Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2 results about "Corynebacterium glutamicum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Corynebacterium glutamicum (previously known as Micrococcus glutamicus) is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium that is used industrially for large-scale production of amino acids. While originally identified in a screen for organisms secreting L-glutamate, mutants of C. glutamicum have also been identified that produce various other amino acids.
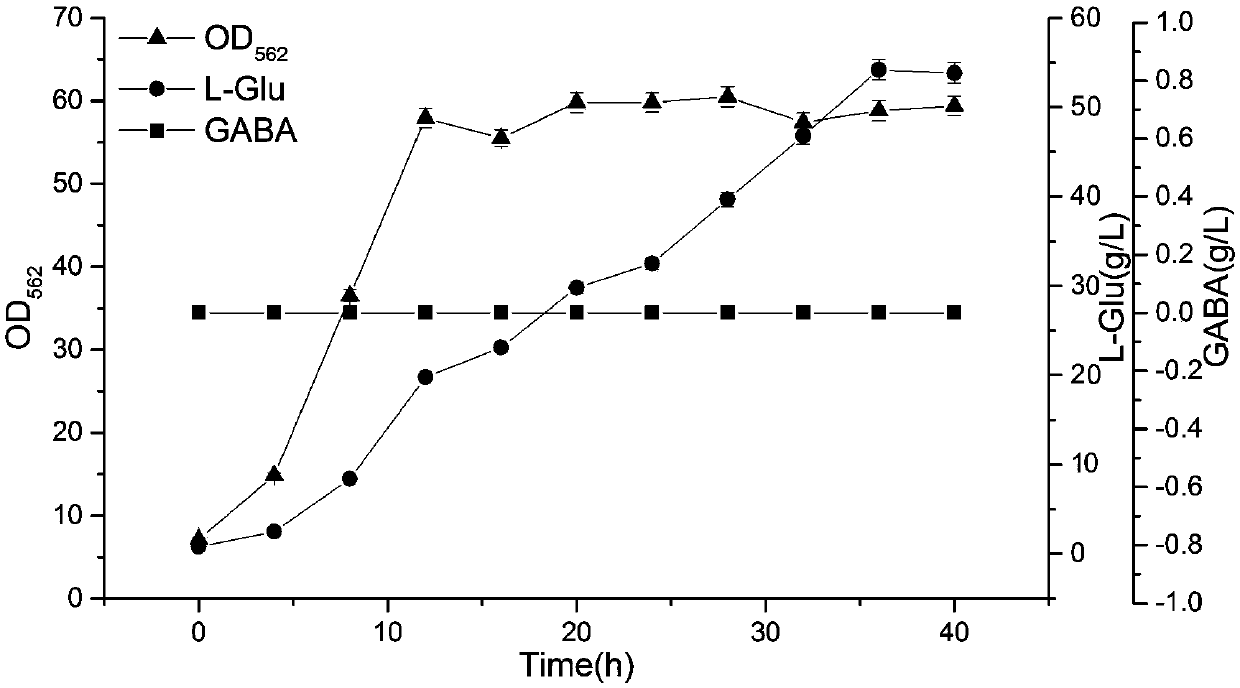
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield L-leucine, and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109294966AEfficient synthetic pathwayLow content of by-productsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNad dependent
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield L-leucine, and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the present invention, the NADP-dependent branched-chain amino acid transaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum is replaced with NAD-dependent leucine dehydrogenase (LeuDH) derived from B.sphaericus by using a genetic engineering method, such that the new efficient L-leucine synthesis pathway is constructed, the disadvantages of excessive accumulation of NADH in the Corynebacterium glutamicum L-leucine producing bacteria and insufficient supply of NADPH are solved, the L-leucine synthesis ability in the recombinant strain is enhanced, and the NADPH accumulation ability of the strainis improved; the shake fermentation experiment results show that the L-leucine accumulation of the recombinant strain achieves 16.7 g.L<-1> and is higher than the L-leucine accumulation of the starting stain of 13.2 g.L<-1>, and the maximum specific growth rate of the recombinant strain is 0.23 g.L<-1>.h<-1>, and is higher than the maximum specific growth rate of the recombinant strain of 0.18 g.L<-1>.h<-1>; and the L-leucine synthesis pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum is successfully modified, the disadvantage of the intracellular cofactor imbalance is improved, and the new idea is provided for the breeding of high-yield L-leucine production bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
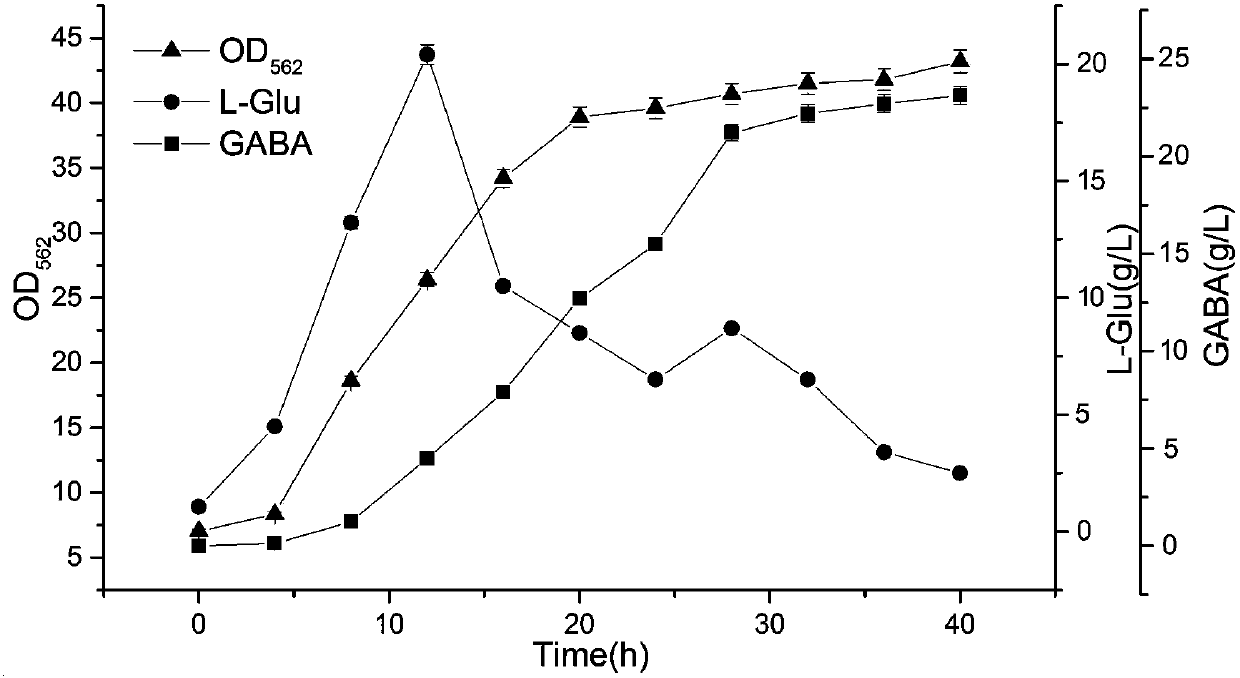
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid, and building method and application thereof
InactiveCN107674855AEfficient productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGamma-Aminobutyric acidGlutamate decarboxylase
Owner:ZHANG ZHOU HALTH VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap