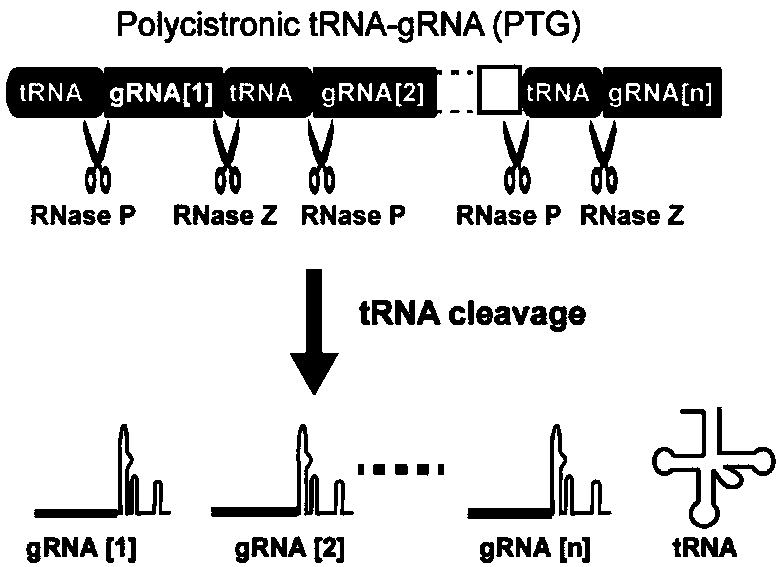
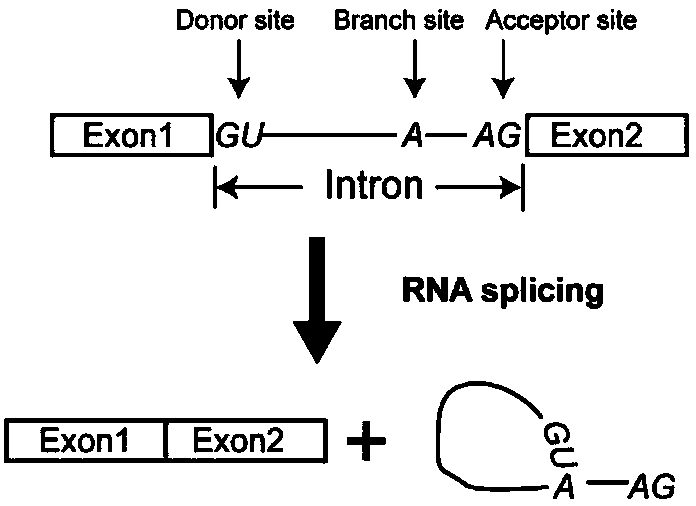
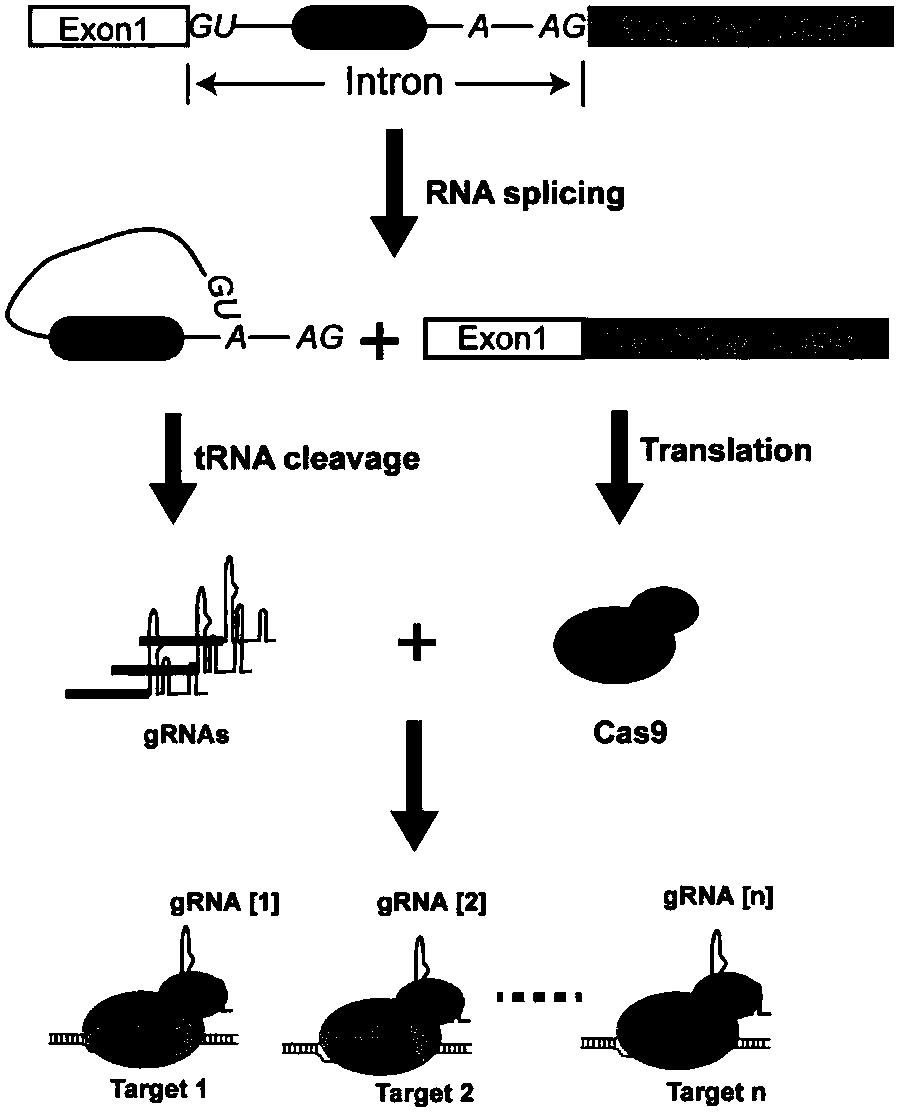
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
136results about "Vector-based foreign material introduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plants and seeds of corn variety cv252827
ActiveUS20080271176A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationAdemetionineTissue culture
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Genome editing method based on CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat) system and application thereof
ActiveCN107937432AImprove editing efficiencyImprove editing abilityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionInteinFusion gene
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
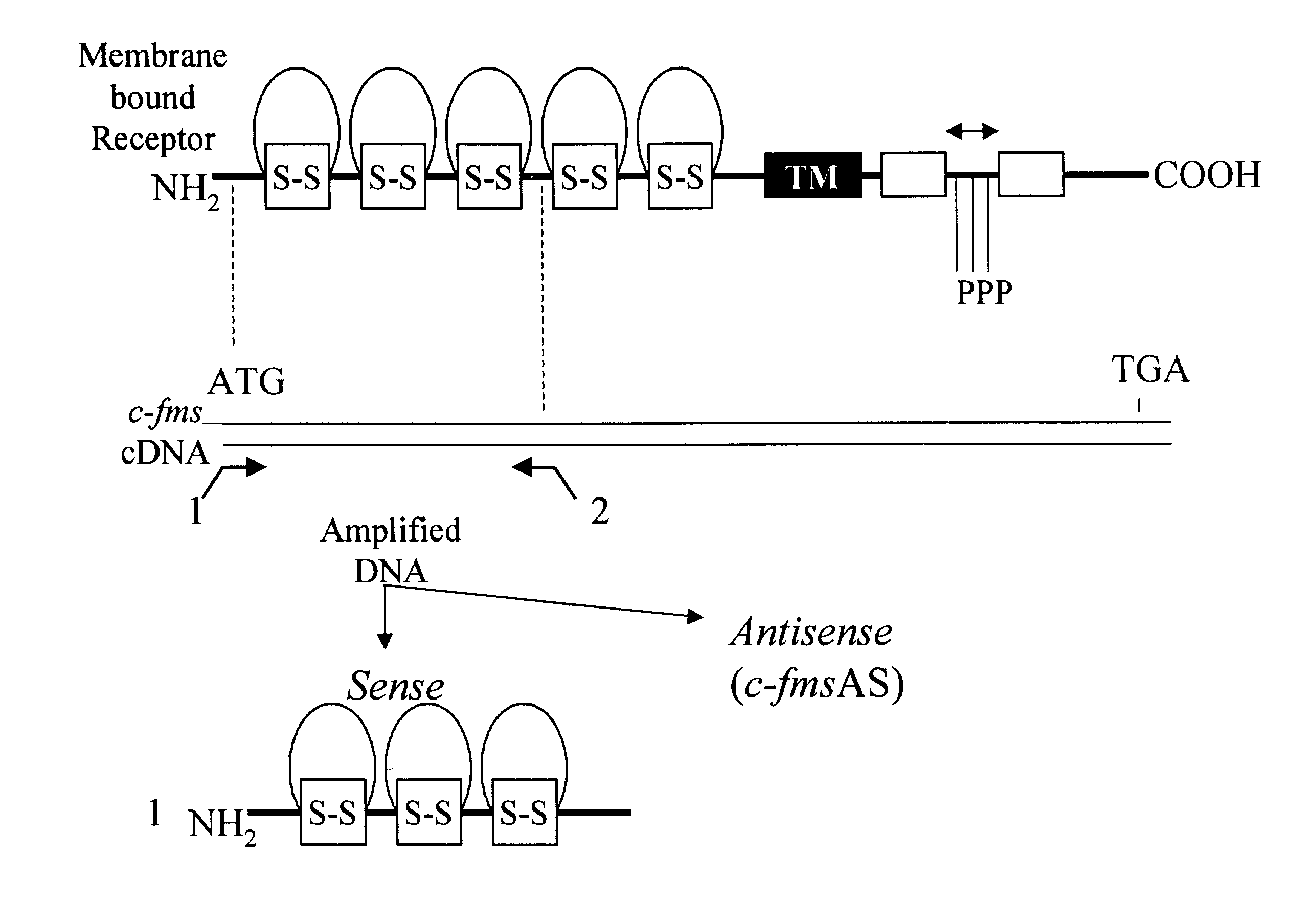
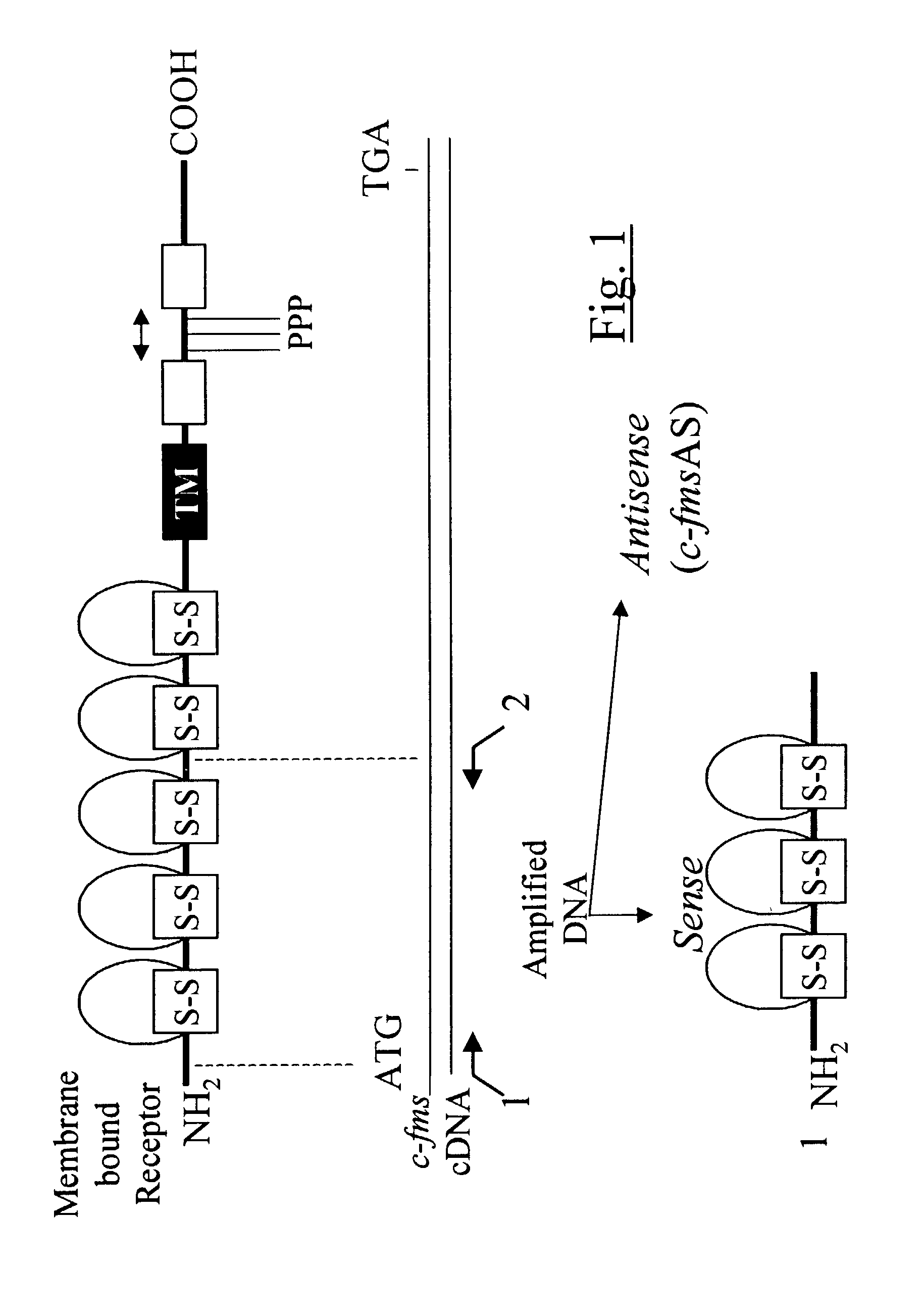
Methods for inhibiting macrophage colony stimulating factor and c-FMS-dependent cell signaling
Owner:RAJAVASHISTH TRIPATHI
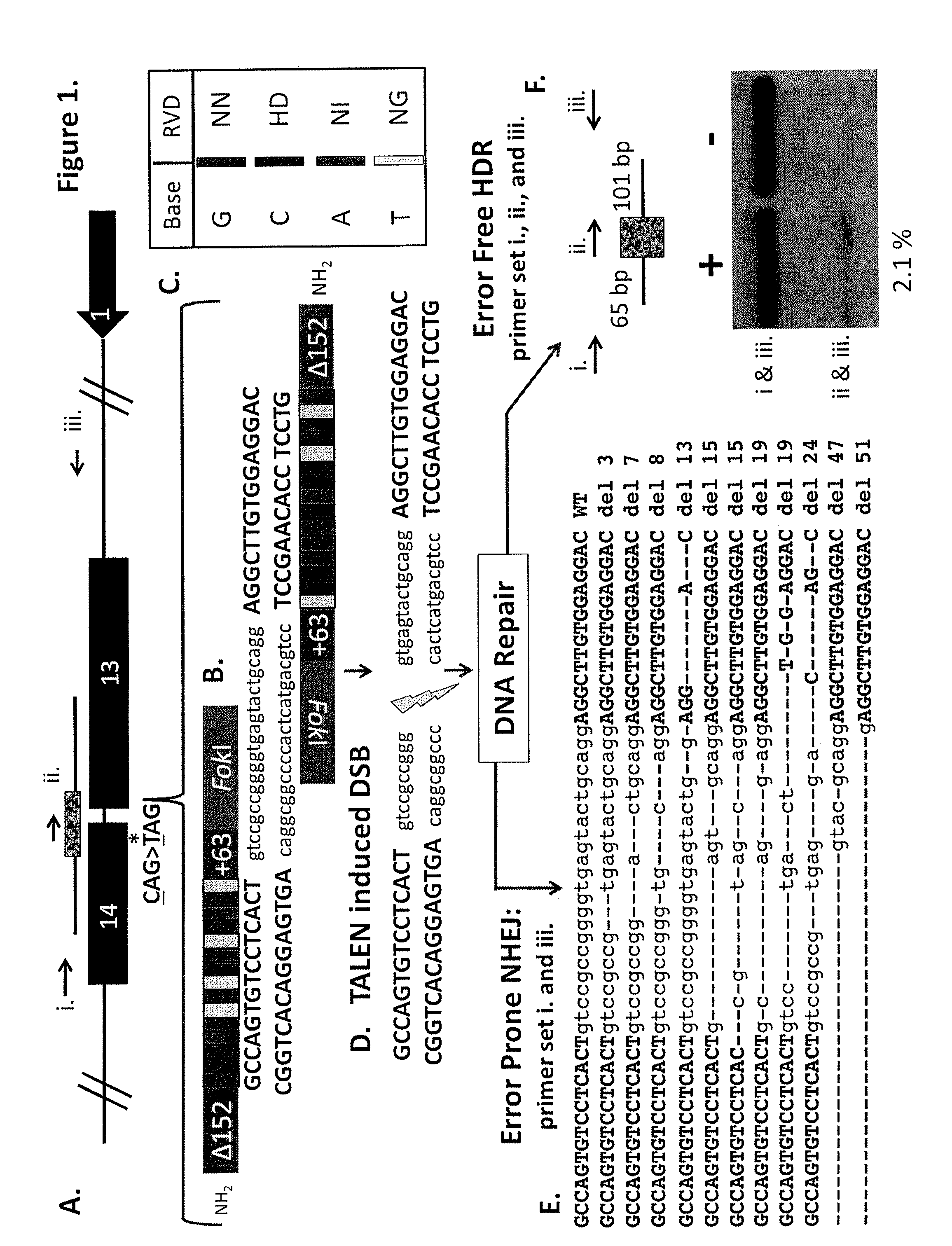
Talen-based gene correction
ActiveUS20140256798A1Restores correct gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingHuman cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method and circuit arrangement for treating biomaterial
ActiveUS20060094095A1Successful cell treatmentAvoid and offsetBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityVoltage pulse
The invention relates to a method for treating biomaterial using at least one electrical field generated by a first voltage pulse which is terminated once the value for an electrical parameter has exceeded or dropped below a preset limit. After the first voltage pulse has been terminated, it is continued by an additional voltage pulse. The invention also relates to a circuit arrangement comprising at least one storage device for electrical charges to generate at least one voltage pulse by selectively discharging the storage device, and at least one control unit for controlling the discharge. The present invention provides a controller for monitoring the chronological progression of the voltage pulse, said controller controlling at least one continuation of discharge after termination.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE AG
Adenovirus vector containing a heterologous peptide epitope in the hi loop of the fiber knob
InactiveUS7297542B2Efficient transductionRaise transfer toBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousEpitope
The present invention provides means to modify the tropism of recombinant adenoviral vectors using genetic methods to alter the adenoviral fiber cell-binding protein. The present invention generates an adenovirus with modified fiber gene such that novel tropism is achieved. This recombinant adenovirus has a fiber gene modified in the HI loop domain.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Soybean Variety XB49Q07
ActiveUS20070130647A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologySoya bean
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
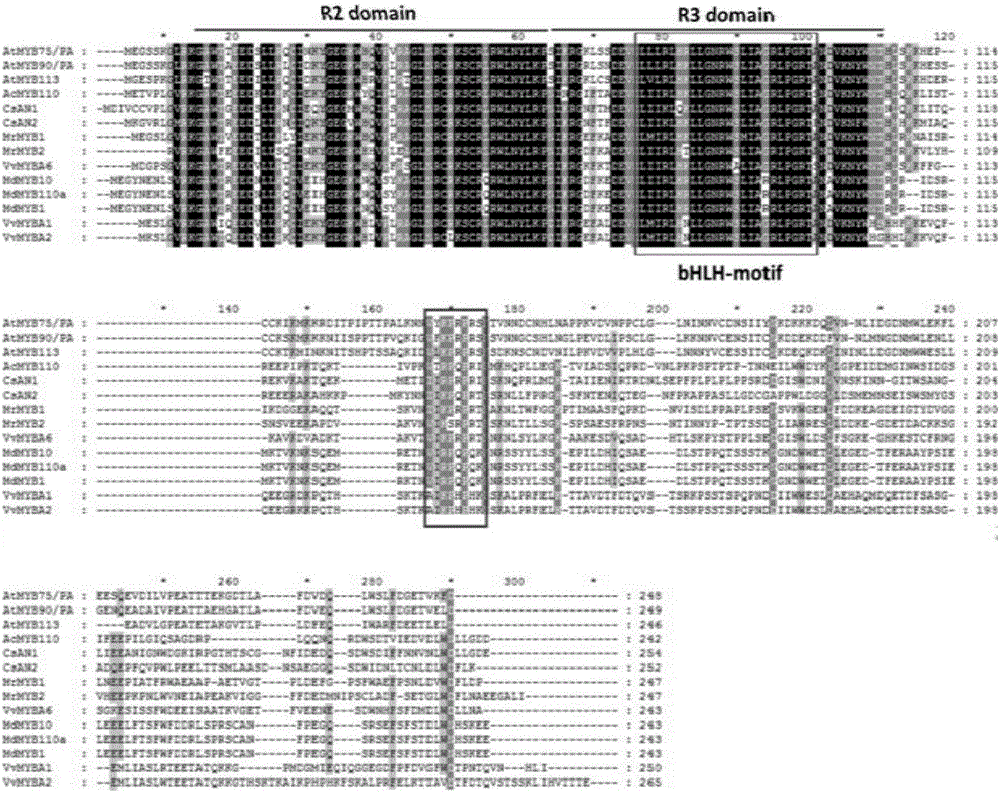
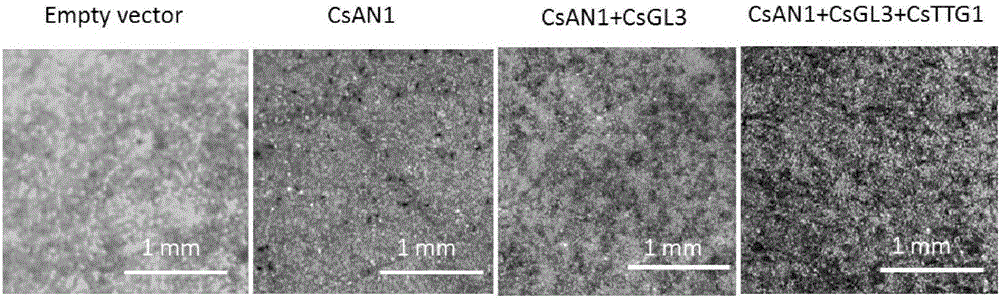
Tea tree MYB transcription factor CsAN1 and application thereof in regulation of anthocyanin metabolism
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103773729AAbundant resourcesGood synthesis effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLycopene
The invention relates to a recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Particularly, an escherichia coli endogenous 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphoric acid (MEP) precursor pathway is reconstructed; the reconstructed escherichia coli base cell is utilized to perform the efficient biological synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds; the reconstruction of the precursor pathway mainly comprises the steps of fully digging the MEP precursor pathway gene modules of the sources of other natural microorganisms, screening gene modules with excellent characteristics to be expressed in the escherichia coli, and at the same time, performing the downstream synthesis pathway for integrally assembling the colibacillus chemical compounds in the reconstructed base cell, wherein the colibacillus chemical compounds include sesquiterpene chemical compounds such as amorphadiene, diterpene chemical compounds such as shell alkene, tetraterpenes chemical compounds such as lycopene, polyterpene chemical compounds, other terpene alkaloid chemical compounds and the like. The escherichia coli base cell can remarkably facilitate the synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
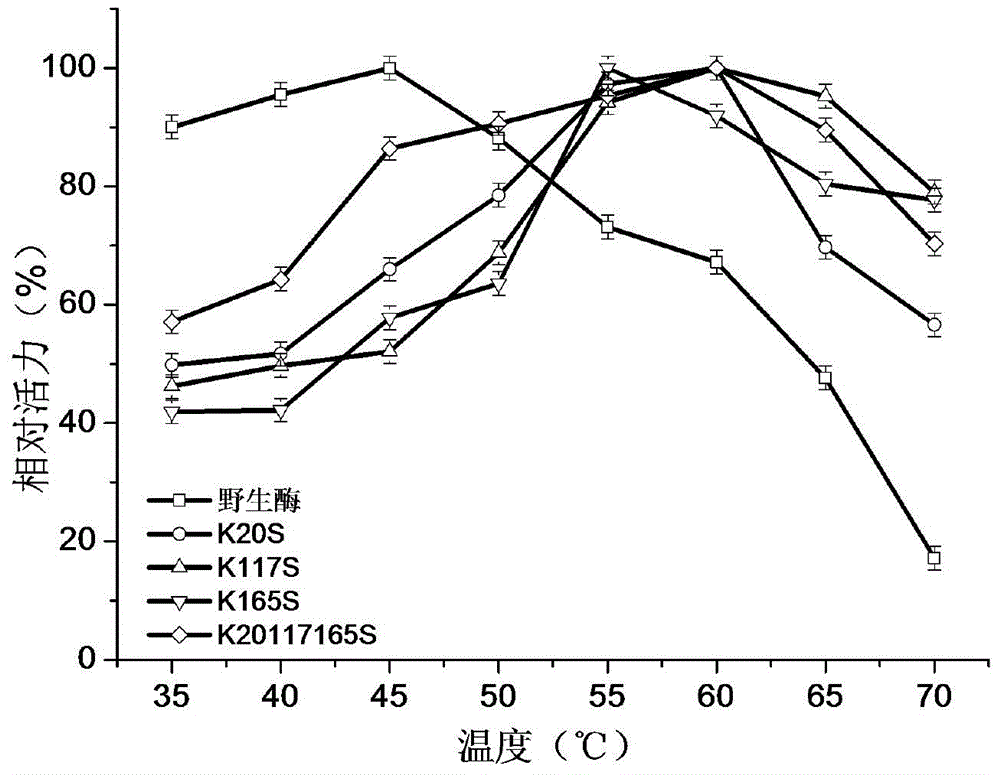
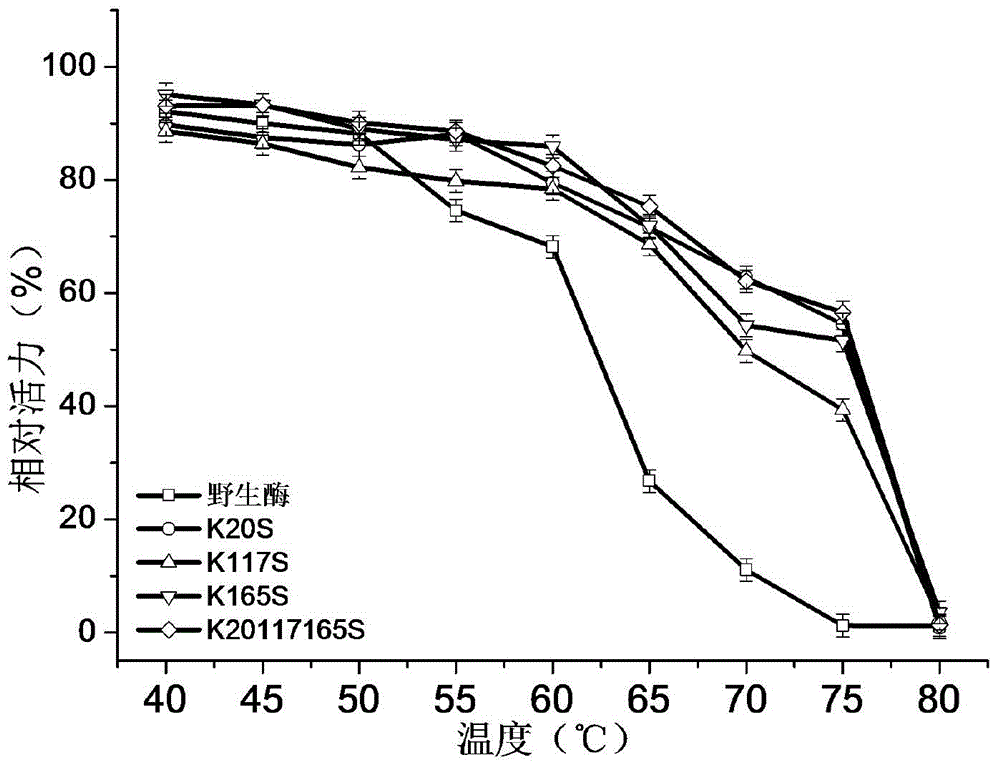
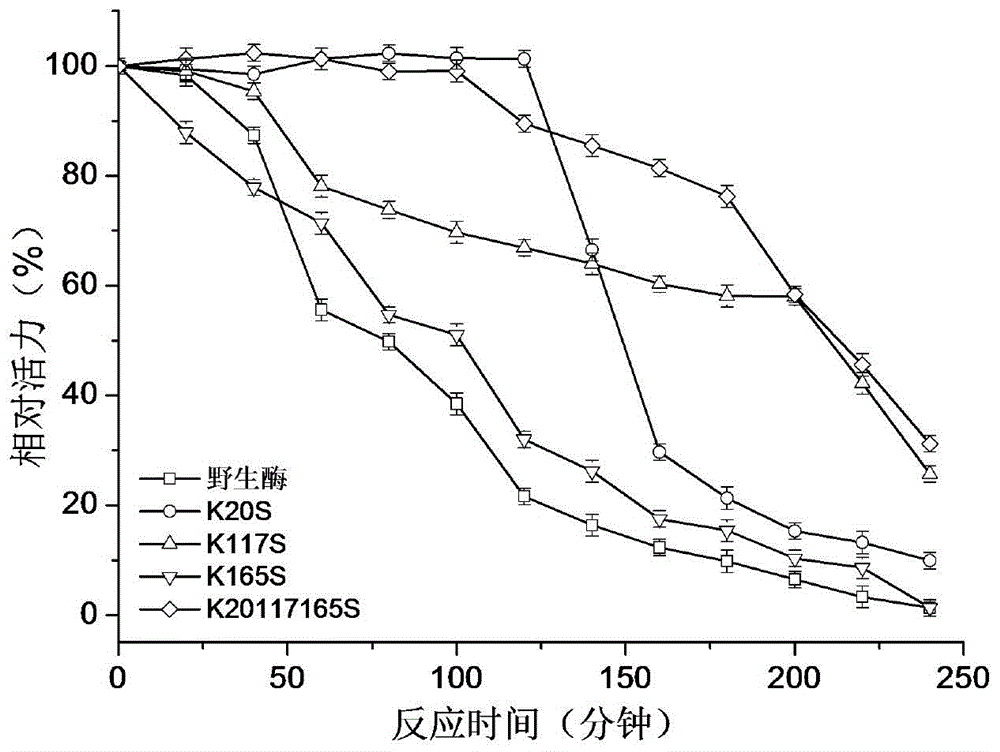
1,3-1,4-Beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN104130988AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaWort preparationMutaseGlucanase
Owner:无锡正元生物科技有限公司
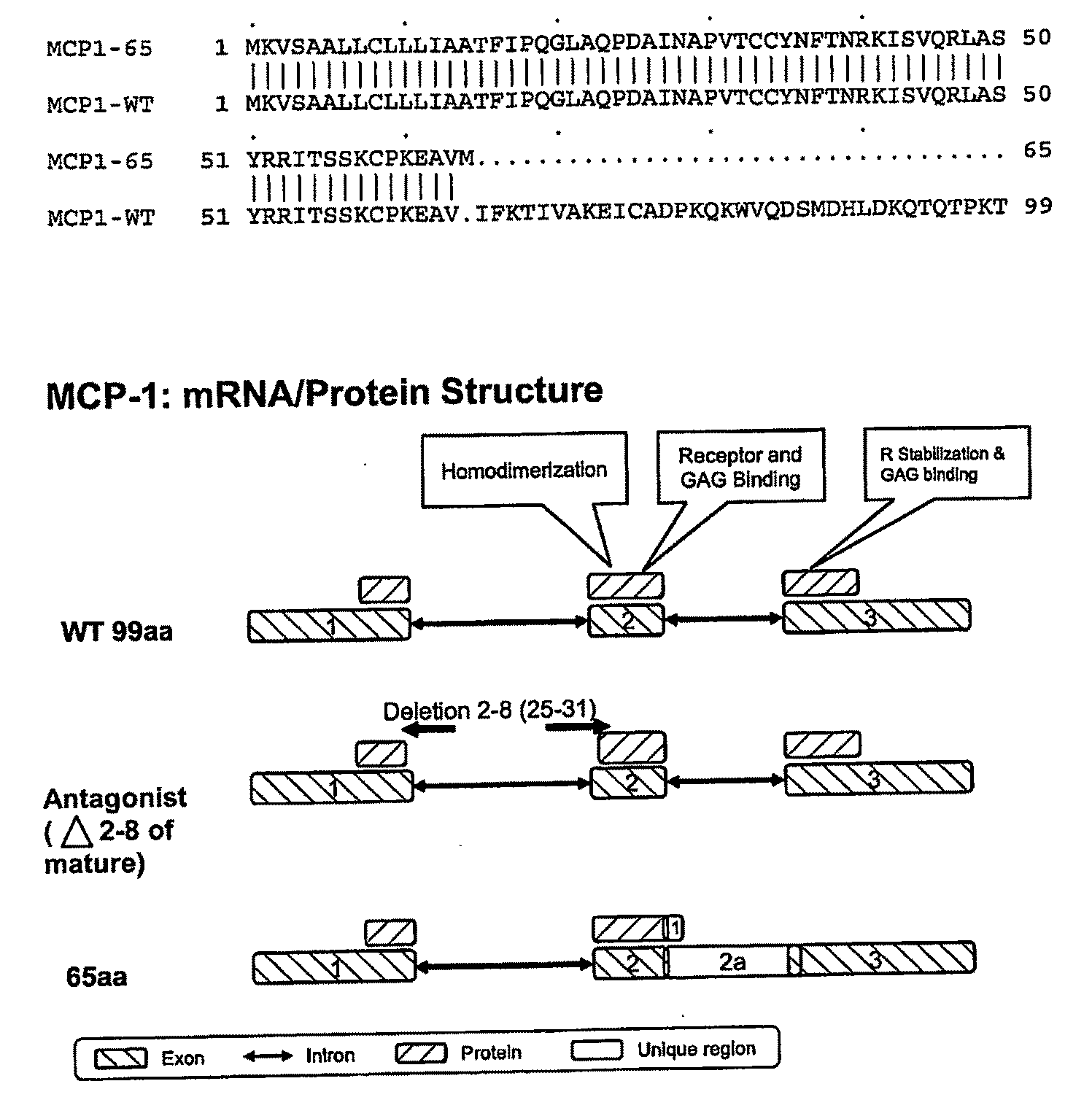
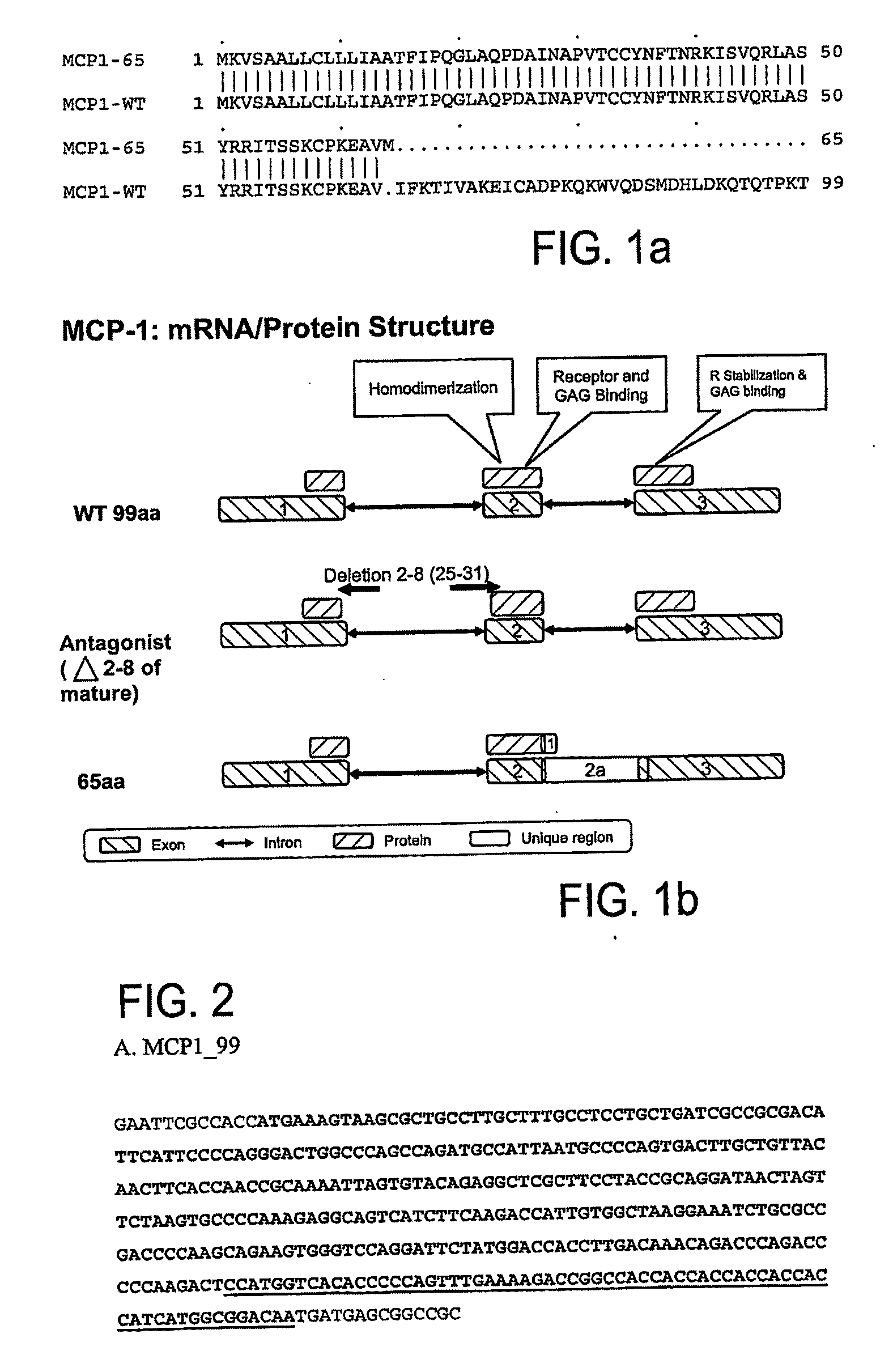
Mcp-1 splice variants and methods of using same
Owner:COMPUGEN
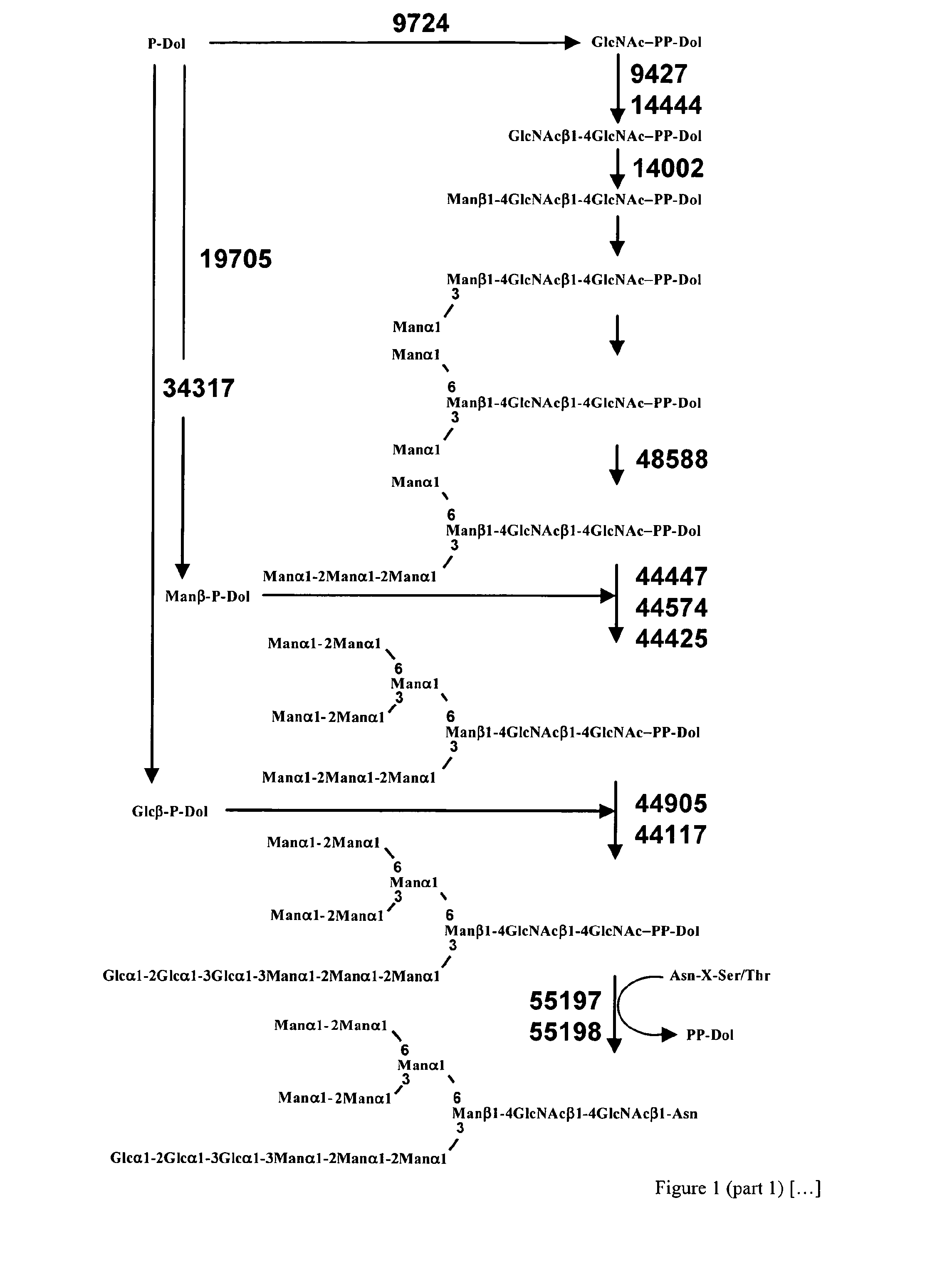
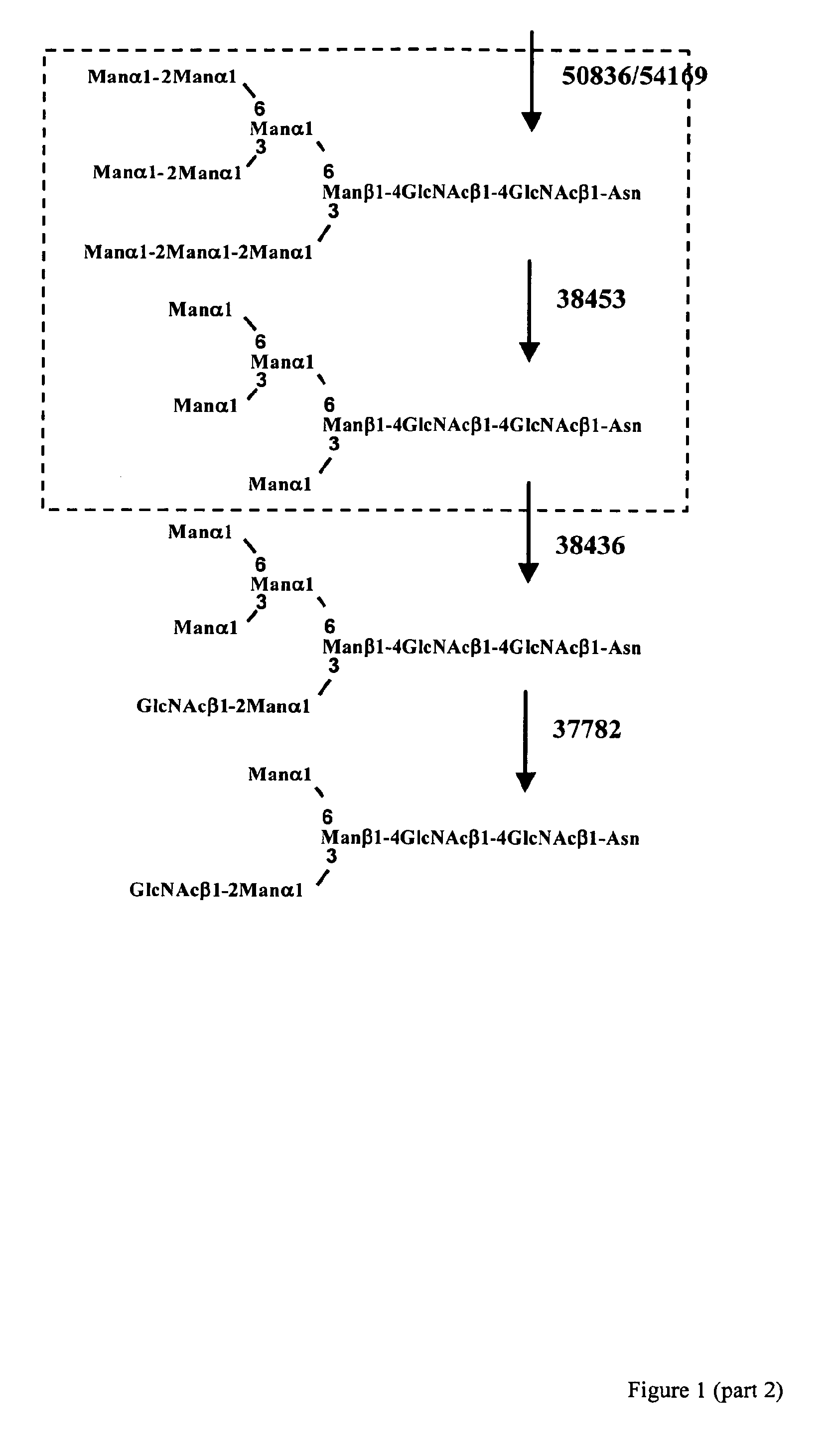
Production of glycosylated polypeptides in micro algae
Owner:INSTITUT FR DE RES & DEV POUR LEXPL DE LA MER IFREMER +2
Novel immunostimulating vector system
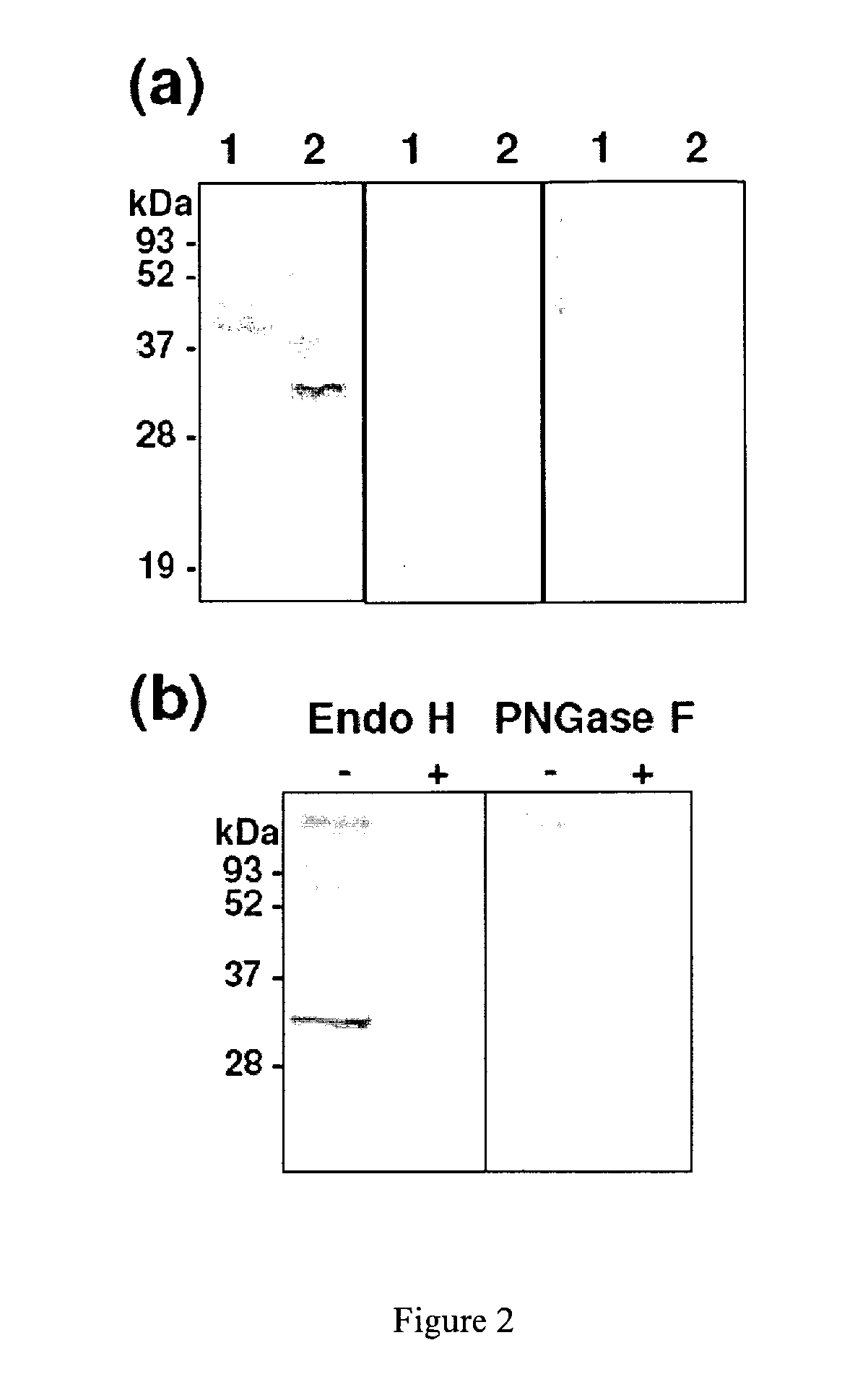
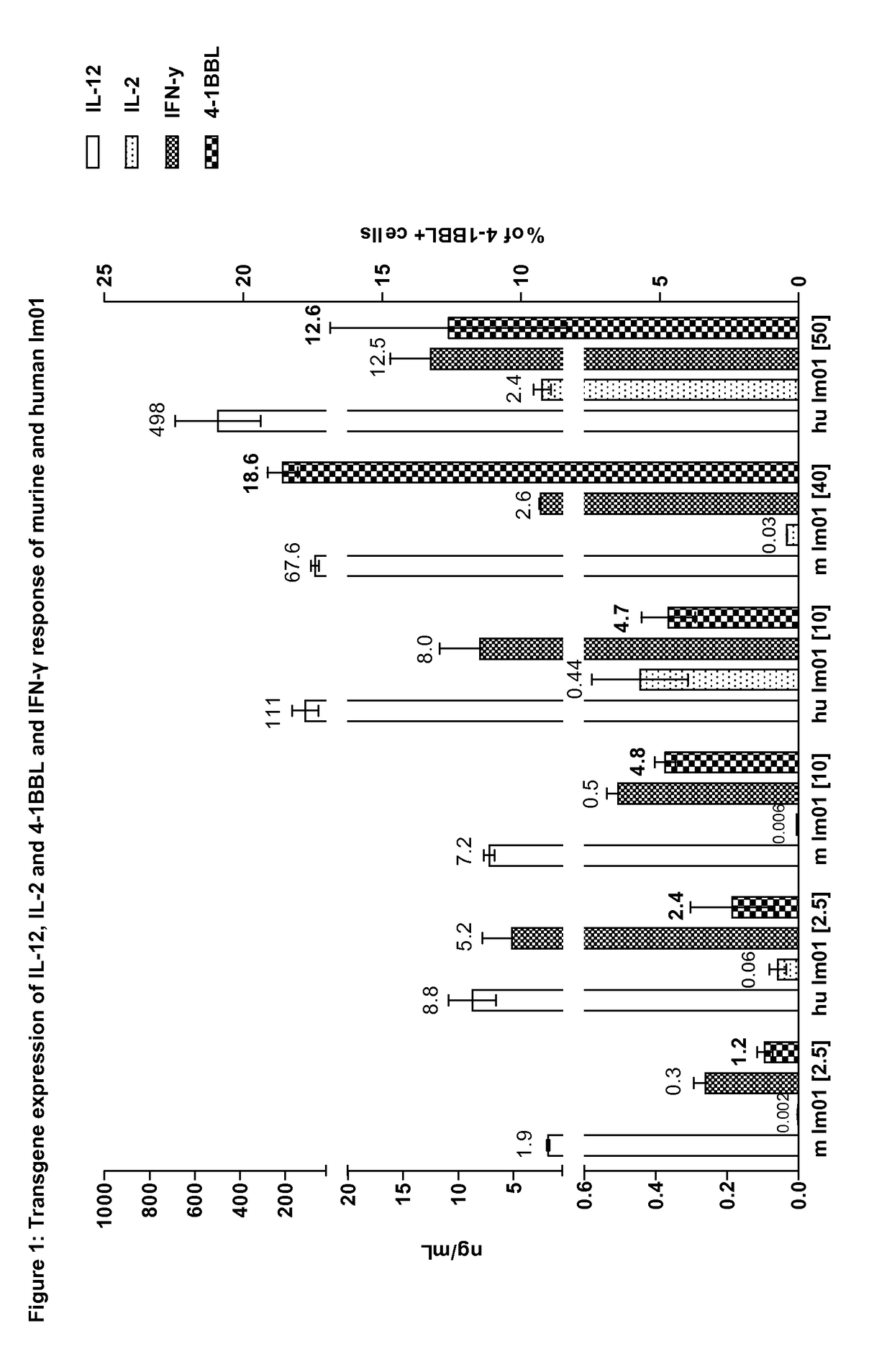
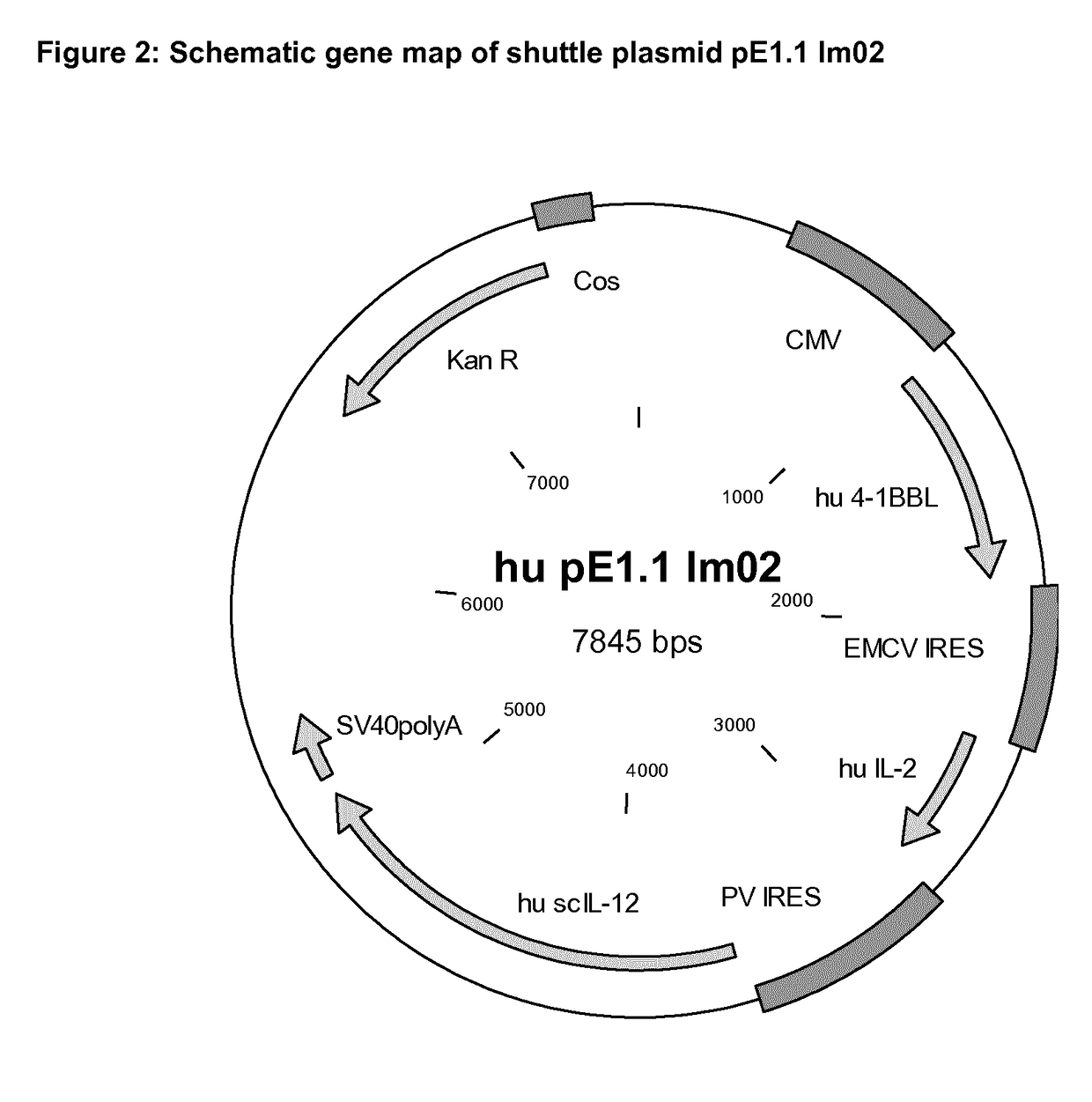
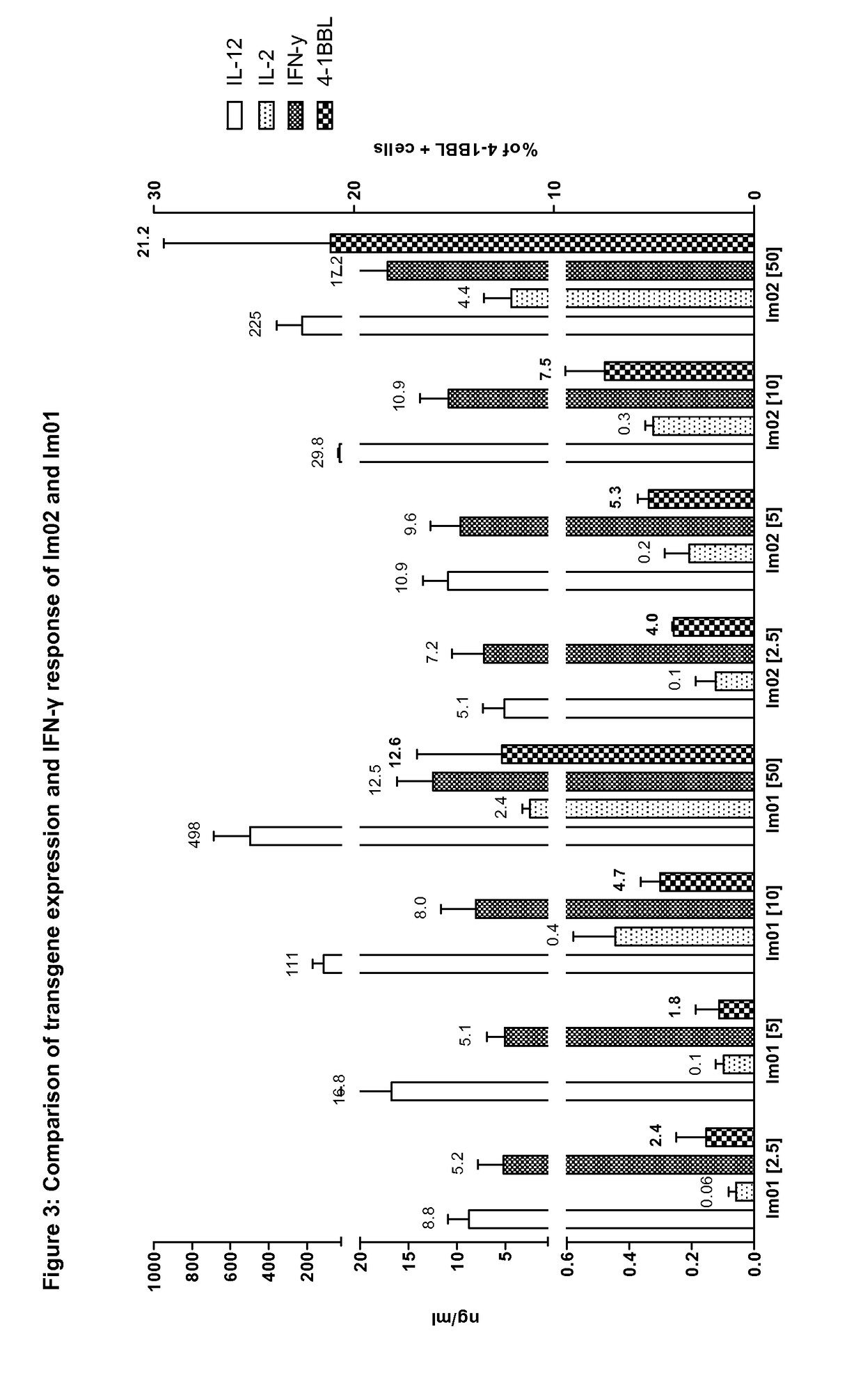
ActiveUS20190046664A1High expressionGenetic therapy composition manufactureNGF/TNF-superfamilyVector system4-1BB ligand
Owner:PROVECS MEDICAL
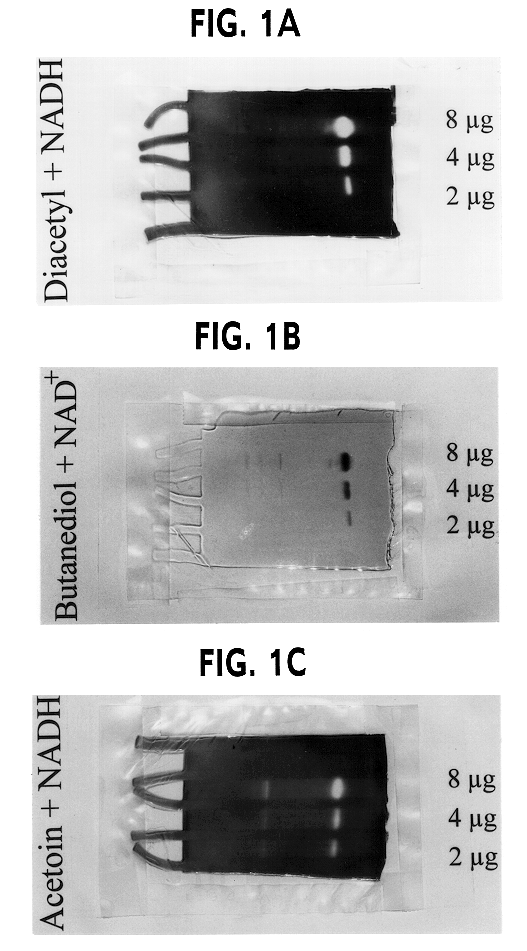
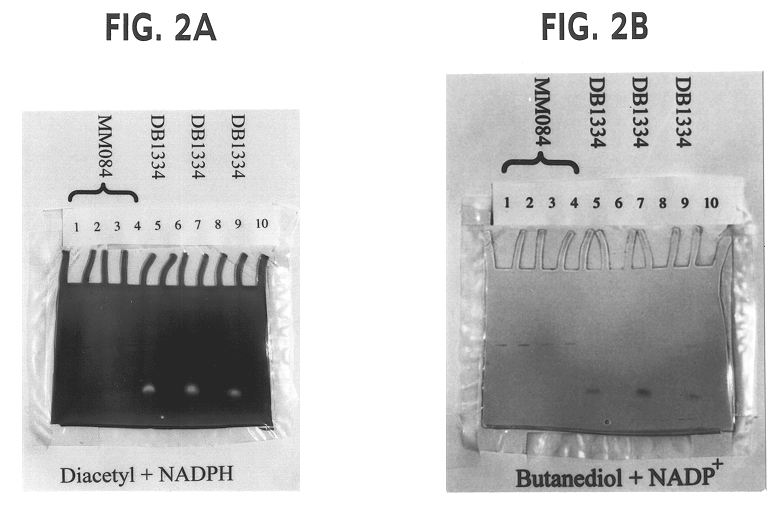
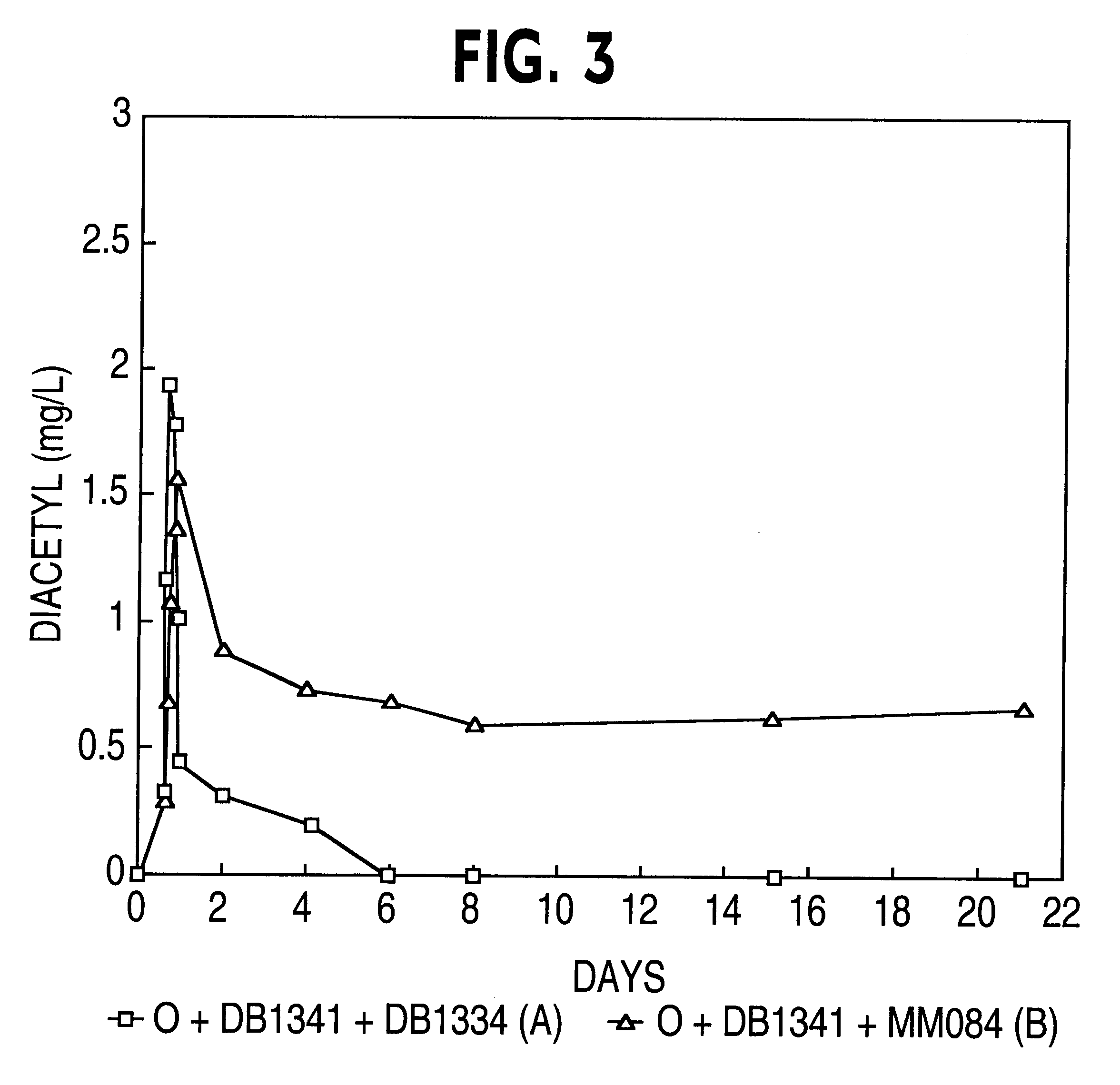
Genetically modified lactic acid bacteria having modified diacetyl reductase activities
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Artificial synthesised scorpion chloride ion neurotoxin gene-rBmK CTa
The invention makes 24-site mutation on natural scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin gene BmK CT according to the principle of Escherichia coli partial to codon, designs DNA sequence suitable to be expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), adopts PCR technique to complete artificial synthesis of recombinant scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin gene rBmK CTa. On this basis, it clones rBmK CTa into pEXSecI expression system to transfer in the BL21 (DE3), screens and obtains high-performance expressed bacterial strain, detects that the expressed product of the rBmK CTa accounts for 19.936% of the all-bacterium protein by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and by affinity chromatography, obtains purer protein with bioactivity, and can obtain 2.4mg protein from one liter culture liquor by purifying. The obtained modified recombinant scorpion chlorine ion channel neurotoxin has inhibition effect on neuroglia cell and can be used in preparing medicines curing diseases by inhibiting neuroglia cell and also be used in research on the space structure and pharmacological activity of scorpion neurotoxin.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Protein, DNA coding for same and method of producing the protein
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Plants and seeds of hybrid corn variety CH744817
ActiveUS9999194B1Plant genotype modificationVector-based foreign material introductionAdemetionineTissue culture
According to the invention, there is provided seed and plants of the hybrid corn variety designated CH744817. The invention thus relates to the plants, seeds and tissue cultures of the variety CH744817, and to methods for producing a corn plant produced by crossing a corn plant of variety CH744817 with itself or with another corn plant, such as a plant of another variety. The invention further relates to genetic complements of plants of variety CH744817.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Inbred corn line D601
InactiveUS20050177896A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
An inbred corn line, designated D601, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of inbred corn line D601, to the plants of inbred corn line D601 and to methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the inbred line D601 with itself or another corn line. The invention further relates to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from the inbred D601.
Owner:CENT GOLDEN HARVEST RES
GTP cyclohydrolase I gene folE and application
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Prepn and application of epiderm or hair follicle stem cell from souce of human early embryo
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Vector for knocking out L-lactic dehydrogenase 1 gene and construction method of vector
InactiveCN104673819AUse lessAvoid joiningMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
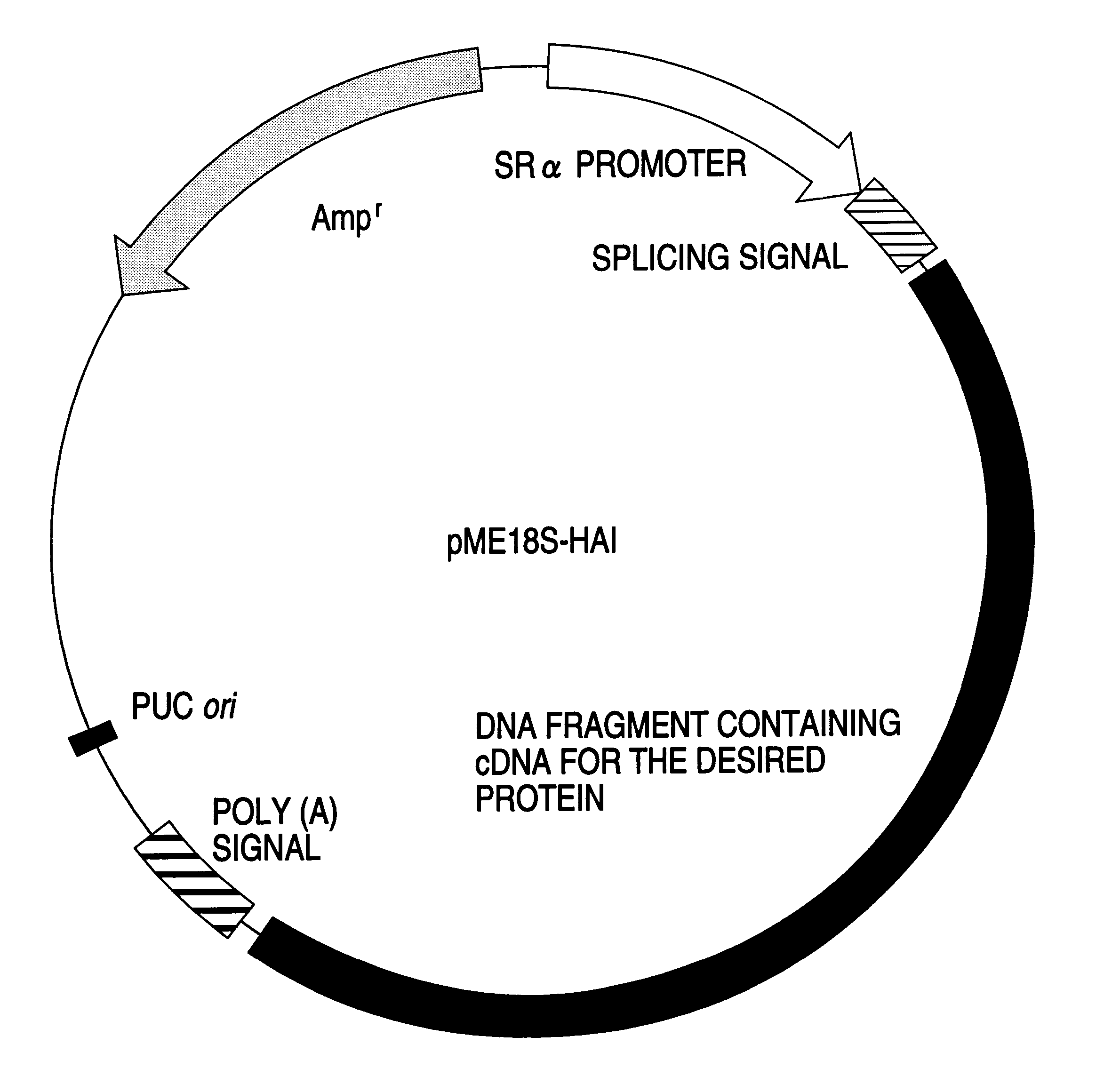
Recombinant vector and use in gene therapy
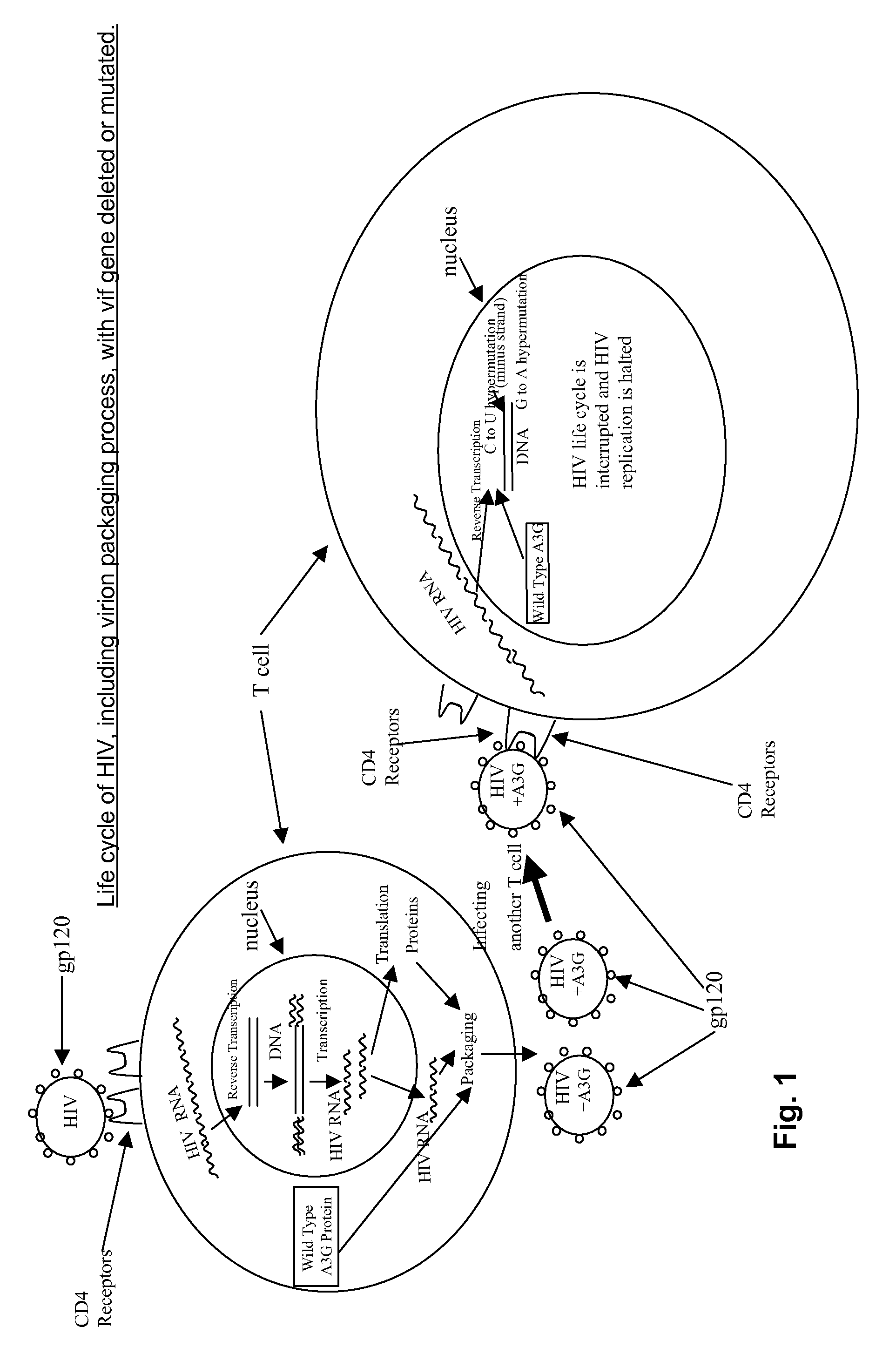
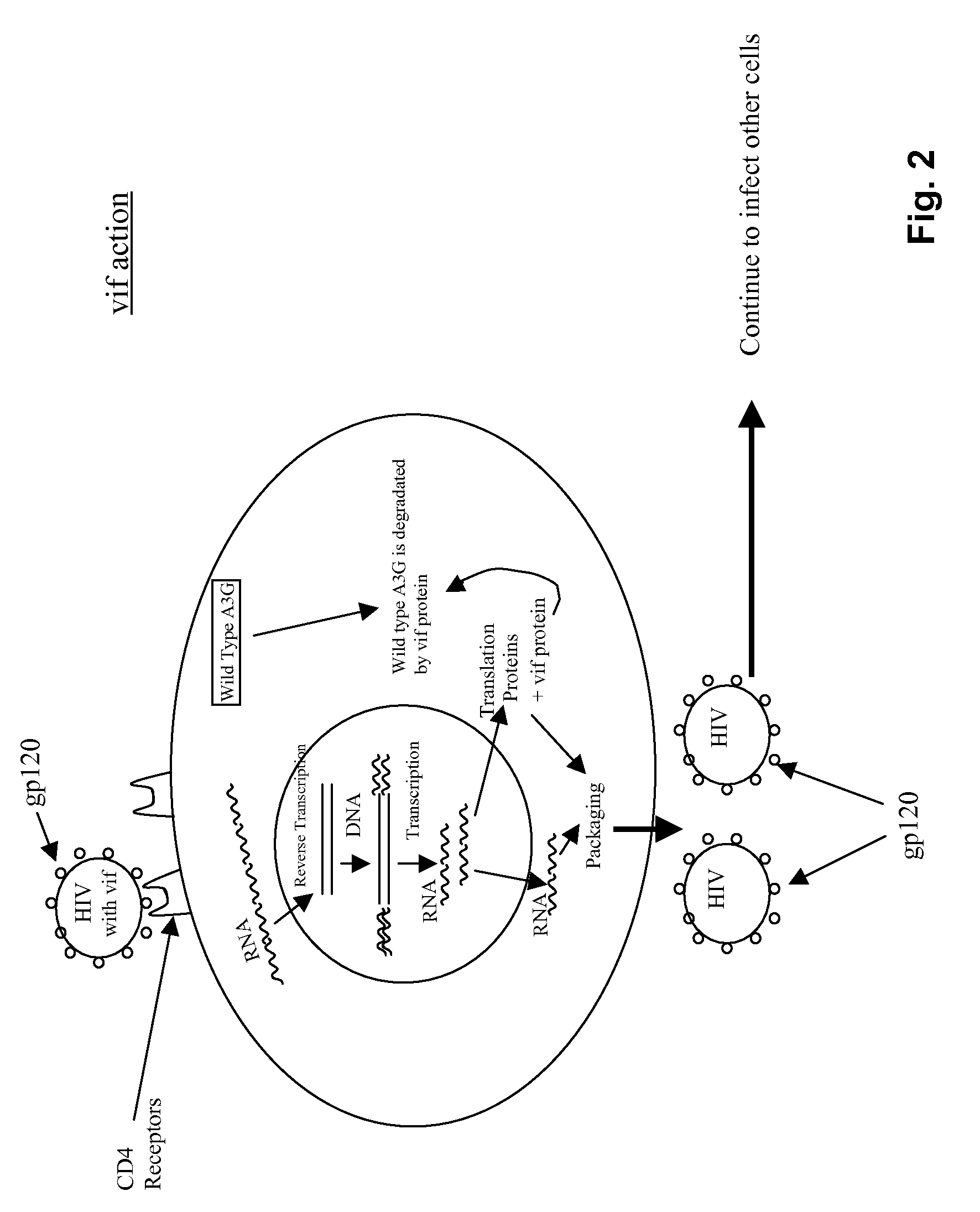
InactiveUS20080226675A1Preventing HIV infectionHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsWild typeHuman cell
Owner:XU HONGZHAN
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield L-leucine, and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109294966AEfficient synthetic pathwayLow content of by-productsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNad dependent
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield L-leucine, and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the present invention, the NADP-dependent branched-chain amino acid transaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum is replaced with NAD-dependent leucine dehydrogenase (LeuDH) derived from B.sphaericus by using a genetic engineering method, such that the new efficient L-leucine synthesis pathway is constructed, the disadvantages of excessive accumulation of NADH in the Corynebacterium glutamicum L-leucine producing bacteria and insufficient supply of NADPH are solved, the L-leucine synthesis ability in the recombinant strain is enhanced, and the NADPH accumulation ability of the strainis improved; the shake fermentation experiment results show that the L-leucine accumulation of the recombinant strain achieves 16.7 g.L<-1> and is higher than the L-leucine accumulation of the starting stain of 13.2 g.L<-1>, and the maximum specific growth rate of the recombinant strain is 0.23 g.L<-1>.h<-1>, and is higher than the maximum specific growth rate of the recombinant strain of 0.18 g.L<-1>.h<-1>; and the L-leucine synthesis pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum is successfully modified, the disadvantage of the intracellular cofactor imbalance is improved, and the new idea is provided for the breeding of high-yield L-leucine production bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant Microorganisms Having Enhanced Propanol and Method for Preparing Propanol Using the Same
The present invention relates to mutant microorganisms having the ability to produce propanol in high concentration and high yield, and to a method of producing propanol using the same. More particularly, the invention relates to mutant microorganisms having the ability to produce propanol in high concentration and high yield, which have introduced therein genes that encodes enzymes which are involved in the biosynthesis of propanol from threonine, and to a method of producing propanol using the same
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for expressing and purifying recombinant ethanol oxidase in pichia pastoris
The invention discloses a method for expressing and purifying recombinant ethanol oxidase rAOX. According to the method, an ethanol oxidase-poly-L-histidine expression vector pPIC9K-AOX-HIS is constructed first by a molecular biological technique, then the expression vector pPIC9K-AOX-HIS is linearized and transferred to pichia pastoris GS115, and thus, pichia pastoris engineering bacteria capable of expressing active recombinant ethanol oxidase are obtained, and part of recombinant ethanol oxidase can be secreted and expressed. Through optimization of the expression conditions of recombinant ethanol oxidase, the ethanol oxidase produced by the engineering bacteria may reach 1,862U / L. Meanwhile, the secretion and expression of the ethanol oxidase and the introduction of a poly-L-histidine tag simplify the purification process of the recombinant ethanol oxidase. According to the result of tests, the recombinant ethanol oxidase expressed by the engineering bacteria has much higher thermostability than pichia pastoris wide type ethanol oxidase. The operation in the whole process of the method is simple, so the method is suitable for industrial production and can create certain economic benefit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DEQING HUINING BIOTECH
Long-acting HIV fusion inhibitor and application thereof
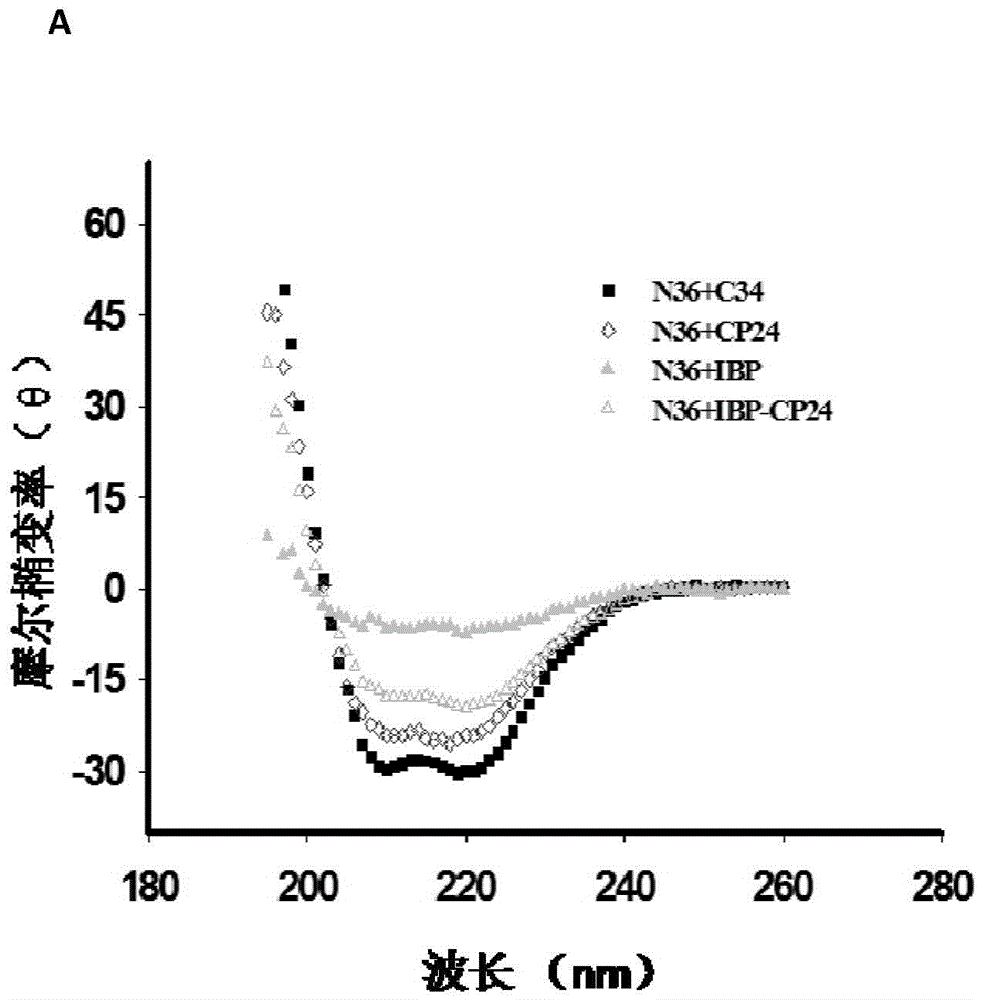
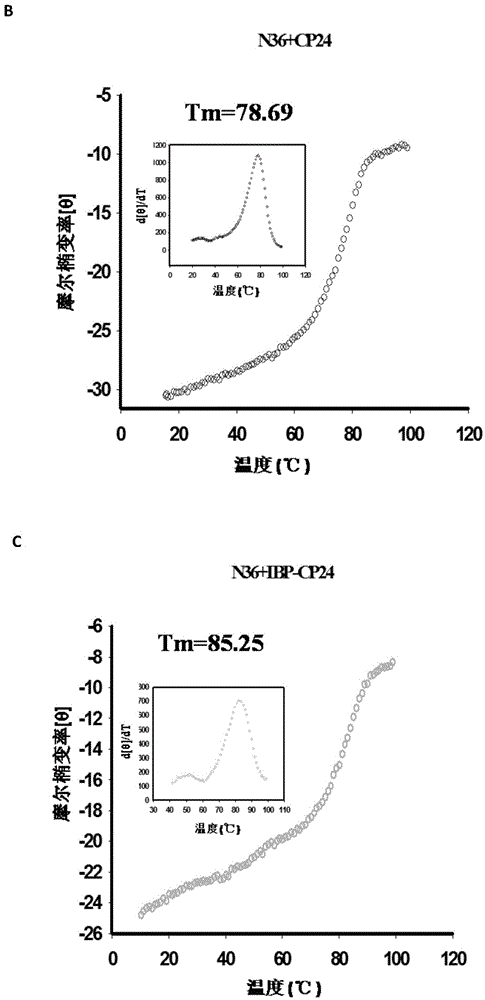
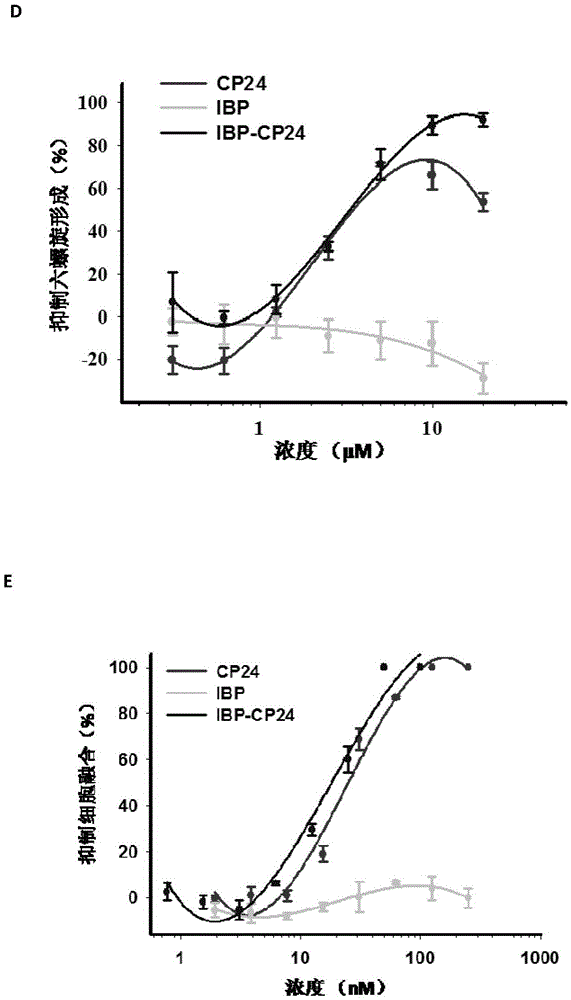
ActiveCN105646717APromote research and developmentExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHalf-lifeTherapy HIV
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Plant activation of insect toxin
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Callery pear ascorbate peroxidase gene and use thereof in resisting heavy metal stress
The invention relates to a callery pear ascorbate peroxidase gene and a use thereof in resisting heavy metal stress. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in the sequence SEQ ID No. 1. The total RNAs of the leaves of the callery pear are extracted after cadmium treatment and the ascorbate peroxidase gene Pc. APX is cloned by combination of bioinformatics and PCR so that the complete coding genesequence of 753 bp is obtained. The escherichia coli expression vector pET-22b(+)-Pc. APX is constructed and through the escherichia coli heterologous expression system, the functions of the cloned ascorbate peroxidase gene Pc. APX are identified and the recombinant escherichia coli with the cloned ascorbate peroxidase genes Pc. APX have strong tolerance to cadmium. At the same time, a binary plant expression vector pRI201-AN-GUS-Pc. APX is contructed, the vector is transferred into agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 cells by a freezing-thawing method, and the cells are transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana, and the obtained transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana has higher cadmium tolerance than wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean gene GmTCM1 and obtaining method and application thereof
ActiveCN112646818AEasy to synthesizeIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention relates to a soybean gene GmTCM1 and an obtaining method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soybean genetic breeding. In order to increase the soybean isoflavone content and obtain transgenic soybean plants with high isoflavone content, the soybean gene GmTCM1 is cloned from soybeans 27 in a soybean variety with high isoflavone content, and biological information analysis and preliminary analysis of gene functions of the gene show that the gene GmTCM1 can increase the soybean isoflavone content and participate in resistance reactions to abiotic stress such as drought and salt and biotic stress such as sclerotinia sclerotiorum, phytophthora and gray-spot bacteria. In addition, the obtained transgenic material can become a stable disease-resistant genetic material through subsequent subculture reproduction and identification. The soybean gene GmTCM1 has important theoretical significance and practical value for accelerating the breeding process of new varieties of high-isoflavone disease-resistant stress-resistant soybeans and improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap