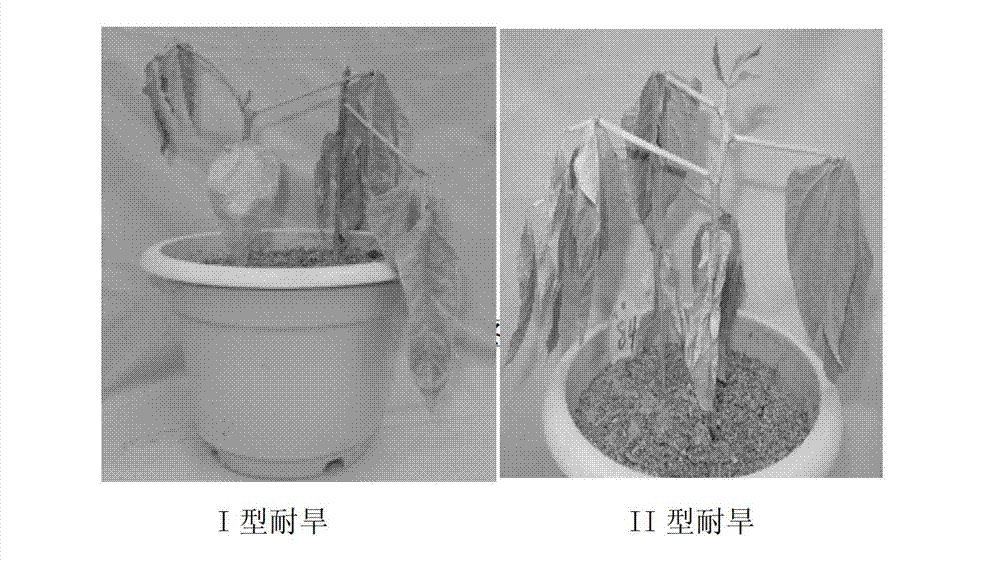
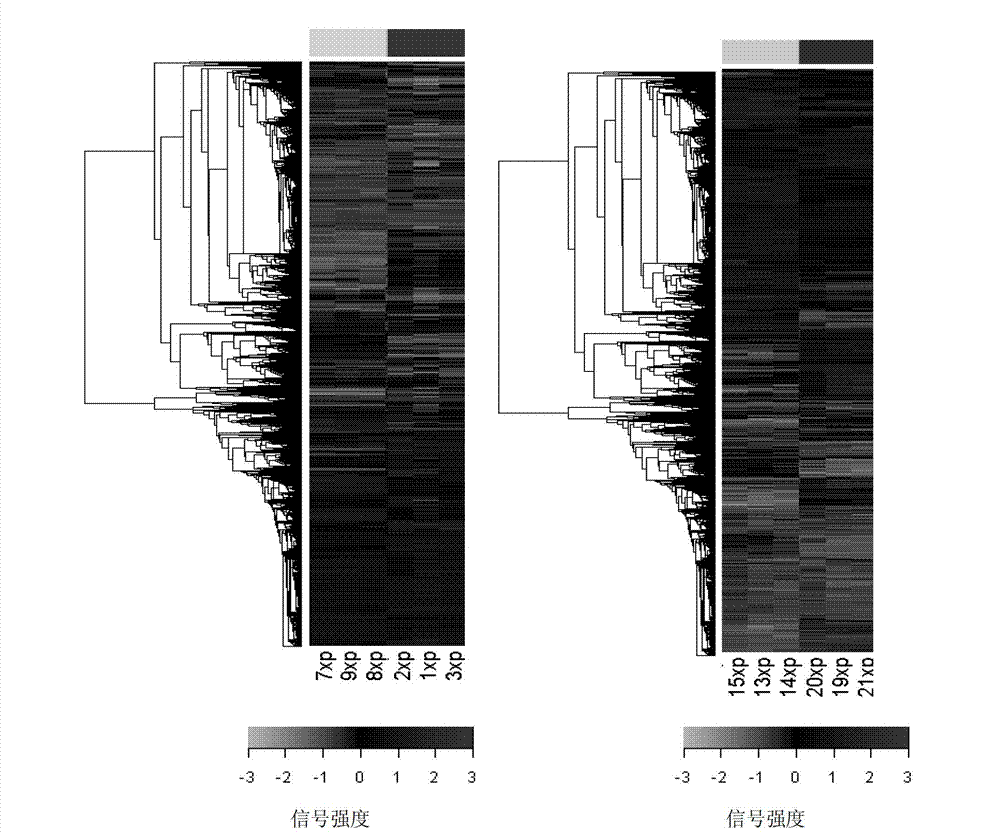
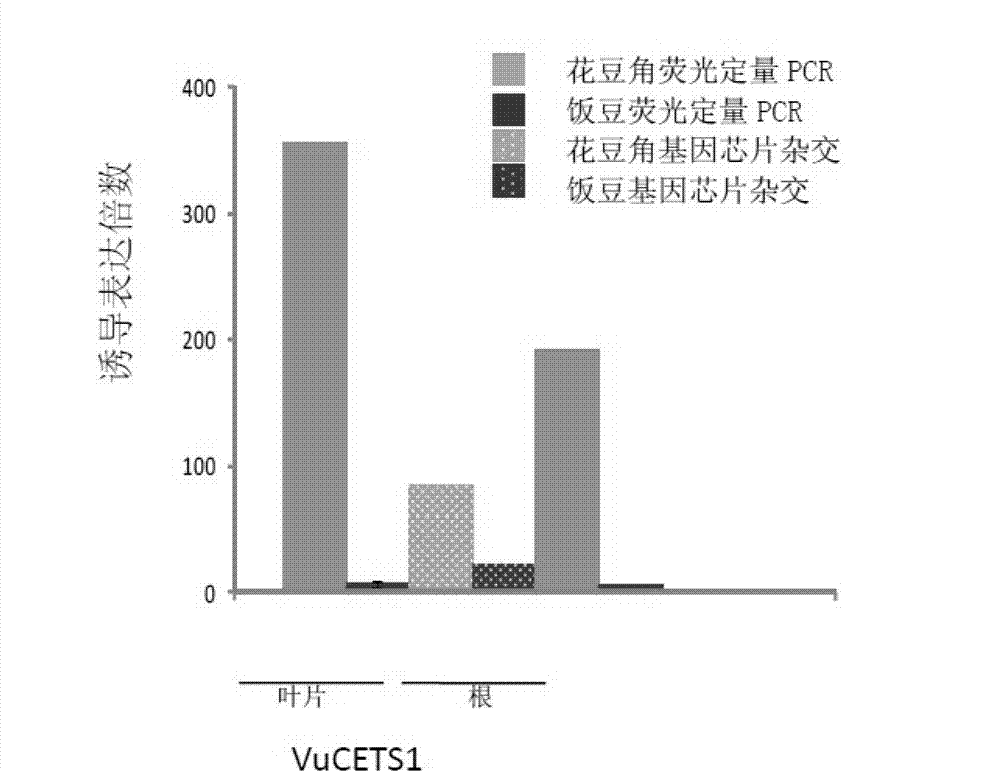
Method for testing drought tolerances of vigna unguiculata type I and vigna unguiculata type II by fluorogenic quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction), diagnostic genes and primers
A fluorescent quantitative and drought-tolerant technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve problems that have not yet been reported or developed, and achieve the effect of promoting drought-tolerant breeding of cowpea and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The method for screening diagnostic genes and primers for specifically distinguishing cowpea type I and type II drought tolerance comprises the following steps:
[0030] (1) Download and preprocessing of cowpea non-redundant gene sequence: from Harvest cowpea DNA database UP12 (http: / / www.harvest-web.org / hweb / bin / wc.dll?hwebProcess~hmain~&versid=68) Batch download of cowpea unigene sequences, a total of 29,728. Run the VecScreen program (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / VecScreen / VecScreen.html) to scan and remove vector and adapter sequences contained on the downloaded sequences.
[0031] (2) Cowpea gene chip design: After scanning all 29,728 unigene sequences in the UP12 database, 4 oligonucleotide DNA sequences were designed as probes at different base positions of each sequence. These 4 sequences were in The weighted average of the signal values in the microarray hybridization will define the signal value of a gene. The technical standards for design a
Embodiment 2
[0037] The differential expression information of the diagnostic gene VuCETS1 in leaf tissue was analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR to identify type I and type II drought-tolerant materials.
[0038] (1) Material preparation: select a plump seed of 1 type I drought-tolerant cowpea variety and 1 type II drought-tolerant cowpea variety seeds and sow them in a nutrient bowl, and the substrate is vermiculite: nutrient soil = 3:1. After the cotyledons were flattened, the water was thoroughly watered, and then the watering was stopped, and the RNA of the leaves under normal growth and under stress conditions was extracted by the conventional Trizol method 14 days after the treatment.
[0039] (2) RAN extraction and reverse transcription: Take 0.1 g of leaf tissue and add liquid nitrogen to grind it into powder, and extract total RNA according to the kit instructions. Dilute the extracted RNA to 0.1 g / L with DEPC-treated water, and add 2 μL of anchor primer (AP) and 2 μL of RNA in
Embodiment 3
[0042] Differential expression information of the diagnostic gene VuCETS1 in root tissue was analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR to identify type I and type II drought-tolerant materials.
[0043] (1) Material preparation: Select a plump seed of 1 type I drought-tolerant cowpea variety and 1 type II drought-tolerant cowpea variety seeds and sow them in a nutrient bowl, the substrate is vermiculite: nutrient soil = 3:1. After the cotyledons were flattened, the watering was stopped, and the roots of the plants were carefully pulled out 14 days after the treatment, washed with water quickly, and the RNA of the roots under normal growth and stress conditions was extracted by the conventional Trizol method.
[0044] (2) RAN extraction and reverse transcription: Take 0.1 g of root tissue and add liquid nitrogen to grind it into powder, and extract total RNA according to the kit instructions. Dilute the extracted RNA to 0.1 g / L with DEPC-treated water, and add 2 μL of anchor primer
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap