Method and device for performance optimization of embedded Linux system
A system performance and embedded technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as the real-time performance of the embedded Linux system, and achieve the effect of improving real-time performance and optimizing real-time performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the solution of the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. Apparently, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
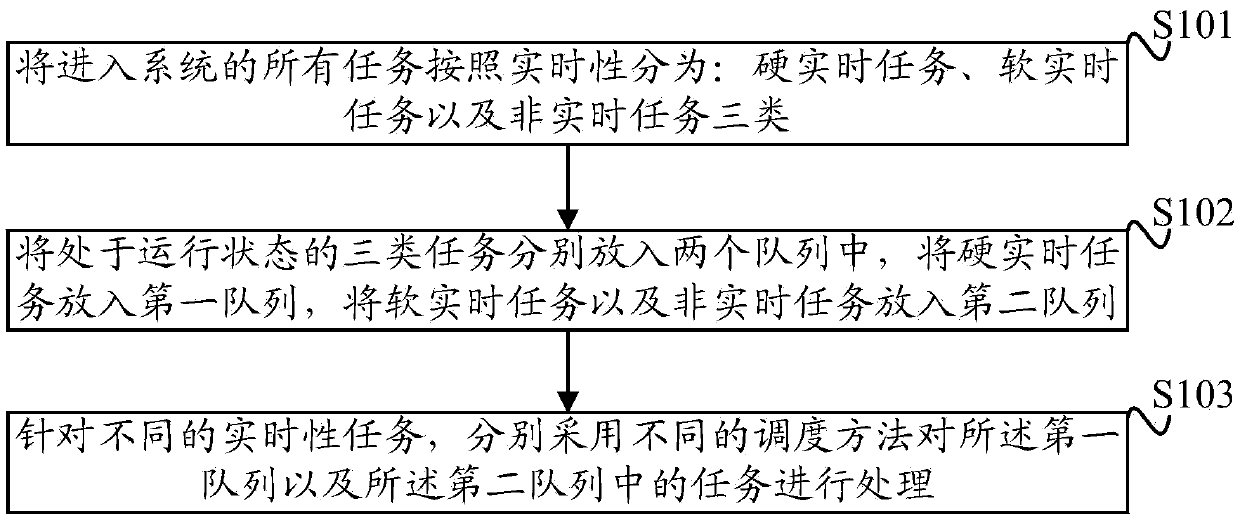
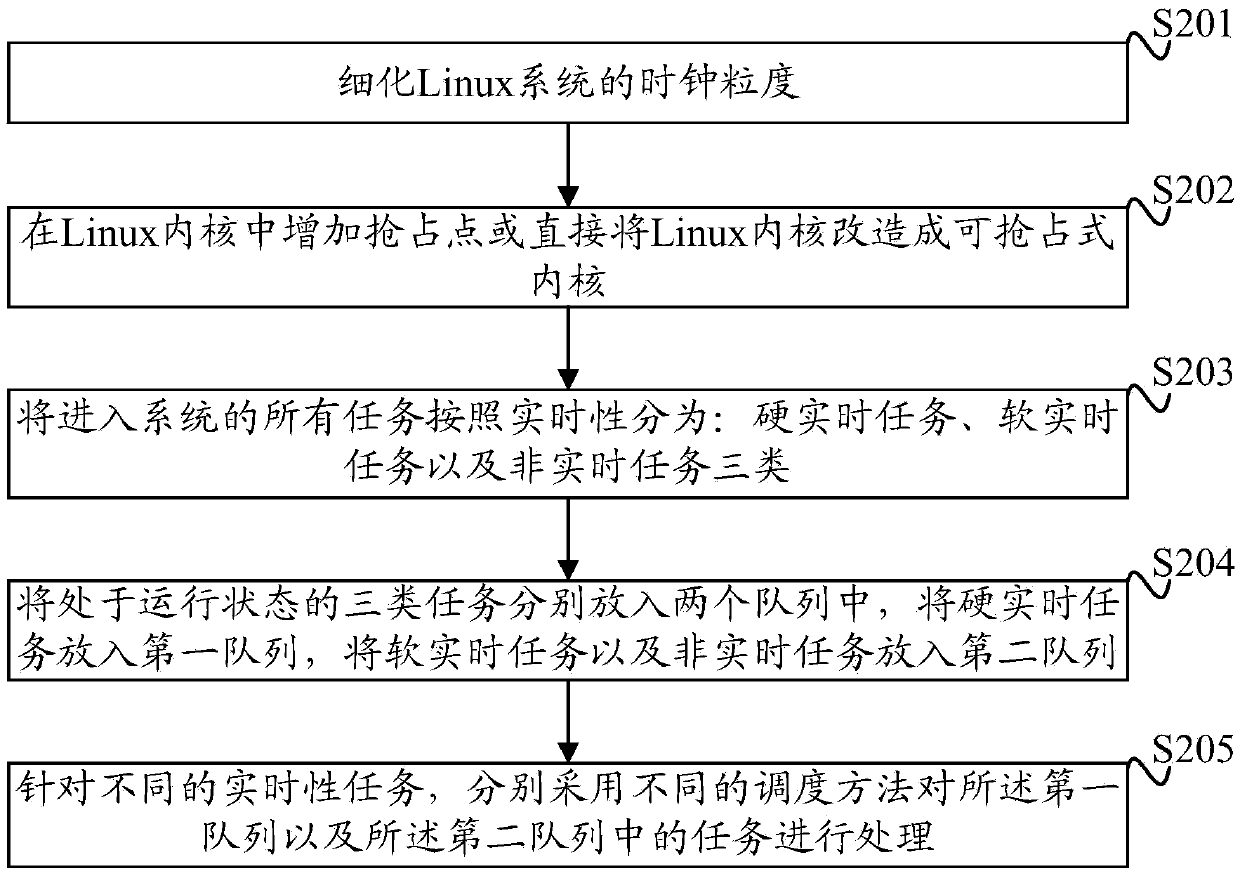
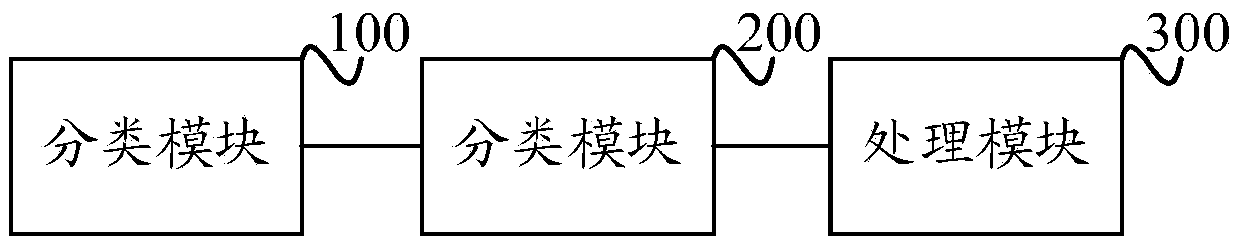
[0033] A flow chart of a specific embodiment of the method for performance optimization of the embedded Linux system provided by the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0034] Step S101: Divide all tasks entering the system into three categories according to real-time performance: hard real-time tasks, soft real-time tasks, and non-real-time tasks; wherein, the hard real-time tasks
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap