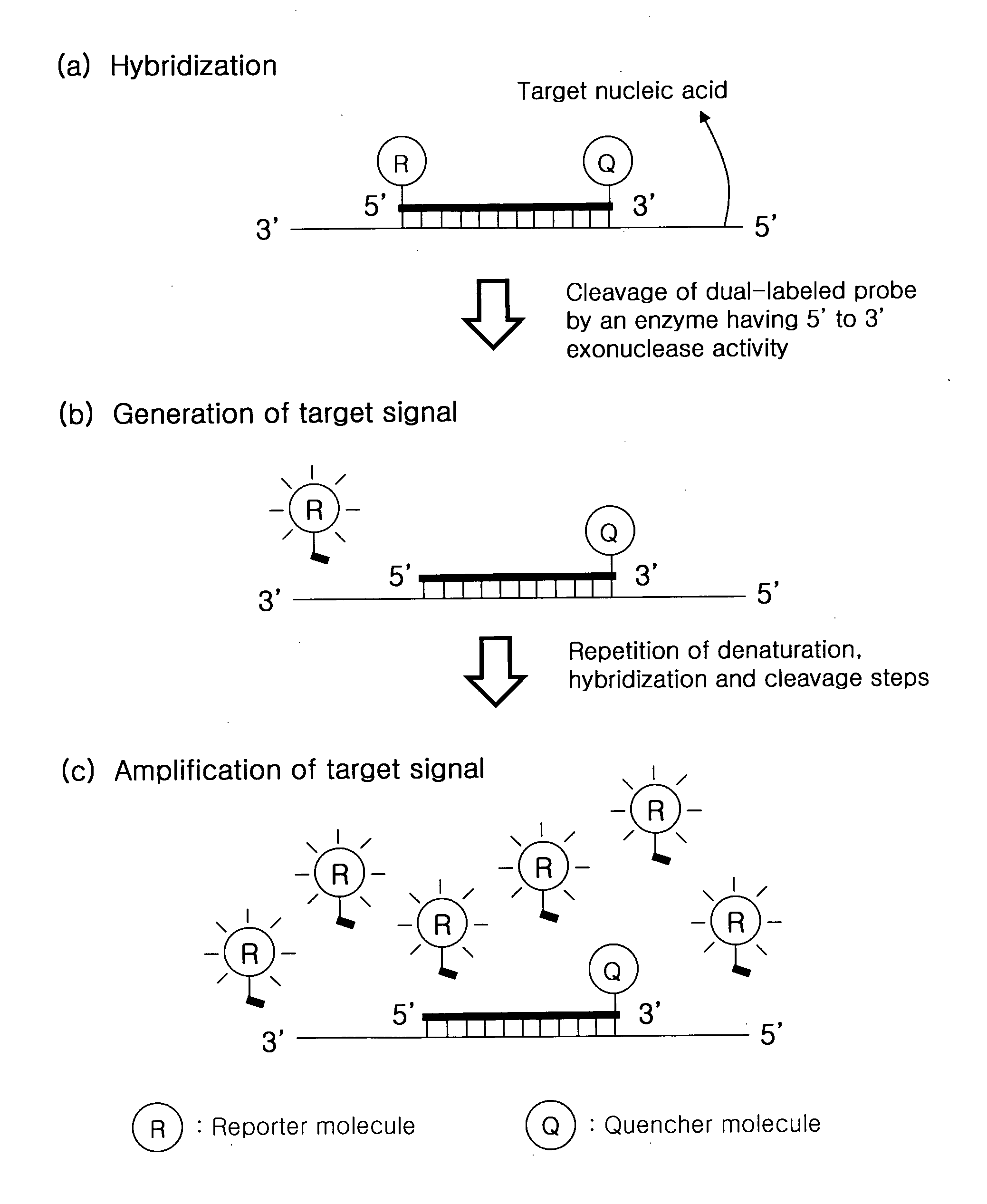
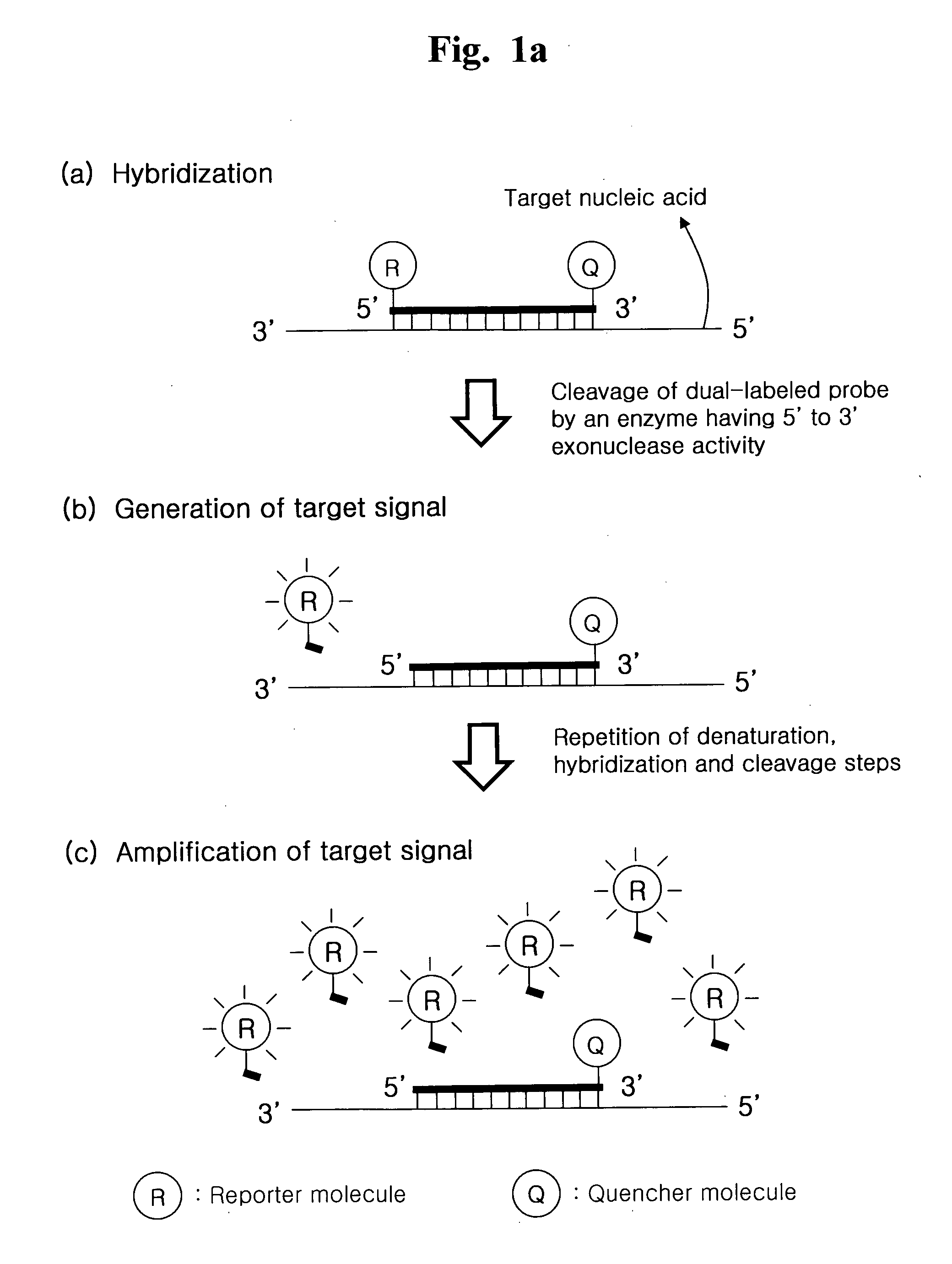
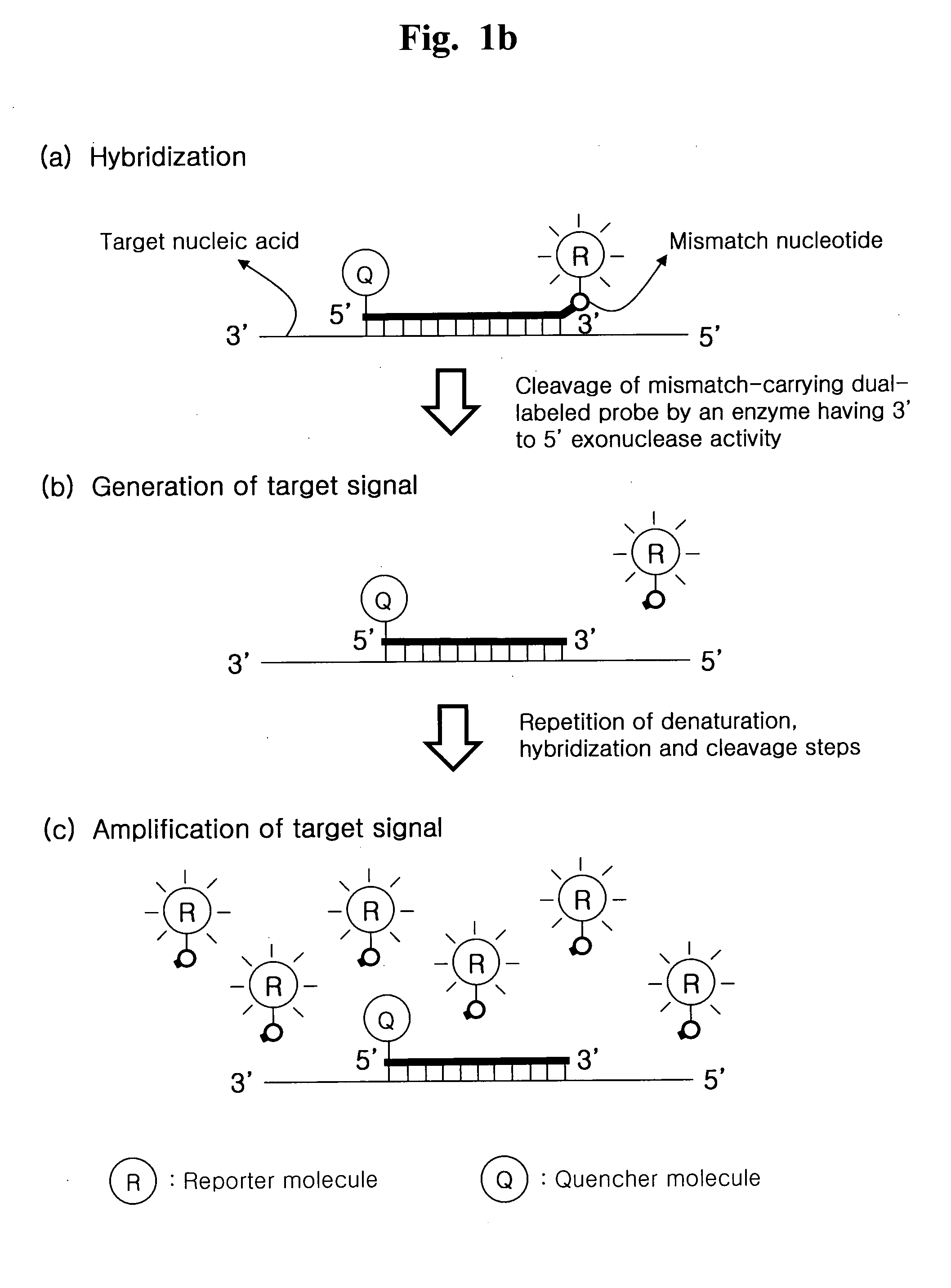
Detection of Target Nucleic Acid Sequences by Cyclic Exonucleolytic Reactions
ActiveUS20120190030A1Efficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceOligonucleotideDigestion
The present invention relates to the detection of a target nucleic acid sequence by a cyclic exonucleolytic reaction. The present method enabling to generate signals by probe digestion with no help of primers and to amplify signals with no help of simultaneous target amplification reactions may enable to detect multiple target sequences without any problems accounted in the conventional real-time PCR methods such as false positive signals and difficulties in oligonucleotides (primer and probe) selection and reaction condition optimization.
Owner:SEEGENE INC
Serum-free culture medium, preparation method thereof and culture method of mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN110923196AImprove proliferative abilityImprove performanceCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPolyvinyl alcoholHydrocortisone
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing stem cells from human amniotic membrane
ActiveCN103642751AKeep aliveA large amountMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDigestionMolecular biology
The invention discloses a method for preparing stem cells from a human amniotic membrane, specifically relates to a method for separating epithelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells from the amniotic membrane, and relates to the technical field of cell separation. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a placenta by self-made sterile, efficient and stable placenta protecting liquid; and separating amniotic membrane epithelial cells and amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells by combining a digestion process and a climbing process to respectively obtain high-purity amniotic membrane epithelial cells and high-purity amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells. The method disclosed by the invention solves a problem that subsequent cell separation and culture is directly affected by high human amniotic membrane collecting pollution rate and poor activity of the collected cells in the prior art. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the method for separating the stem cells from the amniotic membrane is improved and created to form a standard separating scheme, so that the stem cell resource can be utilized more stably and sufficiently, pollution is avoided, purity is high and the number of the cells is large; while the cell activity is kept, original characteristics of the stem cells are ensured.
Owner:山西省干细胞基因工程有限公司
Analogs and prodrugs of buprenorphine
InactiveUS20040192714A1Improve lipophilicityImprove solubilityBiocideOrganic chemistryBuprenophineProdrug
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
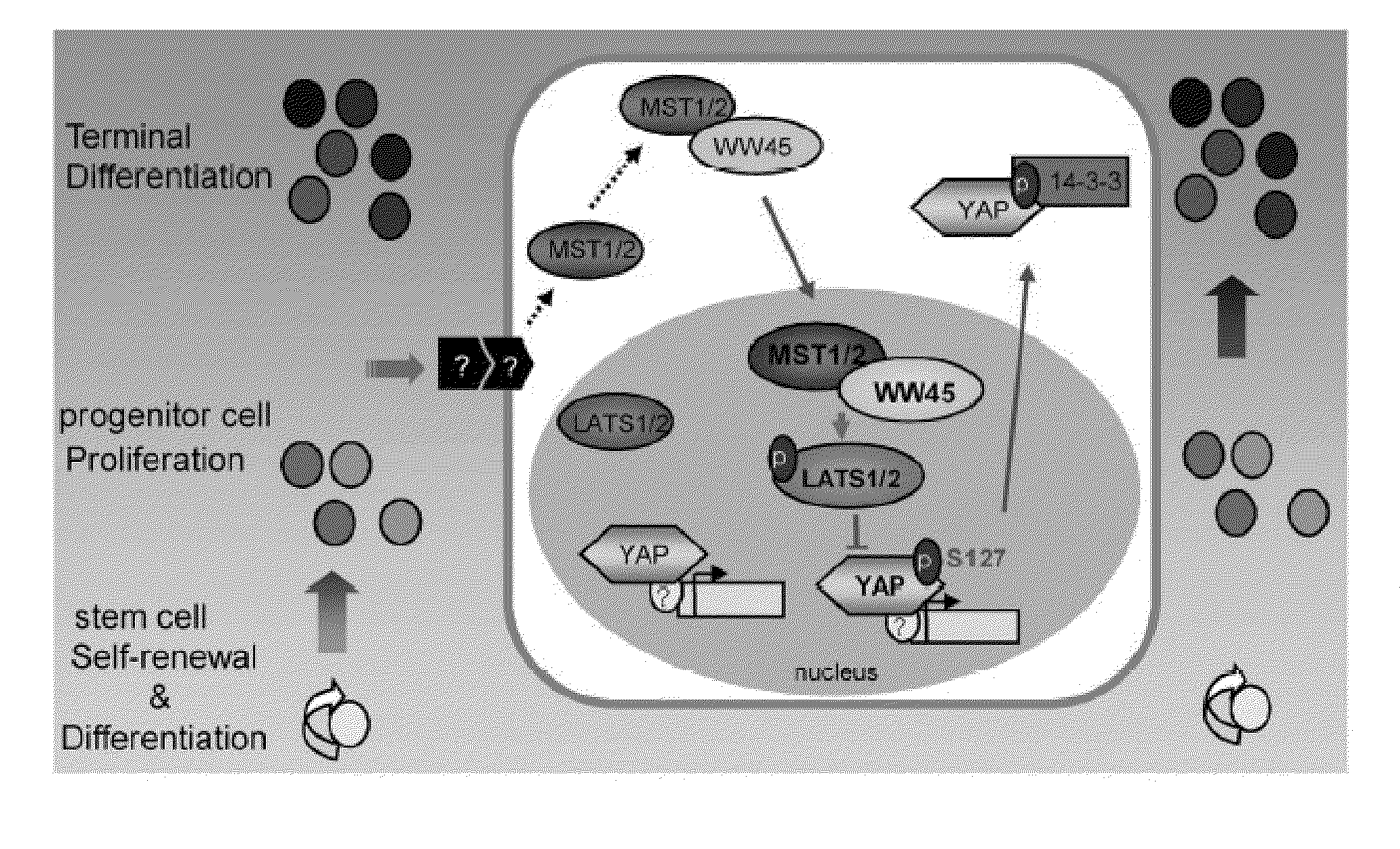
Methods of regulating differentiation in mammals
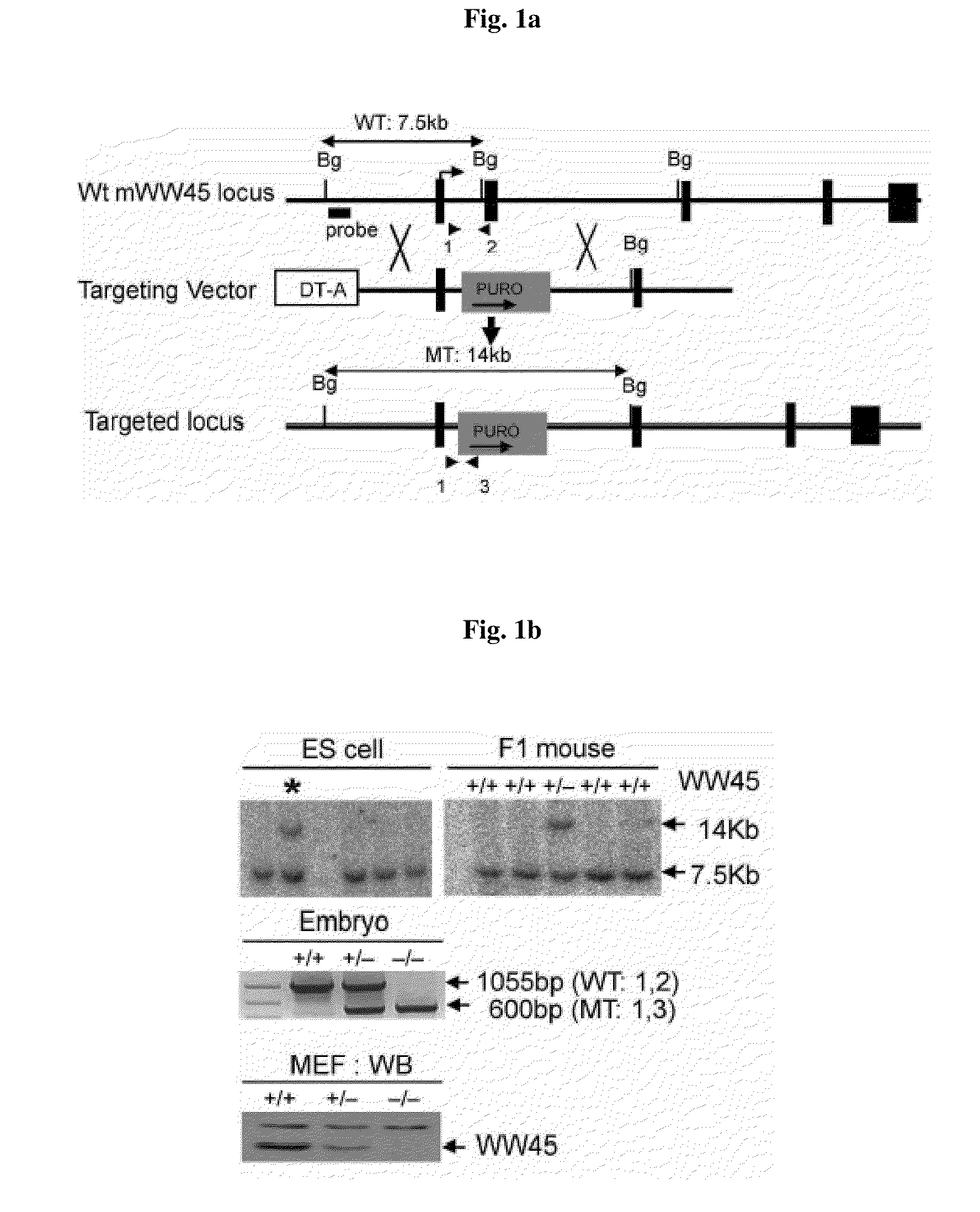
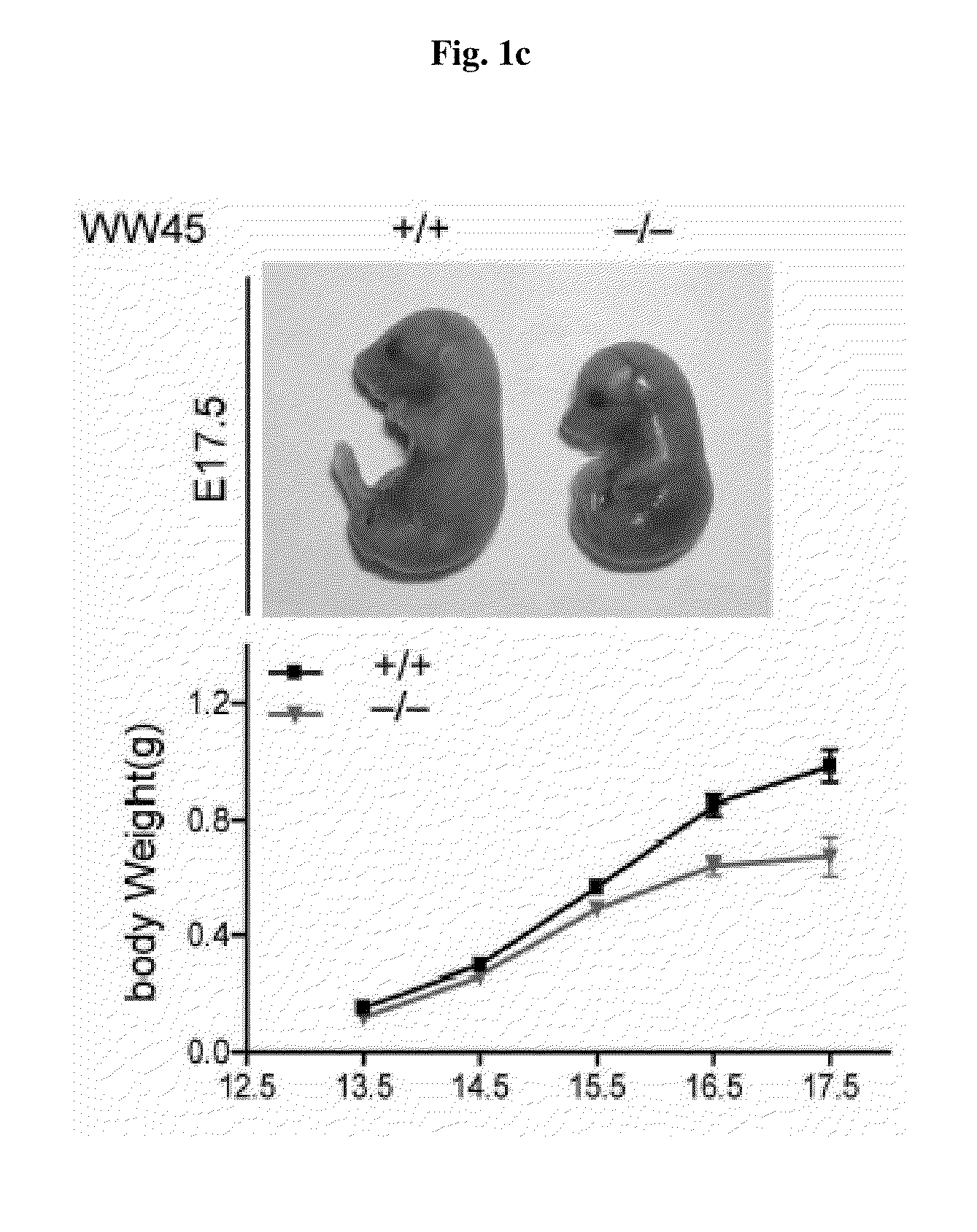
Mechanisms regulating cell proliferation stop and differentiation initiation during the development stage of mammalian embryo, and the proteins involved therein, are presented. Differentiation regulators, methods of regulating differentiation, transgenic organisms with loss of expression of the differentiation regulator, and methods of preparing the transgenic organisms, are provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting mirna
ActiveUS20130184331A1Inhibit functioningImprove regenerative abilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicinePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases by targeting a specific miRNA. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit for diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. A miR-206 target found in the present invention, which is highly expressed in both animal models of Alzheimer's disease and human brain samples, is a substantial treatment target selected without artifact errors. An antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention as an inhibitor for miR-206 suggests a successful result in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting miRNA. The antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention inhibits the function of miR-206 to greatly increase the levels of BDNF and IGF-1 and to increase the regeneration of synapses, thereby treating neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
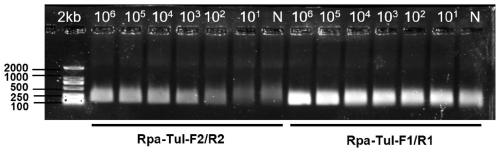
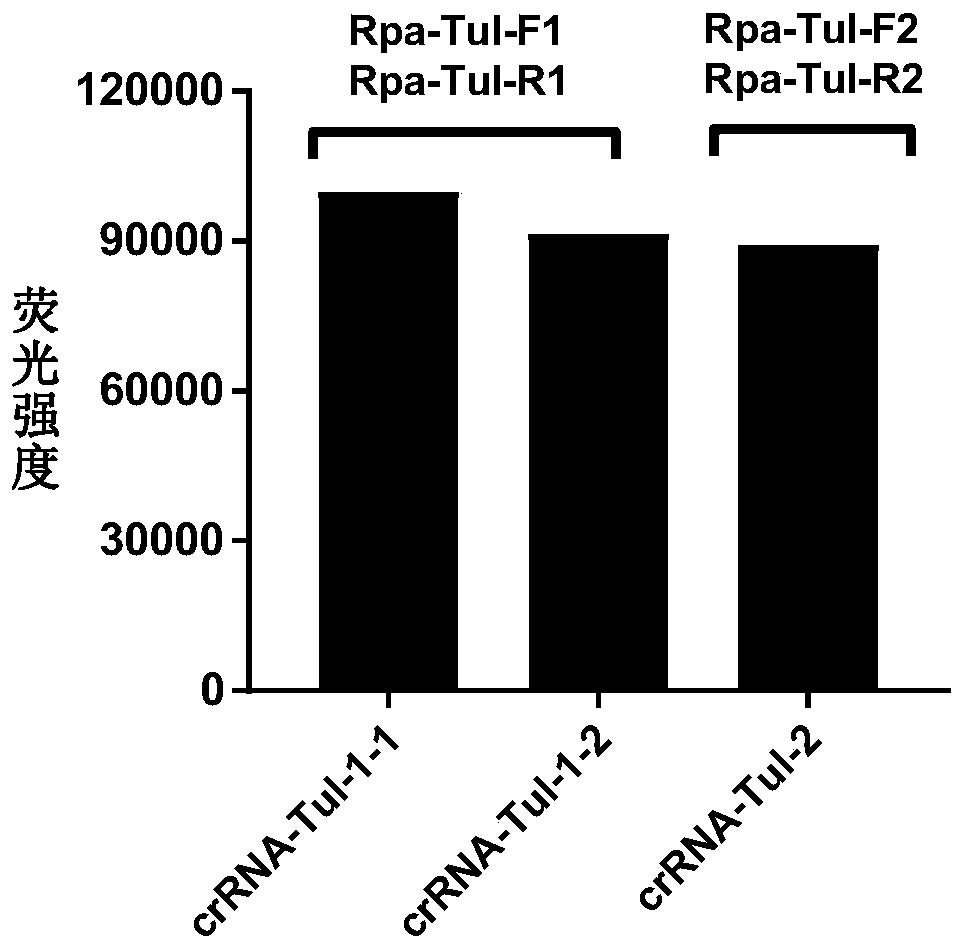
CRISPR-Cas12a detection primer group for francisella tularensis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394490AShort detection timeHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGeneticsNucleotide sequencing
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
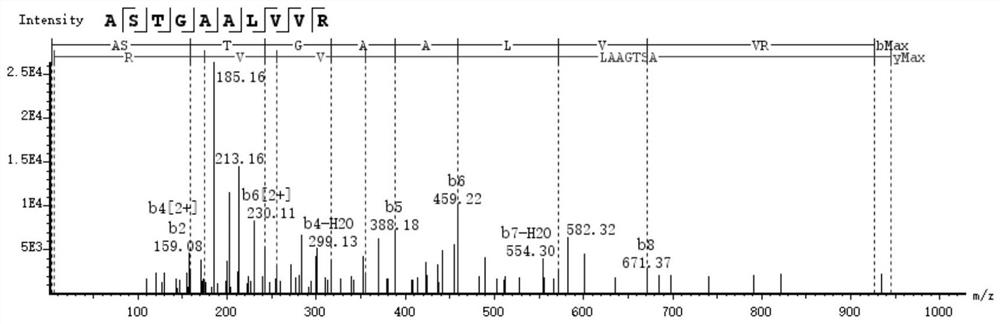
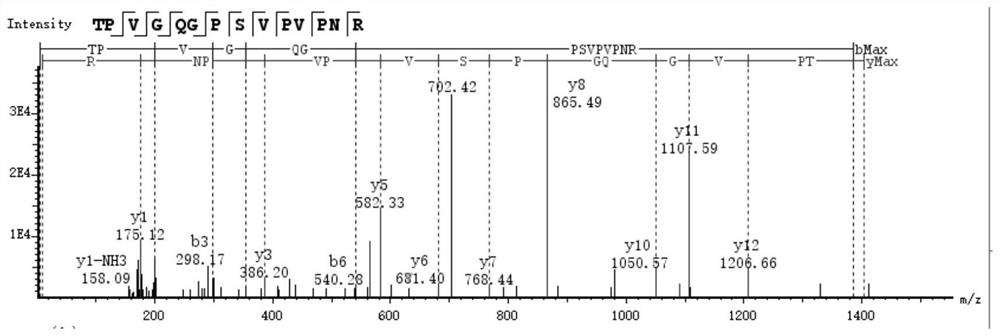
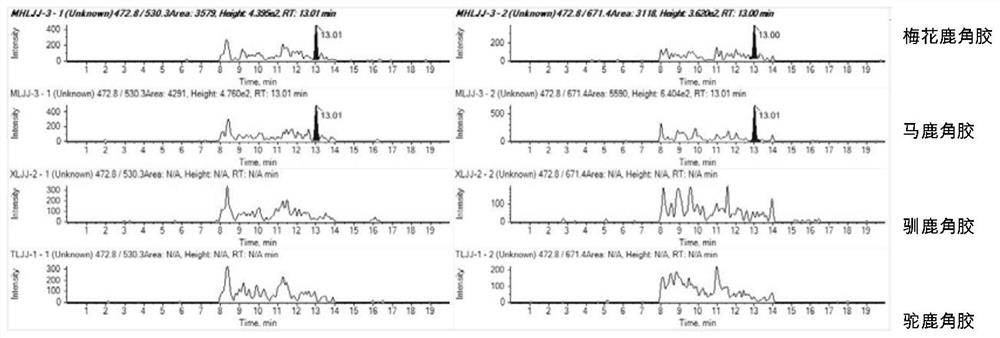
Characteristic polypeptide for identifying deer-horn glue of Cervus nippon or Cervus elaphus, and application of characteristic polypeptide
InactiveCN113480599AStrong specificityImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptidesMedicinal herbsGenetics
Owner:SHANDONG INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Nucleoside prodrug and application thereof
ActiveCN113999237AImprove oral bioavailabilityImprove performanceOrganic chemistryAntiviralsAnimal virusOral treatment
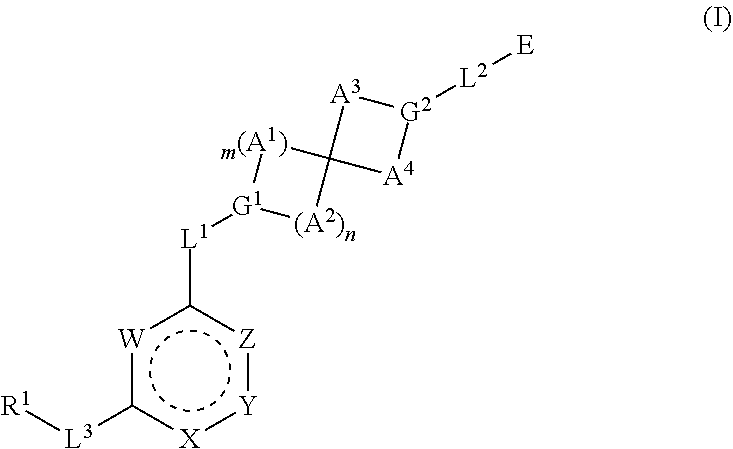
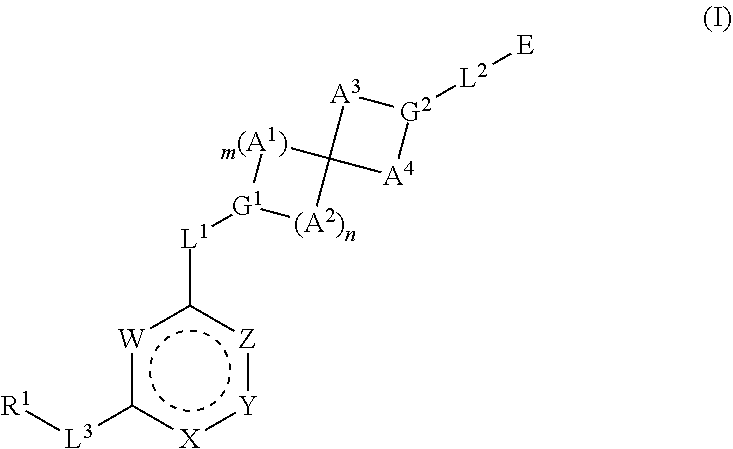
The invention relates to a nucleoside prodrug capable of being orally taken for treating mammalian virus infection, and especially relates to a compound shown as a formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, and application of the compound or the composition in preparation of drugs for treating, inhibiting or preventing diseases caused by virus infection.
Owner:RISEN SUZHOU PHARMA TECH CO LTD
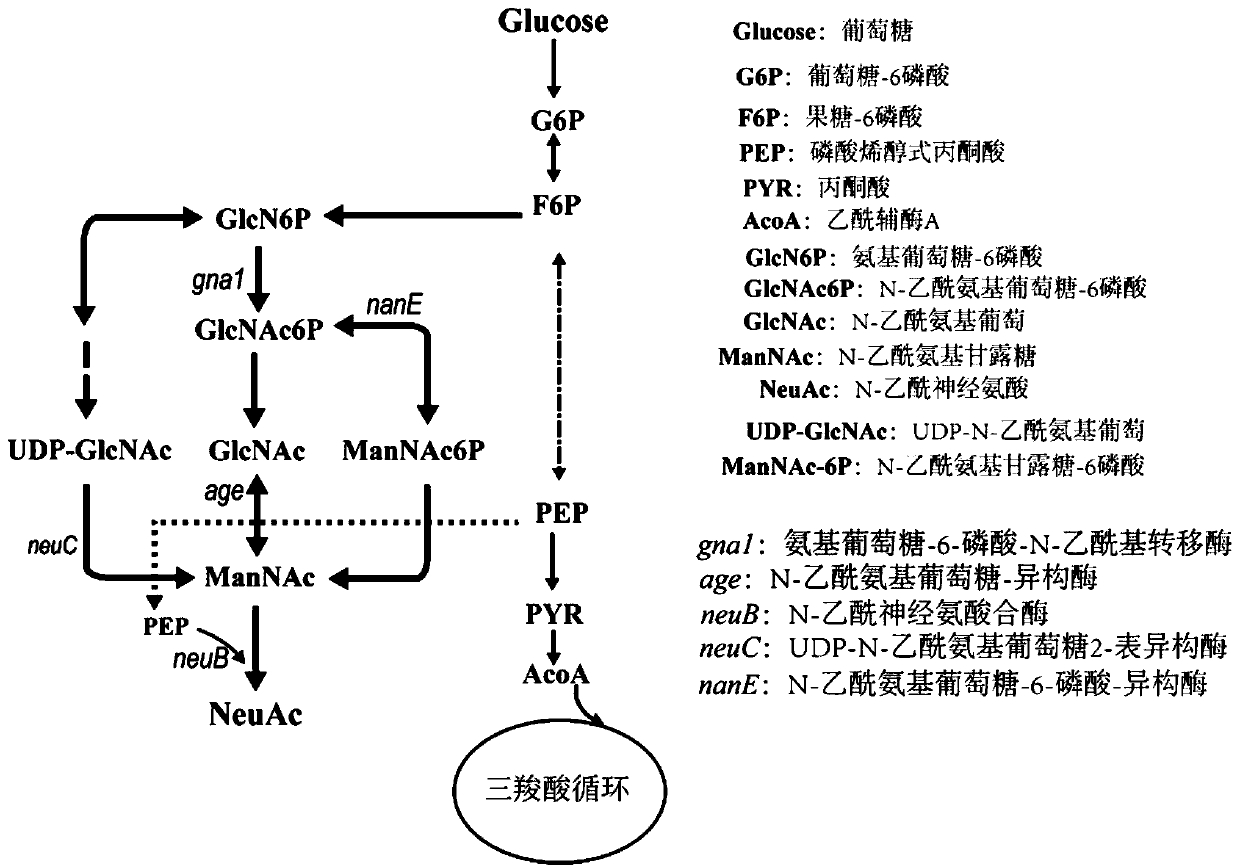
Multipath composite neuraminic acid producing bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394292AHigh catalytic activityReduce synthetic pressureBacteriaTransferasesO-Phosphoric AcidGlucosaminephosphate isomerase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nanosensors and methods for detection of biological markers
PendingUS20200300849A1Easy to moveBiological material analysisLaboratory glasswaresPost translationalCytokine
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
2019-nCoV double-target antibody detection microsphere complex combination, preparation method, kit and use method of kit
PendingCN111896734AReduce dosageEfficient detectionBiological material analysisViral testSpecific antibody
Owner:湖北新纵科病毒疾病工程技术有限公司
Method for preparing autologous hematopoietic stem cells, kit, the stem cells and application
ActiveCN104419660AYield advantagePurity advantageAntinoxious agentsDead animal preservationInterleukin 6Culture fluid
Owner:深圳百年干细胞技术研究院有限公司
Mutant gene OsABCC1 for regulating and controlling cadmium and arsenic accumulation of rice and application of mutant gene OsABCC1
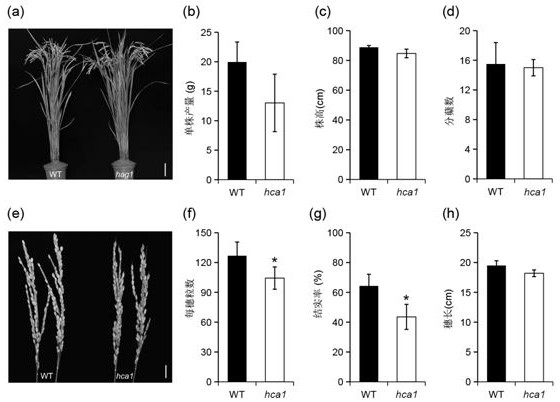
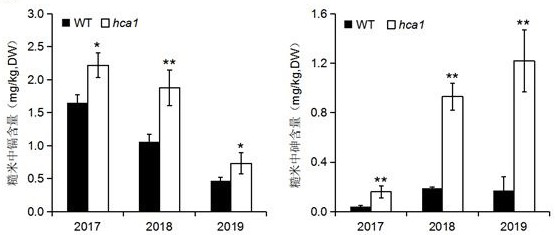
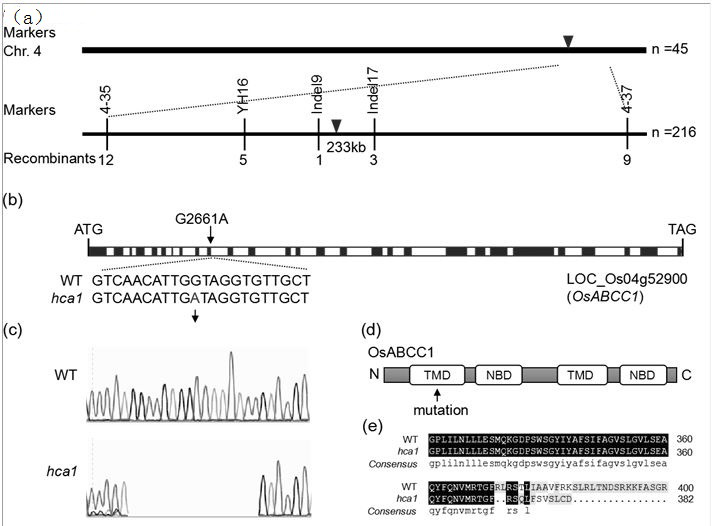
The invention discloses a mutant gene OsABCC1 for regulating and controlling cadmium and arsenic accumulation of rice and application of the mutant gene OsABCC1. According to the mutant gene OsABCC1 for regulating and controlling cadmium and arsenic accumulation of rice, a first base behind a tenth exon of a wild type OsABCC1 gene is subjected to variable shear mutation, namely, a base at a 2261 nucleotide at the downstream of ATG is mutated into A from wild type G, so that 1116 to 1131 nucleotides in a corresponding coding nucleotide sequence are deleted, a mutant is deleted and changed at 372<nd> to 382<nd> amino acids and is translated at a 383<rd> amino acid to be terminated in advance, the coding nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the cadmium and arsenic contents inrice grains of the mutant hca1 are higher than those in wild type rice grains. The amino acid sequence coded by the mutant gene OsABCC1 is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. According to the application of the mutant gene OsABCC1, the rice contains the mutant gene OsABCC1 or contains the coding amino acid of the mutant gene OsABCC1. The cadmium and arsenic contents in the grains of the obtained mutant material hca1 are respectively increased by about 1 time and 5 times.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Modified Antigen Presenting Cells and Methods of Use
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Culture medium for hepatoma organoid cell sphere culture
ActiveCN110878286AHigh activityLong-term stable aggregationCulture processCell culture active agentsNutritionPancreatic hormone
Owner:江苏信安佳医疗科技有限公司
Probe composition for detecting lung cancer mutant genes based on NGS method and kit
ActiveCN110791500AStrong specificityHigh and uniform coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideBlood plasma
The invention discloses a probe composition for detecting lung cancer gene mutation based on an NGS method and a kit thereof. The probe composition is selected from at least one of probes with nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-75, the kit is suitable for lung cancer gene mutation detection of FFPE, tissue and peripheral blood ctDNA based on the NGS method, and then the purposes of earlyscreening of lung cancer mutant genes, real-time monitoring of recurrence and the like are achieved. The uniquely designed UMI bimolecular tag can effectively reduce background noise, eradicate tracepollution, remove false positive and ensure the accuracy of a result, so that the sensitivity in ctDNA detection reaches 0.1%. A universal Short-Y joint is used in tissue detection, and the detectionsensitivity can reach 2%. The more possibilities are provided for accurate targeted therapy of patients. Tissue samples and plasma samples are similar in library building workflow, the simplicity ofthe workflow is guaranteed, time is saved, the efficiency is high, and the operation is easy.
Owner:KEAN BIOTECHNOLOGY (DALIAN) CO LTD
Engineered ketoreductase polypeptide and method for preparing montelukast midbody by means of same
InactiveCN106011092AOvercome poor responsivenessReduce the amount of enzymes usedOxidoreductasesFermentationBiochemistrySubstrate concentration
The invention discloses an engineered ketoreductase polypeptide and a method for preparing a montelukast midbody by means of the same. Compared with the prior art, the engineered ketoreductase polypeptide has the advantages that enzyme consumption is low, reaction time is short, substrate concentration is high, and the engineered ketoreductase polypeptide is more suitable for industrial application when used for preparation of the montelukast midbody.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Additive used for increasing clone number of hybridoma cells and preparation method of additive
ActiveCN105462934APromote growthGrow fastFused cellsCell culture active agentsUltrafiltrationHybridoma cell
The invention provides an additive used for increasing the clone number of hybridoma cells and a preparation method of the additive, and relates to an immunological research technology. The preparation method includes the following steps that 1, culture solution supernatant for eukaryotic cells capable of expressing IL-6 protein is acquired, wherein the cell culture solution supernatant contains expressed IL-6 protein; 2, the cell culture solution supernatant is subjected to ultrafiltration and filtration sterilization in sequence, and a cell culture solution supernatant concentrated solution is obtained; 3, sodium selenite is added into the cell culture solution supernatant concentrated solution, and the additive is obtained. As proved by experimental data, the clone number of the hybridoma cells can be increased by nearly 5 times after the additive is adopted. The invention further provides a hybridoma cell culture medium containing the additive.
Owner:TARCINE BIOMED INC
Soybean gene GmTCM1 and obtaining method and application thereof
ActiveCN112646818AEasy to synthesizeIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention relates to a soybean gene GmTCM1 and an obtaining method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soybean genetic breeding. In order to increase the soybean isoflavone content and obtain transgenic soybean plants with high isoflavone content, the soybean gene GmTCM1 is cloned from soybeans 27 in a soybean variety with high isoflavone content, and biological information analysis and preliminary analysis of gene functions of the gene show that the gene GmTCM1 can increase the soybean isoflavone content and participate in resistance reactions to abiotic stress such as drought and salt and biotic stress such as sclerotinia sclerotiorum, phytophthora and gray-spot bacteria. In addition, the obtained transgenic material can become a stable disease-resistant genetic material through subsequent subculture reproduction and identification. The soybean gene GmTCM1 has important theoretical significance and practical value for accelerating the breeding process of new varieties of high-isoflavone disease-resistant stress-resistant soybeans and improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
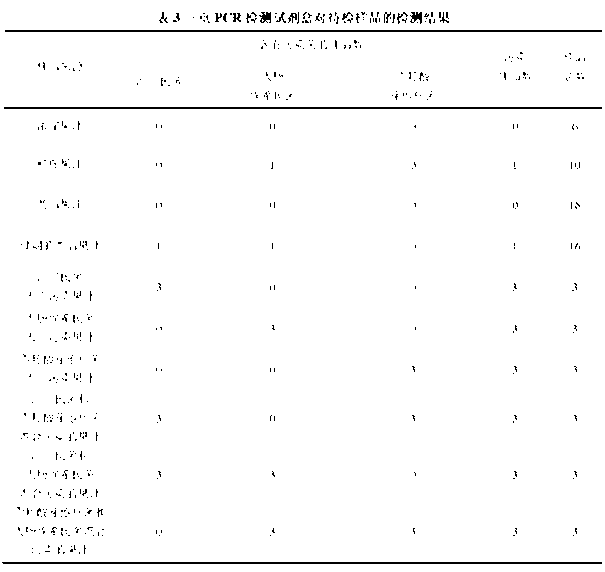
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primers for three bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN102747162AHigh detection sensitivityAvoid False Positive ResultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliAlicyclobacillus
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Method for isothermal amplification of nucleic acids
A method is disclosed for improved isothermal amplification of nucleic acids comprising the step of release of an essential component from a matrix under predetermined conditions. Furthermore, the invention relates to a kit comprising mesophilic enzyme and a matrix with embedded essential components for isothermal amplification. A composition comprising a matrix and a mesophilic enzyme and a method for embedding a mesophilic enzyme are disclosed as well.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Heterocyclic spiro compounds and methods of use thereof for the treatment of cancer
Owner:ARAXES PHARMA LLC
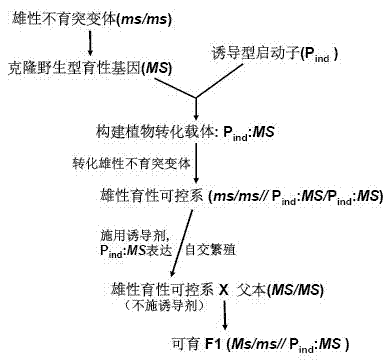
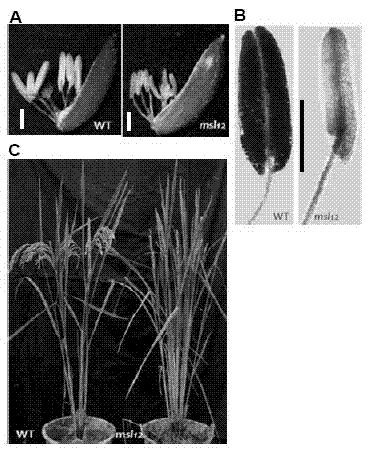
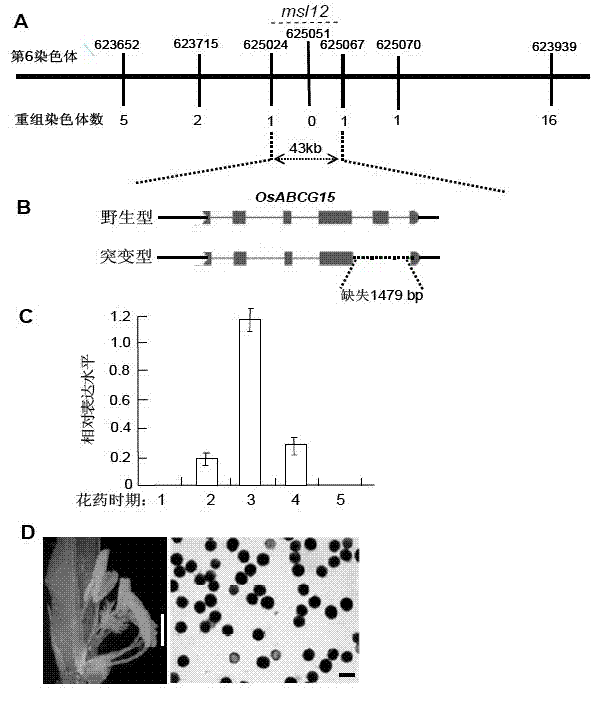
Building method and breeding method for rice male-fertile controllable line
ActiveCN102925478APlant genotype modificationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetic engineeringMolecular biology
Owner:宝应县城西经济发展有限公司
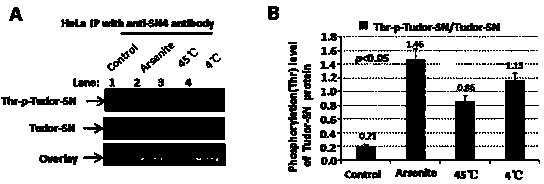
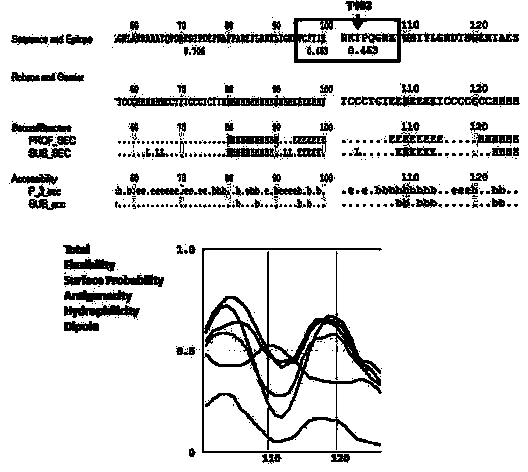
Preparation method of stress phosphorylation antibody aiming at human Tudor-SN protein T103 site
InactiveCN104277109AEasy to explore correlationSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against enzymesDiseaseHumanin
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Providing or Modulating Sweet Taste or Methods of Screening Therefor
ActiveUS20130280371A1Enhance protein expressionIncrease sweetnessOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHeterologousProtein insertion
Owner:MONELL CHEM SENSES CENT
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap