System and method for persisting hardware transactional memory transactions to persistent memory
a hardware transaction and persistent memory technology, applied in the field of system and method for persisting hardware transactional memory transactions to persistent memory, can solve the problems of corrupted pm, high latency, and new main-memory databases (mmdb), and achieve the effect of atomicity and durability of write operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
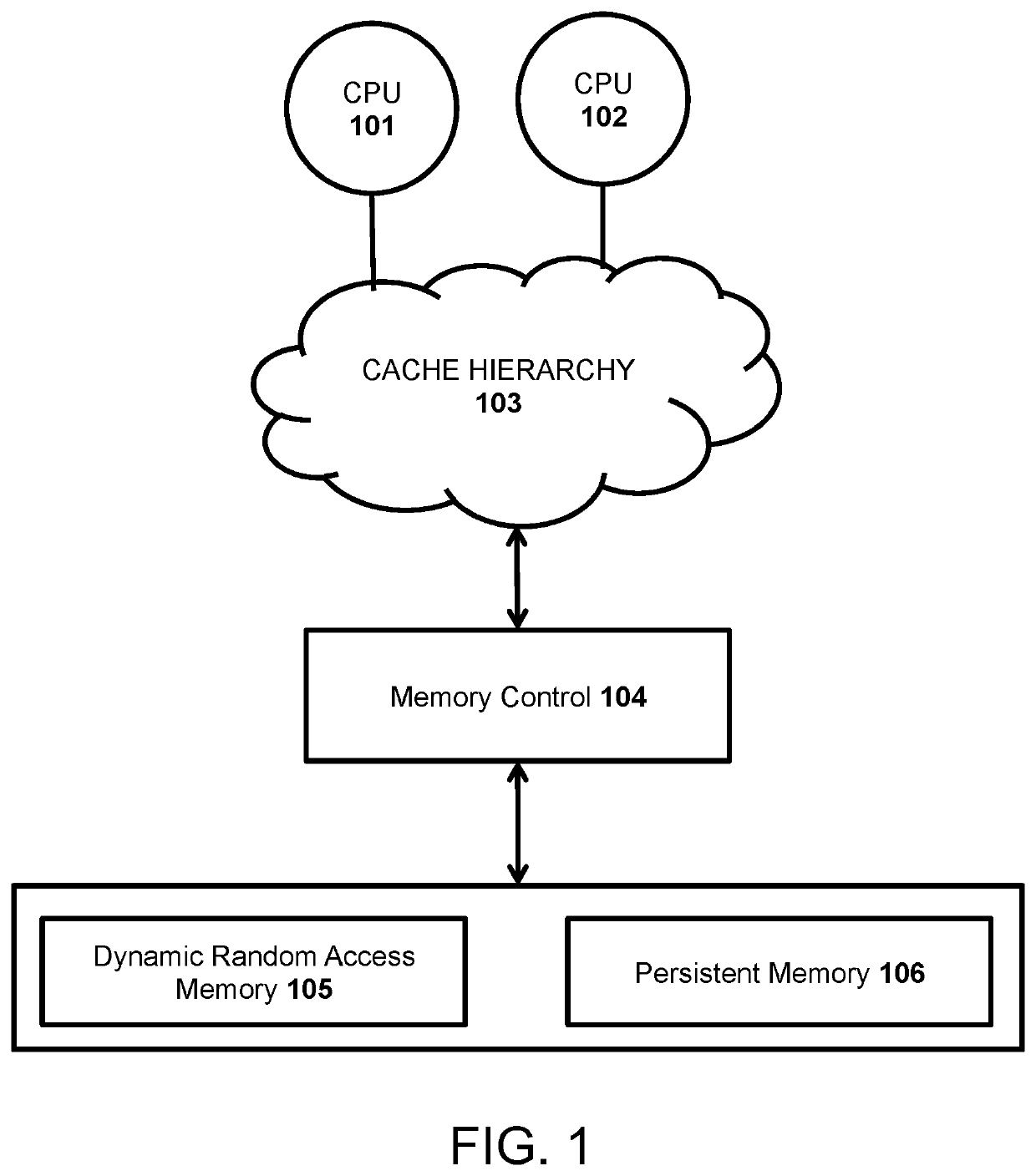
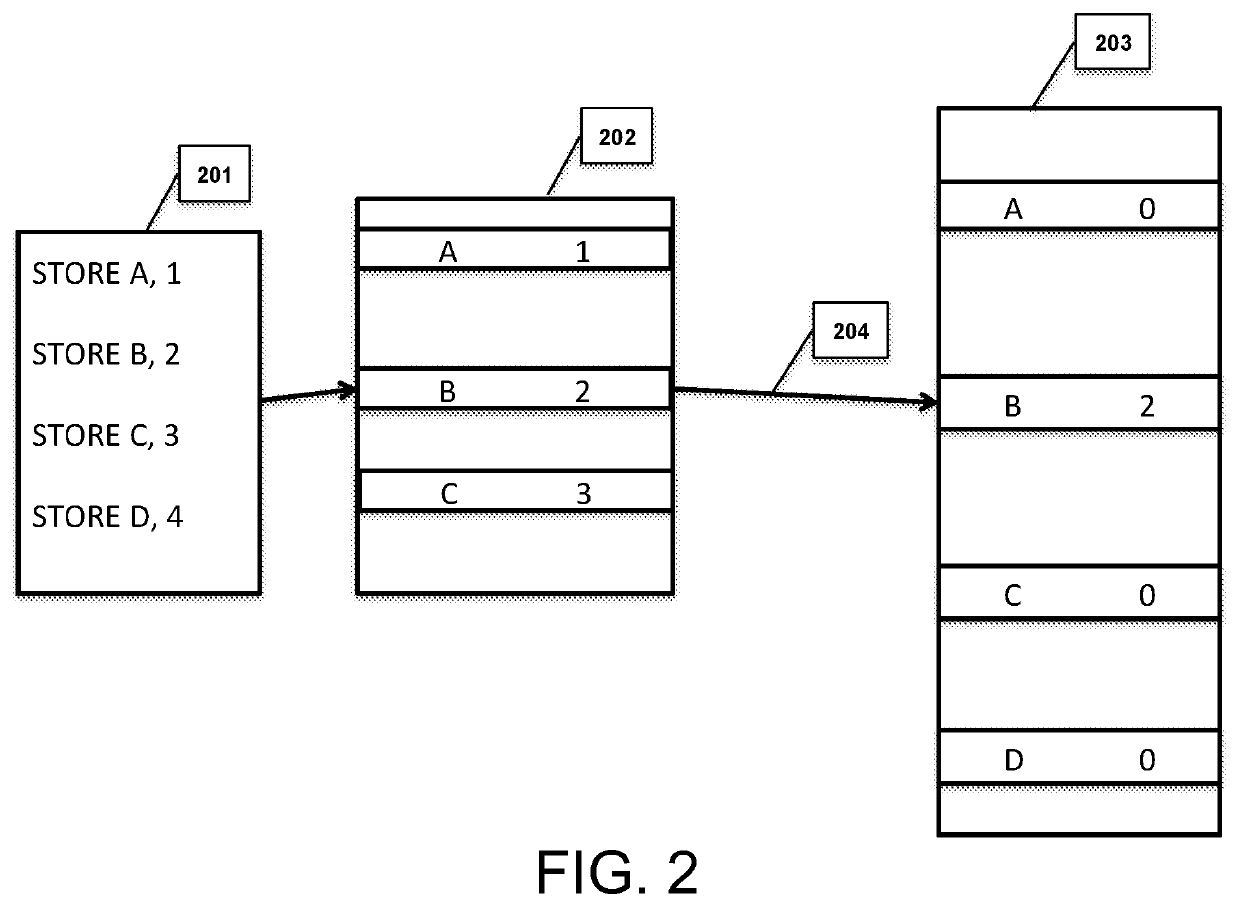
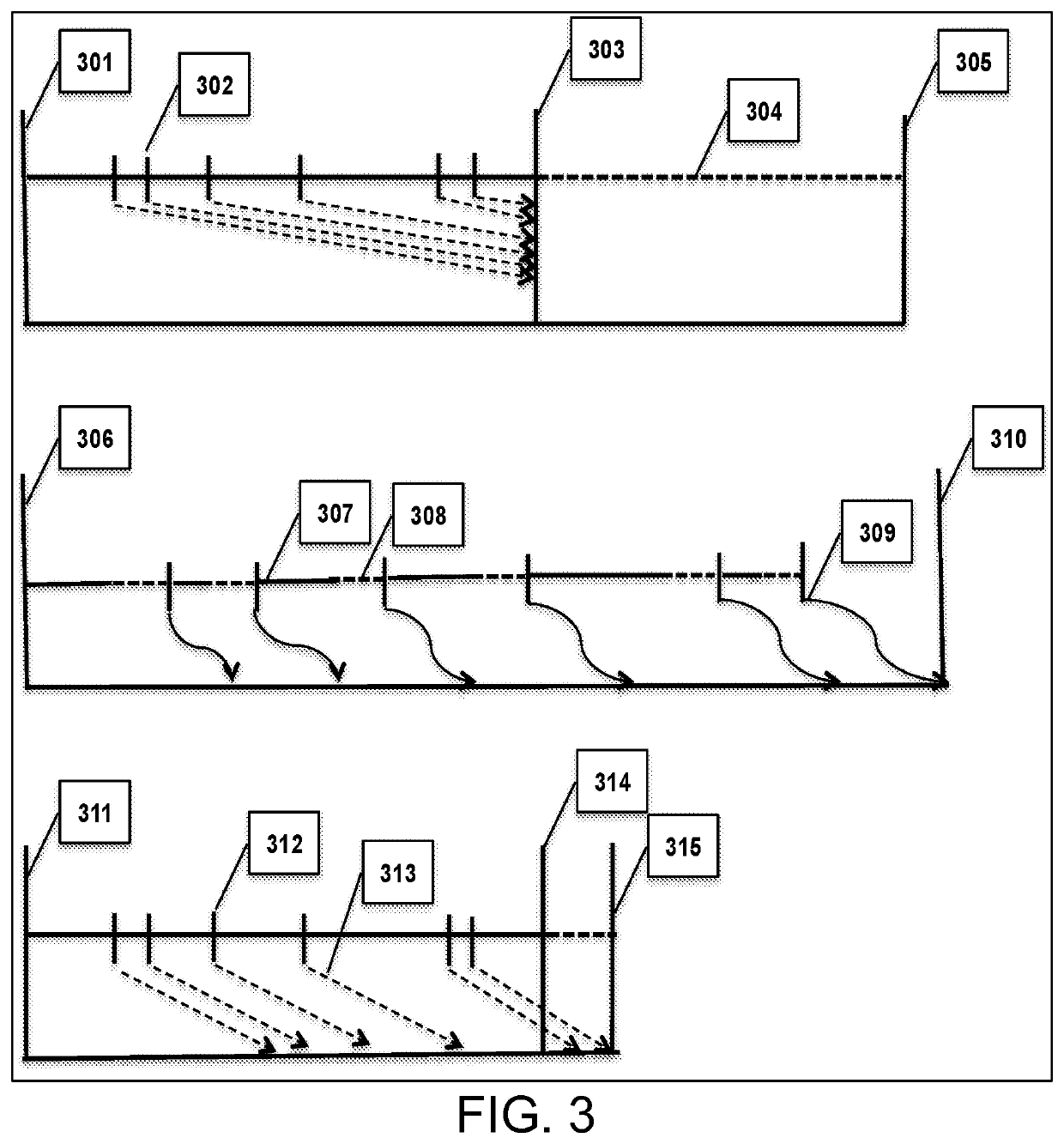
[0059]The emerging field of byte-addressable, Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) technology unveils a new area for researchers in both computer architecture and software design. Persistent Memory (PM) is a group of new technologies that include but is not limited to Phase Change Memory (PCM), battery backed DRAM, Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory, Spin-Transfer Torque Random Access Memory, Flash-backed DRAM, Resistive Random Access Memory, and other memristor based technologies. PCM shows promise in that it can achieve a high chip density and speed. These properties will enable the creation of systems with large amounts of persistent, byte-addressable memory that can replace slow, block based Flash or hard disk drives. Utilizing HTM for concurrency control mechanisms is difficult in that HTM transactions will abort if flushing values to a persistent log and, since all values are visible instantly after the HTM section, a subsequent cache eviction and failure, might corrupt an in-memory data
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap