A Method of Screening for Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways
a cell signalling pathway and pathway technology, applied in the field of cell signalling pathway modulation screening, can solve the problems of insufficient low-throughput approach to routinely isolate new drug target sites for therapeutic intervention, complexity at the proteomic level, and insufficient low-throughput approach
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
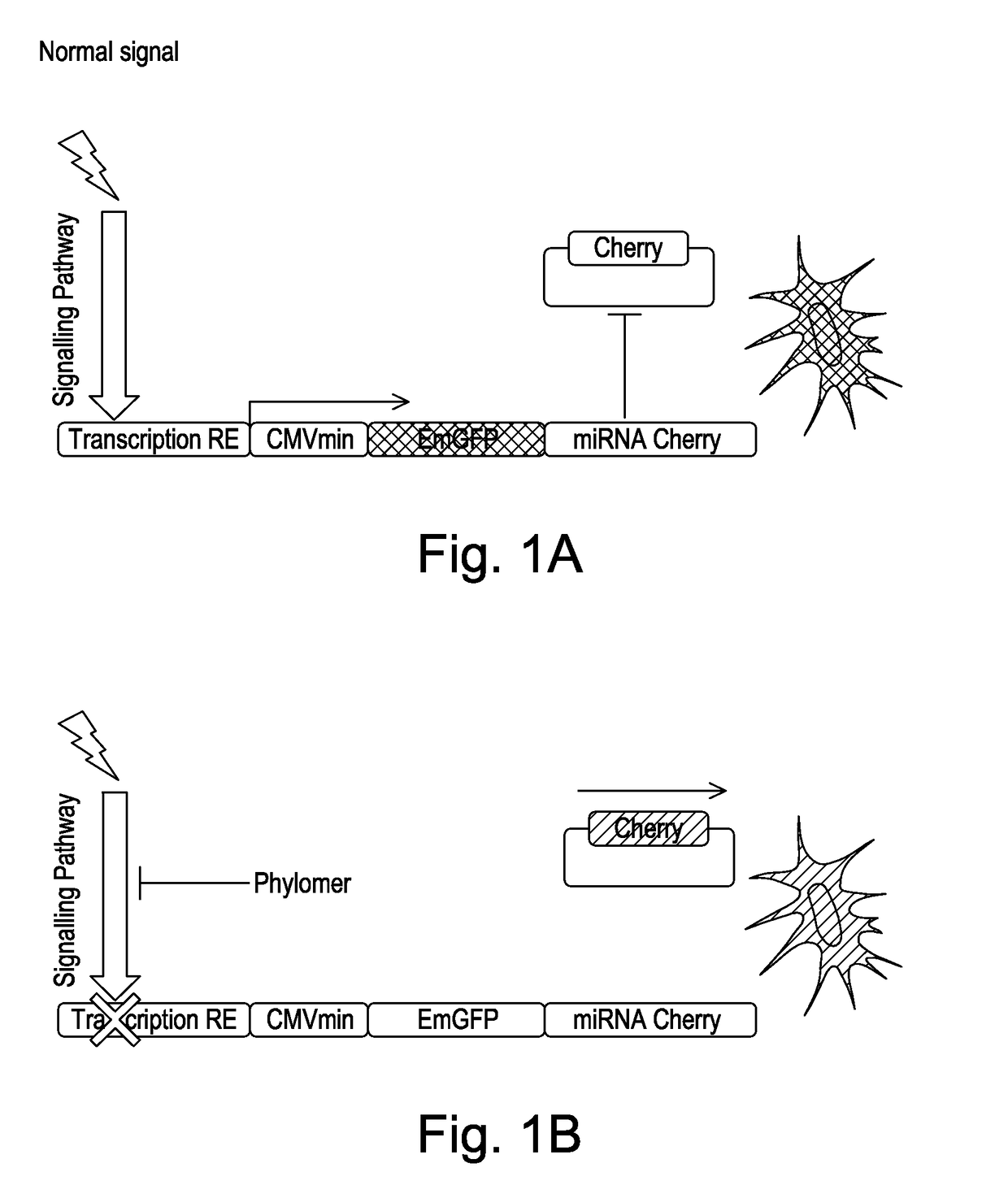
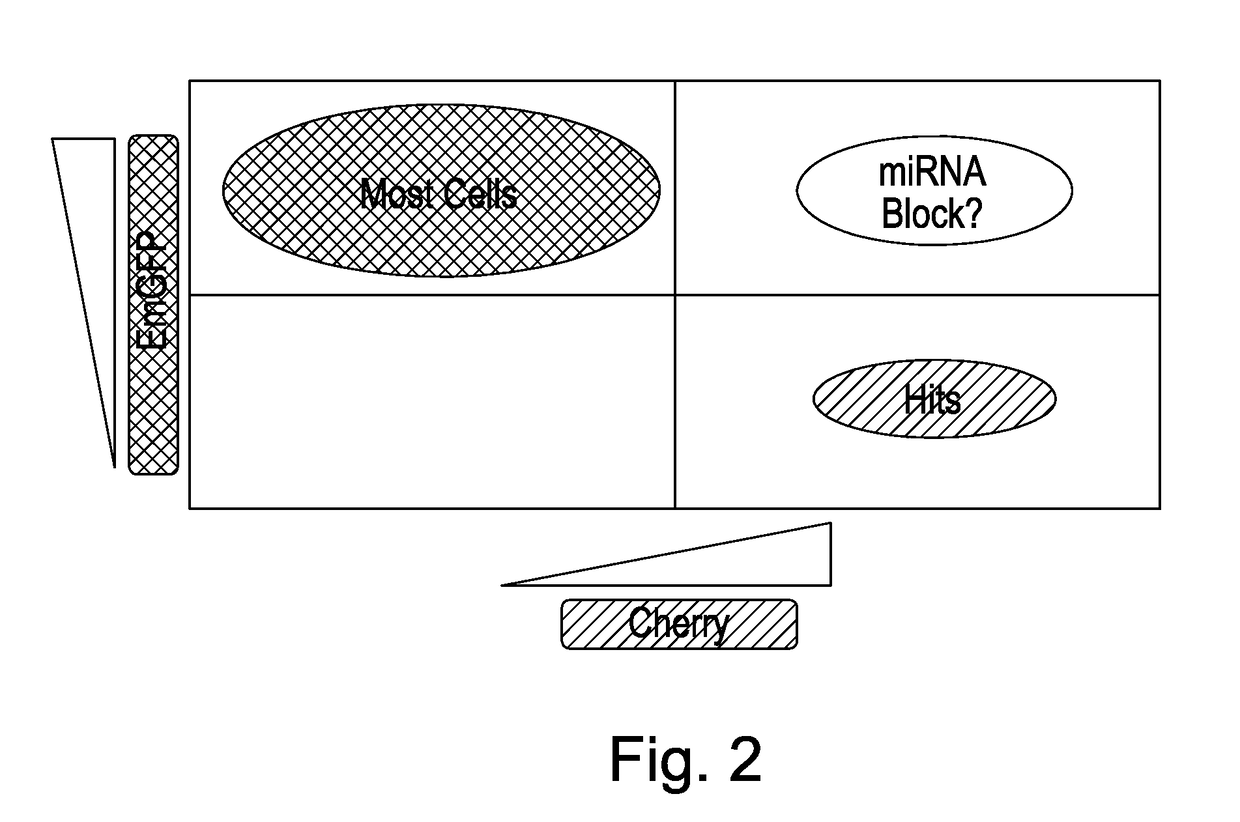
[0204]In order to tune the levels of miRNA and reporter proteins in the screening system to generate an appropriate signal window, a number of approaches were adopted. The presence of residual reporter protein in the screening system, which may have remained in the cells for some time after it has been translated, can mask the detection of mCherry reporter protein and so give sub-optimal results. The following studies were carried out to optimise the detection of the mRNA and reporter protein so that the read-out is enhanced and the method is able to detect signals to a significantly higher degree of accuracy.
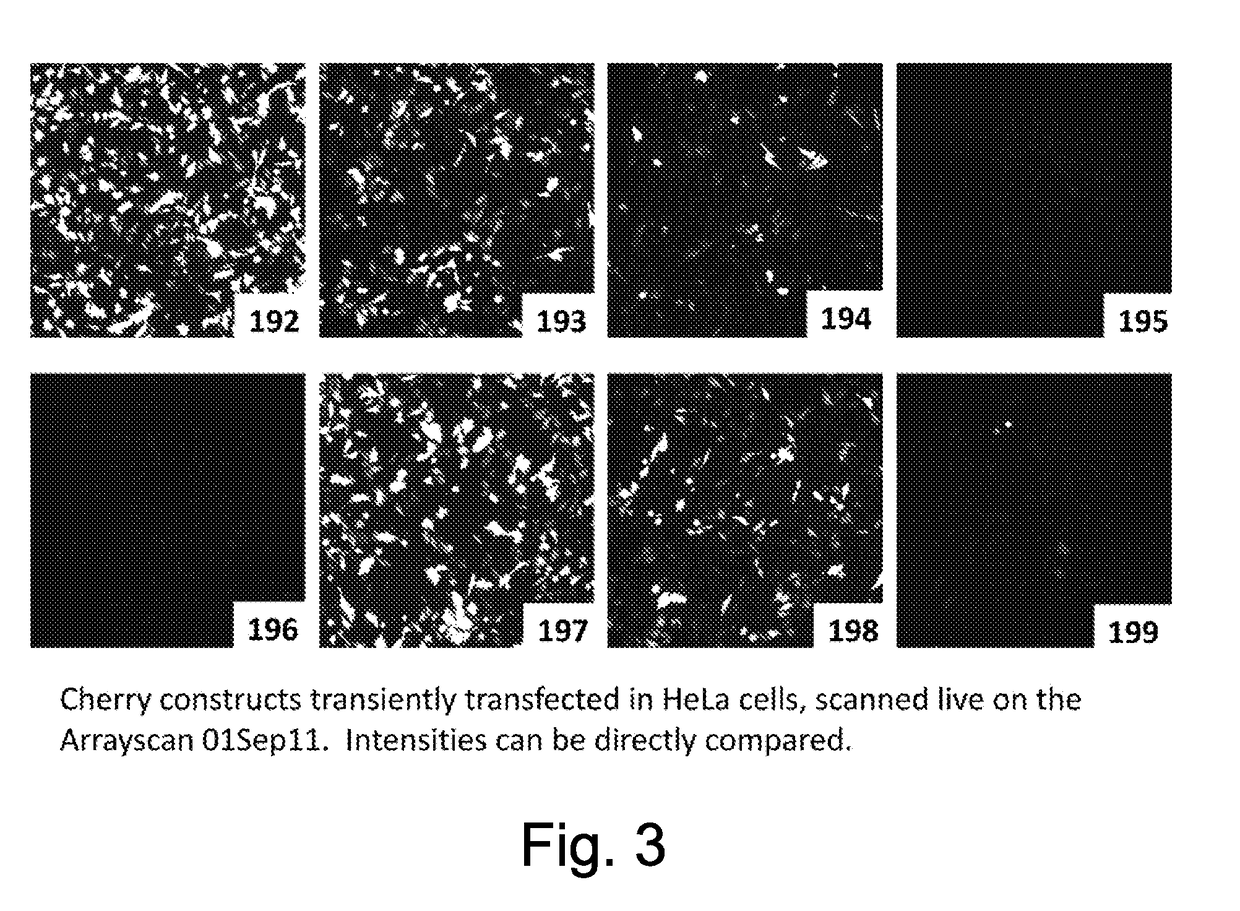
[0205]A representative list of vectors we have used to address these issues is shown in Table 1 below.
TABLE 1VectornumberVector namePromoterDestabilisation192pmC4.10CMVCMVNo destabilisation193pmC4.11CMVCMVPEST destabilisation sequence194pmC4.22CMVCMVCL1 and PEST destabilisation sequences195pmC4.11HSV-TKHSV-TKPEST destabilisation sequence196pmC4.22HSV-TKHSV-TKCL1 and PEST destabili
example 2
[0209]AU-Rich Elements (ARES) were incorporated into the 3′ UTR of its mRNA. FIG. 5 shows a comparison between mCherry reporters engineered to be unmodified (CTRL), to contain a naturally-occurring ARE (C-fos) or to contain a synthetic (Syn) ARE. The data shows the reduction in mCherry signal upon inclusion of an ARE using either the CMV or HSV-TK promoters to drive expression.
[0210]By using various combinations of promoters, destabilization sequences and mRNA degradation sequences, we can “fine-tune” the levels of miRNA and reporter protein so that they are appropriate for use in the screening system.
SequencesSEQ ID No: 15′ TTGATGTTGACGTTGTAGGCGGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACCGCCTACAGTCAACATCAA 3′
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap