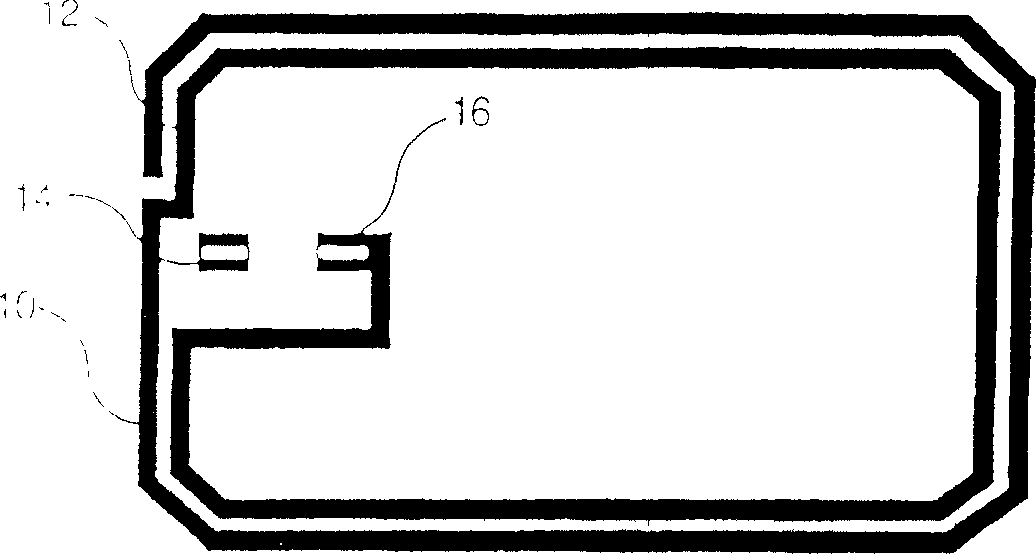
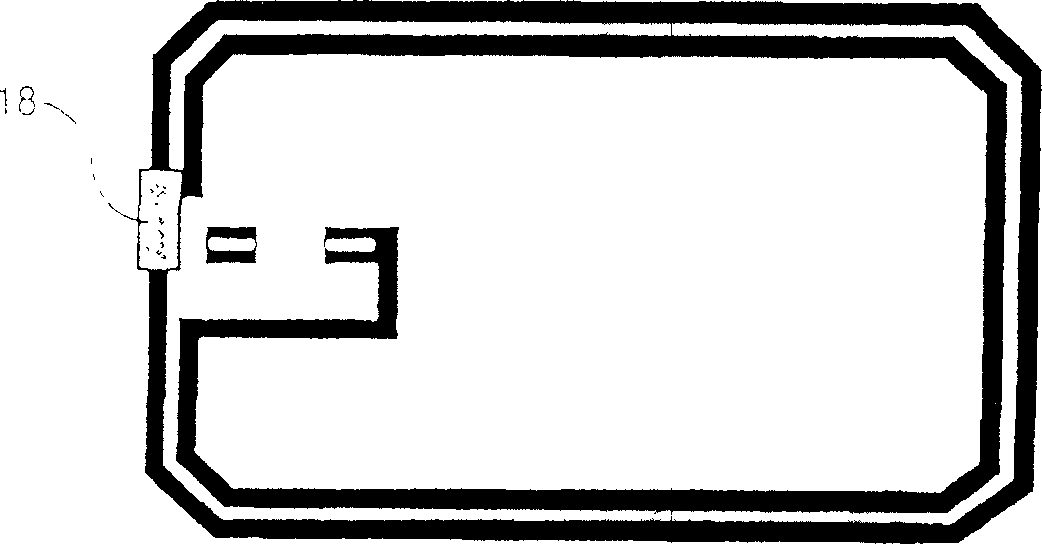
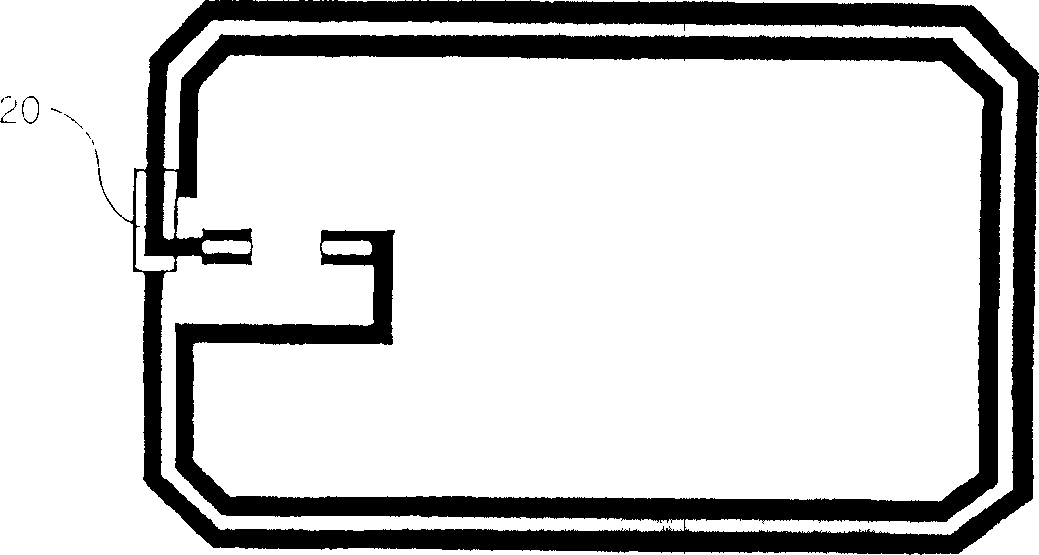
Method for making a non-contact smart card with an antenna support made of fibrous material
A manufacturing method and technology for smart cards, which are applied to record carriers, printed matter, instruments, etc. used by machines, and can solve the problems of fraud, high cost, and inability to produce
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example
[0023] Lamination is achieved by thermoforming. According to a preferred embodiment, two layers of plastic material are used for each card body. This plastic material is typically polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyester (PET, PETG), polycarbonate (PC), or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS). According to a preferred embodiment, PVC is used. The two layers have different stiffnesses. The outer layer is made of hard PVC and the inner layer (the layer in contact with the antenna support) is made of PVC with a low Vicat softening temperature (this is the temperature at which PVC transitions from an air-hard state to a rubber state). Made of soft PVC. The two layers may also have different thicknesses. For example, each card body includes an outer hard PVC layer with a thickness of about 310 microns (μm), and an inner soft PVC layer with a thickness of about 80 μm. The antenna support is made of paper with a thickness of about 125 μm. According to another manufacturing example, wh
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap