Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4 results about "Recombinant escherichia coli" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Escherichia coli is one of the organisms of choice for the production of recombinant proteins. Its use as a cell factory is well-established and it has become the most popular expression platform.
Recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103773729AAbundant resourcesGood synthesis effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLycopene
The invention relates to a recomposed escherichia coli base cell for efficient synthesis of terpene chemical compounds as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Particularly, an escherichia coli endogenous 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphoric acid (MEP) precursor pathway is reconstructed; the reconstructed escherichia coli base cell is utilized to perform the efficient biological synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds; the reconstruction of the precursor pathway mainly comprises the steps of fully digging the MEP precursor pathway gene modules of the sources of other natural microorganisms, screening gene modules with excellent characteristics to be expressed in the escherichia coli, and at the same time, performing the downstream synthesis pathway for integrally assembling the colibacillus chemical compounds in the reconstructed base cell, wherein the colibacillus chemical compounds include sesquiterpene chemical compounds such as amorphadiene, diterpene chemical compounds such as shell alkene, tetraterpenes chemical compounds such as lycopene, polyterpene chemical compounds, other terpene alkaloid chemical compounds and the like. The escherichia coli base cell can remarkably facilitate the synthesis of the terpene chemical compounds.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Callery pear ascorbate peroxidase gene and use thereof in resisting heavy metal stress
The invention relates to a callery pear ascorbate peroxidase gene and a use thereof in resisting heavy metal stress. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in the sequence SEQ ID No. 1. The total RNAs of the leaves of the callery pear are extracted after cadmium treatment and the ascorbate peroxidase gene Pc. APX is cloned by combination of bioinformatics and PCR so that the complete coding genesequence of 753 bp is obtained. The escherichia coli expression vector pET-22b(+)-Pc. APX is constructed and through the escherichia coli heterologous expression system, the functions of the cloned ascorbate peroxidase gene Pc. APX are identified and the recombinant escherichia coli with the cloned ascorbate peroxidase genes Pc. APX have strong tolerance to cadmium. At the same time, a binary plant expression vector pRI201-AN-GUS-Pc. APX is contructed, the vector is transferred into agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 cells by a freezing-thawing method, and the cells are transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana, and the obtained transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana has higher cadmium tolerance than wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Purification and renaturation method for matrix metalloproteinase 13
InactiveCN106544335AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costHydrolasesEscherichia coliProtein target
Owner:威海恒基伟业信息科技发展有限公司
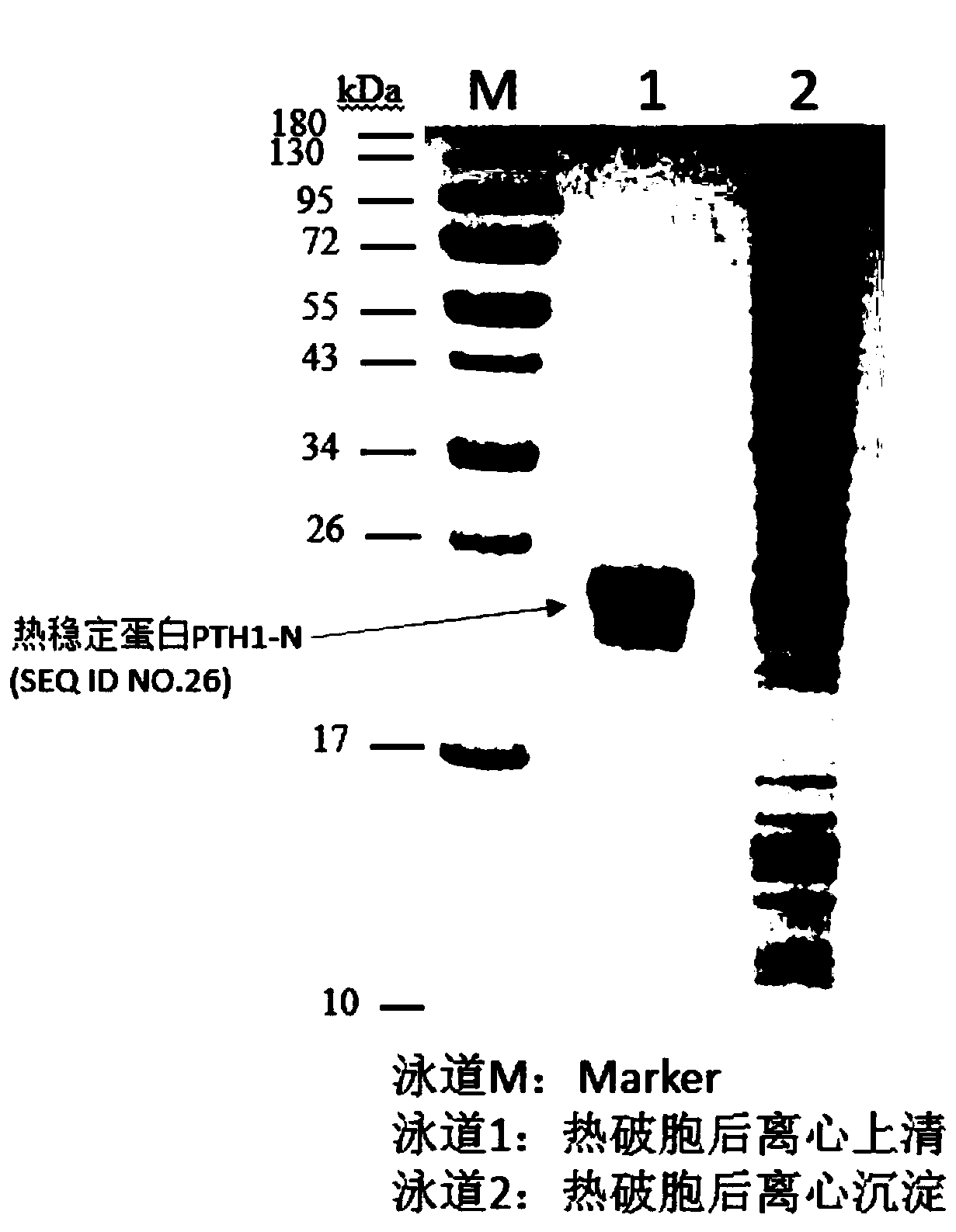
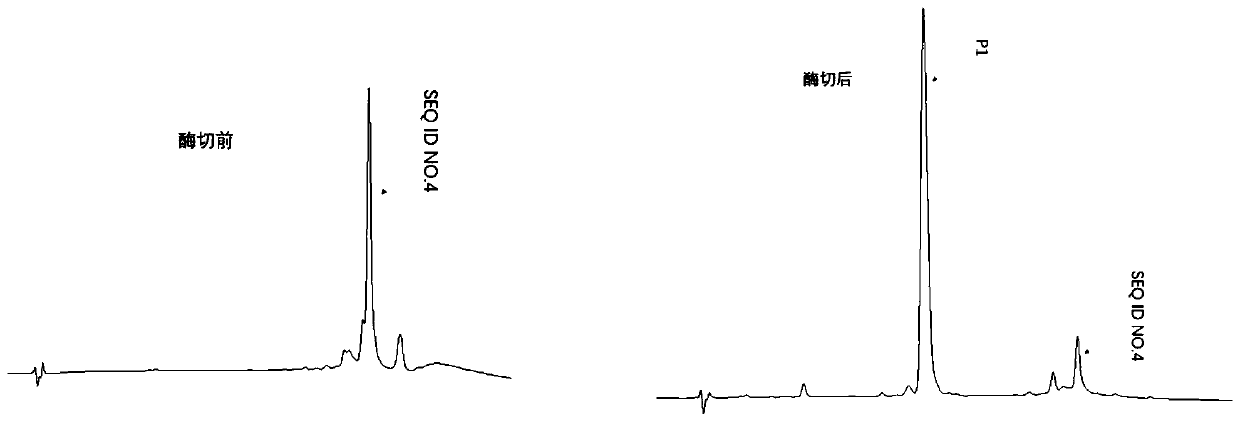
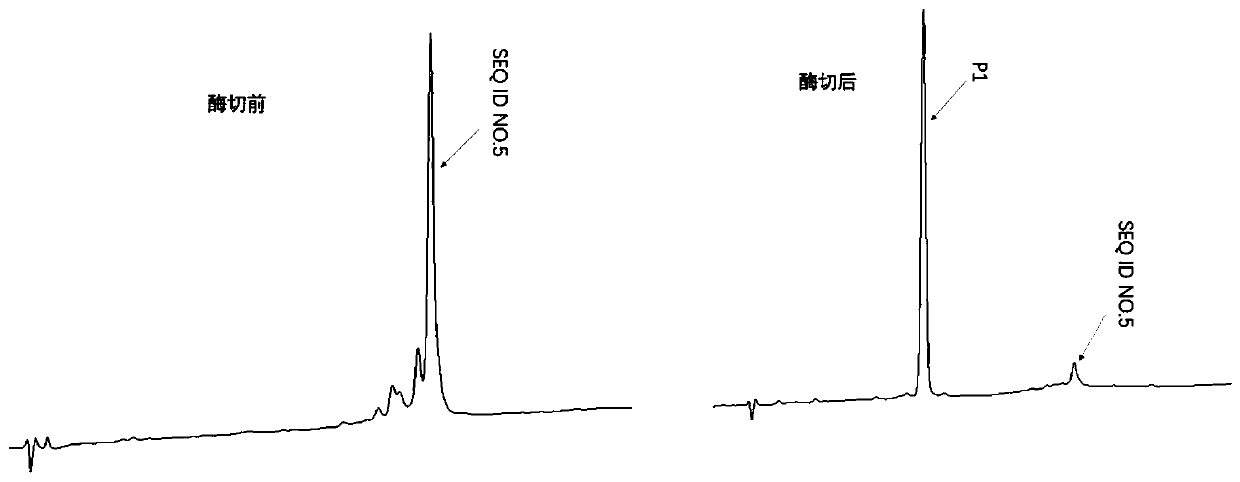
Method for preparing polypeptide by utilizing thermally-stabilised fusion protein
ActiveCN110564797AMicroorganism lysisMicroorganism based processesChemistryRecombinant escherichia coli
Owner:CHENGDU ENZPRO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap