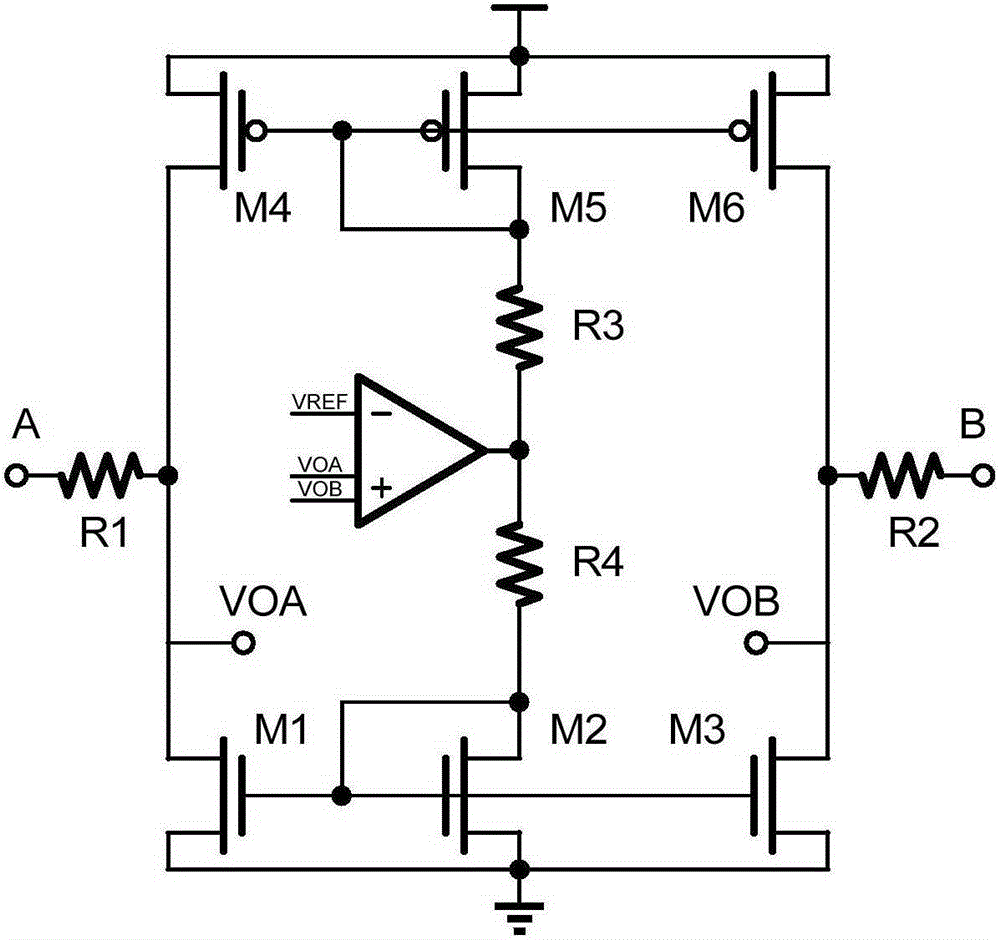
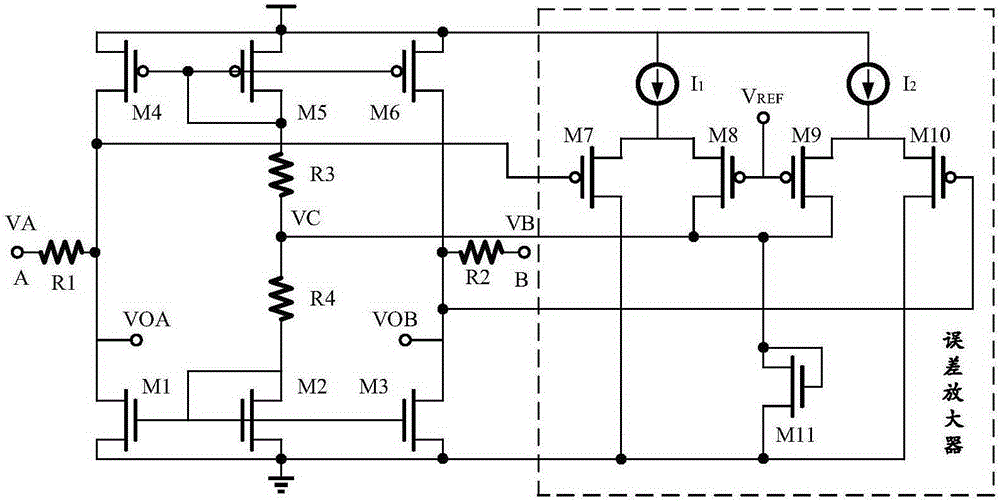
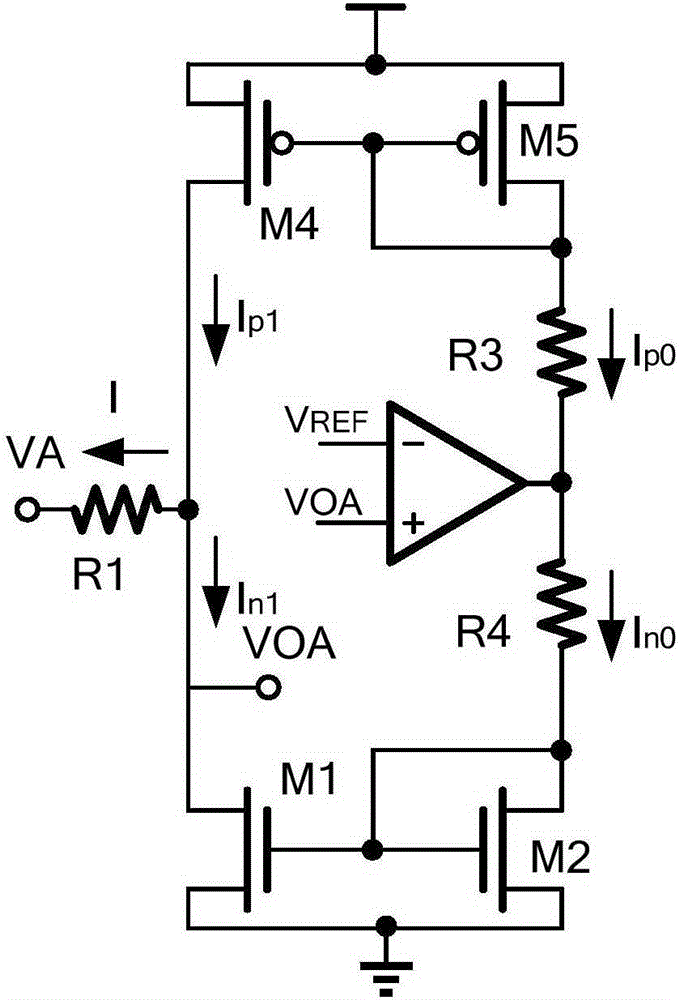
Common mode moving circuit for multipoint low voltage differential signal receiver
A low-voltage differential signal, common-mode transfer technology, applied in instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of interface restricting high-speed data transmission, and achieve the effect of simplifying circuit design, reducing power consumption, and high system signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0021] The following describes in detail the embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals refer to the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below with reference to the accompanying drawings are exemplary and are only used to explain the present invention, but not to be construed as a limitation of the present invention.
[0022] The following disclosure provides many different embodiments or examples for implementing different structures of the invention. In order to simplify the disclosure of the present invention, the components and arrangements of specific examples are descr
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap