Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microscope (from the Ancient Greek: μικρός, mikrós, "small" and σκοπεῖν, skopeîn, "to look" or "see") is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
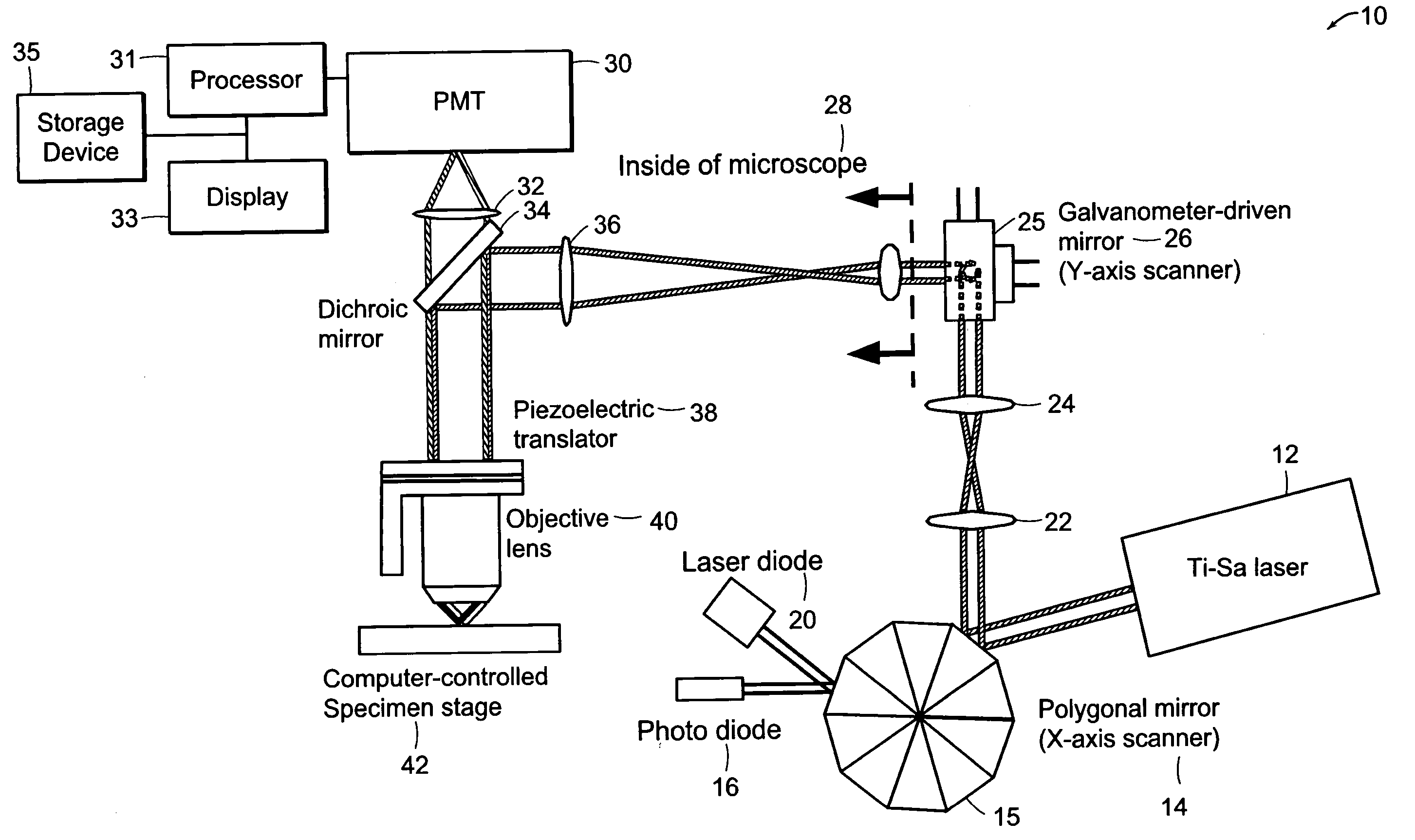
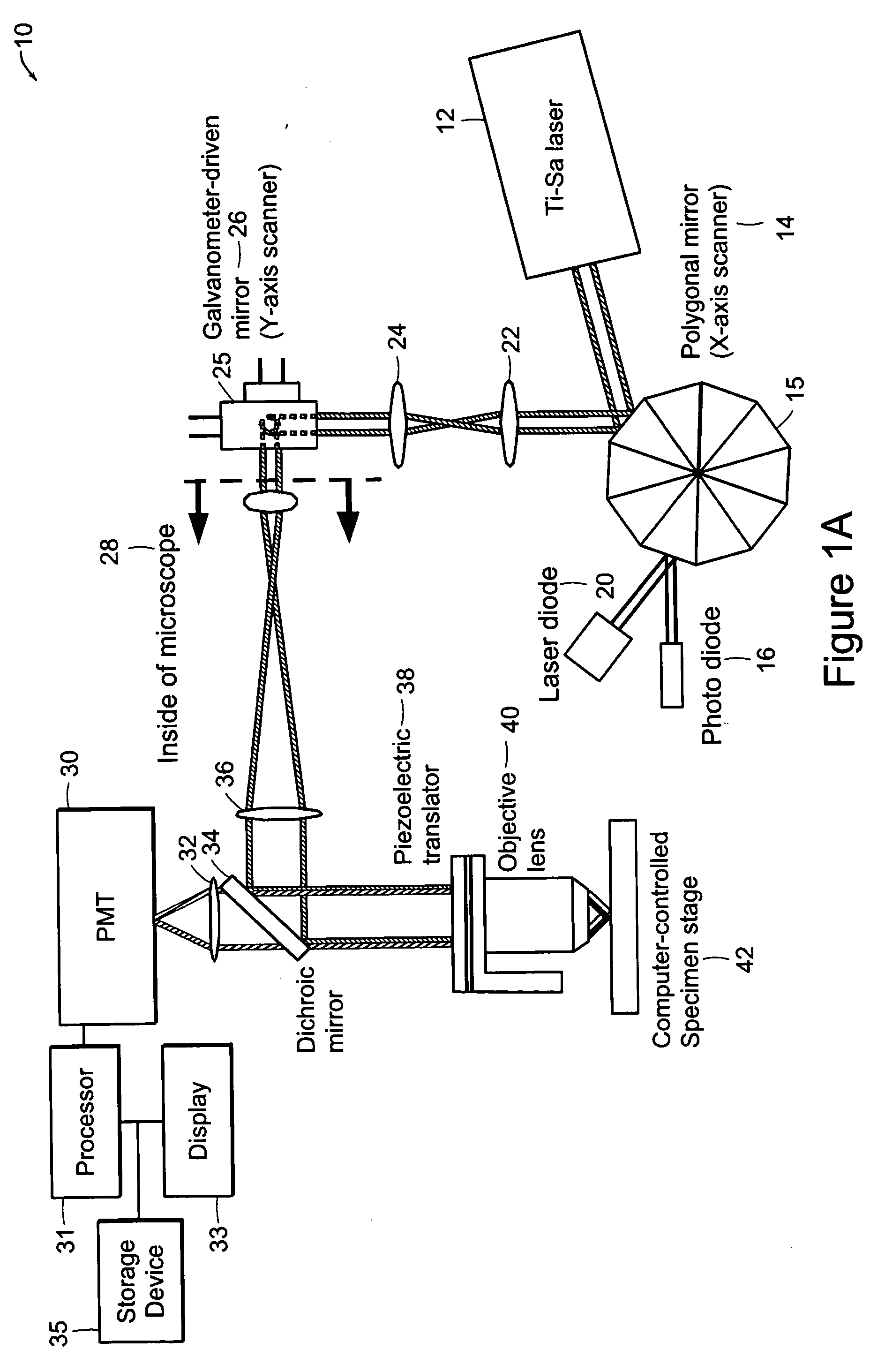
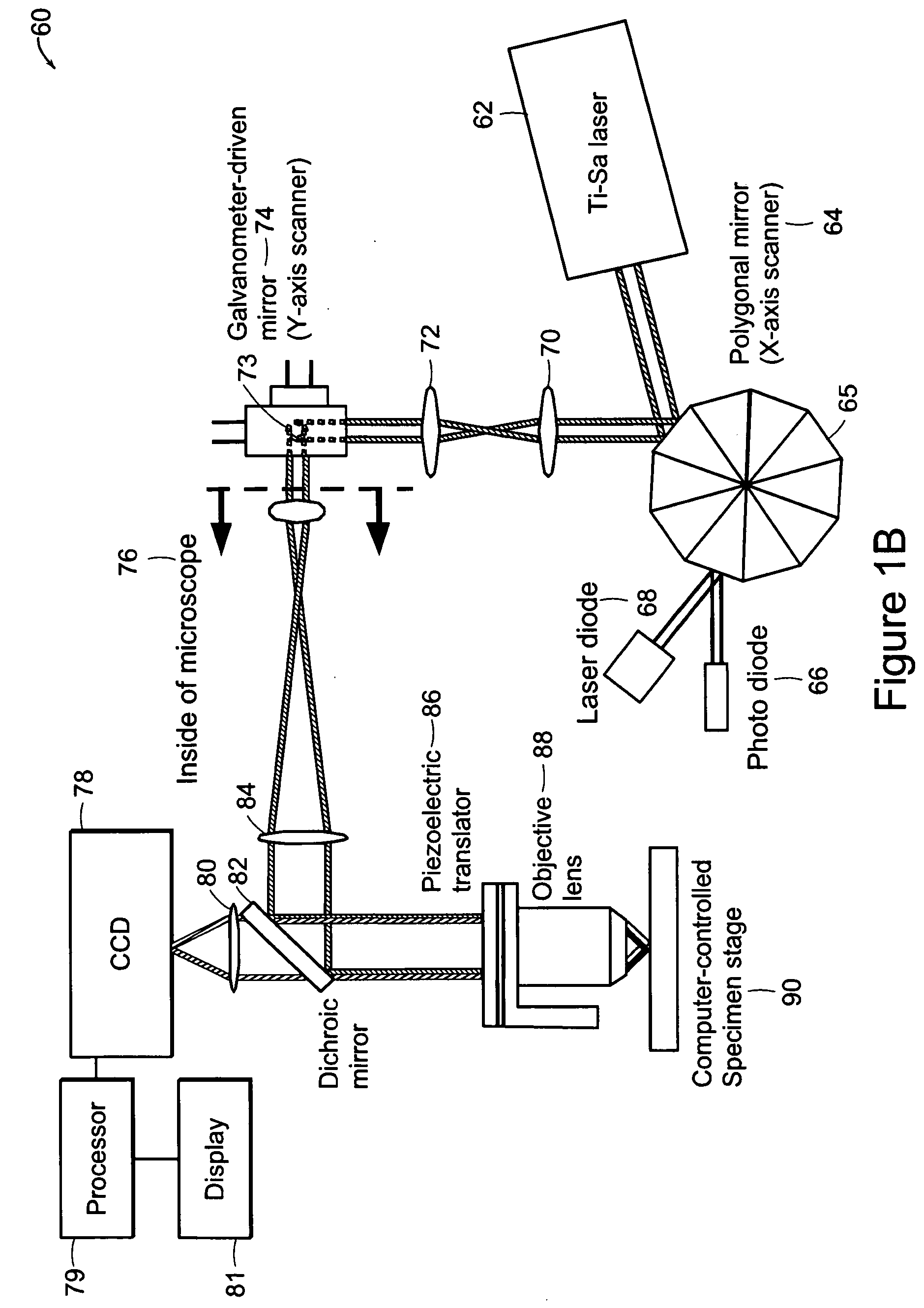
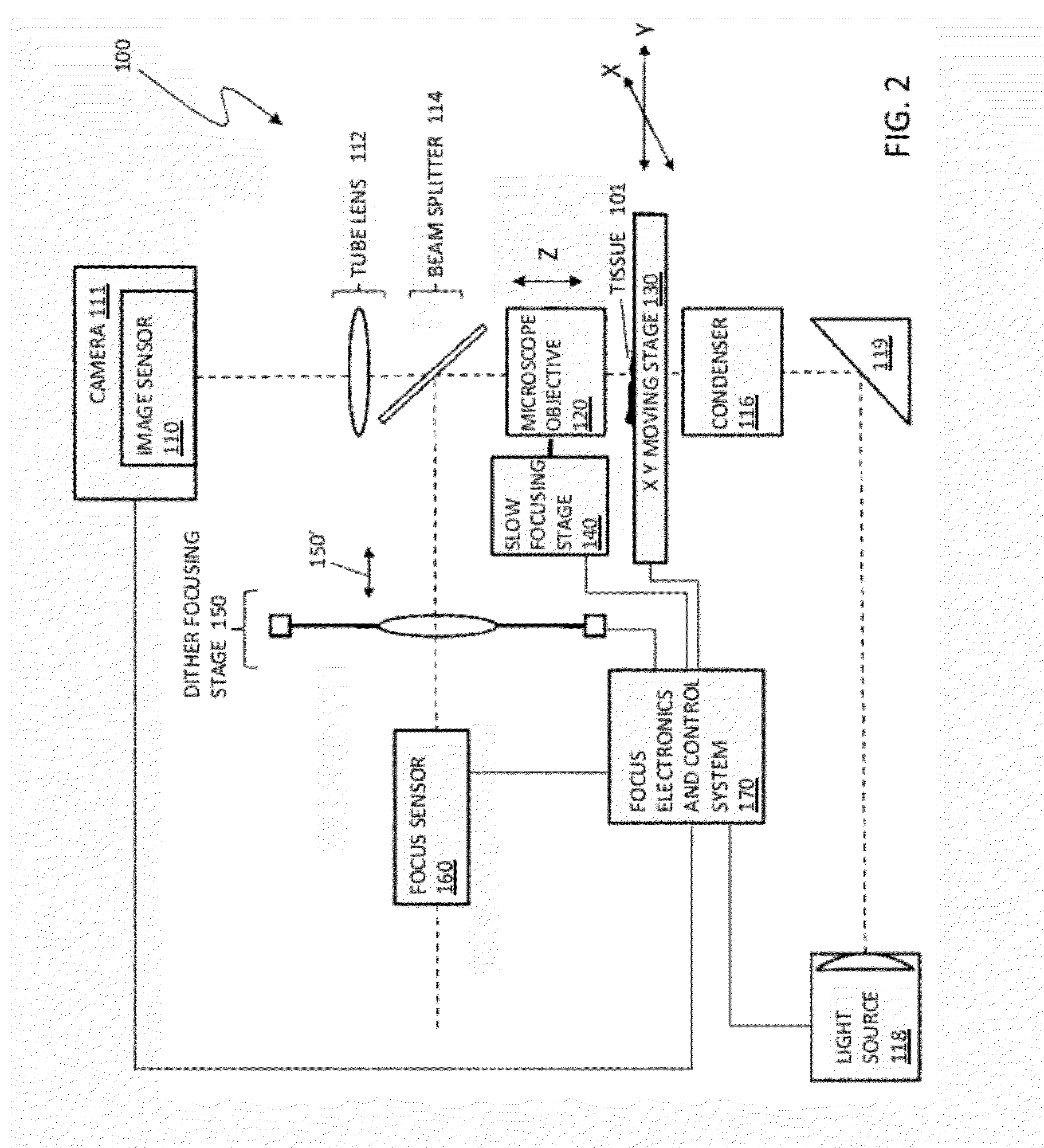
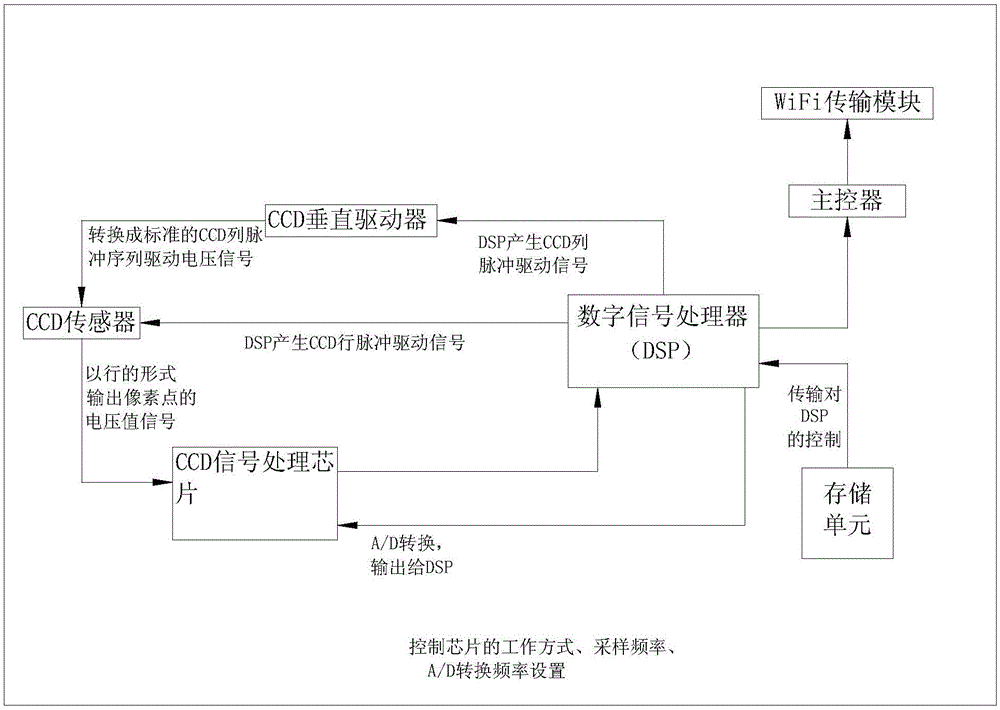
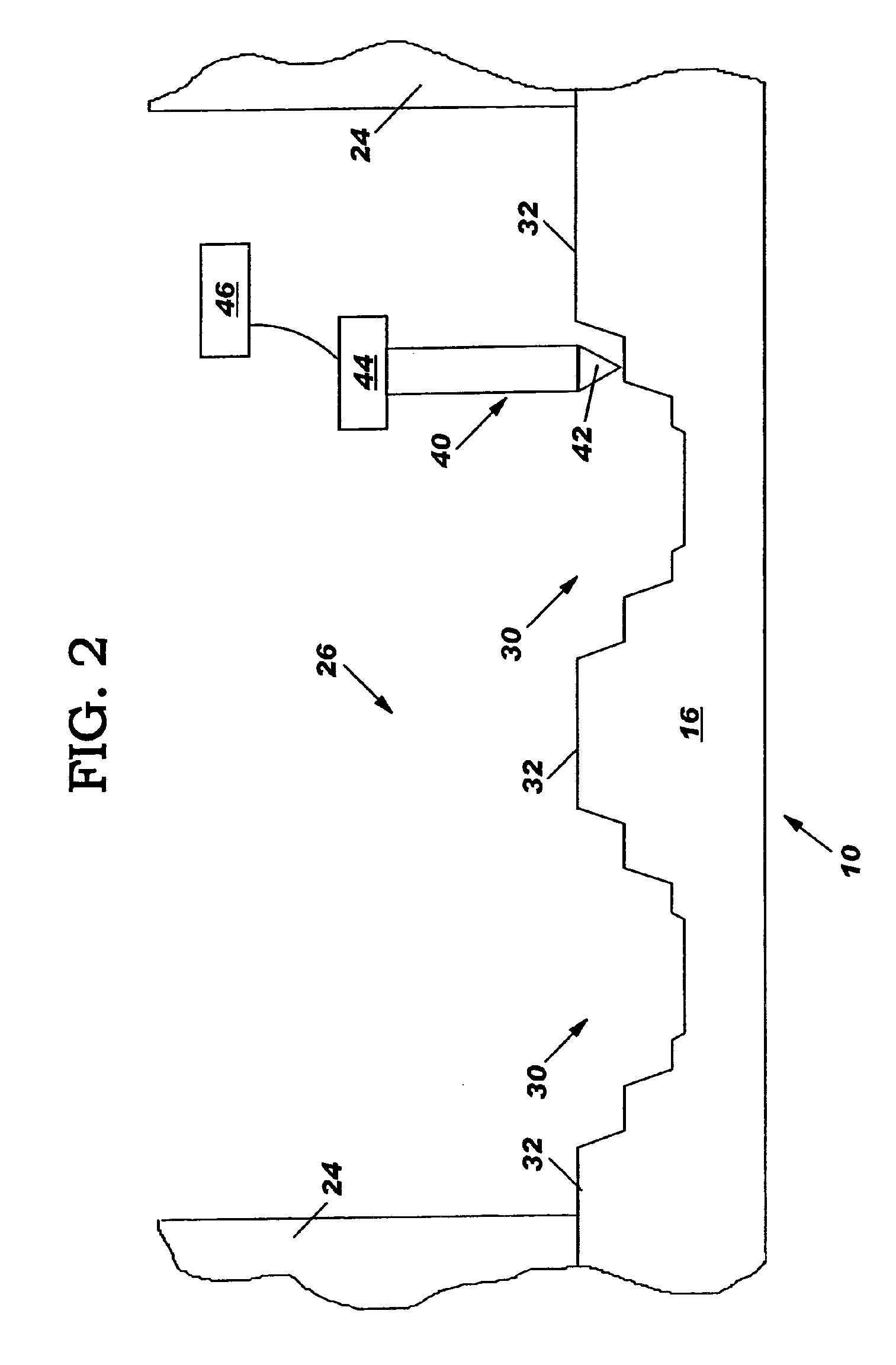
Systems and methods for volumetric tissue scanning microscopy
ActiveUS20050036667A1Minimal photodamageReduce phototoxicitySamplingAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsVolumetric imagingFluorescence
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
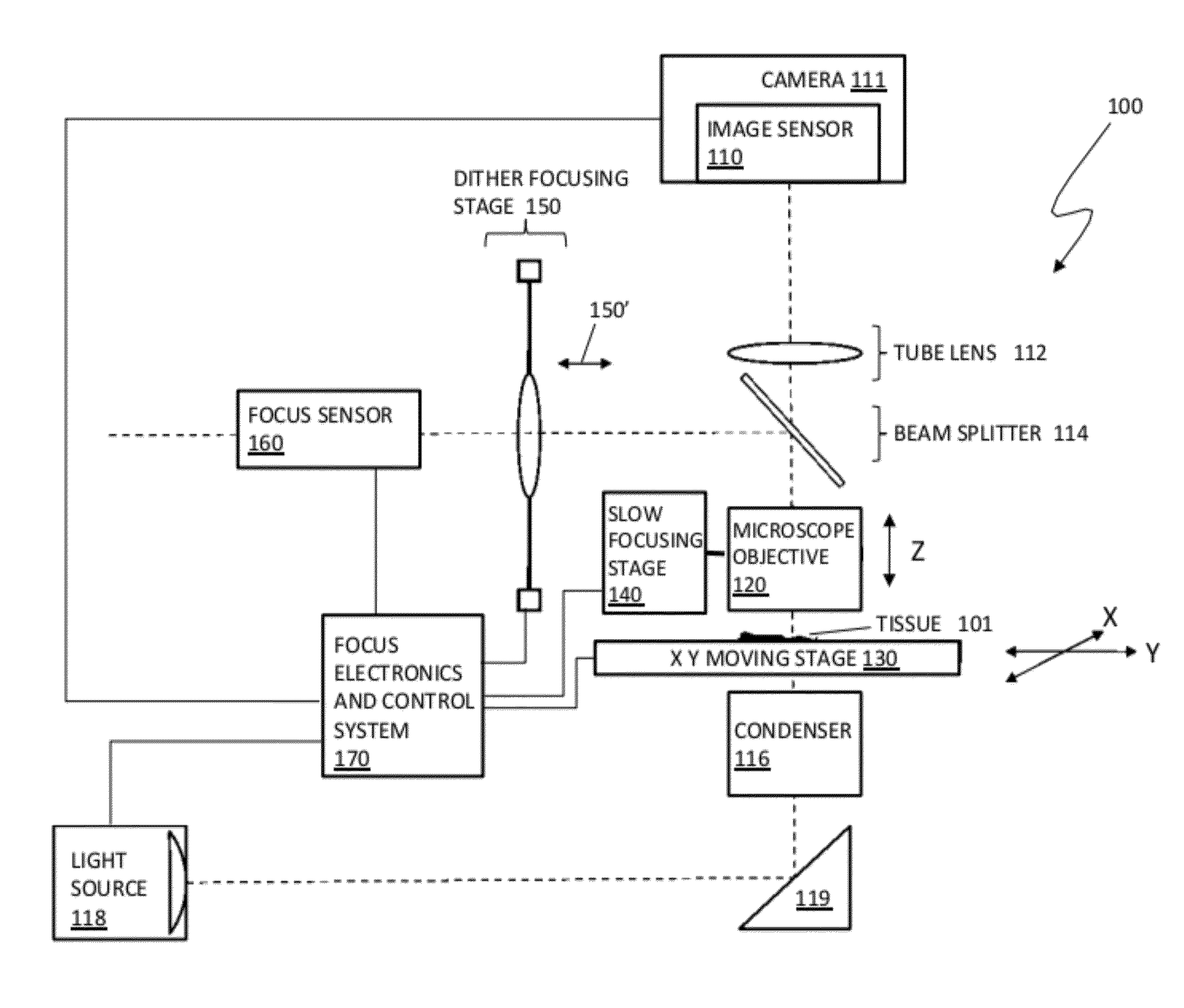
Imaging system and techniques
ActiveUS20120312957A1SamplingProjector focusing arrangementTissue sampleDigital image
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Optical microscopic imaging system and imaging method
The invention relates to an optical microscopic imaging system and imaging method, belonging to field of optical microscopes. The system comprises a laser, a half-wave plate, a polarization beam splitter prism, a beam expander collimator, a microscope objective, a reflective mirror, a beam combining mirror, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a computer. After the laser emits laser light, the polarization beam splitter prism divides the laser light into two light beams, and one of the light beams transmits a transparent object. The two light beams pass through the beam combining mirror and interfere with each other to form an image on the CCD, and the CCD transmits the obtained image into the computer. A microscopic strength image and a phase image of the object are obtained through digital reconstruction in the computer, so that a three-dimensional microscopic of the object is obtained.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG
Microscopic section rapid digital scanning device and method with real-time focusing function
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Insect Image Recognition and Instant Active Response
Owner:FRYSHMAN BERNARD
Optical fiber Bragg grating sensor and method for on-line measuring microbial film thickness thereof
InactiveCN101021596AHigh sensitivityHigh strengthUsing optical meansOptical light guidesGratingFiber bragg grating sensor
Owner:重庆工学院
Microscope optical system with a stationary sample stage and stationary viewing ports suited for viewing various fields of view of a sample
A microscope optical system in which both a sample and the viewing optics can be maintained stationary, while at the same time different points or fields of view of the sample can be examined. In the microscope optical system a sample is provided, e.g. on a stage, to be maintained in a stationary position when the sample is viewed. Further, viewing optics of the microscope optical system can be maintained in a stationary position when the sample is viewed. Intermediate optics between the stage and the viewing optics are moveable so that different portions of the sample can be examined without having to move the sample and without having to move the viewing optics.
Owner:ATTO BIOSCI
Holographic method and device for cytological diagnostics
InactiveUS20140193850A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVialMicroscope
Owner:OVIZIO IMAGING SYST NV SA
Cellulose nanosheet material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose nanosheet material. The thickness and the transverse size of the cellulose nanosheet material can be both adjusted and controlled, the thickness is 1-100 nm, the transverse size is 0.1-30 [mu] m, more than 80% of the cellulose nanosheet material is a single layer, the thickness of the single layer is 4 nm+ / -1 nm, in addition, the cellulose nanosheet material is smooth in surface, and the AFM (Atomic Force Microscope) measurement shows that the fluctuation of the surface is within 0.1 nm. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the cellulose nanosheet material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing mixed grinding on a cellulosic material and a lyophobic material so as to gradually separate cellulose into flakes, and further performing ultrasonic dispersion and separation to remove the lyophobic material, thereby obtaining the cellulose nanosheet material. The cellulose nanosheet material disclosed by the invention is of a layered, orientated and crystal structure, and is high in polydispersity in transverse size and morphology.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Network-based intelligent imaging analyzer for living cell culture in box
ActiveCN105136665ARealize the screenEnable mobilityMaterial analysis by optical meansRotary stageStudy observation
Owner:NINGBO JIANYI ELECTRONICS INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Non-radioactive agents for neuroblastoma imaging
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Integrated circuit and methods of measurement and preparation of measurement structure
InactiveUS20050283335A1Shorten analysis timeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Owner:IBM CORP
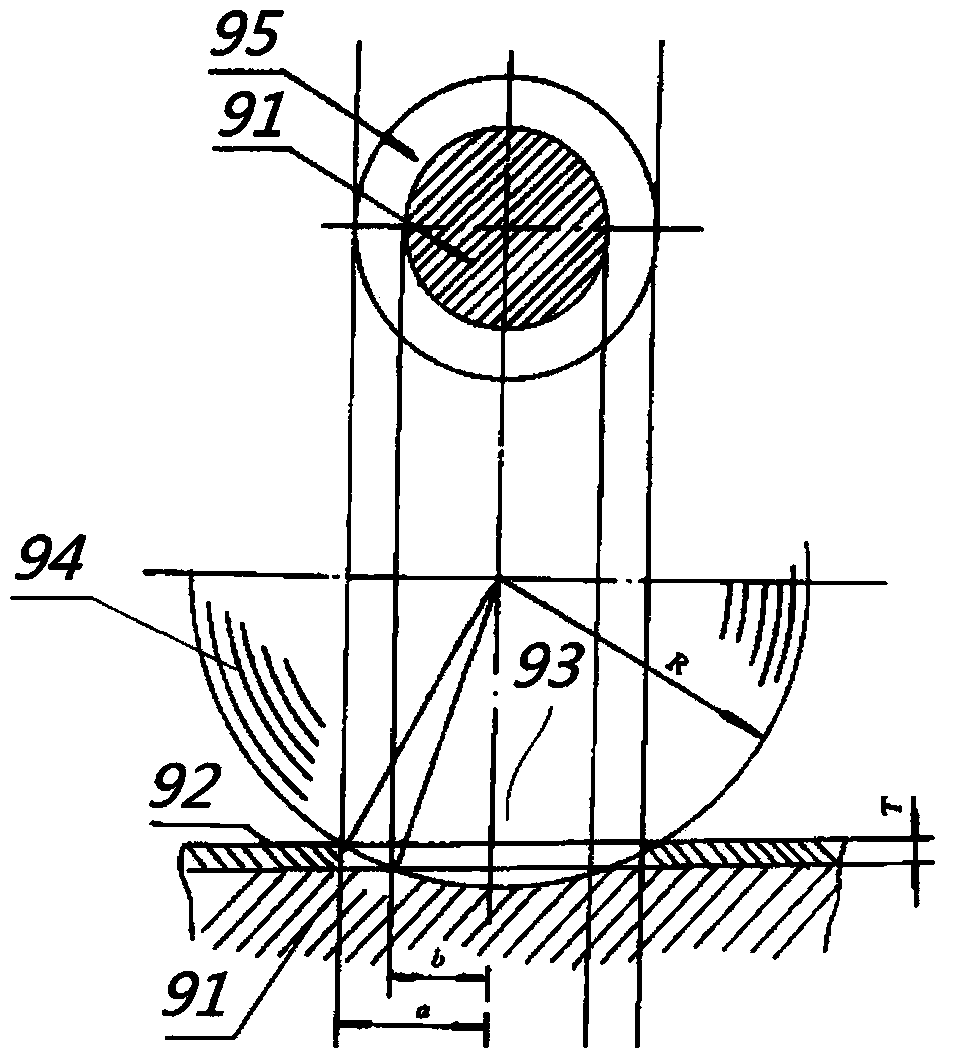
Method for detecting hard coating quality
ActiveCN104142280AAvoid damageAvoid problems with polished coated surfacesUsing optical meansInvestigating material hardnessHardnessGreat circle
Owner:FUNIK ULTRAHARD MATERIAL
Preparation method of micrometer-scale dispensing tungsten needle
InactiveCN104741292ASimple technical meansEasy to make raw materialsLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsMolten stateMicrometer scale
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Mobile phone camera connector
Owner:EASTCOLIGHT ENTERPRISE ZHONGSHAN
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveCN102906563ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicroscopeVoltage
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
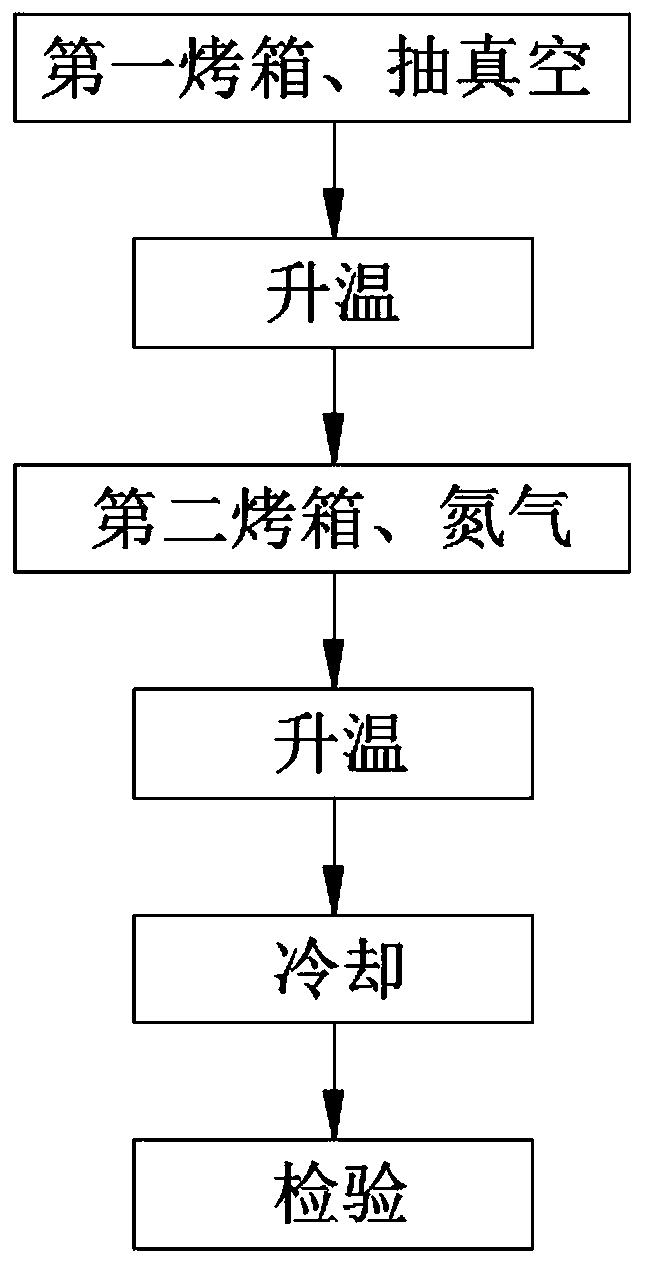
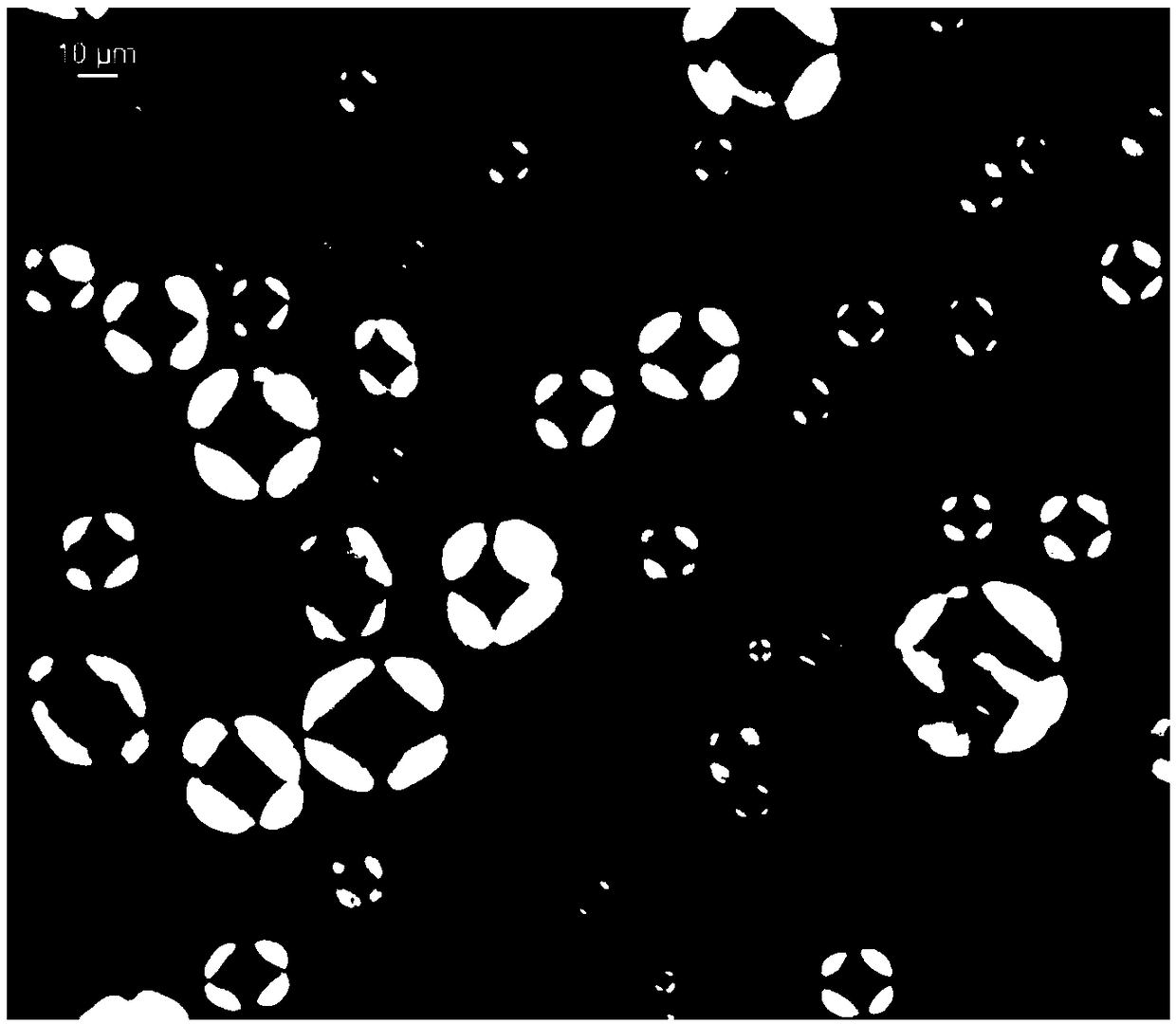
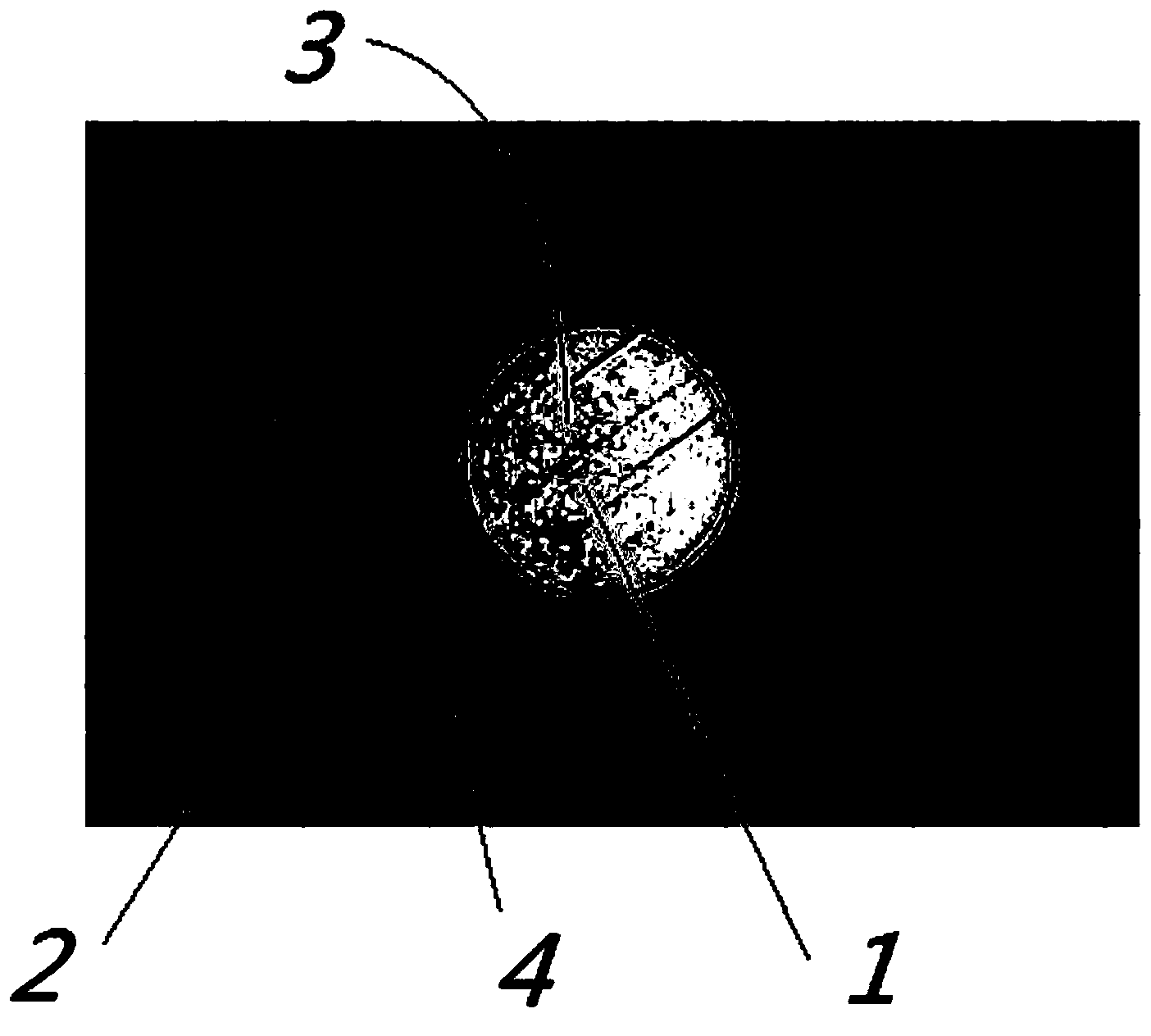
Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method
InactiveCN104862702ADislocation display validEtching is effective for dislocation displayPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWater bathsWafering
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical arrangement and a microscope
InactiveUS20090059357A1Compensation attenuationSimple structureMicroscopesTelescopesMicroscopeIntermediate image
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
USBC cable testing circuit
Owner:BIZLINK ELECTRONICS KUNSHAN CO LTD
Core heat setting process method
Owner:南通海美电子有限公司
No-wash sleep mask having layered structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109223696ASimple preparation processSave energyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientCell membrane
Owner:HUANAN IND TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Zinc oxide nano material resistance measurement method and device
InactiveCN105652094ALow costResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceNanogenerator
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cryoelectron microscope sample transfer system and method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN113109376AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesPhysicsMicroscope
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microscope base milling fixture
ActiveCN105014433AEasy clampingIncrease productivityWork clamping meansPositioning apparatusEngineeringMachining
Owner:WUZHOU OKA OPTICAL INSTR
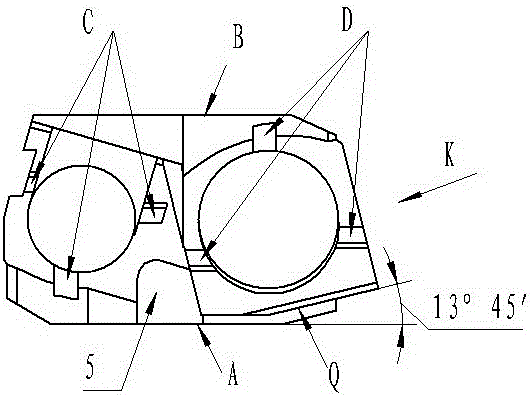
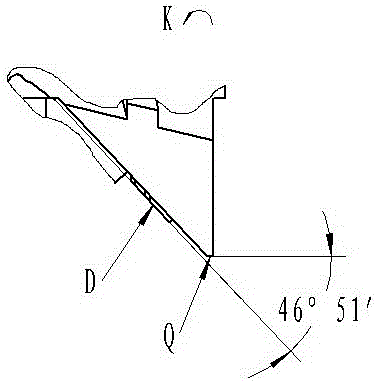
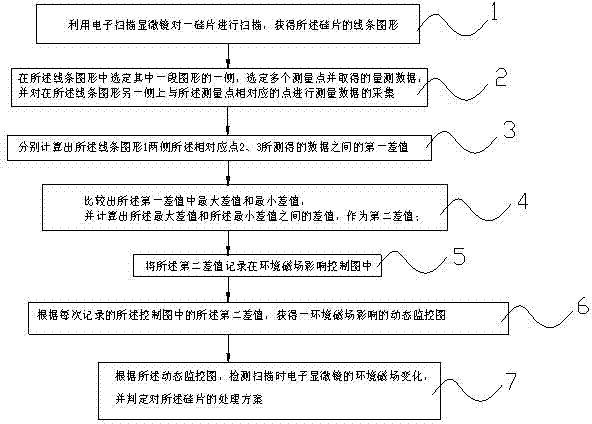
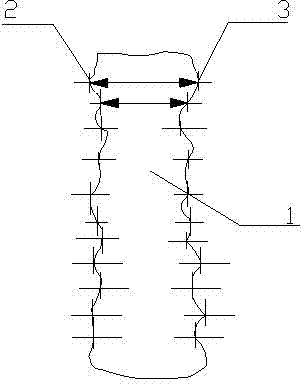
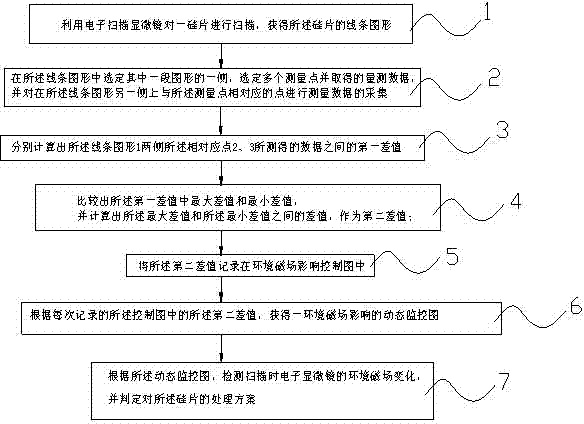
Monitoring method of environmental magnetic shield of electronic scanning microscope
ActiveCN102445567AAvoid misjudgmentScanning probe techniquesMeasurement pointLine width
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
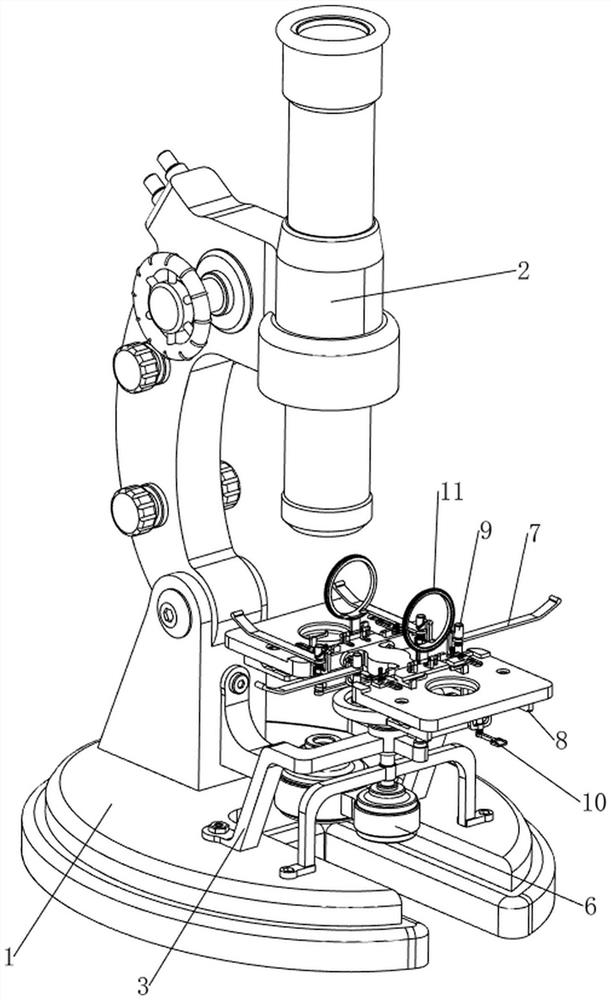
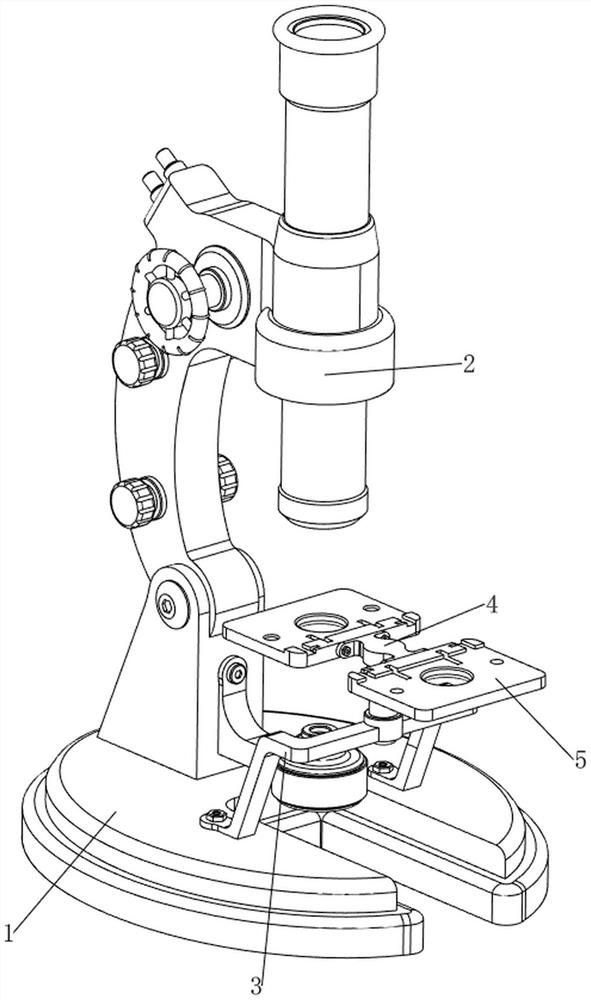
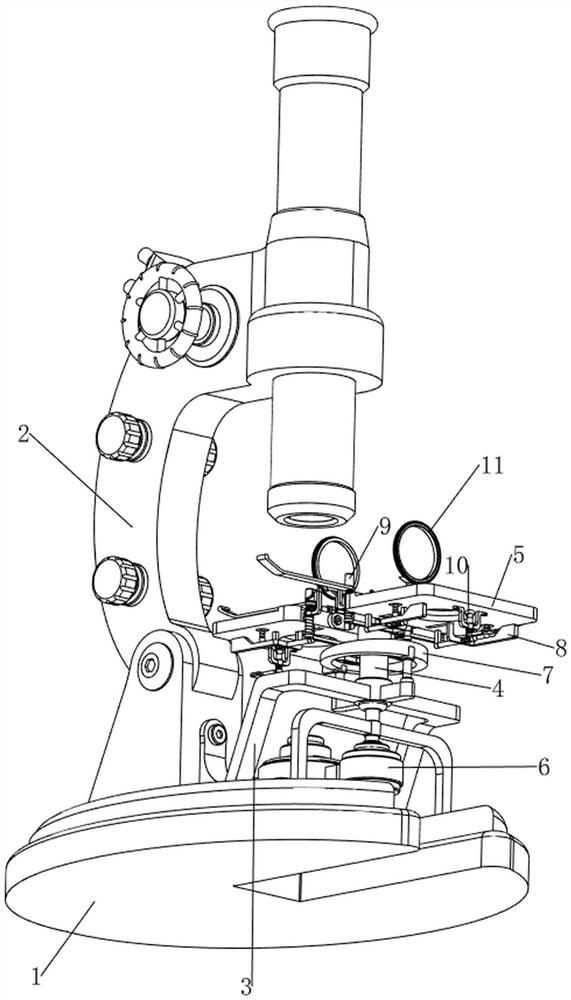
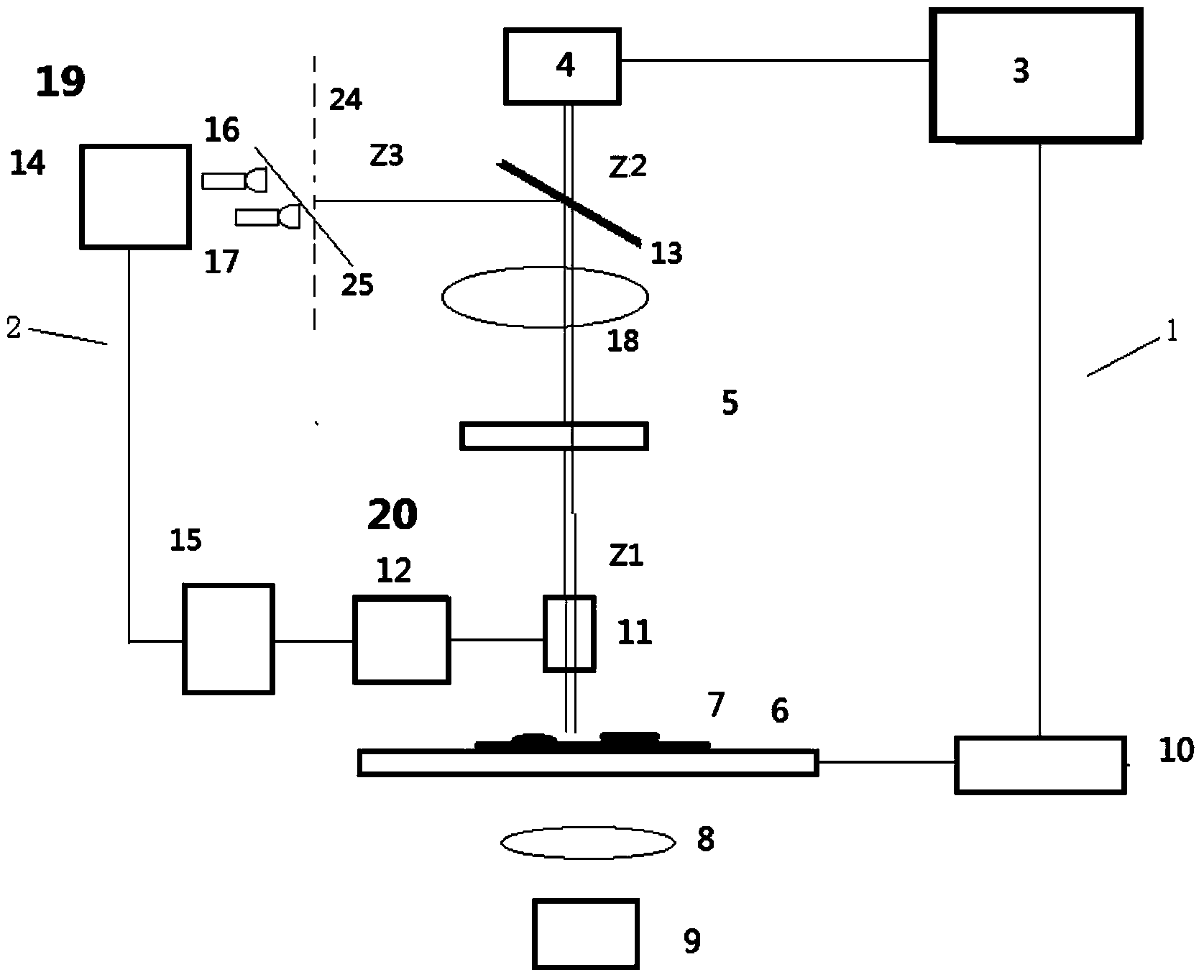
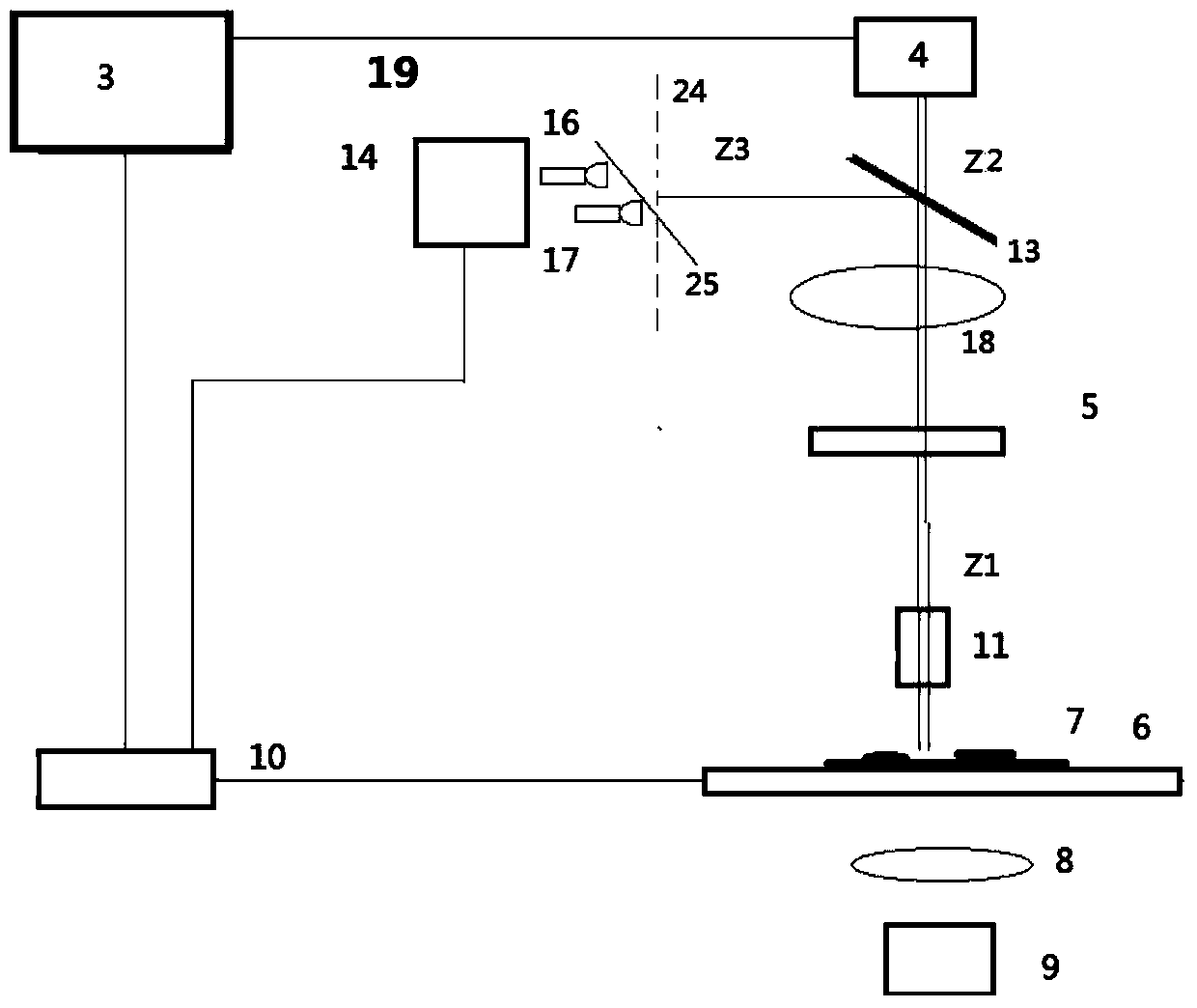
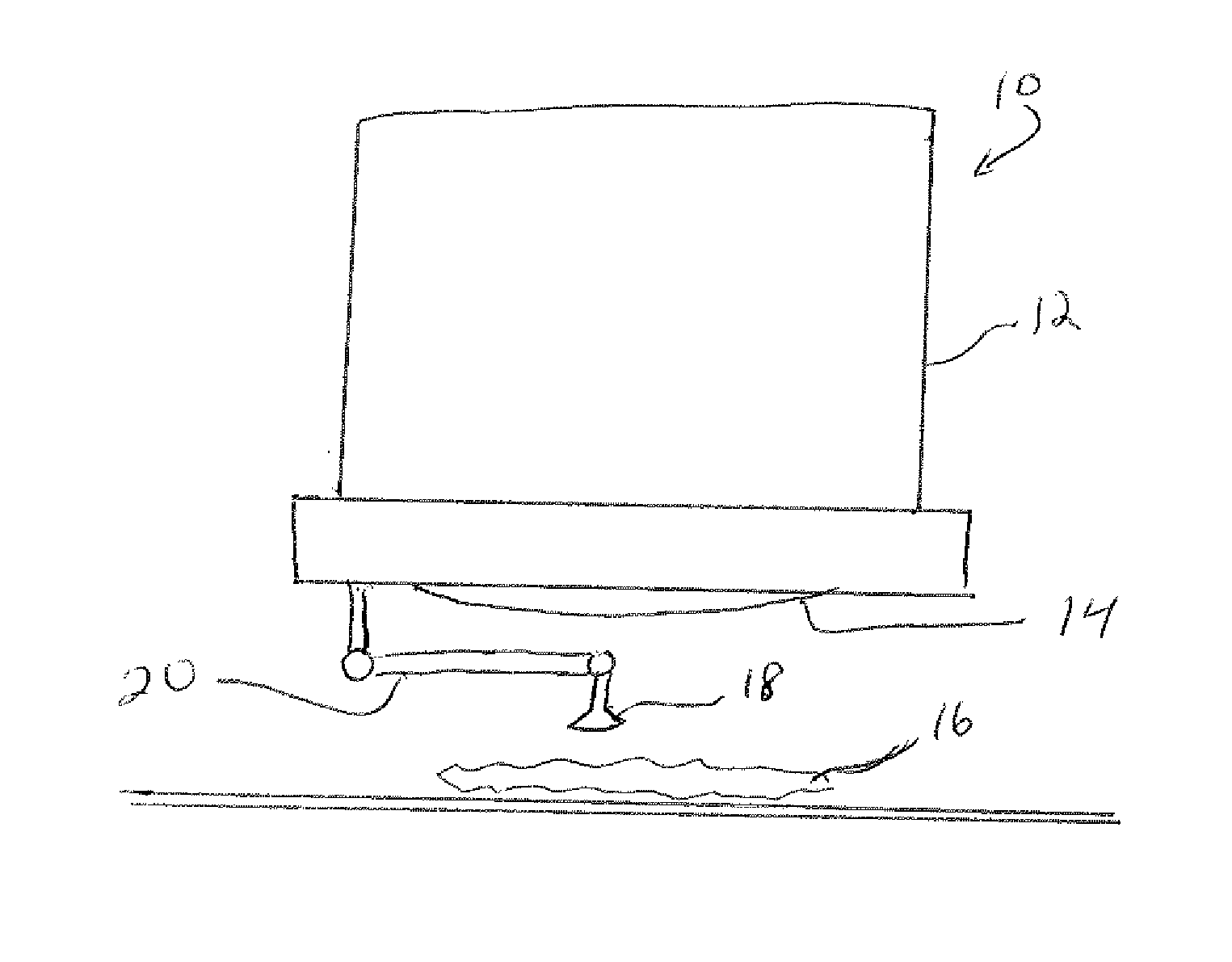
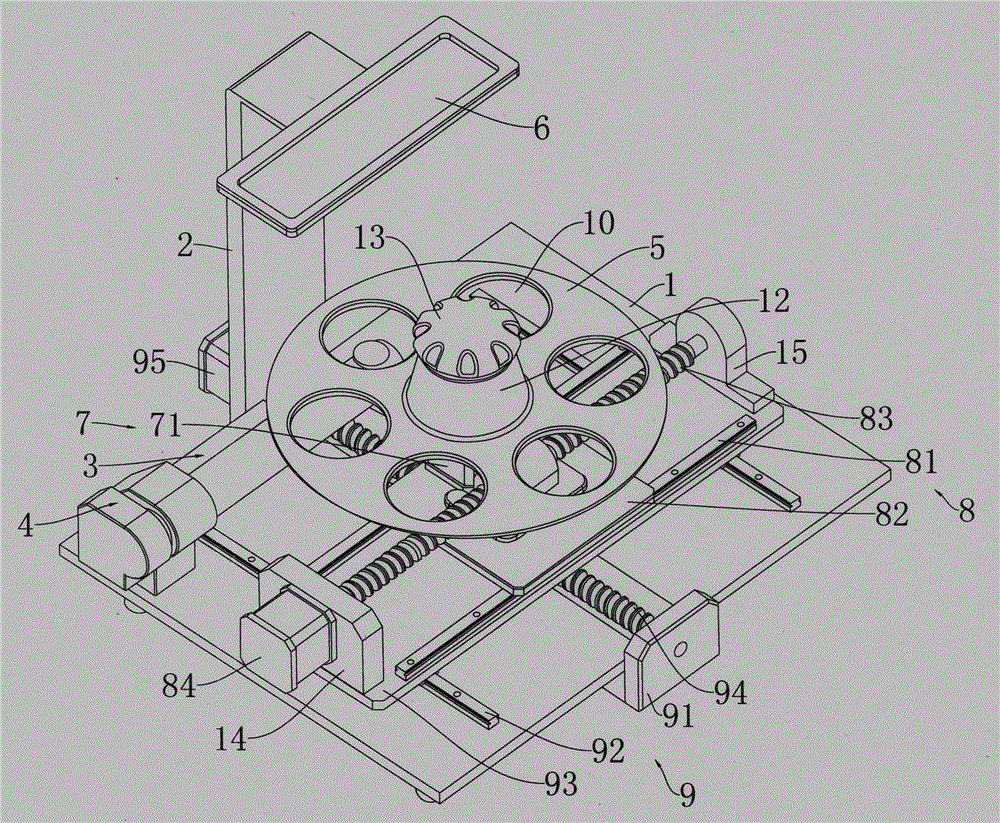
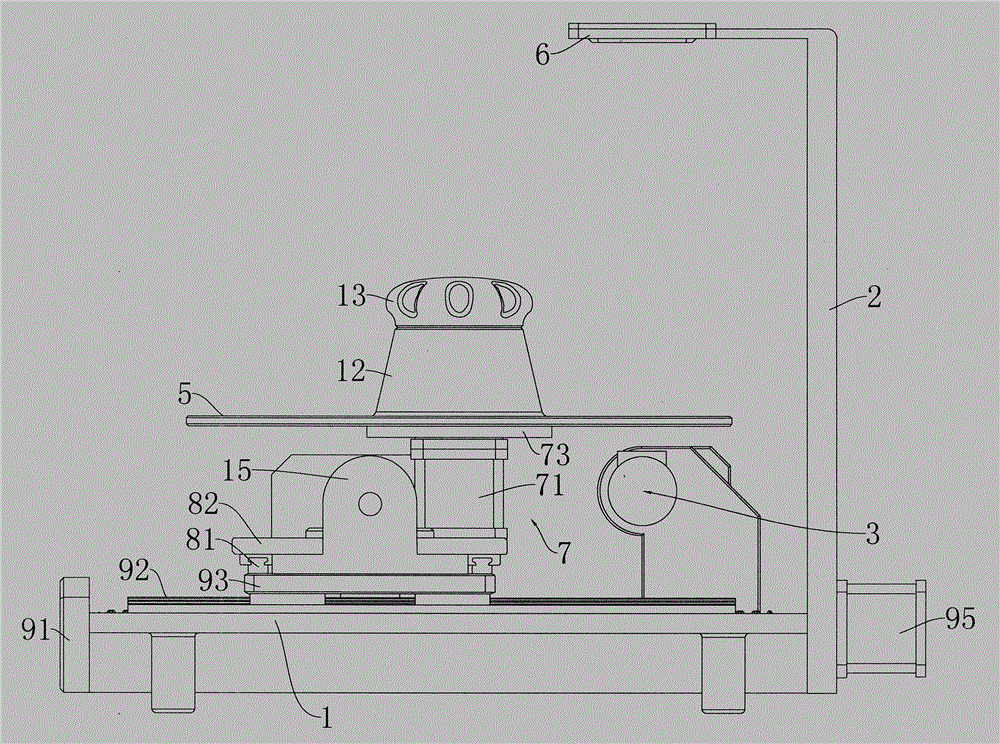
Device convenient for placing slide on electric microscope platform
The invention relates to a device for placing a slide, in particular to a device convenient for placing a slide on an electric microscope platform. The invention provides a device for limiting a slide so as to prevent the slide from slipping and facilitating placement of the slide on an electric microscope platform. A device facilitating placement of a slide on an electric microscope platform comprises a base, an electric microscope body, a first support, a first rotating block, a material receiving plate, a driving mechanism and a limiting mechanism, the electric microscope body is arranged on the rear side of the top of the base, the first support is arranged in the middle of the top of the base, and the first rotating block is rotationally arranged in the middle of the first support; material receiving plates are arranged on the front side and the rear side of the upper portion of the first rotating block, a driving mechanism for achieving automatic rotation of the first rotating block is arranged on the front side of the top of the base, and a limiting mechanism for limiting the slides is arranged between the first support and the two material receiving plates. The slide is pressed by the iron clamping plates, so that the slide is limited, and the slide is prevented from falling off due to loosening.
Owner:福建朗健生物科技有限公司
Cultivation method for observing Plasmodium infestation of Brassicaceae plants
InactiveCN103931476BHigh transparencyImprove permeabilityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsOrganismOperation safety
Owner:云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所
A rapid preparation method for ex vivo dyed epidermal sheets of macroalgae
InactiveCN103033401BAccurate separationIncrease the areaPreparing sample for investigationStainingElectron microscope
The invention discloses a rapid tableting method of a large-sized alga in-vitro dyeing epidermal lamella. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a mixing reagent; completing dissociation at one step, and dyeing a large-sized alga epidermal lamella; and manually operating to rapidly prepare an epidermal cell lamella of which the area can be up to 1cm<2>. The method is easy and convenient to operate, has a high preparation speed, a good color development effect and high stability, and is suitable for observation through microscopes and electron microscopes and observation and research of epidermal cell ultrastructures.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
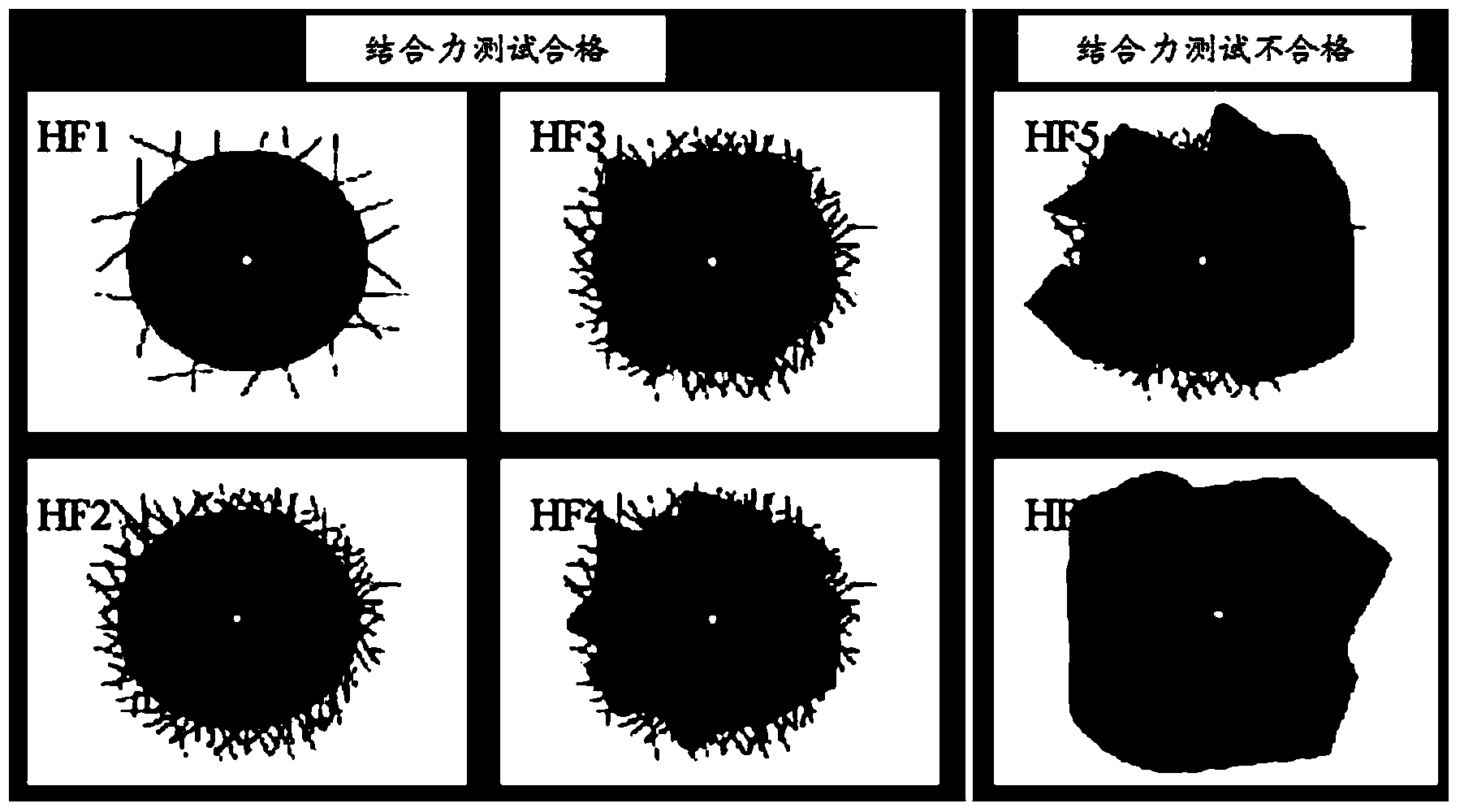
Sample for detecting dispersion state of filler and preparation method and use method of sample
ActiveCN108507856ASimple structureWith self-locking abilityInvestigating composite materialsPreparing sample for investigationPolymer compositesMaterials science
The invention discloses a sample for detecting the dispersion state of filler. The sample is used for detecting the dispersion state of the filler in a polymer composite. The sample comprises the polymer composite and a loading device for applying a load to the polymer composite, wherein the polymer composite deforms through loading by the loading device and is located on the loading device through a locating mechanism, so that the polymer composite remains deformed and forms a sample core with the loading device; the sample core is wrapped in a cured body formed by curing of a curing agent. The invention further provides a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: applying the load to the polymer composite for deformation, keeping deformation of the polymercomposite on the loading device by the locating mechanism to form the sample core, and curing the sample core. The invention also provides a use method. The use method comprises the following steps:slicing the sample and observing the slice under an atomic force microscope. The shape and dispersion state of the filler in the composite under different load conditions can be tested simply and effectively.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap


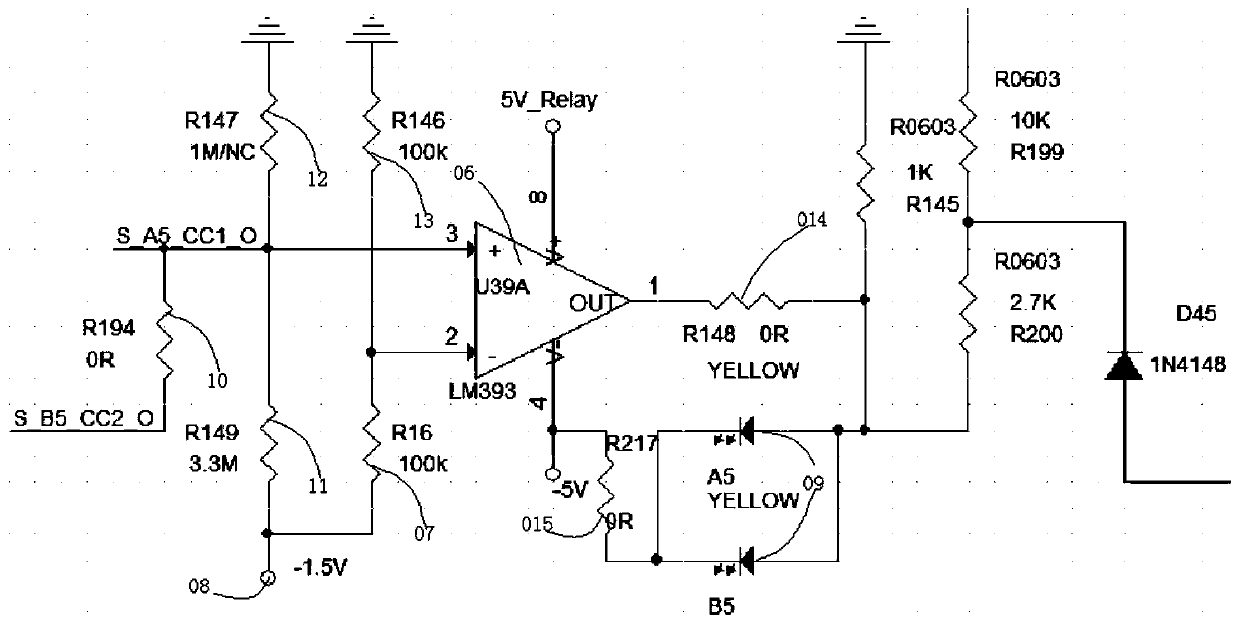
![Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/38585591-87d6-4f06-8e07-ed0eac7d2896/HDA0000721352810000011.PNG)
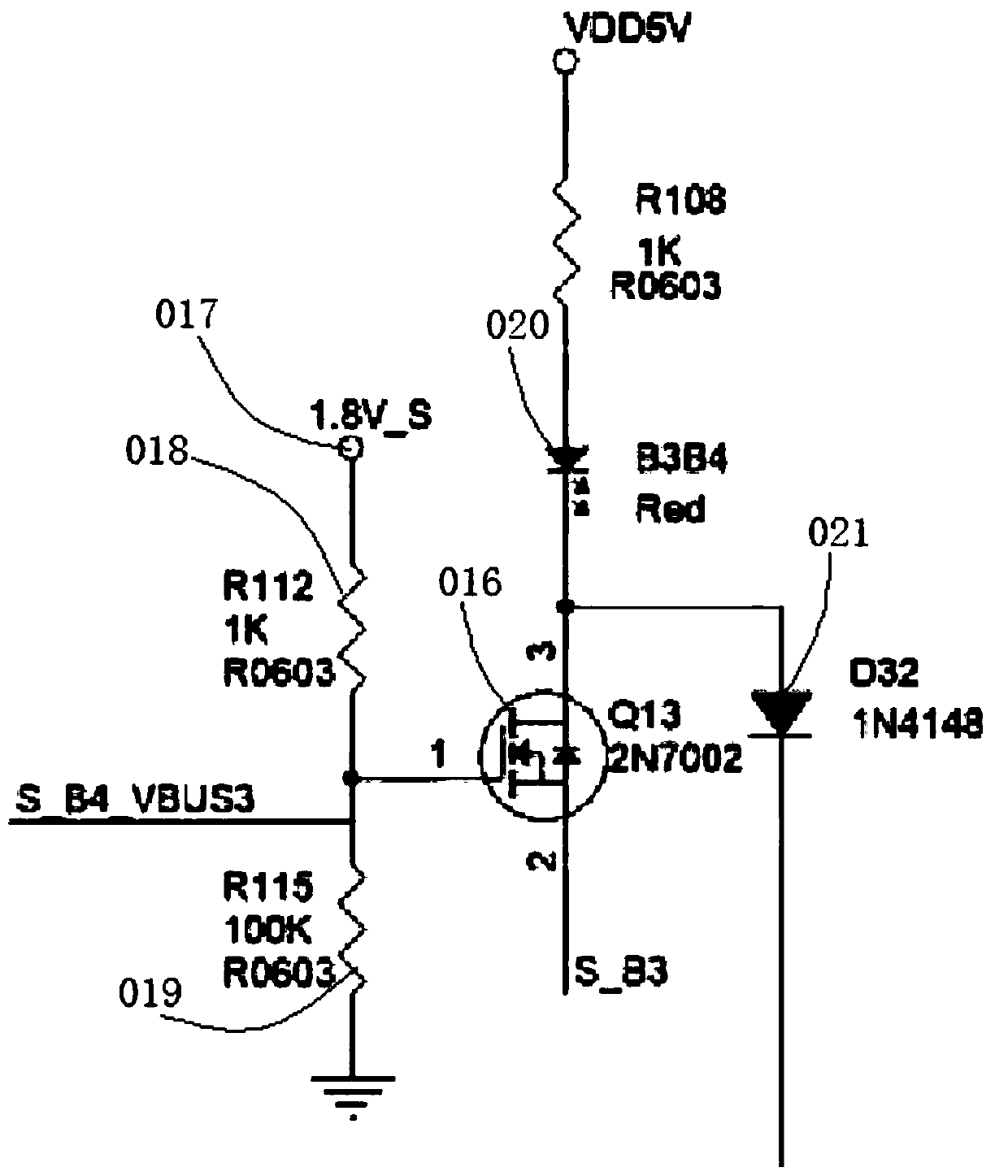
![Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/38585591-87d6-4f06-8e07-ed0eac7d2896/HDA0000721352810000021.PNG)
![Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method Etching solution for dislocation display of monocrystal germanium wafer deflecting to crystal orientation [111] and etching method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/38585591-87d6-4f06-8e07-ed0eac7d2896/HDA0000721352810000022.PNG)