Targeted Sensor Data Collection for Generating Map Information
a technology of map information and sensor data, applied in the field of map information generation, can solve the problems of difficult to collect complete map information for a given geographical region, difficult to cover multiple countries at large scale, and inability to match tasks, so as to achieve the effect of greater likelihood of matching tasks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
I. System Overview
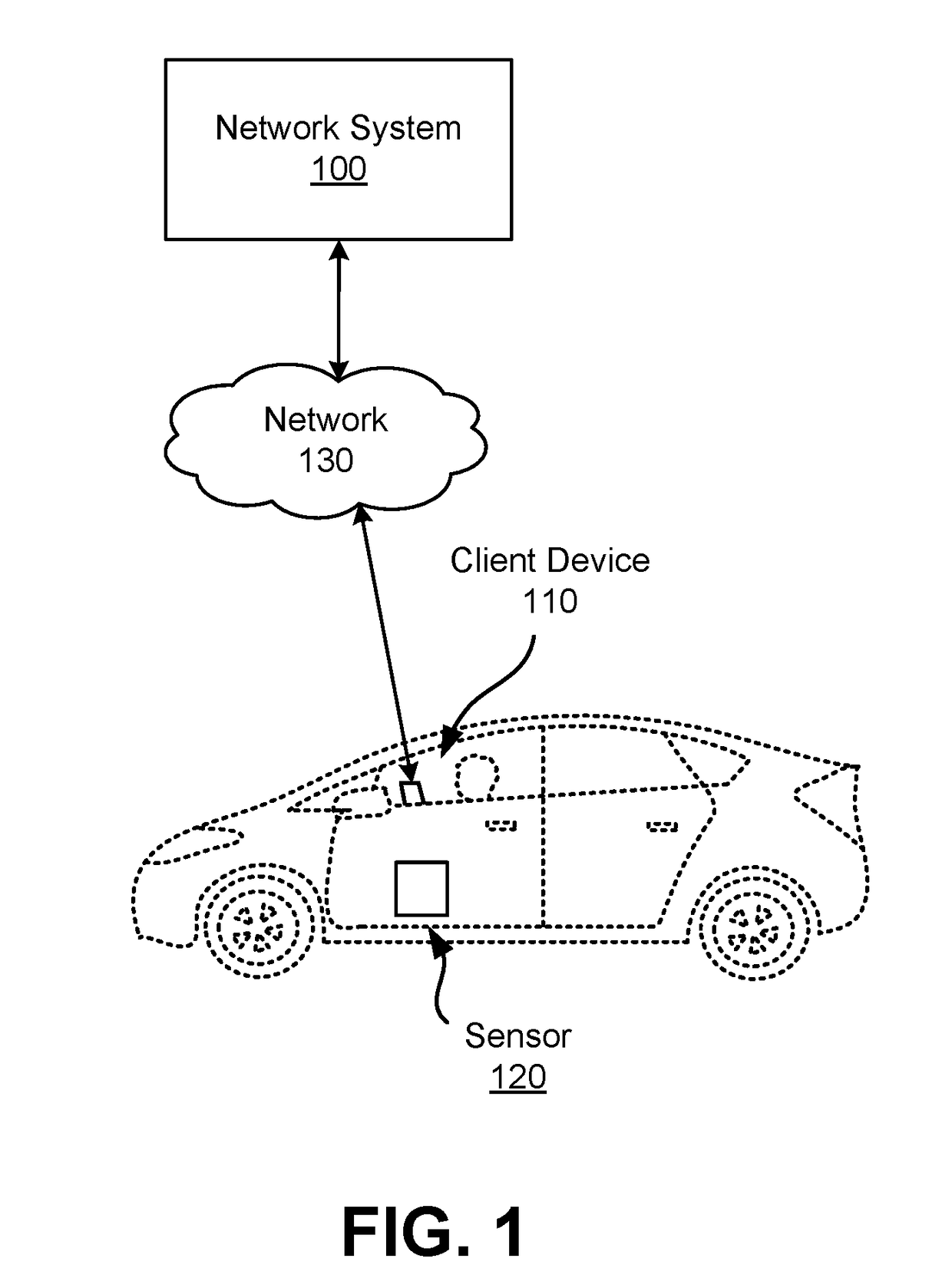
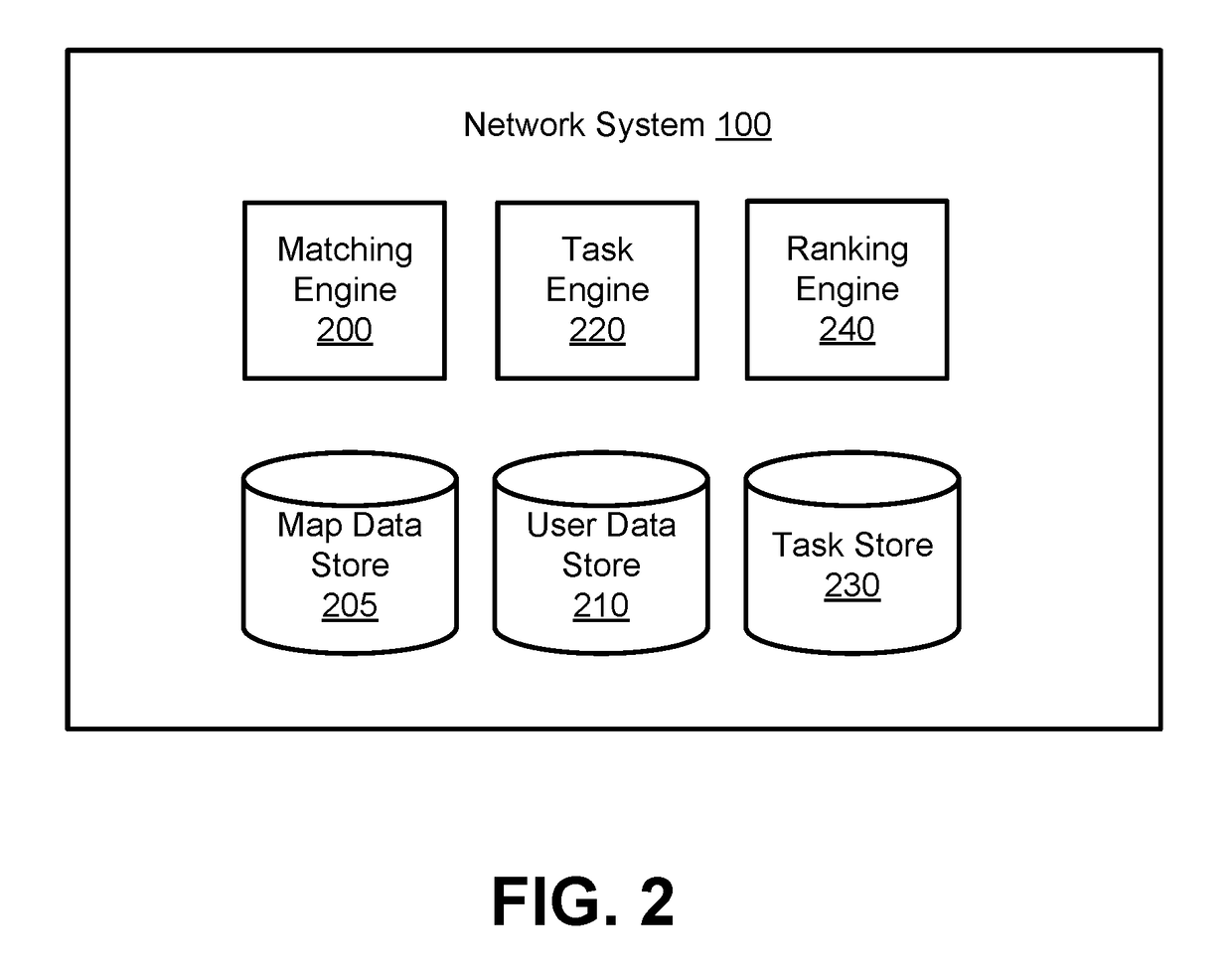
[0013]FIG. 1 is a diagram of a system environment for a network system 100 according to one embodiment. Users of the network system 100 may include providers that provide service to other users. Users may both receive service and provide service as providers of the network system 100. In an example use case, a provider operates a vehicle to transport a user from a first location, referred to herein as a “pickup location,” to a second location, referred to herein as a “destination location.” The network system 100 may determine pickup locations and coordinate providers to pick up users at the pickup locations. Other types of service include, for example, delivery of goods such as mail, packages, or consumable items. In addition to coordinating services between users, the network system 100 can also provide different tasks to providers or users. For example, the network system 100 provides mapping tasks for providers to collect sensor data, which the network system 100
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap